Capture of Massless and Massive Particles by Parameterized Black Holes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Equations of Motion
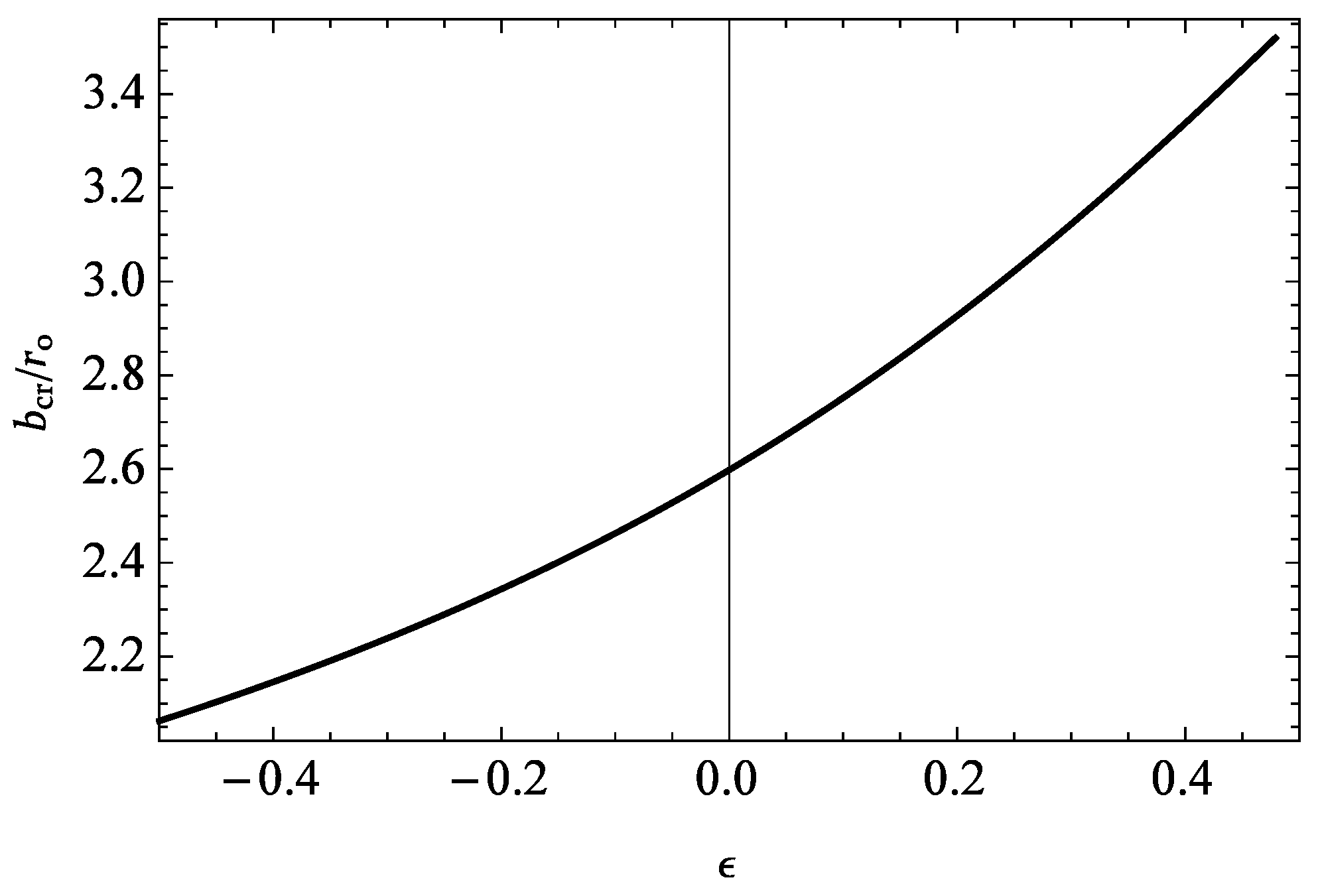
3. Capture of Photons
- (i)
- Two turning points : in this case , i.e., either the photon coming from infinity reaches the periastron () and again escapes to infinity, or if the photon is emitted from near the horizon (), it reaches an apastron () and falls back to the black hole.
- (ii)
- Ine turning point : in this case , i.e., the photon moves along an unstable circular orbit that corresponds to the peak of the effective potential. Any deviation from the trajectory causes the photon to fall into or escape from the black hole.
- (iii)
- No turning point: in this case , i.e., either the photon coming from infinity falls into the black hole or the photon emitted from near the horizon escapes to infinity.
4. Capture of Massive Particles
- (i)
- Three turning points : in this case , i.e., either the particle moves along the stable elliptic orbit between periastron () and apastron (), or if the particle is emitted from near the horizon (), it reaches an apastron () and falls back to the black hole.
- (ii)
- Two turning points : this corresponds to , i.e., either the particle coming from infinity reaches the periastron () and escapes back to infinity along the hyperbolic orbit, or if it is emitted close to the event horizon, it reaches an apastron () and falls back to the black hole.
