Abstract
In the dawn of the multi-messenger era of gravitational wave astronomy, which was marked by the first ever coincident detection of gravitational waves and electromagnetic radiation, it is important to take a step back and consider our current established knowledge. Numerical simulations of binary neutron star mergers and simulations of short GRB jets must combine efforts to understand such complicated and phenomenologically rich explosions. We review the status of numerical relativity simulations with respect to any jet or magnetized outflow produced after merger. We compare what is known from such simulations with what is used and obtained from short GRB jet simulations propagating through the BNS ejecta. We then review the established facts on this topic, as well as discuss things that need to be revised and further clarified.
1. Introduction
The detection of GW170817 marked the dawn of the multi-messenger gravitational-wave era [1,2]. The subsequent observation of a short gamma-ray burst (GRB) almost ∼1.7 s after merger [3,4] showed that a least a subset of short GRBs is produced by binary neutron star (BNS) mergers. Hours after merger, a precise localization was established through optical observations of GW170817 [5,6], identifying the host galaxy as NGC 4993, which is at a distance of 40 megaparsecs (Mpc). Further detection in UV/optical/Infrared established the perennial connection between BNS mergers and a kilonova (macronova) [6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21].
A coincident detection of a GW and a short GRB from a BNS merger was long ago conjectured to be from short-duration GRBs come from BNS mergers [22,23,24]. These unprecedented observations open new windows and insights for the detailed study of such objects and events. These observations also opened the possibility of constraining the maximum mass of neutron stars and the equation of state (EOS) [25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39].
It was proposed some time ago that a BNS merger would give rise to emission powered by the radioactive decay of r-process nuclei [40,41]. Several groups concluded that this was the case for the optical/NIR emission that followed GW170817 [11,12,14,18,42,43,44,45,46,47,48]. This observation triggered further modelling for the actual components that give rise to this emission and how these components were produced.
The prompt gamma-ray emission was reported in [3,4]. It was the faintest (short or long) GRB ever detected [3]. The first X-ray afterglow observations came nine days after merger [19,49,50]. The first radio counterparts came later, sixteen days after merger [51,52]. All information that would come from the afterglow observations would be invaluable to reveal the nature of the outflow and its structure. A relativistic outflow from a BNS merger was indeed observed [52,53]. Was that the most peculiar short GRB ever detected [14,54]? The continuous rising of the afterglow the first 100 days suggested that a simple top-hat1 jet model seen off-axis is not adequate for explanation [52,55,56,57,58,59]. However, at a 100 days after merger, the data could not exclude other jet structure or cocoon models. Energy injection was evident at that time [60,61]. Then, a turnover in the light curve appeared after nearly 200 days [62,63,64]. This emission is well understood and comes from the interaction of the outflow as it smashes into the inter-stellar medium producing a shock which accelerates electrons that radiate synchrotron radiation and can give a great insight in the whole structure of the initial outflow.
The expected number of BNS mergers from LIGO/Virgo in the years to come is 1–4 detections per year [65]. To digest all these new insightful observations, and those yet to come, we have to combine all the available data. What has been achieved from BNS numerical relativity simulations has to be part of any adequate modelling of short GRB outflows. These outflows are: the ejected matter and the production of neutrino-driven winds, the enormous magnetic field evolved in the merger process and its amplification during merger, and the actual possibility of launching a relativistic outflow after merger, which are the starting points given by numerical relativity. Is it a stable magnetar or the collapse to a black hole (BH) torus system that powers an outflow? In what follows, we try to present results from numerical relativity BNS simulations relevant for short GRBs. Afterwards, we turn our attention to efforts in short GRB jet simulations propagating through the BNS ejecta.
This is a rather focused review on what we know from numerical relativity concerning short GRBs and how this knowledge is applied to short GRB simulations. It will not at all follow the path of excellent reviews that exist on the subject of BNS mergers. For the interested reader, we cite several detailed reviews of subjects relevant to the detection of a BNS merger, a short GRB and a kilonova. Detailed reviews of all the aspects of numerical relativity and its applications to BNS mergers are given in [66,67], a focused review on BH–neutron star binaries is given in [68], review on the connection between BNS mergers and short GRBs in numerical relativity results are found in Refs. [69,70], observational aspects of short GRBs and connection to BNS mergers are reviewed in [71,72], the BNS merger and electromagnetic counterparts from kilonova are reviewed in [73,74,75,76], a review of rotating stars in relativity with applications on the post merger phase is given in [77], and reviews of short GRBs and entire aspects of GRBs are given in [78,79,80,81,82], respectively. In Section 2, we review the relevant knowledge from BNS simulations. We mainly follow results from magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) simulations in BNS studies. At the end of Section 2, we show the different paths that a BNS may follow after merger with respect to the achieved magnetic energy growth during merger. This translates to the total mass of the binary. In Section 3, we follow the studies that focus on the interaction of a BNS relativistic outflow passing through the matter that has been ejected during merger. In Section 4, we present the conclusions.
2. BNS Numerical Simulations
Sixteen systems of double neutron stars have been observed in our Galaxy. The observational data for the total mass of double neutron stars from our Galaxy show a narrow distribution in the range 2.58–2.88 [83]. A double neutron star system will inspiral and emit gravitational waves that result in orbital decay, shrinking their separation. When they come close enough, tidal forces result in deformation of the shape of the two neutron stars. Only numerical relativity can adequately describe the inspiral process beyond this point.
When the two neutron stars come into contact with one another, a merger product is formed. If this is massive enough and cannot support itself against gravitational collapse, a BH is formed in the first millisecond after merger, surrounded by a negligible disk. If the configuration is less massive, it can live longer. The merger product is differentially rotating and thus it can support more mass than the limit for a uniformly rotating star. At this stage, the merger product is called a hypermassive neutron star (HMNS) [84]. Gravitational-wave emission and magnetic field instabilities can remove angular momentum and make the HMNS unstable. The loss of thermal pressure due to neutrino cooling could also trigger the collapse of the HMNS [85,86], see also [87] for a slightly different conclusion. Moreover, if the total mass of the object is smaller than the mass that can be supported when allowing for maximal uniform rotation—the supramassive limit—it can also lose differential rotation and not collapse. This would result in a uniformly rotating supramassive neutron star (SMNS) surrounded by a disk. The SMNS will continue to loose angular momentum through magnetic spin down and also accrete mass from the surrounding disk. Its lifetime varies from a second to millions of seconds, in the latter case it can be considered as a stable configuration.
In the last years, a robust picture has been drawn regarding the ejected matter during and after merger from numerical simulations. These include matter ejected dynamically during merger and secularly after merger, such as neutrino driven winds and magnetic winds [88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108]. Other important properties of the merger product such as the spin and the rotation profile have been studied [109,110,111]. We continue focusing on the properties of the magnetic field, its amplification during merger and all the variety of observational outcomes that depend on the collapse time of the merger product and are dictated by the magnetic field.
Magnetic Field Amplification. The importance of the Kelvin-Helmholtz (KH) instability in BNS mergers was pointed out by Rasio and Shapiro [112]. As the stellar surfaces come into contact, a vortex sheet (shear layer) is developed which is KH unstable. The first simulation reporting on the KH instability for BNS is reported in [113]. It is reported in [114] that the KH instability could amplify the magnetic field beyond the magnetar level. They reported a lower value of . However, they mentioned that numerical difficulties do not allow to reach the realistic values of amplification, which could be far above this limit. To address the full problem in numerical relativity is not so easy because high-resolution simulations are necessary, since the KH instability growth rate is proportional to the wave number of the mode, the shortest wavelengths grow the most rapidly. Studies of BNS mergers tried to clarify the picture and indeed showed some amplification, yet the saturation level was not pinpointed [115,116,117,118,119,120,121].
Another approach is local simulations that imitate the conditions of shear layers and study in detail the different phases of such a procedure. The growth phase where the KH vortex is formed, the amplification phase where the magnetic field is wound up by the evolving KH vortex, and the last phase where the magnetic field has locally reached equipartition that results in the KH vortex to lose its energy. In Figure 1, such a configuration is depicted after the end of the amplification phase. The blueish regions in the lower panel of Figure 1 indicate strongly magnetized regions that occur after amplification. Local simulations do not have such stringent resolution limitations as global simulations [122,123].
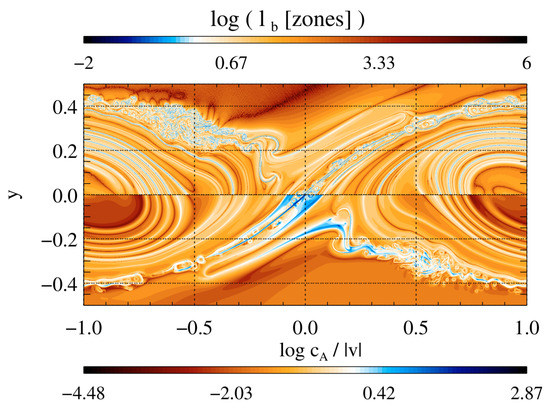
Figure 1.
Snapshots of a certain model from [122]. It is taken shortly after the termination of the kinetic amplification phase. The top panel shows the characteristic length scale of the magnetic field, in units of the zone size. Regions where magnetic structures are larger than one computational zone are depicted in orange-red colors and blue colors where they are smaller than one zone size. The bottom panel shows the ratio between the Alfvén velocity and the modulus of the fluid velocity. Strongly magnetized regions are depicted in blue, whereas weakly magnetized regions are depicted in orange-red. (Reproduced with permission from [122], © ESO, 2010).
A high resolution study by Kiuchi [124] showed that, for an initial maximum magnetic field of , the maximum magnetic field during merger and in the first 4–5 ms can reach . They showed that the saturation magnetic energy is above erg, which is of the bulk kinetic energy. Going to even higher resolution and running for a longer time, the upper bound for the amplified magnetic energy has not been reached yet. Higher values of the amplified magnetic energy live in denser regions [125]. This may indicate that the higher values of the magnetic field are either trapped in the dense core, or that they need a diffusion timescale to diffuse out from the core and reorder [126]. These results have built stable foundations that magnetic field amplification is an integral part of the BNS merger and happen in the first millisecond after merger, as seen in Figure 2. Another important point to make here is that this is true only if the binary does not experience a prompt collapse, in which case there is no time to amplify the magnetic field and the EM output of the remnant follows a different path. We focus on this in more detail later.
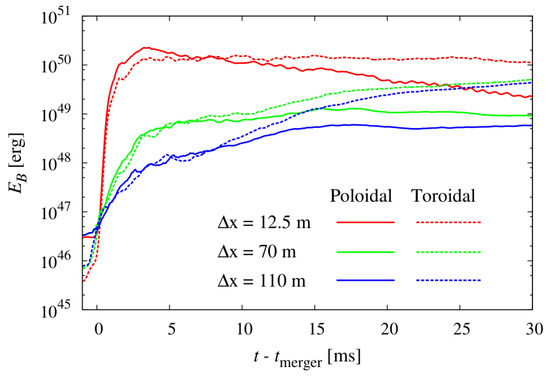
Figure 2.
The evolution of the magnetic-field energy as a function of time from [125]. The growth of the magnetic field is evident in the first five milliseconds. However, the strong dependence on resolution indicates that the upper limit of amplification is unknown. Solid and dashed curves indicate the poloidal and toroidal magnetic field components, respectively. (Reprinted with permission from [125]. © (2018) by the American Physical Society.)
Another cause for magnetic field amplification is magnetic winding due to differential rotation, which continues to function even after the KH instability may saturate. Furthermore, there are indications from studies of core-collapse supernovae that the magneto-rotational instability (MRI) can also be important [127]. From such simulations, it has been shown that the MRI can amplify the magnetic field by a factor of 100. The importance of parasitic instabilities that may quench such mechanisms have also to be taken into account [128].
Observational signatures during magnetic field amplification. Are there direct observational signatures of the field amplification? The magnetic energy increases to extreme values. It has been proposed that if only a fraction of this energy dissipates through reconnection it yields an EM counterpart at the time of merger. This could be observable up to a distance of 200 Mpc [129]. This radiation can only escape if produced in an optically thin surface layer. However, the higher values for amplification were reported in the dense core of the merger remnant [125]. The evolution of this turbulent magnetic field is not yet fully understood, and it may take a much longer time than the merger timescale to diffuse out of the dense core [126]. If the merger remnant lives for at least a second, then the Hall effect becomes important, and would govern the structure of the magnetic field at late times [126].
BH torus from BNS in MHD. Strong magnetic fields are present during and after the merger of a BNS. The next meaningful ingredient is the outcome and lifetime of the merger remnant. Due to numerical limitations, existing studies cover the collapse of the merger remnant to a BH only if it happens prior to ∼100 ms after merger. It was long ago proposed that BNS mergers could launch a short GRB. This connection had been made clear by recent observations [52,53]. However, it is still something yet to be achieved by global simulations. The first attempts in a magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) setting and in full GR did not show any signs of jet production following merger and the subsequent collapse of the merger remnant [115,116]. In subsequent studies, a magnetic jet structure was reported as a low density funnel with ordered poloidal magnetic field above the BH [130]. This is indeed the first step to imagine the production of a relativistic magnetized jet. Another important aspect is that an ordered poloidal magnetic field is needed to account for energy extraction from the BH in a Blandford-Znajek framework [131]. However, even if the magnetic field is not poloidal there could be other outcomes for an outflow. Another simulation by a different group did not find such a structure, instead the conclusion drawn from their simulations indicated an expanding toroidal field [121], which is also capable of producing a jet configuration with a different underlying mechanism [132].
