Abstract
One way to improve fuel efficiency in today’s jet aircraft engines is to create an environment for higher operating temperatures and speeds. New and improved lubricants and bearing materials must be developed to remain stable in these elevated operating temperatures. Three lubricants, with varying amounts of tricresyl phosphate added as an anti-wear/extreme pressure additive were tested on two different stainless steels at varying temperatures ranging from 300 °C to 350 °C in vacuum. Significant decomposition of the lubricant base-stocks and the phosphate ester additive did occur in most of the trials resulting in the formation of carboxylic acids and phenols. In these cases a film containing phosphorus was deposited onto the stainless steel substrate.
1. Introduction
Modern, energy efficient engines for aerospace and other purposes are pushing the limits of many materials, both for bearings and for lubricants. Aerospace engines, in particular are being pushed to higher speeds and higher operating temperatures to meet the military needs of the twenty-first century [1]. These needs have led to the development of high performance bearing materials and lubricants and additives which can withstand higher temperatures. The increased hardness of these materials arises in part from the heat treating of alloys in the presence of a carbon source and the incorporation of high levels of alloying elements. The increase in surface hardness has been attributed to a combination of grain size and a well-defined balance of Cr, W, Mo, V and Co, all of which are known to form carbides [2]. Recently a new group of alloys have been developed with substantially lower chromium content that have excellent mechanical properties [3]. Carburization of the metal surface results in the formation of metal carbides, causing a dramatic increase in surface hardness [4].
Traditional bearings, based on metal alloys have an oxide film which is important in the functioning of the lubricant and additives [5]. The change from a primarily oxide surface to a mixture of oxides and carbides is expected to change the nature of the lubricant-surface chemistry [6]. Metal carbides can be lubricated with liquids, including alcohols which form an incomplete, loosely packed monolayer on the surface [7]. A loosely packed monolayer is not expected to provide adequate lubrication. Tribological properties can be influenced by the molecular composition, structure of surface and interfacial film [8]. In an effort to model esters and phosphate esters on a carbide surfaces, Perry et al. completed a study of methyl formate and alkyl phosphates on a vanadium carbide surface, which indicated significant changes in reactivity [9].
Higher temperature requirements and higher stresses due to higher speeds and temperatures also influence the choice of lubricant [10] and lubricant additives [11]. Aviation lubricants generally consist of an ester basestock which has added to it amine antioxidants and phosphate esters. A recent study has demonstrated the utility of carburized case hardened bearings with ester based lubricants and phosphate ester additives [12]. Phosphate esters have been shown to form short chain polyphosphate glasses which form a protective film on the bearing surface [13]. Another study at higher temperatures has shown that the combination of ester based lubricants, phosphate ester lubricants and metal carbides results in higher reactivity than combinations where any component is missing [14]. In this report, we describe the reactions between stainless steel and polyol ester based lubricants with phosphate ester additives.
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials and Supplies
The 440C stainless steel coupons were provided by MetaSpec (San Antonio, TX, USA). The not heat-treated (not carburized) Pyrowear 675 rod samples were provided by Wright Patterson Air Force Base from Timken Bearings. Lubricant samples were a commercially available MIL-PRF-7808 basestock, supplied by Wright Patterson Air Force Base. Tricresyl phosphate as a mixture of four major isomers was obtained from FMC Corporation. Solutions (5% and 10% m/m) of the lubricant containing tricresyl phosphate (TCP) were prepared by weighing the appropriate amounts of TCP and unformulated lubricant and mixing thoroughly.
2.2. Sample Preparation
The first metal alloy tested was a 440C stainless steel coupon. Once all testing on the coupons were completed, the heating of the Pyrowear 675 rods were then begun. The coupons and rods were heated at various incremental temperatures ranging from 300 °C to 350 °C and time durations ranging from 4 h to 96 h. The reactions all took place in thick walled sealed glass tubes approximately one foot long with about a one inch diameter. The tubes were evacuated and then sealed. Enough lubricant was added to sufficiently submerge each metal sample. In order to ensure that each trial encountered no leaking of gasses through the cap, the mass of the sealed tube including the metal sample and lubricant was taken before and after each trial. If the mass was the same before and after, it could be deduced that no leaking took place. The mass of the metal sample before and after heating were also taken to observe how much decomposed lubricant built up upon the metal itself. The tubes were then clamped to a ring stand and inserted about halfway into a furnace with adjustable temperature settings. New coupons or rod samples were used for each trial.
2.3. Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry
Gas chromatography/mass spectrometric analysis was conducted on each of the stressed and unstressed samples. The injector was operated in a splitless mode at a temperature of 350 °C. The column (HT-5, 100 μM film thickness, 25 m length) was heated from an initial temperature of 130 °C for 2 min, increasing at 10 °C/min to 325 °C and holding at 325 °C for 15 min. Mass spectral data was collected over the mass range of 50–700 AMU with a peak threshold of 100 counts. The mass spectrometer was calibrated daily using perfluorotributylamine throughout this work. Compounds were identified by comparison of their mass spectra with mass spectra contained in the NIST Library of Mass Spectra [15] with a minimum match quality of 90 used for identification. The mass spectra of compounds not contained in the library were interpreted using techniques described by McLafferty [16]. All compounds identified in this way showed strong molecular ion peaks as is common for aromatic compounds in electron impact mass spectrometry and fragment ions that are appropriate for the compound identification [17].
2.4. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
Fourier transform infrared spectra of deposits on the metal coupons were collected using a Perkin-Elmer Spectrum GX Fourier transform infrared spectrometer equipped with a Perkin-Elmer i-series microscope in reflectance mode. Spectra were collected at several positions on the metal surface in order to obtain representative results. Samples were placed on a small mirror for analysis. The background of the mirror was measured immediately before measuring the sample. Spectra were collected at an 8 cm−1 resolution and 512 spectra were averaged to come up with each of the spectra presented.
2.5. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
Phosphorus-31 NMR spectra were measured at 121 mHz in proton decoupled mode using a Bruker Advance 300 NMR system. An 85% phosphoric acid sample was used as an external standard. The entire range of chemical shifts (−100 to +100 ppm) was examined. Solutions were made to be 5 percent lubricant in deuterochloroform. A total of 128 scans were averaged to arrive at the final spectrum.
2.6. Raman Spectroscopy
Raman spectra were obtained using a Renishaw inVia Micro Raman instrument equipped with a 300 mW diode laser (785 nm excitation). The instrument was operated in the syncro-scan mode over the range of 100 cm−1–3200 cm−1. A laser power of 30 mW and a sampling time of 10 s was found to yield an adequate spectrum.
2.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy
Scanning electron micrographs and surface composition were measured using a Zeis EVO 60 scanning electron microscope in the high vacuum mode. The pictures were captured using a 10 keV beam voltage and a 44 μm spot size. Surface composition was measures using an EDAX X-ray detector attached to the scanning electron microscope. Samples were washed with tetrahydrofuran to remove any residual sample and air dried before analysis. The samples were attached to an aluminum sample holder using carbon paint and allowed to dry before analysis. Samples were placed in the vacuum chamber 1 h before analysis was begun.
