Variable Magellanic HMXB Sources versus Variable ULX Sources: Nothing to Brag about the ULX Sources
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. X-ray Data Sets
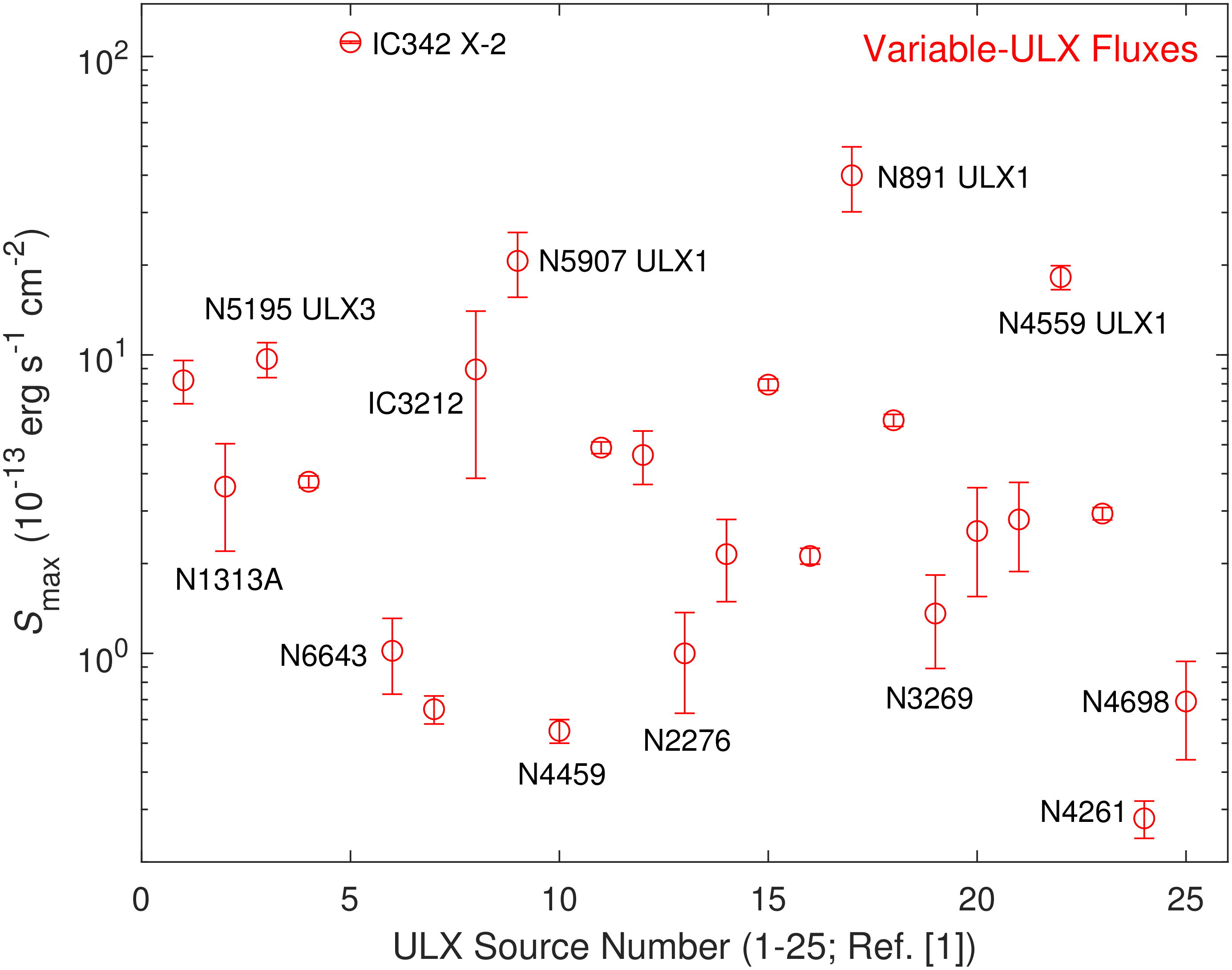
- The strongly variable ULX data set (25 sources) in the 0.3–10 keV band [1];
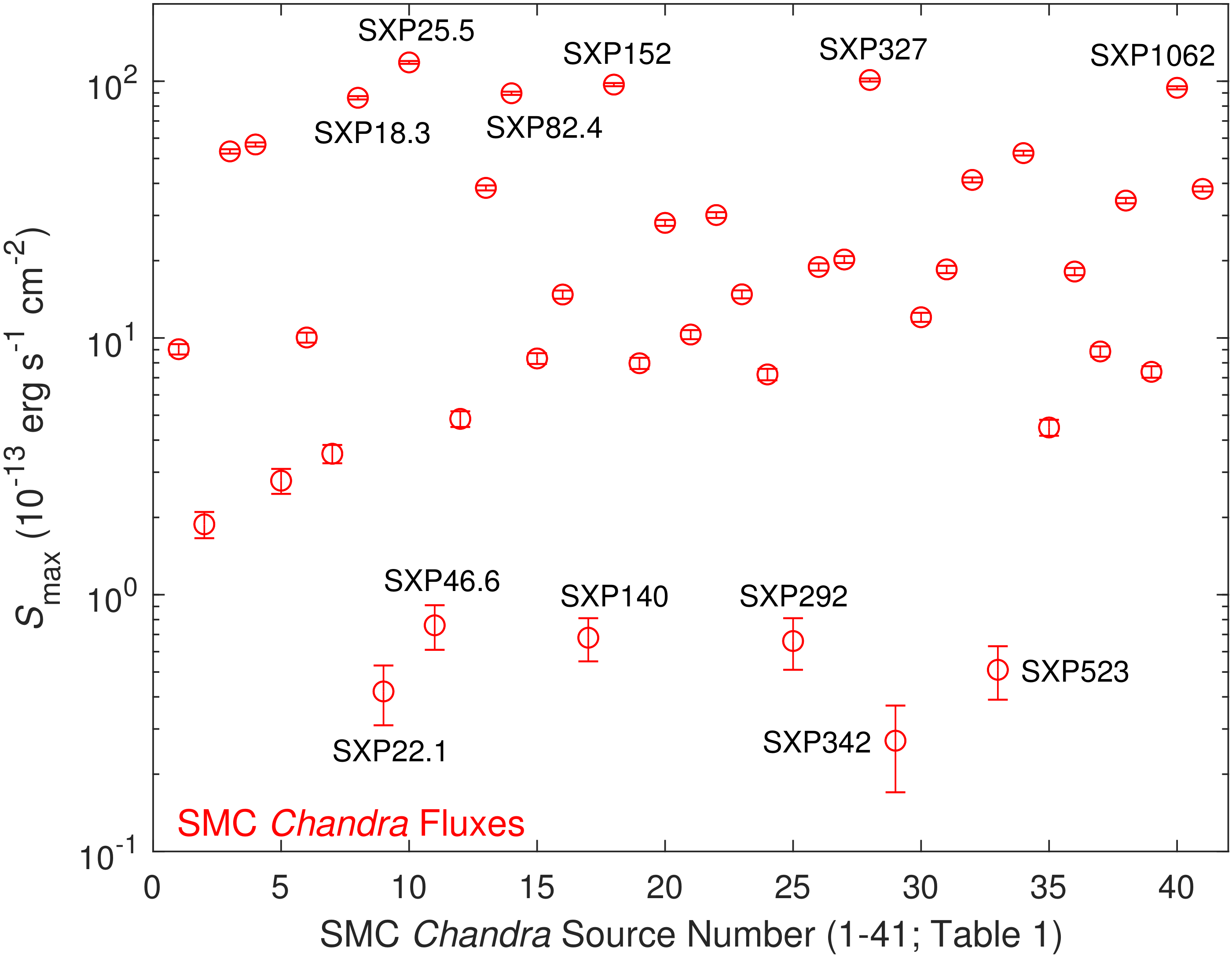
- Our library’s sample of SMC Chandra data (41 sources) in the 0.3–8 keV band (Table 1);
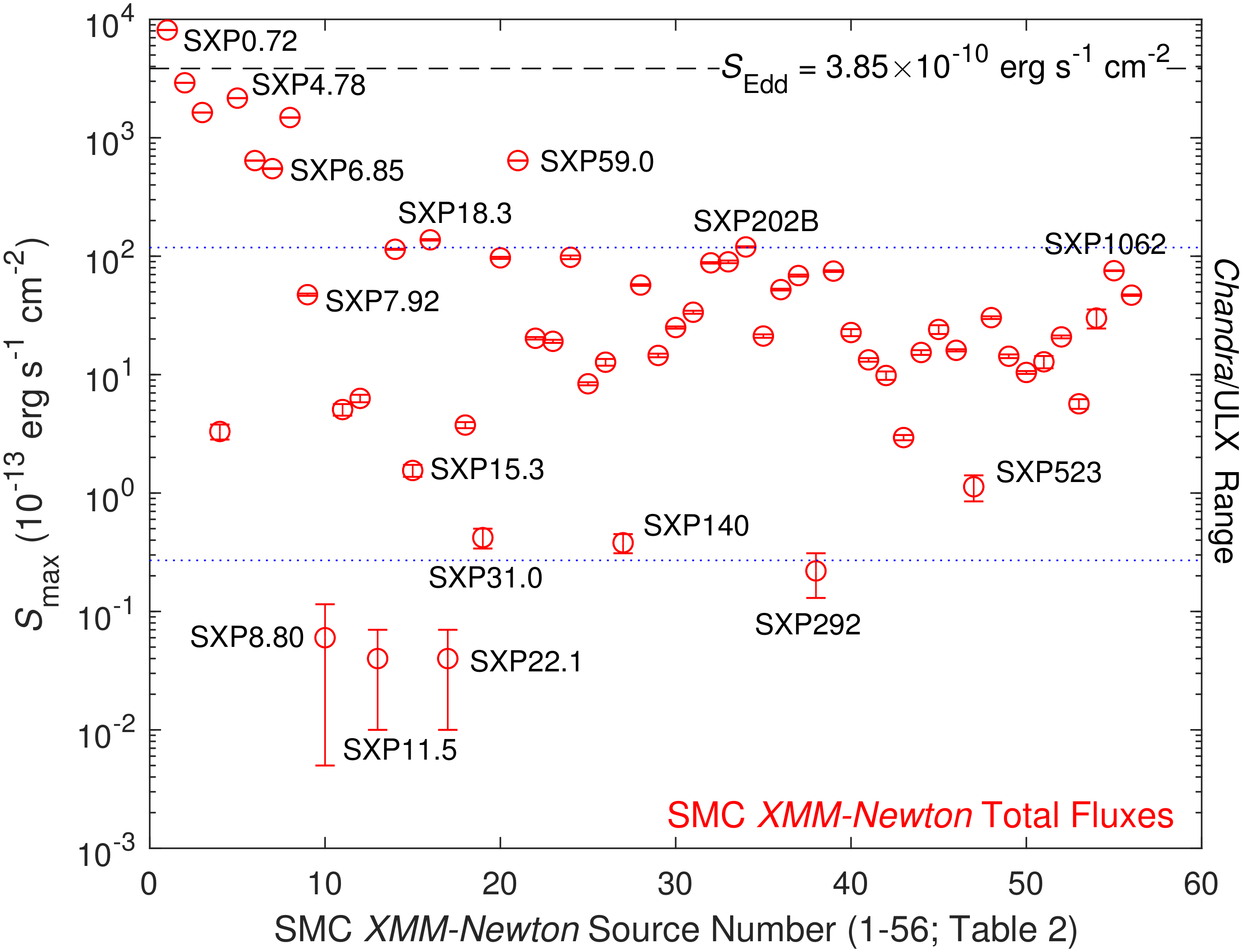
- Our library’s sample of SMC XMM-Newton data (56 sources) in the 0.2–12 keV band (Table 2);
- The combined (2 + 3) SMC data set (58 sources) considering the maximum flux for each source;
- A pseudo-data set (1 + 4) that naively combines the SMC with the ULX luminosities (83 sources).