It was further shown and confirmed in a resistive MHD framework that, at least for merger remnants that collapse in the first ∼10 ms, the BH-torus system produces a low density funnel above the BH [119]. The excess of the internal energy in this low density region above the newly formed BH could lead to the production of a jet (Figure 3). However, how low is low? To launch an outflow, it is necessary that at least the magnetic pressure in the jet interior can accelerate the fluid in the polar region. Previous studies [119,130] used an ideal fluid equation of state (EOS), whereas in [121], a piece-wise polytrope was used, and it was pointed out in [69,133] that the jet structure indeed depends on the EOS. Other studies have also reported the production of a magnetic structures when using a different EOS [134,135], also including a neutrino treatment [120]. In Figure 4, such a configuration with a BH-torus system is depicted. In this specific model, the merger product collapsed to a BH at 8.7 ms. The snapshot is taken at 35.1 ms after merger. In the low density funnel above, the BH the magnetic structure is clearly seen.
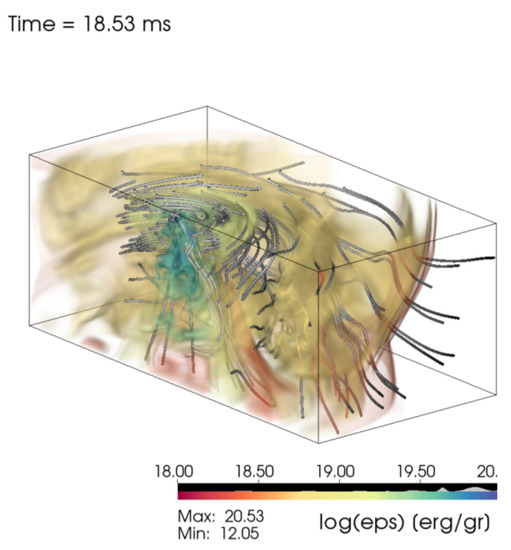
Figure 3.
The structure of the torus for a model from [119]. 3D snapshot of the specific internal energy and the magnetic field lines at t = 18.3 ms. Two main points are illustrated in the figure: (i) the structure of the toroidal magnetic field inside the torus; and (ii) the excess of internal energy close to the polar axis where the low density funnel is produced. (Reprinted with permission from [119]. © (2016) by the American Physical Society).
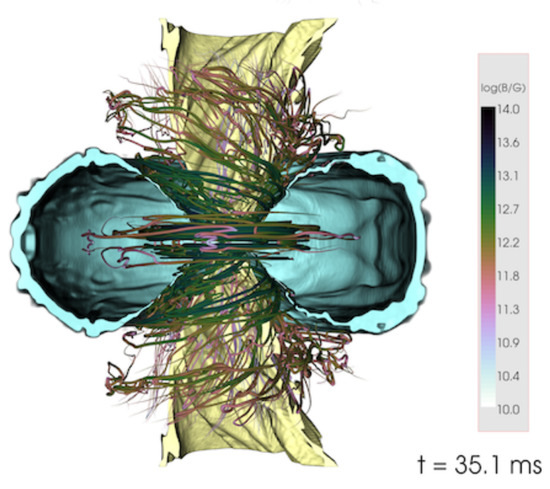
Figure 4.
The magnetic field structure for a model from [134] depicted at 35.1 ms after merger. Two isosurfaces of density are shown in yellow ( g/cm) and cyan g/cm). The field lines are colored by magnetic field strength. The toroidal field inside the torus is easily seen, together with a poloidal funnel above the BH. This model collapsed to a BH at 8.7 ms after merger. Due to the limited resolution, the KH instability is not entirely accounted for in these simulations. (Reprinted with permission from [134]. © (2016) by the American Physical Society).
Recently, a production of an incipient jet (as termed by the authors) was reported, which attained a Poynting luminosity of ∼ erg/s and a maximum Lorentz factor of [133]. Towards the end of the simulation, they reported a magnetically dominated funnel above the BH, which can be seen in the lower panel of Figure 5. The snapshot is taken at 67.7 ms, whereas the merger product collapsed to a BH at 18 ms after merger. It is clear that at late times the low density funnel above the BH is decreasing even more rapidly in density. This allows a magnetically dominated region to evolve. Using the magnetization of the outflow, they estimated the half opening angle of the jet funnel to be ∼20–30 [133].
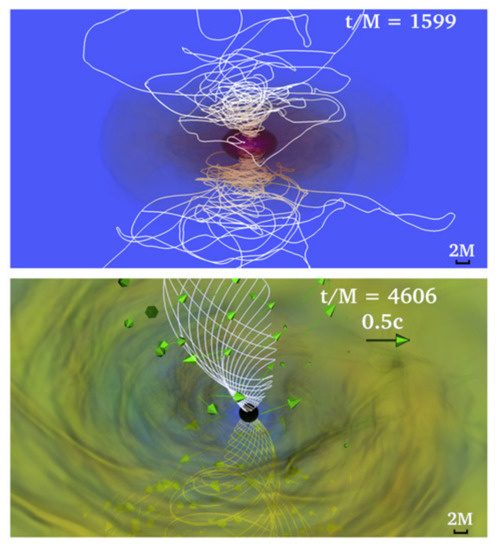
Figure 5.
Snapshots of the rest-mass density of a model from [133]. Magnetic field lines are depicted as white lines and arrows indicate plasma velocities. In this model, the merger remnant collapses to a BH at 1215 M = 18 ms after merger. The upper panel is at a slightly later time after collapse, whereas the lower panel is at 67.7 ms. We point out that, while the density contours are selected far from the magnetic jet structure, the funnel is filled with low density matter which supports the collimation of the magnetic structure. The length scale of the plots is . (Reprinted from [133]. © AAS. Reproduced with permission).
EM luminosity. It is natural to ask why there is so much discussion about magnetic fields and their role in the production of jets. Other mechanisms have been proposed, such as neutrino annihilation [22,136]. However, recent studies in which neutrinos are also treated to study a BNS merger and the evolution of accretion to a BH, it was found that due to a highly baryon-loaded environment such a mechanism alone does not suffice [47,137]. On the other hand, the electromagnetic energy extraction from a BH (the BZ mechanism) has been widely studied (numerically [138,139], semi-analytically [140] and analytically [141]) and widely understood and accepted. It needs only two ingredients, a rotating BH and an ordered poloidal magnetic field to extract this rotational energy.
where is the magnetic flux accumulated on the BH horizon, is the angular velocity of the BH, is the poloidal magnetic field on the BH horizon, is the spin parameter of the BH and is the mass of the BH [142].
In a BNS merger, one has both: when the merger remnant collapses a BH is formed, and in all reported cases it attains a spin of ∼0.8. The magnetic field is known to be an essential ingredient of a neutron star and as we have already discussed it is further amplified during merger. In a baryon-polluted environment such as the one that exists around the remnant after merger, there are also other things to worry about. The ram pressure from the material from the polar regions, or even fall-back material in this region, may not allow this outflow to form and evolve. This is perhaps the reason, together with a low magnetic field, that in some studies with limited amount of evolution time no outflow was formed [134]. If this is the case, then it is expected that some hundreds of milliseconds later the overall pressure of the funnel could decrease significantly, allowing for a magnetically dominated outflow to emerge.
Duration of a BH torus. Following the above discussion, it is natural to ask how long this configuration will last. This is indicated by the mass of the surrounding disk plus the mass accretion rate. We briefly discuss the duration connected with the mass of the torus. It is usually assumed that the duration of the short GRB (<2 s) is due to the accretion timescale of the surrounding torus. Studies have shown that the mass of the torus can be as large as 0.001–0.2 [108,115,134,143,144,145,146]. Through numerical simulations a simple phenomenological expression can be derived that reproduces the mass from the surrounding torus [91,144]. A general result is that unequal mass binaries have a more massive torus around the BH that is formed. On the other hand, equal mass binaries acquire less massive torii. Of course, in the case of prompt collapse, the surrounding torus is negligible, but this is something we discuss after commenting on the accretion timescale. Furthermore, in the case of a late collapse the surrounding disk is expected to be negligible [147,148].
The duration of any event coming from the BH torus depends on the lifetime of the torus, and this torus will persist on an accretion timescale. A rough estimate for the viscous accretion timescale can be given as:
where and are the radius and the typical vertical scale height of the torus, is the speed of sound and is the -parameter that describes the efficiency of angular momentum transport due to turbulence in the torus [149]. As such, if the BNS merger produces a BH torus system, the accretion timescale sets the duration of the outflow, if any outflow is produced. However, we note here that it is also important to discuss the duration of a gamma-ray pulse produced by a relativistic outflow in a different fashion. The photosphere is defined as the radius that the outflow first becomes transparent and the first photons are emitted. If an outflow has attained a Lorentz factor , then photons emitted at any point on the jet are beamed within a cone, as seen in the lab frame. Thus, assuming that the outflow has a conical shape with opening angle 2, initially when , an observer can see only radiation from a small fraction of the jet. The duration of the pulse can be interpreted as photons coming from this cone that the observer is able to see, the cone. For a mildly relativistic outflow with , the relevant timescale of the pulse is
where is the emission radius [80]. The key point here is that, even if the accretion timescale is shorter and a relativistic outflow is produced, the duration can also be explained by other robust physical arguments. For an ultra-relativistic outflow, the duration of the pulse is very small and as such the accretion timescale can enter as a justification of the duration of the event.
The discussion thus far is mainly for a merger remnant that collapses to a BH after 10 ms or more. The effect of the collapse of the merger remnant when it occurs in the first milliseconds is different. The general thinking in the community leads to no expectations for an EM counterpart, if the BNS merger undergoes a prompt collapse to a BH. This is based on results of simulations that showed some robust features of this evolution track in the case of an equal mass binary. These features show that a limited amount of mass is dynamically ejected, and thus no expectation whatsoever of a kilonova. Another feature is the limited amount of time between merger and collapse, which prohibits significant magnetic field amplification, and as a result the magnetic energy will not reach such large values. However, a detailed high-resolution study of a prompt collapse has not yet been performed.
Lastly, the limited amount of mass left around the BH cannot sustain any magnetic structure for longer than a few milliseconds. This means that whatever is formed after merger will be lost on this timescale. However, the magnetic field that remains outside the BH will dissipate away on this timescale. Most of the matter will be lost behind the BH horizon, but the magnetic field lines will snap violently. This will produce a magnetic shock that dissipates a significant fraction of the magnetic energy by accelerating electrons, producing a massive burst, similar to a blitzar [150]. This can produce an EM counterpart on such a timescale. Prompt collapse events produce less massive accretion disks than those arising from delayed collapse. Studies have shown that the result of a prompt collapse is a spinning BH and an accretion disk with a negligible mass of 0.0001–0.001 [115,143,144,151,152,153]. A negligible mass for the surrounding torus in the delayed collapse scenario can of course also be due to the underlying EOS [91,144].
Prompt Collapse. The prompt collapse also has an impact on the magnetic field evolution. Since the HMNS lifetime is limited, the magnetic field amplification is also limited [30]. However, a precise value for this upper limit is not known. The mass threshold at which the HMNS promptly collapses to a BH strongly depends on the EOS [144,152,154,155,156]. It is clear that a soft EOS, meaning that matter can be compressed in a more effective way, is more compact and the threshold mass to collapse to a BH is smaller. Conversely, a stiff EOS does not allow for such compression and a star is less compact, and therefore allowed to have a larger threshold mass [144]. A BNS with a total mass of 2.8 can in principle promptly collapse to a BH, whereas for a slightly less massive system it can lead to a delayed collapse some milliseconds after merger [152]. Reducing even further the total mass to be ≲2.7 , a stable configuration can be achieved. Interestingly, from the known double neutron star systems observed in our Galaxy, the total mass is around ∼2.7 [157]. This means that we could expect all outcomes: i.e., prompt collapse, delayed collapse or a stable configuration.
It was reported that following a prompt collapse to a BH no kind of jet can be formed [158]. The system does not have the time to develop a jet structure. However, it possesses a magnetic field for which we do not know precisely the level of amplification. When the negligible torus is eventually accreted, all this magnetic energy will be dissipated away. As discussed previously, prompt collapse also leads to a very small torus. The torus lifetime can be as small as ms [158]. We may estimate the energy stored in the nearby magnetosphere to be
assuming no amplification has taken place. It has a millisecond duration and an energy close to the requirement for a fast radio burst (FRB [159,160]). Overall, this could be similar to the model proposed for FRBs where a supramassive neutron star collapses to a BH [150,161]. Thus, a prompt collapse is lacking many interesting features arising from the delayed collapse, but could provide answers to other mysterious EM signals (see also [162]). We must add that in the event that the magnetic field energy is amplified to above in the first millisecond after merger and the remnant subsequently collapses to a BH, the interaction of the emergent magnetic pulse with the ejected matter could give rise to a different variety of low luminosity short GRBs.
SMNS spin down. A stable neutron star configuration may also be the end point of a BNS merger. If the total mass of the binary is below a certain limit, then even significant accretion of the surrounding matter cannot trigger its collapse. This may have distinct observational features and could explain X-ray plateaus in the afterglow of short GRBs [163]. It has been suggested that a long-lived magnetar as a BNS merger product can power such emission by its spin down dipolar radiation [164,165,166,167,168]. Such simulations showed that a stable neutron star with a surrounding disk can be a BNS merger product and the luminosity from such a configuration is significant [169,170]. However, the first gamma-rays from the short GRB could not be explained. To overcome this drawback, different scenarios have been proposed. The production of the gamma-rays is attributed to the collapse of this long-lived object to a BH, which happens after the production of the X-ray radiation. The observational features of such a model, together with the prompt gamma-rays of a short GRB, come from diffusion arguments [171,172].