3. Results and Discussion
Samples of 440C Stainless steel and Pyrowear 675 were heated in MIL-PRF 7808 basestock and MIL-PRF 7808 basestock with 5 and 10% tricresyl phosphate to examine the degree of deposit formation and the types of deposit formed. The lubricant samples were examined initially after heating by observing the color of the lubricant and the amount of deposit on the metal coupon. For samples heated to temperature of 300 °C and below, little decomposition of the lubricant was observed and there did not appear to be any deposit formed on the metal coupon. At temperatures of 325 °C–350 °C, significant amounts of deposit were observed on the coupon and a dramatic discoloration of the lubricant was observed. These temperatures are significantly higher than the normal operating range for this lubricant, but were chosen in order to significant reaction in a reasonable time. In addition, tricresyl phosphate concentrations of 5 and 10% were chosen to increase the deposition rates and obtain weighable amounts of deposit. These samples were used for further study. At temperatures greater than 350 °C, the metal coupons were coated with a thick layer of deposit and the lubricant had turned black, indicating severe decomposition of the lubricant.
3.1. Analysis of the Residual Lubricant
The liquid lubricant was examined by GC-MS to identify the lubricant degradation products. In all samples, the primary decomposition products of the lubricant were identified as the component acids from the ester based lubricants. Other products that were identified were partial esters of the lubricant, indicating partial hydrolysis of the lubricant. Samples heated at 350 °C showed significantly more degradation of the lubricant than samples heated at 325 °C for a fixed reaction time. No other products of the reaction were observed.
The heated samples that contained tricresyl phosphate as an anti-wear additive showed some decomposition of the phosphate ester in addition to the products of the decomposition of the lubricant. In samples heated at 350 °C for 96 h very little of the tricresyl phosphate remained. In samples heated for shorter periods of time or at lower temperatures, the quantity of tricresyl phosphate was significantly reduced. The primary product identified by GC/MS in the arising from the decomposition of the phosphate ester was cresol. Cresol arises from the cleavage of the P–O bond of the phosphate ester. This process should lead to the formation of other phosphorus containing products, however such products were not observed by GC-MS indicating that the phosphorus is included in the deposit on the metal coupon.
In an effort to learn more about the phosphorus containing products of the lubricant decomposition, the 31P NMR spectra of an unheated lubricant sample and a sample heated at 350 °C for 96 h were measured. The spectra of the two samples are shown in Figure 1.
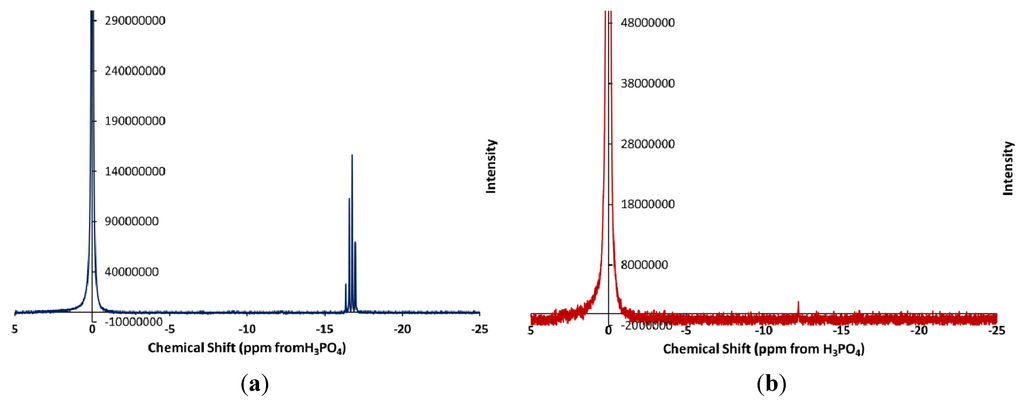
Figure 1.
Phosphorus-31 NMR Spectrum of (a) 5% tricresyl phosphate (TCP) in basestock before heating; and (b) the same sample after heating at 325 °C for 96 h.
Figure 1.
Phosphorus-31 NMR Spectrum of (a) 5% tricresyl phosphate (TCP) in basestock before heating; and (b) the same sample after heating at 325 °C for 96 h.
The spectrum of the unstressed lubricant showed the four peaks between −16.5 and −17.1 ppm from external H3PO4 one peak for each of the isomers of tricresyl phosphate present in the mixture. After heating, the sample shows no phosphorus other than the external reference solution. A very small peak is observed at −12.2 ppm which is due to a monoester of phosphoric acid [18]. Removal of the external reference solution indicates that the peak observed at 0.00 ppm is due entirely to the reference H3PO4 and that there is no H3PO4 in the lubricant sample.
3.2. Analysis of the Solids
For each type of metals samples heated with lubricant alone, and with 5% and 10% tricresyl phosphate were examined and the pre-test and post-test mass of the sample determined. The results of these measurements are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Mass of deposits formed on the metal coupon in the reaction of stainless steels with lubricants.
| Lubricant | Time (h) | Temperature (°C) | Mass Increase 440C Stainless Steel (g) | Mass Increase Pyrowear 675 Steel (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basestock | 24 | 325 | −0.0003 | +0.0004 |
| 24 | 350 | −0.0004 | −0.0002 | |
| 96 | 325 | −0.0006 | −0.0004 | |
| 96 | 350 | −0.0007 | −0.0006 | |
| Basestock +5% Tricresyl Phosphate | 24 | 325 | +0.0004 | +0.0005 |
| 24 | 350 | +0.0008 | +0.0009 | |
| 96 | 325 | +0.0030 | +0.0028 | |
| 96 | 350 | +0.0044 | +0.0032 | |
| Basestock +10% Tricresyl Phosphate | 24 | 325 | +0.0012 | +0.0009 |
| 24 | 350 | +0.0032 | +0.0032 | |
| 96 | 325 | +0.0159 | +0.0158 | |
| 96 | 350 | +0.0215 | +0.0210 |
Samples heated with the basestock alone showed no increase in mass, indicative of no formation of a deposit. In most of these samples, a slight decrease in mass was observed which is indicative of the removal of a small amount of surface water. All of the samples containing phosphate ester as an anti-wear additive showed an increase in the mass of the metal sample. These results are similar to results obtained with 52100 and M-50 steels [16]. The increase in mass is largest for the higher percentage of tricresyl phosphate in the lubricant and for the longer exposure times. A visual examination of the coupons shows a thin black film on samples heated for 24 h in the presence of TCP and a heavier coating on those samples heated for 96 h.
The surfaces of the solid samples were examined by scanning electron microscopy and the composition of the surfaces determined by energy dispersive X-ray analysis (EADX). Samples exposed to the lubricant basestock showed no deposition of a film, consistent with a small loss of mass for these coupons. These samples are visually identical to the unheated metal coupons. The loss of mass is likely due to the loss of surface water upon heating. The surface of samples of 440C stainless steel coupons exposed to the lubricant base stock and lubricants formulated with tricresyl phosphate are shown in Figure 2.
