Phase-Space Correlations among Systems of Satellite Galaxies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Phase-Space Correlations
2.1. An Impending Observational Revolution: Satellite Galaxy Systems and Their Phase-Space Distribution
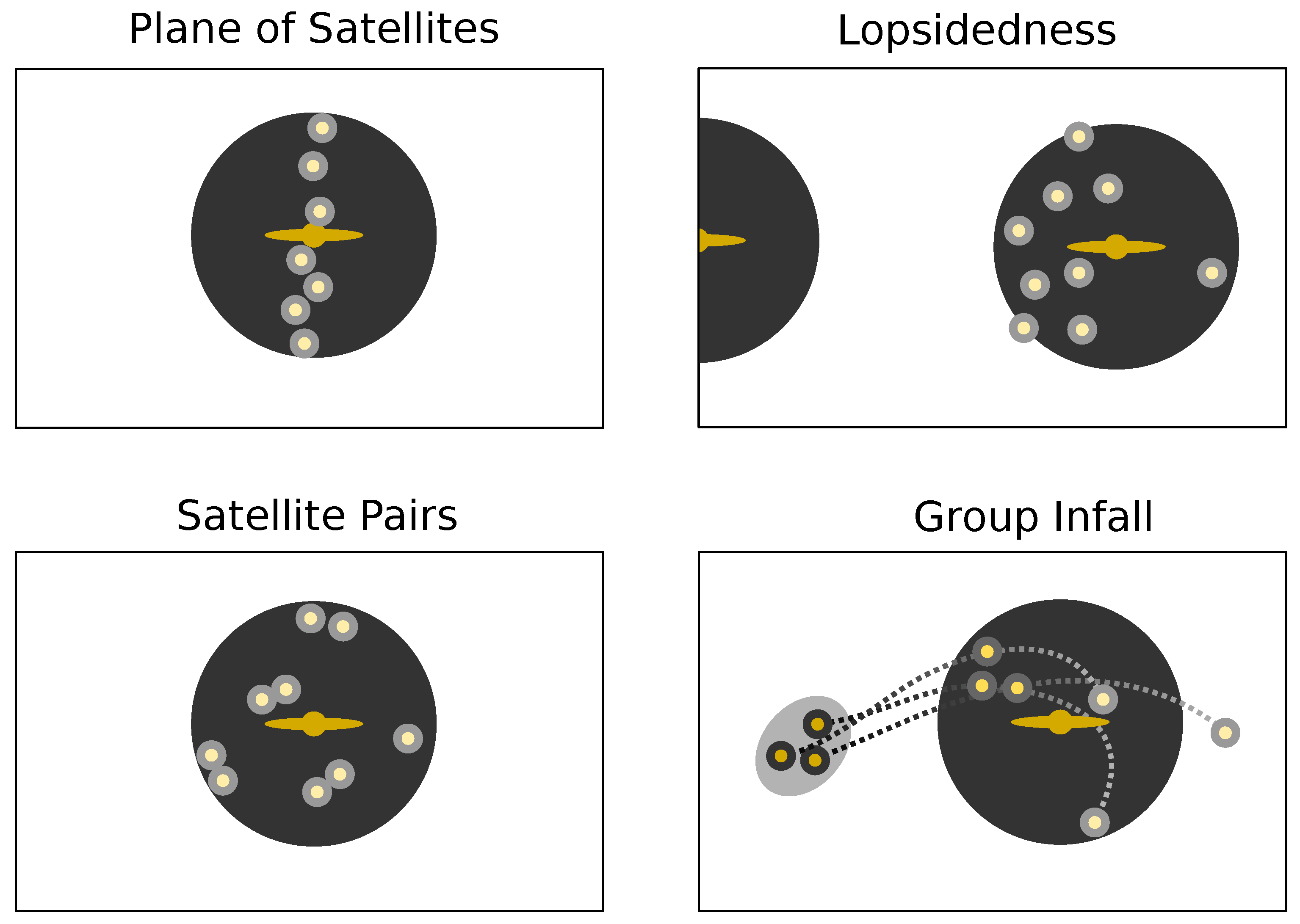
2.2. Planes of Satellite Galaxies
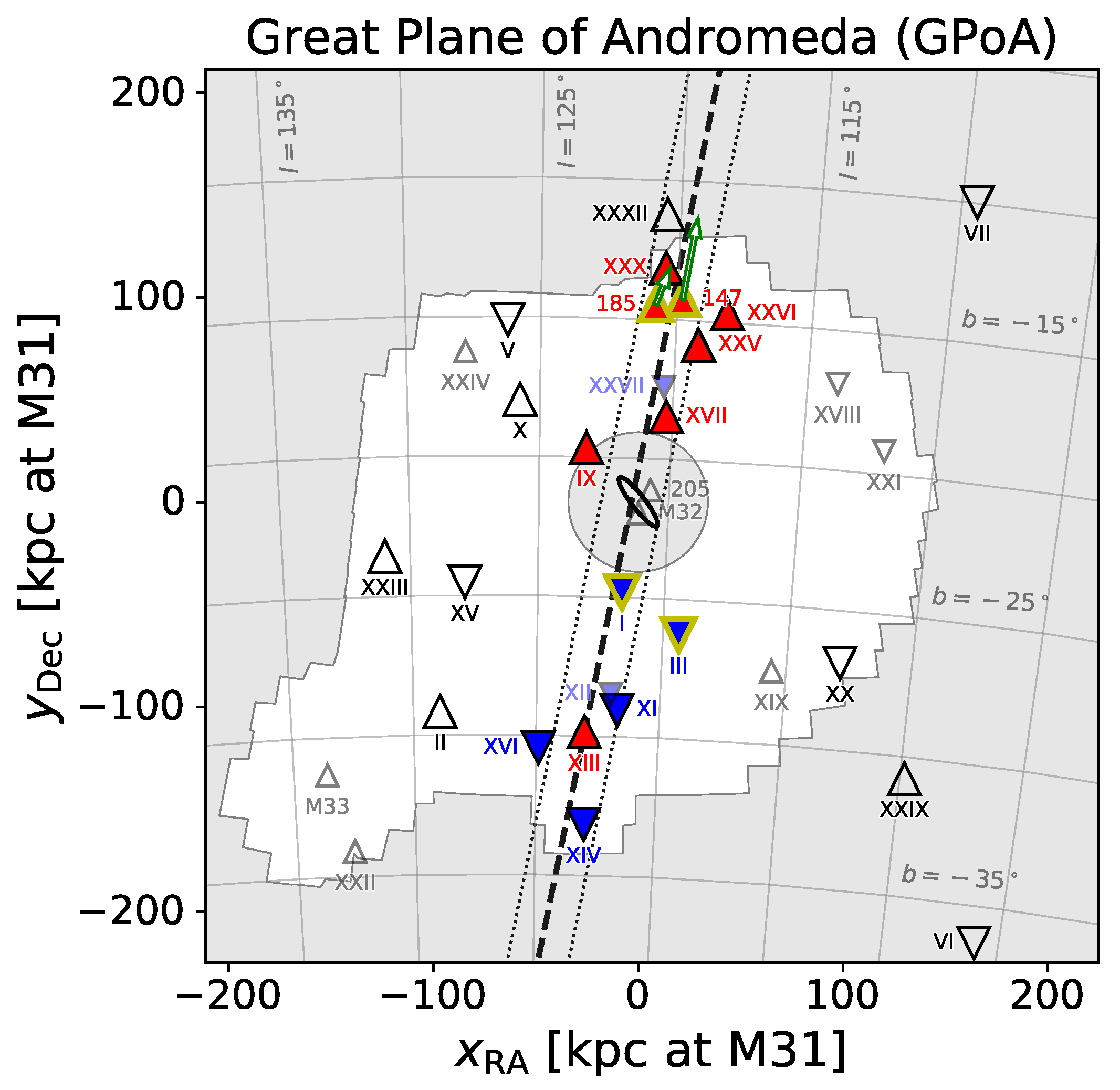
2.2.1. The Satellite Planes around the MW and M31
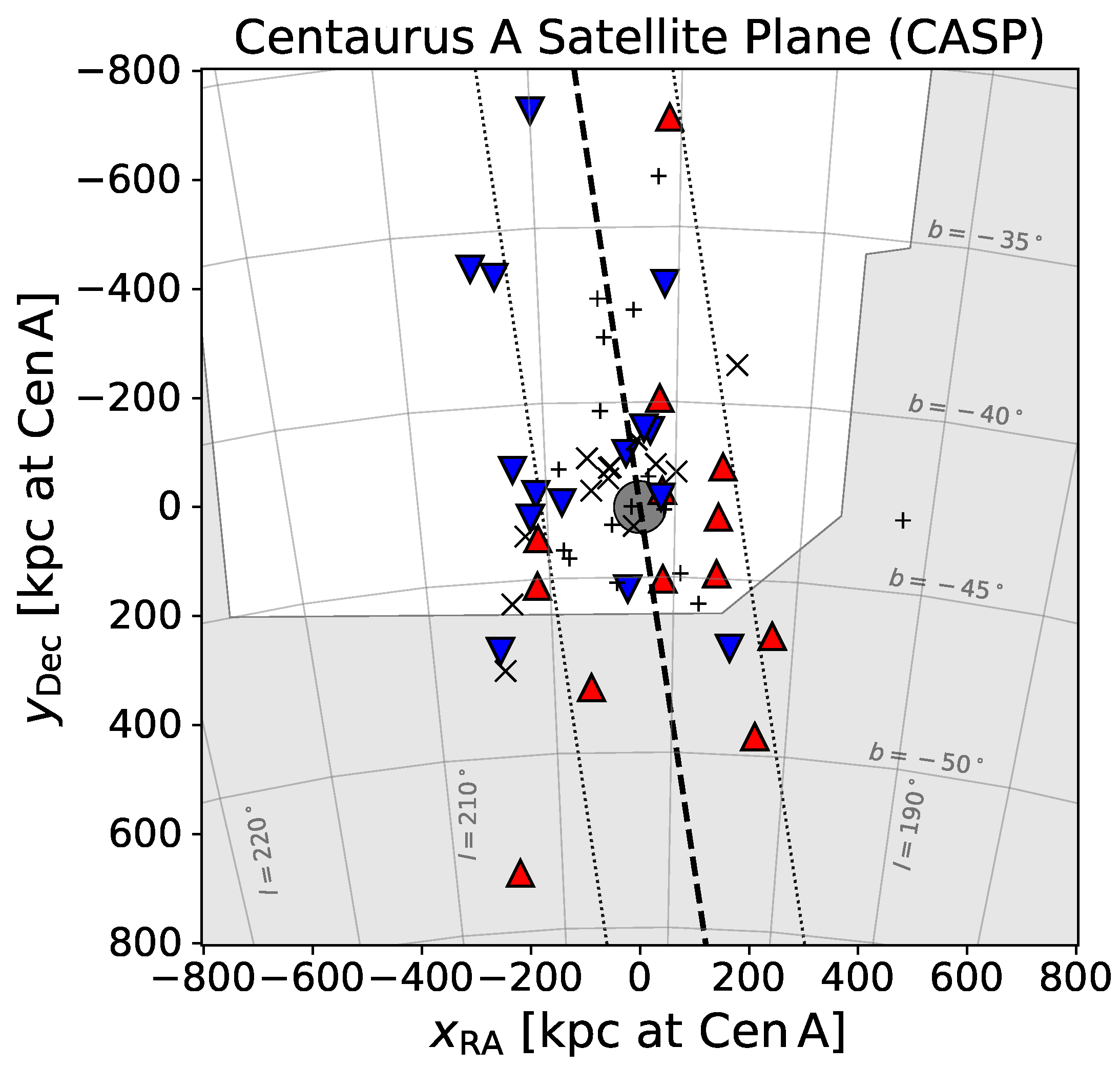
2.2.2. Satellite Planes outside of the Local Group
2.2.3. Comparison to Cosmological Expectations: The Planes of Satellite Galaxies Problem
2.2.4. Proposed Origins of Planes of Satellite Galaxies
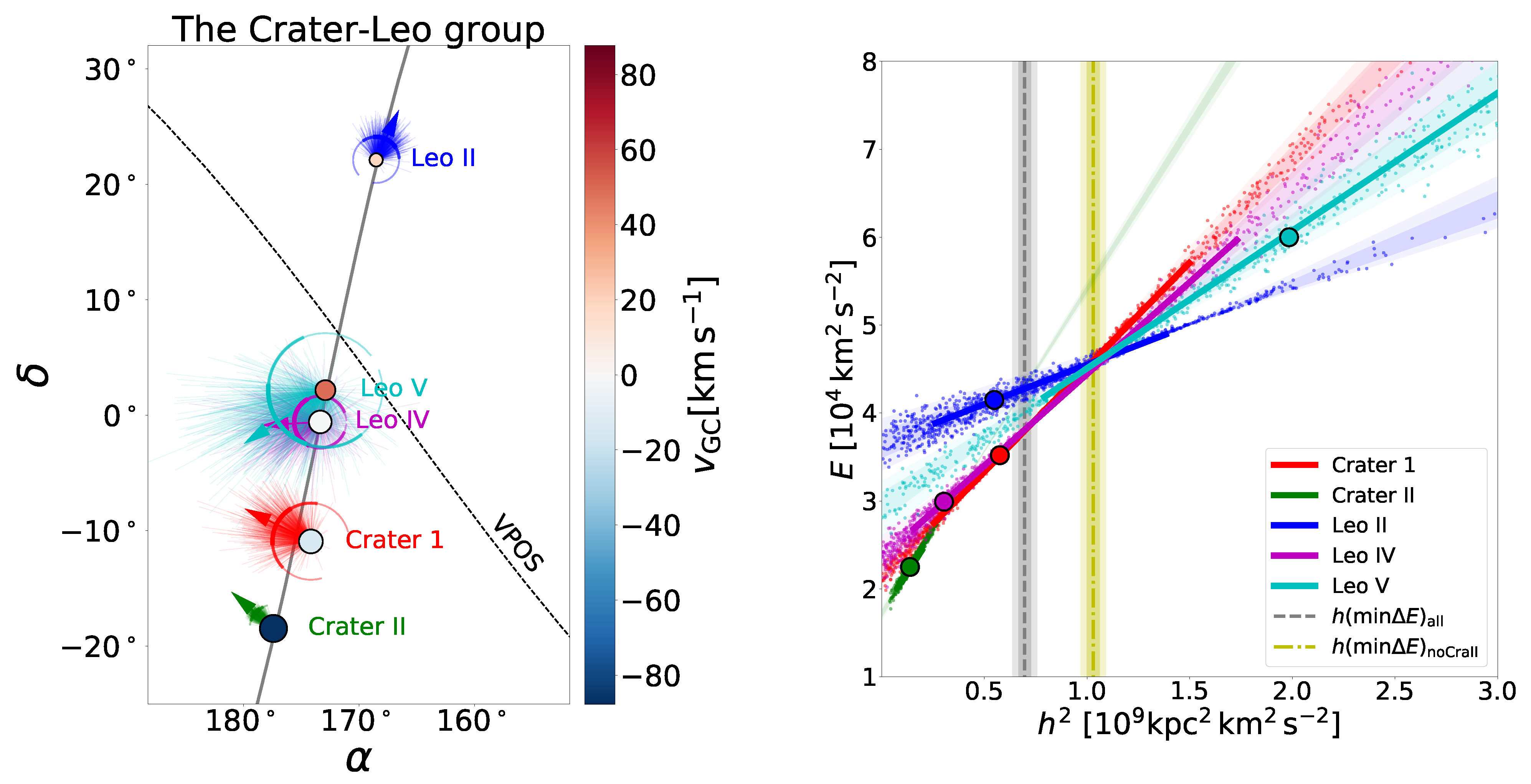
2.3. Group Infall
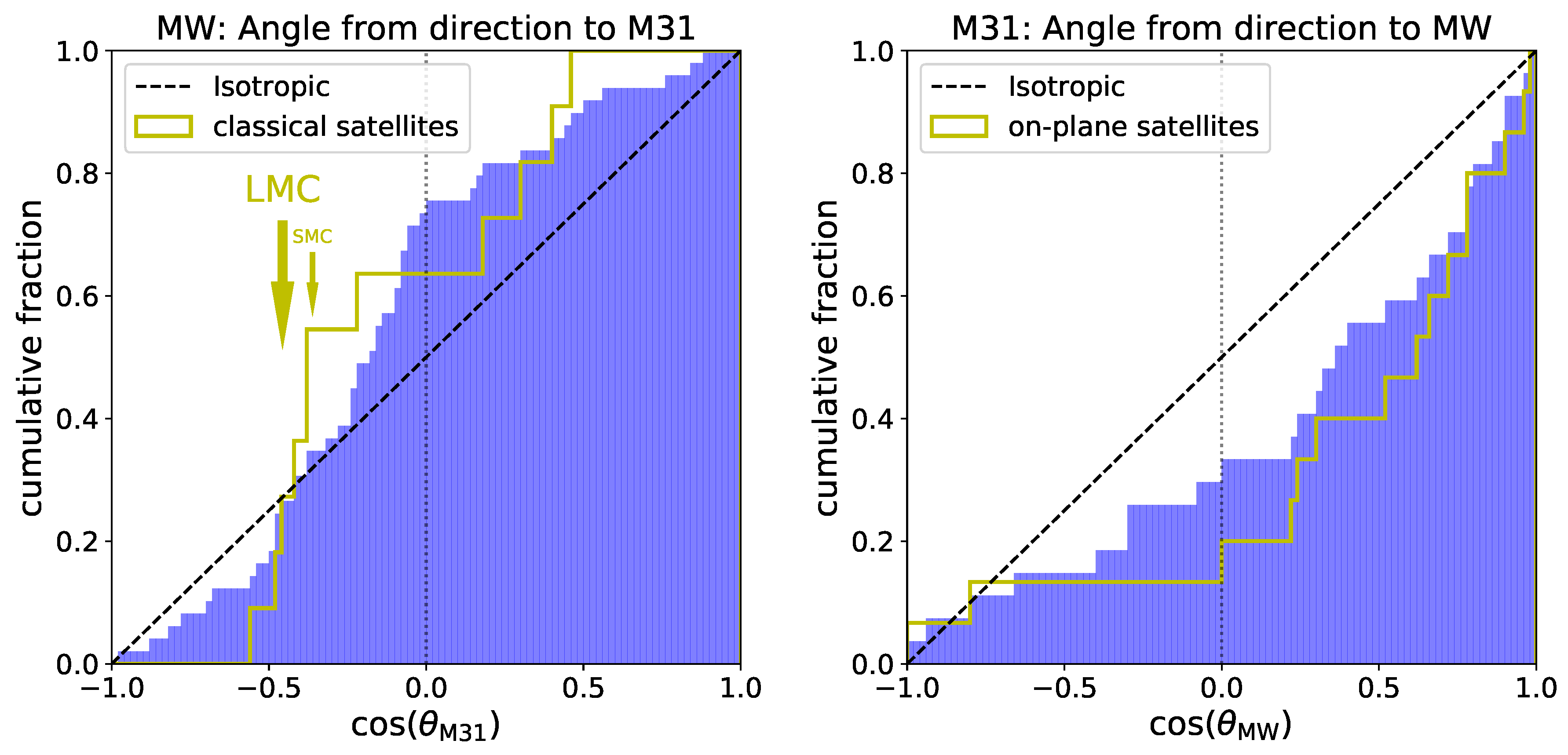
2.4. Lopsidedness
3. Other Studies of Satellite Galaxy Phase-Space Distributions
3.1. Pairs of Satellite Galaxies
3.2. Tangential Velocity Excess
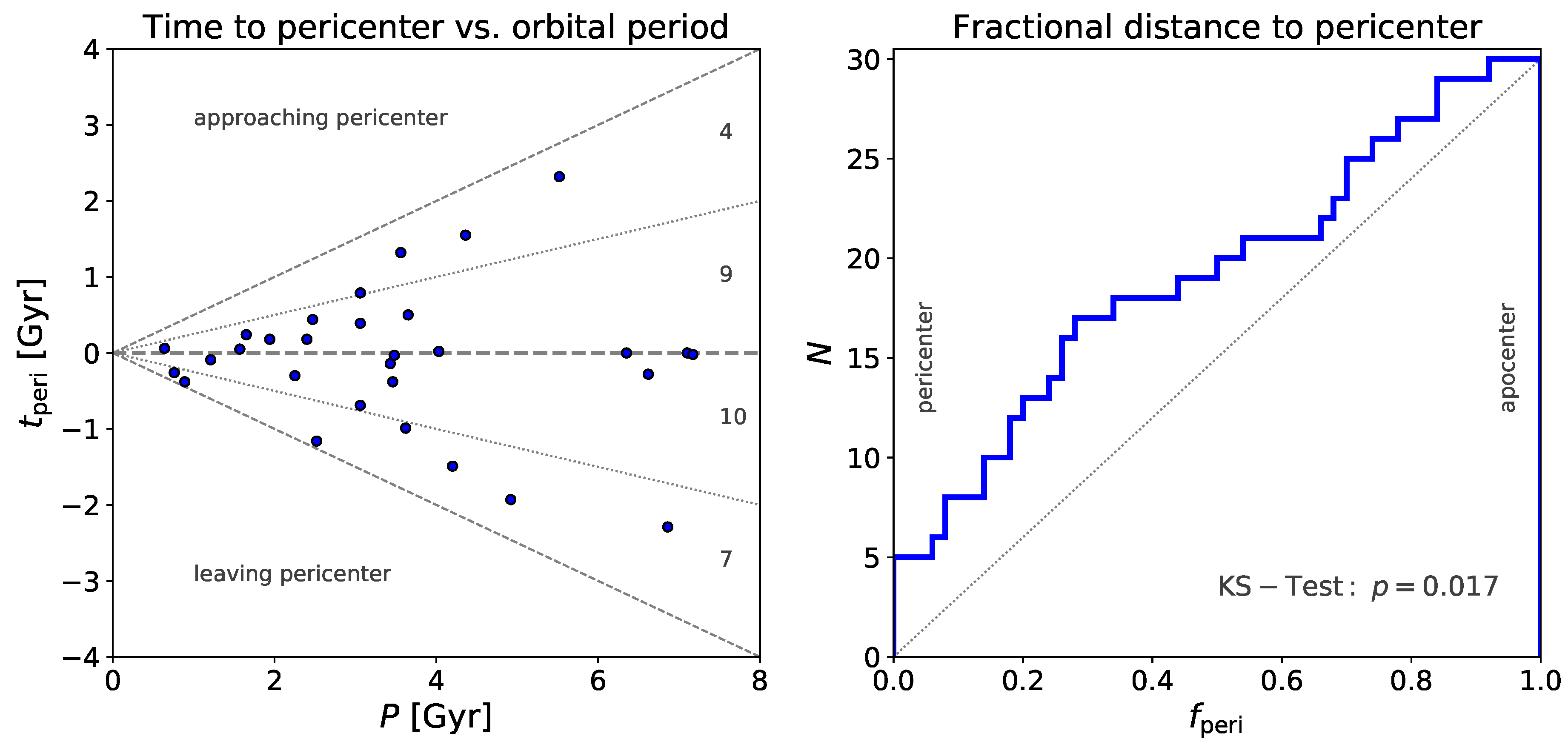
3.3. Closeness to Pericenter
4. Interdependencies between Different Types of Satellite Galaxy Phase-Space Correlations
5. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bullock, J.S.; Boylan-Kolchin, M. Small-Scale Challenges to the ΛCDM Paradigm. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 55, 343–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klypin, A.; Kravtsov, A.V.; Valenzuela, O.; Prada, F. Where Are the Missing Galactic Satellites? Astrophys. J. 1999, 522, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, B.; Ghigna, S.; Governato, F.; Lake, G.; Quinn, T.; Stadel, J.; Tozzi, P. Dark Matter Substructure within Galactic Halos. Astrophys. J. 1999, 524, L19–L22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubinski, J.; Carlberg, R.G. The Structure of Cold Dark Matter Halos. Astrophys. J. 1991, 378, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, M.G.; Peñarrubia, J. A Method for Measuring (Slopes of) the Mass Profiles of Dwarf Spheroidal Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2011, 742, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boylan-Kolchin, M.; Bullock, J.S.; Kaplinghat, M. Too big to fail? The puzzling darkness of massive Milky Way subhaloes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 415, L40–L44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroupa, P. The Dark Matter Crisis: Falsification of the Current Standard Model of Cosmology. Publ. Astron. Soc. Aust. 2012, 29, 395–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genina, A.; Benítez-Llambay, A.; Frenk, C.S.; Cole, S.; Fattahi, A.; Navarro, J.F.; Oman, K.A.; Sawala, T.; Theuns, T. The core-cusp problem: A matter of perspective. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 474, 1398–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawala, T.; Frenk, C.S.; Fattahi, A.; Navarro, J.F.; Bower, R.G.; Crain, R.A.; Dalla Vecchia, C.; Furlong, M.; Helly, J.C.; Jenkins, A.; et al. The APOSTLE simulations: Solutions to the Local Group’s cosmic puzzles. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 457, 1931–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, J.I.; Agertz, O.; Collins, M.L.M. Dark matter cores all the way down. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 459, 2573–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, A.M.; Zolotov, A. Why Baryons Matter: The Kinematics of Dwarf Spheroidal Satellites. Astrophys. J. 2014, 786, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papastergis, E.; Giovanelli, R.; Haynes, M.P.; Shankar, F. Is there a “too big to fail” problem in the field? Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 574, A113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, A.M.; Papastergis, E.; Christensen, C.R.; Governato, F.; Stilp, A.; Quinn, T.R.; Wadsley, J. How to Reconcile the Observed Velocity Function of Galaxies with Theory. Astrophys. J. 2017, 850, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutton, A.A.; Obreja, A.; Macciò, A.V. NIHAO-XVII. The diversity of dwarf galaxy kinematics and implications for the H I velocity function. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 482, 5606–5624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viel, M.; Lesgourgues, J.; Haehnelt, M.G.; Matarrese, S.; Riotto, A. Constraining warm dark matter candidates including sterile neutrinos and light gravitinos with WMAP and the Lyman-α forest. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 71, 063534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderhalden, D.; Schneider, A.; Macciò, A.V.; Diemand, J.; Bertone, G. Hints on the nature of dark matter from the properties of Milky Way satellites. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2013, 2013, 014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spergel, D.N.; Steinhardt, P.J. Observational Evidence for Self-Interacting Cold Dark Matter. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 84, 3760–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.L.M.; Martin, N.F.; Rich, R.M.; Ibata, R.A.; Chapman, S.C.; McConnachie, A.W.; Ferguson, A.M.; Irwin, M.J.; Lewis, G.F. Comparing the Observable Properties of Dwarf Galaxies on and off the Andromeda Plane. Astrophys. J. 2015, 799, L13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- York, D.G.; Adelman, J.; Anderson, J.E., Jr.; Anderson, S.F.; Annis, J.; Bahcall, N.A.; Bakken, J.A.; Barkhouser, R.; Bastian, S.; Berman, E.; et al. The Sloan Digital Sky Survey: Technical Summary. Astrophys. J. 2000, 120, 1579–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowski, M.S. The alignment of SDSS satellites with the VPOS: Effects of the survey footprint shape. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 456, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechtol, K.; Drlica-Wagner, A.; Balbinot, E.; Pieres, A.; Simon, J.D.; Yanny, B.; Santiago, B.; Wechsler, R.H.; Frieman, J.; Walker, A.R.; et al. Eight New Milky Way Companions Discovered in First-year Dark Energy Survey Data. Astrophys. J. 2015, 807, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowski, M.S.; McGaugh, S.S.; Jerjen, H. The new Milky Way satellites: Alignment with the VPOS and predictions for proper motions and velocity dispersions. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 453, 1047–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, J.D. The Faintest Dwarf Galaxies. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 57, 375–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, N.F.; Ibata, R.A.; McConnachie, A.W.; Mackey, A.D.; Ferguson, A.M.N.; Irwin, M.J.; Lewis, G.F.; Fardal, M.A. The PAndAS View of the Andromeda Satellite System. I. A Bayesian Search for Dwarf Galaxies Using Spatial and Color-Magnitude Information. Astrophys. J. 2013, 776, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crnojević, D.; Sand, D.J.; Spekkens, K.; Caldwell, N.; Guhathakurta, P.; McLeod, B.; Seth, A.; Simon, J.D.; Strader, J.; Toloba, E. The Extended Halo of Centaurus A: Uncovering Satellites, Streams, and Substructures. Astrophys. J. 2016, 823, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, O.; Jerjen, H.; Binggeli, B. New low surface brightness dwarf galaxies in the Centaurus group. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 597, A7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiboucas, K.; Jacobs, B.A.; Tully, R.B.; Karachentsev, I.D. Confirmation of Faint Dwarf Galaxies in the M81 Group. Astrophys. J. 2013, 146, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merritt, A.; van Dokkum, P.; Abraham, R. The Discovery of Seven Extremely Low Surface Brightness Galaxies in the Field of the Nearby Spiral Galaxy M101. Astrophys. J. 2014, 787, L37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, O.; Scalera, R.; Binggeli, B.; Jerjen, H. The M 101 group complex: New dwarf galaxy candidates and spatial structure. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 602, A119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsten, S.G.; Greene, J.E.; Greco, J.P.; Beaton, R.L.; Kado-Fong, E. ELVES I: Structures of Dwarf Satellites of MW-like Galaxies; Morphology, Scaling Relations, and Intrinsic Shapes. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.03435. [Google Scholar]
- Geha, M.; Wechsler, R.H.; Mao, Y.Y.; Tollerud, E.J.; Weiner, B.; Bernstein, R.; Hoyle, B.; Marchi, S.; Marshall, P.J.; Muñoz, R.; et al. The SAGA Survey. I. Satellite Galaxy Populations around Eight Milky Way Analogs. Astrophys. J. 2017, 847, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.Y.; Geha, M.; Wechsler, R.H.; Weiner, B.; Tollerud, E.J.; Nadler, E.O.; Kallivayalil, N. The SAGA Survey. II. Building a Statistical Sample of Satellite Systems around Milky Way-like Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2021, 907, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habas, R.; Marleau, F.R.; Duc, P.A.; Durrell, P.R.; Paudel, S.; Poulain, M.; Sánchez-Janssen, R.; Sreejith, S.; Ramasawmy, J.; Stemock, B.; et al. Newly discovered dwarf galaxies in the MATLAS low-density fields. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 491, 1901–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javanmardi, B.; Martinez-Delgado, D.; Kroupa, P.; Henkel, C.; Crawford, K.; Teuwen, K.; Gabany, R.J.; Hanson, M.; Chonis, T.S.; Neyer, F. DGSAT: Dwarf Galaxy Survey with Amateur Telescopes. I. Discovery of low surface brightness systems around nearby spiral galaxies. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 588, A89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henkel, C.; Javanmardi, B.; Martínez-Delgado, D.; Kroupa, P.; Teuwen, K. DGSAT: Dwarf Galaxy Survey with Amateur Telescopes. II. A catalogue of isolated nearby edge-on disk galaxies and the discovery of new low surface brightness systems. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 603, A18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pawlowski, M.S.; Famaey, B.; Jerjen, H.; Merritt, D.; Kroupa, P.; Dabringhausen, J.; Lüghausen, F.; Forbes, D.A.; Hensler, G.; Hammer, F.; et al. Co-orbiting satellite galaxy structures are still in conflict with the distribution of primordial dwarf galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 442, 2362–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piatek, S.; Pryor, C.; Bristow, P.; Olszewski, E.W.; Harris, H.C.; Mateo, M.; Minniti, D.; Tinney, C.G. Proper Motions of Dwarf Spheroidal Galaxies from Hubble Space Telescope Imaging. IV. Measurement for Sculptor. Astrophys. J. 2006, 131, 1445–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kallivayalil, N.; van der Marel, R.P.; Besla, G.; Anderson, J.; Alcock, C. Third-epoch Magellanic Cloud Proper Motions. I. Hubble Space Telescope/WFC3 Data and Orbit Implications. Astrophys. J. 2013, 764, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, S.T.; Besla, G.; van der Marel, R.P.; Boylan-Kolchin, M.; Majewski, S.R.; Bullock, J.S. The Space Motion of Leo I: Hubble Space Telescope Proper Motion and Implied Orbit. Astrophys. J. 2013, 768, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pryor, C.; Piatek, S.; Olszewski, E.W. Proper Motion of the Draco Dwarf Galaxy Based On Hubble Space Telescope Imaging. Astron. J. 2015, 149, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sohn, S.T.; Patel, E.; Besla, G.; van der Marel, R.P.; Bullock, J.S.; Strigari, L.E.; van de Ven, G.; Walker, M.G.; Bellini, A. Space Motions of the Dwarf Spheroidal Galaxies Draco and Sculptor Based on HST Proper Motions with a ∼10 yr Time Baseline. Astrophys. J. 2017, 849, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaia Collaboration; Prusti, T.; de Bruijne, J.H.J.; Brown, A.G.A.; Vallenari, A.; Babusiaux, C.; Bailer-Jones, C.A.L.; Bastian, U.; Biermann, M.; Evans, D.W.; et al. The Gaia mission. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 595, A1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, J.D. Gaia Proper Motions and Orbits of the Ultra-faint Milky Way Satellites. Astrophys. J. 2018, 863, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, T.K.; Battaglia, G.; Pawlowski, M.S.; Kallivayalil, N.; van der Marel, R.; Sohn, S.T.; Brook, C.; Besla, G. Gaia DR2 proper motions of dwarf galaxies within 420 kpc. Orbits, Milky Way mass, tidal influences, planar alignments, and group infall. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 619, A103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallivayalil, N.; Sales, L.V.; Zivick, P.; Fritz, T.K.; Del Pino, A.; Sohn, S.T.; Besla, G.; van der Marel, R.P.; Navarro, J.F.; Sacchi, E. The Missing Satellites of the Magellanic Clouds? Gaia Proper Motions of the Recently Discovered Ultra-faint Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2018, 867, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massari, D.; Helmi, A. With and without spectroscopy: Gaia DR2 proper motions of seven ultra-faint dwarf galaxies. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 620, A155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, A.B.; Li, T.S. Proper Motions of Milky Way Ultra-faint Satellites with Gaia DR2 x DES DR1. Astrophys. J. 2019, 875, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, T.K.; Carrera, R.; Battaglia, G.; Taibi, S. Gaia DR 2 and VLT/FLAMES search for new satellites of the LMC. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 623, A129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hammer, F.; Babusiaux, C.; Pawlowski, M.S.; Yang, Y.; Arenou, F.; Du, C.; Wang, J. Gaia EDR3 Proper Motions of Milky Way Dwarfs. I. 3D Motions and Orbits. Astrophys. J. 2021, 916, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnachie, A.W.; Venn, K.A. Updated Proper Motions for Local Group Dwarf Galaxies Using Gaia Early Data Release 3. Res. Notes Am. Astron. Soc. 2020, 4, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, G.; Taibi, S.; Thomas, G.F.; Fritz, T.K. Gaia early DR3 systemic motions of Local Group dwarf galaxies and orbital properties with a massive Large Magellanic Cloud. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.08819. [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel, W.E.; Demers, S. The Magellanic Plane; Dickens, R.J., Perry, J.E., Smith, F.G., King, I.R., Eds.; Royal Greenwich Observatory Bulletins; The Galaxy and the Local Group: London, UK, 1976; Volume 182, p. 241. [Google Scholar]
- Lynden-Bell, D. Dwarf galaxies and globular clusters in high velocity hydrogen streams. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1976, 174, 695–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowski, M.S.; Pflamm-Altenburg, J.; Kroupa, P. The VPOS: A vast polar structure of satellite galaxies, globular clusters and streams around the Milky Way. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 423, 1109–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, A.H.; Strigari, L.E. The Milky Way’s stellar streams and globular clusters do not align in a Vast Polar Structure. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 494, 983–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metz, M.; Kroupa, P.; Jerjen, H. Discs of satellites: The new dwarf spheroidals. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2009, 394, 2223–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowski, M.S.; Kroupa, P. The rotationally stabilized VPOS and predicted proper motions of the Milky Way satellite galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 435, 2116–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowski, M.S.; Kroupa, P. The Milky Way’s disc of classical satellite galaxies in light of Gaia DR2. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 491, 3042–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, E.; Kallivayalil, N.; Garavito-Camargo, N.; Besla, G.; Weisz, D.R.; van der Marel, R.P.; Boylan-Kolchin, M.; Pawlowski, M.S.; Gómez, F.A. The Orbital Histories of Magellanic Satellites Using Gaia DR2 Proper Motions. Astrophys. J. 2020, 893, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibata, R.A.; Lewis, G.F.; Conn, A.R.; Irwin, M.J.; McConnachie, A.W.; Chapman, S.C.; Collins, M.L.; Fardal, M.; Ferguson, A.M.N.; Ibata, N.G.; et al. A vast, thin plane of corotating dwarf galaxies orbiting the Andromeda galaxy. Nature 2013, 493, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conn, A.R.; Lewis, G.F.; Ibata, R.A.; Parker, Q.A.; Zucker, D.B.; McConnachie, A.W.; Martin, N.F.; Valls-Gabaud, D.; Tanvir, N.; Irwin, M.J.; et al. The Three-dimensional Structure of the M31 Satellite System; Strong Evidence for an Inhomogeneous Distribution of Satellites. Astrophys. J. 2013, 766, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillet, N.; Ocvirk, P.; Aubert, D.; Knebe, A.; Libeskind, N.; Yepes, G.; Gottlöber, S.; Hoffman, Y. Vast Planes of Satellites in a High-resolution Simulation of the Local Group: Comparison to Andromeda. Astrophys. J. 2015, 800, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, T.; Dutton, A.A.; Macciò, A.V. Simulated ΛCDM analogues of the thin plane of satellites around the Andromeda galaxy are not kinematically coherent structures. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 460, 4348–4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, S.T.; Patel, E.; Fardal, M.A.; Besla, G.; van der Marel, R.P.; Geha, M.; Guhathakurta, P. HST Proper Motions of NGC 147 and NGC 185: Orbital Histories and Tests of a Dynamically Coherent Andromeda Satellite Plane. Astrophys. J. 2020, 901, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, N.; Arias, V.; Guglielmo, M.; Lewis, G.F.; Ibata, R.A.; Power, C. On the stability of satellite planes-I. Effects of mass, velocity, halo shape and alignment. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 465, 641–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, N.; Arias, V.; Lewis, G.F.; Ibata, R.A.; Power, C. Stability of satellite planes in M31 II: Effects of the dark subhalo population. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 473, 2212–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Delgado, D.; Makarov, D.; Javanmardi, B.; Pawlowski, M.S.; Makarova, L.; Donatiello, G.; Lang, D.; Román, J.; Vivas, K.; Carballo-Bello, J.A. Tracing satellite planes in the Sculptor group. I. Discovery of three faint dwarf galaxies around NGC 253. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 652, A48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu-Pakdil, B.; Sand, D.J.; Crnojević, D.; Jones, M.G.; Caldwell, N.; Guhathakurta, P.; Seth, A.C.; Simon, J.D.; Spekkens, K.; Strader, J.; et al. Hubble Space Telescope Observations of NGC 253 Dwarf Satellites: Discovery of Three Ultra-faint Dwarf Galaxies. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.09312. [Google Scholar]
- Paudel, S.; Yoon, S.J.; Smith, R. A Corotating Group of Dwarf Galaxies around NGC 2750 as a Centaurus A Analog. Astrophys. J. 2021, 917, L18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tully, R.B.; Libeskind, N.I.; Karachentsev, I.D.; Karachentseva, V.E.; Rizzi, L.; Shaya, E.J. Two Planes of Satellites in the Centaurus A Group. Astrophys. J. 2015, 802, L25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, O.; Jerjen, H.; Pawlowski, M.S.; Binggeli, B. Testing the two planes of satellites in the Centaurus group. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 595, A119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, O.; Pawlowski, M.S.; Jerjen, H.; Lelli, F. A whirling plane of satellite galaxies around Centaurus A challenges cold dark matter cosmology. Science 2018, 359, 534–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, O.; Fahrion, K.; Rejkuba, M.; Hilker, M.; Lelli, F.; Lutz, K.; Pawlowski, M.S.; Coccato, L.; Anand, G.S.; Jerjen, H. The properties of dwarf spheroidal galaxies in the Cen A group. Stellar populations, internal dynamics, and a heart-shaped Hα ring. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 645, A92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, O.; Pawlowski, M.S.; Lelli, F.; Fahrion, K.; Rejkuba, M.; Hilker, M.; Kanehisa, J.; Libeskind, N.; Jerjen, H. The coherent motion of Cen A dwarf satellite galaxies remains a challenge for ΛCDM cosmology. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 645, L5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hammer, F.; Rejkuba, M.; Crnojević, D.; Yang, Y. A recent major merger tale for the closest giant elliptical galaxy Centaurus A. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 498, 2766–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowski, M.S.; Kroupa, P.; Jerjen, H. Dwarf galaxy planes: The discovery of symmetric structures in the Local Group. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 435, 1928–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, O.; Rejkuba, M.; Jerjen, H. Distances from the tip of the red giant branch to the dwarf galaxies dw1335-29 and dw1340-30 in the Centaurus group. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 615, A96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibata, N.G.; Ibata, R.A.; Famaey, B.; Lewis, G.F. Velocity anti-correlation of diametrically opposed galaxy satellites in the low-redshift Universe. Nature 2014, 511, 563–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.I.; Cooper, M.C.; Bullock, J.S.; Boylan-Kolchin, M. Are rotating planes of satellite galaxies ubiquitous? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 453, 3839–3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cautun, M.; Wang, W.; Frenk, C.S.; Sawala, T. A new spin on discs of satellite galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 449, 2576–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibata, R.A.; Famaey, B.; Lewis, G.F.; Ibata, N.G.; Martin, N. Eppur si Muove: Positional and Kinematic Correlations of Satellite Pairs in the Low Z Universe. Astrophys. J. 2015, 805, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heesters, N.; Habas, R.; Marleau, F.R.; Müller, O.; Duc, P.A.; Poulain, M.; Durrell, P.; Sánchez-Janssen, R.; Paudel, S. Flattened structures of dwarf satellites around massive host galaxies in the MATLAS low-to-moderate density fields. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.10189. [Google Scholar]
- Kroupa, P.; Theis, C.; Boily, C.M. The great disk of Milky-Way satellites and cosmological sub-structures. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 431, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zentner, A.R.; Kravtsov, A.V.; Gnedin, O.Y.; Klypin, A.A. The Anisotropic Distribution of Galactic Satellites. Astrophys. J. 2005, 629, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libeskind, N.I.; Knebe, A.; Hoffman, Y.; Gottlöber, S.; Yepes, G.; Steinmetz, M. The preferred direction of infalling satellite galaxies in the Local Group. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 411, 1525–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garaldi, E.; Romano-Díaz, E.; Borzyszkowski, M.; Porciani, C. ZOMG-III. The effect of halo assembly on the satellite population. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 473, 2234–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowski, M.S.; Kroupa, P.; Angus, G.; de Boer, K.S.; Famaey, B.; Hensler, G. Filamentary accretion cannot explain the orbital poles of the Milky Way satellites. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 424, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.; Springel, V.; Pillepich, A.; Rodriguez-Gomez, V.; Torrey, P.; Genel, S.; Vogelsberger, M.; Pakmor, R.; Marinacci, F.; Weinberger, R.; et al. The IllustrisTNG simulations: Public data release. Comput. Astrophys. Cosmol. 2019, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowski, M.S.; Sohn, S.T. On the Co-Orbitation of Satellite Galaxies Along the Great Plane of Andromeda: NGC 147, NGC 185, and Expectations from Cosmological Simulations. Astrophys. J. 2021, 1–25, submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Ibata, R.A.; Ibata, N.G.; Lewis, G.F.; Martin, N.F.; Conn, A.; Elahi, P.; Arias, V.; Fernando, N. A Thousand Shadows of Andromeda: Rotating Planes of Satellites in the Millennium-II Cosmological Simulation. Astrophys. J. 2014, 784, L6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowski, M.S.; McGaugh, S.S. Co-orbiting Planes of Sub-halos are Similarly Unlikely around Paired and Isolated Hosts. Astrophys. J. 2014, 789, L24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pawlowski, M.S.; Bullock, J.S.; Kelley, T.; Famaey, B. Do Halos that Form Early, Have High Concentration, Are Part of a Pair, or Contain a Central Galaxy Potential Host More Pronounced Planes of Satellite Galaxies? Astrophys. J. 2019, 875, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, J.; Wetzel, A.; Chapman, S.; Tollerud, E.; Hopkins, P.F.; Boylan-Kolchin, M.; Bailin, J.; Faucher-Giguère, C.A. Planes of satellites around Milky Way/M31-mass galaxies in the FIRE simulations and comparisons with the Local Group. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 504, 1379–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Cautun, M.; Frenk, C.S. Evolution of galactic planes of satellites in the EAGLE simulation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 488, 1166–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovell, M.R.; Eke, V.R.; Frenk, C.S.; Jenkins, A. The link between galactic satellite orbits and subhalo accretion. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 413, 3013–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Frenk, C.S.; Cooper, A.P. The spatial distribution of galactic satellites in the Λ cold dark matter cosmology. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 429, 1502–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahl, H.; Baumgardt, H. A comparison of the distribution of satellite galaxies around Andromeda and the results of ΛCDM simulations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 438, 2916–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowski, M.S.; Famaey, B.; Merritt, D.; Kroupa, P. On the Persistence of Two Small-scale Problems in ΛCDM. Astrophys. J. 2015, 815, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowski, M.S. The planes of satellite galaxies problem, suggested solutions, and open questions. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2018, 33, 1830004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cautun, M.; Bose, S.; Frenk, C.S.; Guo, Q.; Han, J.; Hellwing, W.A.; Sawala, T.; Wang, W. Planes of satellite galaxies: When exceptions are the rule. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 452, 3838–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowski, M.S.; Dabringhausen, J.; Famaey, B.; Flores, H.; Hammer, F.; Hensler, G.; Ibata, R.A.; Kroupa, P.; Lewis, G.F.; Libeskind, N.I.; et al. Considerations on how to investigate planes of satellite galaxies. Astron. Nachrichten 2017, 338, 854–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Libeskind, N.I.; Knebe, A.; Hoffman, Y.; Gottlöber, S. The universal nature of subhalo accretion. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 443, 1274–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Cautun, M.; Frenk, C.S.; Grand, R.J.J.; Gómez, F.A.; Marinacci, F.; Simpson, C.M. The multiplicity and anisotropy of galactic satellite accretion. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 476, 1796–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowski, M.S.; Kroupa, P.; de Boer, K.S. Making counter-orbiting tidal debris. The origin of the Milky Way disc of satellites? Astron. Astrophys. 2011, 532, A118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milgrom, M. A modification of the Newtonian dynamics as a possible alternative to the hidden mass hypothesis. Astrophys. J. 1983, 270, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Famaey, B.; Lüghausen, F.; Kroupa, P. Local Group timing in Milgromian dynamics. A past Milky Way-Andromeda encounter at z > 0.8. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 557, L3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bílek, M.; Thies, I.; Kroupa, P.; Famaey, B. MOND simulation suggests an origin for some peculiarities in the Local Group. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 614, A59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banik, I.; O’Ryan, D.; Zhao, H. Origin of the Local Group satellite planes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 477, 4768–4791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroupa, P. Dwarf spheroidal satellite galaxies without dark matter. New A 1997, 2, 139–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klessen, R.S.; Kroupa, P. Dwarf Spheroidal Satellite Galaxies without Dark Matter: Results from Two Different Numerical Techniques. Astrophys. J. 1998, 498, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, F.; Yang, Y.; Fouquet, S.; Pawlowski, M.S.; Kroupa, P.; Puech, M.; Flores, H.; Wang, J. The vast thin plane of M31 corotating dwarfs: An additional fossil signature of the M31 merger and of its considerable impact in the whole Local Group. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 431, 3543–3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Hammer, F.; Fouquet, S.; Flores, H.; Puech, M.; Pawlowski, M.S.; Kroupa, P. Reproducing properties of MW dSphs as descendants of DM-free TDGs. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 442, 2419–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, F.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Arenou, F.; Puech, M.; Flores, H.; Babusiaux, C. On the Absence of Dark Matter in Dwarf Galaxies Surrounding the Milky Way. Astrophys. J. 2019, 883, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massari, D.; Breddels, M.A.; Helmi, A.; Posti, L.; Brown, A.G.A.; Tolstoy, E. Three-dimensional motions in the Sculptor dwarf galaxy as a glimpse of a new era. Nat. Astron. 2018, 2, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massari, D.; Helmi, A.; Mucciarelli, A.; Sales, L.V.; Spina, L.; Tolstoy, E. Stellar 3D kinematics in the Draco dwarf spheroidal galaxy. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 633, A36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.S.; Helmi, A. Infall of substructures on to a Milky Way-like dark halo. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 385, 1365–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Onghia, E.; Lake, G. Small Dwarf Galaxies within Larger Dwarfs: Why Some Are Luminous while Most Go Dark. Astrophys. J. 2008, 686, L61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales, L.V.; Navarro, J.F.; Kallivayalil, N.; Frenk, C.S. Identifying true satellites of the Magellanic Clouds. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 465, 1879–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkal, D.; Belokurov, V.A. Limit on the LMC mass from a census of its satellites. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 495, 2554–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, M.; Colless, J.; Colless, M.; Bland-Hawthorn, J. Accretion of the Magellanic System onto the Galaxy. Astrophys. J. 2011, 742, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Santos, I.M.E.; Fattahi, A.; Sales, L.V.; Navarro, J.F. Magellanic satellites in ΛCDM cosmological hydrodynamical simulations of the Local Group. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 504, 4551–4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzel, A.R.; Deason, A.J.; Garrison-Kimmel, S. Satellite Dwarf Galaxies in a Hierarchical Universe: Infall Histories, Group Preprocessing, and Reionization. Astrophys. J. 2015, 807, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynden-Bell, D.; Lynden-Bell, R.M. Ghostly streams from the formation of the Galaxy’s halo. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1995, 275, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrealba, G.; Koposov, S.E.; Belokurov, V.; Irwin, M. The feeble giant. Discovery of a large and diffuse Milky Way dwarf galaxy in the constellation of Crater. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 459, 2370–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angus, G.W.; Coppin, P.; Gentile, G.; Diaferio, A. The potential role of NGC 205 in generating Andromeda’s vast thin corotating plane of satellite galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 462, 3221–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libeskind, N.I.; Guo, Q.; Tempel, E.; Ibata, R. The Lopsided Distribution of Satellite Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2016, 830, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowski, M.S.; Ibata, R.A.; Bullock, J.S. The Lopsidedness of Satellite Galaxy Systems in ΛCDM Simulations. Astrophys. J. 2017, 850, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.C.; Libeskind, N.I.; Tempel, E.; Guo, Q.; Gottlöber, S.; Yepes, G.; Wang, P.; Sorce, J.; Pawlowski, M. The origin of lopsided satellite galaxy distribution in galaxy pairs. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 488, 3100–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brainerd, T.G.; Samuels, A. Lopsided Satellite Distributions around Isolated Host Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2020, 898, L15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Libeskind, N.I.; Pawlowski, M.S.; Kang, X.; Wang, W.; Guo, Q.; Tempel, E. The Lopsided Distribution of Satellites of Isolated Central Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2021, 914, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmberg, E. A study of physical groups of galaxies. Ark. Astron. 1969, 5, 305–343. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; van den Bosch, F.C.; Mo, H.J.; Mao, S.; Kang, X.; Weinmann, S.M.; Guo, Y.; Jing, Y.P. The alignment between the distribution of satellites and the orientation of their central galaxy. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2006, 369, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Besla, G.; Kallivayalil, N.; Hernquist, L.; van der Marel, R.P.; Cox, T.J.; Kereš, D. The role of dwarf galaxy interactions in shaping the Magellanic System and implications for Magellanic Irregulars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 421, 2109–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Bergh, S. The Binary Galaxies NGC 147 and NGC 185. Astron. J. 1998, 116, 1688–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geha, M.; van der Marel, R.P.; Guhathakurta, P.; Gilbert, K.M.; Kalirai, J.; Kirby, E.N. Local Group Dwarf Elliptical Galaxies. II. Stellar Kinematics to Large Radii in NGC 147 and NGC 185. Astrophys. J. 2010, 711, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belokurov, V.; Walker, M.G.; Evans, N.W.; Faria, D.C.; Gilmore, G.; Irwin, M.J.; Koposov, S.; Mateo, M.; Olszewski, E.; Zucker, D.B. Leo V: A Companion of a Companion of the Milky Way Galaxy? Astrophys. J. 2008, 686, L83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, J.T.A.; Martin, N.F.; Rix, H.W.; Smith, K.W.; Jin, S.; Macciò, A.V. The Enigmatic Pair of Dwarf Galaxies Leo IV and Leo V: Coincidence or Common Origin? Astrophys. J. 2010, 710, 1664–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaña, M.; Fellhauer, M.; Smith, R. Leo IV and V—A possible dwarf galaxy pair? Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 542, A61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattahi, A.; Navarro, J.F.; Starkenburg, E.; Barber, C.R.; McConnachie, A.W. Galaxy pairs in the local group. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 431, L73–L77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geha, M.; Weisz, D.; Grocholski, A.; Dolphin, A.; van der Marel, R.P.; Guhathakurta, P. HST/ACS Direct Ages of the Dwarf Elliptical Galaxies NGC 147 and NGC 185. Astrophys. J. 2015, 811, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evslin, J. Binary satellite galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 440, 1225–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bovy, J. Galpy: A python Library for Galactic Dynamics. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2015, 216, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cautun, M.; Frenk, C.S. The tangential velocity excess of the Milky Way satellites. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 468, L41–L45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, A.H.; Fattahi, A.; Pace, A.B.; Strigari, L.E.; Frenk, C.S.; Gómez, F.A.; Grand, R.J.J.; Marinacci, F.; Navarro, J.F.; Pakmor, R.; et al. The velocity anisotropy of the Milky Way satellite system. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 486, 2679–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drlica-Wagner, A.; Bechtol, K.; Mau, S.; McNanna, M.; Nadler, E.O.; Pace, A.B.; Li, T.S.; Pieres, A.; Rozo, E.; Simon, J.D.; et al. Milky Way Satellite Census. I. The Observational Selection Function for Milky Way Satellites in DES Y3 and Pan-STARRS DR1. Astrophys. J. 2020, 893, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, F.; Yang, Y.; Arenou, F.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Bonifacio, P.; Babusiaux, C. Orbital Evidences for Dark-matter-free Milky Way Dwarf Spheroidal Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2020, 892, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Oliver, W.H.; Lewis, G.F.; Read, J.I.; Collins, M.L.M. On the origin of the asymmetric dwarf galaxy distribution around andromeda. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 492, 456–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astropy Collaboration; Price-Whelan, A.M.; Sipocz, B.M.; Günther, H.M.; Lim, P.L.; Crawford, S.M.; Conseil, S.; Shupe, D.L.; Craig, M.W.; Dencheva, N.; et al. The Astropy Project: Building an Open-science Project and Status of the v2.0 Core Package. Astron. J. 2018, 156, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astropy Collaboration; Robitaille, T.P.; Tollerud, E.J.; Greenfield, P.; Droettboom, M.; Bray, E.; Aldcroft, T.; Davis, M.; Ginsburg, A.; Price-Whelan, A.M.; et al. Astropy: A community Python package for astronomy. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 558, A33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, F.; Granger, B.E. IPython: A System for Interactive Scientific Computing. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2007, 9, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J.D. Matplotlib: A 2D graphics environment. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2007, 9, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, C.R.; Millman, K.J.; van der Walt, S.J.; Gommers, R.; Virtanen, P.; Cournapeau, D.; Wieser, E.; Taylor, J.; Berg, S.; Smith, N.J.; et al. Array programming with NumPy. Nature 2020, 585, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virtanen, P.; Gommers, R.; Oliphant, T.E.; Haberland, M.; Reddy, T.; Cournapeau, D.; Burovski, E.; Peterson, P.; Weckesser, W.; Bright, J.; et al. SciPy 1.0: Fundamental algorithms for scientific computing in Python. Nat. Methods 2020, 17, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


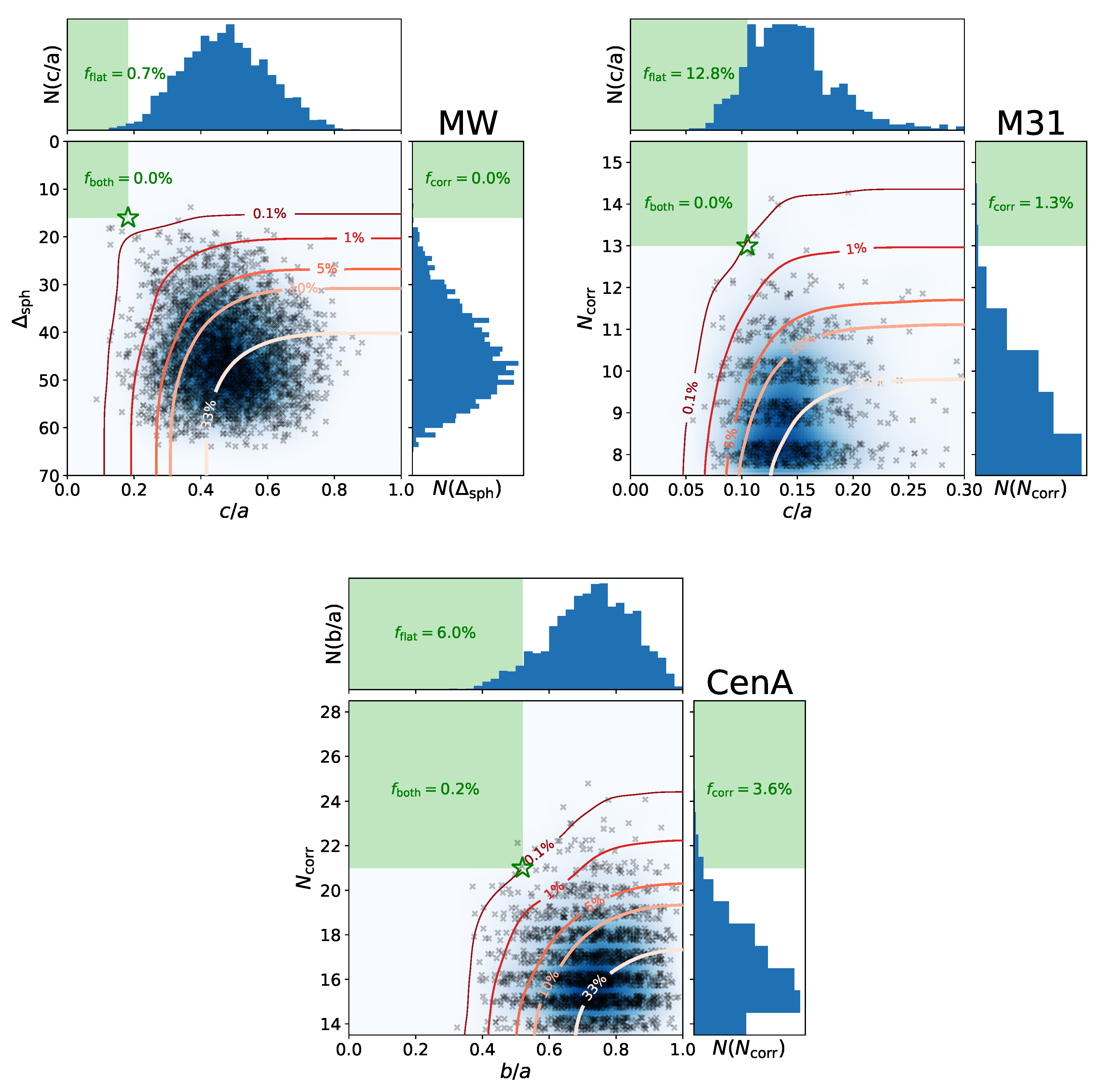
| Host | Extent | Spatial Flattening | Kinematic Coherence | LSS | Refs. | Comments | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MW | 11 | 250 kpc | , kpc | 8 aligned orbital poles | [54,58] | classical satellites only | |
| 40–50 | –, –30 kpc | 50–75% aligned orbital poles | [22,49] | 3 counter-orbit | |||
| M31 | 15–19 | 400 kpc | , kpc | 13/15 have coherence | [60,76] | ||
| 2/2 with PMs co-orbit | [64] | ||||||
| Cen A | 28 | 800 kpc | 21/28 have coherence | [74] | |||
| M 81 | 19 | 600 kpc | , kpc | unknown | SGP aligned | [27] | gas-poor satellites only |
| M 83 | 6 | 210 kpc | kpc | unknown | [77] | ||
| M 101 | 11 | 1.5 Mpc | kpc | unknown | [29] | filament? | |
| NGC 253 | 7 | 600 kpc | , kpc | 4/5 have coherence | [67] | filament? | |
| NGC 2750 | 7 | 150 kpc | N/A | 6 with show strong coherence | N/A | [69] | lower-mass Cen A analog? |
| Pair | Host | Satellite Plane Alignment | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| LMC + SMC | MW | yes (in pos + 3D vel) | group bringing in a number of smaller satellites, too |
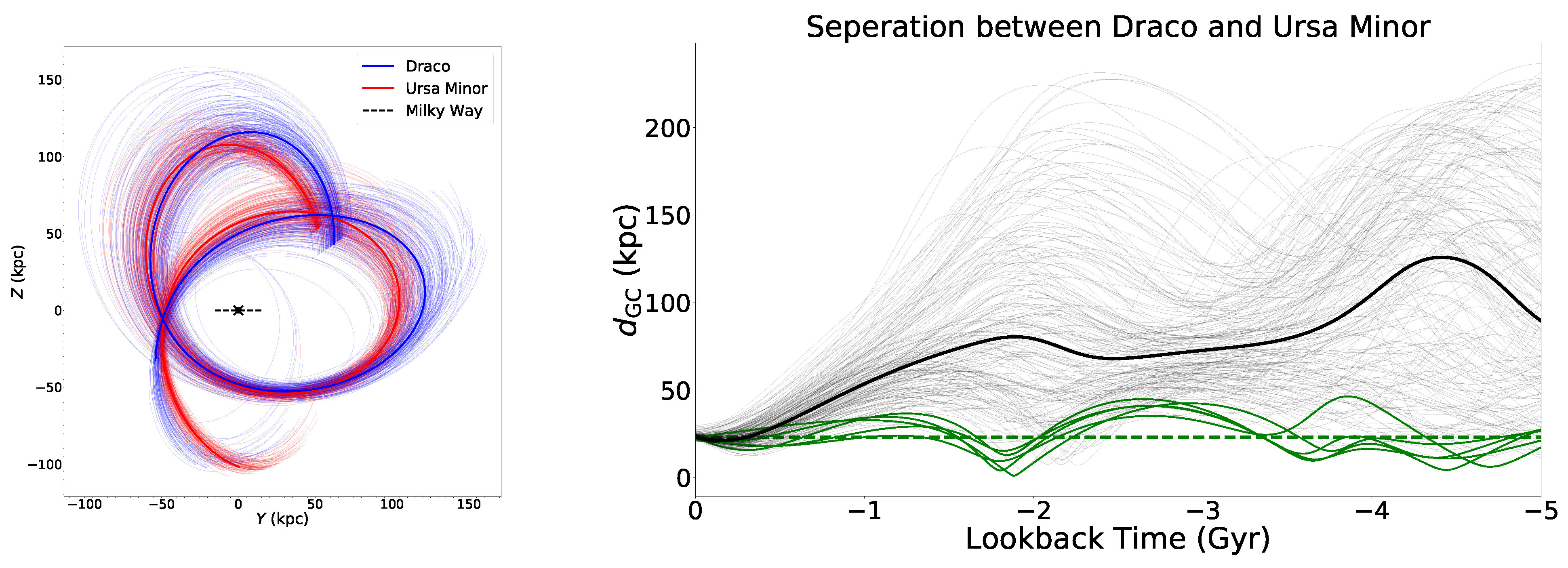
| Draco + Ursa Minor | MW | yes (in pos + 3D vel) | within PM uncertainties, small separation possible for long time |
| Leo IV + Leo V | MW | yes (in pos, 3D vel unclear) | possible group with Crater 1, Crater II, Leo II? |
| And I + And III | M31 | yes (in pos, los vel) | no PMs available yet |
| NGC 147 + NGC 185 | M31 | yes (pos + 3D vel) | PMs indicate similar orbital plane but different orbits |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pawlowski, M.S. Phase-Space Correlations among Systems of Satellite Galaxies. Galaxies 2021, 9, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies9030066
Pawlowski MS. Phase-Space Correlations among Systems of Satellite Galaxies. Galaxies. 2021; 9(3):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies9030066
Chicago/Turabian StylePawlowski, Marcel S. 2021. "Phase-Space Correlations among Systems of Satellite Galaxies" Galaxies 9, no. 3: 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies9030066
APA StylePawlowski, M. S. (2021). Phase-Space Correlations among Systems of Satellite Galaxies. Galaxies, 9(3), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies9030066