In most studies, the long-lived SMNS is losing angular momentum due to magnetic spin down and the production of dipolar radiation where energy is lost at a rate
where is the magnetic dipole moment, B is the dipole magnetic field, is the neutron star radius, is the angular velocity and is the inclination angle between the magnetic and the rotation axis [173,174]. However, if a stable object is produced, it lives entirely in the environment of a surrounding torus starting exactly at the surface of the star [169]. This means that it is impossible for this neutron star to acquire a dipolar magnetic field, since the magnetic field loops cannot close through the torus, but have instead opened up either during merger or due to differential rotation [98]. Additionally, if any closed field lines remain, they are influenced by neutrino heating [175,176,177]. However, this effect will be lost in 1–2 s. The last, but most significant, argument is that field lines which thread the disk will open up, due to the differential rotation of the two footpoints of the magnetic field line, one anchored on the SMNS and the other threading the disk, similar to the BH case [178,179,180]. Even if most of the mass of the disk is accreted or expelled, the remaining negligible mass will not allow the field lines to close. Thus, the structure of the magnetosphere of the merger remnant can be approximated by a split-monopole configuration [27]. A neutron star with a split-monopole configuration spins down with a different dependence on rotation, similar to a BH spin down where all field lines are also open [181,182]. The spin down follows an exponential decrease
where . Essentially, the spin down of such a configuration progresses more rapidly than the dipolar case, since all the field lines are open and contribute to the spin down process.
SMNS and the surrounding disk. The next thing that we want to focus is the evolution of the disk that surrounds the SMNS and the outcome of the collapse of the SMNS after one second from merger. Due to transfer of angular momentum the disk expands over time and due to accretion onto the compact remnant, its mass decreases over time [108]. As in Equation (2) the viscous accretion timescale estimated for the torus:
where is the typical vertical scale height of the torus and is its radius. Therefore, the mass accretion rate onto the SMNS yields
where is the mass of the torus. The mass of the torus decreases in time as the torus expands, thus this accretion rate is not stationary. This effect is seen in Figure 6, where the density profile is shown in the equatorial plane at different time slices. As time goes by, the torus expands and the torus density decreases significantly. The radius of the torus may reach 140 km in 1 s. The total mass accreted can be estimated to be ∼0.12 in 1 s [108].
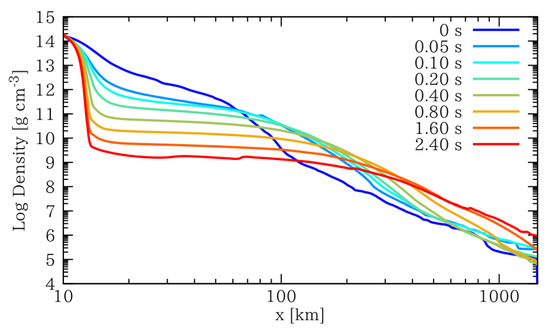
Figure 6.
Density profiles on the equatorial plane at different time slices 0, 0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.4, 0.8, 1.6, and 2.4 s. The torus gradually expands with time and its density decreases. This is due to viscous angular momentum transport. Even one second after merger the SMNS resides in a low density torus, in contrast to its inherent nuclear densities. (Reprinted from [108]. © AAS. Reproduced with permission).
If the SMNS is close to its maximum mass limit, this significant mass accretion in one second may trigger its collapse. Furthermore, the expansion of the torus is also significant during this time. The density of the torus in the vicinity of the SMNS could designate the outcome of the collapse to an induced magnetic explosion. The estimation for the density of the torus at 1s yields:
where quantities are for the expanded torus at 1 s after merger. The density in the poloidal plane is shown in Figure 7 at time 1.6 s after merger. The density drops around 5–6 orders of magnitude in the first 1300–1500 km. The possibility that no debris disk is formed at all has also been discussed [147,148].
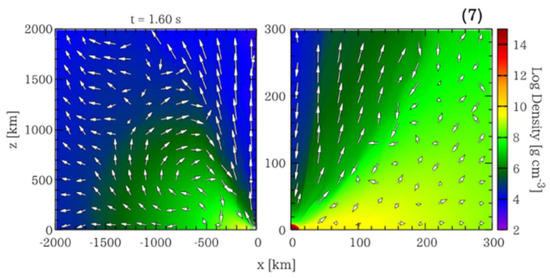
Figure 7.
Snapshots of the density and poloidal velocity field for a model from [108]. The velocity vectors and their length correspond to the logarithm of the velocity in the poloidal plane. The left panel shows a region of 2000 km, whereas the right panel a narrower region of 300 km. This profile corresponds to 1.6 s after merger. (Reprinted from [108]. © AAS. Reproduced with permission).
Jet or magnetic explosion. Previously, we discussed the production of a low density funnel that appears after the collapse of the merger remnant to a BH. All results from simulations so far describe such an evolution in the case that the collapse occurred in the first milliseconds after merger. Here, we describe the conditions and the outcome of the collapse to a BH, if this happens after 1 s from merger. The foremost point is the condition for the establishment of a magnetic jet. A stable magnetic jet configuration needs the torus pressure to balance the magnetic pressure from the jet itself. Due to magnetic field amplification discussed earlier, we assume that the mean magnetic field of the SMNS is G. This yields:
At later times, the torus has expanded even more and the establishment of a magnetic jet becomes more problematic due to the imbalance between the magnetic pressure and the disk ram pressure. We may also use the accretion rate at as reported in [108], which is ∼0.02 . This yields:
Figure 8 summarizes the above discussion. The main point is that if the collapse is triggered around or after ∼1 s after merger, the magnetic energy of the SMNS is released and induces a powerful explosion of erg, contrary to the expectations of a magnetic jet [183].
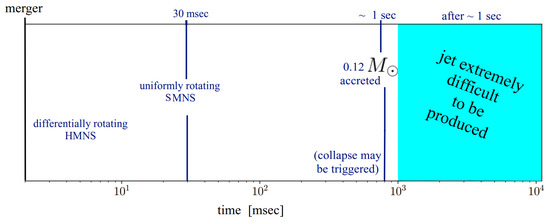
Figure 8.
The lifetime of the merger remnant of mass close to the maximum for uniform rotation. The remnant does not collapse when differential rotation is lost, but collapse may be triggered when almost 0.1 has been accreted. If collapse is triggered after one second, then the production of a jet may not be favoured. In this case, an explosion is triggered, releasing the enormous amounts of magnetic energy stored in the magnetosphere of the SMNS as discussed in [183]. (Reprinted from [183]. © AAS. Reproduced with permission).
We may summarize the understanding of the outcome of the collapse of the merger remnant, which strongly depends on the time that the collapse is triggered. Of course, the triggering of the collapse depends on the EOS and the total mass of the binary, however we do not go to that great a depth here and instead characterize only the outcome with respect to the collapse time. The possible outcomes are summarized in Table 1. The four columns represent four different types for the outcome of a BNS merger. The different rows show characteristics that are essential to the observable outcome of a BNS merger.

Table 1.
Outcome of the collapse of the merger remnant, the different columns indicate the different possible outcomes for the merger remnant. The different outcomes depend on the collapse time to a BH. Different rows, from top to bottom, are: the collapse time to a BH , if magnetic field amplification occurs or not, the amount of magnetic energy , if there is ejected matter, the amount of mass surrounding the BH when it is formed, the lifetime of this disk around the BH, whether the EM outcome will be produced either by collapse or by the absence of collapse, and the estimated energy that is released during the collapse or the absence of collapse.
The prompt collapse that is characterized by the collapse of the merger product in the first 1–2 ms (first column of Table 1) does not have an effective magnetic field amplification phase and also no significant ejecta, but due to the negligible disk that surrounds the newly formed BH the lifetime of this disk is on the order of few milliseconds. As a result, all its magnetic energy will dissipate on that timescale. The energetics of such an explosion (depicted in Equation (4)) and its timescale point to an event similar to FRBs. In all cases that the remnant lives longer than the first few milliseconds, it is certain that the magnetic field is amplified to high values. The case where the merger product (a HMNS at this stage) collapses in a few milliseconds to tens of milliseconds, is the most discussed case. This is expected to produce a canonical magnetic jet that interacts with the merger ejecta. If the collapse is delayed for a second (or more), then the low density of the torus may be insufficient to act as a boundary for a magnetic jet and a magnetic explosion is triggered.
At the end of this section, we list some interesting and critical points known from numerical simulations of BNS mergers and provide some comparison with points known from short GRBs.
Critical points:
- If the merger product does not collapse in the first millisecond, then the magnetic energy is amplified to values higher than erg [125].
- The saturation level of magnetic field amplification is not yet known [125].
- The amplified magnetic field is turbulent and requires time (more than a second) to rearrange in a coherent large-scale structure [126].
- After the collapse to a BH in , a magnetic jet structure is produced [130,133,134].
- An ordered poloidal magnetic field above is needed for a BZ luminosity of ∼ erg/s [131].
- The production of an ultra relativistic outflow has never been reported in BNS simulations [119,120,121,130,133,134].
- The magnetic jet funnel reported in BNS simulations has an opening angle of ≳20–30, and a maximum Lorentz factor reported as [133].
- If the collapse of the SMNS to a BH occurs late enough, the mass of the surrounding disk is negligible [147,148].
All these critical points should be taken into account for the understanding of any magnetized outflow (relativistic or non-relativistic) that emerges from the merger remnant or the collapse of the merger remnant to a BH. To help comparisons with observations, we should also mention here that there are short GRBs observed with a lower limit on the opening angle and some observed short GRBs that have jets with opening angles of 7–8, [72]. However, the opening angle given from numerical relativity simulations at the base of the jet may (most probably) change through the interaction with the BSN ejecta. This is discussed in the next section.
3. Short GRB Jet Simulations
It is understood that if the merger does not follow a quick prompt collapse then significant mass is ejected following the BNS merger. Mass can be ejected dynamically, by winds driven from the newly formed HMNS and from the debris disk that forms around it [88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108]. As a result, any outflow that emerges from the merger remnant or the collapse of the merger remnant has to pass through this dynamical ejecta.
To continue further in the discussion of the interaction between the BNS ejecta and a (perhaps mildly) relativistic outflow that emerges after merger, we need to define characteristic names widely used in the literature. We follow the terminology as is clearly given by Nakar and Piran [184]:
It is important to define the angle with which the observer is looking at the emission produced from the outflow with respect to the motion of the outflow itself. Assuming that an emitting region moves relativistically with a Lorentz factor , then the emission is termed:
On-axis emission: If the angle between the line-of-sight and the velocity of the emitting material satisfies . This emission is Lorentz boosted for relativistically moving material.
Off-axis emission: If the angle satisfies . In this case, relativistically moving emitting material appears fainter than being on-axis. It is clear that emission, which originally is observed off-axis, will become on-axis when the emitting material decelerates significantly and expands sideways. Originally, on-axis emission always remains on-axis. We should also point out that the observer angle is usually defined as the angle between the jet axis (the symmetry axis) and the line-of-sight. For BNS mergers it is generally supposed that the jet axis coincides with angular momentum axis of the BNS system. Next, we define characteristic names concerning the intrinsic properties and structure of the emitting material.
Structured relativistic jet: As the name indicates, this is a relativistic jet along the symmetry axis that acquires a certain structure. This structure can be angular and/or radial. A simple example can be a “top-hat” jet, a blast wave where the energy and radial velocity are uniform inside a cone (Blandford-McKee [185]). Another example, usually inferred for short GRBs, is a successful jet with a cocoon, where the cocoon term is defined below. In general, a jet can be composed of a fast core at small polar angles surrounded by a slower, underluminous sheath. The presence of a spine-sheath structure can be independent from that of a cocoon.
Cocoon: If a jet propagates within a dense medium, then the jet transfers energy and shocks this material. There is also a reverse shock that goes down to the jet itself. The resulting configuration is called a cocoon. In the case of BNS mergers, the dense medium is the ejected material (dynamical and secular ejecta). Thus, if a jet is produced after merger, then a cocoon is also produced. There remains a differentiating factor of whether the jet was successful.
Choked jet with cocoon: The jet that produced a cocoon from the interaction with a dense medium did not have enough energy to break out of the medium and it is choked. The jet transfers all of its energy to the medium and the shocked material may acquire a certain angular structure. The reverse shock may also produce a radial structure inside the cocoon in the region of the choked jet. In the case of BNS mergers, a choked jet would mean that no usual short GRB was produced. However, a mildly relativistic outflow may be produced.
Successful jet with cocoon: The jet that produced a cocoon from the interaction with a dense medium had enough energy to break out of the medium. An ultra-relativistic outflow passed through the medium and eventually decelerates through the interaction with the inter-stellar medium (ISM). The jet transferred some of its energy to the medium and a cocoon was produced. In the case of a BNS merger, a successful jet would mean that a usual short GRB was produced, pointing along the jet (BNS) axis. However, a mildly relativistic outflow may also be produced. In this case, two components can be identified, an ultra-relativistic core which is surrounded by a mildly-relativistic cocoon.
Successful explosion (not jet): Assuming the possibility discussed in the previous section that a jet is never formed, we could rephrase the last case to a successful explosion with a cocoon. This means that no jet was formed but rather an instantaneous explosion occurred which followed the delayed (over a second) collapse of the remnant [183]. In such a scenario, the core is not ultra-relativistic, but just slightly faster than the surrounding cocoon itself.
It is important to note that there exist previous studies that have discussed the formation of cocoons in a slightly different context, namely, for long GRBs where the jet has to propagate through the stellar envelopes and not the BNS ejecta. The main differences should be in the density profile and how it falls off. Cocoons in long GRBs have been discussed in [186]. The mixing of the cocoon components has been discussed in [187,188,189,190,191].
In what follows, we review studies that have developed a robust picture regarding the outcome of a BNS merger with respect to the prompt emission which is a short GRB and the afterglow emission which can provide physical insight into the outflow that produced it. The common understanding for the prompt emission is that it is powered by some internal dissipation mechanism within the jet. The common interpretation of the late afterglow is that the interaction of the produced outflow with the ISM, during which the outflow sweeps up matter from the ISM, results in the eventual deceleration of the outflow.
