A Statistical Estimation of the Occurrence of Extraterrestrial Intelligence in the Milky Way Galaxy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
- Initiated a 3D spatial hash table of Milky Way with distributed gas mass;
- Generated Sun-like stars harboring Earth-like planets and activated supernova explosion with the same distribution as observations;
- For each Earth-like planet, allow life to emerge with the Poisson process of abiogenesis;
- For each life-bearing planet free from transient events (e.g., supernova), follow life’s evolution into intelligence.
2.1. Formation of Sun-Like Star Harboring Earth-Like Planet
2.1.1. Prevalence of Sun-Like Star Harboring Earth-Like Planets
2.1.2. Spatial Hash Table and Distribution of Gas
2.1.3. Upper Limit of Star Formation
2.1.4. Stellar Mass and Main Sequence Lifetime
2.1.5. Star Formation Model
2.2. Supernova
2.3. Poisson Process of Abiogenesis
2.4. Sufficient Time for the Evolution of Intelligence
2.5. Annihilation of Intelligence
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Spatial–Temporal Analysis on the Occurrence of ETI
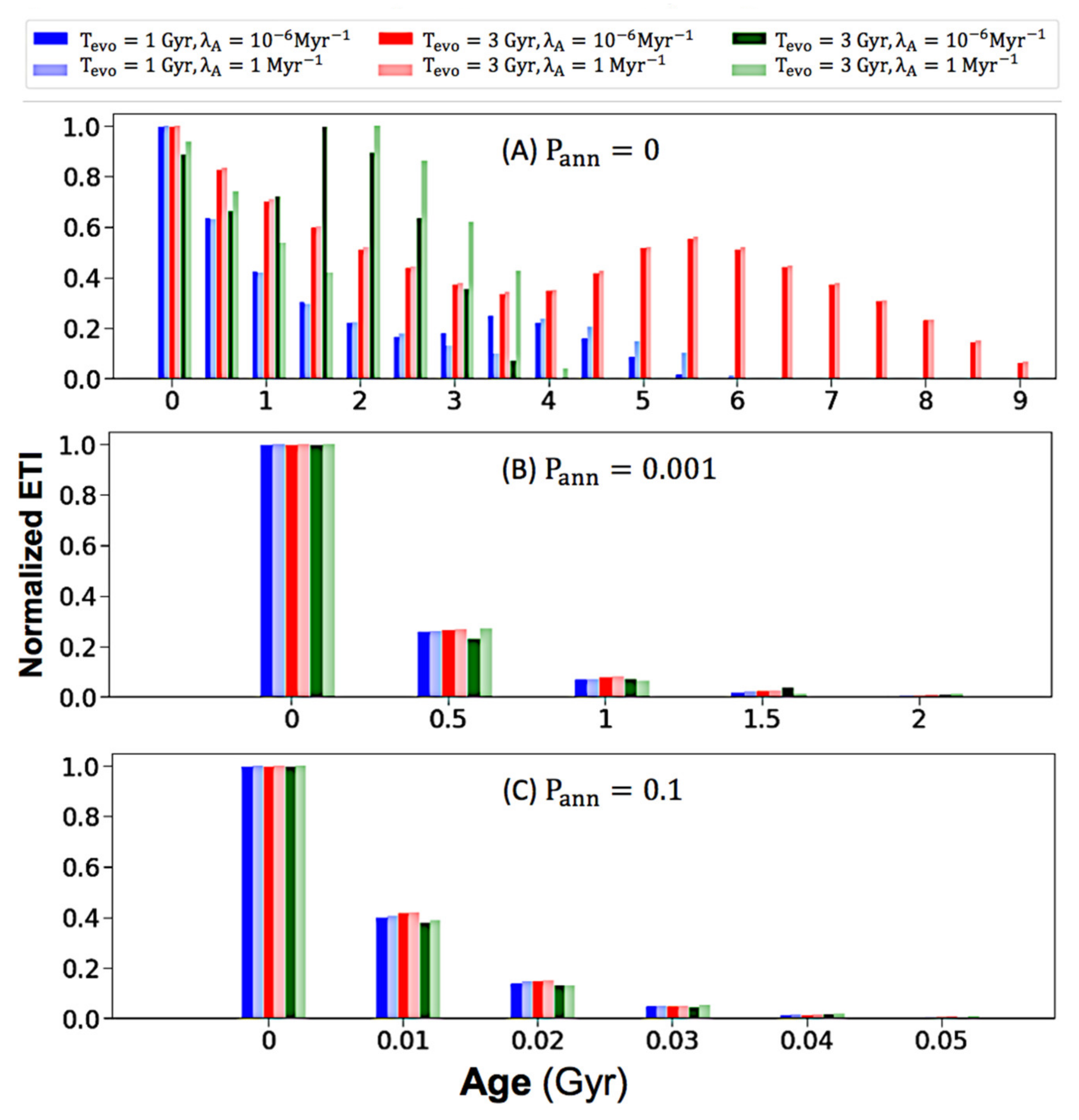
3.2. The Effect of Intelligence Annihilation Parameter on Age Distributions
3.3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tarter, J. The search for extraterrestrial intelligence (SETI). Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2001, 39, 511–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, M.H. Explanation for the absence of extraterrestrials on Earth. Q. J. R. Astron. Soc. 1975, 16, 128. [Google Scholar]
- Carroll-Nellenback, J.; Frank, A.; Wright, J.; Scharf, C. The Fermi Paradox and the Aurora effect: Exo-civilization settlement, expansion, and steady states. Astron. J. 2019, 158, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foucher, F.; Hickman-Lewis, K.; Westall, F.; Brack, A. A statistical approach to illustrate the challenge of astrobiology for public outreach. Life 2017, 7, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drake, F.D. The Radio Search for Intelligent Extraterrestrial Life. In Current Aspects of Exobiology; Mamikunian, G., Briggs, M.H., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1965; pp. 323–345. [Google Scholar]