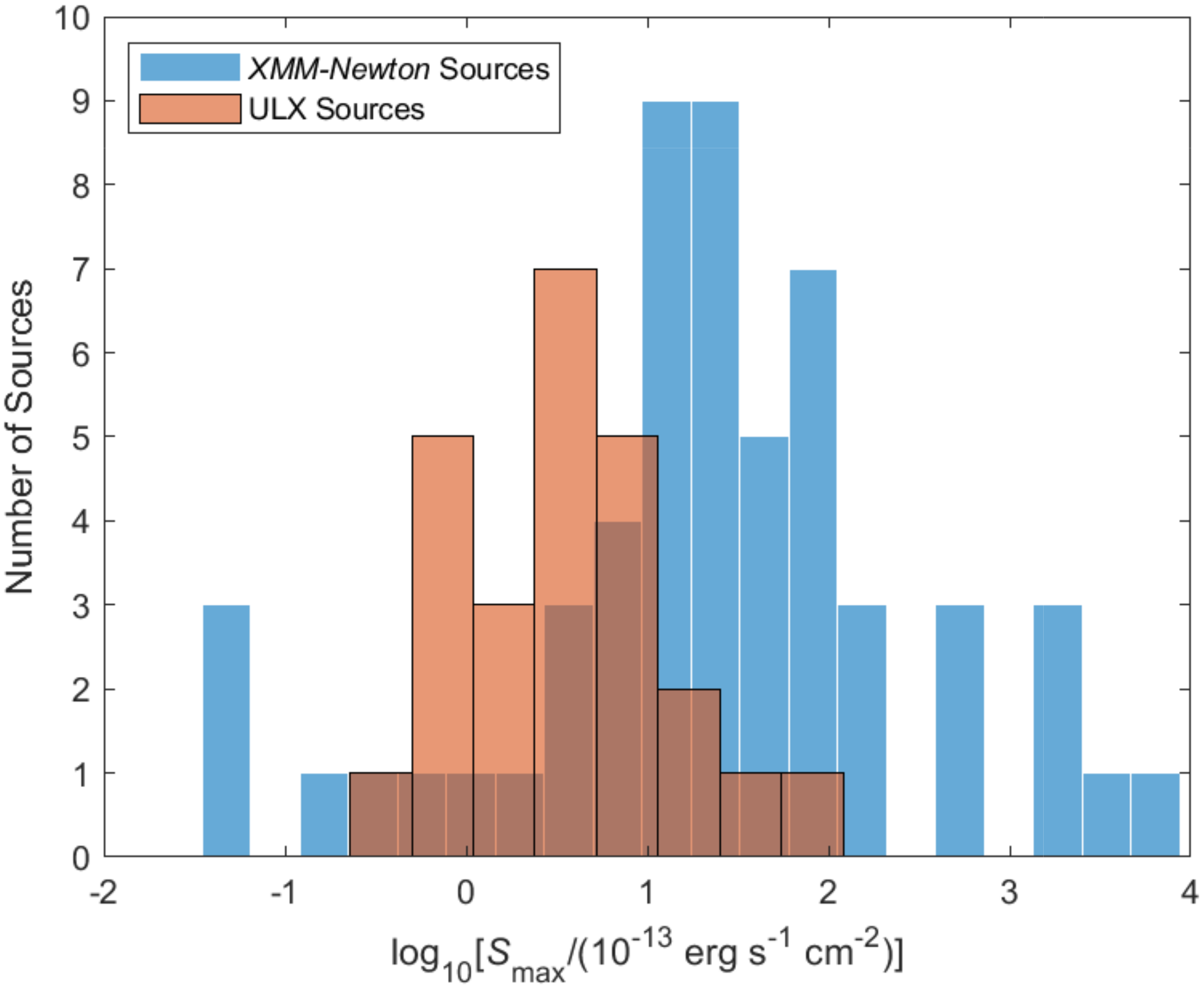
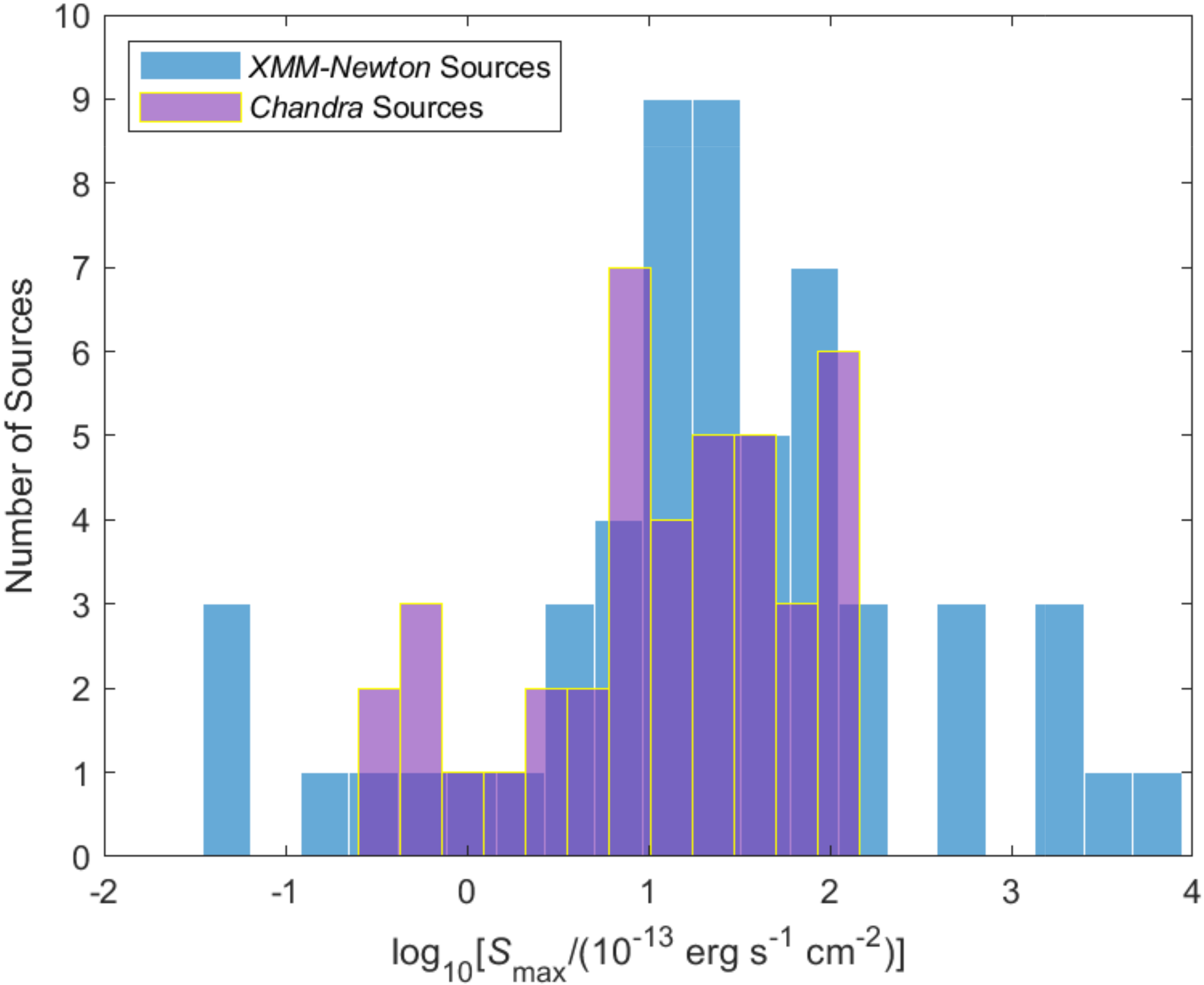
2.1. Histograms
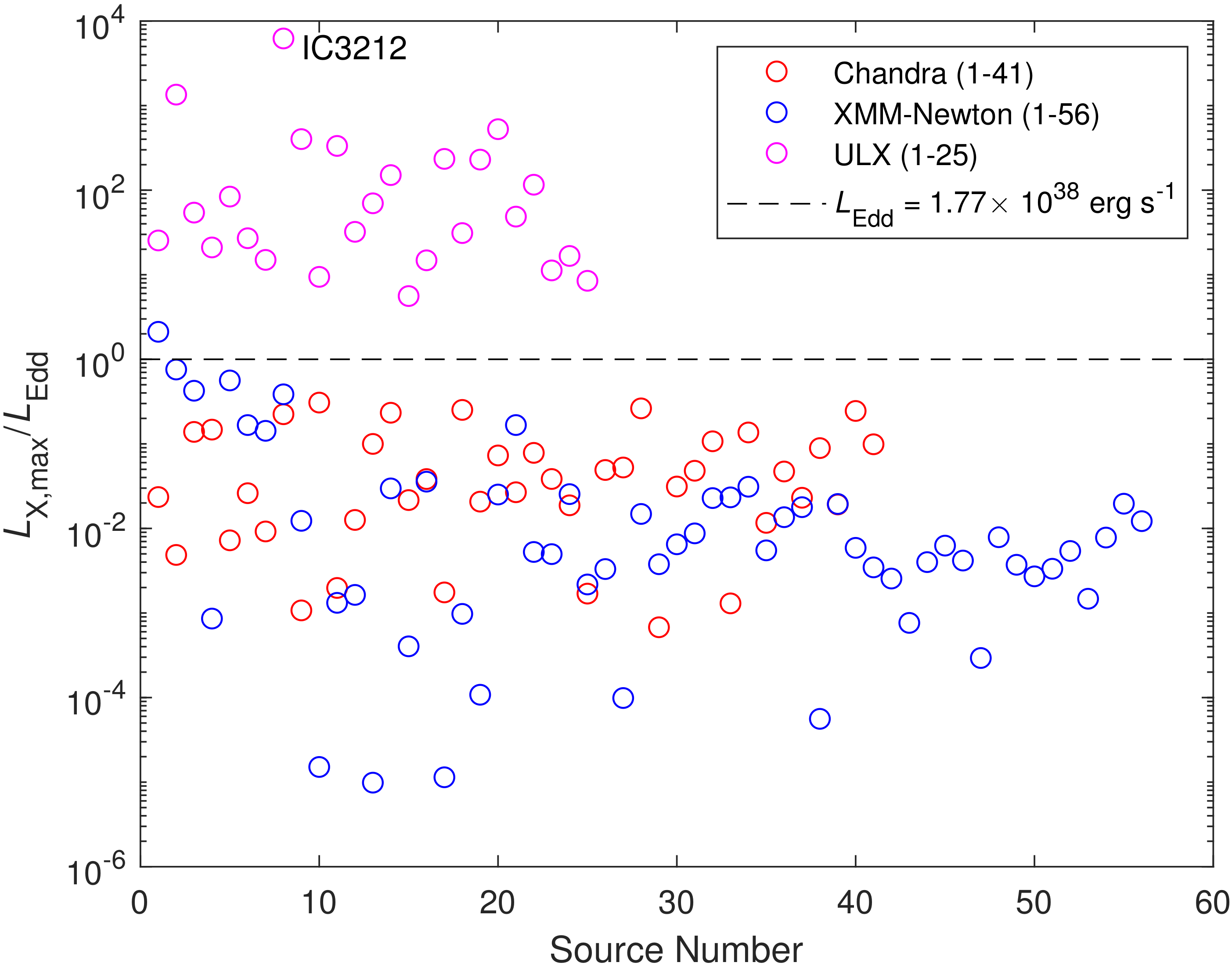
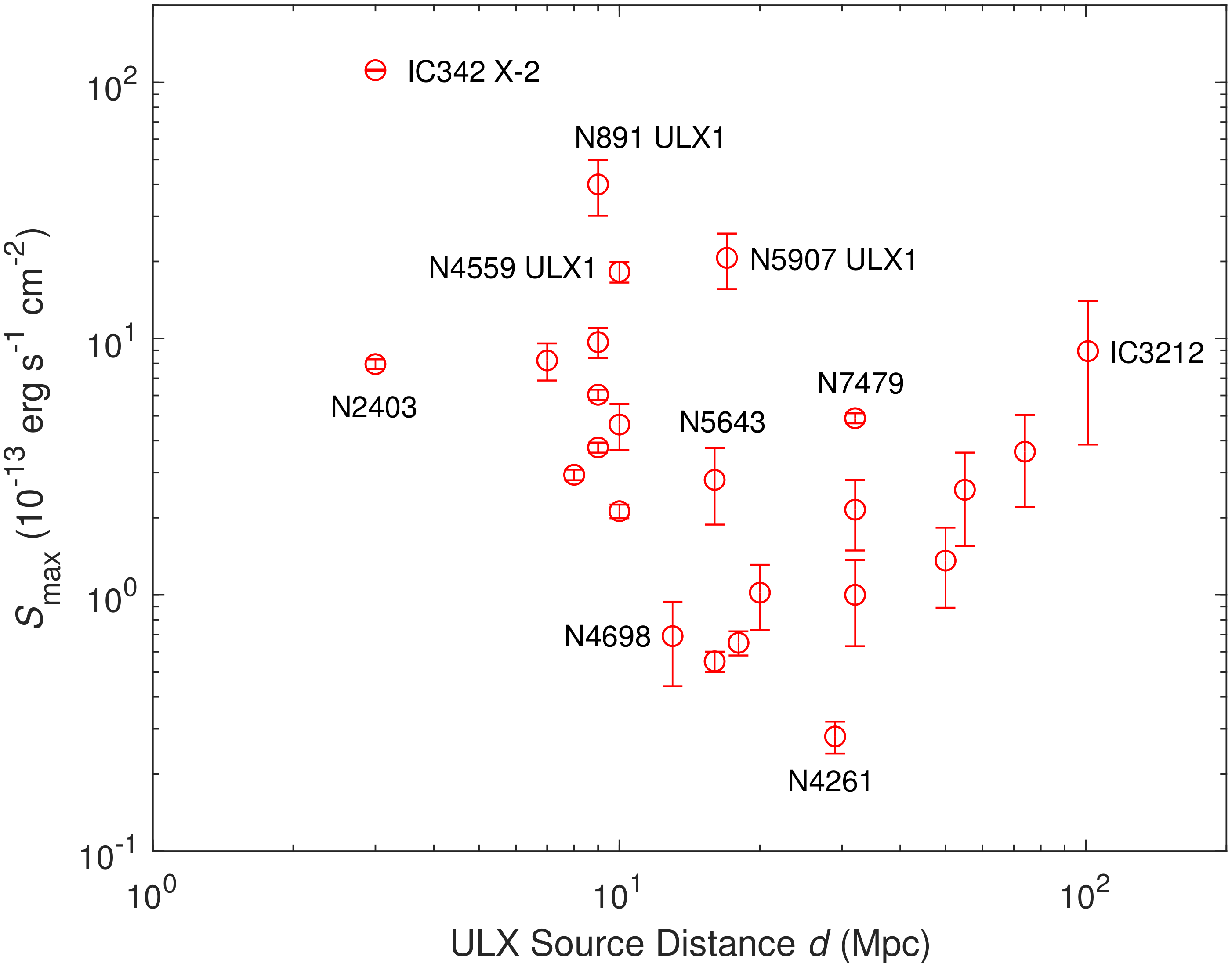
2.2. Maximum Fluxes and Maximum X-ray Luminosities
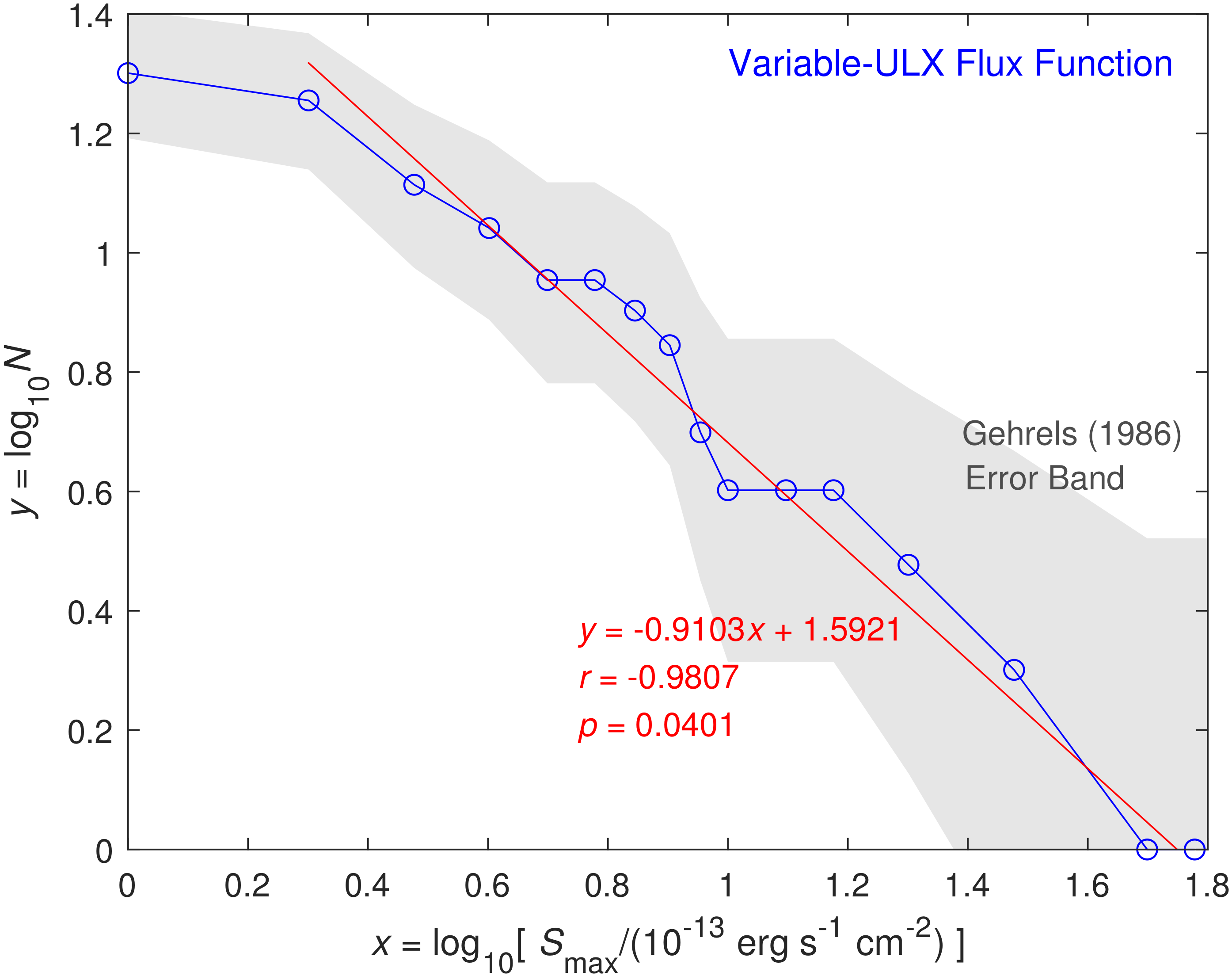
3. X-Ray Flux/Luminosity Functions
3.1. ULX Sources
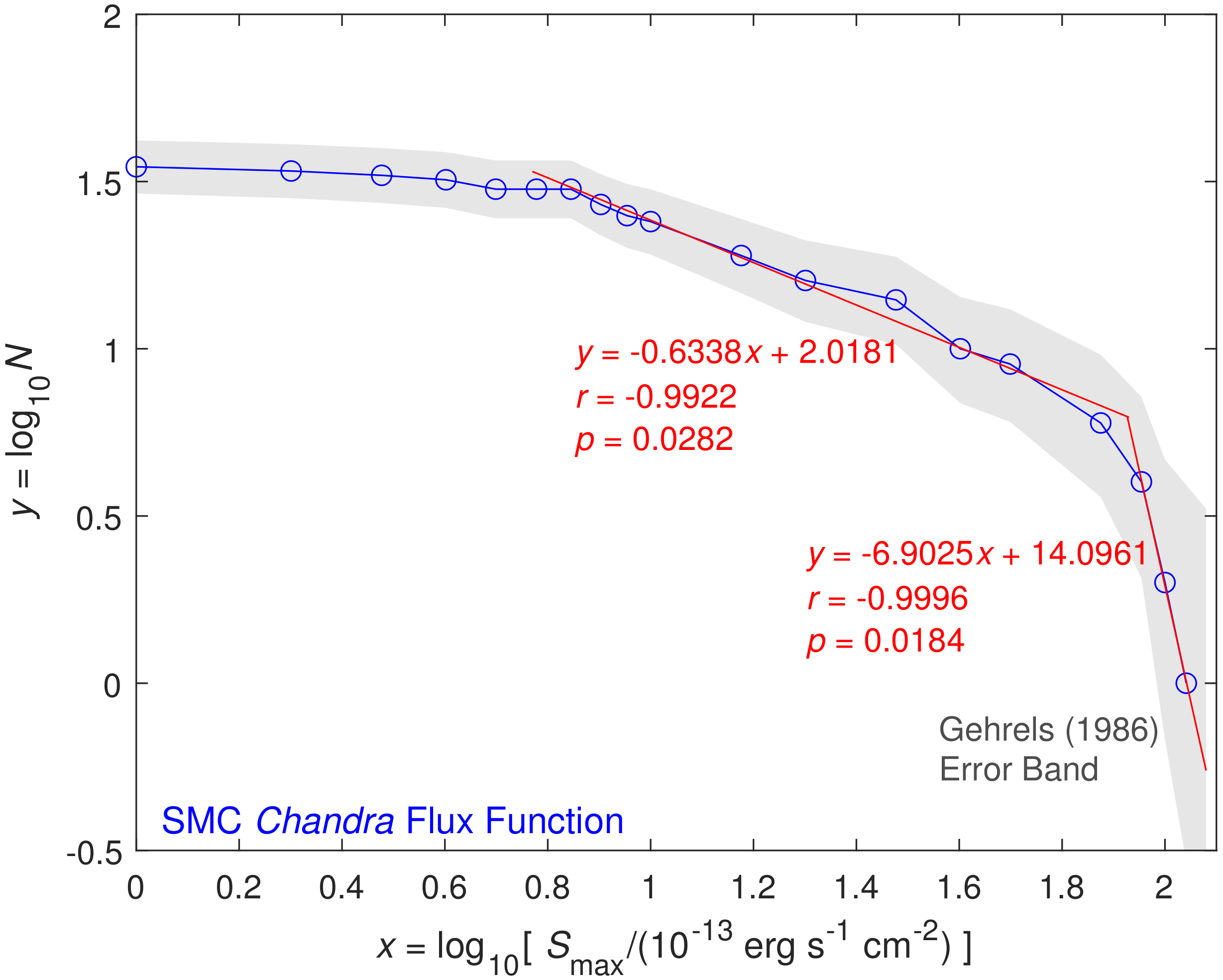
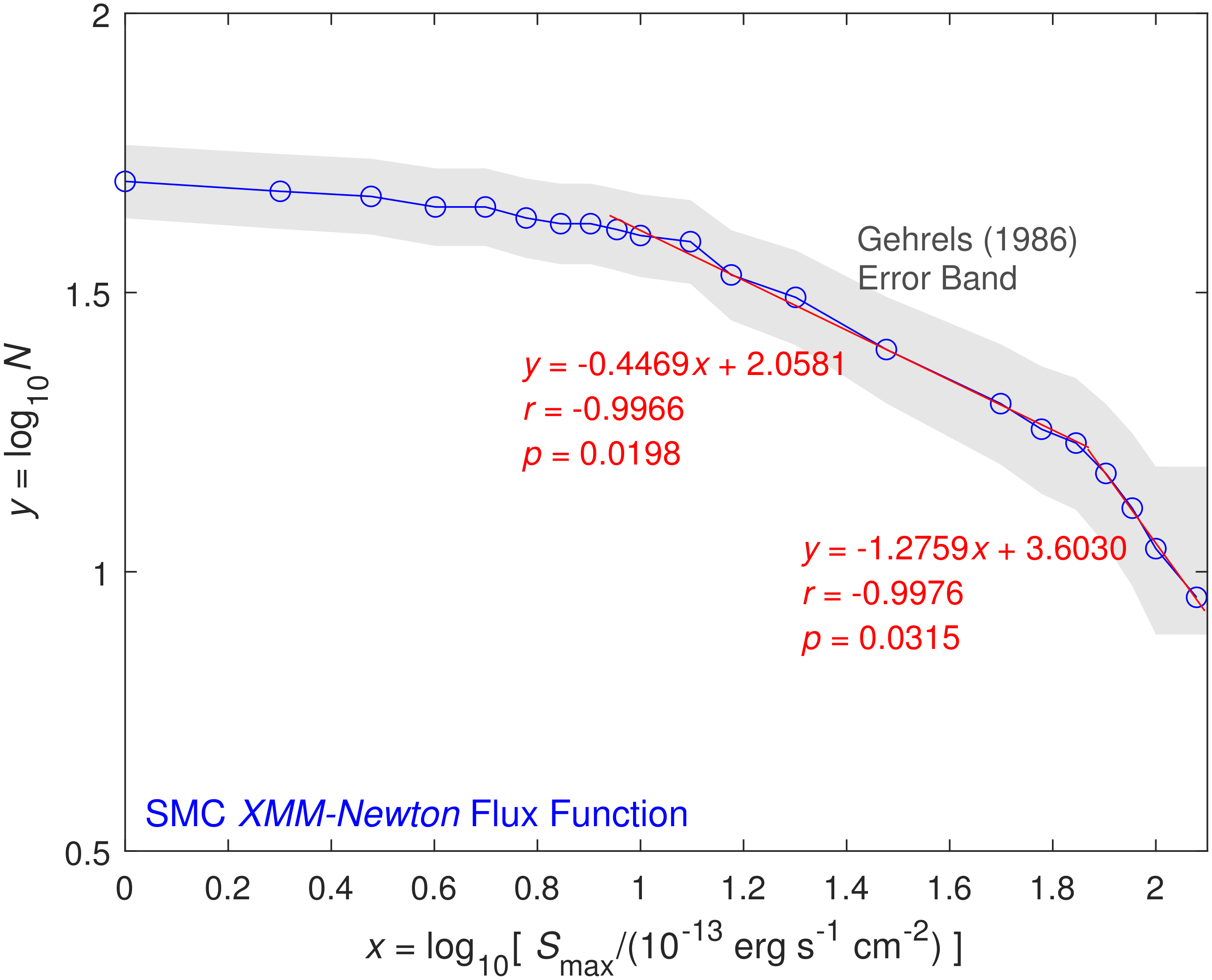
3.2. SMC Sources