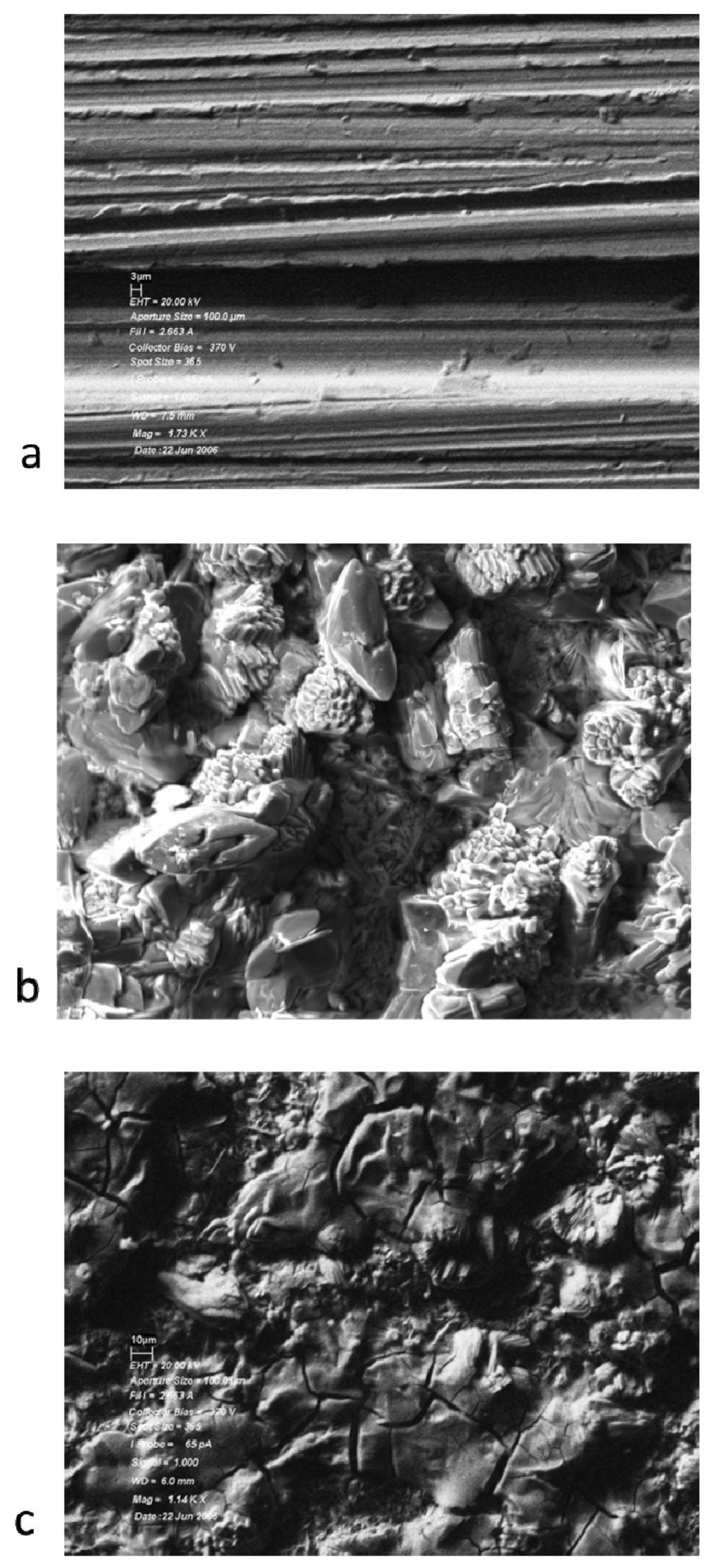
Figure 2.
Scanning electron micrographs of 440C Stainless Steel samples: (a) heated at 325 °C for 96 h in basestock; (b) heated at 325 °C for 24 h in 5% TCP; (c) heated at 325 °C for 96 h in 10% TCP.
Figure 2.
Scanning electron micrographs of 440C Stainless Steel samples: (a) heated at 325 °C for 96 h in basestock; (b) heated at 325 °C for 24 h in 5% TCP; (c) heated at 325 °C for 96 h in 10% TCP.
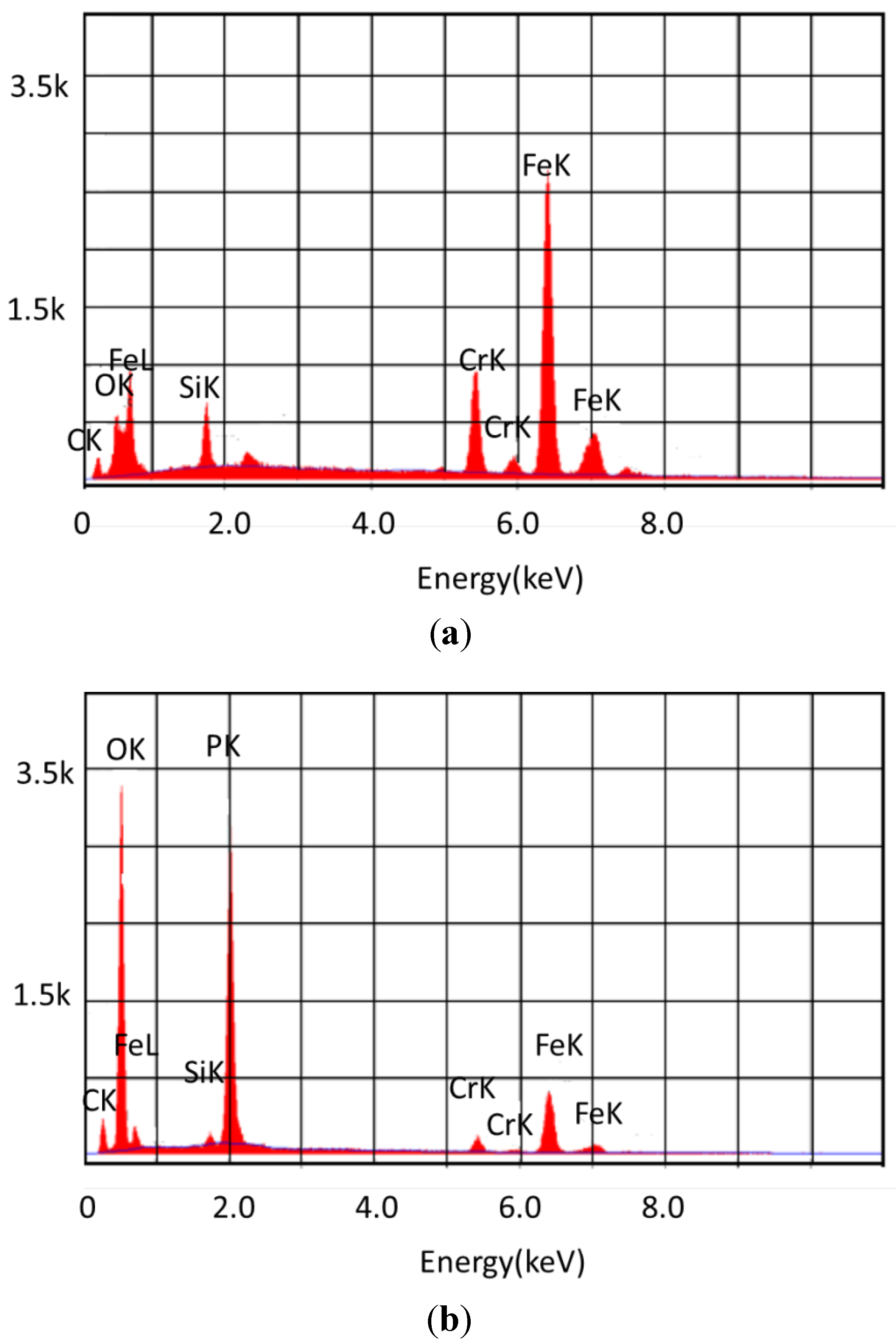
The SEM pictures show that there is no evidence of deposit formation when only the lubricant basestock is present. The presence of 5% tricresyl phosphate leads to the beginnings of deposit formation after 24 h. Increasing the tricresyl phosphate concentration to 10% and increasing the reaction time to 96 h leads to the formation of a thick deposit on the metal coupon. The elemental composition of the deposits was examined by EDAX. The EDAX data is shown in Figure 3.