Jet through the BNS ejecta. In this respect, Nagakura et al. [192] took into account the density profile of a BNS numerical relativity simulation [96] to study the propagation of a hydrodynamical jet through such ejecta and develop a picture of whether the jet could break out from them or not. Such studies built a consensus that even if the outflow emerging from the BNS has a wide opening angle, it will be subsequently collimated as it tries to pass through the ejecta [192,193,194]. These works described a density distribution that the jet should pass through, and that this density distribution of matter has been ejected primarily during merger. Any outflow produced in the base of the merger configuration has to pass through these ejecta and may change its shape through collimation or loose some energy by the interaction with the ejecta. This way, some energy deposits to the ejecta producing a cocoon structure.
In the work of [192], the jet opening angle was placed to be 15–45, with an injected luminosity of erg/s. As they pointed out, their results were similar to equivalent simulations in the context of the collapsar model [191,195]. The opening angle at the base of the jet is determined through the interaction of the jet and the surrounding disk. An important consequence of this study is the finding that irrespective of the initial opening angle, all jets succeed in breaking out and form what we would call a structured jet with a cocoon. Only for the model with an initial opening angle of is this not the case, and a choked jet with cocoon is formed instead. Due to the large cross section of the jet, it cannot move sideways into the cocoon and expands quasi-spherically.
In Figure 9, a model from [192] is shown. The ejected mass is and the initial jet is injected with an opening angle of . The density profile of the produced structure is shown for two snapshots, one at the time that the jet breaks out from the ejecta and the other at the end of the simulation. The average opening angle of the jet after break out, which has changed due to the interaction with the surrounding ejecta is . Interestingly, except the break out of the jet, a cocoon is formed and is clearly shown in the above mentioned Figure 9. However, there does not exist in this study a detailed description of this component. The density profile for the ejecta used in this study has a steep profile with a spherical shape.
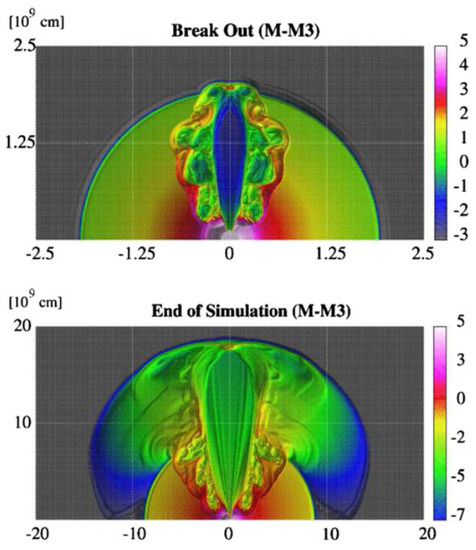
Figure 9.
Two snapshots from a model of [192]. The top panel is at the time where the jet breaks out and the lower panel at the end of the simulation. The jet was injected at 50 ms after merger with an opening angle of . The average opening angle of the jet after break out is . (Reprinted from [192]. © AAS. Reproduced with permission).
In [193], they studied the influence of the neutrino driven wind on the expansion and propagation of the formed jet, considering the post-merger production of neutrino fluxes that contribute to a wind density profile. They quantified this wind as [90,196,197]:
which results in a limiting Lorentz factor for the jet as:
Their wind profile depends on how long the neutrino driven wind was active. At the time that the wind stops, a jet is injected. In Figure 10 (left panel), a parameter study is presented on whether the jet can break out or not from such a wind. The axes are the luminosity of the jet versus time, where depicts the time that the neutrino wind stops, supposedly when the merger remnant collapses to a BH. Matter is injected in the wind as with a velocity of . The coloured lines indicate a different termination time for the neutrino wind, where is the time that the neutrino wind stops. As a comparisonm the distribution (the duration distribution of short GRBs from [78,198]) is overplotted to show that when the neutrino wind operates for more than s then jet duration times that exceed the observed ones are needed. Interestingly, all jets with luminosities less than erg s are choked and never break out from the neutrino wind. This can be regarded as the limiting value for the production of a structured jet with a cocoon or a choked jet with a cocoon.
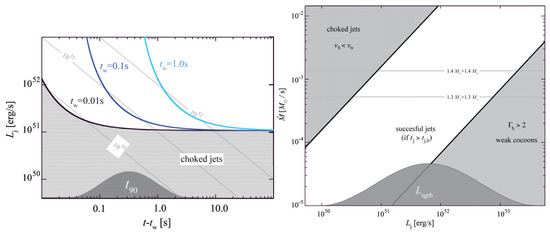
Figure 10.
The left panel shows luminosity versus time, where is the lifetime of the neutrino wind and the time that the jet begins to expand. The coloured lines indicate a model from [193], that has a wind injection rate of s with a velocity of . Each line indicate a different termination time 0.01, 0.1, 1 s. For such a heavy wind, the luminosity of the jet has to be above erg s and operate for at least the same time as the wind. (Reprinted from [193]. © AAS. Reproduced with permission).
However, this result strongly depends on the amount of mass that is ejected through this process. Thus, the next thing to compare is jet luminosity with respect to the mass injection from the neutrino wind. This result is shown in Figure 10 (right panel). The mass injection rate is plotted versus the jet luminosity and depicts different regions in the parameter space. If the luminosity is low (on the left part of the figure), then the velocity of the head of the jet is not exceeding the velocity of the wind and consequently never breaks out, resulting in a choked jet with a cocoon. Even for smaller luminosities, if the mass injection is less than –, then a successful jet can be formed. It is also known that in order to produce a successful jet, the jet injection time has to exceed the break out time through any medium. They further comment on the production of a cocoon as the jet advances through the ejecta and deposits some of its energy to form such a cocoon [186].
Spherical versus oblate BNS ejecta. In the previously mentioned studies, the shape of the density profile that is mimicking the BNS ejecta was spherical. Thus, all results have to be interpreted as arising from within a spherically expanding mass cloud. However, there is a possibility that this is not true [199]. Recent simulations of BNS mergers indeed show that the merger ejecta and/or the post-merger-driven winds are not at all spherical [101,102,103,105,106,108,120]. In [200], they considered the interaction of the jet with an oblate mass cloud mimicking the BNS ejecta, as opposed to a spherical one. The earlier idea that the ejecta can provide the collimation of the jet [201] is stronger in the case where the BNS ejecta have an elongated shape. They inject a luminosity of:
where is the mass of the cloud, e is the ratio of the energy deposited in the mass cloud and is the engine duration. Engines that act through an oblate cloud can collimate even wider initial angles. When the overall injected energy from the injected luminosity (Equation (13)) is low, then the kinetic energy of the dynamical ejecta can be higher and this does not allow for collimation. In the other limit where the injected energy is large, then the mass of the ejecta cannot provide sufficient collimation of the outflow. In the latter case, the outflow maintains the initial opening angle. For an initial opening angle of , with a mass cloud of and oblate in shape, a jet with luminosity of – erg s is significantly collimated with a resulting opening angle of 5–8 when breaking out from the cloud. In Figure 11, a model is shown from [200]. In this model, the mass cloud that mimics the BNS ejecta has an oblate shape. It is clearly seen that the interaction through the oblate mass cloud produces a narrow outflow with high Lorentz factor. We should also note here the possibility that jet formation may also account for the production of a magentar after the BNS merger [202,203].
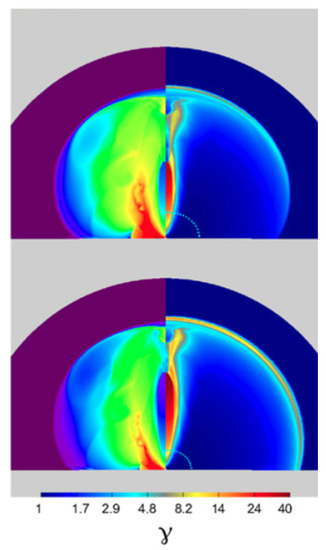
Figure 11.
A model from [200] where the shape of the BNS ejecta is assumed to be oblate. In the upper and lower rows, two different times are depicted: , where km is the initial radius of the mass cloud. The initial opening angle of both models is . The left panel of each plot shows the density and the right panel of each plot shows the Lorentz factor. The outer surface of the expanding mass ejecta is depicted with a dashed cyan curve. The model depicted in this figure with the oblate shaped cloud clearly produces a narrow relativistic outflow. In both cases, the ratio between the energy of the engine to the rest mass energy of the ejecta is , where is the mass of the cloud ejecta. (Reprinted from [200]. © AAS. Reproduced with permission).
The next step was to use more realistic profiles taken from [98,204] to continue a more detailed study of the interaction of the jet with the neutrino-driven and magnetically-driven wind, as studied in [194]. They concluded that a jet with luminosity comparable to the observed ones from short GRBs can break out from such winds with the requirement of having an initial opening angle of . They further used the observed duration of short GRBs to set limits on the lifetime of the production of winds from a HMNS, which is determined by the time that the jet needs to break out.
Observables from off-axis emission. All such simulations act as a first step towards understanding the jet and cocoon observables that follow a BNS merger. The next step was to see how these components would show up when observed off-axis. Furthermore, late radio counterparts from BNS mergers have long been proposed and expected [205]. Wide angle signatures from jet and cocoon interactions were presented through semi-analytical calculations in [206]. They calculated the on-axis and off-axis emission of a short GRB. They included the prompt and afterglow emission from a relativistic jet, as well as the prompt and afterglow emission from the cocoon formed through the interaction of the jet and the surrounding ejected material. The energy of the cocoon was found to amount to approximately of the energy of the burst itself. However, the cocoon energy strongly depends on the structure and size of the ejected material.
In the case of long GRBs, the propagation of the jet through a baryon loaded region (such as the interior of a massive star) has been studied and provides a clear and robust observational picture. Nakar and Piran [207] made a comprehensive (mostly analytical) study of the observable signatures of GRB cocoons. Their main focus was on the collapsar model for long GRBs, which envisions the propagation of a jet inside a massive star. While their focus was on cocoons emerging from long GRBs, short GRB cocoons should have an analogous signature (maybe weaker) as they indicated. All the formulas and equations reported in this study can provide a quick in-depth description of the characteristics of a cocoon and its emission. The analytical modelling in [208], calibrated by numerical results from [191], can be used to estimate the cocoon parameters through the jet break out time and the characteristics of the ejected matter.
Simulations of short GRB cocoons can provide more details on the production of the cocoon itself, together with realistic characteristics for its shape and initial Lorentz factor, which are key elements for a realistic description of any observables coming from it [209,210]. The numerical setup by Lazzati et al. [209] is an injected jet with luminosity of erg s, an initial opening angle of and the duration of this engine was defined to be s.
Through the isotropic equivalent energy three different components can be identified. The core of the outflow, which is the initially injected jet modified through the interaction with the ejecta and is the brightest part confined in . The surrounding material of the jet that forms a hot bubble is the energized cocoon which occupies a region within 15–45. The third component is a fairly isotropic wide-angle structure that stops at an angle of . From the initial energy of erg that was injected, erg remains in the confined jet, erg are given to the surrounding cocoon and erg are found in the shocked ambient medium. The rest of the energy is stored in slow moving material (). Figure 12 shows the results from [209], where the left panel shows the isotropic equivalent energy where the three components can be identified, and the right panel the peak photon energy is plotted as seen from different angles. The cocoon emission was also studied in detail by [210]. Their main focus was the appearance of a kilonova following the radioactive heating of the merger ejecta.
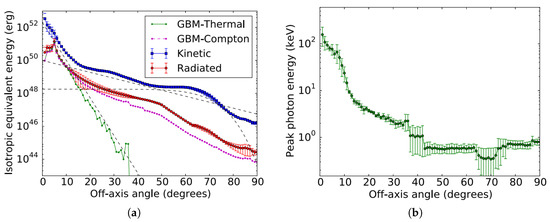
Figure 12.
Both figures are taken from [209]. (a) Off-axis distribution of the isotropic equivalent energy. The error bars show the range of variation at each specific angle. The kinetic energy is shown in blue squares, while the bolometric energy is shown in red dots. The energy that Fermi (Gamma-ray Burst Monitor (GBM)) would detect is shown as lines with dots, green solid line is for a thermal spectrum and magenta dashed line for a Comptonized spectrum. The three components: the jet (exponential), the cocoon (exponential), and the shocked ambient medium (constant with sharp cutoff) are overlaid on the kinetic energy profile as black dashed lines. (b) Off-axis emission from the jet/cocoon photosphere. The peak photon energy is depicted, while the symbols are as defined above. (Reprinted from [209]. © AAS. Reproduced with permission).
Jet with core and sheath. In a similar spirit, Kathirgamaraju et al. [211] simulated the off-axis emission from a short GRB jet including magnetic field. They argued that for a realistic jet model, one whose Lorentz factor and luminosity vary smoothly with angle, detection can be achieved for a broader range of viewing angles. In Figure 13, the luminosity and Lorentz factor is shown from their model. It is clear that even for angles larger than the luminosity from the jet is significant. As the jet breaks out from the cocoon, the prompt emission is released [203,212]. The time that the shock breaks out is pictured from a simulation of [212], illustrated in their Figure 1. As the shock propagates through the expanding BNS ejecta it accumulates mass on top of the jet head. The wide parts of the jet are not collimated and they propagate conically inside the mass cloud. If the engine operates for long enough, the shock breaks out and it is not choked inside the ejecta after giving all its energy to them. The break out of this shock in the magentized case was studied by [203].
