Very High-Energy Emission from the Direct Vicinity of Rapidly Rotating Black Holes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Pulsar Outer Gap Model
3. The Black Hole Gap Model
3.1. Stationary Gap Models
3.2. Force-Free Magnetosphere and the Necessity of a Gap
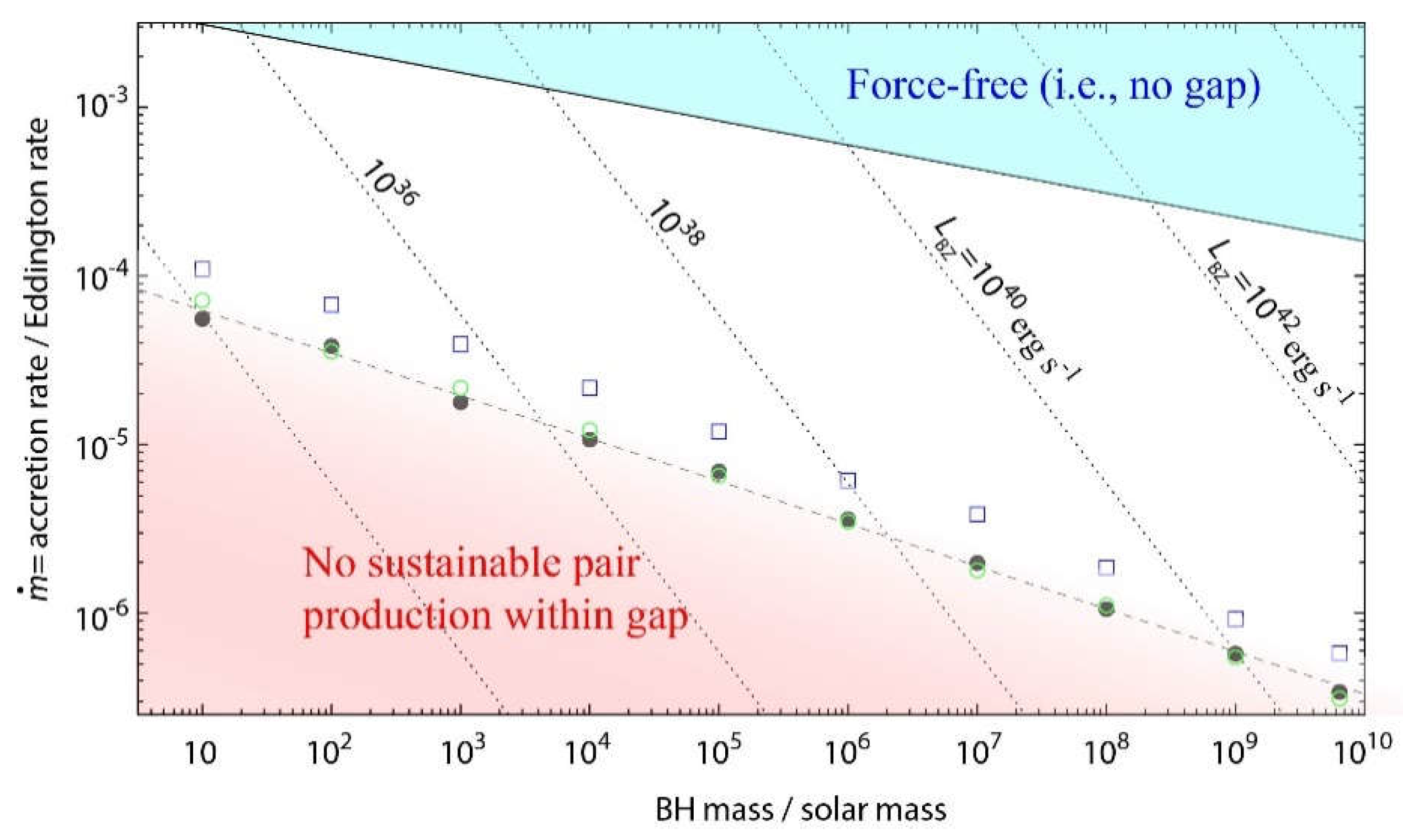
3.3. Detectability of Gap Emissions
3.4. Criticism of the Stationary Black Hole (BH) Gap Model
3.5. Background Space-Time Geometry
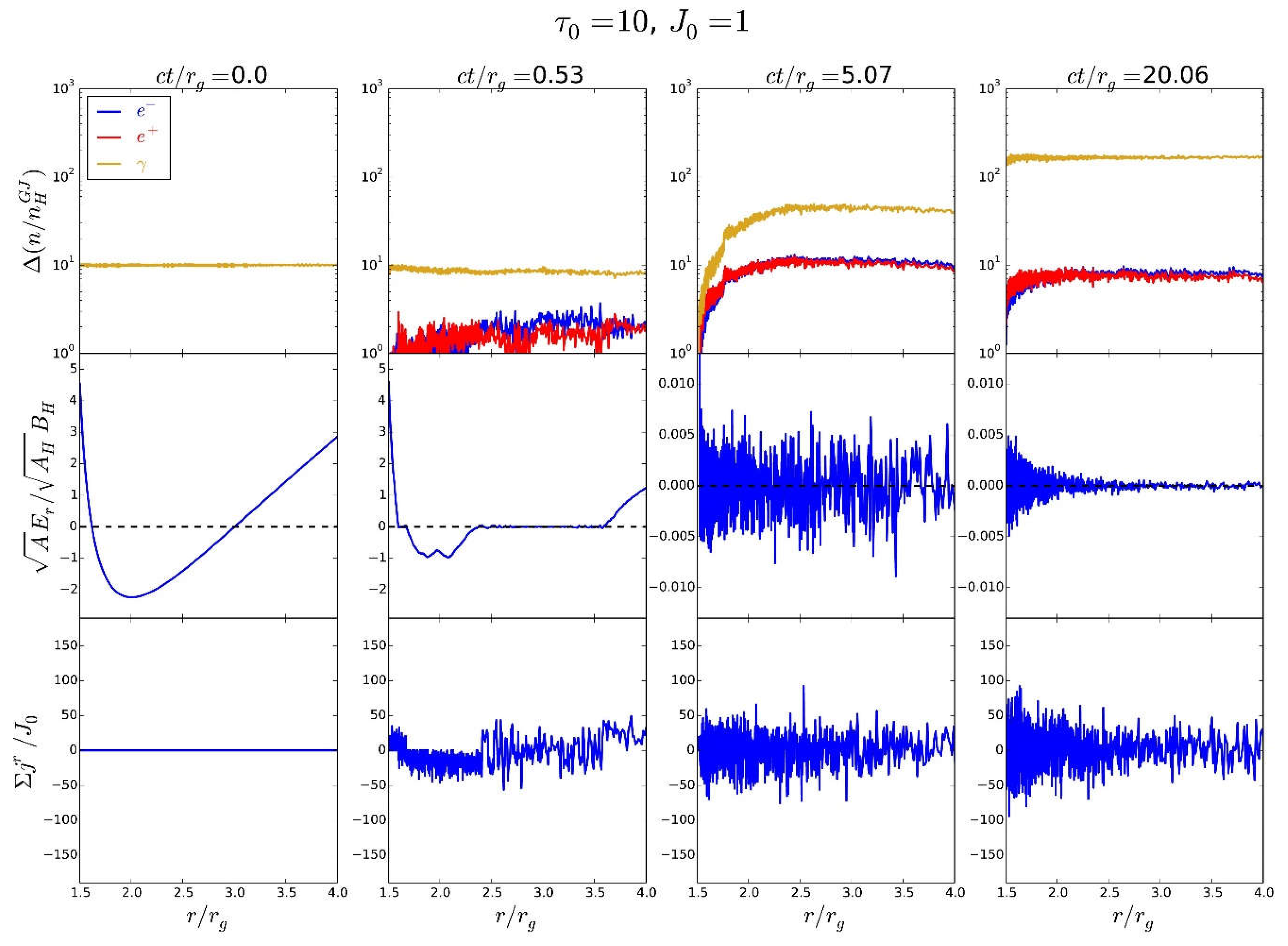
3.6. Non-Stationary BH Gap Model
4. Advection-Dominated Accretion Flow
5. Stationary, Two-Dimensional Gap Electrodynamics
5.1. Poisson Equation for the Non-Corotational Potential
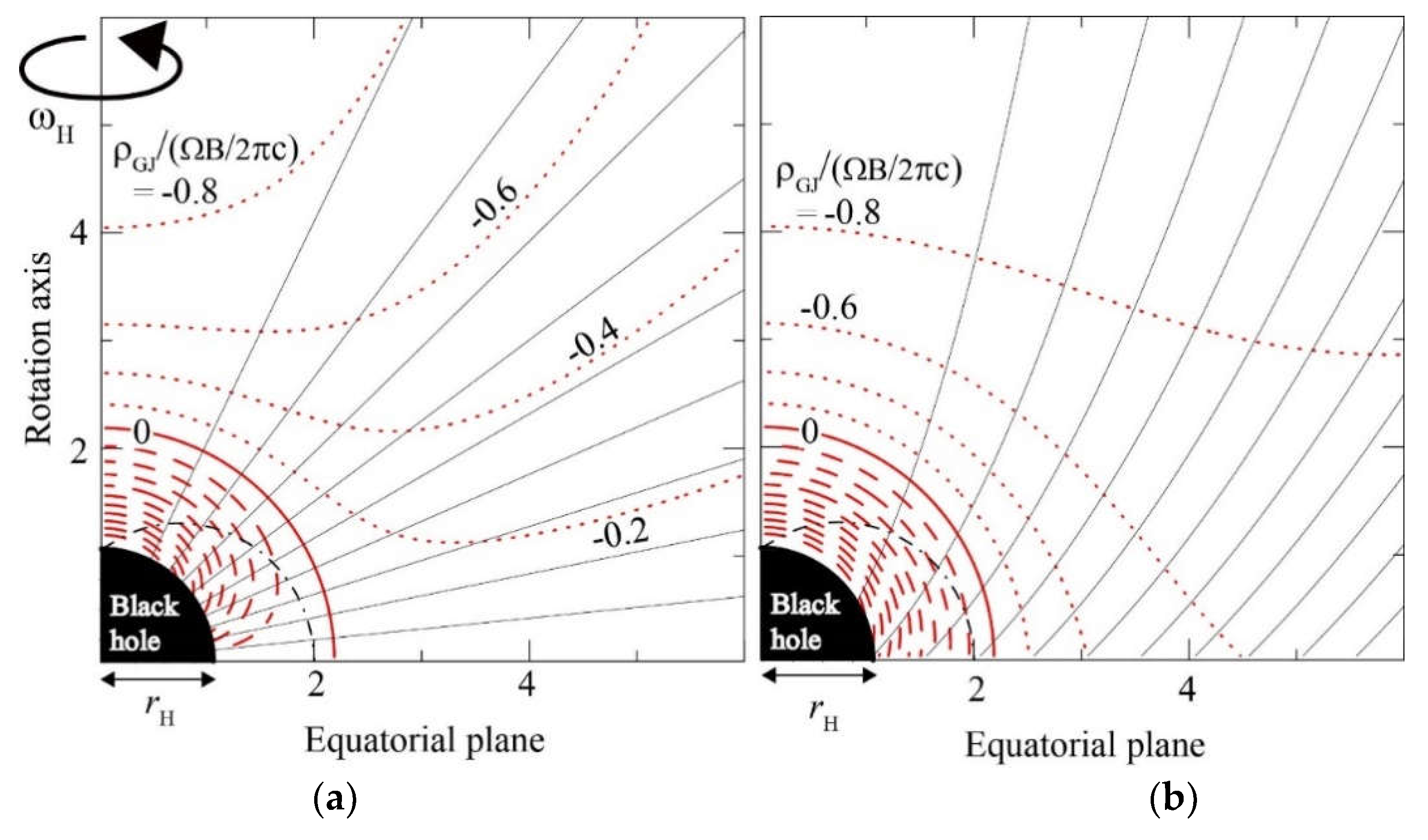
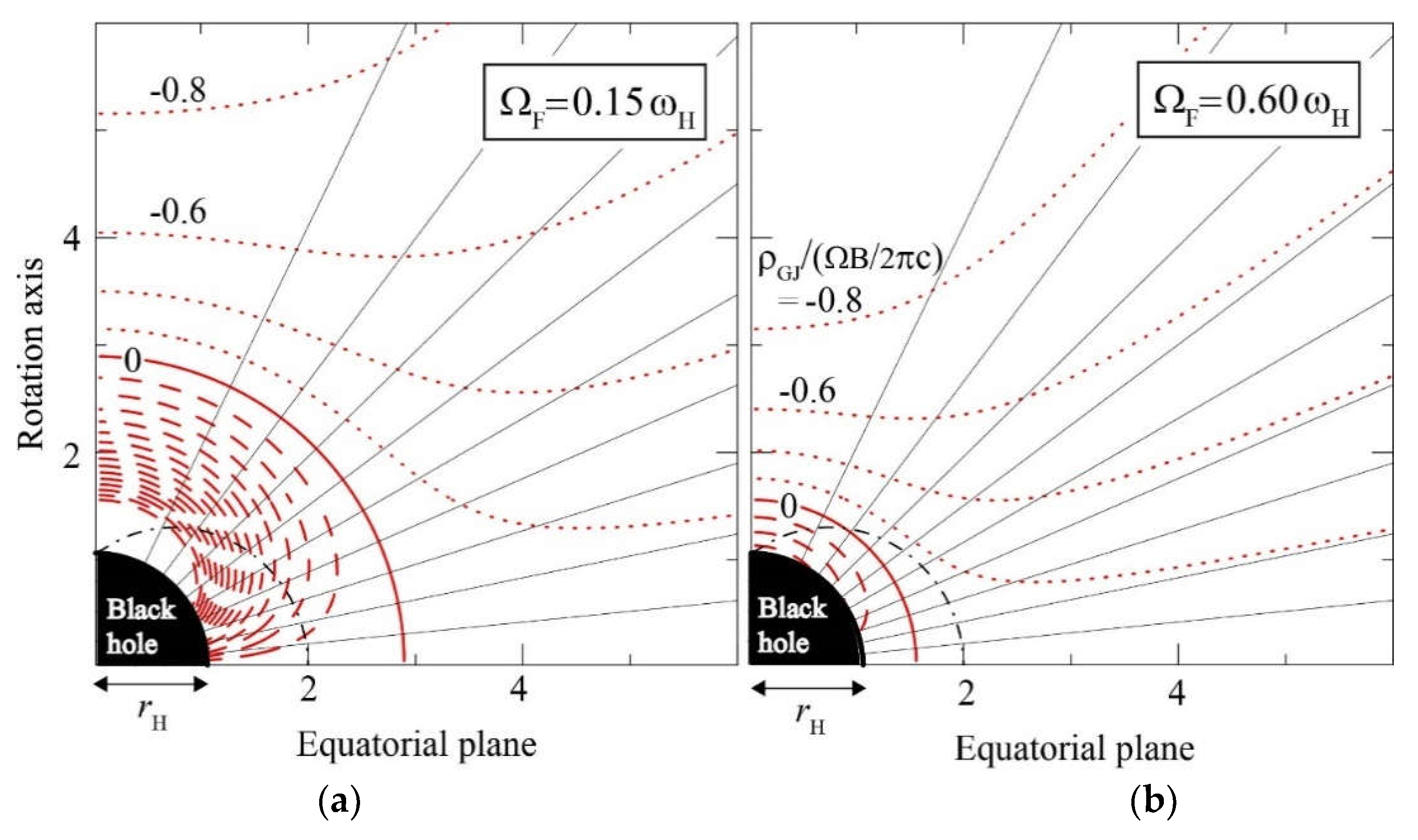
5.2. The Null-Charge Surface
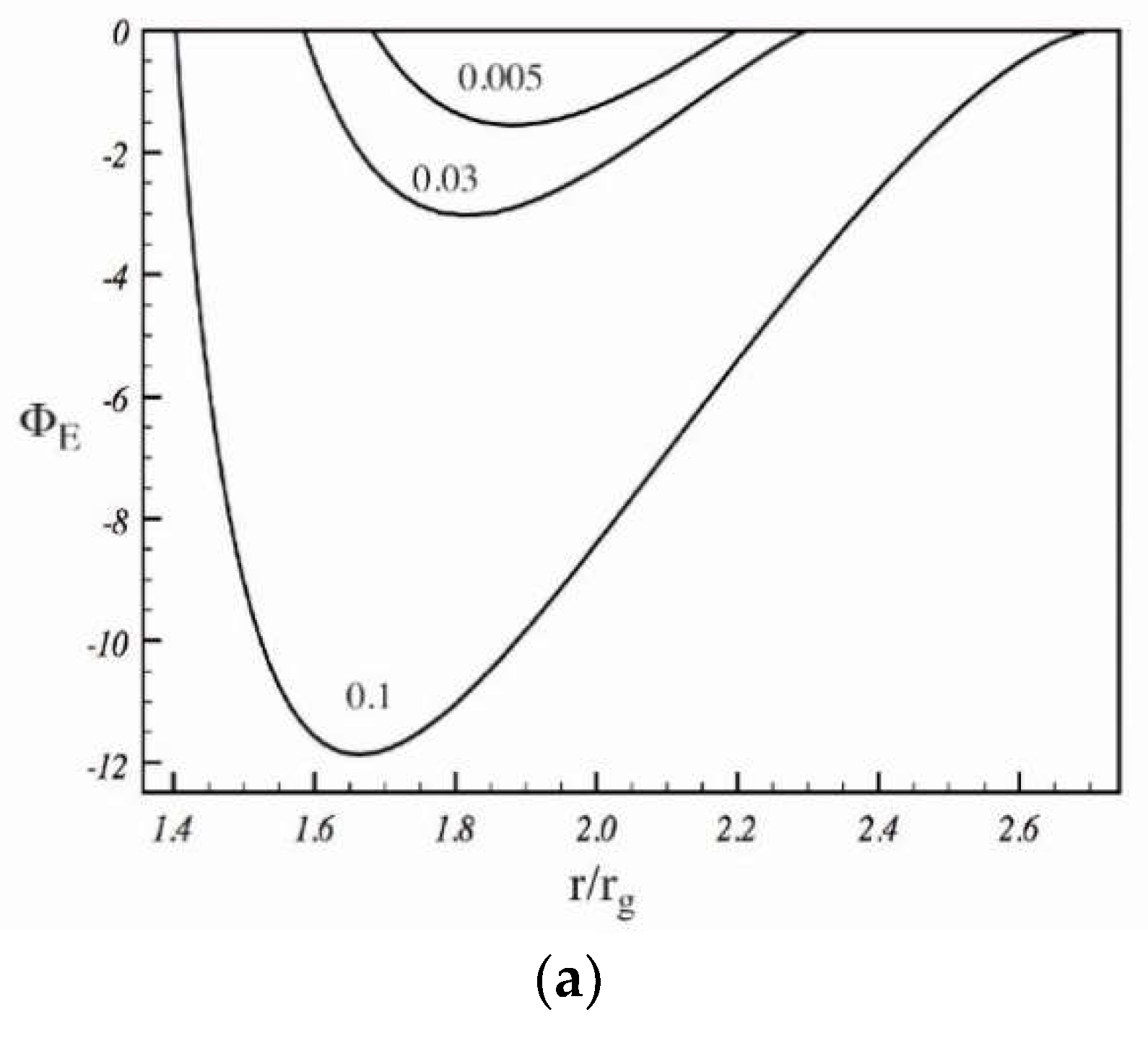
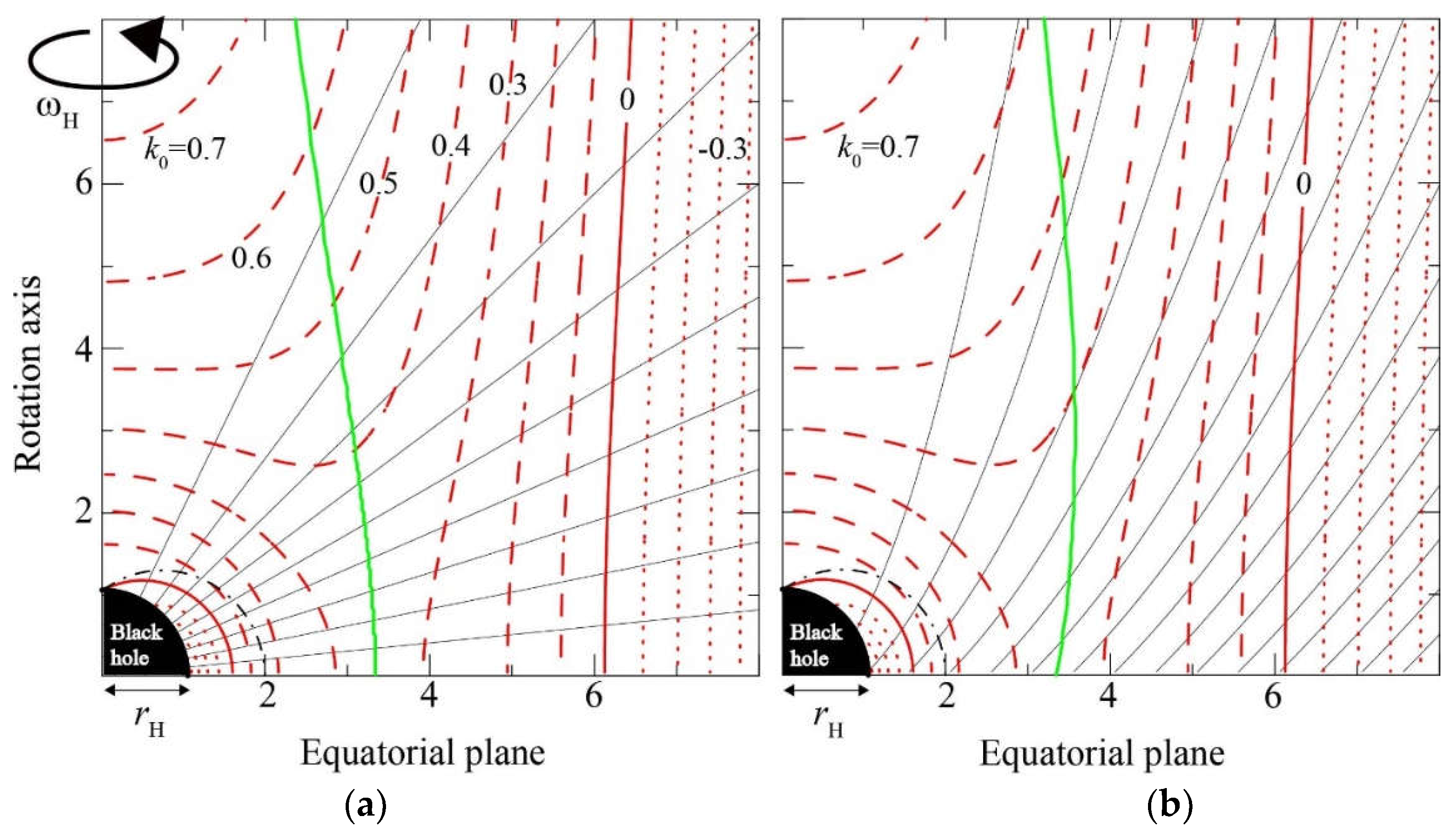
5.3. The Stagnation Surface
5.4. The Gap Position
5.5. Advection-Dominated Accretion Flow (ADAF)-Emitted Soft Photon Field in the Magnetosphere
5.6. The Poisson Equation in the Tortoise Coordinate
5.7. Boltzmann Equations for Electrons and Positrons
5.8. Radiative Transfer Equation
5.9. Boundary Conditions
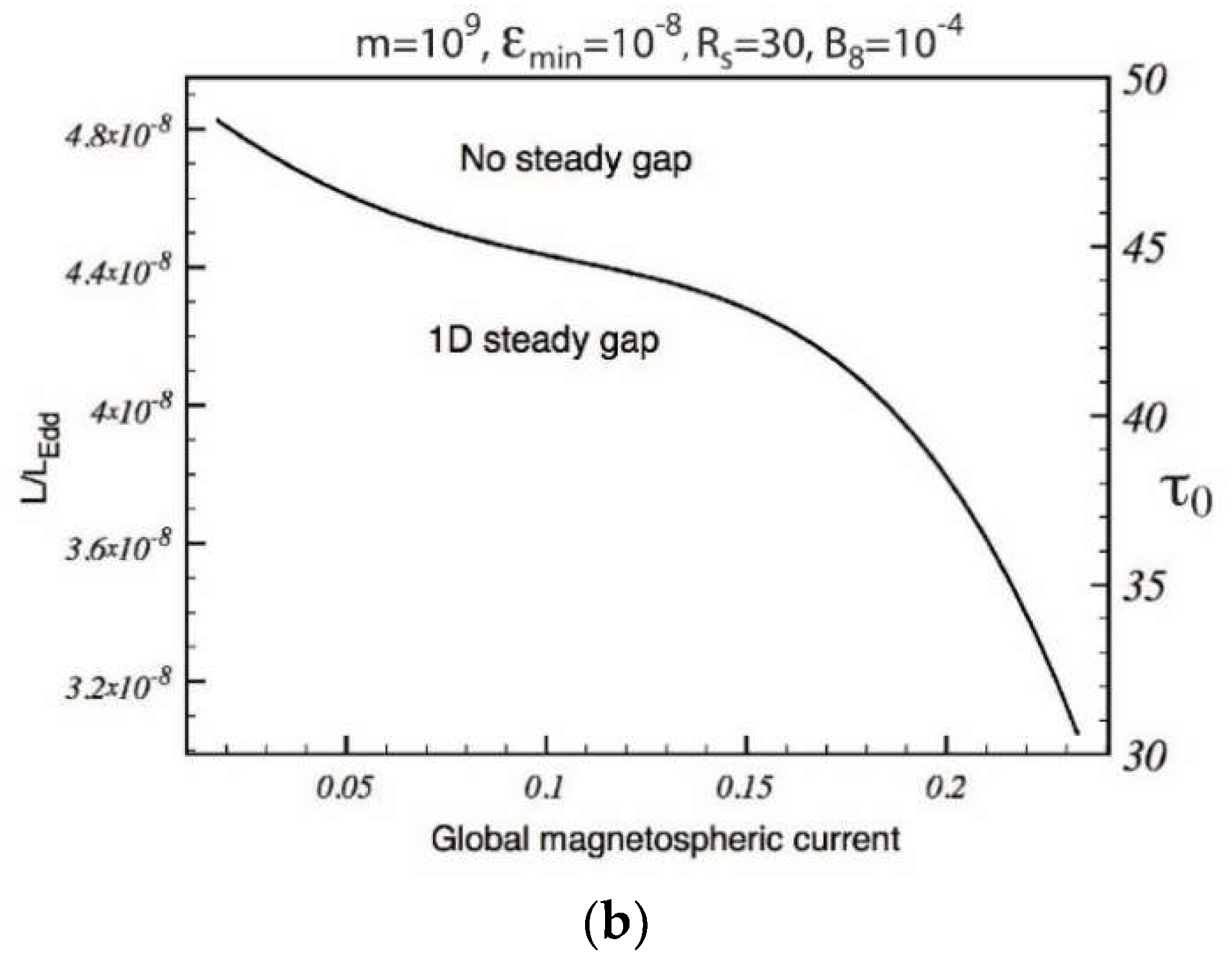
5.10. Gap Closure Condition
6. Lepton Accelerator around Stellar-Mass Black Holes
6.1. Black Hole Accretion in a Gaseous Cloud
6.2. Lepton Accelerator around Stellar-Mass Black Holes
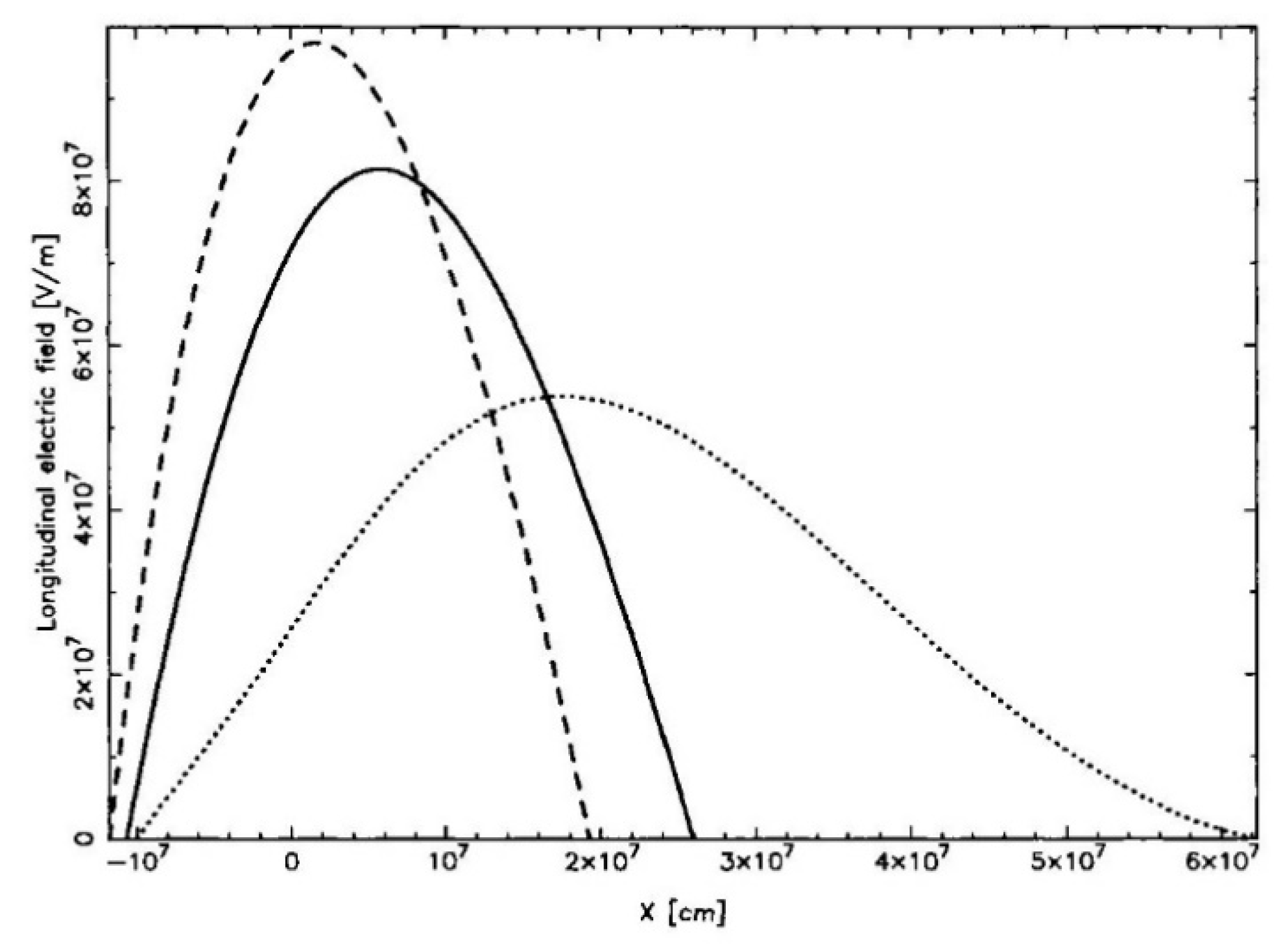