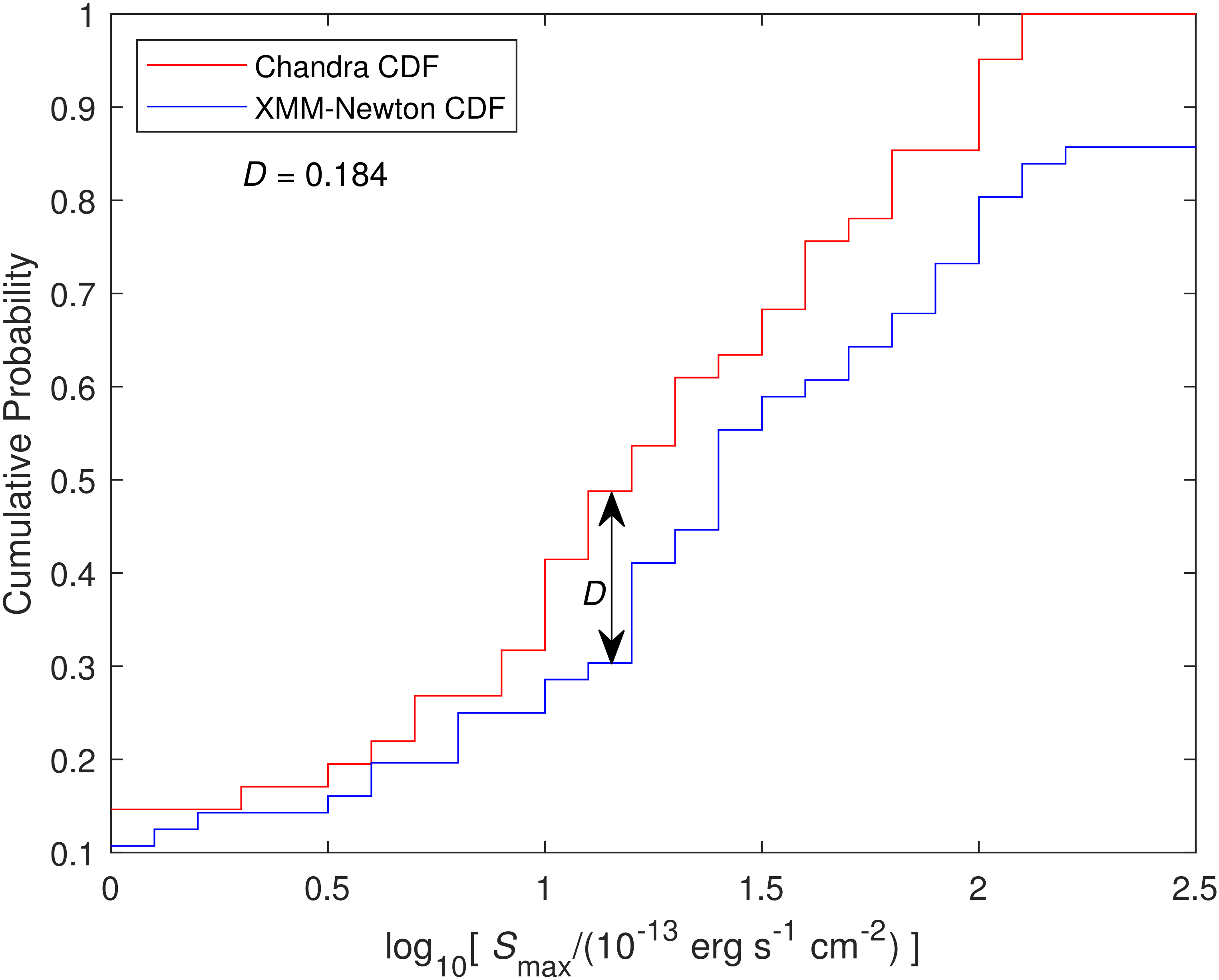
4. Two-Sample Kolmogorov–Smirnov Tests
- The ULX data set is not derived from the same continuous distribution as any one of the SMC data sets at a confidence level of . We reject the null hypothesis at probability levels of −. The D statistic values (the largest deviation in cumulative probabilities between the two samples) are also consistently larger than the critical values of the KS tests (Table 4), which also leads to rejection of . Here, we calculate the critical values of the D statistic for [45] from the equationwhere and are the sizes of the two paired data sets. The coefficient is determined from the the inverse of Equation (15) given by [45] in their Section 3.3.1, viz.If , then we accept the null hypothesis , but this not the case here. The null hypothesis is clearly rejected since for all ULX cases listed at the top section of Table 4.
