Abstract
Recently, many studies indicate that the GeV gamma ray excess signal from the central Milky Way can be best explained by ∼40–50 GeV dark matter annihilating via the channel. However, this model appears to be disfavored by the recent Fermi-LAT data for dwarf spheroidal galaxies and the constraint from synchrotron radiation. In this article, we describe a consistent picture to relieve the tensions between the dark matter annihilation model and the observations. We show that a baryonic feedback process is the key to alleviate the tensions and the ∼40–50 GeV dark matter model is still the best one to account for the GeV gamma ray excess in the Milky Way.
1. Introduction
In the past few years, a considerable amount of excess GeV gamma rays emitted from our Galactic center were reported [1,2]. This excess signal, of GeV gamma rays, is difficult to explain with cosmic ray and pulsar emission [3,4]. Also, the energy dependence of the excess signal does not match the one emitted from pulsars [5]. Although some studies are still examining the astrophysical interpretation of the GeV gamma ray excess [6,7,8,9,10], many recent studies are focusing on the possibility of dark matter annihilation to explain the excess [4,5,11,12,13,14].
In particular, Daylan et al. (2014) [4] claimed that the gamma ray spectrum obtained from Fermi-LAT can be best fit with –40 GeV dark matter annihilation via the channel, with cross section – cm s. Abazajian et al. (2014) [12] used similar methods and obtain a slightly different best-fit mass GeV and cross section cm s. Interestingly, the cross sections obtained are close to the expected canonical thermal relic abundance cross section cm s. Moreover, the inner slope of the dark matter density determined from the morphology of the gamma ray flux is – (best-fit is ) [4,14], which is consistent with the theoretical expectation from dark matter-only numerical simulations (–) [15,16,17,18]. Later, by considering the foreground and background uncertainties, Calore et al. (2015) [14] obtained a new best-fit dark matter mass and cross section for the annihilation channel ( GeV and cm s).
However, the last six years of Fermi-LAT data for Milky Way dwarf spheroidal galaxies give a stringent constraint on the annihilation cross section [19]. The upper limit of the cross section for 50 GeV dark matter annihilating via the channel is cm s [19], which is smaller than all of the best-fit cross sections mentioned above. By marginalizing the parameters of the Milky Way, Abazajian and Keeley (2015) [20] obtained a very small parameter space which can satisfy both the excess GeV gamma ray data for the Milky Way and the gamma ray flux upper limit for the Milky Way dwarf spheroidal galaxies. Nevertheless, the required concentration parameter is very high (), which is disfavored by observations [20].
Furthermore, the data from synchrotron radiation also provide a stringent constraint on the annihilation cross section. By using the observed radio flux at 408 MHz emitted from a small region ( pc) near the Galactic center [21], the largest annihilation cross section is constrained to cm s for GeV and [22], which is smaller than the best-fit annihilation cross section. Also, it has been suggested that the supermassive black hole would steepen the dark matter density profile in its sphere of influence (within 1.7 pc) [23]. If the supermassive black hole grows adiabatically from a smaller seed, the density spike would give a strong enhancement of the annihilation signal [23,24]. If this is the case, the resulting upper limit based on radio observations would be much tighter. In fact, based on the gamma ray observations, Fields et al. (2014) [24] showed that the popular model with the density spike does not satisfy the observed upper limit within of the Galactic center for .
Based on the above discussion, it seems that the most popular dark matter annihilation model is in considerable tension with observations. In this article, we point out that one important process, the baryonic feedback process, has not been seriously taken into account in the above evaluations. If the baryonic feedback process can remove the cusp structure of dark matter, then ∼40–50 GeV dark matter annihilating via can escape from all of the above constraints. In other words, this dark matter annihilation model can still provide the best explanation of the GeV gamma ray excess in the Galactic center. In fact, if we include the confidence levels of the exclusion limits (95%) for all of the observed constraints, the tension would be much milder. Nevertheless, it is still important to consider the effect of baryons if they can alleviate the tension to a large extent. This description can also give a complete and better picture for the GeV gamma ray excess problem.
