Lighting Up Dark Matter Haloes
Abstract
1. Introduction
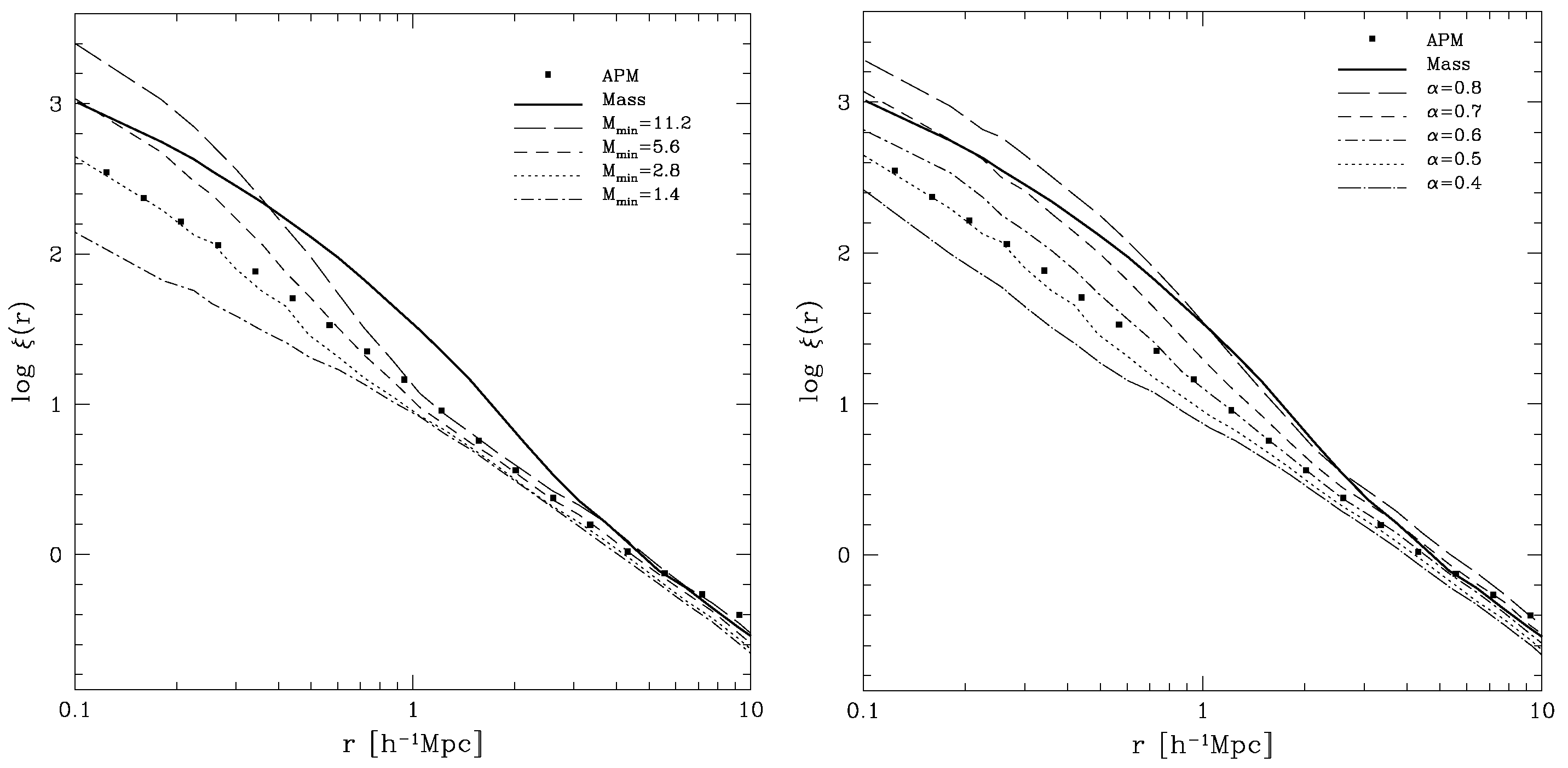
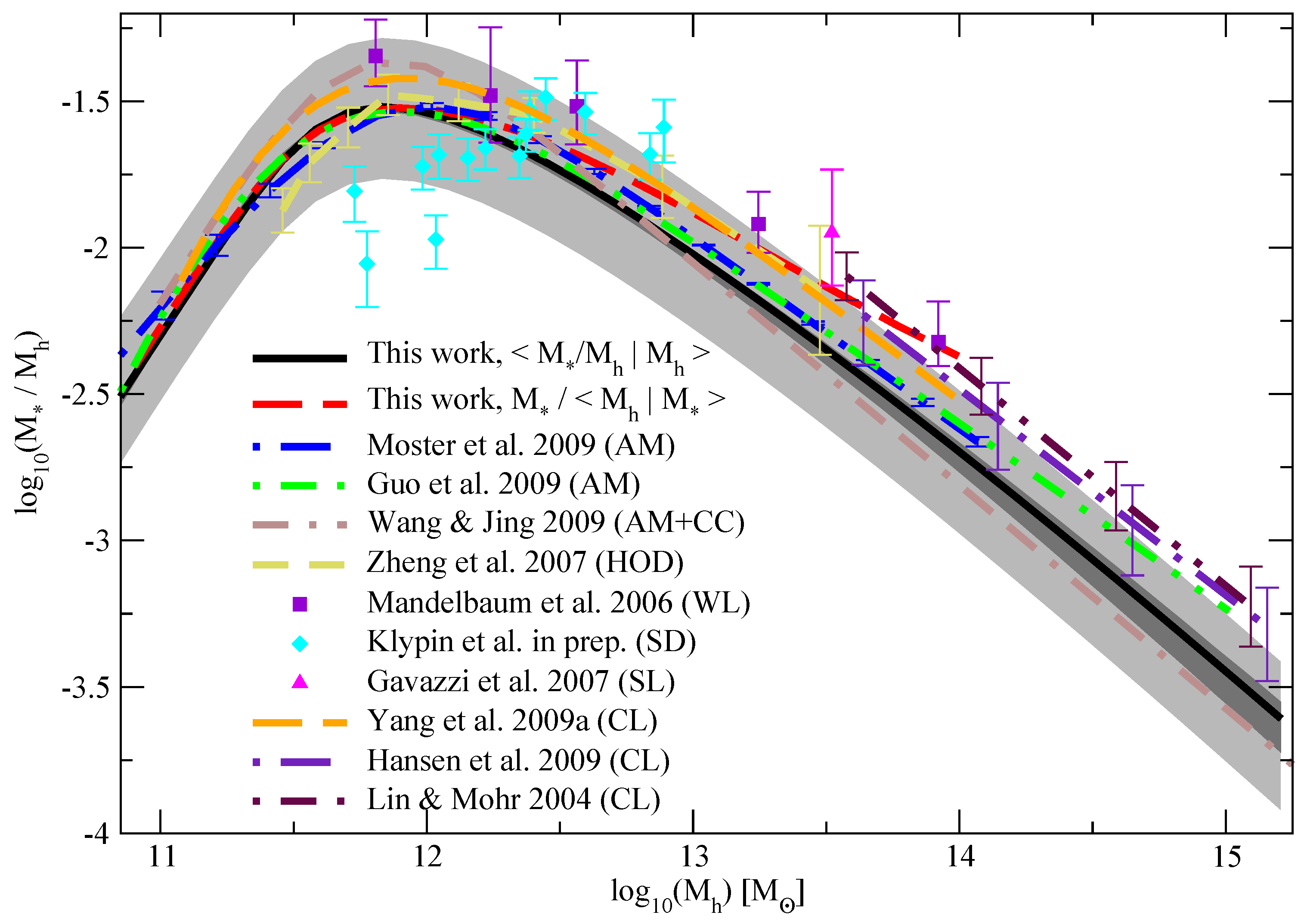
2. Statistical/Empirical Methods to Populate Dark Matter Halos
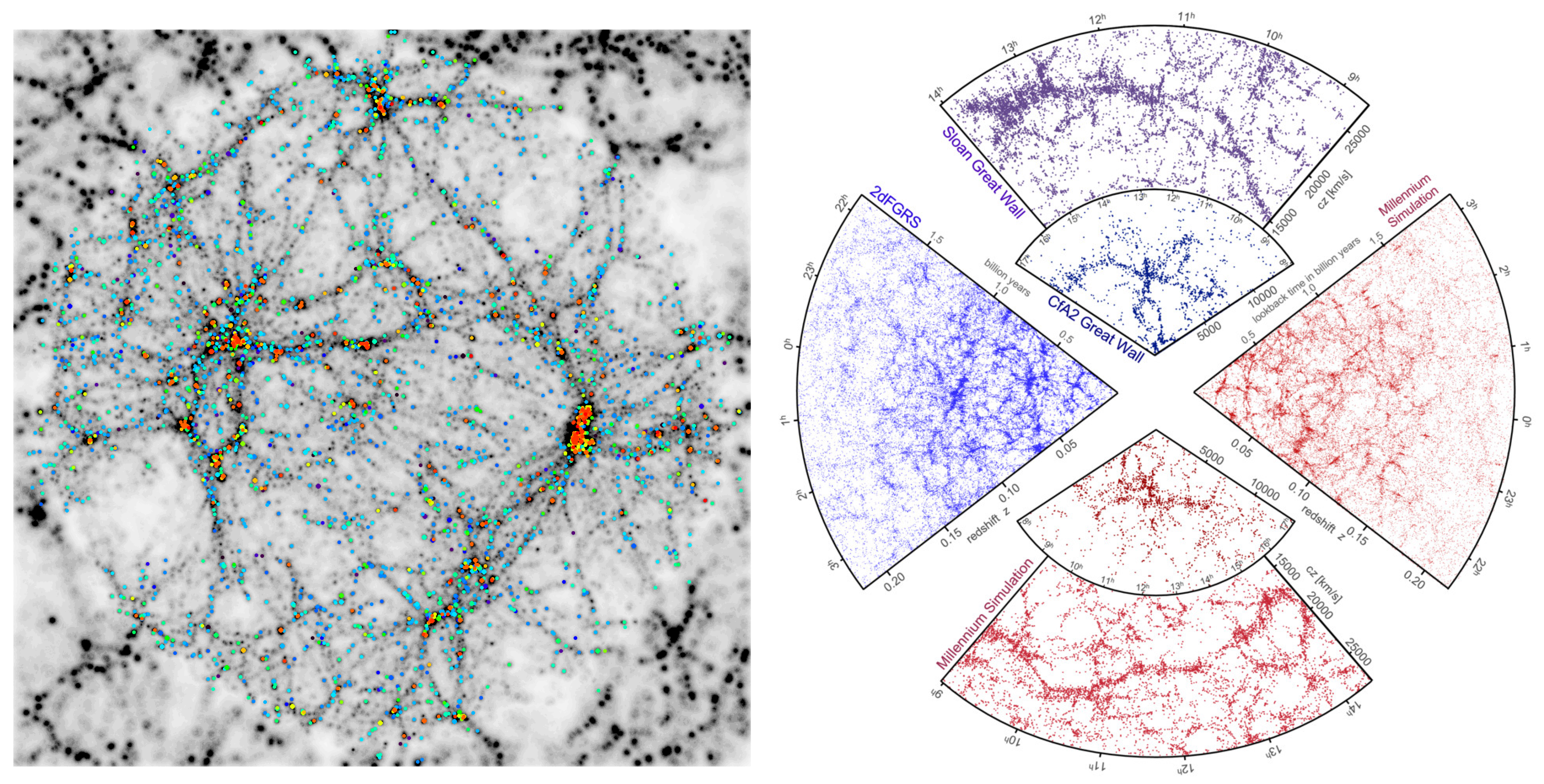
3. Semi-Analytic Models of Galaxy Formation