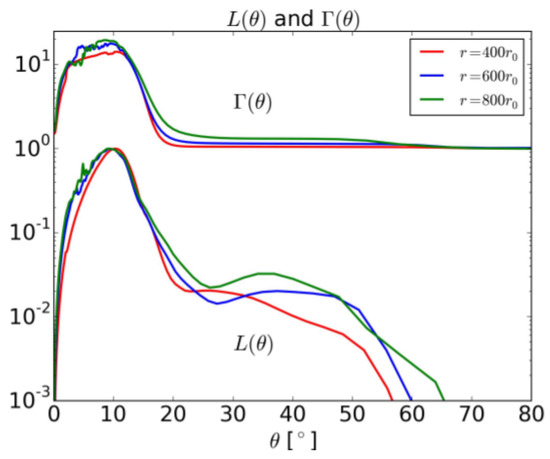
Figure 13.
The appearance of a jet model after break out from the BNS ejecta. A model from [211]. This figure presents the jet luminosity (in arbitrary units) and Lorentz factor as a function of the observer’s angle. Quantities are extracted at three different radii. It is evident that even for angles greater than , the luminosity is reduced but still significant. (Reprinted from [211]. © Oxford University Press. Reproduced with permission).
Magnetic explosion. It was argued in the last part of Section 2 that if the collapse of the compact remnant comes late (after a second), then the small amount of mass left at the torus cannot give a sufficient boundary for a magnetic jet to be launched. As such, all the magnetic energy dissipates away and produces an explosion. In Figure 14, such an explosion is depicted at the time that the outflow has entered a low density region. The main characteristics of a cocoon are still entering this picture. A main difference is that there does not exist an easily distinguishable relativistic core with a small opening angle. Faster moving material can be found at larger angles, as can be seen in Figure 14. This is a model from an upcoming work.
Figure 14.
A late magnetic explosion triggered by the collapse of the compact remnant is shown, a model similar to the one from an upcoming work. The amount of magnetic energy released is on the order of . The left panel shows the density and the right panel the Lorentz factor. The snapshot is taken at the time that the shock enters the low density region and expands sideways. It is interesting to note that there is no clear relativistic core with a small opening angle, although there are regions of the outflow at larger angles that move slightly faster.
Afterglow. In late observations, following a BNS merger event, it is important to understand the signatures from different components and the differences in observations from different models. As the outflow that was produced from the BNS merger hits the ISM, a shock is produced wherein particles are energized and emit synchrotron radiation. The outflow continues to sweep up matter and begin to decelerate. This is the standard picture for the source of a GRB afterglow. In the case of short GRBs from BNS mergers this has been discussed significantly before the detection of GW170817 [205,213,214]. Afterglow model predictions from numerical simulations have been studied in the context of long GRBs (e.g., [215]), and also as seen off-axis [216]. After the coincident detection of GW170817 together with GRB170817A and the following afterglow observations, there is an enormous effort to analyze the data and fit them with realistic models in order to clarify what are the actual components that powered such emission. It would be unrealistic to review such ongoing efforts. We restrict ourselves to a brief overview of observations and the corresponding modelling of them.
The prompt gamma-ray emission was reported in [3,4]. The first detection of X-rays from the event came nine days later [49,50], whereas the first radio observations came sixteen days after merger [51]. The first interpretation acknowledged that we are observing something quite different to other short GRBs [14,54].
Ongoing efforts in understanding the EM counterparts of GW170817 include: afterglow modelng through hydrodynamic simulations of a jet propagating through the merger ejecta [217,218,219], radio imaging that could show the exact morphology of the outflow and polarization measurements that could help to distinguish different outflow structures [220,221,222,223]. Ideas that the merger event did not include a jet have been proposed [224,225,226] or models that follow the canonical picture with a short GRB jet [227,228]. Observation of GW170817 can provide a deep understanding of short GRB modelling [184,229,230]. It has also been proposed that the afterglow may come from the interaction of the fast tail of the BNS ejecta with the ISM [231]. Another indicator may be the appearance of the counter jet [232], and how to probe short GRB properties from GW events [233]. Furthermore, one may also ask how the magnetar model can be in the picture [234].
Before finishing this section, we would like to gather some important points that should be kept in mind for the study of a relativistic outflow passing through the BNS ejecta.
Critical points:
- The amount of dynamically ejected matter strongly depends on the total mass of the binary and the mass ratio [88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108].
- The BNS ejecta are not spherical, rather they have a unique structure for every different EOS used [106].
- The time that the engine begins to produce an outflow is extremely important, since this will depict how much mass has been ejected by neutrino and magnetic winds [98,194,204].
4. Conclusions
In the years to come, more detections of BNS mergers are expected from ground-based interferometers. Combined observations of GW and EM radiation of such events would have a great impact on theoretical and numerical studies discussed here. The theoretical modeling of such events will have enormous benefit from the observational signatures of BNS mergers expected to be gathered in the next years. Our understanding of such extreme events lies in the comparison of these theoretical models against observations. It is important to analyze in detail observations of GW170817 and all its EM counterparts, starting with GRB170817A. It is equally important to reproduce realistic physics through numerical simulations to match and explain observations. This brief review can act as a quick introduction to BNS numerical relativity simulations for people interested in short GRB outflows through BNS ejecta, or as a brief introduction to short GRB jet simulations and setups used by people working on BNS merger simulations. Overall, we want to point out the importance of combining knowledge from both paths in order for a consistent picture to be drawn at the end.
In Section 2, we went through studies from numerical relativity for magnetized BNS mergers. We highlight important aspects of this physical process as given in the literature. Issues, such as the magnetic field amplification, the difficulty of launching a relativistic jet, the mass ejection during merger, and all possible winds produced after merger, can become clear through detailed studies. At the end of the section, we state several important points (importance is a subjective criterion).
The next step is to take these different ingredients from BNS simulations and study any outflow emerging after merger. A relativistic outflow has been observed from a BNS merger [52,53]. Thus, we need to understand how it was launched, what is the initial structure of this outflow, and how it will evolve through its interaction with the BNS ejecta. In Section 3, we briefly go through previous works on these aspects. This is a rapidly evolving sub-field, especially after the detection. Now, any model and idea can be simulated and be exposed to the data that followed GW170817. However, we should keep in mind that a BNS can have a different evolution, even with a very small difference in mass. In the end, modelling and studying outflows of such events should be inspired by GW170817.
Funding
This research was funded by [Alexander von Humboldt-Stiftung].
Acknowledgments
It is a pleasure to thank D. Giannios, R. Gold, E. Most and V. Paschalidis for reading the manuscript and giving valuable comments. The author is supported by an Alexander von Humboldt Fellowship.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- The LIGO Scientific Collaboration; The Virgo Collaboration. GW170817: Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Neutron Star Inspiral. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 161101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The LIGO Scientific Collaboration; The Virgo Collaboration; Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; et al. Multi-messenger Observations of a Binary Neutron Star Merger. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 848, L12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, A.; Veres, P.; Burns, E.; Briggs, M.S.; Hamburg, R.; Kocevski, D.; Wilson-Hodge, C.A.; Preece, R.D.; Poolakkil, S.; Roberts, O.J.; et al. An Ordinary Short Gamma-Ray Burst with Extraordinary Implications: Fermi-GBM Detection of GRB 170817A. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 848, L14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savchenko, V.; Ferrigno, C.; Kuulkers, E.; Bazzano, A.; Bozzo, E.; Brandt, S.; Chenevez, J.; Courvoisier, T.J.L.; Diehl, R.; Domingo, A.; et al. INTEGRAL Detection of the First Prompt Gamma-Ray Signal Coincident with the Gravitational-wave Event GW170817. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 848, L15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulter, D.A.; Foley, R.J.; Kilpatrick, C.D.; Drout, M.R.; Piro, A.L.; Shappee, B.J.; Siebert, M.R.; Simon, J.D.; Ulloa, N.; Kasen, D.; et al. Swope Supernova Survey 2017a (SSS17a), the optical counterpart to a gravitational wave source. Science 2017, 358, 1556–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares-Santos, M.; Holz, D.E.; Annis, J.; Chornock, R.; Herner, K.; Berger, E.; Brout, D.; Chen, H.Y.; Kessler, R.; Sako, M.; et al. The Electromagnetic Counterpart of the Binary Neutron Star Merger LIGO/Virgo GW170817. I. Discovery of the Optical Counterpart Using the Dark Energy Camera. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 848, L16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcavi, I.; Hosseinzadeh, G.; Howell, D.A.; McCully, C.; Poznanski, D.; Kasen, D.; Barnes, J.; Zaltzman, M.; Vasylyev, S.; Maoz, D.; et al. Optical emission from a kilonova following a gravitational-wave-detected neutron-star merger. Nature 2017, 551, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholl, M.; Berger, E.; Kasen, D.; Metzger, B.D.; Elias, J.; Briceño, C.; Alexander, K.D.; Blanchard, P.K.; Chornock, R.; Cowperthwaite, P.S.; et al. The Electromagnetic Counterpart of the Binary Neutron Star Merger LIGO/Virgo GW170817. III. Optical and UV Spectra of a Blue Kilonova from Fast Polar Ejecta. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 848, L18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pian, E.; D’Avanzo, P.; Benetti, S.; Branchesi, M.; Brocato, E.; Campana, S.; Cappellaro, E.; Covino, S.; D’Elia, V.; Fynbo, J.P.U.; et al. Spectroscopic identification of r-process nucleosynthesis in a double neutron-star merger. Nature 2017, 551, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smartt, S.; Chen, T.-W.; Jerkstrand, A.; Coughlin, M.; Kankare, E.; Sim, S.A.; Fraser, M.; Inserra, C.; Maguire, K.; Chambers, K.C.; et al. A kilonova as the electromagnetic counterpart to a gravitational-wave source. Nature 2017, 551, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanvir, N.R.; Levan, A.J.; González-Fernández, C.; Korobkin, O.; Mandel, I.; Rosswog, S.; Hjorth, J.; D’Avanzo, P.; Fruchter, A.S.; Fryer, C.L.; et al. The Emergence of a Lanthanide-rich Kilonova Following the Merger of Two Neutron Stars. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 848, L27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utsumi, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Tominaga, N.; Yoshida, M.; Barway, S.; Nagayama, T.; Zenko, T.; Aoki, K.; Fujiyoshi, T.; Furusawa, H.; et al. J-GEM observations of an electromagnetic counterpart to the neutron star merger GW170817. Publ. Astr. Soc. Jpn. 2017, 69, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilpatrick, C.D.; Foley, R.J.; Kasen, D.; Murguia-Berthier, A.; Ramirez-Ruiz, E.; Coulter, D.A.; Drout, M.R.; Piro, A.L.; Shappee, B.J.; Boutsia, K.; et al. Electromagnetic evidence that SSS17a is the result of a binary neutron star merger. Science 2017, 358, 1583–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasliwal, M.M.; Nakar, E.; Singer, L.P.; Kaplan, D.L.; Cook, D.O.; Van Sistine, A.; Lau, R.M.; Fremling, C.; Gottlieb, O.; Jencson, J.E.; et al. Illuminating gravitational waves: A concordant picture of photons from a neutron star merger. Science 2017, 358, 1559–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covino, S.; Wiersema, K.; Fan, Y.Z.; Toma, K.; Higgins, A.B.; Melandri, A.; D’Avanzo, P.; Mundell, C.G.; Wijers, R.A.M.J. The unpolarized macronova associated with the gravitational wave event GW 170817. Nat. Astron. 2017, 1, 791–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowperthwaite, P.S.; Berger, E.; Villar, V.A.; Metzger, B.D.; Nicholl, M.; Chornock, R.; Blanchard, P.K.; Fong, W.; Margutti, R.; Soares-Santos, M.; et al. The Electromagnetic Counterpart of the Binary Neutron Star Merger LIGO/Virgo GW170817. II. UV, Optical, and Near-infrared Light Curves and Comparison to Kilonova Models. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 848, L17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, D.A.H.; Andreoni, I.; Barway, S.; Cooke, J.; Crawford, S.M.; Gorbovskoy, E.; Gromadzki, M.; Lipunov, V.; Mao, J.; Potter, S.B.; et al. A comparison between SALT/SAAO observations and kilonova models for AT 2017gfo: The first electromagnetic counterpart of a gravitational wave transient—GW170817. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 474, L71–L75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drout, M.R.; Piro, A.L.; Shappee, B.J.; Kilpatrick, C.D.; Simon, J.D.; Contreras, C.; Coulter, D.A.; Foley, R.J.; Siebert, M.R.; Morrell, N.; et al. Light Curves of the Neutron Star Merger GW170817/SSS17a: Implications for R-Process Nucleosynthesis. Science 2017, 358, 1570–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, P.A.; Cenko, S.B.; Kennea, J.A.; Emery, S.W.K.; Kuin, N.P.M.; Korobkin, O.; Wollaeger, R.T.; Tagliaferri, G.; Tanvir, N.R.; Tohuvavohu, A. Swift and NuSTAR observations of GW170817: Detection of a blue kilonova. Science 2017, 358, 1565–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcavi, I. The First Hours of the GW170817 Kilonova and the Importance of Early Optical and Ultraviolet Observations for Constraining Emission Models. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2018, 855, L23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenti, S.; David, J.S.; Yang, S.; Cappellaro, E.; Tartaglia, L.; Corsi, A.; Jha, S.W.; Reichart, D.E.; Haislip, J.; Kouprianov, V. The Discovery of the Electromagnetic Counterpart of GW170817: Kilonova AT 2017gfo/DLT17ck. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 848, L24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichler, D.; Livio, M.; Piran, T.; Schramm, D.N. Nucleosynthesis, neutrino bursts and gamma-rays from coalescing neutron stars. Nature 1989, 340, 126–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, R.; Paczynski, B.; Piran, T. Gamma-ray bursts as the death throes of massive binary stars. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1992, 395, L83–L86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochkovitch, R.; Hernanz, M.; Isern, J.; Martin, X. Gamma-ray bursts as collimated jets from neutron star/black hole mergers. Nature 1993, 361, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annala, E.; Gorda, T.; Kurkela, A.; Vuorinen, A. Gravitational-Wave Constraints on the Neutron-Star-Matter Equation of State. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 120, 172703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauswein, A.; Just, O.; Janka, H.T.; Stergioulas, N. Neutron-star Radius Constraints from GW170817 and Future Detections. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 850, L34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margalit, B.; Metzger, B.D. Constraining the Maximum Mass of Neutron Stars from Multi-messenger Observations of GW170817. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 850, L19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radice, D.; Perego, A.; Zappa, F.; Bernuzzi, S. GW170817: Joint Constraint on the Neutron Star Equation of State from Multimessenger Observations. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2018, 852, L29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezzolla, L.; Most, E.R.; Weih, L.R. Using Gravitational-wave Observations and Quasi-universal Relations to Constrain the Maximum Mass of Neutron Stars. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2018, 852, L25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, M.; Shapiro, S.L.; Tsokaros, A. GW170817, general relativistic magnetohydrodynamic simulations, and the neutron star maximum mass. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 97, 021501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, M.; Fujibayashi, S.; Hotokezaka, K.; Kiuchi, K.; Kyutoku, K.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Tanaka, M. Modeling GW170817 based on numerical relativity and its implications. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 96, 123012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, S.; Finstad, D.; Lattimer, J.M.; Brown, D.A.; Berger, E.; Biwer, C.M. Constraining the nuclear equation of state with GW170817. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1804.08583. [Google Scholar]