- (iii)
- One turning point : in this case , i.e., the particle moves along the unstable circular orbit that corresponds to the peak of the effective potential.
- (iv)
- No turning point: in this case , i.e., either the particle coming from infinity falls into the black hole or the particle emitted from near the horizon escapes to infinity.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Will, C.M. The Confrontation between General Relativity and Experiment. Living Rev. Relativ. 2014, 17, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Abernathy, M.R.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; et al. GW151226: Observation of Gravitational Waves from a 22-Solar-Mass Binary Black Hole Coalescence. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 241103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scientific, L.I.G.O.; Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; et al. GW170104: Observation of a 50-Solar-Mass Binary Black Hole Coalescence at Redshift 0.2. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 118, 221101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; et al. GW170814: A Three-Detector Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Black Hole Coalescence. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 141101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; et al. GW170608: Observation of a 19 Solar-mass Binary Black Hole Coalescence. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 851, L35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; et al. GW170817: Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Neutron Star Inspiral. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 161101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Event Horizon Telescope Collaboration. First M87 Event Horizon Telescope Results. I. The Shadow of the Supermassive Black Hole. Astrophys. J. 2019, 875, L1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konoplya, R.; Zhidenko, A. Detection of gravitational waves from black holes: Is there a window for alternative theories? Phys. Lett. B 2016, 756, 350–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannsen, T.; Psaltis, D. Metric for rapidly spinning black holes suitable for strong-field tests of the no-hair theorem. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 83, 124015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezzolla, L.; Zhidenko, A. New parametrization for spherically symmetric black holes in metric theories of gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 90, 084009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psaltis, D.; Medeiros, L.; Christian, P.; Özel, F.; Akiyama, K.; Alberdi, A.; Alef, W.; Asada, K.; Azulay, R.; Ball, D.; et al. Gravitational Test beyond the First Post–Newtonian Order with the Shadow of the M87 Black Hole. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 125, 141104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas-Avendaño, A.; Nampalliwar, S.; Yunes, N. Gravitational-wave versus x-ray tests of strong-field gravity. Class. Quantum Gravity 2020, 37, 135008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkotas, K.D.; Konoplya, R.A.; Zhidenko, A. Analytical approximation for the Einstein-dilaton-Gauss–Bonnet black hole metric. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 96, 064004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Völkel, S.H.; Barausse, E. Bayesian metric reconstruction with gravitational wave observations. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 084025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Völkel, S.H.; Barausse, E.; Franchini, N.; Broderick, A.E. EHT tests of the strong-field regime of General Relativity. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2011.06812. [Google Scholar]
- Suvorov, A.G.; Völkel, S.H. Exact theory for the Rezzolla-Zhidenko metric and self-consistent calculation of quasinormal modes. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 103, 044027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konoplya, R.A.; Zhidenko, A. General parametrization of black holes: The only parameters that matter. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 124004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nampalliwar, S.; Xin, S.; Srivastava, S.; Abdikamalov, A.B.; Ayzenberg, D.; Bambi, C.; Dauser, T.; García, J.A.; Tripathi, A. Testing general relativity with x-ray reflection spectroscopy: The Konoplya-Rezzolla-Zhidenko parametrization. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 124071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misner, C.W.; Thorne, K.S.; Wheeler, J.A. Gravitation; W. H. Freeman: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Landau, L.D.; Lifshitz, E.M. The Classical Theory of Fields; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Zakharov, A.F. Capture of photons and slow uncharged particles by a spherically symmetric charged compact body in the relativistic theory of gravitation. Theor. Math. Phys. 1992, 90, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharov, A.F. Particle capture cross sections for a Reissner–Nordström black hole. Class. Quantum Gravity 1994, 11, 1027–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimov, O.G.; Abdujabbarov, A.A.; Ahmedov, B.J. Magnetized Particle Capture Cross Section for Braneworld Black Hole. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2011, 335, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Toshmatov, B.; Rahimov, O.; Ahmedov, B.; Ahmedov, A. Capture of Massless and Massive Particles by Parameterized Black Holes. Galaxies 2021, 9, 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies9030065
Toshmatov B, Rahimov O, Ahmedov B, Ahmedov A. Capture of Massless and Massive Particles by Parameterized Black Holes. Galaxies. 2021; 9(3):65. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies9030065
Chicago/Turabian StyleToshmatov, Bobir, Ozodbek Rahimov, Bobomurat Ahmedov, and Abdumirhakim Ahmedov. 2021. "Capture of Massless and Massive Particles by Parameterized Black Holes" Galaxies 9, no. 3: 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies9030065
APA StyleToshmatov, B., Rahimov, O., Ahmedov, B., & Ahmedov, A. (2021). Capture of Massless and Massive Particles by Parameterized Black Holes. Galaxies, 9(3), 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies9030065