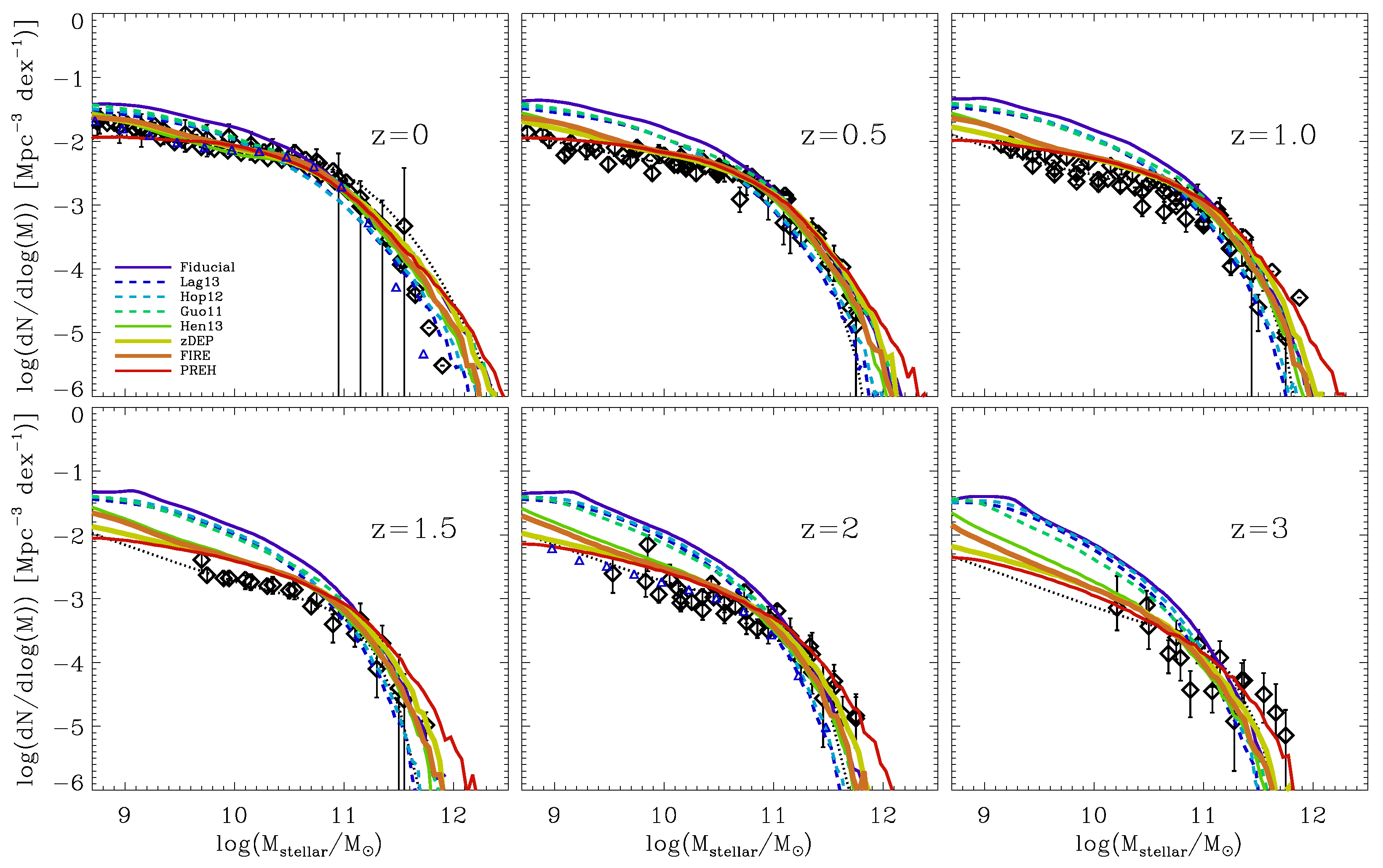
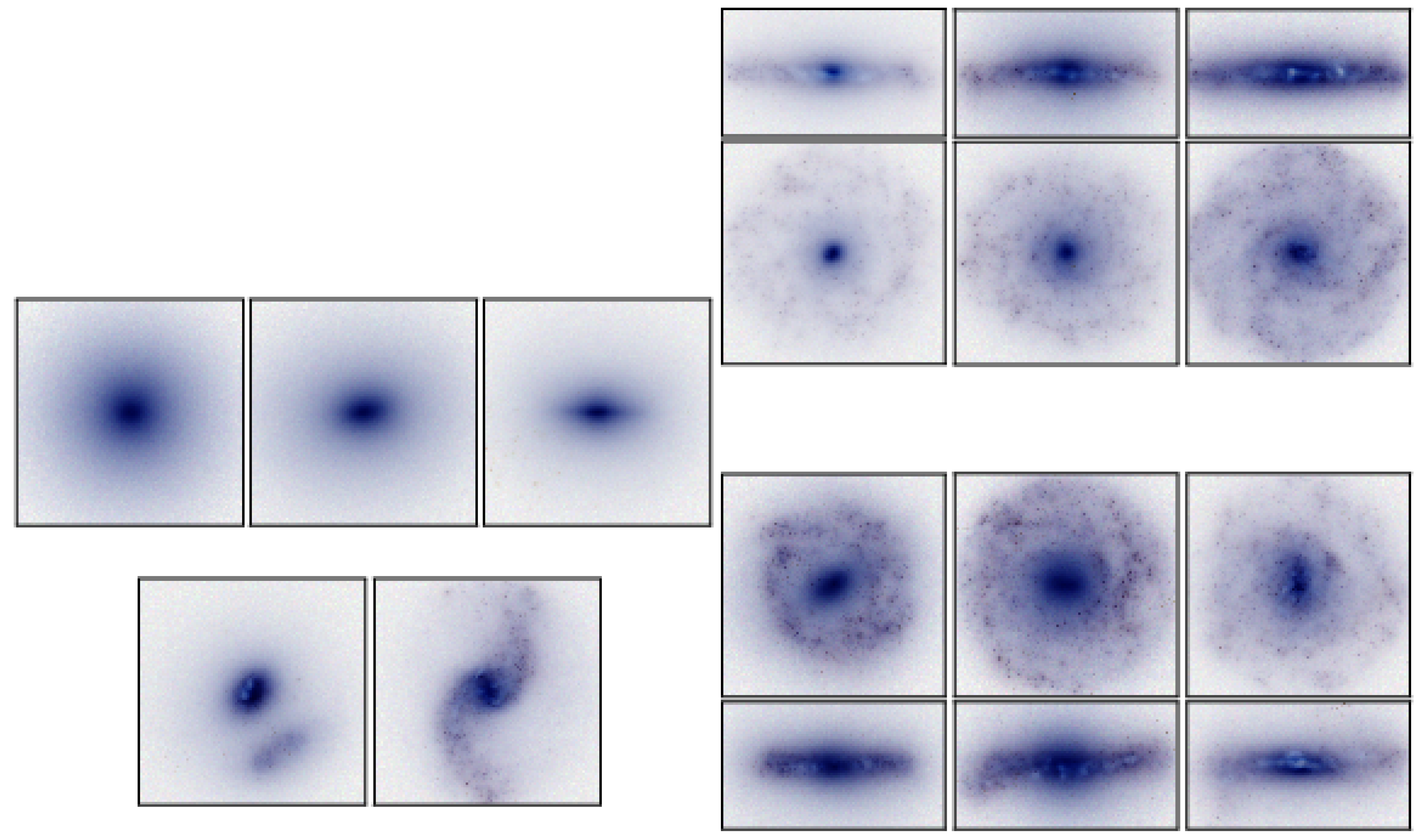
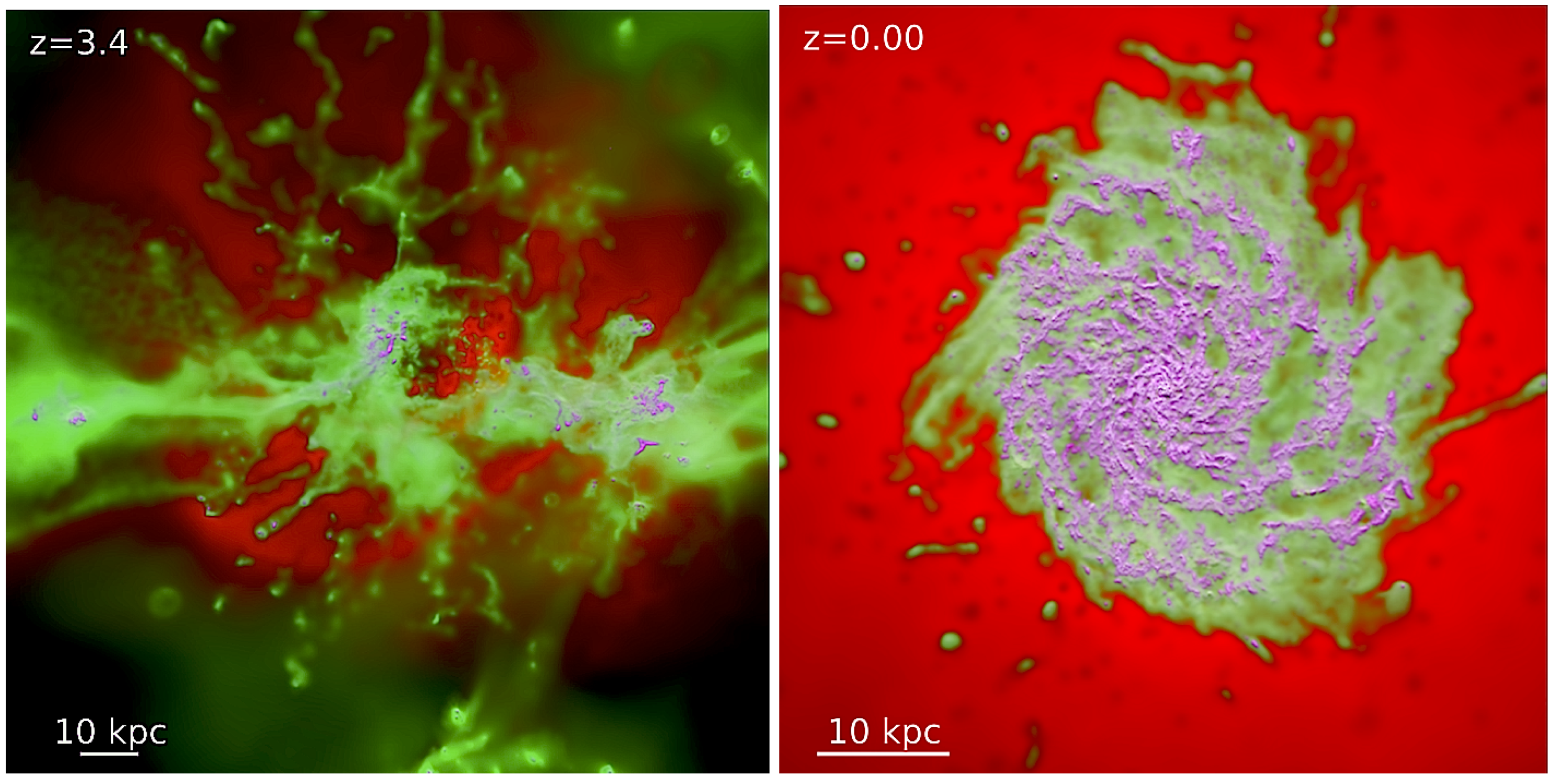
4. Hydrodynamical Simulations
5. Complementarities of the Different Approaches
- Empirical/statistical methods are characterized by a very intuitive framework and a very limited computational demand. They are able to provide useful statistical constraints on galaxy formation, but it remains difficult to translate this information into a deeper physical understanding of the galaxy formation process;
- Semi-analytic models are very flexible, have limited computational costs, and allow access to a large dynamical range in spatial and mass resolution. They neglect, however, an explicit treatment of the gas dynamics, and only a limited amount of information is accessible as for the spatial distribution of the baryonic components.