- Tews, I.; Carlson, J.; Gandolfi, S.; Reddy, S. Constraining the speed of sound inside neutron stars with chiral effective field theory interactions and observations. Astrophys. J. 2018, 860, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tews, I.; Margueron, J.; Reddy, S. How well does GW170817 constrain the equation of state of dense matter? arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1804.02783. [Google Scholar]
- Alsing, J.; Silva, H.O.; Berti, E. Evidence for a maximum mass cut-off in the neutron star mass distribution and constraints on the equation of state. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 478, 1377–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgio, G.F.; Drago, A.; Pagliara, G.; Schulze, H.J.; Wei, J.B. Has deconfined quark matter been detected during GW170817/AT2017gfo? arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1803.09696. [Google Scholar]
- Raithel, C.; Özel, F.; Psaltis, D. Tidal deformability from GW170817 as a direct probe of the neutron star radius. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1803.07687. [Google Scholar]
- Paschalidis, V.; Yagi, K.; Alvarez-Castillo, D.; Blaschke, D.B.; Sedrakian, A. Implications from GW170817 and I-Love-Q relations for relativistic hybrid stars. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 97, 084038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.; Holt, J.W. Neutron Star Tidal Deformabilities Constrained by Nuclear Theory and Experiment. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 121, 062701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lattimer, J.M.; Schramm, D.N. Black-hole-neutron-star collisions. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1974, 192, L145–L147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.X.; Paczynski, B. Transient events from neutron star mergers. Astrophys. J. 1998, 507, L59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasen, D.; Metzger, B.; Barnes, J.; Quataert, E.; Ramirez-Ruiz, E. Origin of the heavy elements in binary neutron-star mergers from a gravitational-wave event. Nature 2017, 551, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Utsumi, Y.; Mazzali, P.A.; Tominaga, N.; Yoshida, M.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Morokuma, T.; Motohara, K.; Ohta, K.; Kawabata, K.S.; et al. Kilonova from post-merger ejecta as an optical and near-Infrared counterpart of GW170817. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 2017, 69, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murguia-Berthier, A.; Ramirez-Ruiz, E.; Kilpatrick, C.D.; Foley, R.J.; Kasen, D.; Lee, W.H.; Piro, A.L.; Coulter, D.A.; Drout, M.R.; Madore, B.F.; et al. A Neutron Star Binary Merger Model for GW170817/GRB 170817A/SSS17a. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 848, L34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waxman, E.; Ofek, E.; Kushnir, D.; Gal-Yam, A. Constraints on the ejecta of the GW170817 neutron-star merger from its electromagnetic emission. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1711.09638. [Google Scholar]
- Villar, V.A.; Guillochon, J.; Berger, E.; Metzger, B.D.; Cowperthwaite, P.S.; Nicholl, M.; Alexander, K.D.; Blanchard, P.K.; Chornock, R.; Eftekhari, T.; et al. The Combined Ultraviolet, Optical, and Near-infrared Light Curves of the Kilonova Associated with the Binary Neutron Star Merger GW170817: Unified Data Set, Analytic Models, and Physical Implications. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 851, L21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perego, A.; Radice, D.; Bernuzzi, S. AT 2017gfo: An Anisotropic and Three-component Kilonova Counterpart of GW170817. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 850, L37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, B.D.; Thompson, T.A.; Quataert, E. A Magnetar Origin for the Kilonova Ejecta in GW170817. Astrophys. J. 2018, 856, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troja, E.; Piro, L.; van Eerten, H.; Wollaeger, R.T.; Im, M.; Fox, O.D.; Butler, N.R.; Cenko, S.B.; Sakamoto, T.; Fryer, C.L.; et al. The X-ray counterpart to the gravitational-wave event GW170817. Nature 2017, 551, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margutti, R.; Berger, E.; Fong, W.; Guidorzi, C.; Alexander, K.D.; Metzger, B.D.; Blanchard, P.K.; Cowperthwaite, P.S.; Chornock, R.; Eftekhari, T.; et al. The Electromagnetic Counterpart of the Binary Neutron Star Merger LIGO/Virgo GW170817. V. Rising X-ray Emission from an Off-axis Jet. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 848, L20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallinan, G.; Corsi, A.; Mooley, K.P.; Hotokezaka, K.; Nakar, E.; Kasliwal, M.M.; Kaplan, D.L.; Frail, D.A.; Myers, S.T.; Murphy, T.; et al. A radio counterpart to a neutron star merger. Science 2017, 358, 1579–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, K.D.; Berger, E.; Fong, W.; Williams, P.K.G.; Guidorzi, C.; Margutti, R.; Metzger, B.D.; Annis, J.; Blanchard, P.K.; Brout, D.; et al. The Electromagnetic Counterpart of the Binary Neutron Star Merger LIGO/Virgo GW170817. VI. Radio Constraints on a Relativistic Jet and Predictions for Late-time Emission from the Kilonova Ejecta. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 848, L21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haggard, D.; Nynka, M.; Ruan, J.J.; Kalogera, V.; Cenko, S.B.; Evans, P.; Kennea, J.A. A Deep Chandra X-ray Study of Neutron Star Coalescence GW170817. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 848, L25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granot, J.; Guetta, D.; Gill, R. Lessons from the Short GRB 170817A: The First Gravitational-wave Detection of a Binary Neutron Star Merger. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 850, L24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooley, K.P.; Nakar, E.; Hotokezaka, K.; Hallinan, G.; Corsi, A.; Frail, D.A.; Horesh, A.; Murphy, T.; Lenc, E.; Kaplan, D.L.; et al. A mildly relativistic wide-angle outflow in the neutron-star merger event GW170817. Nature 2018, 554, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, J.J.; Nynka, M.; Haggard, D.; Kalogera, V.; Evans, P. Brightening X-ray Emission from GW170817/GRB 170817A: Further Evidence for an Outflow. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2018, 853, L4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pooley, D.; Kumar, P.; Wheeler, J.C.; Grossan, B. GW170817 Most Likely Made a Black Hole. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2018, 859, L23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margutti, R.; Alexander, K.D.; Xie, X.; Sironi, L.; Metzger, B.D.; Kathirgamaraju, A.; Fong, W.; Blanchard, P.K.; Berger, E.; MacFadyen, A.; et al. The Binary Neutron Star Event LIGO/Virgo GW170817 160 Days after Merger: Synchrotron Emission across the Electromagnetic Spectrum. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2018, 856, L18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyman, J.D.; Lamb, G.P.; Levan, A.J.; Mandel, I.; Tanvir, N.R.; Kobayashi, S.; Gompertz, B.; Hjorth, J.; Fruchter, A.S.; Kangas, T.; et al. The optical afterglow of the short gamma-ray burst associated with GW170817. Nat. Astron. 2018, 2, 751–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, L.B.; Huang, Y.F.; Geng, J.J.; Yu, Y.B.; Song, L.M. Continued Brightening of the Afterglow of GW170817/GRB 170817A as Being Due to a Delayed Energy Injection. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2018, 859, L3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.J.; Dai, Z.G.; Huang, Y.F.; Wu, X.F.; Li, L.B.; Li, B.; Meng, Y.Z. Brightening X-ray/Optical/Radio Emission of GW170817/SGRB 170817A: Evidence for an Electron-Positron Wind from the Central Engine? Astrophys. J. Lett. 2018, 856, L33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobie, D.; Kaplan, D.L.; Murphy, T.; Lenc, E.; Mooley, K.P.; Lynch, C.; Corsi, A.; Frail, D.; Kasliwal, M.; Hallinan, G. A Turnover in the Radio Light Curve of GW170817. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2018, 858, L15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, K.D.; Margutti, R.; Blanchard, P.K.; Fong, W.; Berger, E.; Hajela, A.; Eftekhari, T.; Chornock, R.; Cowperthwaite, P.S.; Giannios, D.; et al. A Decline in the X-ray through Radio Emission from GW170817 Continues to Support an Off-Axis Structured Jet. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1805.02870. [Google Scholar]
- Nynka, M.; Ruan, J.J.; Haggard, D.; Evans, P.A. Fading of the X-ray Afterglow of Neutron Star Merger GW170817/GRB170817A at 260 days. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1805.04093. [Google Scholar]
- Kruckow, M.U.; Tauris, T.M.; Langer, N.; Kramer, M.; Izzard, R.G. Progenitors of gravitational wave mergers: Binary evolution with the stellar grid-based code COMBINE. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 481, 1908–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faber, J.A.; Rasio, F.A. Binary Neutron Star Mergers. Living Rev. Relativ. 2012, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baiotti, L.; Rezzolla, L. Binary neutron-star mergers: A review of Einstein’s richest laboratory. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2017, 80, 096901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, M.; Liu, Y.T.; Shapiro, S.L.; Stephens, B.C. Magnetorotational collapse of massive stellar cores to neutron stars: Simulations in full general relativity. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 74, 104026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paschalidis, V. General relativistic simulations of compact binary mergers as engines for short gamma-ray bursts. Class. Quantum Gravity 2017, 34, 084002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciolfi, R. Short gamma-ray burst central engines. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1804.03684. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, E. Short-Duration Gamma-Ray Bursts. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 52, 43–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, W.; Berger, E.; Margutti, R.; Zauderer, B.A. A Decade of Short-duration Gamma-Ray Burst Broadband Afterglows: Energetics, Circumburst Densities, and Jet Opening Angles. Astrophys. J. 2015, 815, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosswog, S. The multi-messenger picture of compact binary mergers. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2015, 24, 1530012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, R.; Quataert, E.; Schwab, J.; Kasen, D.; Rosswog, S. The interplay of disc wind and dynamical ejecta in the aftermath of neutron star-black hole mergers. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 449, 390–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thielemann, F.K.; Eichler, M.; Panov, I.V.; Wehmeyer, B. Neutron Star Mergers and Nucleosynthesis of Heavy Elements. Annu. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 2017, 67, 253–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, B.D. Kilonovae. Living Rev. Relativ. 2017, 20, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paschalidis, V.; Stergioulas, N. Rotating stars in relativity. Living Rev. Relativ. 2017, 20, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakar, E. Short-hard gamma-ray bursts. Phys. Rep. 2007, 442, 166–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.H.; Ramirez-Ruiz, E. The Progenitors of Short Gamma-Ray Bursts. New J. Phys. 2007, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piran, T. The physics of gamma-ray bursts. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2005, 76, 1143–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meszaros, P. Gamma-Ray Bursts. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2006, 69, 2259–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Smoot, G.F. Some implications of inverse-Compton scattering of hot cocoon radiation by relativistic jets in gamma-ray bursts. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 445, 528–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauris, T.M.; Kramer, M.; Freire, P.C.C.; Wex, N.; Janka, H.T.; Langer, N.; Podsiadlowski, P.; Bozzo, E.; Chaty, S.; Kruckow, M.U.; et al. Formation of Double Neutron Star Systems. Astrophys. J. 2017, 846, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgarte, T.W.; Shapiro, S.L.; Shibata, M. On the Maximum Mass of Differentially Rotating Neutron Stars. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2000, 528, L29–L32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiguchi, Y.; Kiuchi, K.; Kyutoku, K.; Shibata, M. Gravitational Waves and Neutrino Emission from the Merger of Binary Neutron Stars. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 051102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paschalidis, V.; Etienne, Z.B.; Shapiro, S.L. Importance of cooling in triggering the collapse of hypermassive neutron stars. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 86, 064032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, J.D. Where Tori Fear to Tread: Hypermassive Neutron Star Remnants and Absolute Event Horizons or Topics in Computational General Relativity. Ph.D. Thesis, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Rosswog, S.; Liebendörfer, M.; Thielemann, F.K.; Davies, M.B.; Benz, W.; Piran, T. Mass ejection in neutron star mergers. Astron. Astrophys. 1999, 341, 499–526. [Google Scholar]