- The two main SMC data sets (2 and 3) are derived from the same continuous distribution. This result makes sense since XMM-Newton and Chandra have been looking at the same exclusive group of SMC HMXB sources for more than 20 years, albeit at different campaigns and exposure times. The asymptotic p-value of the two-sample D statistic is , and the MatlabD statistic agrees since (Table 4). Figure 2 also shows that the two distributions are quite similar. Thus, the null hypothesis is accepted for the two main SMC data sets at the confidence limit. Indeed, they are derived from the same continuous distribution (although this is not a normal distribution; see bottom part of Table 4).
5. A Timid Look into X-ray Luminosities and ULX Cosmic Distances
- The one-sample KS test shows that sample 5 is not drawn from a normal distribution (Table 4).
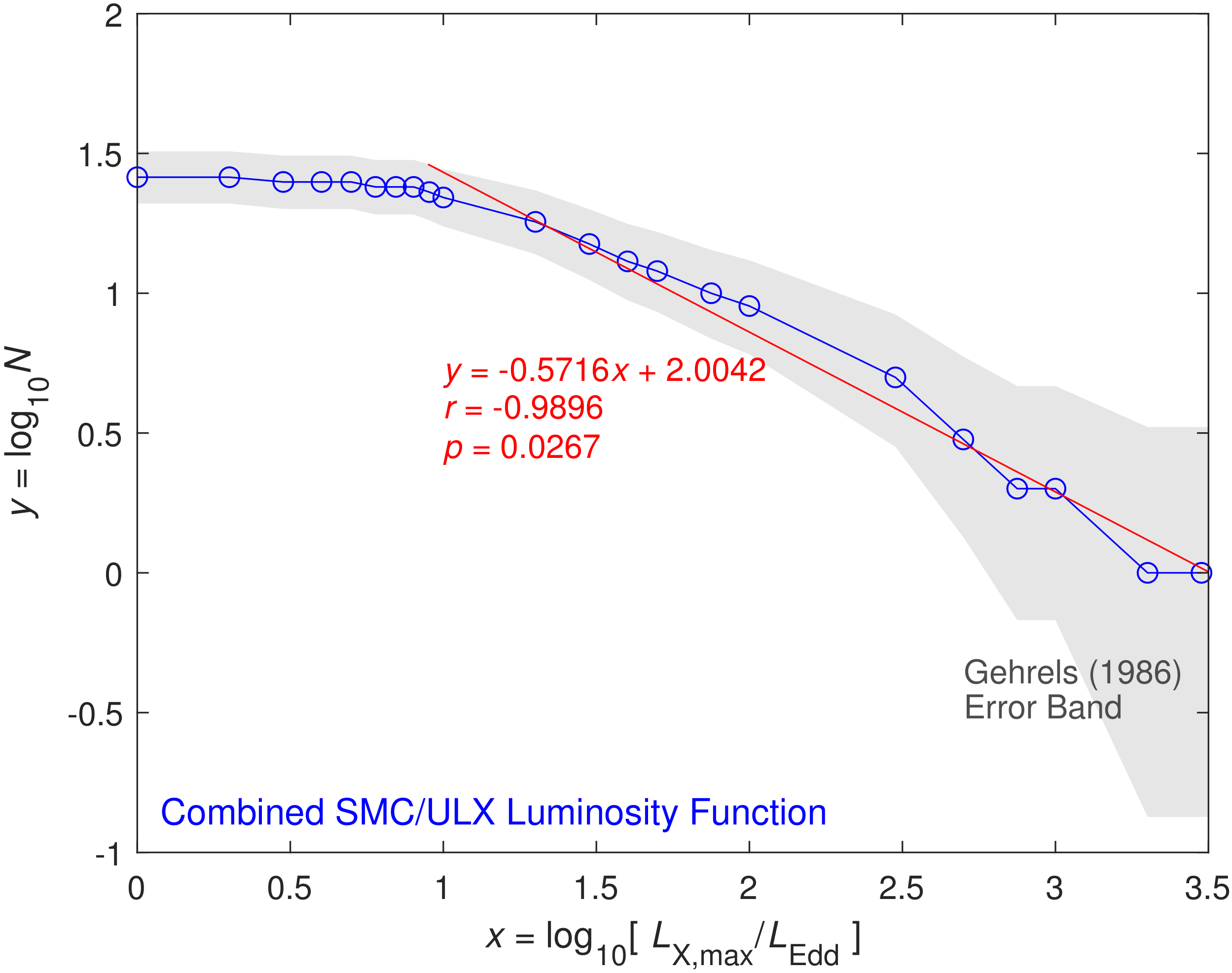
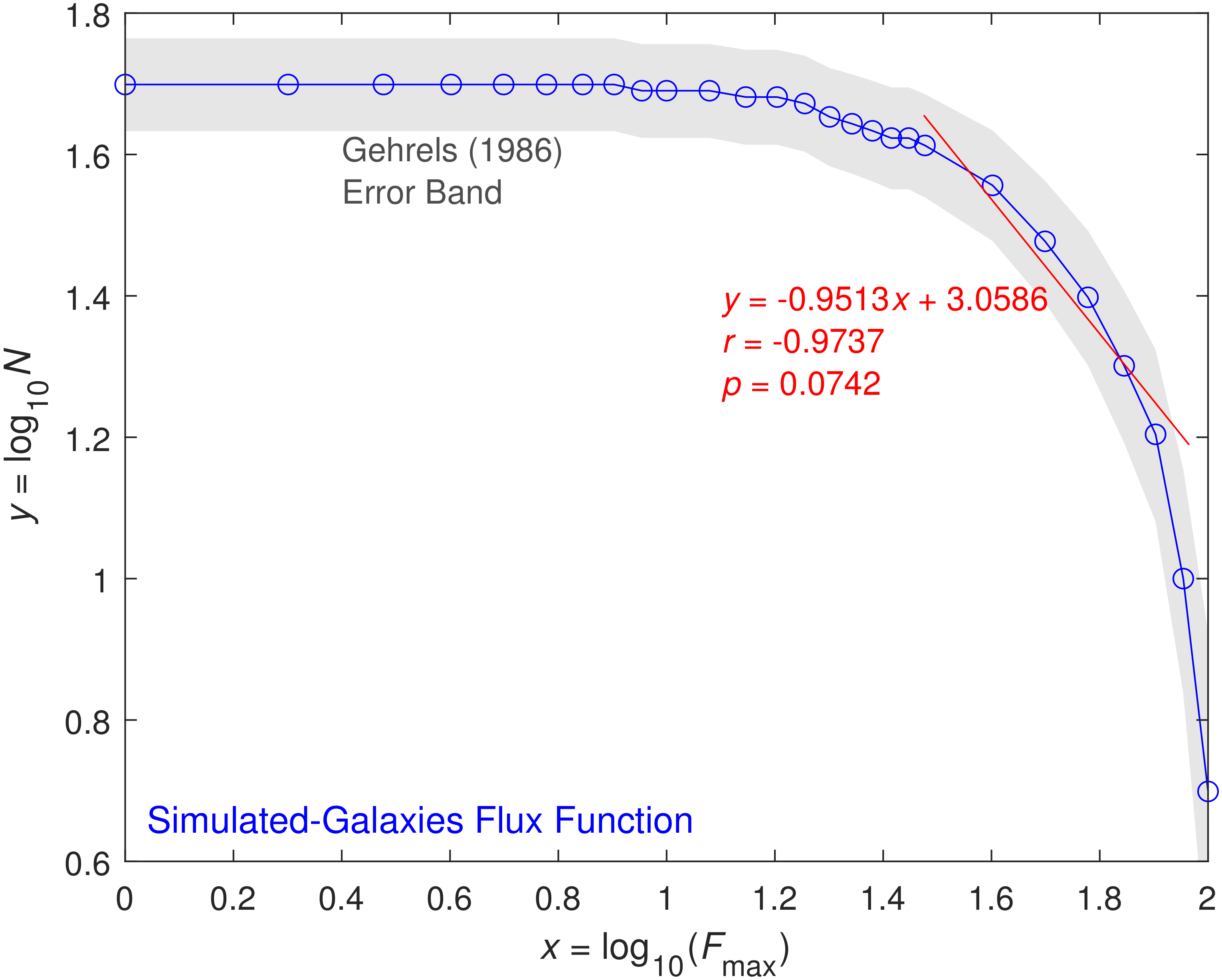
- The second kink observed at higher values in the SMC samples is gone. So we can fit the X-ray luminosity function of data set 5 with a single power law of slope m beyond the completeness limit.
- The slope m in the luminosity function (Figure 12) lies between the slopes of data sets 1 and 4 (Table 3); we find that , which is close to the average value () obtained from “contaminated” HMXB samples that contain also other types of X-ray sources (see Section 1 and Section 3.2).