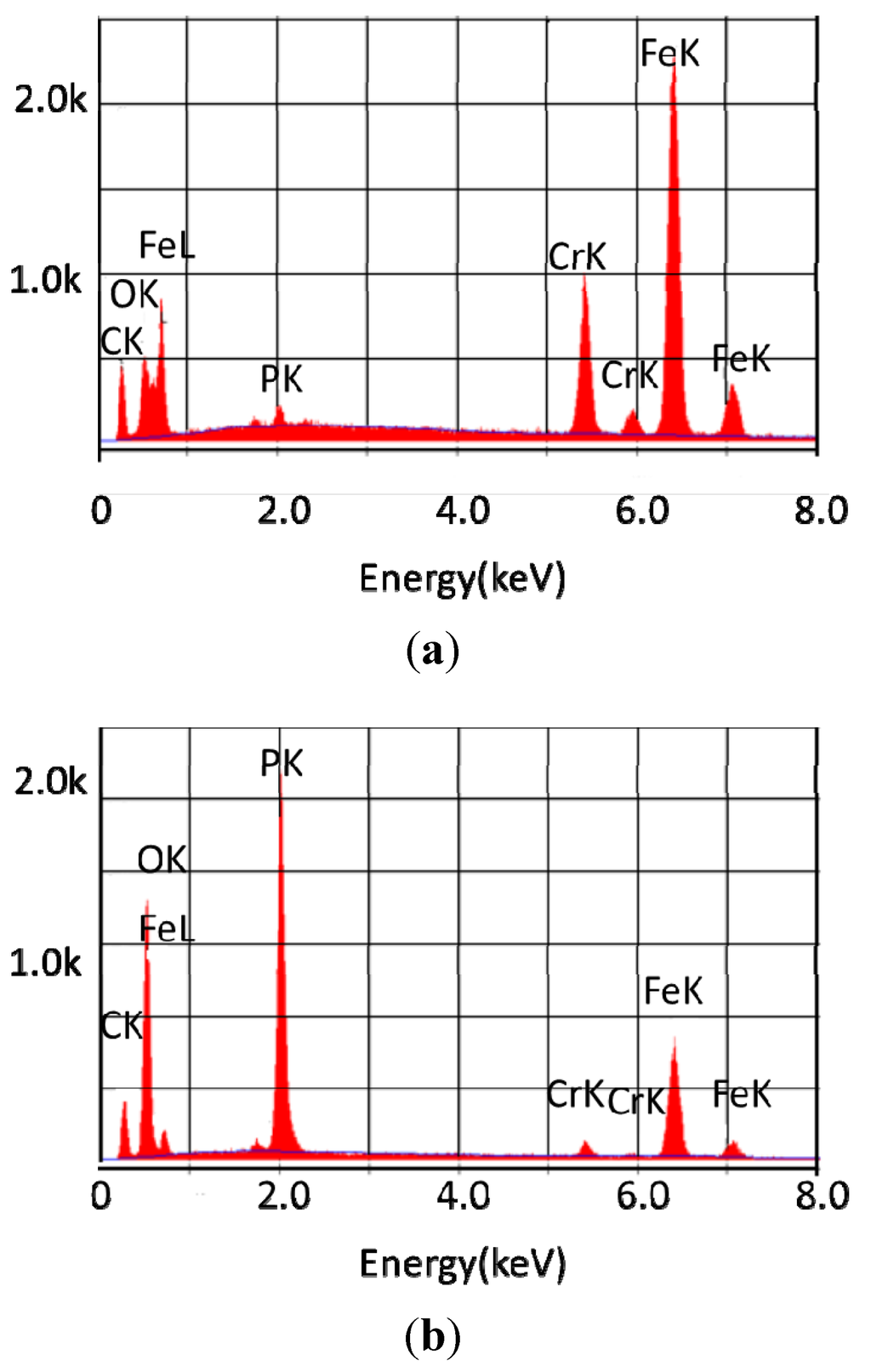
Figure 3.
Elemental composition of the surface of 440C stainless steel (a) reacted with basestock for 96 h at 325 °C; (b) reacted with 10% tricresyl phosphate for 96 h at 325 °C.
Figure 3.
Elemental composition of the surface of 440C stainless steel (a) reacted with basestock for 96 h at 325 °C; (b) reacted with 10% tricresyl phosphate for 96 h at 325 °C.
The X-ray fluorescence data shows that the coupon treated in the absence of tricresyl phosphate was of the same composition as an untreated coupon. The coupon treated with 10% tricresyl phosphate, however had a surface with large amounts of phosphorus and a greatly diminished metal content. Previous work has shown that in the presence of limited oxygen, decomposition of the phosphate ester yields a polymeric material with chains of aromatic rings bound as phosphate esters [19]. The atomic percentage of each of the various elements found on the surface of the coupons is shown in Table 2. The results for samples exposed to tricresyl phosphate show a surface that contains a significant deposition of phosphorus, while the samples exposed to the lubricant alone are similar to the unreacted coupon.

Table 2.
Surface composition of metal coupons exposed to various lubricants.
| Lubricant | Atom% C | Atom% O | Atom% P | Atom% Cr | Atom% Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 440C Stainless Steel | |||||
| Basestock | 40.46 | 15.17 | <1 | 9.68 | 33.26 |
| 5% TCP | 47.86 | 24.68 | 6.38 | 1.25 | 14.35 |
| 10% TCP | 54.97 | 31.25 | 8.32 | 0.58 | 4.53 |
| Pyrowear 675 Steel | |||||
| Basestock | 25.1 | 14.98 | <1 | 8.33 | 39.67 |
| 5% TCP | <5 | 70.97 | 18.77 | 1.3 | 7.75 |
| 10% TCP | <5 | 63.77 | 20.86 | 1.27 | 12.79 |
Samples of Pyrowear 675 exposed to the various lubricant formulations were also examined by scanning electron microscopy. The results of this examination are shown in Figure 4.