- Aloy, M.A.; Janka, H.; Müller, E. Relativistic outflows from remnants of compact object mergers and their viability for short gamma-ray bursts. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 436, 273–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessart, L.; Ott, C.D.; Burrows, A.; Rosswog, S.; Livne, E. Neutrino Signatures and the Neutrino-Driven Wind in Binary Neutron Star Mergers. Astrophys. J. 2009, 690, 1681–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezzolla, L.; Baiotti, L.; Giacomazzo, B.; Link, D.; Font, J.A. Accurate evolutions of unequal-mass neutron-star binaries: Properties of the torus and short GRB engines. Class. Quantum Gravity 2010, 27, 114105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, L.F.; Kasen, D.; Lee, W.H.; Ramirez-Ruiz, E. Electromagnetic Transients Powered by Nuclear Decay in the Tidal Tails of Coalescing Compact Binaries. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2011, 736, L21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyutoku, K.; Ioka, K.; Shibata, M. Ultrarelativistic electromagnetic counterpart to binary neutron star mergers. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 437, L6–L10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosswog, S. The dynamic ejecta of compact object mergers and eccentric collisions. R. Soc. Lond. Philos. Trans. Ser. A 2013, 371, 20272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauswein, A.; Goriely, S.; Janka, H.T. Systematics of Dynamical Mass Ejection, Nucleosynthesis, and Radioactively Powered Electromagnetic Signals from Neutron-star Mergers. Astrophys. J. 2013, 773, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotokezaka, K.; Kiuchi, K.; Kyutoku, K.; Okawa, H.; Sekiguchi, Y.I.; Shibata, M.; Taniguchi, K. Mass ejection from the merger of binary neutron stars. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 87, 024001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foucart, F.; Deaton, M.B.; Duez, M.D.; O’Connor, E.; Ott, C.D.; Haas, R.; Kidder, L.E.; Pfeiffer, H.P.; Scheel, M.A.; Szilagyi, B. Neutron star-black hole mergers with a nuclear equation of state and neutrino cooling: Dependence in the binary parameters. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 90, 024026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, D.M.; Ciolfi, R.; Rezzolla, L. Magnetically Driven Winds from Differentially Rotating Neutron Stars and X-ray Afterglows of Short Gamma-Ray Bursts. Astrophys. J. 2014, 785, L6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanajo, S.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Nishimura, N.; Kiuchi, K.; Kyutoku, K.; Shibata, M. Production of All the r-process Nuclides in the Dynamical Ejecta of Neutron Star Mergers. Astrophys. J. 2014, 789, L39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiguchi, Y.; Kiuchi, K.; Kyutoku, K.; Shibata, M. Dynamical mass ejection from binary neutron star mergers: Radiation-hydrodynamics study in general relativity. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 91, 064059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radice, D.; Galeazzi, F.; Lippuner, J.; Roberts, L.F.; Ott, C.D.; Rezzolla, L. Dynamical Mass Ejection from Binary Neutron Star Mergers. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 460, 3255–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiguchi, Y.; Kiuchi, K.; Kyutoku, K.; Shibata, M.; Taniguchi, K. Dynamical mass ejection from the merger of asymmetric binary neutron stars: Radiation-hydrodynamics study in general relativity. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 93, 124046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehner, L.; Liebling, S.L.; Palenzuela, C.; Caballero, O.L.; O’Connor, E.; Anderson, M.; Neilsen, D. Unequal mass binary neutron star mergers and multimessenger signals. Class. Quantum Gravity 2016, 33, 184002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, D.M.; Metzger, B.D. Three-Dimensional General-Relativistic Magnetohydrodynamic Simulations of Remnant Accretion Disks from Neutron Star Mergers: Outflows and r-Process Nucleosynthesis. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 231102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, T.; Ujevic, M.; Tichy, W.; Bernuzzi, S.; Brügmann, B. Gravitational waves and mass ejecta from binary neutron star mergers: Effect of the mass ratio. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 95, 024029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovard, L.; Martin, D.; Guercilena, F.; Arcones, A.; Rezzolla, L.; Korobkin, O. On r-process nucleosynthesis from matter ejected in binary neutron star mergers. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 96, 124005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujibayashi, S.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Kiuchi, K.; Shibata, M. Properties of Neutrino-driven Ejecta from the Remnant of a Binary Neutron Star Merger: Pure Radiation Hydrodynamics Case. Astrophys. J. 2017, 846, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujibayashi, S.; Kiuchi, K.; Nishimura, N.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Shibata, M. Mass Ejection from the Remnant of a Binary Neutron Star Merger: Viscous-radiation Hydrodynamics Study. Astrophys. J. 2018, 860, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastaun, W.; Galeazzi, F. Properties of hypermassive neutron stars formed in mergers of spinning binaries. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 91, 064027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastaun, W.; Ciolfi, R.; Endrizzi, A.; Giacomazzo, B. Structure of stable binary neutron star merger remnants: Role of initial spin. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 96, 043019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanauske, M.; Takami, K.; Bovard, L.; Rezzolla, L.; Font, J.A.; Galeazzi, F.; Stöcker, H. Rotational properties of hypermassive neutron stars from binary mergers. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 96, 043004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasio, F.; Shapiro, S. TOPICAL REVIEW: Coalescing binary neutron stars. Class. Quantum Gravity 1999, 16, R1–R29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosswog, S.; Ramirez-Ruiz, E.; Davies, M.B. High-resolution calculations of merging neutron stars—III. Gamma-ray bursts. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2003, 345, 1077–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, D.J.; Rosswog, S. Producing Ultrastrong Magnetic Fields in Neutron Star Mergers. Science 2006, 312, 719–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.T.; Shapiro, S.L.; Etienne, Z.B.; Taniguchi, K. General relativistic simulations of magnetized binary neutron star mergers. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 78, 024012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.; Hirschmann, E.W.; Lehner, L.; Liebling, S.L.; Motl, P.M.; Neilsen, D.; Palenzuela, C.; Tohline, J.E. Magnetized Neutron-Star Mergers and Gravitational-Wave Signals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 191101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacomazzo, B.; Rezzolla, L.; Baiotti, L. Accurate evolutions of inspiralling and magnetized neutron stars: Equal-mass binaries. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 83, 044014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomazzo, B.; Zrake, J.; Duffell, P.C.; MacFadyen, A.I.; Perna, R. Producing Magnetar Magnetic Fields in the Merger of Binary Neutron Stars. Astrophys. J. 2015, 809, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dionysopoulou, K.; Alic, D.; Rezzolla, L. General-relativistic resistive-magnetohydrodynamic simulations of binary neutron stars. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 92, 084064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palenzuela, C.; Liebling, S.L.; Neilsen, D.; Lehner, L.; Caballero, O.L.; O’Connor, E.; Anderson, M. Effects of the microphysical equation of state in the mergers of magnetized neutron stars with neutrino cooling. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 92, 044045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiuchi, K.; Kyutoku, K.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Shibata, M.; Wada, T. High resolution numerical relativity simulations for the merger of binary magnetized neutron stars. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 90, 041502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obergaulinger, M.; Aloy, M.A.; Müller, E. Local simulations of the magnetized Kelvin-Helmholtz instability in neutron-star mergers. Astron. Astrophys. 2010, 515, A30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zrake, J.; MacFadyen, A.I. Magnetic Energy Production by Turbulence in Binary Neutron Star Mergers. Astrophys. J. 2013, 769, L29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiuchi, K.; Cerdá-Durán, P.; Kyutoku, K.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Shibata, M. Efficient magnetic-field amplification due to the Kelvin-Helmholtz instability in binary neutron star mergers. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 92, 124034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiuchi, K.; Kyutoku, K.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Shibata, M. Global simulations of strongly magnetized remnant massive neutron stars formed in binary neutron star mergers. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 97, 124039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harutyunyan, A.; Nathanail, A.; Rezzolla, L.; Sedrakian, A. Electrical Resistivity and Hall Effect in Binary Neutron-Star Mergers. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1803.09215. [Google Scholar]
- Moesta, P.; Mundim, B.; Faber, J.; Noble, S.; Bode, T.; Haas, R.; Loeffler, F.; Ott, C.; Reisswig, C.; Schnetter, E. General relativistic magneto-hydrodynamics with the Einstein Toolkit. In Proceedings of the 2013 APS Meeting Abstracts, Baltimore, MD, USA, 18–22 March 2013; p. 10001. [Google Scholar]
- Rembiasz, T.; Guilet, J.; Obergaulinger, M.; Cerdá-Durán, P.; Aloy, M.A.; Müller, E. On the maximum magnetic field amplification by the magnetorotational instability in core-collapse supernovae. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 460, 3316–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zrake, J.; MacFadyen, A.I. Spectral and Intermittency Properties of Relativistic Turbulence. Astrophys. J. 2013, 763, L12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezzolla, L.; Giacomazzo, B.; Baiotti, L.; Granot, J.; Kouveliotou, C.; Aloy, M.A. The Missing Link: Merging Neutron Stars Naturally Produce Jet-like Structures and Can Power Short Gamma-ray Bursts. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2011, 732, L6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandford, R.D.; Znajek, R.L. Electromagnetic extraction of energy from Kerr black holes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1977, 179, 433–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contopoulos, J. A Simple Type of Magnetically Driven Jets: An Astrophysical Plasma Gun. Astrophys. J. 1995, 450, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, M.; Lang, R.N.; Paschalidis, V.; Shapiro, S.L. Binary Neutron Star Mergers: A Jet Engine for Short Gamma-Ray Bursts. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2016, 824, L6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura, T.; Giacomazzo, B.; Kastaun, W.; Ciolfi, R.; Endrizzi, A.; Baiotti, L.; Perna, R. Binary neutron star mergers and short gamma-ray bursts: Effects of magnetic field orientation, equation of state, and mass ratio. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 94, 064012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endrizzi, A.; Ciolfi, R.; Giacomazzo, B.; Kastaun, W.; Kawamura, T. General relativistic magnetohydrodynamic simulations of binary neutron star mergers with the APR4 equation of state. Class. Quantum Gravity 2016, 33, 164001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffert, M.; Janka, H.T. Gamma-ray bursts from accreting black holes in neutron star mergers. Astron. Astrophys. 1999, 344, 573–606. [Google Scholar]
- Just, O.; Obergaulinger, M.; Janka, H.T.; Bauswein, A.; Schwarz, N. Neutron-star Merger Ejecta as Obstacles to Neutrino-powered Jets of Gamma-Ray Bursts. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2016, 816, L30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komissarov, S.S. Direct numerical simulations of the Blandford-Znajek effect. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2001, 326, L41–L44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komissarov, S.S.; Barkov, M.; Lyutikov, M. Tearing instability in relativistic magnetically dominated plasmas. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2007, 374, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathanail, A.; Contopoulos, I. Black Hole Magnetospheres. Astrophys. J. 2014, 788, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gralla, S.E.; Lupsasca, A.; Rodriguez, M.J. Electromagnetic jets from stars and black holes. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 93, 044038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, S.L. Black holes, disks, and jets following binary mergers and stellar collapse: The narrow range of electromagnetic luminosities and accretion rates. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 95, 101303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, M.; Taniguchi, K.; Uryū, K. Merger of binary neutron stars of unequal mass in full general relativity. Phys. Rev. D 2003, 68, 084020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, M.; Taniguchi, K. Merger of binary neutron stars to a black hole: Disk mass, short gamma-ray bursts, and quasinormal mode ringing. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 73, 064027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiotti, L.; Giacomazzo, B.; Rezzolla, L. Accurate evolutions of inspiralling neutron-star binaries: Prompt and delayed collapse to a black hole. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 78, 084033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezzolla, L.; Macedo, R.P.; Jaramillo, J.L. Understanding the ’anti-kick’ in the merger of binary black holes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 221101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margalit, B.; Metzger, B.D.; Beloborodov, A.M. Does the Collapse of a Supramassive Neutron Star Leave a Debris Disk? Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 115, 171101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camelio, G.; Dietrich, T.; Rosswog, S. Disk formation in the collapse of supramassive neutron stars. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1806.07775. [Google Scholar]
- Shakura, N.I.; Sunyaev, R.A. Black holes in binary systems. Observational appearance. Astron. Astrophys. 1973, 24, 337–355. [Google Scholar]
- Falcke, H.; Rezzolla, L. Fast radio bursts: The last sign of supramassive neutron stars. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 562, A137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, M.; Uryū, K. Gravitational Waves from Merger of Binary Neutron Stars in Fully General Relativistic Simulation. Prog. Theor. Phys. 2002, 107, 265–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotokezaka, K.; Kyutoku, K.; Okawa, H.; Shibata, M.; Kiuchi, K. Binary neutron star mergers: Dependence on the nuclear equation of state. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 83, 124008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauswein, A.; Baumgarte, T.W.; Janka, H.T. Prompt Merger Collapse and the Maximum Mass of Neutron Stars. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 111, 131101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, M.; Taniguchi, K.; Uryū, K. Merger of binary neutron stars with realistic equations of state in full general relativity. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 71, 084021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oechslin, R.; Janka, H.T.; Marek, A. Relativistic neutron star merger simulations with non-zero temperature equations of state. I. Variation of binary parameters and equation of state. Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 467, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studzińska, A.M.; Kucaba, M.; Gondek-Rosińska, D.; Villain, L.; Ansorg, M. Effect of the equation of state on the maximum mass of differentially rotating neutron stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 463, 2667–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.M.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.H.; Yin, H.X.; Song, L.M.; Menezes, D.P.; Wickramasinghe, D.T.; Ferrario, L.; Chardonnet, P. Study of measured pulsar masses and their possible conclusions. Astron. Astrophys. 2011, 527, A83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, M.; Shapiro, S.L. General relativistic magnetohydrodynamics simulations of prompt-collapse neutron star mergers: The absence of jets. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 96, 084063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorimer, D.R.; Bailes, M.; McLaughlin, M.A.; Narkevic, D.J.; Crawford, F. A Bright Millisecond Radio Burst of Extragalactic Origin. Science 2007, 318, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rane, A.; Lorimer, D. Fast Radio Bursts. J. Astrophys. Astron. 2017, 38, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Most, E.R.; Nathanail, A.; Rezzolla, L. Electromagnetic emission from blitzars and its impact on non-repeating fast radio bursts. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1801.05705. [Google Scholar]
- Paschalidis, V.; Ruiz, M. Are fast radio bursts the most likely electromagnetic counterpart of neutron star mergers resulting in prompt collapse? arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1808.04822. [Google Scholar]