2. The Spike Structure and the Synchrotron Radiation Constraint
It is commonly believed that the supermassive black hole, with mass , at the Galactic center dominates the gravitational potential. Assume that dark matter particles are collisionless and the supermassive black hole grows adiabatically from a small seed. Within its sphere of influence ( pc) [24], the inner slope of the dark matter density for would increase to a larger value, which is given by the following relation (for ) [24]:
For the best-fit value in the interpretation of the GeV excess [4,14], we have . Fields et al. (2014) [24] showed that this effect would greatly increase the annihilation signal within 0.0031 pc. The expected gamma ray flux for 35.25 GeV dark matter annihilating via the channel is cm s, which is much larger than the observed upper limit cm s [24]. In other words, the emission from a canonical adiabatic black hole spike is inconsistent with a dark matter interpretation of the Galactic center GeV gamma ray excess [24].
However, if the original inner slope is not 1.26, but a value close to zero, the resulting enhanced slope would be 1.5 instead. The corresponding dark matter density profile is given by [23]:
where is the central dark matter density, is the velocity dispersion, and is the Schwarzschild radius. In fact, recent simulations suggest that baryonic effects on the dark matter distribution are not negligible [25]. For example, the feedback from supernova explosions and star formation can generate outflows and transfer energy to dark matter components that form core-like structures [25,26,27]. If baryonic gas is locally removed on a short timescale due to supernova explosions or star formation, the gravitational force holding the dark matter would decrease, such that the dark matter particles would move outwards (to a larger radius). In other words, dark matter gains energy and the central dark matter density would decrease [25]. If this process repeats, the effect of energy transfer would be accumulative and the slope of the central dark matter density becomes flatter. This global effect of baryonic feedback has been verified by numerical simulations [27] and the result is consistent with the observations that many galaxies exhibit a flatter central dark matter density slope or core-like dark matter structures [28,29,30]. Therefore, the baryonic feedback model can provide a possible solution to address a serious problem in cold dark matter cosmology; the core-cusp problem [26]. Based on numerical simulations, the inner slope at pc is approximately given by [27]:
where is the enclosed stellar mass within 500 pc. By using the latest Milky Way bulge profile from Reference [31], the total stellar mass within 500 pc is . Hence, from Equation (3), we get , which is close to a flat central density. In other words, due to the baryonic feedback, the inner slope of the dark matter density decreases from 1.26 to 0.17 when r is decreased from kpc to pc. Therefore, it is very likely that the inner slope decreases to when . Notice that this argument does not affect the best empirical fit of the density slope () from the Fermi-LAT data, since most of the data obtained are for kpc [14]. Therefore, we are suggesting for kpc and for kpc. The density profile is neither a generalized Navarro-Frenk-White (NFW) profile nor a Burkert profile.
According to Equation (2), the enhanced inner slope due to the supermassive black hole would give . From Reference [24], the resulting gamma ray flux would not exceed the observational upper limit if . Therefore, this model can escape from the central gamma ray constraint.
In fact, the shallower density profile in the Milky Way is supported by the recent numerical simulation results of References [32,33]. N-body simulations show that Milky Way-like galaxies exhibit a flattening in the dark matter density profile for kpc and the density profile’s slope is steeper than 1 [32,33]. However, the analysis in Reference [32] shows that this model fails to reproduce the right morphology of the excess in the innermost regions, for the shallower profile. Observational data favor within 1–10 kpc of the Milky Way [14]. Nevertheless, if we include the `spike contribution’, this problem would be reconciled. Based on the results in Reference [24], the spike-enhanced gamma ray flux () at GeV within is ∼ cm s sr GeV, which matches the observed flux within [14]. For the outer region, the flux at GeV can be given by , where kpc, is the central dark matter density and is the gamma ray spectrum of dark matter annihilation. Combining it with the spike-enhanced gamma ray flux within , the total flux can be obtained (see Figure 1), which is close to the observed flux. However, the flux at about may be overestimated because the actual dark matter density is somewhat lower than the central density, as assumed in this simplified model. Therefore, the spike-enhanced flux together with the flux due to the shallower density emission can generally account for the observed morphology.
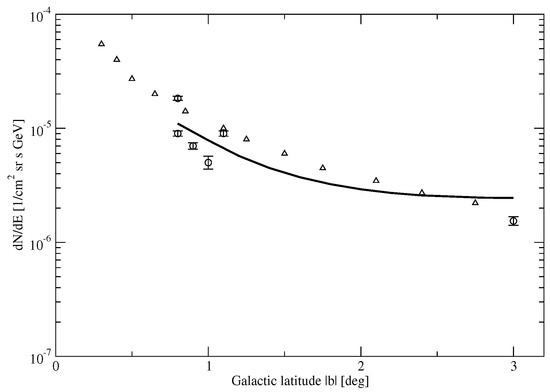
Figure 1.