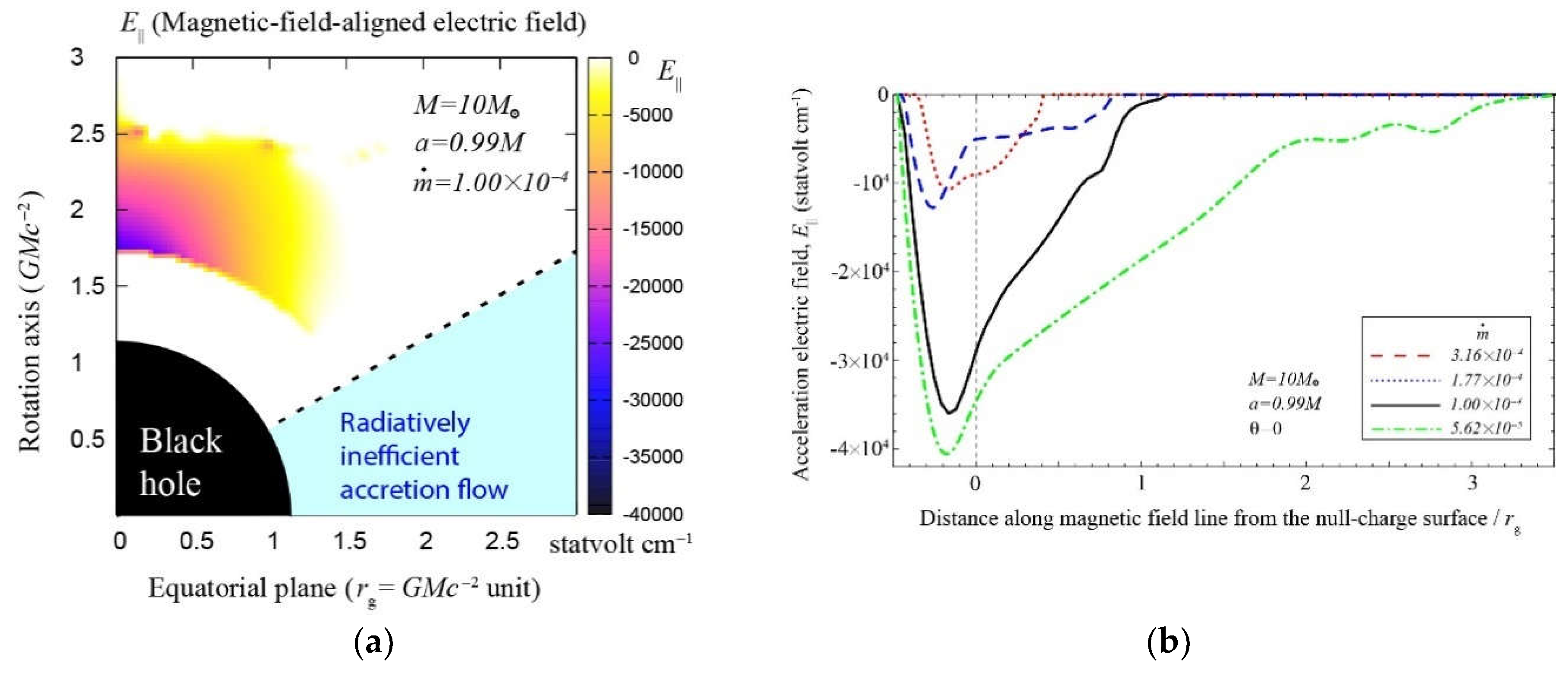
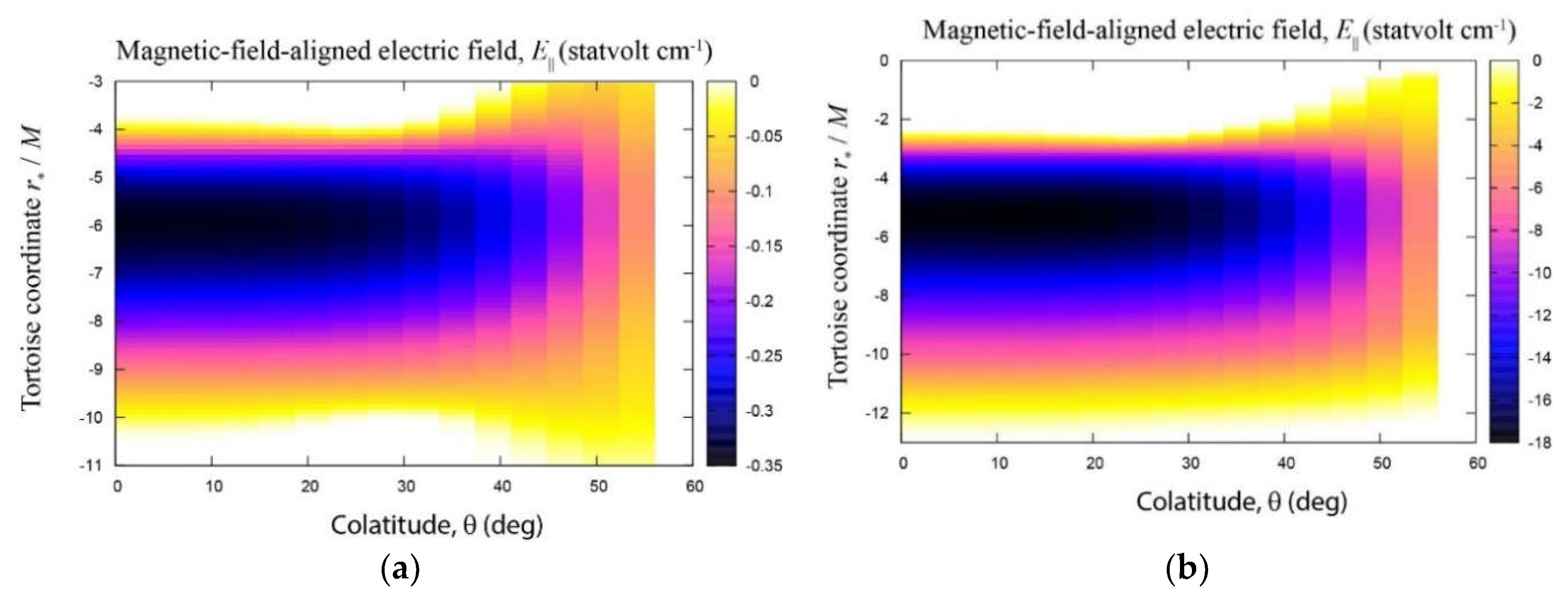
6.3. Results: Acceleration Electric Field
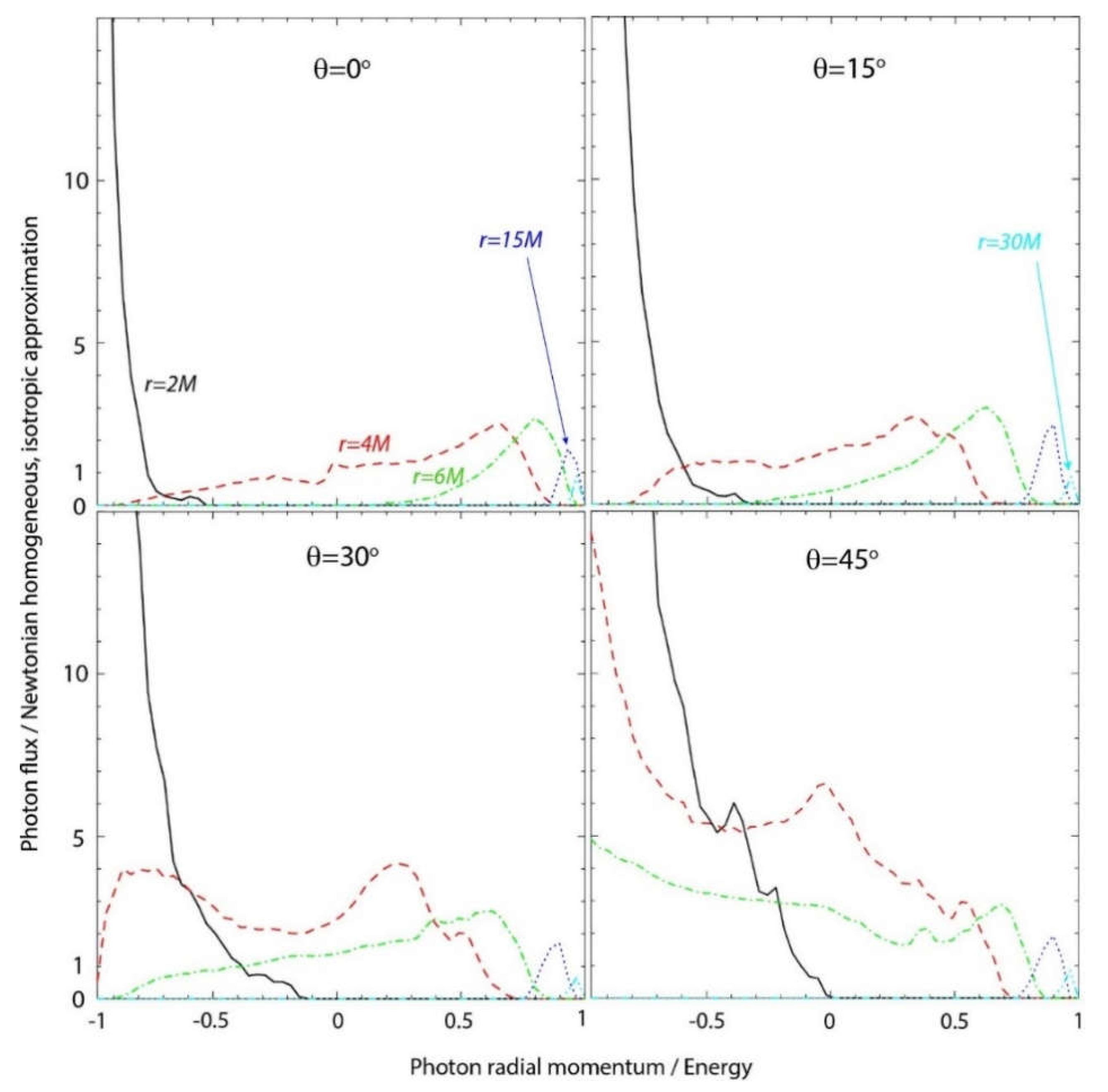
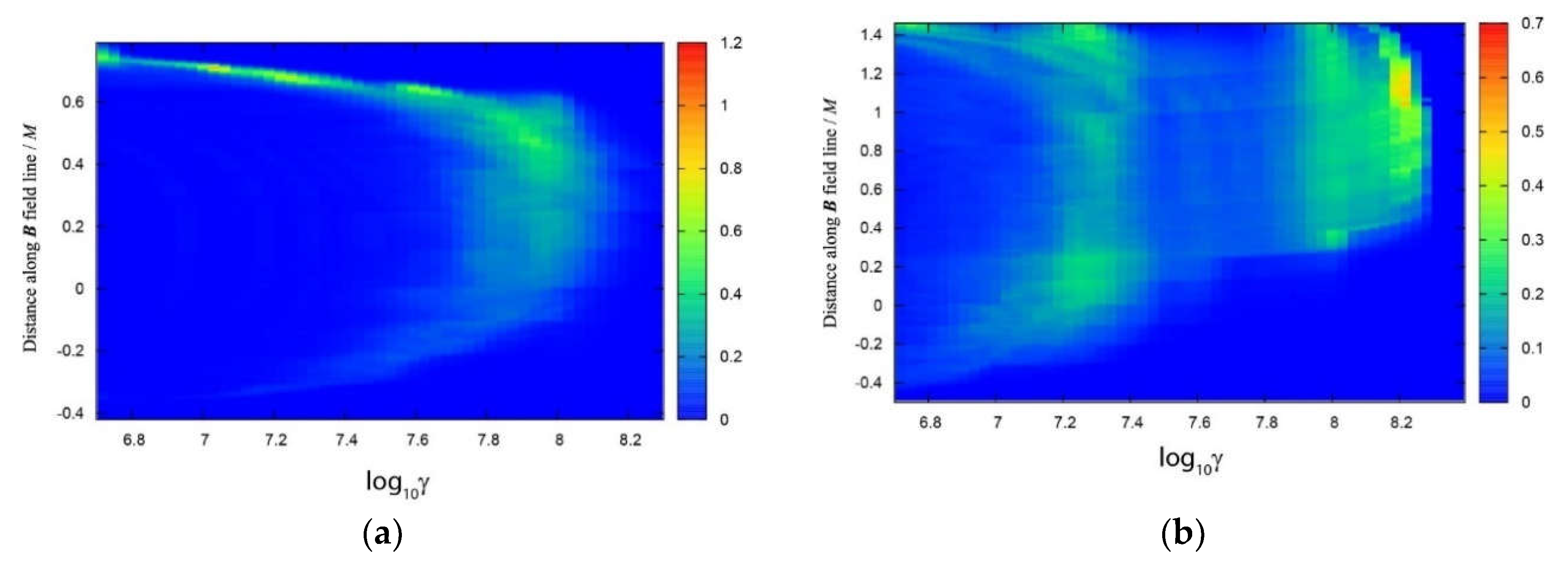
6.4. Results: Ultra-Relativistic Leptons
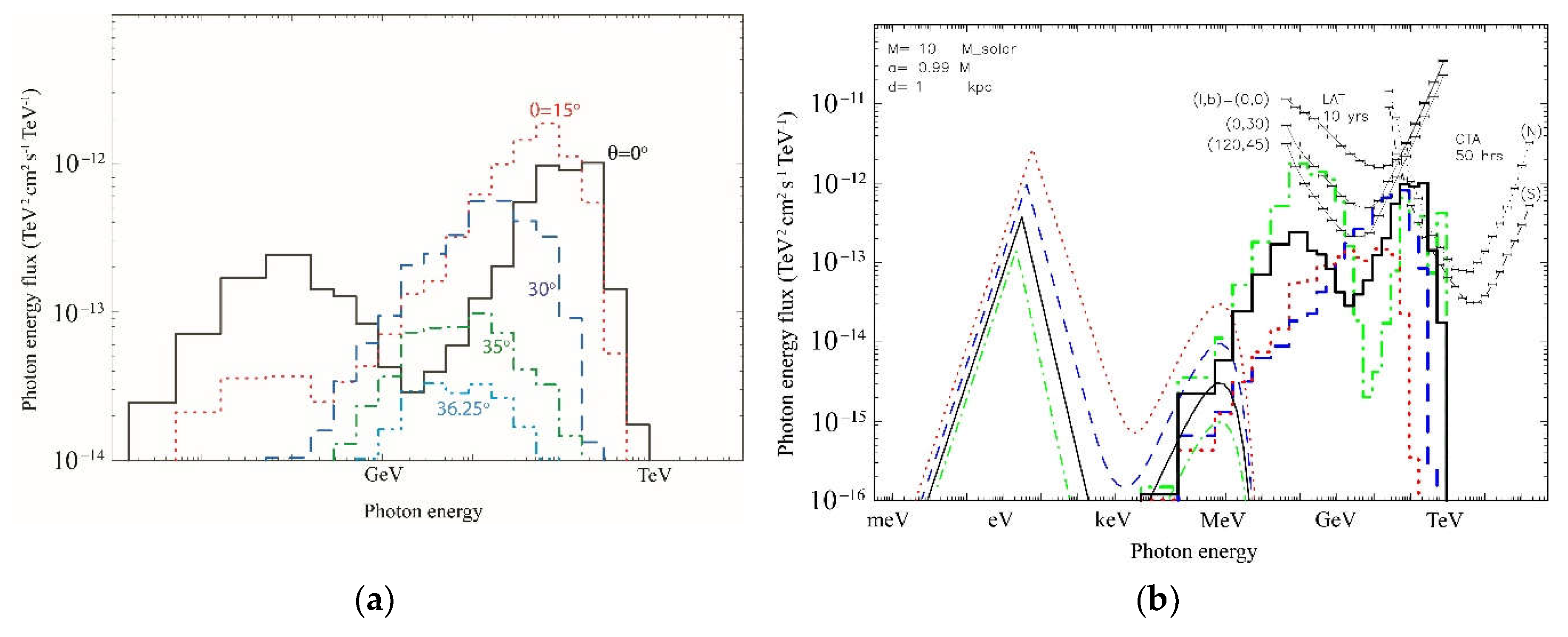
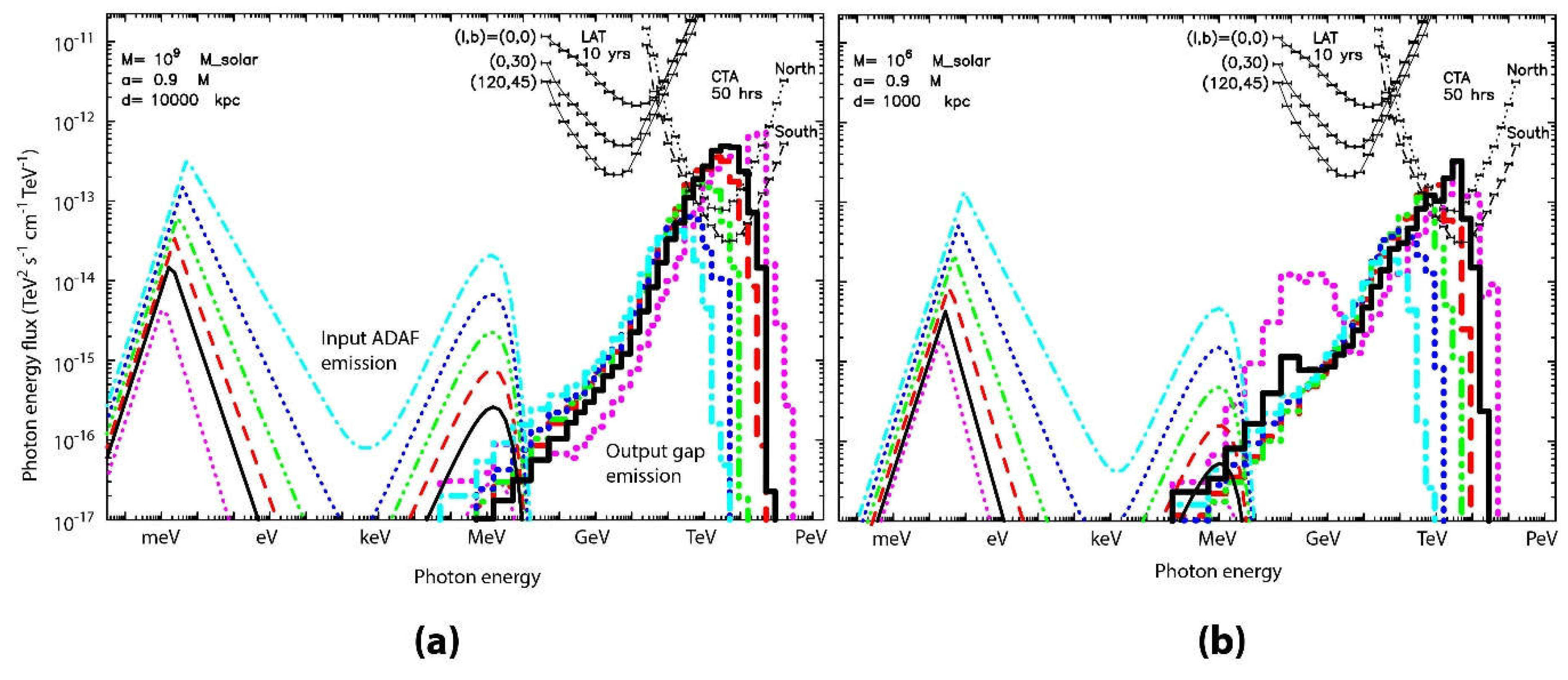
6.5. Results: Gamma-Ray Spectra
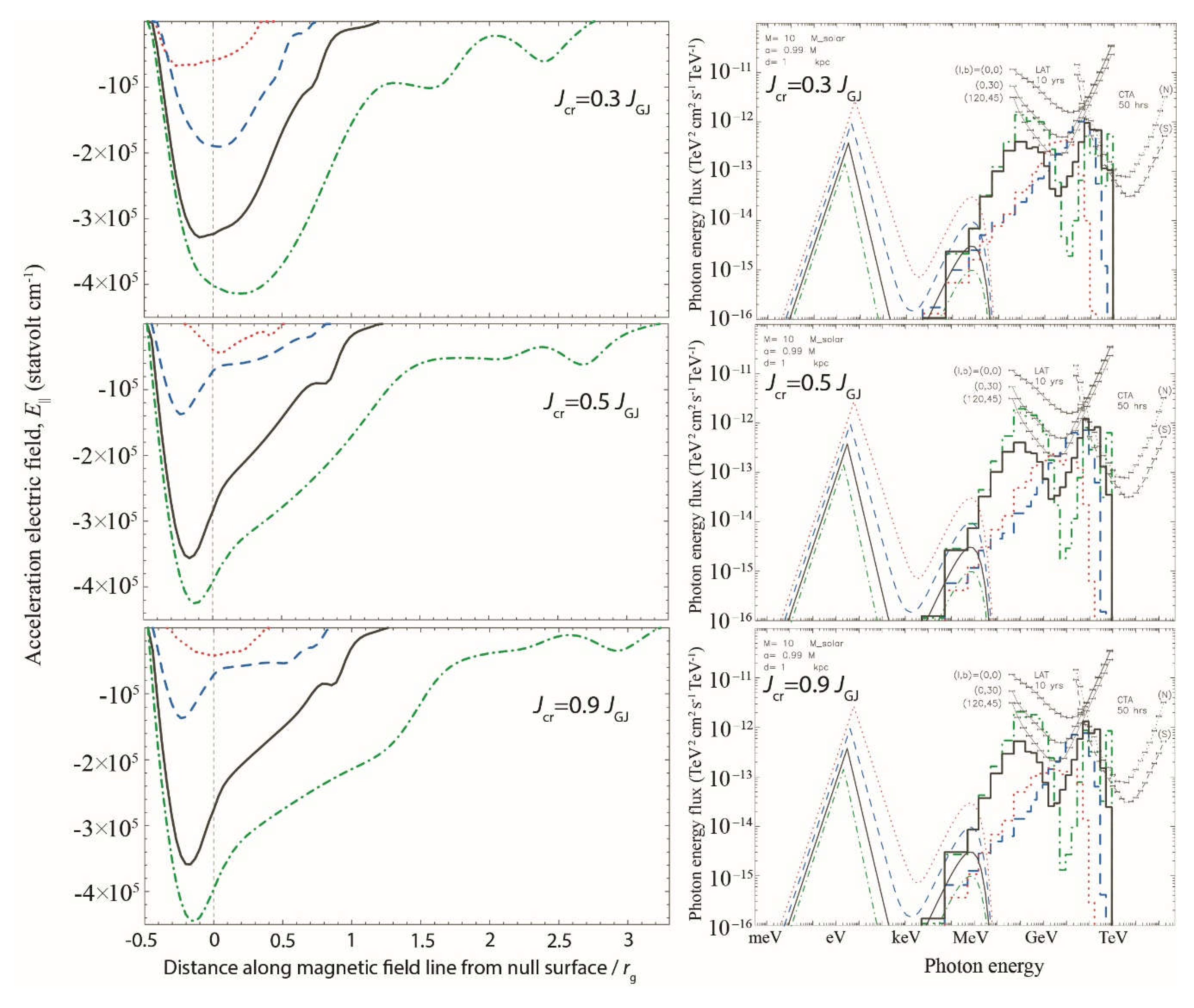
6.6. Results: Dependence on the Current Created in the Gap
7. Lepton Accelerator around Super-Massive Black Holes
7.1. Very High-Energy Observations of Active Galaxies
7.2. Results: Acceleration Electric Field
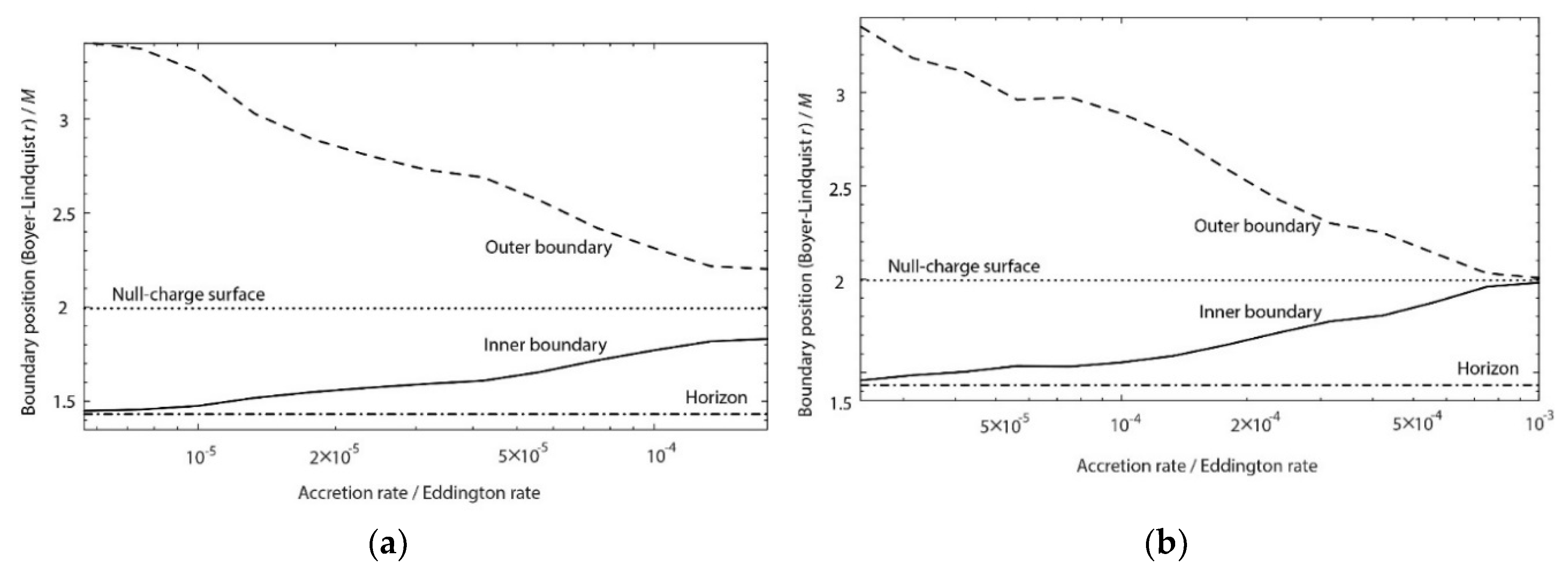
7.3. Results: Gap Width
7.4. Results: Distribution Function of Electrons
7.5. Results: Gamma-Ray Spectra
8. Discussion
8.1. The Case of Very Small Accretion Rate
8.2. Gap Emission Versus Jet Emission
8.3. Comparison with Pulsar Gap Models
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferrarese, L.; Ford, H.C.; Jaffe, W. Evidence for a Massive Black Hole in the Active Galaxy NGC 4261 from Hubble Space Telescope Images and Spectra. Astrophys. J. 1996, 470, 444–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, A.C.; McLaughlin, D.E. Dark-matter haloes and the M-σ relation for supermassive black holes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 462, 1864–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bosch, R.C.E. Unification of the