- Walters, C.; Hoover, R.A.; Kotra, R.K. Inter-stellar colonization: A new parameter for the Drake equation? Icarus 1980, 41, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burchell, M.J. W(h)ither the Drake equation? Int. J. Astrobiol. 2006, 5, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forgan, D.H. A numerical testbed for hypotheses of extraterrestrial life and intelligence. Int. J. Astrobiol. 2009, 8, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirkovic, M.M. Earths: Rare in time, not space? J. Br. Interplanet. Soc. 2004, 57, 53. [Google Scholar]
- Maccone, C. The statistical Drake equation. Acta Astronaut. 2010, 67, 1366–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glade, N.; Ballet, P.; Bastien, O. A stochastic process approach of the Drake equation parameters. Int. J. Astrobiol. 2012, 11, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balazs, B. The Galactic Belt of Intelligent Life. In Bioastronomy—The Next Steps; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1988; pp. 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, G.; Brownlee, D.; Ward, P. The galactic habitable zone: Galactic chemical evolution. Icarus 2001, 152, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lineweaver, C.H.; Fenner, Y.; Gibson, B.K. The Galactic habitable zone and the age distribution of complex life in the Milky Way. Science 2004, 303, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowanlock, M.G.; Patton, D.R.; McConnell, S. A model of habitability within the Milky Way Galaxy. Astrobiology 2011, 11, 855–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naab, T.; Ostriker, J.P. A simple model for the evolution of disc galaxies: The Milky Way. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2006, 366, 899–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurić, M.; Ivezić, Ž.; Brooks, A.; Lupton, R.H.; Schlegel, D.; Finkbeiner, D.; Padmanabhan, N.; Bond, N.; Sesar, B.; Rockosi, C.M.; et al. The Milky Way Tomography with SDSS. I. stellar number density distribution. Astrophys. J. 2008, 673, 864–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prantzos, N. On the “galactic habitable zone”. Space Sci. Rev. 