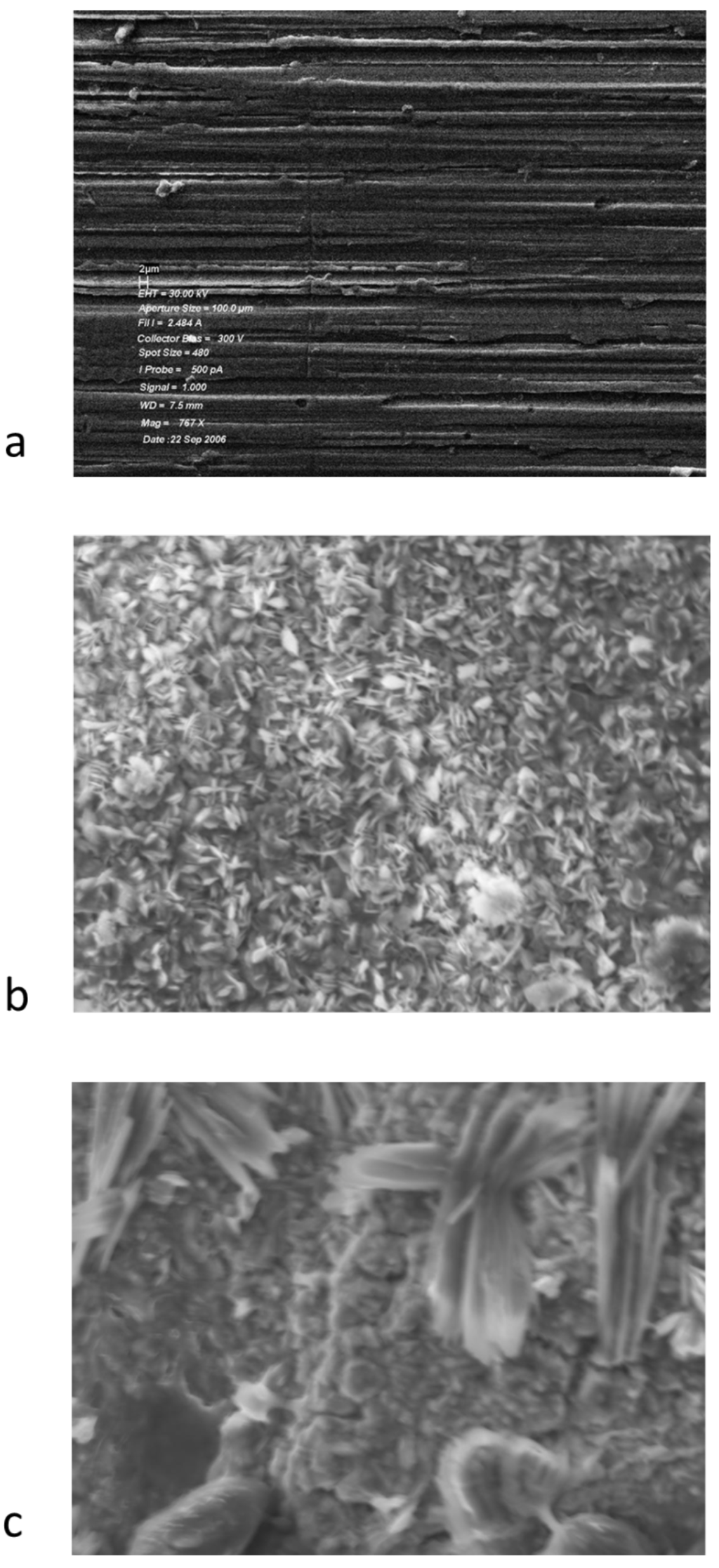
Figure 4.
Scanning electron micrographs of Pyrowear 675 steel samples: (a) heated at 325 °C for 96 h in basestock; (b) heated at 325 °C for 24 h in 5% TCP; (c) heated at 325 °C for 96 h in 10% TCP.
Figure 4.
Scanning electron micrographs of Pyrowear 675 steel samples: (a) heated at 325 °C for 96 h in basestock; (b) heated at 325 °C for 24 h in 5% TCP; (c) heated at 325 °C for 96 h in 10% TCP.
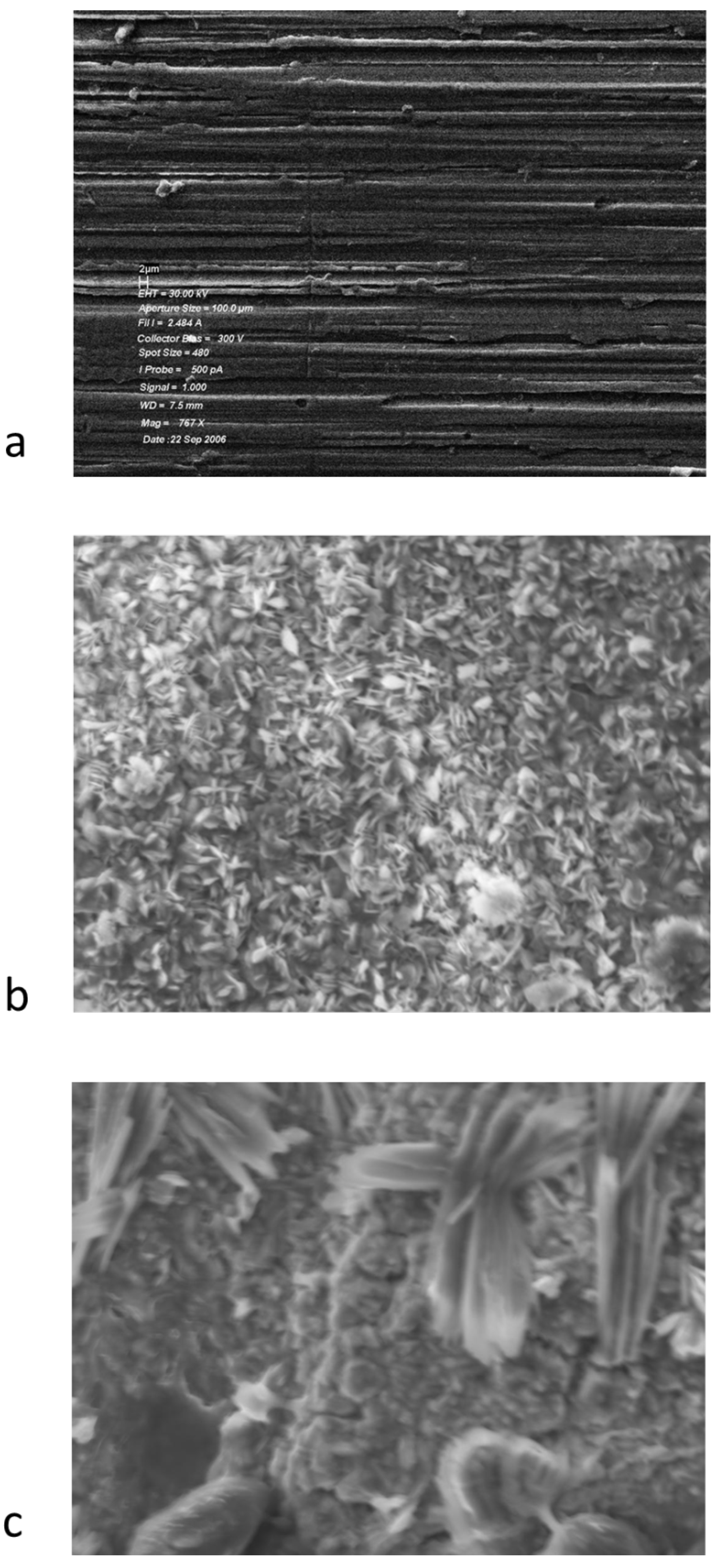
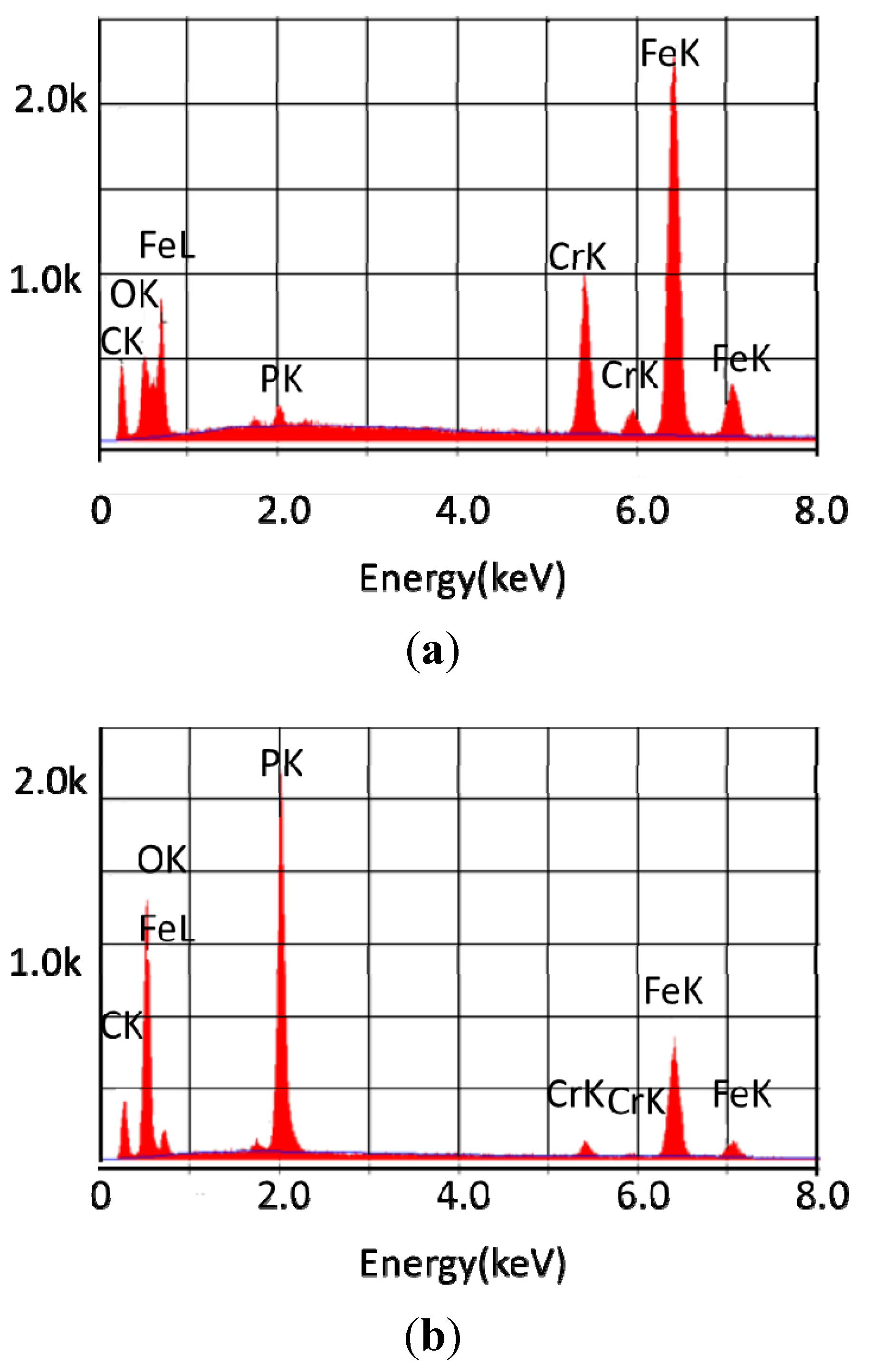
The scanning electron micrographs of the rod exposed to lubricants with tricresyl phosphate