fundamental plane and super massive black hole masses. Astrophys. J. 2016, 831, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentz, M.C.; Manne-Nicholas, E. Black hole-galaxy scaling relationships for Active Galactic Nuclei with reverberation masses. Astrophys. J. 2018, 864, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kormendy, J.; Richstone, D. Inward Bound-The Search for Supermassive Black Holes in Galactic Nuclei. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1995, 33, 581–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kormendy, J.; Ho, L.C. Coevolution (or not) of supermassive black holes and host galaxies. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 51, 511–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, M.; Moran, J.; Herrnstein, J.; Greenhill, L.; Nakai, N.; Diamond, P.; Inoue, M. Evidence for a black hole from high rotation velocities in a sub-parsec region of NGC4258. Nature 1995, 373, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogorrian, J.; Tremaine, S.; Richstone, D.; Bender, R.; Bower, G.; Dressler, A.; Faber, S.M.; Gebhardt, K.; Green, R.; Grillmair, C.; et al. The Demography of Massive Dark Objects in Galaxy Centers. Astron. J. 1998, 115, 2285–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrarese, L.; Merritt, D. A Fundamental Relation between Supermassive Black Holes and Their Host Galaxies. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2000, 539, L9–L12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebhardt, K.; Bender, R.; Bower, G. A Relationship between Nuclear Black Hole Mass and Galaxy Velocity Dispersion. Astrophys. J. 2000, 539, L13–L16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentz, M.C.; Katz, S. The AGN black hole mass database. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2015, 127, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynden-bell, D. Galactic Nuclei as Collapsed Old Quasars. Nature 1969, 223, 690–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandford, R.D.; Znajek, R.L. Electromagnetic extraction of energy from Kerr black holes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1977, 179, 433–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misner, C.W.; Thorne, K.S.; Wheeler, J.A. Gravitation; W.H. Freeman: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1973; p. 875. [Google Scholar]
- Meier, D.L.; Koide, S.; Uchida, U. Magnetohydrodynamic Production of Relativistic Jets. Science 2001, 291, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hujeirat, A. A model for electromagnetic extraction of rotational energy and formation of accretion-powered jets in radio galaxies. Astron. Astrophys. 2004, 416, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadowski, A.; Sikora, M. Launching of jets by cold, magnetized disks in Kerr metric. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 517, A18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koide, S.; Shibata, K.; Kudoh, T.; Meier, D.L. Extraction of black hole rotational energy by a magnetic field and the formation of relativistic jets. Science 2002, 295, 1688–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKinney, J.C. General relativistic magnetohydrodynamic simulations of the jet formation and large-scale propagation from black hole accretion systems. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2006, 368, 1561–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, J.C.; Tchekhovskoy, A.; Blandford, R.D. General relativistic magnetohydrodynamic simulations of magnetically choked accretion flows around black holes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 423, 3083–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punsly, B. Evidence on the origin of ergospheric disc field line topology in simulations of black hole accretion. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 418, L138–L142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, S.; Krolik, J.; de Villiers, J.-P.; Hawley, J.F. Magnetically Driven Accretion Flows in the Kerr Metric. II. Structure of the Magnetic Field. Astrophys. J. 2004, 606, 1083–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, J.C.; Gammie, C.F. A Measurement of the Electromagnetic Luminosity of a Kerr Black Hole. Astrophys. J. 2004, 611, 977–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchekhovskoy, A.; Narayan, R.; McKinney, J.C. Black Hole Spin and the Radio Loud/Quiet Dichotomy of Active Galactic Nuclei. Astrophys. J. 2010, 711, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawley, J.F.; Krolik, J.H. Magnetically Driven Jets in the Kerr Metric. Astrophys. J. 2006, 641, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, J.C.; Narayan, R. Disc-jet coupling in black hole accretion systems—I. General relativistic magnetohydrodynamical models. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2007, 375, 513–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, J.C.; Narayan, R. Disc-jet coupling in black hole accretion systems—II. Force-free electrodynamical models. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2007, 375, 531–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichimaru, S. Bimodal behavior of accretion disks - Theory and application to Cygnus X-1 transitions. Astrophys. J. 1977, 214, 840–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, R.; Yi, I. Advection-dominated accretion: A self-similar solution. Astrophys. J. 1994, 428, L13–L16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Public List of LAT-Detected Gamma-Ray Pulsars. Available online: https://confluence.slac.stanford.edu/display/GLAMCOG/Public+List+of+LAT-Detected+Gamma-Ray+Pulsars (accessed on 21 November 2018).