- Rowlinson, A.; O’Brien, P.T.; Metzger, B.D.; Tanvir, N.R.; Levan, A.J. Signatures of magnetar central engines in short GRB light curves. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 430, 1061–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Mészáros, P. Gamma-Ray Burst Afterglow with Continuous Energy Injection: Signature of a Highly Magnetized Millisecond Pulsar. Astrophys. J. 2001, 552, L35–L38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.H.; Fan, Y.Z. Short-living Supermassive Magnetar Model for the Early X-ray Flares Following Short GRBs. Chin. J. Astron. Astrophys. 2006, 6, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.Z.; Xu, D. The X-ray afterglow flat segment in short GRB 051221A: Energy injection from a millisecond magnetar? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2006, 372, L19–L22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, B.D.; Piro, A.L.; Quataert, E. Time-dependent models of accretion discs formed from compact object mergers. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 390, 781–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, B.D.; Martínez-Pinedo, G.; Darbha, S.; Quataert, E.; Arcones, A.; Kasen, D.; Thomas, R.; Nugent, P.; Panov, I.V.; Zinner, N.T. Electromagnetic counterparts of compact object mergers powered by the radioactive decay of r-process nuclei. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 406, 2650–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomazzo, B.; Perna, R. Formation of Stable Magnetars from Binary Neutron Star Mergers. Astrophys. J. 2013, 771, L26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Osso, S.; Giacomazzo, B.; Perna, R.; Stella, L. Gravitational Waves from Massive Magnetars Formed in Binary Neutron Star Mergers. Astrophys. J. 2015, 798, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezzolla, L.; Kumar, P. A Novel Paradigm for Short Gamma-Ray Bursts with Extended X-ray Emission. Astrophys. J. 2015, 802, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciolfi, R.; Siegel, D.M. Short Gamma-Ray Bursts in the “Time-reversal” Scenario. Astrophys. J. 2015, 798, L36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitkovsky, A. Time-dependent Force-free Pulsar Magnetospheres: Axisymmetric and Oblique Rotators. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2006, 648, L51–L54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contopoulos, I.; Spitkovsky, A. Revised Pulsar Spin-down. Astrophys. J. 2006, 643, 1139–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, T.A.; Burrows, A.; Pinto, P.A. Shock Breakout in Core-Collapse Supernovae and Its Neutrino Signature. Astrophys. J. 2003, 592, 434–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komissarov, S.S. Multidimensional numerical scheme for resistive relativistic magnetohydrodynamics. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2007, 382, 995–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, T.A.; ud-Doula, A. High-entropy ejections from magnetized proto-neutron star winds: Implications for heavy element nucleosynthesis. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 476, 5502–5515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzdensky, D.A. Force-Free Magnetosphere of an Accretion Disk-Black Hole System. II. Kerr Geometry. Astrophys. J. 2005, 620, 889–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parfrey, K.; Giannios, D.; Beloborodov, A.M. Black hole jets without large-scale net magnetic flux. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 446, L61–L65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contopoulos, I.; Nathanail, A.; Katsanikas, M. The Cosmic Battery in Astrophysical Accretion Disks. Astrophys. J. 2015, 805, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathanail, A.; Contopoulos, I. Are ultralong gamma-ray bursts powered by black holes spinning down? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 453, L1–L5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathanail, A.; Strantzalis, A.; Contopoulos, I. The rapid decay phase of the afterglow as the signature of the Blandford-Znajek mechanism. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 455, 4479–4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathanail, A. An Explosion is Triggered by the Late Collapse of the Compact Remnant from a Neutron Star Merger. Astrophys. J. 2018, 864, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakar, E.; Piran, T. Implications of the radio and X-ray emission that followed GW170817. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 478, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandford, R.D.; McKee, C.F. Fluid dynamics of relativistic blast waves. Phys. Fluids 1976, 19, 1130–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Ruiz, E.; Celotti, A.; Rees, M.J. Events in the life of a cocoon surrounding a light, collapsar jet. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2002, 337, 1349–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsony, B.J.; Lazzati, D.; Begelman, M.C. Temporal and Angular Properties of Gamma-Ray Burst Jets Emerging from Massive Stars. Astrophys. J. 2007, 665, 569–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzati, D.; Morsony, B.J.; Begelman, M.C. Short-duration Gamma-ray Bursts From Off-axis Collapsars. Astrophys. J. 2010, 717, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuta, A.; Aloy, M.A. Angular Energy Distribution of Collapsar-Jets. arXiv, 2008; arXiv:0812.4813. [Google Scholar]
- López-Cámara, D.; Morsony, B.J.; Begelman, M.C.; Lazzati, D. Three-dimensional Adaptive Mesh Refinement Simulations of Long-duration Gamma-Ray Burst Jets inside Massive Progenitor Stars. Astrophys. J. 2013, 767, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuta, A.; Ioka, K. Opening Angles of Collapsar Jets. Astrophys. J. 2013, 777, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagakura, H.; Hotokezaka, K.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Shibata, M.; Ioka, K. Jet Collimation in the Ejecta of Double Neutron Star Mergers: A New Canonical Picture of Short Gamma-Ray Bursts. Astrophys. J. 2014, 784, L28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murguia-Berthier, A.; Montes, G.; Ramirez-Ruiz, E.; De Colle, F.; Lee, W.H. Necessary Conditions for Short Gamma-Ray Burst Production in Binary Neutron Star Mergers. Astrophys. J. 2014, 788, L8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murguia-Berthier, A.; Ramirez-Ruiz, E.; Montes, G.; De Colle, F.; Rezzolla, L.; Rosswog, S.; Takami, K.; Perego, A.; Lee, W.H. The Properties of Short Gamma-Ray Burst Jets Triggered by Neutron Star Mergers. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2016, 835, L34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagakura, H.; Ito, H.; Kiuchi, K.; Yamada, S. Jet Propagations, Breakouts, and Photospheric Emissions in Collapsing Massive Progenitors of Long-duration Gamma-ray Bursts. Astrophys. J. 2011, 731, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.Z.; Woosley, S.E. Nucleosynthesis in Neutrino-driven Winds. I. The Physical Conditions. Astrophys. J. 1996, 471, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosswog, S.; Ramirez-Ruiz, E. Jets, winds and bursts from coalescing neutron stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2002, 336, L7–L11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrels, N.; Ramirez-Ruiz, E.; Fox, D.B. Gamma-Ray Bursts in the Swift Era. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 47, 567–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotokezaka, K.; Kyutoku, K.; Tanaka, M.; Kiuchi, K.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Shibata, M.; Wanajo, S. Progenitor Models of the Electromagnetic Transient Associated with the Short Gamma Ray Burst 130603B. Astrophys. J. 2013, 778, L16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffell, P.C.; Quataert, E.; MacFadyen, A.I. A Narrow Short-duration GRB Jet from a Wide Central Engine. Astrophys. J. 2015, 813, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosswog, S.; Ramirez-Ruiz, E. On the diversity of short gamma-ray bursts. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2003, 343, L36–L40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucciantini, N.; Metzger, B.D.; Thompson, T.A.; Quataert, E. Short gamma-ray bursts with extended emission from magnetar birth: Jet formation and collimation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 419, 1537–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromberg, O.; Tchekhovskoy, A.; Gottlieb, O.; Nakar, E.; Piran, T. The γ-rays that accompanied GW170817 and the observational signature of a magnetic jet breaking out of NS merger ejecta. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 475, 2971–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perego, A.; Rosswog, S.; Cabezón, R.M.; Korobkin, O.; Käppeli, R.; Arcones, A.; Liebendörfer, M. Neutrino-driven winds from neutron star merger remnants. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 443, 3134–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakar, E.; Piran, T. Detectable radio flares following gravitational waves from mergers of binary neutron stars. Nature 2011, 478, 82–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzati, D.; Deich, A.; Morsony, B.J.; Workman, J.C. Off-axis emission of short γ-ray bursts and the detectability of electromagnetic counterparts of gravitational-wave-detected binary mergers. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 471, 1652–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakar, E.; Piran, T. The Observable Signatures of GRB Cocoons. Astrophys. J. 2017, 834, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromberg, O.; Nakar, E.; Piran, T.; Sari, R. The Propagation of Relativistic Jets in External Media. Astrophys. J. 2011, 740, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzati, D.; López-Cámara, D.; Cantiello, M.; Morsony, B.J.; Perna, R.; Workman, J.C. Off-axis Prompt X-ray Transients from the Cocoon of Short Gamma-Ray Bursts. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 848, L6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, O.; Nakar, E.; Piran, T. The cocoon emission—An electromagnetic counterpart to gravitational waves from neutron star mergers. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 473, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathirgamaraju, A.; Barniol Duran, R.; Giannios, D. Off-axis short GRBs from structured jets as counterparts to GW events. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 473, L121–L125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, O.; Nakar, E.; Piran, T.; Hotokezaka, K. A cocoon shock breakout as the origin of the γ-ray emission in GW170817. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 479, 588–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piran, T.; Nakar, E.; Rosswog, S. The electromagnetic signals of compact binary mergers. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 430, 2121–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotokezaka, K.; Piran, T. Mass ejection from neutron star mergers: Different components and expected radio signals. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 450, 1430–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eerten, H.J.; MacFadyen, A.I. Synthetic Off-axis Light Curves for Low-energy Gamma-Ray Bursts. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2011, 733, L37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eerten, H.; van der Horst, A.; MacFadyen, A. Gamma-Ray Burst Afterglow Broadband Fitting Based Directly on Hydrodynamics Simulations. Astrophys. J. 2012, 749, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzati, D.; Perna, R.; Morsony, B.J.; López-Cámara, D.; Cantiello, M.; Ciolfi, R.; giacomazzo, B.; Workman, J.C. Late time afterglow observations reveal a collimated relativistic jet in the ejecta of the binary neutron star merger GW170817. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1712.03237. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.; Zrake, J.; MacFadyen, A. Numerical simulations of the jet dynamics and synchrotron radiation of binary neutron star merger event GW170817/GRB170817A. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1804.09345. [Google Scholar]
- Duffell, P.C.; Quataert, E.; Kasen, D.; Klion, H. Jet Dynamics in Compact Object Mergers: GW170817 Likely had a Successful Jet. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1806.10616. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, R.; Granot, J. Afterglow Imaging and Polarization of Misaligned Structured GRB Jets and Cocoons: Breaking the Degeneracy in GRB 170817A. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 4, 4128–4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakar, E.; Gottlieb, O.; Piran, T.; Kasliwal, M.M.; Hallinan, G. From γ to Radio—The Electromagnetic Counterpart of GW 170817. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1803.07595. [Google Scholar]
- Zrake, J.; Xie, X.; MacFadyen, A. Radio sky maps of the GRB 170817A afterglow from simulations. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1806.06848. [Google Scholar]
- Granot, J.; De Colle, F.; Ramirez-Ruiz, E. Off-axis afterglow light curves and images from 2D hydrodynamic simulations of double-sided GRB jets in a stratified external medium. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1803.05856. [Google Scholar]
- Salafia, O.S.; Ghisellini, G.; Ghirlanda, G.; Colpi, M. GRB170817A: A giant flare from a jet-less double neutron-star merger? arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1711.03112. [Google Scholar]
- Salafia, O.S.; Ghisellini, G.; Ghirlanda, G. Jet-driven and jet-less fireballs from compact binary mergers. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 474, L7–L11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, H.; Yu, C.; Huang, L. A magnetically driven origin for the low luminosity GRB 170817A associated with GW170817. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 18, 067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, G.P.; Kobayashi, S. GRB 170817A as a jet counterpart to gravitational wave trigger GW 170817. arXiv, 2017; arXiv:1710.05857. [Google Scholar]
- Ziaeepour, H. Prompt gamma-ray emission of GRB 170817A associated with GW 170817: A consistent picture. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, arXiv:1801.06124478, 3233–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veres, P.; Mészáros, P.; Goldstein, A.; Fraija, N.; Connaughton, V.; Burns, E.; Preece, R.D.; Hamburg, R.; Wilson-Hodge, C.A.; Briggs, M.S.; et al. Gamma-ray burst models in light of the GRB 170817A—GW170817 connection. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1802.07328. [Google Scholar]
- Beniamini, P.; Petropoulou, M.; Barniol Duran, R.; Giannios, D. A lesson from GW170817: Most neutron star mergers result in tightly collimated successful GRB jets. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1808.04831. [Google Scholar]
- Hotokezaka, K.; Kiuchi, K.; Shibata, M.; Nakar, E.; Piran, T. Synchrotron radiation from the fast tail of dynamical ejecta of neutron star mergers. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1803.00599. [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki, R.; Ioka, K.; Nakamura, T. Prompt emission from the counter jet of a short gamma-ray burst. Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys. 2018, 2018, 033E01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Messenger, C.; Heng, I.S. Probing Intrinsic Properties of Short Gamma-Ray Bursts with Gravitational Waves. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 181102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzger, B.D.; Beniamini, P.; Giannios, D. Effects of Fallback Accretion on Protomagnetar Outflows in Gamma-Ray Bursts and Superluminous Supernovae. Astrophys. J. 2018, 857, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1. | A top-hat jet is one with constant Lorentz factor and emissivity within the jet that goes sharply to zero outside of jet opening angle. It is the simplest model to explain GRBs have been widely used to explain GRB properties. |
| 2. | An outflow that has a finite angular extent that ends at the boundary of a cone has an opening angle defined by the axis of the cone and the cone itself. |
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).