show the formation of a deposit on the metal surface. The deposit has a semi crystalline appearance with what appear to be fine needles spread over the majority of the surface and some areas where larger needles appear to be forming. This observation is in contrast to the observation of 440C stainless steel coupons where the deposit appeared to be amorphous. The chemical composition of these deposits was determined by EDAX, indicating the presence of a significant amount of phosphorus on the surface. The EDAX results for these samples are shown in Figure 5.
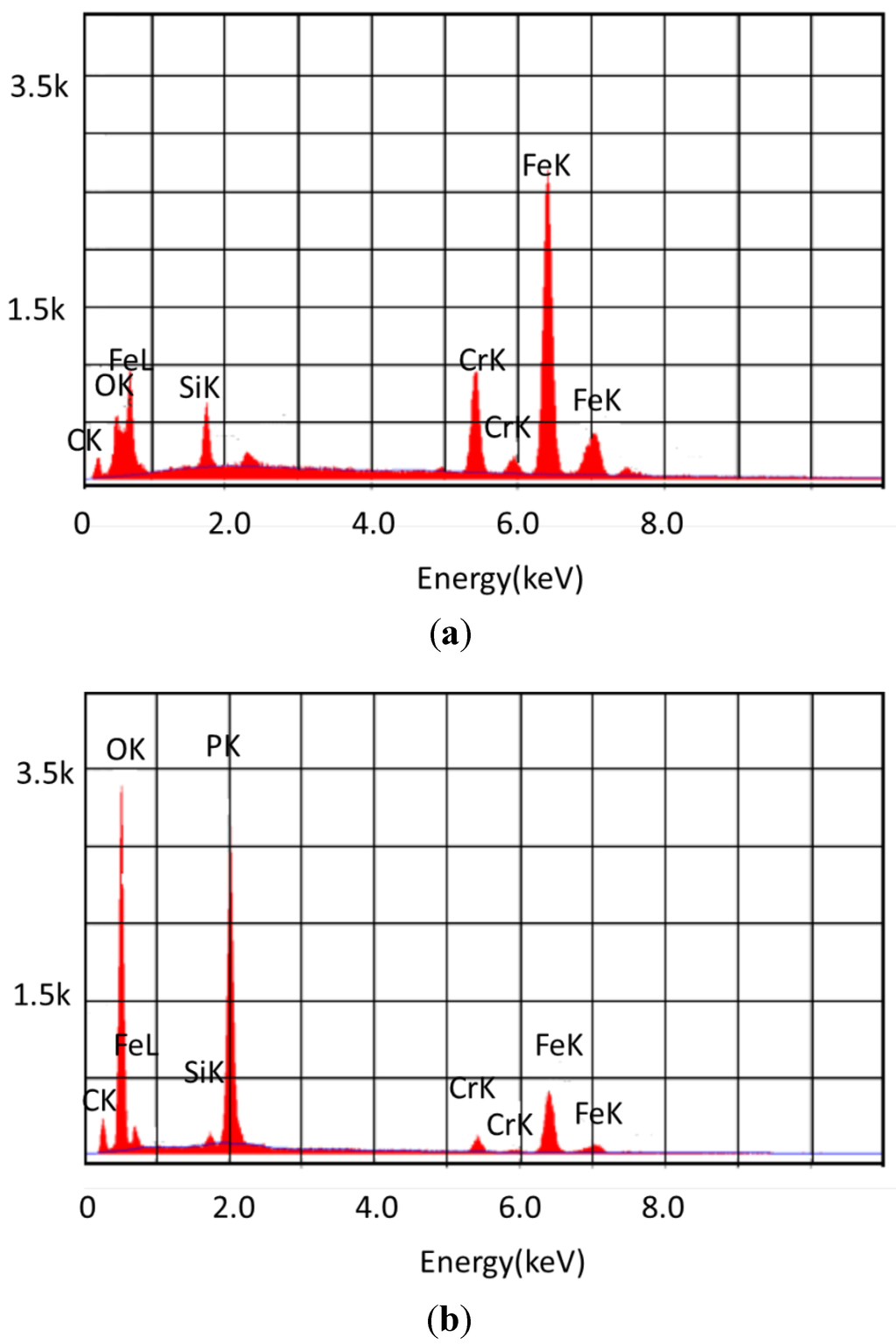
Figure 5.