2008, 135, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, I.S.; Gowanlock, M.G. Extending galactic habitable zone modeling to include the emergence of intelligent life. Astrobiology 2015, 15, 683–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forgan, D.H.; Rice, K. Numerical testing of the Rare Earth Hypothesis using Monte Carlo realization techniques. Int. J. Astrobiol. 2010, 9, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hair, T.W. Temporal dispersion of the emergence of intelligence: An inter-arrival time analysis. Int. J. Astrobiol. 2011, 10, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegel, D.; Turner, E. Bayesian analysis of the astrobiological implications of life’s early emergence on Earth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharf, C.; Cronin, L. Quantifying the origins of life on a planetary scale. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 8127–8132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Kipping, D. On the rate of abiogenesis from a Bayesian informatics perspective. Astrobiology 2018, 18, 1574–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kipping, D. An objective Bayesian analysis of life’s early start and our late arrival. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 11995–12003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livio, M. How rare are extraterrestrial intelligence, and when did they emerge? Astrophys. J. 1999, 511, 429–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, B. Five- or six-step scenario for evolution? Int. J. Astrobiol. 2008, 7, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salpeter, E.E. The luminosity function and stellar evolution. Astrophys. J. 1955, 121, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petigura, E.A.; Howard, A.W.; Marcy, G.W. Prevalence of Earth-size planets orbiting Sun-like stars. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 19273–19278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastings, E.J.; Mesit, J.; Guha, R.K. Optimization of large-scale, real-timesimulations by spatial hashing. In Proceedings of the 2005 Summer Computer Simulation Conference, Cherry Hill, NJ, USA, 24–28 July 2005; Part of the 2005 Summer Simulation Multiconference (SummerSim’05). Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Fuentes, S.A.; De Ridder, J.; Debosscher, J. Stellar halo hierarchical density structure identification using (F)OPTICS. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 599, A143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, F.; Gentile, G.; Salucci, P.; Martins, C.F.; Wilkinson, M.I.; Gilmore, G.; Grebel, E.K.; Koch, A.; Wyse, R. A Constant Dark Matter Halo Surface Density in Galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2009, 397, 1169–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M. The Rate of star formation. Astrophysics 1959, 129, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennicutt, R.C., Jr. The global Schmidt law in star forming galaxies. Astrophysics 1998, 498, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arifyanto, M.I.; Fuchs, B.; Jahreiß, H.; Wielen, R. Kinematics of nearby subdwarf stars. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 433, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.J.; Kawaler, S.D. Stellar Interiors: Physical Principles, Structure, and Evolution; Springer: Belin, Germany, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Sackmann, I.J.; Boothroyd, A.I.; Kraemer, K.E. Our Sun. III. Present and future. Astrophys. J. 1993, 418, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snaith, O.; Haywood, M.; Matteo, P.; Lehnert, M.; Combes, F.; Katz, D.; Gómez, A. Reconstructing the star formation history of the Milky Way disc(s) from chemical abundances. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 578, A18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmore, G.; Wyse, R.F.G. The chemical evolution of the Galaxy. Nature 1986, 322, 806–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, A.M.; Beacom, J.F. On the normalisation of the cosmic star formation history. Astrophys. J. 2006, 651, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madau, P.; Dickinson, M. Cosmic star formation history. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 52, 415–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenner, Y.; Gibson, B.K. Deriving the metallicity distribution function of galactic systems. PASA 2003, 20, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammann, G.; Loeffler, W.; Schroeder, A. The Galactic supernova rate. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 1994, 92, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutukov, A.V.; Yungelson, L.R.; Iben, I., Jr. The frequencies of supernovae in binaries. Astrophys. J. 1992, 386, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Yang, W. A comprehensive progenitor model for SNe Ia. Astrophys. J. 2010, 710, 1310–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gehrels, N.; Laird, C.M.; Jackman, C.H.; Cannizzo, J.K.; Mattson, B.J.; Chen, W. Ozone depletion from nearby supernovae. Astrophys. J. 2003, 585, 1169–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.; Branch, D. Supernova Absolute-Magnitude Distributions. Astrophys. J. 1990, 100, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, D.; Jenkins, R.; Wright, J.; Maddox, L. Absolute-magnitude distributions of supernovae. Astron. J. 2014, 147, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesson, P. Panspermia, past and present: Astrophysical and biophysical conditions for the dissemination of life in space. Space Sci. Rev. 2010, 156, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoerner, S.V. The search for signals from other civilizations. Science 1961, 134, 1839–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nick, B. Existential risks analyzing human extinction scenarios and related hazards. J. Evol. Technol. 2002, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Billings, L. Alien Anthropocene: How Would Other Worlds Battle Climate Change? Sci. Am. 2018, 28. [Google Scholar]
- Sotos, J.G. Biotechnology and the lifetime of technical civilizations. Int. J. Astrobiol. 2019, 18, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutil, Y.; Dumas, S. Sustainability: A tedious path to galactic colonization. arXiv 2007, arXiv:0711.1777. [Google Scholar]
- Haqq-Misra, J.D.; Baum, S.D. The sustainability solution to the Fermi paradox. arXiv 2009, arXiv:0906.0568. [Google Scholar]