6. Discussion
- (1)
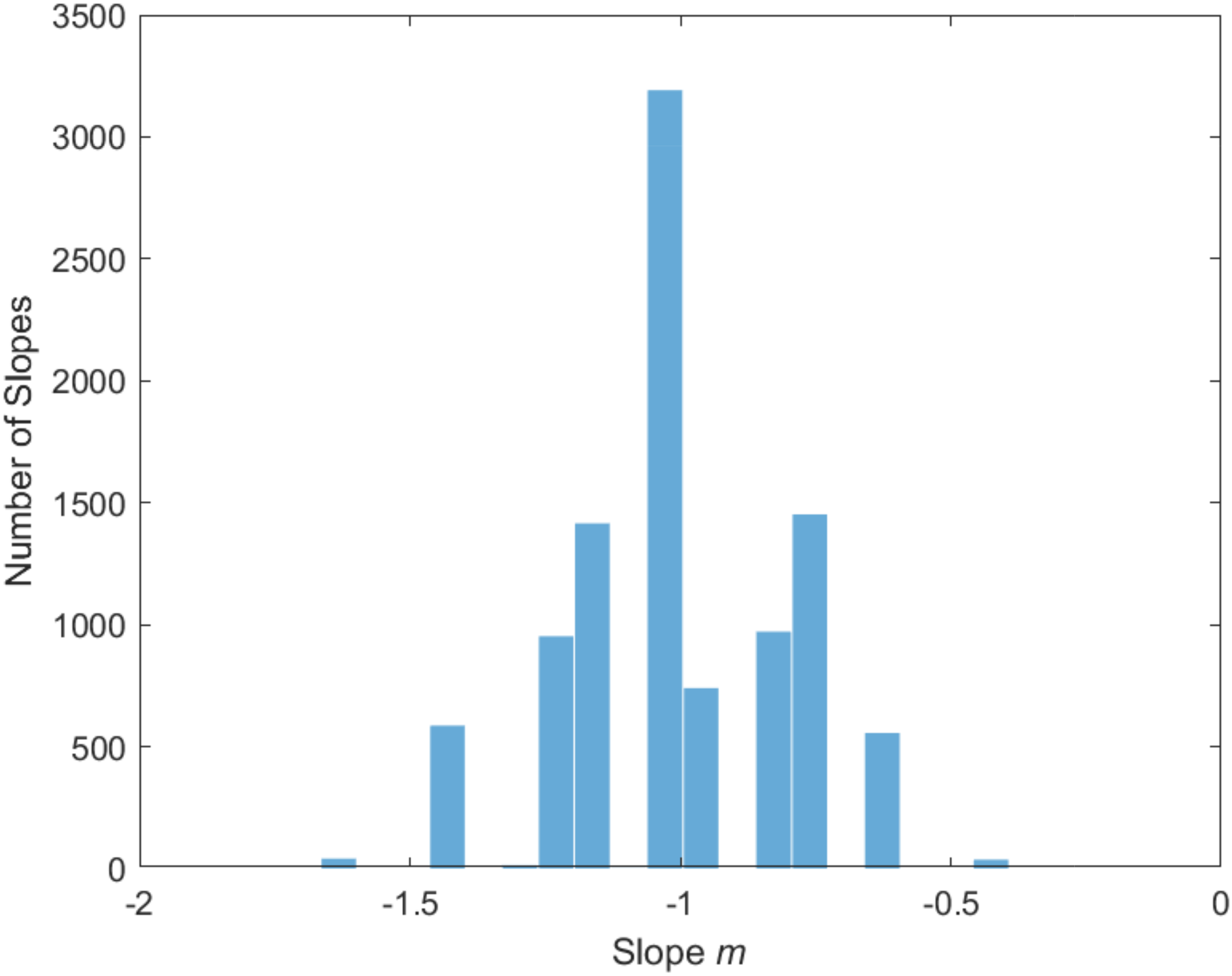
- When we changed the preset slope of the 50 initial samples of “galaxies” to , we obtained - diagrams with slopes aggregating near two or three unrelated values.
- (2)
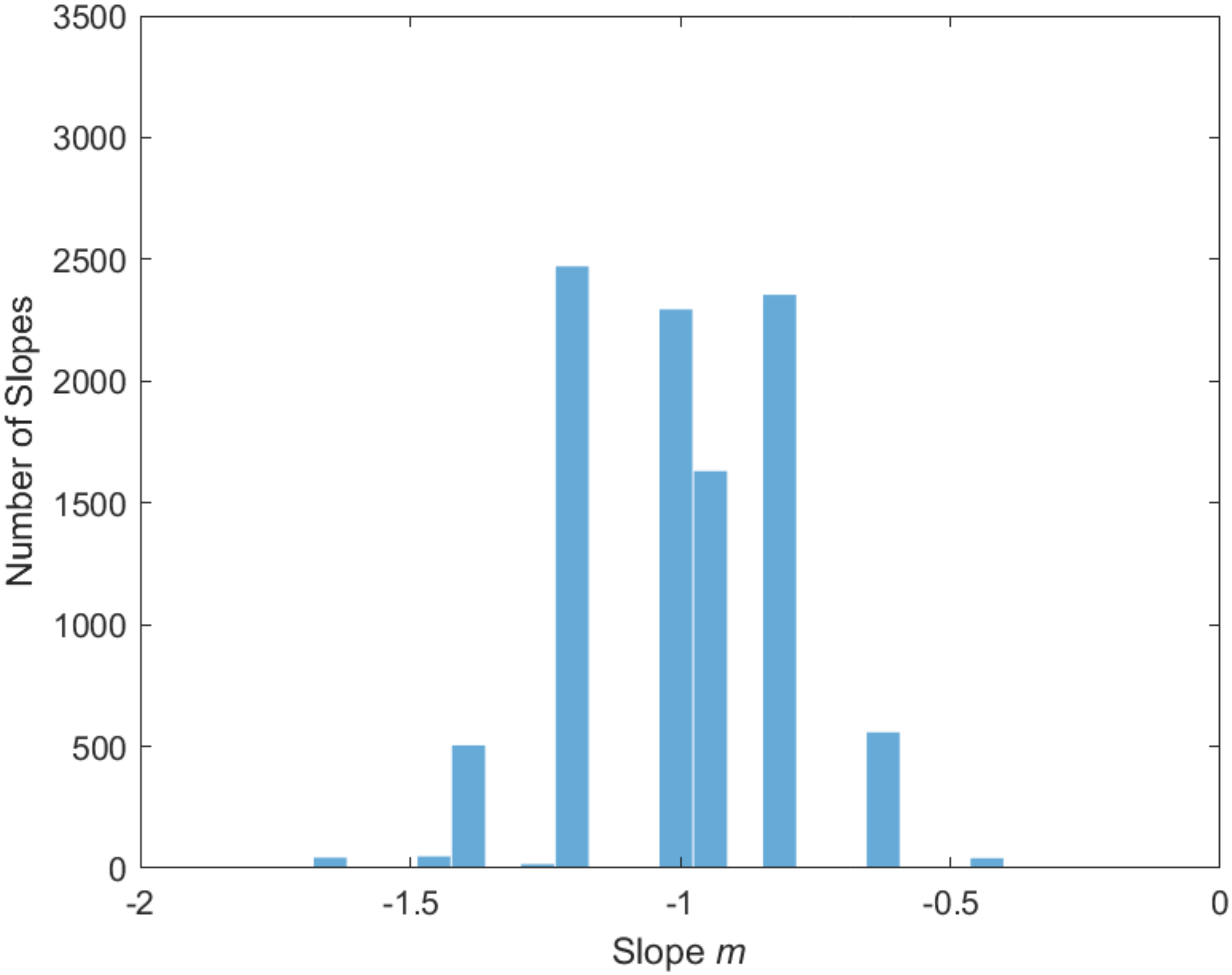
- When we chose the preset slope of the “galaxy” samples randomly between and , some experiments produced - slopes peaking near (as in Figure 14), but others did not show this trend.
- (3)
- When we expanded the preset range of slopes to (), aggregation of slopes at did not occur. An example of this case is shown in Figure 15, where the 10,000 - slopes are distributed about equally within a range of m-values.
- (4)
- When we repeated the simulations with a random y-intercept in the generating Function (7) ( plus a positive random number ), the qualitative properties of the above histograms did not change in a substantial manner, although the - slopes spread out to nearly all the bins.
7. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, X.; Walton, D.J.; Lansbury, G.B.; Evans, P.A.; Fabian, A.C.; Earnshaw, H.; Roberts, T.P. The hunt for pulsating ultraluminous X-ray sources. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 491, 1260–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Laycock, S.G.T.; Christodoulou, D.M.; Fingerman, S.; Coe, M.J.; Drake, J.J. A comprehensive library of X-ray pulsars in the Small Magellanic Cloud: Time evolution of their luminosities and spin periods. Astrophys. J. 2017, 839, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachetti, M.; Harrison, F.A.; Walton, D.J.; Grefenstette, B.W.; Chakrabarty, D.; Fürst, F.; Barrett, D.; Beloborodov, A.; Boggs, S.E.; Christensen, F.E.; et al. An ultraluminous X-ray source powered by an accreting neutron star. Nature 2014, 514, 202–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kluźniak, W.; Lasota, J.-P. An ultraluminous nascent millisecond pulsar. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 2015, 448, L43–L47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israel, G.L.; Belfiore, A.; Stella, L.; Esposito, P.; Casella, P.; De Luca, A.; Marelli, M.; Papitto, A.; Perri, M.; Puccetti, S.; et al. An accreting pulsar with extreme properties drives an ultraluminous X-ray source in NGC 5907. Science 2017, 355, 817–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israel, G.L.; Papitto, A.; Esposito, P.; Stella, L.; Zampieri, L.; Belfiore, A.; Rodriguez Castillo, G.A.; De Luca, A.; Tiengo, A.; Haberl, F.; et al. Discovery of a 0.42-s pulsar in the ultraluminous X-ray source NGC 7793 P13. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 2017, 466, L48–L52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaaret, P.; Feng, H.; Roberts, T.P. Ultraluminous X-ray sources. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 55, 303–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladstone, J.C.; Roberts, T.P.; Done, C. The ultraluminous state. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 2009, 397, 1836–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Soria, R. Ultraluminous X-ray sources in the Chandra and XMM-Newton era. New Astron. Rev. 2011, 55, 166–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, B.; Williams, B.F.; Eracleous, M.; Garcia, M.R.; Anderson, S.F.; Gaetz, T.J. A deep Chandra observation of the Wolf-Rayet + black hole binary NGC 300 X-1. Astrophys. J. 2011, 742, 128. [Google Scholar]
- Luangtip, W.; Roberts, T.P.; Mineo, S.; Lehmer, B.D.; Alexander, D.M.; Jackson, F.E.; Goulding, A.D.; Fischer, J.L. A deficit of ultraluminous X-ray sources in luminous infrared galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 2015, 446, 470–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motch, C.; Pakull, M.W.; Soria, R.; Grisé, F.; Pietrzyński, G. A mass of less than 15 solar masses for the black hole in an ultraluminous X-ray source. Nature 2014, 514, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middleton, M.J.; Heil, L.; Pintore, F.; Walton, D.J.; Roberts, T.P. A spectral-timing model for ULXs in the supercritical regime. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 2015, 447, 3243–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, T.; Mineshige, S.; Ohsuga, K.; Ogawa, T. A radiation-hydrodynamics model of accretion columns for ultra-luminous X-ray pulsars. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 2016, 68, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, D.M.; Laycock, S.G.T.; Yang, J.; Fingerman, S. Tracing the lowest propeller line in Magellanic high-mass X-ray binaries. Astrophys. J. 2016, 829, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urquhart, R.; Soria, R. Two eclipsing ultraluminous X-ray sources in M51. Astrophys. J. 2016, 831, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, D.J.; Middleton, M.J.; Pinto, C.; Fabian, A.C.; Bachetti, M.; Barrett, D.; Brightman, M.; Fuerst, F.; Harrison, F.A.; Miller, J.M.; et al. An iron K component to the ultrafast outflow in NGC 1313 X-1. Astrophys. J. 2016, 826, L26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-C. Constraining the dipolar magnetic field of M82 X-2 by the accretion model. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 2017, 465, L6–L9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauser, T.; Middleton, M.; Wilms, J. Modelling the light curves of ultraluminous X-ray sources as precession. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 2017, 466, 2236–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fürst, F.; Walton, D.J.; Stern, D.; Bachetti, M.; Barrett, D.; Brightman, M.; Harrison, F.A.; Rana, V. Spectral changes in the hyperluminous pulsar in NGC 5907 as a function of super-orbital phase. Astrophys. J. 2017, 834, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, A.D.; Swartz, D.A.; Roberts, T.P.; Middleton, M.J.; Soria, R.; Done, C. Crossing the Eddington limit: Examining disk spectra at high accretion rates. Astrophys. J. 2017, 836, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, D.M.; Laycosk, S.G.T.; Kazanas, D.; Cappallo, R.; Contopoulos, I. The great pretenders among the ULX class. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 17, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, A.; Lasota, J.-P. No magnetars in ULXs. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 2019, 485, 3588–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Inoue, H.; Tsuru, T.; Sakano, M.; Ishisaki, Y.; Ogasaka, Y.; Makishima, K.; Yamada, T.; Akiyama, M. logN-logS relations and spectral properties of sources from the ASCA Large Sky Survey: Their implications for the origin of the Cosmic X-ray Background (CXB). Astrophys. J. 1999, 518, 656–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shtykovskiy, P.; Gilfanov, M. High-mass X-ray binaries in the Small Magellanic Cloud: The luminosity function. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 2005, 362, 879–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpano, S.; Wilms, J.; Schirmer, M.; Kendziorra, E. X-ray properties of NGC 300. I. Global properties of X-ray point sources and their optical counterparts. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 443, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zezas, A.; Fabbiano, G.; Baldi, A.; Schweizer, F.; King, A.R.; Rots, A.H.; Ponman, T.J. Chandra monitoring observations of the Antennae galaxies. II. X-ray luminosity functions. Astrophys. J. 2007, 661, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos, S.; Warwick, R.S.; Carrera, F.J.; Stewart, G.C.; Ebrero, J.; Della Ceca, R.; Caccianiga, A.; Gilli, R.; Page, M.J.; Treister, E.; et al. High precision X-ray logN-logS distributions: Implications for the obscured AGN population. Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 492, 51–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, B.; Williams, B.F.; Eracleous, M.; Gaetz, T.J.; Plucinsky, P.P.; Skillman, E.D.; Dalcanton, J.J.; Anderson, S.F.; Weisz, D.R.; Kong, A.K.H. The Chandra local volume survey: The X-ray point-source catalog of NGC 300. Astrophys. J. 2012, 758, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, B.; Gross, J.; Williams, B.F.; Eracleous, M.; Gaetz, T.J.; Plucinsky, P.P.; Skillman, E.D. The effect of variability on X-ray binary luminosity functions: Multiple-epoch observations of NGC 300 with Chandra. Astrophys. J. 2017, 834, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mineo, S.; Gilfanov, M.; Sunyaev, R. X-ray emission from star-forming galaxies—I. High-mass X-ray binaries. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 2012, 419, 2095–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilgard, R.E.; Kaaret, P.; Krauss, M.I.; Prestwich, A.H.; Raley, M.T.; Zezas, A. A minisurvey of X-ray point sources in starburst and nonstarburst galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2002, 573, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Grimm, H.-J.; Gilfanov, M.; Sunyaev, R. High-mass X-ray binaries as a star formation rate indicator in distant galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 2003, 339, 793–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earnshaw, H.P.; Roberts, T.P.; Middleton, M.J.; Walton, D.J.; Mateos, S. A new, clean catalogue of extragalactic non-nuclear X-ray sources in nearby galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 2019, 483, 5554–5573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, M.J.; King, A. Geometrical beaming of stellar mass ULXs. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 2016, 462, L71–L74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.; Lasota, J.-P. ULXs: Neutron stars versus black holes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 2016, 458, L10–L13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, D.M.; Laycosk, S.G.T.; Kazanas, D. Meta-analysis of electron cyclotron resonance absorption features detected in high-mass X-ray binaries. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 19, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coe, M.J.; McBride, V.A.; Corbet, R.H.D. Exploring accretion theory with X-ray binaries in the Small Magellanic Cloud. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 2010, 401, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vasilopoulos, G.; Haberl, F.; Sturm, R.; Maggi, P.; Udalski, A. Spectral and temporal properties of RX J0520.5-6932 (LXP 8.04) during a type-I outburst. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 567, A129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tendulkar, S.P.; Fürst, F.; Pottschmidt, K.; Bachetti, M.; Bhalerao, V.B.; Boggs, S.E.; Christensen, F.E.; Craig, W.W.; Hailey, C.A.; Harrison, F.A.; et al. NuSTAR discovery of a cyclotron line in the Be/X-ray binary RX J0520.5-6932 during outburst. Astrophys. J. 2014, 795, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graczyk, D.; Pietrzyński, G.; Thompson, I.B.; Gieren, W.; Pilecki, B.; Konorski, P.; Udalski, A.; Soszyński, I.; Villanova, S.; Górski, M. The Araucaria project. The distance to the Small Magellanic Cloud from late-type eclipsing binaries. Astrophys. J. 2014, 780, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturm, R.; Haberl, F.; Pietsch, W.; Ballet, J.; Hatzidimitriou, D.; Buckley, D.A.H.; Coe, M.; Ehle, M.; Filipović, M.D.; La Palombara, N.; et al. The XMM-Newton survey of the Small Magellanic Cloud: The X-ray point-source catalogue. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 558, A3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coe, M.J.; Kirk, J. Catalogue of Be/X-ray binary systems in the Small Magellanic Cloud: X-ray, optical and IR properties. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. Lett. 2015, 452, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrels, N. Confidence limits for small numbers of events in astrophysical data. Astrophys. J. 1986, 303, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knuth, D.E. The Art of Computer Programming, Volume 2 (Seminumerical Algorithms), 3rd ed.; Addison-Wesley: Reading, MA, USA, 1998; pp. 48–55. [Google Scholar]
- Scowcroft, V.; Freedman, W.L.; Madore, B.F.; Monson, A.; Persson, S.E.; Rich, J.; Seibert, M.; Rigby, J.R. The Carnegie Hubble program: The distance and structure of the SMC as revealed by mid-infrared observations of Cepheids. Astrophys. J. 2016, 816, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1. | A detailed Chandra study of N300 by Binder et al. [29] resulted in comparable results: at the 0.5–2 keV band, the statistical X-ray luminosity function had an overall slope of and that of the pure-HMXB subsample had a slope of . |
| Source | SXP | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Name | (erg s cm) | (erg s cm) | (erg s cm) | (erg s cm) | (erg s) | (erg s) | |
| 1 | 3.34 | 9.04 | 0.42 | 84 | 0.25 | 0.07 | 4.16 | 0.19 |
| 2 | 6.88 | 1.88 | 0.22 | 3 | 1.42 | 0.17 | 0.86 | 0.10 |
| 3 | 7.78 | 53.29 | 1.05 | 5 | 0.52 | 0.15 | 24.51 | 0.48 |
| 4 | 7.92 | 56.69 | 1.05 | 2 | 7.84 | 0.4 | 26.08 | 0.48 |
| 5 | 8.8 | 2.78 | 0.31 | 3 | 2.1 | 0.21 | 1.28 | 0.14 |
| 6 | 9.13 | 10.04 | 0.45 | 7 | 3.75 | 0.27 | 4.62 | 0.21 |
| 7 | 15.3 | 3.54 | 0.29 | 3 | 1.6 | 0.19 | 1.63 | 0.13 |
| 8 | 18.3 | 86.18 | 1.29 | 2 | 3.73 | 0.27 | 39.65 | 0.59 |
| 9 | 22.1 | 0.42 | 0.11 | 1 | ⋯ | ⋯ | 0.19 | 0.05 |
| 10 | 25.5 | 118.35 | 1.51 | 2 | 1.95 | 0.22 | 54.44 | 0.69 |
| 11 | 46.6 | 0.76 | 0.15 | 3 | 0.13 | 0.05 | 0.35 | 0.07 |
| 12 | 59.0 | 4.84 | 0.34 | 4 | 0.79 | 0.13 | 2.23 | 0.16 |
| 13 | 65.8 | 38.41 | 0.86 | 1 | ⋯ | ⋯ | 17.67 | 0.40 |
| 14 | 82.4 | 89.75 | 1.31 | 2 | 0.36 | 0.1 | 41.29 | 0.60 |
| 15 | 101 | 8.32 | 0.4 | 1 | ⋯ | ⋯ | 3.83 | 0.18 |
| 16 | 138 | 14.76 | 0.54 | 3 | 2.97 | 0.24 | 6.79 | 0.25 |
| 17 | 140 | 0.68 | 0.13 | 2 | 0.18 | 0.07 | 0.31 | 0.06 |
| 18 | 152 | 96.98 | 1.38 | 1 | ⋯ | ⋯ | 44.61 | 0.63 |
| 19 | 153 | 7.97 | 0.4 | 19 | 0.18 | 0.06 | 3.67 | 0.18 |
| 20 | 172 | 28.07 | 0.74 | 3 | 10.88 | 0.46 | 12.91 | 0.34 |
| 21 | 175 | 10.31 | 0.42 | 4 | 4.34 | 0.34 | 4.74 | 0.19 |
| 22 | 214 | 30.11 | 0.78 | 1 | ⋯ | ⋯ | 13.85 | 0.36 |
| 23 | 264 | 14.79 | 0.53 | 3 | 2.55 | 0.23 | 6.8 | 0.24 |
| 24 | 280 | 7.21 | 0.37 | 2 | 3.59 | 0.31 | 3.32 | 0.17 |
| 25 | 292 | 0.66 | 0.15 | 3 | 0.34 | 0.09 | 0.3 | 0.07 |
| 26 | 304 | 18.9 | 0.61 | 24 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 8.69 | 0.28 |
| 27 | 323 | 20.21 | 0.63 | 4 | 7.3 | 0.38 | 9.3 | 0.29 |
| 28 | 327 | 101.11 | 1.42 | 2 | 82.54 | 1.28 | 46.51 | 0.65 |