- Harding, A.K.; Tademaru, E.; Esposito, L.S. A curvature-radiation-pair-production model for gamma-ray pulsars. Astrophys. J. 1978, 225, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daugherty, J.K.; Harding, A.K. Electromagnetic cascades in pulsars. Astrophys. J. 1982, 252, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dermer, C.D.; Sturner, S.J. On the energetics and number of gamma-ray pulsars. Astrophys. J. 1994, 420, L75–L78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timokhin, A.N.; Arons, J. Current flow and pair creation at low altitude in rotation-powered pulsars’ force-free magnetospheres: Space charge limited flow. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 429, 20–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timokhin, A.N.; Harding, A.K. On the Polar Cap Cascade Pair Multiplicity of Young Pulsars. Astrophys. J. 2015, 810, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.F.; Ruderman, M.A.; Sutherland, P.G. Current flow in pulsar magnetospheres. Astrophys. J. 1976, 203, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.S.; Ho, C.; Ruderman, M. Energetic radiation from rapidly spinning pulsars. I—Outer magnetosphere gaps. Astrophys. J. 1986, 300, 500–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.S.; Ho, C.; Ruderman, M. Energetic radiation from rapidly spinning pulsars. II. Vela and Crab. Astrophys. J. 1986, 300, 522–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, J.; Romani, R.W. Gamma radiation from pulsar magnetospheric gaps. Astrophys. J. 1992, 400, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, R. Gamma-ray pulsars: Radiation processes in the outer magnetosphere. Astrophys. J. 1996, 470, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.S.; Ruderman, M.; Zhang, L. A Three-dimensional Outer Magnetospheric Gap Model for Gamma-Ray Pulsars: Geometry, Pair Production, Emission Morphologies, and Phase-resolved Spectra. Astrophys. J. 2000, 537, 964–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takata, J.; Shibata, S.; Hirotani, K. A pulsar outer gap model with trans-field structure. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2004, 354, 1120–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirotani, K. High-energy emission from pulsar magnetospheres. Mod. Phys. Lett. A Brief Rev. 2006, 21, 1319–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, R.; Watters, K.P. Constraining Pulsar Magnetosphere Geometry with γ-ray Light Curves. Astrophys. J. 2010, 714, 810–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirotani, K. Luminosity Evolution of Gamma-Ray Pulsars. Astrophys. J. 2013, 766, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takata, J.; Ng, C.W.; Cheng, K.S. Probing gamma-ray emissions of Fermi-LAT pulsars with a non-stationary outer gap model. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 455, 4249–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigano, D.; Torres, D.F.; Hirotani, K.; Pessah, M.E. An assessment of the pulsar outer gap model.—I. Assupmtions, uncertainties, and implications on the gap size and the accelerating field. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 447, 2631–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.S.; Zhang, L. General Radiation Formulae for a Relativistic Charged Particle Moving in Curved Magnetic Field Lines: The Synchrocurvature Radiation Mechanism. Astrophys. J. 1996, 463, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigano, D.; Torres, D.F.; Hirotani, K.; Pessah, M.E. Compact formulae, dynamics and radiation of charged particles under synchro-curvature losses. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 447, 1164–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirotani, K.; Harding, A.K.; Shibata, S. Electrodynamics of an Outer Gap Accelerator: Formation of a Soft Power-Law Spectrum between 100 MeV and 3 GeV. Astrophys. J. 2003, 591, 334–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reville, B.; Kirk, J. Linear acceleration emission in pulsar magnetospheres. Astrophys. J. 2010, 715, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beskin, V.S.; Istomin, Y.N.; Par’ev, V.I. Filling the Magnetosphere of a Supermassive Black-Hole with Plasma. Soviet Astron. 2002, 36, 642–649. [Google Scholar]
- Hirotani, K.; Okamoto, I. Pair Plasma Production in a Force-free Magnetosphere around a Supermassive Black Hole. Astrophys. J. 1998, 497, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neronov, A.; Aharonian, F.A. Production of TeV gammaradiation in the vicinity of the supermassive black hole in the giant radio galaxy M87. Astrophys. J. 2007, 671, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marconi, A.; Axon, D.J.; Macchetto, F.D.; Cappetti, A.; Sparks, W.B.; Crane, P. Is there really a supermassive black hole in M87? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1997, 289, L21–L25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macchetto, F.; Marconi, A.; Axon, D.J.; Capetti, A.; Sparks, W.; Crane, P. The supermassive black hole of M87 and the kinematics of its associated gaseous disk. Astrophys. J. 1997, 489, 579–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebhardt, K.; Adams, J.; Richstone, D.; Lauer, T.R.; Faber, S.M.; Gültekin, K.; Murphy, J.; Tremaine, S. The black hole mass in M87 from Gemini/NIFS adaptive optics observations. Astrophys. J. 2011, 729, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, J.L.; Barth, A.J.; Ho, C.; Sarzi, M. The M87 Black Hole Mass from Gas-dynamical Models of Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph Observations. Astrophys. J. 2013, 770, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinson, A.; Rieger, F. Variable TeV emission as a manifestation of jet formation in M87? Astrophys. J. 2011, 730, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broderick, A.E.; Tchekhovskoy, A. Horizon-scale lepton acceleration in jets: Explaining the compact radio emission in M87. Astrophys. J. 2015, 809, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirotani, K.; Pu, H.-Y. Energetic gamma radiation from rapidly rotating black holes. Astrophys. J. 2016, 818, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirotani, K.; Pu, H.-Y.; Lin, L.C.-C.; Chang, H.-K.; Inoue, M.; Kong, A.K.H.; Matsushita, S.; Tam, P.-H.T. Lepton acceleration in the vicinity of the event horizon: High-energy and very-high-energy emissions from rotating black holes with various masses. Astrophys. J. 2016, 833, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirotani, K.; Pu, H.-Y.; Lin, L.C.-C.; Kong, A.K.H.; Matsushita, S.; Asada, K.; Chang, H.-K.; Tam, P.-H.T. Lepton acceleration in the vicinity of the event horizon: Very high energy emissions from supermassive black holes. Astrophys. J. 2017, 845, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.C.-C.; Pu, H.-Y.; Hirotani, K.; Kong, A.K.H.; Matsushita, S.; Chang, H.-K.; Inoue, M.; Tam, P.-H.T. Searching for high-energy, horizon-scale emissions from galactic black hole transients during quiescence. Astrophys. J. 2017, 845, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Pu, H.-Y.; Hirotani, K.; Matsushita, S.; Kong, A.K.H.; Chang, H.-K. Enhanced gamma radiation towards the rotation axis from the immediate vicinity of extremely rotating black holes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 471, L135–L139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komissarov, S.S.; McKinney, J.C. The ‘Meissner effect’ and the Blandford-Znajek mechanism in conductive black hole magnetospheres. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2007, 377, L49–L53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirotani, K.; Pu, H.-Y.; Matsushita, S. Lightning black holes as unidentified TeV sources. Astrophys. J. 2018, 39, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirotani, K.; Pu, H.-Y.; Outmani, S.; Huang, H.; Kim, D.; Song, Y.; Matsushita, S.; Kong, A.K.H. High-energy and very-high-energy emissions from stellar-mass black holes moving in gaseous clouds. Astrophys. J. 2018, 867, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tababe, K.; Nagataki, S. Extended monopole solution of the Blandford-Znajek mechanism: Higher order terms for a Kerr parameter. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 78, 024004. [Google Scholar]
- Znajek, R.L. Black hole electrodynamics and the Carter tetrad. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1977, 179, 457–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bower, G.C.; Wright, M.C.H.; Falcke, H.; Backer, D.C. Interferometric detection of linear polarization from Sagittarius A* at 230 GHz. Astrophys. J. 2003, 588, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrone, D.P.; Moran, J.M.; Zhao, J.; Rao, R. Interferometric Measurements of Variable 340 GHz Linear Polarization in Sagittarius A*. Astrophys. J. 2006, 640, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macquart, J.-P.; Bower, G.C.; Wright, M.C.H.; Backer, D.C.; Falcke, H. The Rotation Measure and 3.5 Millimeter Polarization of Sagittarius A*. Astrophys. J. 2006, 646, L111–L114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.Y.; Asada, K.; Rao, R.; Nakamura, M.; Algaba, J.C.; Liu, H.B.; Inoue, M.; Koch, P.M.; Ho, P.T.P.; Matsushita, S.; et al. Measuring Mass Accretion Rate onto the Supermassive Black Hole in M87 Using Faraday Rotation Measure with the Submillimeter Array. Astrophys. J. 2014, 783, L33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sijbring, D.; de Bruyn, A.G. Multifrequency radio continuum observations of head-tail galaxies in the Perseus cluster. Astrophys. J. 1998, 331, 901–915. [Google Scholar]
- Aleksic, J.; Ansoldi, S.; Antonelli, L.A.; Antoranz, P.; Babic, A.; Bangale, P.; Barrio, J.A.; González, J.B.; Bednarek, W.; Bernardini, E.; et al. Black hole lightning due to particle acceleration at subhorizon scales. Science 2014, 346, 1080–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levinson, A.; Segev, F. On the existence of steady gap solutions in rotating black hole magnetospheres. PRD 2017, 96, 123006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirotani, K.; Shibata, S. Electrodynamic structure of an outer-gap accelerator: Invisibility of the TeV emission from a pulsar magnetosphere. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 2000, 52, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, R.P. Gravitational Field of a Spinning Mass as an Example of Algebraically Special Metrics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1963, 11, 237–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, R.H.; Lindquist, R.W.J. Maximal Analytic Extension of the Kerr Metric. Math. Phys. 1967, 8, 265–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinson, A.; Cerutti, B. Particle-in-cell simulations of pair discharges in a starved magnetosphere of a Kerr black hole. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 616, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinson, A.; Melrose, D.; Judge, A.; Luo, Q. Large-Amplitude, Pair-creating Oscillations in Pulsar and Black Hole Magnetospheres. Astrophys. J. 2005, 631, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.Y.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, H. Physics of Pair Producing Gaps in Black Hole Magnetospheres. Astrophys. J. 2018, 863, L31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, F.C. Rotating Magnetospheres: An Exact 3-D Solution. Astrophys. J. 1973, 180, L133–L137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krolik, J.H.; Hawley, J.F.; Hirose, S. Magnetically driven accretion flows in the Kerr metric. IV. Dynamical properties of the inner disk. Astrophys. J. 2005, 622, 1008–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punsly, B.; Igumenshchev, I.V.; Hirose, S. Three-dimensional simulations of vertical magnetic flux in the immediate vicinity of black holes. Astrophys. J. 2009, 704, 1065–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, M.J.; Begelman, M.C.; Blandford, R.D.; Phinney, E.S. Ion-supported tori and the origin of radio jets. Nature 1982, 295, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, R.; Yi, I. Advection-dominated Accretion: Underfed Black Holes and Neutron Stars. Astrophys. J. 1995, 452, 710–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramowicz, M.A.; Chen, X.; Kato, S.; Lasota, J.-P.; Regev, O. Thermal equilibria of accretion disks. Astrophys. J. 1995, 438, L37–L39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadevan, R. Scaling Laws for Advection-dominated Flows: Applications to Low-Luminosity Galactic Nuclei. Astrophys. J. 1997, 477, 585–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manmoto, T. Advection-dominated Accretion Flow around a Kerr Black Hole. Astrophys. J. 2000, 534, 734–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Narayan, R. Hot Accretion Flows Around Black Holes. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 52, 529–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadevan, R. Reconciling the spectrum of Sagittarius A* with a two-temperature plasma model. Nature 1998, 394, 651–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özel, F.; Psaltis, D.; Narayan, R. Hybrid Thermal-Nonthermal Synchrotron Emission from Hot Accretion Flows. Astrophys. J. 2000, 541, 234–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Quataert, E.; Narayan, R. Nonthermal Electrons in Radiatively Inefficient Accretion Flow Models of Sagittarius A*. Astrophys. J. 2003, 598, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wu, Q. Possible Origin of Radio Emission from Nonthermal Electrons in Hot Accretion Flows for Low-luminosity Active Galactic Nuclei. Astrophys. J. 2013, 764, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisnovatyi-Kogan, G.S.; Lovelace, R.V.E. Influence of Ohmic Heating on Advection-dominated Accretion Flows. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1997, 486, L43–L46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quataert, E.; Gruzinov, A. Turbulence and Particle Heating in Advection-dominated Accretion Flows. Astrophys. J. 1999, 520, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Yuan, F.; Liang, E. Electron Heating and Acceleration by Magnetic Reconnection in Hot Accretion Flows. Astrophys. J. 2010, 708, 1545–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, M. Stochastic Particle Acceleration in Multiple Magnetic Islands during Reconnection. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 135003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshino, M. Particle Acceleration during Magnetorotational Instability in a Collisionless Accretion Disk. Astrophys. J. 2013, 773, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quataert, E. Particle Heating by Alfvénic Turbulence in Hot Accretion Flows. Astrophys. J. 1998, 500, 978–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackman, E.G. On particle energization in accretion flows. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1999, 302, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvedev, M.V. Particle Heating by Nonlinear Alfvénic Turbulence in Advection-dominated Accretion Flows. Astrophys. J. 2000, 541, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehe, R.; Parrish, I.J.; Quataert, E. The Heating of Test Particles in Numerical Simulations of Alfvénic Turbulence. Astrophys. J. 2009, 707, 404–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Quataert, E.; Hammett, G.W.; Stone, J.M. Electron Heating in Hot Accretion Flows. Astrophys. J. 2007, 667, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camenzind, M.A. Centrifugally driven MHD-winds in active galactic nuclei. Astron. Astrophys. 1986, 156, 137–151. [Google Scholar]
- Camenzind, M.A. Hydromagnetic flows from rapidly rotating compact objects. I—Cold relativistic flows from rapid rotators. Astron. Astrophys. 1986, 162, 32–44. [Google Scholar]
- Bogovalov, S.V. On the physics of cold MHD winds from oblique rotators. Astron. Astrophys. 1999, 349, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar]
- Pètri, J.; Kirk, J.G. The Polarization of High-Energy Pulsar Radiation in the Striped Wind Model. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2005, 627, L37–L40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pètri, J. Phase-resolved polarization properties of the pulsar striped wind synchrotron emission. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 434, 2636–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirotani, K.; Shibata, S. Electrodynamic structure of an outer gap accelerator: Location of the gap and the gamma-ray emission from the Crab pulsar. Astrophys. J. 2001, 558, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beskin, V.S.; Zheltoukhov, A.A. On the structure of the magnetic field near a black hole in active galactic nuclei. AstL 2013, 39, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikora, M.; Begelmann, M.C. Magnetic Flux Paradigm for Radio Loudness of Active Galactic Nuclei. Astrophys. J. 2013, 764, L24–L28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Nitta, S.; Tatematsu, Y.; Tomimatsu, A. Magnetohydrodynamic flows in Kerr geometry-Energy extraction from black holes. Astrophys. J. 1990, 363, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirotani, K.; Shibata, S. One-dimensional electric field structure of an outer gap accelerator—III. Location of the gap and the gamma-ray spectrum. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2001, 325, 1228–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirotani, K.; Shibata, S. Gamma-ray emission from an outer gap accelerator: Constraints on magnetospheric current, magnetic inclination, and distance for PSR B1055–52. Astrophys. J. 2002, 564, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-R.; Yuan, Y.-F.; Wang, J.-M.; Wang, J.-C.; Zhang, S. Spins of Supermassive Black Holes in M87. II. Fully General Relativistic Calculations. Astrophys. J. 2009, 699, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, A.K. Pulsar gamma-rays - Spectra, luminosities, and efficiencies. Astrophys. J. 1981, 245, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondi, H. On spherically symmetrical accretion. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1952, 112, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondi, H.; Hoyle, F. On the mechanism of accretion by stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1944, 104, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetarenko, B.E.; Sivakoff, G.R.; Heinke, C.O.; Gladstone, J.C. WATCHDOG: A Comprehensive All-sky Database of Galactic Black Hole X-ray Binaries. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 2016, 222, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corral-Santana, J.M.; Casares, J.; Muñoz-Darias, T.; Bauer, F.E.; Martínez-Pais, I.G.; Russell, D.M. BlackCAT: A catalogue of stellar-mass black holes in X-ray transients. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 587, A61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirotani, K.; Shibata, S. One-dimensional electric field structure of an outer gap accelerator—I. gamma-ray production resulting from curvature radiation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1999, 308, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TeVCAT. Available online: http://tevcat.uchicago.edu/ (accessed on 21 November 2018).
- Rieger, F.M.; Levinson, A. Radio galaxies at VHE energies. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1810.05409v1. [Google Scholar]
- Ansoldi, S.; Antonelli, L.A.; Arcaro, C.; Baack, D.; Babić, A.; Banerjee, B.; Bangale, P.; de Almeida, U.B.; Barrio, J.A.; González, J.B.; et al. Gamma-ray flaring activity of NGC 1275 in 2016–2017 measured by MAGIC. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 617, A91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, J.; Aliu, E.; Anderhub, H.; Biland, A.; Britvitch, I.; Commichau, S.; Kranich, D.; Lorenz, E.; Pauss, F.; Rissi, M.T.; et al. Very High Energy Gamma-Ray Observations of Strong Flaring Activity in M87 in 2008 February. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2008, 685, L23–L26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acciari, V.A.; Aliu, E.; Arlen, T. Radio Imaging of the Very-High-Energy γ-Ray Emission Region in the Central Engine of a Radio Galaxy. Science 2009, 325, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Acciari, V.A.; Aliu, E.; Arlen, T.; Aune, T.; Beilicke, M.; Benbow, W.; Boltuch, D.; Bradbury, S.M.; Buckley, J.H.; Bugaev, V.; et al. Veritas 2008–2009 Monitoring of the Variable Gamma-ray Source M87. Astrophys. J. 2010, 716, 819–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliu, E.; Arlen, T.; Aune, T.; Beilicke, M.; Benbow, W.; Bouvier, A.; Bradbury, S.M.; Buckley, J.H.; Bugaev, V.; Byrum, K.; et al. VERITAS observations of day-scale flaring of M87 in 2010 April. Astrophys. J. 2012, 746, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharonian, F.; Akhperjanian, A.G.; Bazer-Bachi, A.R.; Beilicke, M.; Benbow, W.; Berge, D.; Bernlöhr, K.; Boisson, C.; Bolz, O.; Borrel, V.; et al. Fast Variability of Tera-Electron Volt γ Rays from the Radio Galaxy M87. Science 2006, 314, 1424–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acciari, V.A.; Beilicke, M.; Blaylock, G.; Bradbury, S.M.; Buckley, J.H.; Bugaev, V.; Butt, Y.; Celik, O.; Cesarini, A.; Ciupik, L.; et al. Observation of Gamma-Ray Emission from the Galaxy M87 above 250 GeV with VERITAS. Astrophys. J. 2008, 679, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksić, J.; Alvarez, E.A.; Antonelli, L.A.; Antoranz, P.; Asensio, M.; Backes, M.; Barrio, J.A.; Bastieri, D.; Gonzalez, J.B.; Bednarek, W.; et al. MAGIC observations of the giant radio galaxy M 87 in a low-emission state between 2005 and 2007. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 544, A96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramowski, A.; Acero, F.; Aharonian, F.; Akhperjanian, A.G.; Anton, G.; Balzer, A.; Barnacka, A.; de Almeida, U.B.; Becherini, Y.; Becker, J.; et al. The 2010 very high energy gamma-ray flare and 10 years of multi-wavelength observations of M87. Astrophys. J. 2012, 746, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharonian, F.A.; Barkov, M.V.; Khangulyan, D. Scenarios for ultrafast gamma-ray variability in AGN. Astrophys. J. 2017, 841, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arons, J. Pair creation above pulsar polar caps: Geometrical structure and energetics of slot gap. Astrophys. J. 1983, 266, 215–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muslimov, A.G.; Harding, A.K. Extended acceleration in slot gaps and pulsar hig-energy emission. Astrophys. J. 2003, 588, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: http://www.slac.stanford.edu/exp/glast/groups/canda/lat_Performance.htm (accessed on 21 November 2018).
- Available online: https://www.cta-observatory.org/science/cta-performance/ (accessed on 21 November 2018).
- Ackermann, M.; Ajello, M.; Atwood, W.B.; Baldini, L.; Ballet, J.; Barbiellini, G.; Bastieri, D.; Becerra Gonzalez, J.; Bellazzini, R.; Bissaldi, E.; et al. The Third Catalog of Active Galactic Nuclei Detected by the Fermi Large Area Telescope. Astrophys. J. 2015, 810, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, M.; Ajello, M.; Atwood, W.B.; Baldini, L.; Ballet, J.; Barbiellini, G.; Bastieri, D.; Becerra Gonzalez, J.; Bellazzini, R.; Bissaldi, E.; et al. 2FHL: The Second Catalog of Hard Fermi-LAT Sources. Astrophys. J. 2016, 222, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, S.; Ackermann, M.; Ajello, M.; Albert, A.; Baldini, L.; Ballet, J.; Barbiellini, G.; Bastieri, D.; Becerra Gonzalez, J.; Bellazzini, R.; et al. The second catalog of flaring gamma-ray sources from the Fermi all-sky variability analysis. Astrophys. J. 2017, 846, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, B. Radio galaxies-the TeV challenge. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1811.00567 (accessed on 5 November 2018).
- Madejski, G.; Sikora, M. Gamma-ray observations of active galactic nuclei. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astroph. 2016, 54, 725–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, A.A.; Ajello, M.; Allafort, A.; Baldini, L.; Ballet, J.; Barbiellini, G.; Baring, M.G.; Bastieri, D.; Belfiore, A.; Bellazzini, R.; et al. The second FERMI LARGE AREA TELESCOPE catalog of gamma-ray pulsars. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 2013, 208, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirotani, K. Particle acceleration in pulsar magnetospheres: Super-Goldreich-Julian current with ion emission from the neutron star surface. Astrophys. J. 2006, 652, 1475–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lense, J.; Thirring, H. Ueber den Einfluß der Eigenrotation der Zentralkoerper auf die Bewegung der Planeten und Monde nach der Einsteinschen Gravitationstheorie. Physikalische Zeitschrift 1984, 19, 156–163, Translation in Gener. Relativ. Gravit. 1984, 16, 727–741. [Google Scholar]



© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hirotani, K. Very High-Energy Emission from the Direct Vicinity of Rapidly Rotating Black Holes. Galaxies 2018, 6, 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies6040122
Hirotani K. Very High-Energy Emission from the Direct Vicinity of Rapidly Rotating Black Holes. Galaxies. 2018; 6(4):122. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies6040122
Chicago/Turabian StyleHirotani, Kouichi. 2018. "Very High-Energy Emission from the Direct Vicinity of Rapidly Rotating Black Holes" Galaxies 6, no. 4: 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies6040122
APA StyleHirotani, K. (2018). Very High-Energy Emission from the Direct Vicinity of Rapidly Rotating Black Holes. Galaxies, 6(4), 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies6040122