Elemental composition of the surface of Pyrowear 675 (a) reacted with basestock for 96 h at 325 °C; (b) reacted with 10% tricresyl phosphate for 96 h at 325 °C.
Figure 5.
Elemental composition of the surface of Pyrowear 675 (a) reacted with basestock for 96 h at 325 °C; (b) reacted with 10% tricresyl phosphate for 96 h at 325 °C.
The EDAX results show the definite presence of phosphorus on the surface of the sample, indicating that the phosphate ester is definitely involved in the deposition. The metal atoms of the sample are somewhat diminished in comparison to the coupon that was exposed to the basestock alone.
The deposits formed on the two different metal samples were further characterized by infrared spectroscopy and Raman spectroscopy to determine the molecular nature of the deposits. The infrared spectra of the samples heated with tricresyl phosphate are shown in Figure 6.
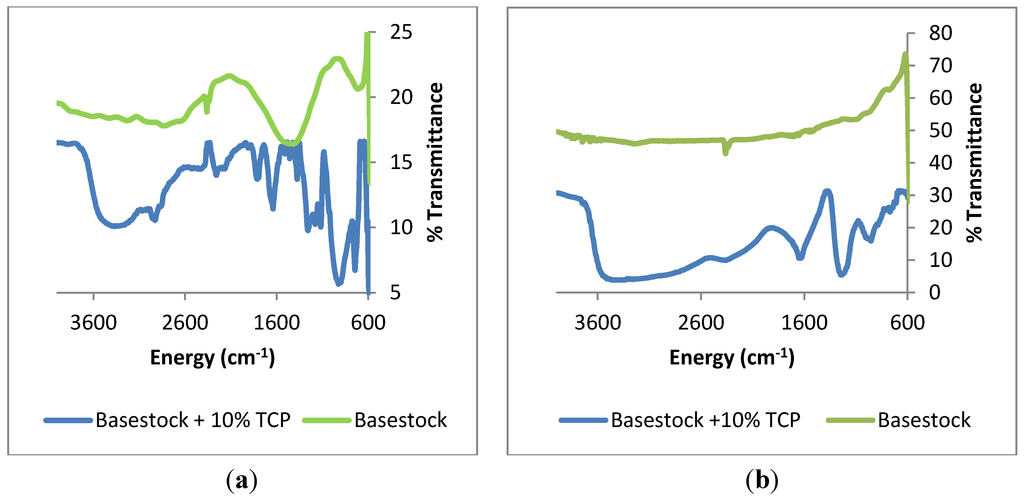
Figure 6.
Infrared spectra of samples of (a) 440C Stainless Steel; and (b) Pyrowear 675 heated at 325 °C for 96 h with lubricants of varying TCP concentration.
Figure 6.
Infrared spectra of samples of (a) 440C Stainless Steel; and (b) Pyrowear 675 heated at 325 °C for 96 h with lubricants of varying TCP concentration.
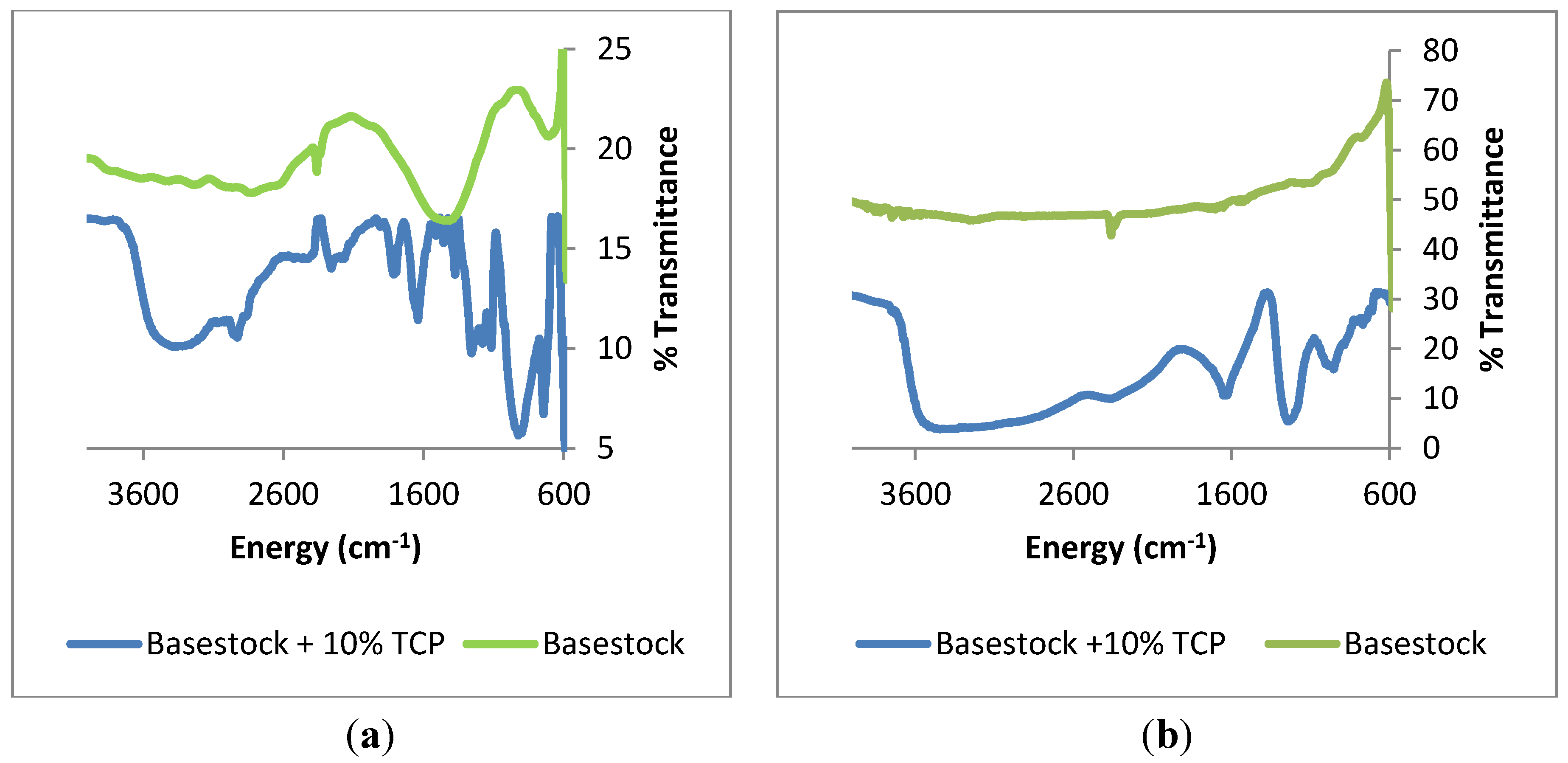
In the spectra of Figure 6 show that metal coupons exposed to the basestock alone are largely uncoated. There is some evidence of surface water in both infrared spectra; however there does not appear to be a significant deposition layer. The metal coupons heated with basestock and phosphate ester are similar in that they both show peaks between 950 and 1050 cm−1 which are generally assigned to phosphate with differing degrees of polymerization [20]. Both spectra also show strong peaks at 1660 cm−1 and 1270 cm−1 which are frequently associated with aromatic carbon-carbon bond stretching and carbon-oxygen bond stretching [21]. The infrared spectrum of the 440C coupon exposed to phosphate ester appears to have a greater amount of fine structure than the Pyrowear 675 coupon exposed to phosphate ester. This observation may be due to a greater amount of non-polymeric material trapped within the coating. Raman spectra of the metal coupons shows the presence of two bands at 1590 and 1355 cm−1 which are commonly associated with sp2 and sp3 carbons in graphite and diamond, respectively [22]. No other bands were observed in the Raman spectra of the metal coupons.