| 29 | 342 | 0.27 | 0.1 | 1 | ⋯ | ⋯ | 0.12 | 0.04 |
| 30 | 348 | 12.04 | 0.49 | 74 | 0.19 | 0.07 | 5.54 | 0.23 |
| 31 | 455 | 18.49 | 0.61 | 18 | 1.98 | 0.19 | 8.51 | 0.28 |
| 32 | 504 | 41.26 | 0.91 | 3 | 9.39 | 0.43 | 18.98 | 0.42 |
| 33 | 523 | 0.51 | 0.12 | 16 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 0.23 | 0.05 |
| 34 | 565 | 52.47 | 1.11 | 4 | 2.29 | 0.21 | 24.14 | 0.51 |
| 35 | 645 | 4.48 | 0.32 | 2 | 2.82 | 0.26 | 2.06 | 0.15 |
| 36 | 701 | 18.14 | 0.59 | 2 | 10.03 | 0.45 | 8.34 | 0.27 |
| 37 | 726 | 8.86 | 0.41 | 53 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 4.08 | 0.19 |
| 38 | 893 | 34.28 | 0.83 | 4 | 0.36 | 0.09 | 15.77 | 0.38 |
| 39 | 967 | 7.38 | 0.38 | 14 | 0.3 | 0.07 | 3.4 | 0.18 |
| 40 | 1062 | 94.25 | 1.34 | 15 | 10.18 | 0.44 | 43.36 | 0.62 |
| 41 | 1323 | 38.05 | 0.87 | 185 | 0.3 | 0.09 | 17.5 | 0.40 |
| Source | SXP | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Name | (erg s cm) | (erg s cm) | (erg s cm) | (erg s cm) | (erg s) | (erg s) | |
| 1 | 0.72 | 8130.74 | 10.27 | 6 | 276.34 | 0.97 | 374.038 | 0.473 |
| 2 | 2.37 | 2913.34 | 3.6 | 4 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 134.022 | 0.166 |
| 3 | 2.76 | 1634.09 | 3.8 | 1 | ⋯ | ⋯ | 75.173 | 0.175 |
| 4 | 3.34 | 3.31 | 0.48 | 49 | 0.33 | 0.12 | 0.152 | 0.022 |
| 5 | 4.78 | 2162.17 | 4.18 | 1 | ⋯ | ⋯ | 99.466 | 0.192 |
| 6 | 5.05 | 641.94 | 1.91 | 3 | 77.14 | 0.98 | 29.531 | 0.088 |
| 7 | 6.85 | 548.69 | 3.85 | 1 | ⋯ | ⋯ | 25.242 | 0.177 |
| 8 | 7.78 | 1482.34 | 5.3 | 5 | 5.3 | 1.21 | 68.192 | 0.244 |
| 9 | 7.92 | 47.33 | 1.05 | 2 | 39.1 | 0.95 | 2.177 | 0.048 |
| 10 | 8.80 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 3 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.003 | 0.003 |
| 11 | 8.02 | 5.07 | 0.57 | 14 | 4.31 | 0.12 | 0.233 | 0.026 |
| 12 | 9.13 | 6.3 | 0.46 | 4 | 3.1 | 0.15 | 0.29 | 0.021 |
| 13 | 11.5 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 1 | ⋯ | ⋯ | 0.002 | 0.001 |
| 14 | 11.9 | 114.38 | 1.2 | 1 | ⋯ | ⋯ | 5.262 | 0.055 |
| 15 | 15.3 | 1.55 | 0.18 | 2 | 1.39 | 0.37 | 0.071 | 0.008 |
| 16 | 18.3 | 137.49 | 1.93 | 5 | 22.72 | 0.93 | 6.325 | 0.089 |
| 17 | 22.1 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 1 | ⋯ | ⋯ | 0.002 | 0.001 |
| 18 | 25.5 | 3.75 | 0.22 | 3 | 0.28 | 0.09 | 0.173 | 0.01 |
| 19 | 31.0 | 0.42 | 0.08 | 2 | 0.18 | 0.12 | 0.019 | 0.004 |
| 20 | 46.6 | 96.84 | 1.95 | 5 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 4.455 | 0.09 |
| 21 | 59.0 | 642.07 | 2.28 | 9 | 0.24 | 0.13 | 29.537 | 0.105 |
| 22 | 65.8 | 20.27 | 0.49 | 2 | 10.74 | 0.39 | 0.932 | 0.022 |
| 23 | 74.7 | 19.11 | 0.58 | 5 | 1.51 | 0.24 | 0.879 | 0.027 |
| 24 | 91.1 | 97.91 | 3.46 | 3 | 12.81 | 1.37 | 4.504 | 0.159 |
| 25 | 101 | 8.37 | 0.25 | 1 | ⋯ | ⋯ | 0.385 | 0.011 |
| 26 | 138 | 12.73 | 0.83 | 7 | 5.86 | 0.17 | 0.586 | 0.038 |
| 27 | 140 | 0.38 | 0.07 | 4 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 0.017 | 0.003 |
| 28 | 152 | 57.07 | 0.89 | 13 | 0.14 | 0.08 | 2.625 | 0.041 |
| 29 | 153 | 14.52 | 0.51 | 1 | ⋯ | ⋯ | 0.668 | 0.023 |
| 30 | 169 | 24.98 | 0.53 | 2 | 23.54 | 0.65 | 1.149 | 0.025 |
| 31 | 172 | 33.64 | 0.99 | 3 | 10.99 | 1.32 | 1.547 | 0.046 |
| 32 | 175 | 87.91 | 1.24 | 6 | 11.01 | 0.39 | 4.044 | 0.057 |
| 33 | 202A | 89.63 | 2.31 | 20 | 8.46 | 0.71 | 4.123 | 0.106 |
| 34 | 202B | 119.74 | 1.43 | 3 | 6.26 | 0.53 | 5.508 | 0.066 |
| 35 | 214 | 21.17 | 0.7 | 1 | ⋯ | ⋯ | 0.974 | 0.032 |
| 36 | 264 | 52.24 | 0.89 | 4 | 0.95 | 0.19 | 2.403 | 0.041 |
| 37 | 280 | 68.63 | 1.35 | 15 | 0.51 | 0.15 | 3.157 | 0.062 |
| 38 | 292 | 0.22 | 0.09 | 3 | 0.1 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.004 |
| 39 | 293 | 74.85 | 1.21 | 6 | 8.86 | 1.46 | 3.443 | 0.056 |
| 40 | 304 | 22.67 | 1.55 | 26 | 0.5 | 0.11 | 1.043 | 0.071 |
| 41 | 323 | 13.32 | 0.46 | 3 | 8.14 | 0.32 | 0.613 | 0.021 |
| 42 | 327 | 9.83 | 0.8 | 5 | 4.57 | 0.7 | 0.452 | 0.037 |
| 43 | 342 | 2.94 | 0.15 | 3 | 0.4 | 0.13 | 0.135 | 0.007 |
| 44 | 348 | 15.38 | 0.71 | 23 | 1.01 | 1.14 | 0.707 | 0.033 |
| 45 | 455 | 24.08 | 2.05 | 18 | 3.88 | 0.35 | 1.108 | 0.094 |
| 46 | 504 | 16.04 | 0.34 | 2 | 3.71 | 0.38 | 0.738 | 0.016 |
| 47 | 523 | 1.13 | 0.28 | 9 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.052 | 0.013 |
| 48 | 565 | 30.28 | 0.79 | 18 | 0.66 | 0.13 | 1.393 | 0.036 |
| 49 | 645 | 14.3 | 0.51 | 7 | 0.42 | 0.11 | 0.658 | 0.023 |
| 50 | 701 | 10.43 | 0.29 | 4 | 0.88 | 0.21 | 0.48 | 0.014 |
| 51 | 726 | 12.83 | 1.53 | 34 | 0.28 | 0.16 | 0.59 | 0.071 |
| 52 | 756 | 20.82 | 0.58 | 3 | 0.7 | 0.35 | 0.958 | 0.027 |
| 53 | 893 | 5.67 | 0.53 | 3 | 0.89 | 0.1 | 0.261 | 0.024 |
| 54 | 967 | 30.01 | 5.5 | 5 | 1.34 | 0.75 | 1.38 | 0.253 |
| 55 | 1062 | 75.42 | 0.5 | 6 | 12.78 | 0.14 | 3.469 | 0.023 |
| 56 | 1323 | 46.9 | 0.69 | 50 | 0.91 | 0.08 | 2.158 | 0.032 |
| No. | Data Set | Figure | Slope | 1 Error | y-Intercept | 1 Error | r | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ULX | 3 | 0.0574 | 1.5921 | 0.0545 | 0.0401 | ||
| 2 | SMC Chandra IR | 4 | 0.0281 | 2.0181 | 0.0356 | 0.0282 | ||
| 2 | SMC Chandra HE | 4 | 0.1996 | 14.0961 | 0.3258 | 0.0184 | ||
| 3 | SMC XMM-Newton IR | 5 | 0.0139 | 2.0581 | 0.0185 | 0.0198 | ||
| 3 | SMC XMM-Newton HE | 5 | 0.0631 | 3.6030 | 0.1085 | 0.0315 | ||
| 4 | SMC Combined IR | ⋯ | 0.0195 | 2.0615 | 0.0259 | 0.0315 | ||
| 4 | SMC Combined HE | ⋯ | 0.1331 | 5.1571 | 0.2289 | 0.0419 | ||
| 5 | All Combined | 11 | 0.0240 | 2.0042 | 0.0529 | 0.0267 |
| Data Sets | p | D | Result | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H (): Two samples from the same continuous distribution | ||||
| Chandra, XMM-Newton | 0.193 | 0.279 | H | |
| Chandra, ULX | 0.425 | 0.345 | H | |
| XMM-Newton, ULX | 0.572 | 0.327 | H | |
| SMC Combined, ULX | 0.616 | 0.325 | H | |
| H (): Samples from a normal distribution | ||||
| ULX | 0.703 | 0.264 | H | |
| Chandra | 0.827 | 0.208 | H | |
| XMM-Newton | 0.856 | 0.178 | H | |
| SMC Combined | 0.877 | 0.175 | H | |
| All Combined | 0.500 | 0.175 | H | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Christodoulou, D.M.; Laycock, S.G.T.; Cappallo, R.; Roy, A.; Bhattacharya , S.; Kazanas, D. Variable Magellanic HMXB Sources versus Variable ULX Sources: Nothing to Brag about the ULX Sources. Galaxies 2020, 8, 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies8040070
Christodoulou DM, Laycock SGT, Cappallo R, Roy A, Bhattacharya S, Kazanas D. Variable Magellanic HMXB Sources versus Variable ULX Sources: Nothing to Brag about the ULX Sources. Galaxies. 2020; 8(4):70. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies8040070
Chicago/Turabian StyleChristodoulou, Dimitris M., Silas G. T. Laycock, Rigel Cappallo, Ankur Roy, Sayantan Bhattacharya , and Demosthenes Kazanas. 2020. "Variable Magellanic HMXB Sources versus Variable ULX Sources: Nothing to Brag about the ULX Sources" Galaxies 8, no. 4: 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies8040070
APA StyleChristodoulou, D. M., Laycock, S. G. T., Cappallo, R., Roy, A., Bhattacharya , S., & Kazanas, D. (2020). Variable Magellanic HMXB Sources versus Variable ULX Sources: Nothing to Brag about the ULX Sources. Galaxies, 8(4), 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies8040070