- Hydro-dynamical simulations include an explicit and accurate treatment of the gas dynamics, as well as full spatial information about the baryons. As a tool to study galaxy formation on cosmological scales, however, they are still limited by relatively high computational costs. In addition, and perhaps more importantly, the complex physical processes driving galaxy formation and evolution still need to be included resorting to sub-resolution/effective models.
6. Concluding Remarks
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neyman, J.; Scott, E.L. A Theory of the Spatial Distribution of Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 1952, 116, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, A.J.; Cole, S.; Frenk, C.S.; Baugh, C.M.; Lacey, C.G. The nature of galaxy bias and clustering. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2000, 311, 793–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlind, A.A.; Weinberg, D.H. The Halo Occupation Distribution: Toward an Empirical Determination of the Relation between Galaxies and Mass. Astrophys. J. 2002, 575, 587–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zentner, A.R.; Berlind, A.A.; Bullock, J.S.; Kravtsov, A.V.; Wechsler, R.H. The Physics of Galaxy Clustering. I. A Model for Subhalo Populations. Astrophys. J. 2005, 624, 505–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehavi, I.; Zheng, Z.; Weinberg, D.H.; Blanton, M.R.; Bahcall, N.A.; Berlind, A.A.; Brinkmann, J.; Frieman, J.A.; Gunn, J.E.; Lupton, R.H.; et al. Galaxy Clustering in the Completed SDSS Redshift Survey: The Dependence on Color and Luminosity. Astrophys. J. 2011, 736, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, J.F.; Frenk, C.S.; White, S.D.M. A Universal Density Profile from Hierarchical Clustering. Astrophys. J. 1997, 490, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baugh, C.M. The real-space correlation function measured from the APM Galaxy Survey. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1996, 280, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- van den Bosch, F.C.; Mo, H.J.; Yang, X. Towards cosmological concordance on galactic scales. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2003, 345, 923–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spergel, D.N.; Bean, R.; Doré, O.; Nolta, M.R.; Bennett, C.L.; Dunkley, J.; Hinshaw, G.; Jarosik, N.; Komatsu, E.; Page, L.; et al. Three-Year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) Observations: Implications for Cosmology. Am. Astron. Soc. 2007, 170, 377–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemson, G.; Kauffmann, G. Environmental influences on dark matter haloes and consequences for the galaxies within them. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1999, 302, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percival, W.J.; Scott, D.; Peacock, J.A.; Dunlop, J.S. The clustering of halo mergers. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2003, 338, L31–L35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sheth, R.K.; Tormen, G. On the environmental dependence of halo formation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2004, 350, 1385–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Springel, V.; White, S.D.M. The age dependence of halo clustering. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2005, 363, L66–L70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wechsler, R.H.; Zentner, A.R.; Bullock, J.S.; Kravtsov, A.V.; Allgood, B. The Dependence of Halo Clustering on Halo Formation History, Concentration, and Occupation. Astrophys. J. 2006, 652, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croton, D.J.; Gao, L.; White, S.D.M. Halo assembly bias and its effects on galaxy clustering. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2007, 374, 1303–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zentner, A.R.; Hearin, A.P.; van den Bosch, F.C. Galaxy assembly bias: A significant source of systematic error in the galaxy-halo relationship. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 443, 3044–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearin, A.P.; Zentner, A.R.; van den Bosch, F.C.; Campbell, D.; Tollerud, E. Introducing decorated HODs: Modelling assembly bias in the galaxy-halo connection. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 460, 2552–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artale, M.C.; Zehavi, I.; Contreras, S.; Norberg, P. The impact of assembly bias on the halo occupation in hydrodynamical simulations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 480, 3978–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehavi, I.; Contreras, S.; Padilla, N.; Smith, N.J.; Baugh, C.M.; Norberg, P. The Impact of Assembly Bias on the Galaxy Content of Dark Matter Halos. Astrophys. J. 2018, 853, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwen, J.E.; Weinberg, D.H. The effects of assembly bias on the inference of matter clustering from galaxy-galaxy lensing and galaxy clustering. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 477, 4348–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, N.; Contreras, S.; Zehavi, I.; Baugh, C.; Norberg, P. The Effect of Assembly Bias on Redshift Space Distortions. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1809.06424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conroy, C.; Wechsler, R.H.; Kravtsov, A.V. Modeling Luminosity-dependent Galaxy Clustering through Cosmic Time. Astrophys. J. 2006, 647, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, C.; Kauffmann, G.; De Lucia, G. Modelling galaxy clustering in a high-resolution simulation of structure formation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2006, 371, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behroozi, P.S.; Conroy, C.; Wechsler, R.H. A Comprehensive Analysis of Uncertainties Affecting the Stellar Mass-Halo Mass Relation for 0 < z < 4. Astrophys. J. 2010, 717, 379–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moster, B.P.; Somerville, R.S.; Maulbetsch, C.; van den Bosch, F.C.; Macciò, A.V.; Naab, T.; Oser, L. Constraints on the Relationship between Stellar Mass and Halo Mass at Low and High Redshift. Astrophys. J. 2010, 710, 903–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; White, S.; Li, C.; Boylan-Kolchin, M. How do galaxies populate dark matter haloes? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 404, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jing, Y.P. Modelling galaxy stellar mass evolution from z ~ 0.8 to today. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 402, 1796–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Coil, A.L.; Zehavi, I. Galaxy Evolution from Halo Occupation Distribution Modeling of DEEP2 and SDSS Galaxy Clustering. Astrophys. J. 2007, 667, 760–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelbaum, R.; Seljak, U.; Kauffmann, G.; Hirata, C.M.; Brinkmann, J. Galaxy halo masses and satellite fractions from galaxy-galaxy lensing in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey: Stellar mass, luminosity, morphology and environment dependencies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2006, 368, 715–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavazzi, R.; Treu, T.; Rhodes, J.D.; Koopmans, L.V.E.; Bolton, A.S.; Burles, S.; Massey, R.J.; Moustakas, L.A. The Sloan Lens ACS Survey. IV. The Mass Density Profile of Early-Type Galaxies out to 100 Effective Radii. Astrophys. J. 2007, 667, 176–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Mo, H.J.; van den Bosch, F.C. Galaxy Groups in the SDSS DR4. III. The Luminosity and Stellar Mass Functions. Astrophys. J. 2009, 695, 900–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, S.M.; Sheldon, E.S.; Wechsler, R.H.; Koester, B.P. The Galaxy Content of SDSS Clusters and Groups. Astrophys. J. 2009, 699, 1333–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.T.; Mohr, J.J. K-band Properties of Galaxy Clusters and Groups: Brightest Cluster Galaxies and Intracluster Light. Astrophys. J. 2004, 617, 879–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; De Lucia, G.; Weinmann, S.M. On the scatter in the relation between stellar mass and halo mass: random or halo formation time dependent? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 431, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lucia, G.; Kauffmann, G.; Springel, V.; White, S.D.M.; Lanzoni, B.; Stoehr, F.; Tormen, G.; Yoshida, N. Substructures in cold dark matter haloes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2004, 348, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; White, S.D.M.; Jenkins, A.; Stoehr, F.; Springel, V. The subhalo populations of ΛCDM dark haloes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2004, 355, 819–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; White, S. Numerical resolution limits on subhalo abundance matching. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 437, 3228–3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springel, V.; White, S.D.M.; Jenkins, A.; Frenk, C.S.; Yoshida, N.; Gao, L.; Navarro, J.; Thacker, R.; Croton, D.; Helly, J.; et al. Simulations of the formation, evolution and clustering of galaxies and quasars. Nature 2005, 435, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boylan-Kolchin, M.; Springel, V.; White, S.D.M.; Jenkins, A.; Lemson, G. Resolving cosmic structure formation with the Millennium-II Simulation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2009, 398, 1150–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, J.R.; Cole, S.; Efstathiou, G.; Kaiser, N. Excursion set mass functions for hierarchical Gaussian fluctuations. Astrophys. J. 1991, 379, 440–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somerville, R.S.; Kolatt, T.S. How to plant a merger tree. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1999, 305, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roukema, B.F.; Quinn, P.J.; Peterson, B.A.; Rocca-Volmerange, B. Merging history trees of dark matter haloes—A tool for exploring galaxy formation models. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1997, 292, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tweed, D.; Devriendt, J.; Blaizot, J.; Colombi, S.; Slyz, A. Building merger trees from cosmological N-body simulations. Towards improving galaxy formation models using subhaloes. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 506, 647–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.D.M.; Rees, M.J. Core condensation in heavy halos - A two-stage theory for galaxy formation and clustering. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1978, 183, 341–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.D.M.; Frenk, C.S. Galaxy formation through hierarchical clustering. Astrophys. J. 1991, 379, 52–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, S. Modeling galaxy formation in evolving dark matter halos. Astrophys. J. 1991, 367, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauffmann, G.; White, S.D.M.; Guiderdoni, B. The Formation and Evolution of Galaxies Within Merging Dark Matter Haloes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1993, 264, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauffmann, G.; Colberg, J.M.; Diaferio, A.; White, S.D.M. Clustering of galaxies in a hierarchical universe—I. Methods and results at z = 0. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1999, 303, 188–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springel, V.; White, S.D.M.; Tormen, G.; Kauffmann, G. Populating a cluster of galaxies—I. Results at [formmu2]z = 0. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2001, 328, 726–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lucia, G.; Kauffmann, G.; White, S.D.M. Chemical enrichment of the intracluster and intergalactic medium in a hierarchical galaxy formation model. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2004, 349, 1101–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lucia, G.; Boylan-Kolchin, M.; Benson, A.J.; Fontanot, F.; Monaco, P. A semi-analytic model comparison—Gas cooling and galaxy mergers. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 406, 1533–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mathis, H.; Lemson, G.; Springel, V.; Kauffmann, G.; White, S.D.M.; Eldar, A.; Dekel, A. Simulating the formation of the local galaxy population. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2002, 333, 739–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinmann, S.M.; Pasquali, A.; Oppenheimer, B.D.; Finlator, K.; Mendel, J.T.; Crain, R.A.; Macciò, A.V. A fundamental problem in our understanding of low-mass galaxy evolution. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 426, 2797–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinmann, S.M.; van den Bosch, F.C.; Yang, X.; Mo, H.J. Properties of galaxy groups in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey—I. The dependence of color, star formation and morphology on halo mass. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2006, 366, 2–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, C.; Kauffmann, G.; De Lucia, G. Modelling and interpreting the dependence of clustering on the spectral energy distributions of galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2007, 377, 1419–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Font, A.S.; Bower, R.G.; McCarthy, I.G.; Benson, A.J.; Frenk, C.S.; Helly, J.C.; Lacey, C.G.; Baugh, C.M.; Cole, S. The colors of satellite galaxies in groups and clusters. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 389, 1619–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinmann, S.M.; Kauffmann, G.; von der Linden, A.; De Lucia, G. Cluster galaxies die hard. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 406, 2249–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; White, S.; Boylan-Kolchin, M.; De Lucia, G.; Kauffmann, G.; Lemson, G.; Li, C.; Springel, V.; Weinmann, S. From dwarf spheroidals to cD galaxies: Simulating the galaxy population in a ΛCDM cosmology. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 413, 101–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschmann, M.; De Lucia, G.; Fontanot, F. Galaxy assembly, stellar feedback and metal enrichment: The view from the GAEA model. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 461, 1760–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, P.F.; Kereš, D.; Oñorbe, J.; Faucher-Giguère, C.A.; Quataert, E.; Murray, N.; Bullock, J.S. Galaxies on FIRE (Feedback In Realistic Environments): Stellar feedback explains cosmologically inefficient star formation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 445, 581–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; De Lucia, G.; Hirschmann, M.; Fontanot, F.; Zoldan, A. H2-based star formation laws in hierarchical models of galaxy formation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 469, 968–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cora, S.A. Metal enrichment of the intracluster medium: A three-dimensional picture of chemical and dynamical properties. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2006, 368, 1540–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, R.M.; Henriques, B.; Thomas, P.A.; Kauffmann, G.; Johansson, J.; White, S.D.M. Modelling element abundances in semi-analytic models of galaxy formation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 435, 3500–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lucia, G.; Tornatore, L.; Frenk, C.S.; Helmi, A.; Navarro, J.F.; White, S.D.M. Elemental abundances in Milky Way-like galaxies from a hierarchical galaxy formation model. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 445, 970–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Guo, Q.; Kauffmann, G.; Krumholz, M.R. The atomic-to-molecular transition and its relation to the scaling properties of galaxy discs in the local Universe. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 409, 515–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagos, C.D.P.; Lacey, C.G.; Baugh, C.M.; Bower, R.G.; Benson, A.J. On the impact of empirical and theoretical star formation laws on galaxy formation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 416, 1566–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somerville, R.S.; Popping, G.; Trager, S.C. Star formation in semi-analytic galaxy formation models with multiphase gas. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 453, 4337–4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popping, G.; Somerville, R.S.; Galametz, M. The dust content of galaxies from z = 0 to z = 9. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 471, 3152–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemson, G.; Virgo Consortium, T. Halo and Galaxy Formation Histories from the Millennium Simulation: Public release of a VO-oriented and SQL-queryable database for studying the evolution of galaxies in the LambdaCDM cosmogony. arXiv 2006, arXiv:astro-ph/0608019. [Google Scholar]
- Agertz, O.; Moore, B.; Stadel, J.; Potter, D.; Miniati, F.; Read, J.; Mayer, L.; Gawryszczak, A.; Kravtsov, A.; Nordlund, Å.; et al. Fundamental differences between SPH and grid methods. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2007, 380, 963–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolag, K.; Vazza, F.; Brunetti, G.; Tormen, G. Turbulent gas motions in galaxy cluster simulations: The role of smoothed particle hydrodynamics viscosity. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2005, 364, 753–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, D.J. Modelling discontinuities and Kelvin Helmholtz instabilities in SPH. J. Comput. Phys. 2008, 227, 10040–10057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.Y.; Naab, T.; Walch, S.; Moster, B.P.; Oser, L. SPHGal: Smoothed particle hydrodynamics with improved accuracy for galaxy simulations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 443, 1173–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.M.; Murante, G.; Arth, A.; Remus, R.S.; Teklu, A.F.; Donnert, J.M.F.; Planelles, S.; Beck, M.C.; Förster, P.; Imgrund, M.; et al. An improved SPH scheme for cosmological simulations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 455, 2110–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springel, V. E pur si muove: Galilean-invariant cosmological hydrodynamical simulations on a moving mesh. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 401, 791–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasker, E.J.; Brunino, R.; Mitchell, N.L.; Michielsen, D.; Hopton, S.; Pearce, F.R.; Bryan, G.L.; Theuns, T. A test suite for quantitative comparison of hydrodynamic codes in astrophysics. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 390, 1267–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, P.F. A new class of accurate, mesh-free hydrodynamic simulation methods. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 450, 53–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, Y.; Pichon, C.; Welker, C.; Le Borgne, D.; Devriendt, J.; Laigle, C.; Codis, S.; Pogosyan, D.; Arnouts, S.; Benabed, K.; et al. Dancing in the dark: Galactic properties trace spin swings along the cosmic web. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 444, 1453–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschmann, M.; Dolag, K.; Saro, A.; Bachmann, L.; Borgani, S.; Burkert, A. Cosmological simulations of black hole growth: AGN luminosities and downsizing. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 442, 2304–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolag, K. The Magneticum Simulations, from Galaxies to Galaxy Clusters. IAU Gen. Assem. 2015, 22, 2250156. [Google Scholar]