4. Conclusions
In this study, it was found that deposits are not formed when stainless steels are exposed to ester lubricant basestock, but phosphate ester additives in ester based lubricants form deposits on both 440C stainless steel and on Pyrowear 675 steel when heated. The deposits formed contain significant amounts of oxygen and phosphorus. Infrared spectroscopy allows for the identification of the deposit as containing phosphate. The presence of significant amounts of carbon in the film indicates that all of the organic groups are not removed during the reaction but that the film includes some of the cresol from the phosphate esters. On both of the stainless steels examined, the coating appears to be quite durable. The polyphosphate coating is thought to act as a lubricant during conditions of startup, when liquid lubricant flow is absent.
References and Notes
- Gschwender, L.J.; Snyder, C.E. Research and development of advanced high-temperature air force Turbine Engine Oil. J. Soc. Tribol. Lubr. Engin. 2000, 56, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Pippel, E.; Woltersdorf, J.; Pockl, G.; Lichtenegger, G. Microstructure and nanochemistry of carbide precipitates in high-speed steel S6-5-2-5. Mater. Charact. 1999, 43, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetzner, D.W.; van Geertruyden, W. Crystallography and metallography of carbides in high alloy steels. Mater. Charact. 2008, 59, 825–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusilovskii, B.A.; Shashko, A.Y. An X-ray study of carbides in the working layer of cold-rolling rolls. Metal Sci. Heat Treat. 2001, 43, 180–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, C.S.; Forster, N.H. Reactions of aromatic phosphate esters with metals and their oxides. Tribol. Lett. 2002, 12, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hils, J.E.; Johnson, D.W.; Benin, V. Computational Investigations of the Interactions between Phosphate Esters and Metal. In Proceedings of 42nd Central Regional Meeting of the American Chemical Society, Dayton, OH, USA, 16–19 June 2010.
- Fernandez-Torres, L.C.; Zhao, X.; Kim, B.; Perry, S.S. Chemical Modification Influence on the Frictional Properties of Small Model Lubricant Molecules Adsorbed on VC(100). In Proceedings of 225th ACS National Meeting, New Orleans, LA, USA, 23–27 March 2003.
- Fernandez-Torres, L.C.; Kim, B.I.; Perry, S.S. The frictional response of VC(100) surfaces: Influence of 1-octanol and 2,2,2-trifluoroetnanol adsorption. Tribol. Lett. 2003, 15, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Torres, L.; Zhao, X.; Chen, Z.; Salmeron, C.; Perry, S. Influence of ethyl acetate and alkyl phosphate adsorption on the frictional properties of VC(100). Tribol. Lett. 2005, 18, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, C.E.; Gschwender, L.J. Trends Toward Synthetic Lubricants in Aerospace. In Synthetics, Mineral Oils, and Bio-Based Lubricants: Chemistry and Technology; Rudnick, L.R., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, Florida, FA, USA, 2006; Volume 10, pp. 811–815. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, C.E.; Gschwender, L.J.; Sharma, S.K. Long-Term Additive Trends in Aerospace Applications. In Lubricant Additives: Chemistry and Applications; Rudnick, L.R., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, Florida, FA, USA, 2009; pp. 637–644. [Google Scholar]
- Trivedi, H.K.; Forster, N.H.; Rosado, L. Rolling contact fatigue evaluation of advanced bearing steels with and without the oil anti-wear additive tricresyl phosphate. Tribol. Lett. 2011, 41, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutler, J.N.; Sanders, J.H.; Zabinski, J.S.; John, P.J.; McCutchen, J.R.; Kasten, L.S.; Tan, K.H. Surface chemistry of new lubrication systems for high-speed spacecraft bearings. Tribol. Lett. 2000, 8, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.W.; Hils, J.E.; Forster, N. Interaction of polyol esters and phosphate esters with metal carbides. Tribol. Lett. 2011, 42, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard Reference Data Program. National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg, MD, Standard Reference Database 1A. Available online: http://www.nist.gov/srd/nist1a.cfm (accessed on 6 May 2013).
- McLafferty, F.W. Interpretation of Mass Spectra; Mill Valley: California, CA, USA, 1980; pp. 119–167. [Google Scholar]
- Litzow, M.R.; Spalding, T.R. Mass Spectrometry of Inorganic and Organometallic Compounds; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 1973; pp. 321–439. [Google Scholar]
- Gorenstein, D.G. Dependence of 31P chemical shifts on oxygen-phosphorus-oxygen bond angles in phosphate esters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1975, 97, 898–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.W.; Morrow, S.; Forster, N.H.; Saba, C.S. Vapor phase lubrication: Reaction of phosphate ester vapors with iron and steel. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 3867–3875. [Google Scholar]
- Molt, K.; Behmer, D.; Pohl, M. Different techniques for determining the coating weight of phosphate layers on galvanized steel by means of FT-IR spectrometry. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 1997, 358, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socrates, G. Infrared and Raman Characteristic Group Frequencies: Tables and Charts; John Wiley & Sons: West Suffix, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, D.W. Application of raman spectroscopy to lubricants, lubricated surfaces and lubrication phenomena. Spectroscopy 2011, 26, 46–50. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
