A Preferred Orientation Angle for Bipolar Planetary Nebulae
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
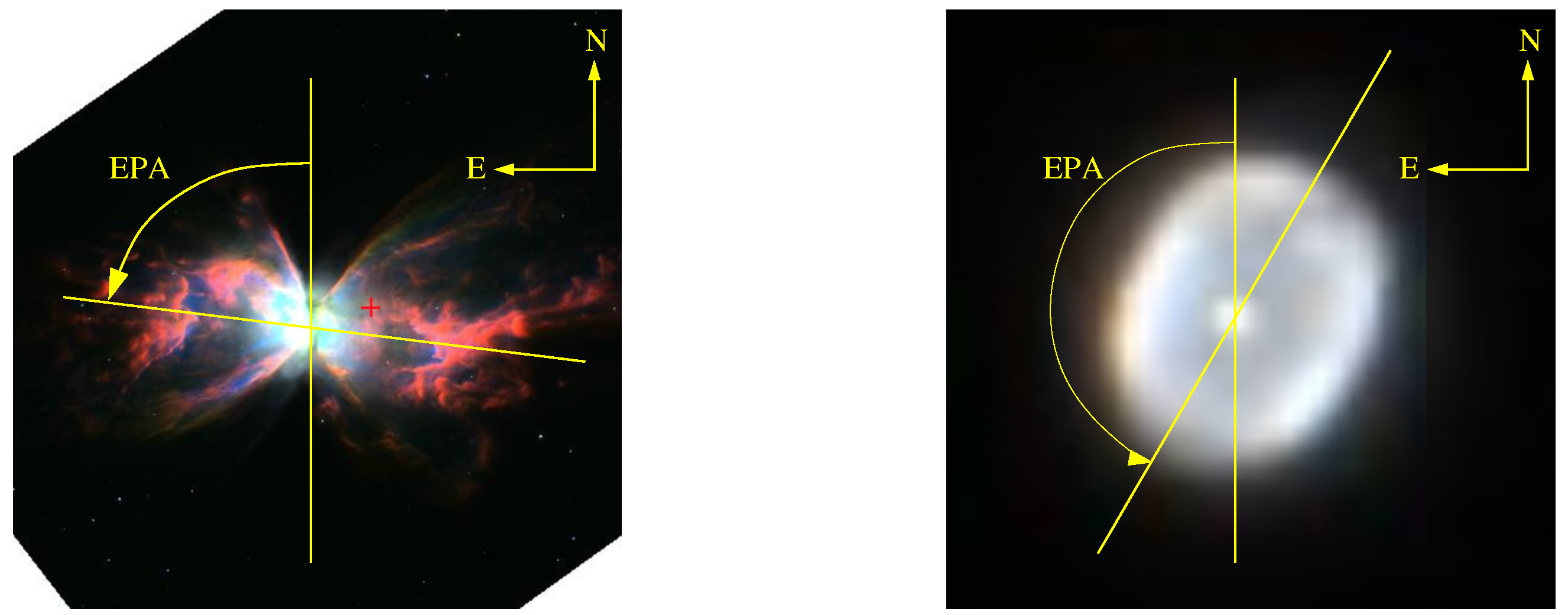
2.1. Sample Selection
2.2. Analysis
2.3. Tests
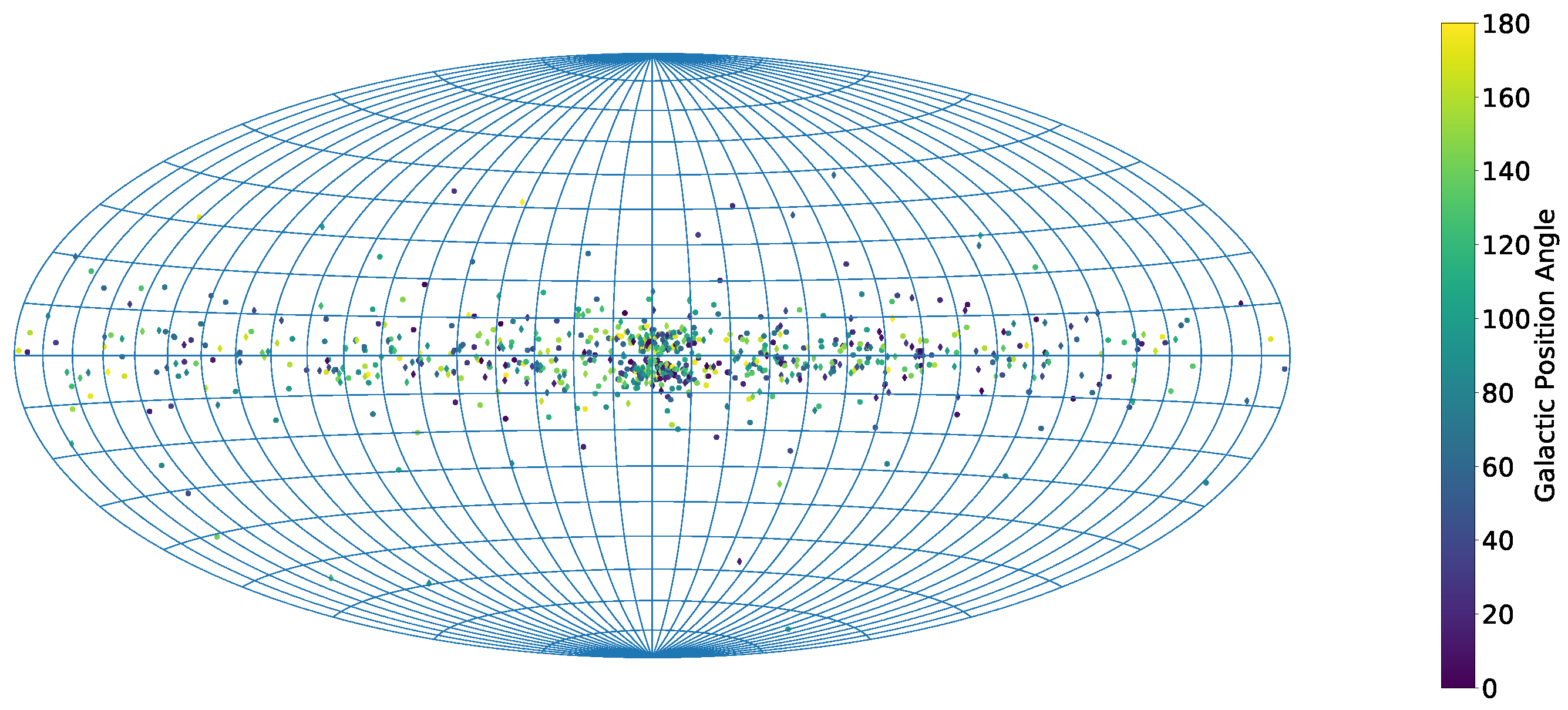
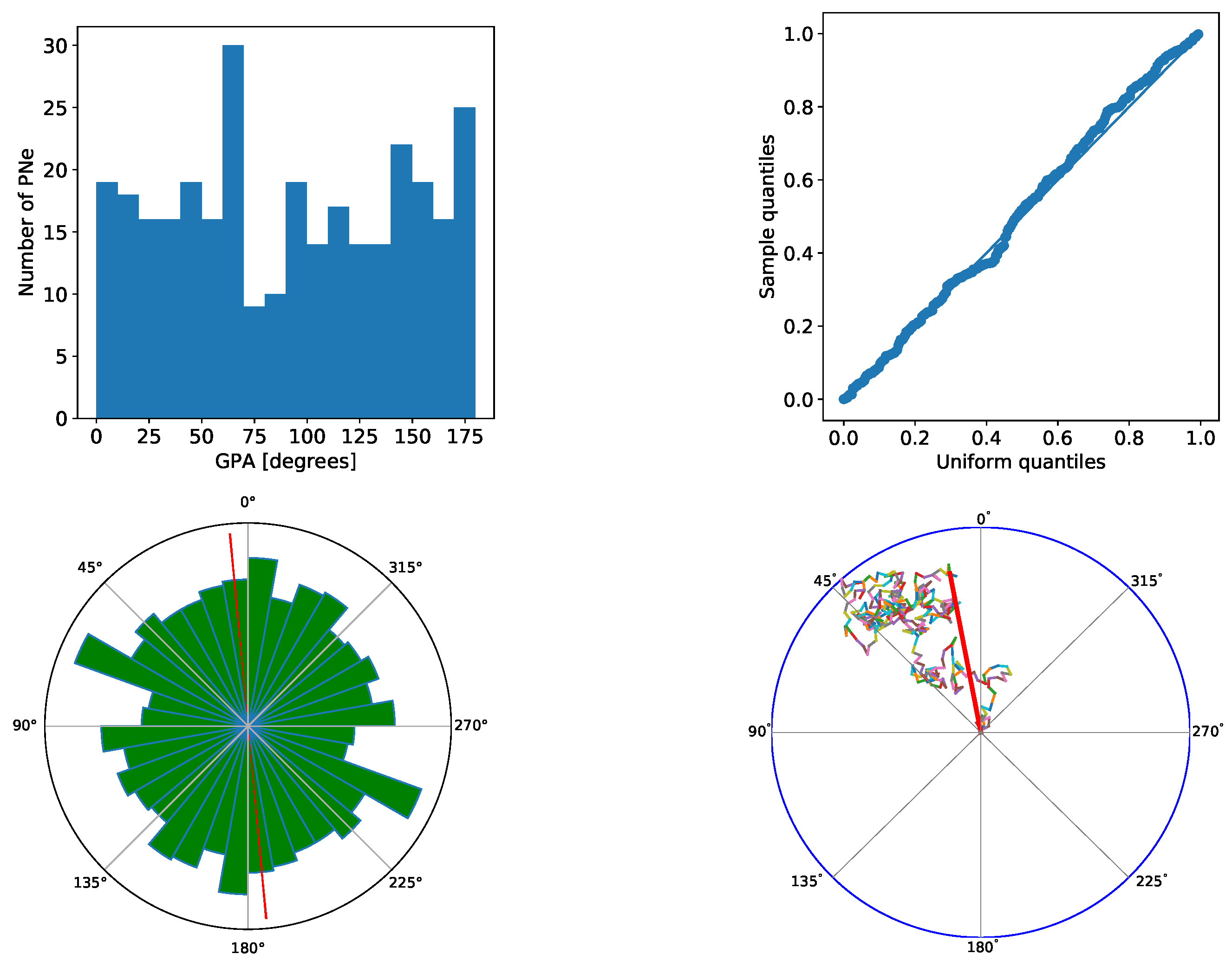
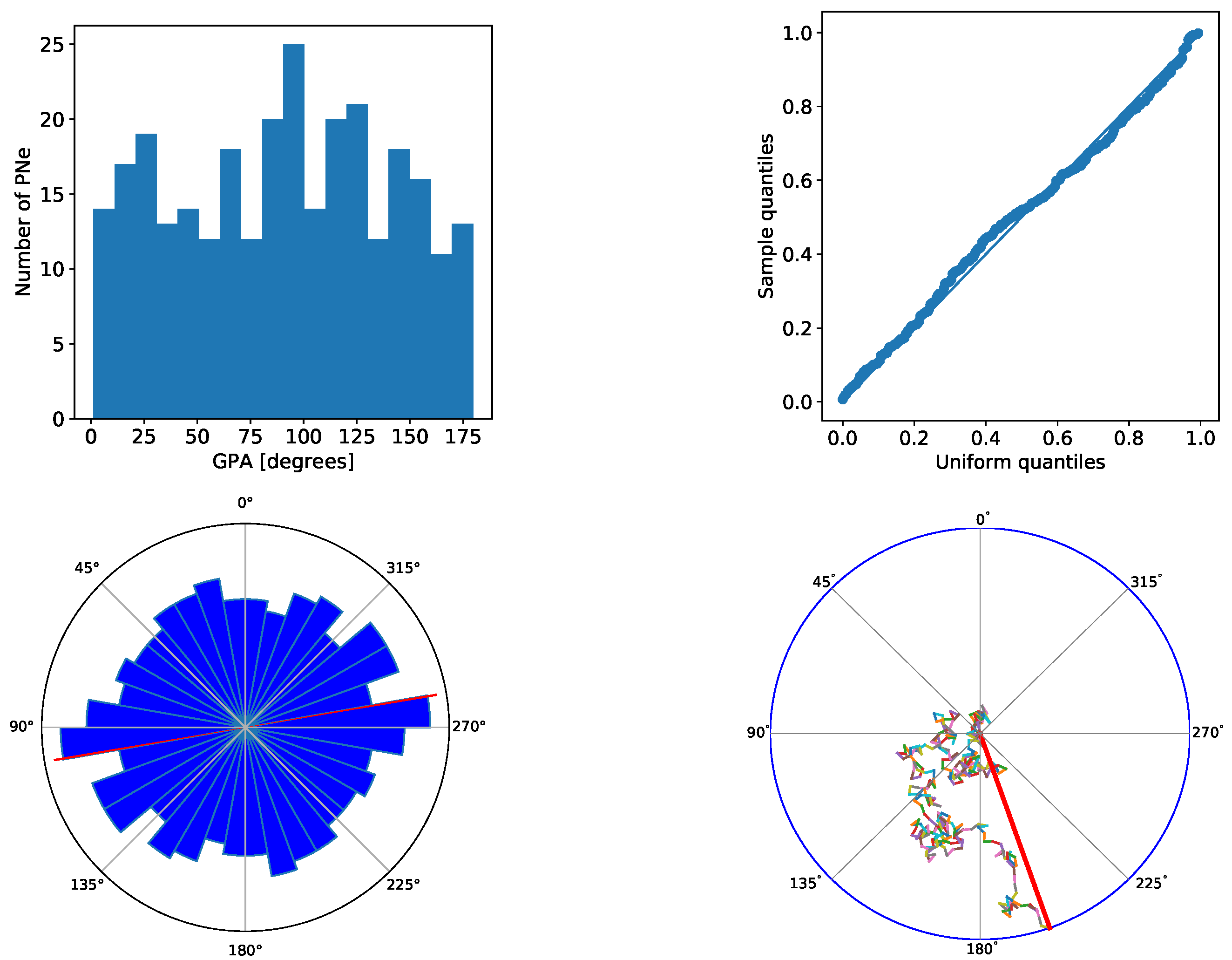
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Falceta-Gonçalves, D.; Monteiro, H. On the alignment of PNe and local magnetic field at the Galactic centre: Magnetohydrodynamical numerical simulations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 438, 2853–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnick, G.; Harwit, M. Orientation of Planetary Nebulae within the Galaxy. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1975, 171, 441–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Phillips, J.P. The spatial orientations of bipolar nebulae. Astron. Astrophys. 1997, 325, 755–757. [Google Scholar]
- Weidmann, W.A.; Diaz, R.J. The Spatial Orientation of Planetary Nebulae within the Milky Way. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2008, 120, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, B.; Zijlstra, A.A. Alignment of the angular momentum vectors of planetary nebulae in the Galactic Bulge. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 435, 975–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danehkar, A.; Parker, Q.A. Orientation of Galactic Bulge Planetary Nebulae toward the Galactic Center. Proc. Int. Astron. Union 2014, 312, 128–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradi, R.L.M.; Aznar, R.; Mampaso, A. Orientation of planetary nebulae within the Galaxy. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1998, 617, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, Q.A.; Bojičić, I.S.; Frew, D.J. HASH: The Hong Kong/AAO/Strasbourg Hα planetary nebula database. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2016, 728, 032008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, Q.A.; Bojičić, I.S.; Frew, D.J. Exploiting the HASH Planetary Nebula Research Platform. Proc. Int. Astron. Union 2017, 323, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frew, D.J.; Parker, Q.A. Planetary Nebulae: Observational Properties, Mimics and Diagnostics. Publ. Astron. Soc. Aust. 2010, 27, 129–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, Q.A.; Acker, A.; Frew, D.J.; Hartley, M.; Peyaud, A.E.J.; Ochsenbein, F.; Phillipps, S.; Russeil, D.; Beaulieu, S.F.; Cohen, M.; et al. The Macquarie/AAO/Strasbourg Hα Planetary Nebula Catalogue: MASH. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2006, 373, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, Q.A.; Phillipps, S.; Pierce, M.J.; Hartley, M.; Hambly, N.C.; Read, M.A.; MacGillivray, H.T.; Tritton, S.B.; Cass, C.P.; Cannon, R.D.; et al. The AAO/UKST SuperCOSMOS Hα survey. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2005, 362, 689–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drew, J.E.; Greimel, R.; Irwin, M.J.; Aungwerojwit, A.; Barlow, M.J.; Corradi, R.L.M.; Drake, J.J.; Gänsicke, B.T.; Groot, P.; Hales, A.; et al. The INT Photometric Hα Survey of the Northern Galactic Plane (IPHAS). Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2005, 362, 753–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, K.C.; Pan-STARRS Team. The Pan-STARRS Surveys. Am. Astron. Soc. 2016, 227, 324.07. [Google Scholar]
- Corradi, R.L.M.; Schwarz, H.E. Morphological populations of planetary nebulae: Which progenitors? I. Comparative properties of bipolar nebulae. Astron. Astrophys. 1995, 293, 871–888. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie, D. Rayleigh Test for Randomness of Circular Data. Appl. Stat. 1983, 32, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, N.I. Statistical Analysis of Circular Data; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Jammalamadaka, S.R.; Sengupta, A. Topics in Circular Statistics; World Scientific: Singapore; Hackensack, NJ, USA; London, UK; Hong Kong, China, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Fragkou, V.; Parker, Q.A.; Zijlstra, A.A.; Crause, L.; Barker, H. A high-mass planetary nebula in a Galactic open cluster. Nat. Astron. 2019, 3, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marco, O. The Origin and Shaping of Planetary Nebulae: Putting the Binary Hypothesis to the Test. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2009, 121, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marco, O.; Izzard, R.G. Dawes Review 6: The Impact of Companions on Stellar Evolution. Publ. Astron. Soc. Aust. 2017, 34, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ritter, A.; Parker, Q.A. A Preferred Orientation Angle for Bipolar Planetary Nebulae. Galaxies 2020, 8, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies8020034
Ritter A, Parker QA. A Preferred Orientation Angle for Bipolar Planetary Nebulae. Galaxies. 2020; 8(2):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies8020034
Chicago/Turabian StyleRitter, Andreas, and Quentin A. Parker. 2020. "A Preferred Orientation Angle for Bipolar Planetary Nebulae" Galaxies 8, no. 2: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies8020034
APA StyleRitter, A., & Parker, Q. A. (2020). A Preferred Orientation Angle for Bipolar Planetary Nebulae. Galaxies, 8(2), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies8020034