- Vogelsberger, M.; Genel, S.; Springel, V.; Torrey, P.; Sijacki, D.; Xu, D.; Snyder, G.; Nelson, D.; Hernquist, L. Introducing the Illustris Project: Simulating the coevolution of dark and visible matter in the Universe. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 444, 1518–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaye, J.; Crain, R.A.; Bower, R.G.; Furlong, M.; Schaller, M.; Theuns, T.; Dalla Vecchia, C.; Frenk, C.S.; McCarthy, I.G.; Helly, J.C.; et al. The EAGLE project: Simulating the evolution and assembly of galaxies and their environments. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 446, 521–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davé, R.; Rafieferantsoa, M.H.; Thompson, R.J.; Hopkins, P.F. MUFASA: Galaxy star formation, gas, and metal properties across cosmic time. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 467, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, I.G.; Schaye, J.; Bird, S.; Le Brun, A.M.C. The BAHAMAS project: Calibrated hydrodynamical simulations for large-scale structure cosmology. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 465, 2936–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baes, M.; Verstappen, J.; De Looze, I.; Fritz, J.; Saftly, W.; Vidal Pérez, E.; Stalevski, M.; Valcke, S. Efficient Three-dimensional NLTE Dust Radiative Transfer with SKIRT. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2011, 196, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahé, Y.M.; Barnes, D.J.; Dalla Vecchia, C.; Kay, S.T.; White, S.D.M.; McCarthy, I.G.; Schaye, J.; Bower, R.G.; Crain, R.A.; Theuns, T.; et al. The Hydrangea simulations: Galaxy formation in and around massive clusters. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 470, 4186–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lucia, G.; Muzzin, A.; Weinmann, S. What Regulates Galaxy Evolution? Open questions in our understanding of galaxy formation and evolution. New Astron. Rev. 2014, 62, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlong, M.; Bower, R.G.; Theuns, T.; Schaye, J.; Crain, R.A.; Schaller, M.; Dalla Vecchia, C.; Frenk, C.S.; McCarthy, I.G.; Helly, J.; et al. Evolution of galaxy stellar masses and star formation rates in the EAGLE simulations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 450, 4486–4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillepich, A.; Springel, V.; Nelson, D.; Genel, S.; Naiman, J.; Pakmor, R.; Hernquist, L.; Torrey, P.; Vogelsberger, M.; Weinberger, R.; et al. Simulating galaxy formation with the IllustrisTNG model. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 473, 4077–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, L.; Governato, F.; Kaufmann, T. The formation of disk galaxies in computer simulations. Adv. Sci. Lett. 2008, 1, 7–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murante, G.; Monaco, P.; Borgani, S.; Tornatore, L.; Dolag, K.; Goz, D. Simulating realistic disc galaxies with a novel sub-resolution ISM model. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 447, 178–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakmor, R.; Gómez, F.A.; Grand, R.J.J.; Marinacci, F.; Simpson, C.M.; Springel, V.; Campbell, D.J.R.; Frenk, C.S.; Guillet, T.; Pfrommer, C.; et al. Magnetic field formation in the Milky Way like disc galaxies of the Auriga project. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 469, 3185–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pais, M.; Pfrommer, C.; Ehlert, K.; Pakmor, R. The effect of cosmic ray acceleration on supernova blast wave dynamics. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 478, 5278–5295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naab, T.; Ostriker, J.P. Theoretical Challenges in Galaxy Formation. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 55, 59–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales, L.V.; Marinacci, F.; Springel, V.; Petkova, M. Stellar feedback by radiation pressure and photoionization. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 439, 2990–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.G.; Ostriker, E.C. Momentum Injection by Supernovae in the Interstellar Medium. Astrophys. J. 2015, 802, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martizzi, D.; Fielding, D.; Faucher-Giguère, C.A.; Quataert, E. Supernova feedback in a local vertically stratified medium: interstellar turbulence and galactic winds. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 459, 2311–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girichidis, P.; Walch, S.; Naab, T.; Gatto, A.; Wünsch, R.; Glover, S.C.O.; Klessen, R.S.; Clark, P.C.; Peters, T.; Derigs, D.; et al. The SILCC (SImulating the LifeCycle of molecular Clouds) project—II. Dynamical evolution of the supernova-driven ISM and the launching of outflows. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 456, 3432–3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriques, B.M.B.; Thomas, P.A.; Oliver, S.; Roseboom, I. Monte Carlo Markov Chain parameter estimation in semi-analytic models of galaxy formation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2009, 396, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bower, R.G.; Vernon, I.; Goldstein, M.; Benson, A.J.; Lacey, C.G.; Baugh, C.M.; Cole, S.; Frenk, C.S. The parameter space of galaxy formation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 407, 2017–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1. | The formation time of a halo is typically defined as the time when the most massive progenitor of the halo first contains half of the final mass. |
| 2. | At low stellar masses, a better treatment of the satellite galaxies is still required. |
| 3. | A similar figure can be found on the public Illustris database: http://www.illustris-project.org/. |
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Lucia, G. Lighting Up Dark Matter Haloes. Galaxies 2019, 7, 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies7020056
De Lucia G. Lighting Up Dark Matter Haloes. Galaxies. 2019; 7(2):56. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies7020056
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Lucia, Gabriella. 2019. "Lighting Up Dark Matter Haloes" Galaxies 7, no. 2: 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies7020056
APA StyleDe Lucia, G. (2019). Lighting Up Dark Matter Haloes. Galaxies, 7(2), 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies7020056