The morphology of our model’s prediction (solid line). The data of the graph are reproduced from Figure 1 of Reference [14]. The triangles represent the profile of .
Since dark matter annihilating via the channel also produces electron and positron pairs, the cooling of these electron and positron pairs would give a large amount of synchrotron radiation if the magnetic field B at the Galactic center is strong. The radio flux (erg cm s) observed at frequency due to dark matter annihilation is given by [34]:
where is the dark matter density, is the electron spectrum of dark matter annihilation, and:
The magnetic field near the Galactic center is usually modeled by [22,35]:
The radio observations at 408 MHz from the Jodrell Bank telescope obtained in Reference [21] provide the most stringent limit on the dark matter annihilation cross section [22]. The flux upper limit from the inner 4 cone around the Galactic center is erg cm s [21,35]. If the inner slope of the dark matter density is , this limit constrains the annihilation cross section to smaller than cm s for GeV [22]. Nevertheless, as mentioned above, if the inner slope is shallower due to baryonic feedback, the predicted flux would be much smaller. By using the dark matter density expression in Equation (2) and assuming 50 GeV dark matter annihilating via the channel with cm s, the radio flux calculated by Equation (4) is erg cm s, which is smaller than the observed upper limit. Therefore, the annihilation model can satisfy the synchrotron radiation constraint if we consider the baryonic feedback process.
Note that the systematic uncertainties of the magnetic field profile in Equation (6) are quite large in the Milky Way (see the discussion in Reference [22]). Since the radio constraint is highly dependent on the magnetic field strength, the resulting radio constraint also has large uncertainties. Nevertheless, here we show that our proposal can relieve the tension between the radio constraint with this specific magnetic field profile (Equation (6)) and the gamma ray constraint.
3. Constraints for Milky Way Dwarf Spheroidal Galaxies
The six years of Fermi-LAT data for Milky Way dwarf spheroidal galaxies put a tight constraint on the dark matter annihilation cross section. For 50 GeV dark matter annihilating via the channel, the 95% confidence level (C.L.) upper limit is cm s (for the NFW dark matter profile) [19], which is in mild tension with the fitted results in Reference [14]. However, recent studies suggest that many dwarf galaxies exhibit core-like structures [25,26]. In particular, the observed rotation curves of the Milky Way dwarf spheroidal galaxies indicate the existence of cored dark matter halos [36,37]. The dark matter density of these galaxies can be well fit by the Burkert profile [36]:
where and are the core radius and core density respectively. The origin of the cored-profile is a controversial issue [26]. Although the total baryonic mass is small in dwarf galaxies, the effect of baryonic feedback on dark matter density may not be negligible. This can be supported by the results of numerical simulations [27]. If we assume that the dark matter density of the dwarf spheroidal galaxies follows the Burkert profile, the upper limit of the annihilation cross section constraint would be larger than cm s since the total dark matter content is overestimated in that case. This effect can be reflected by the J-factor calculation (). For example, the J-factor of the Draco dwarf galaxy is for the NFW profile within sr [19]. If we use the Burkert profile with the parameters in Reference [38], the revised J-factor would be , which is 40% smaller. The parameters of the Burkert profile for each dwarf galaxy can be obtained in Reference [39]. The revised J-factor can be calculated by the stacked analysis [40]. Including this effect from all of the dwarf galaxies, based on the analysis in Reference [19], the upper limit of the stacked analysis would increase by a factor of 1.25 for 50 GeV dark matter. Therefore, the new upper limit is cm s, which is consistent with the fitted result in Reference [14]; cm s (see Figure 2).
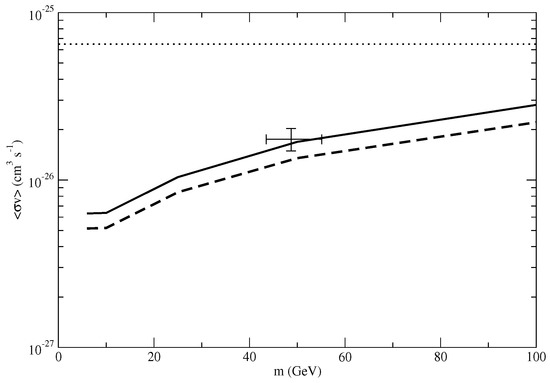
Figure 2.