- Grinspoon, D. Lonely Planets, The Natural Philosophy of Alien Life; HarperCollins Publishers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Nittler, L.R. Looking for Life in Far Distant Places. Science 2004, 303, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forgan, D.H.; Dayal, P.; Cockell, C.; Noam, L. Evaluating galactic habitability using high resolution cosmological simulations of galaxy formation. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.01786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryder, G. Bombardment of the Hadean Earth: Wholesome or Deleterious? Astrobiology 2003, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmieder, M.; Krin, D.A. Earth’s Impact Events through Geologic Time: A List of Recommended Ages for Terrestrial Impact Structures and Deposits. Astrobiology 2020, 20, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
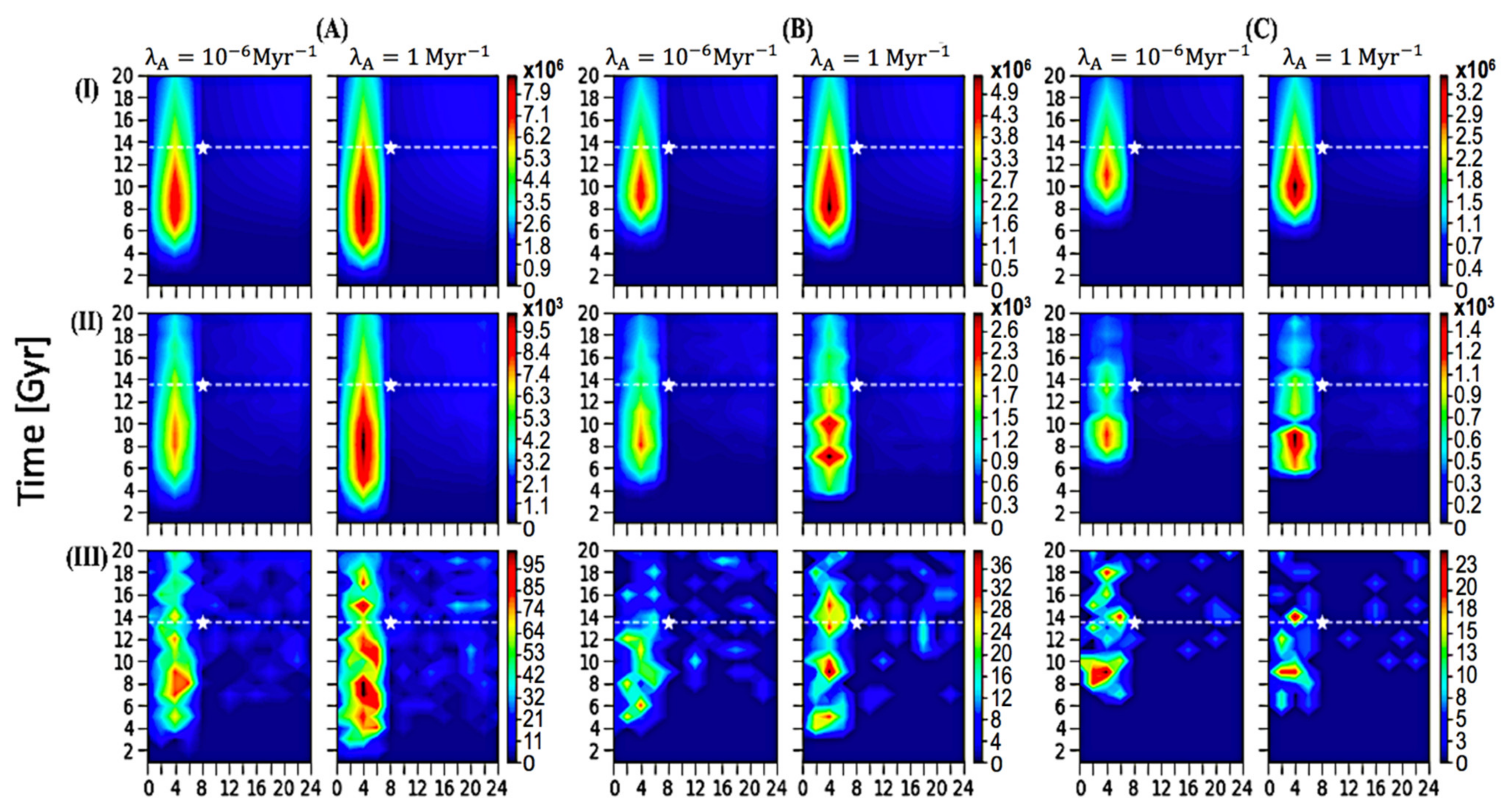
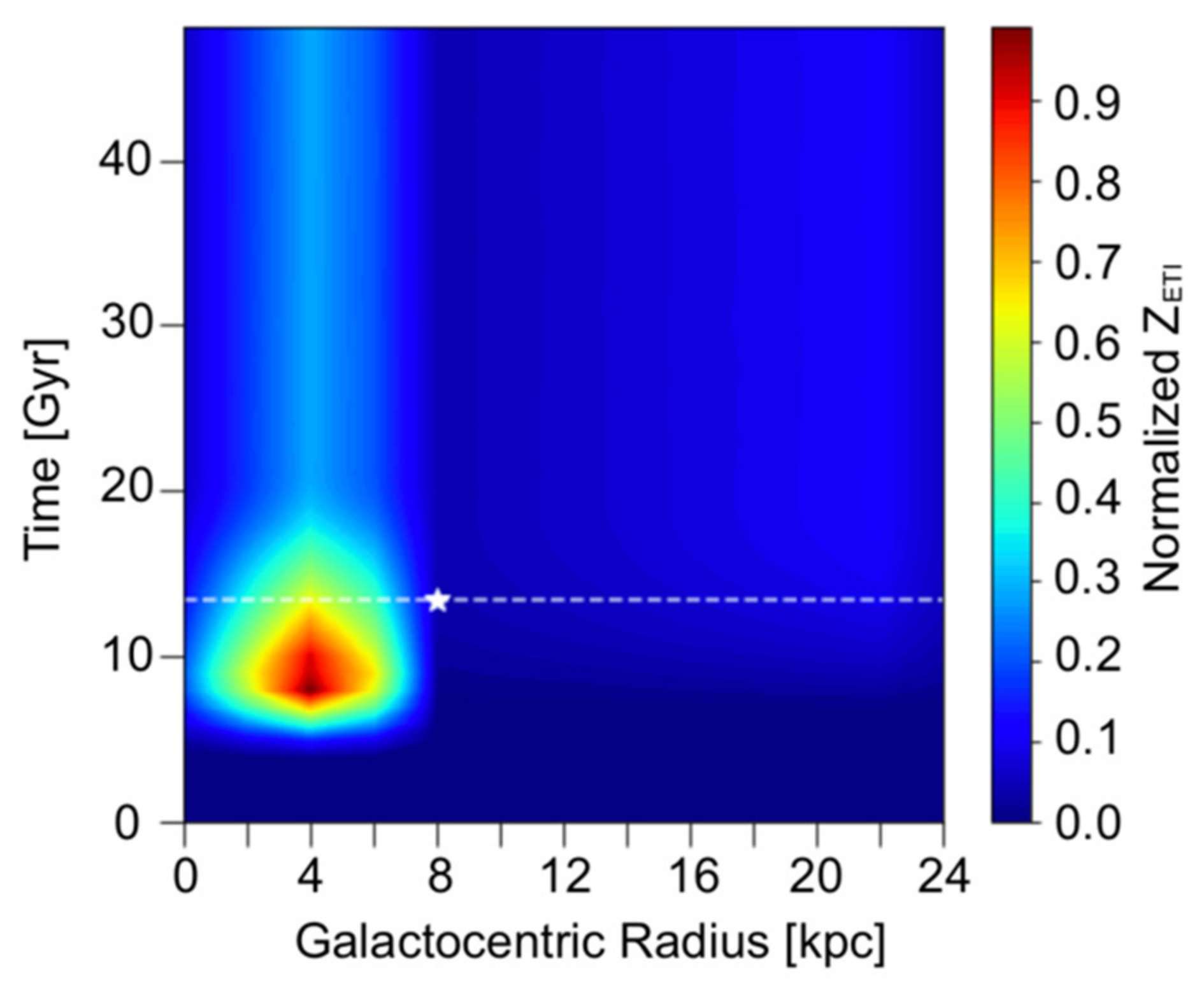
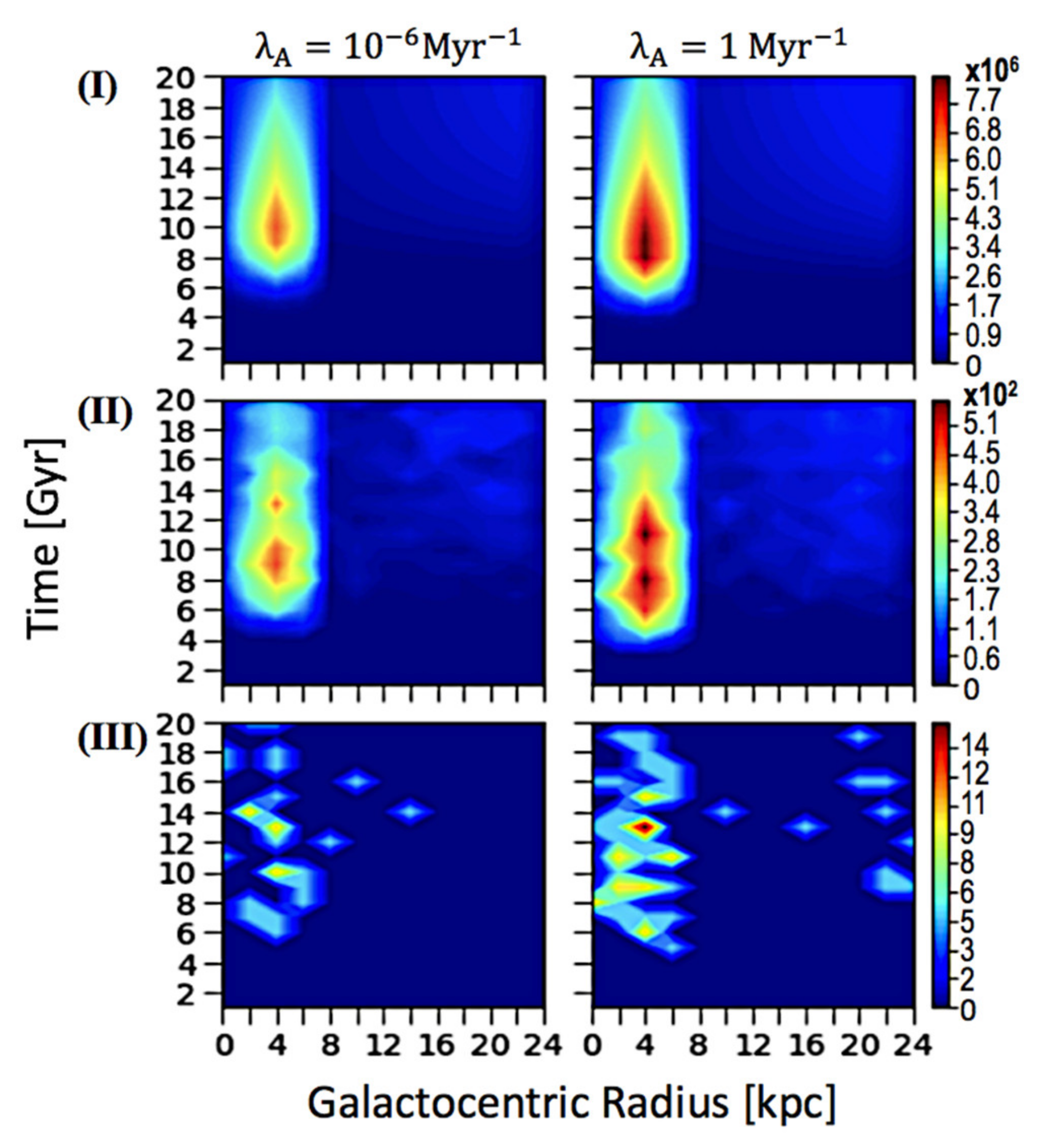
| Tevo = 1 Gyr | Tevo = 3 Gyr | Tevo = 5 Gyr | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pann = 0 | 7,811,780 | 8,729,415 | 4,566,340 | 5,362,915 | 2,832,970 | 3,598,260 |
| Pann = 0.5 | 7805 | 10,455 | 2159 | 2880 | 1117 | 1510 |
| Pann = 0.99 | 80 | 105 | 30 | 40 | 25 | 25 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, X.; Jiang, J.H.; Fahy, K.A.; Yung, Y.L. A Statistical Estimation of the Occurrence of Extraterrestrial Intelligence in the Milky Way Galaxy. Galaxies 2021, 9, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies9010005
Cai X, Jiang JH, Fahy KA, Yung YL. A Statistical Estimation of the Occurrence of Extraterrestrial Intelligence in the Milky Way Galaxy. Galaxies. 2021; 9(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies9010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Xiang, Jonathan H. Jiang, Kristen A. Fahy, and Yuk L. Yung. 2021. "A Statistical Estimation of the Occurrence of Extraterrestrial Intelligence in the Milky Way Galaxy" Galaxies 9, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies9010005
APA StyleCai, X., Jiang, J. H., Fahy, K. A., & Yung, Y. L. (2021). A Statistical Estimation of the Occurrence of Extraterrestrial Intelligence in the Milky Way Galaxy. Galaxies, 9(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies9010005