The upper limits of the annihilation cross section obtained from Fermi-LAT data for Milky Way dwarf spheroidal galaxies (solid line: Burkert profile; dashed line: NFW profile) [19]. The data point with error bars is the best-fit range obtained in Reference [14]. The dotted line is the upper limit obtained from the radio constraint [21].
4. Discussion
In this article, by considering the effect of baryonic feedback, we show that the most popular annihilation model (40–50 GeV dark matter annihilating via ) basically satisfies the most stringent constraint, the synchrotron radiation constraint, even if a density spike exists near the supermassive black hole. Also, based on the analysis in Reference [24], the gamma ray flux from dark matter annihilation due to the density spike would not exceed the current GeV gamma ray upper limit. Therefore, baryonic feedback can relieve the tensions among the adiabatic growth model of the supermassive black hole, the 40–50 GeV dark matter annihilation model (via the channel), and the observational constraint of synchrotron radiation within 4″.
Furthermore, we point out that the annihilation model can satisfy the current upper limit of gamma ray flux for Milky Way spheroidal galaxies, if we assume that the dark matter density profile follows the Burkert profile. This assumption can be supported by numerical simulations which show that the inner slope of the dark matter density is flatter than those obtained in dark matter-only simulations [27]. If we combine the results for the Milky Way and Milky Way dwarf spheroidal galaxies, the revised range of annihilation cross section would be – cm s for GeV. To conclude, baryonic feedback may be an important key to relieve the tensions in the dark matter interpretation of the GeV gamma ray excess. Further observations and numerical simulations are required to test our suggestions.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by a grant from the Education University of Hong Kong (Project No.: 04256).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hooper, D.; Slatyer, T.R. Two emission mechanisms in the Fermi Bubbles: A possible signal of annihilating dark matter. Phys. Dark Universe 2013, 2, 118–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.-C.; Urbano, A.; Xue, W. Fermi Bubbles under dark matter scritiny. Part I: Astrophysical analysis. arXiv. 2013. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1307.6862.pdf (accessed on 22 August 2018).
- Hooper, D.; Cholis, I.; Linden, T.; Siegal-Gaskins, J.; Slatyer, T. Millisecond pulsars cannot account for the inner Galaxy’s GeV excess. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 88, 083009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daylan, T.; Finkbeiner, D.P.; Hooper, D.; Linden, T.; Portillo, S.K.N.; Rodd, N.L.; Slatyer, T.R. The charaterization of the gamma-ray signal from the central Milky Way: A case for annihilating dark matter. Phys. Dark Universe 2016, 12, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calore, F.; Cholis, I.; Weniger, C. Background model systematics for the Fermi GeV excess. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2015, 2015, 038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Zhang, B. Millisecond pulsar interpretation of the Galactic center gamma-ray excess. J. High Energy Astrophys. 2014, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrović, J.; Serpico, P.D.; Zaharijas, G. Millisecond pulsars and the Galactic Center gamma-ray excess: The importance of luminosity function and secondary emission. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2015, 2015, 023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaggero, D.; Taoso, M.; Urbano, A.; Valli, M.; Ullio, P. Towards a realistic astrophysical interpretation of the gamma-ray Galactic center excess. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2015, 2015, 056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, T.D.; Kocsis, B. Disrupted globular clusters can explain the Galactic Center gamma-ray excess. Astrophys. J. 2015, 812, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, R.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Weniger, C. Strong support for the millisecond pulsar origin of the Galactic Center GeV excess. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 051102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, C.; Macias, O. Dark matter and pulsar model constraints from Galactic Center Fermi-LAT gamma-ray observations. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 88, 083521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abazajian, K.N.; Canac, N.; Horiuchi, S.; Kaplinghat, M. Astrophysical and dark matter interpretations of extended gamma-ray emission from the Galactic Center. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 90, 023526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izaguirre, E.; Krnjaic, G.; Shuve, B. Bottom-up approach to the Galactic Center excess. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 90, 055002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calore, F.; Cholis, I.; McCabe, C.; Weniger, C. A tale of tails: Dark matter interpretations of the Fermi GeV excess in light of background model systematics. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 91, 063003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, J.F.; Frenk, C.S.; White, S.D.M. A universal density profile from hierarchical clustering. Astrophys. J. 1997, 490, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, B.; Quinn, T.; Governato, F.; Stadel, J.; Lake, G. Cold collapse and the core catastrophe. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1999, 310, 1147–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, E.; Navarro, J.F.; Power, C.; Jenkins, A.; Frenk, C.S.; White, S.D.M.; Springel, V.; Stadel, J.; Quinn, T.R. The inner structure of ΛCDM haloes—II. Halo mass profiles and low surface brightness galaxy rotation curves. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2004, 355, 794–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diemand, J.; Moore, M.Z.B.; Stadel, J.; Carollo, C.M. Cusps in cold dark matter haloes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2005, 364, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, M.; Albert, A.; Anderson, B.; Atwood, W.B.; Baldini, L.; Barbiellini, G.; Bastieri, D.; Bechtol, K.; Bellazzini, R.; Bissaldi, E.; et al. Searching for dark matter annihilation from Milky Way dwarf spheroidal galaxies with six years of Fermi Large Area Telescope data. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 115, 231301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abazajian, K.N.; Keeley, R.E. Bright gamma-ray Galactic Center excess and dark dwarfs: Strong tension for dark matter annihilation despite Milky Way halo profile and diffuse emission uncertainties. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 93, 083514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, R.D.; Walsh, D.; Booth, R.S. The radio source at the galactic nucleus. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1976, 177, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholis, I.; Hooper, D.; Linden, T. A critical reevaluation of radio constraints on annihilating dark matter. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 91, 083507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondolo, P.; Silk, J. Dark matter annihilation at the Galactic Center. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 83, 1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, B.D.; Shapiro, S.L.; Shelton, J. Galactic Center gamma-ray excess from dark matter annihilation: Is there a black hole spike? Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 151302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontzen, A.; Governato, F. Cold dark matter heats up. Nature 2014, 506, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Blok, W.J.G. The core-cusp problem. Adv. Astron. 2010, 2010, 789293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Governato, F.; Zolotov, A.; Pontzen, A.; Christensen, C.; Oh, S.H.; Brooks, A.M.; Quinn, T.; Shen, S.; Wadsley, J. Cuspy no more: How outflows affect the central dark matter and baryon distribution in Λ cold dark matter galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 422, 1231–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salucci, P.; Burkert, A. Dark matter scaling relations. Astrophys. J. 2000, 537, L9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.-H.; de Blok, W.J.G.; Brinks, E.; Walter, F.; Kennicutt, R.C. Dark and luminous matter in THINGS dwarf galaxies. Astron. J. 2011, 141, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeb, A.; Weiner, N. Cores in dwarf galaxies from dark matter with a Yukawa potential. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 171302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binney, J.; Piffl, T. The distribution function of the Galaxy’s dark halo. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 454, 3653–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calore, F.; Bozorgnia, N.; Lovell, M.; Bertone, G.; Schaller, M.; Frenk, C.S.; Crain, R.A.; Schaye, J.; Theuns, T.; Trayford, J.W. Simulated Milky Way analogues: Implications for dark matter indirect searches. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2015, 2015, 053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaller, M.; Frenk, C.S.; Theuns, T.; Calore, F.; Bertone, G.; Bozorgnia, N.; Crain, R.A.; Fattahi, A.; Navarro, J.F.; Sawala, T.; et al. Dark matter annihilation radiation in hydrodynamic simulations of Milky Way haloes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 455, 4442–4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Profumo, S.; Ullio, P. Multi-wavelength studies. In Particle Dark Matter: Observations, Models and Searches; Bertone, G., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bertone, G.; Cirelli, M.; Strumia, A.; Taoso, M. Gamma-ray and radio tests of the e± excess from DM annihilations. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2009, 2009, 009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salucci, P.; Wilkinson, M.I.; Walker, M.G.; Gilmore, G.F.; Grebel, E.K.; Koch, A.; Martins, C.F.; Wyse, R.F.G. Dwarf spheroidal galaxy kinematics and spiral galaxy scaling laws. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 420, 2034–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkert, A. The structure and dark halo core properties of dwarf spheroidal galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2015, 808, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringmann, T.; Doro, M.; Fornasa, M. Dark matter signals from Draco and Willman 1: Prospects for MAGIC II and CTA. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2009, 2009, 016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, G.D. A robust determination of Milky Way satellite properties using hierarchical mass modelling. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 451, 2524–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Morales, A.X.; Profumo, S.; Queiroz, F.S. Effect of black holes in local dwarf spheroidal galaxies on gamma-ray constraints on dark matter annihilation. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 90, 103508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).