A Study of Background Conditions for Sphinx—The Satellite-Borne Gamma-Ray Burst Polarimeter
Abstract
:1. Introduction
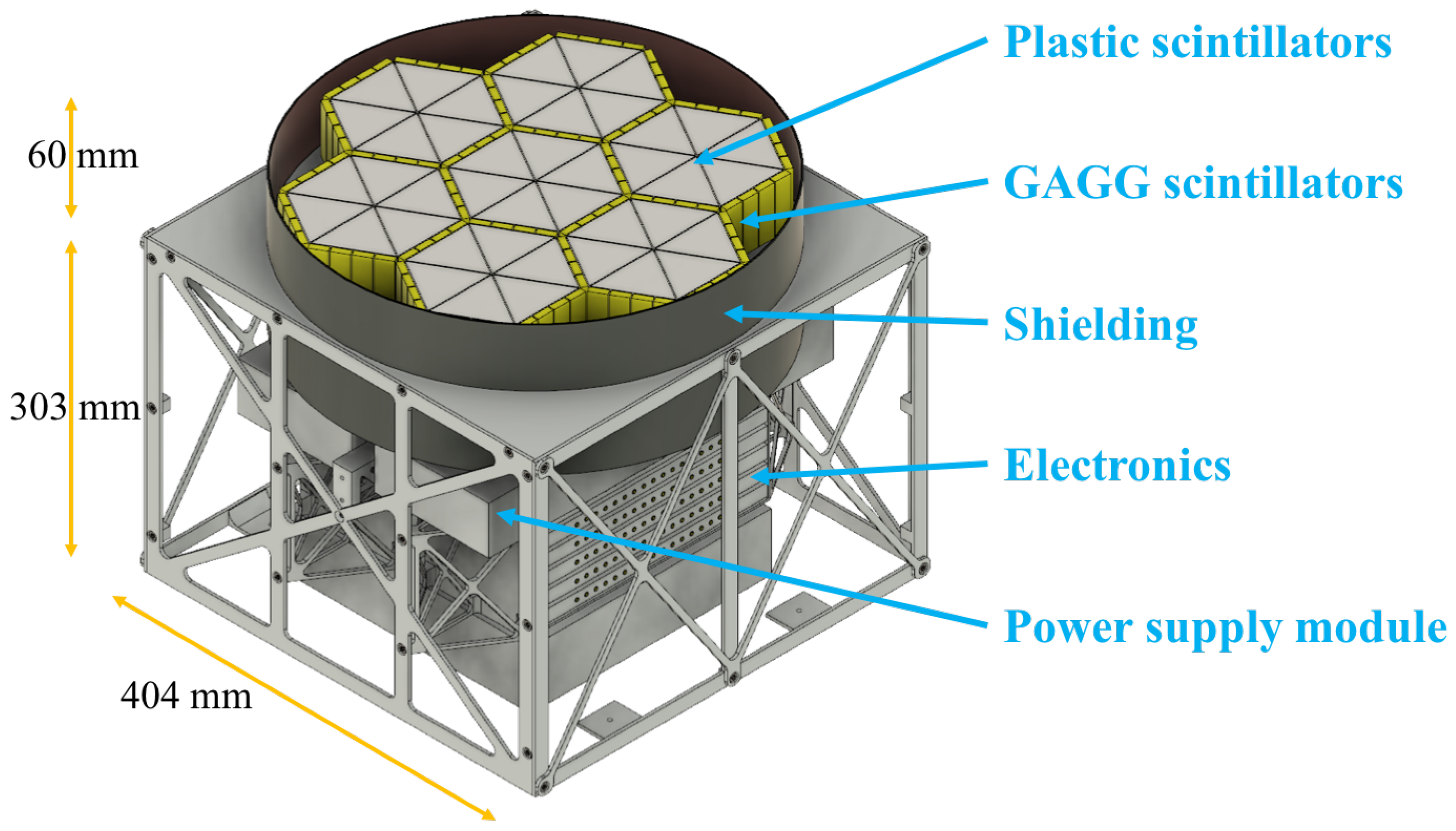
2. Instrument Design and Properties
3. Geant4 Simulation
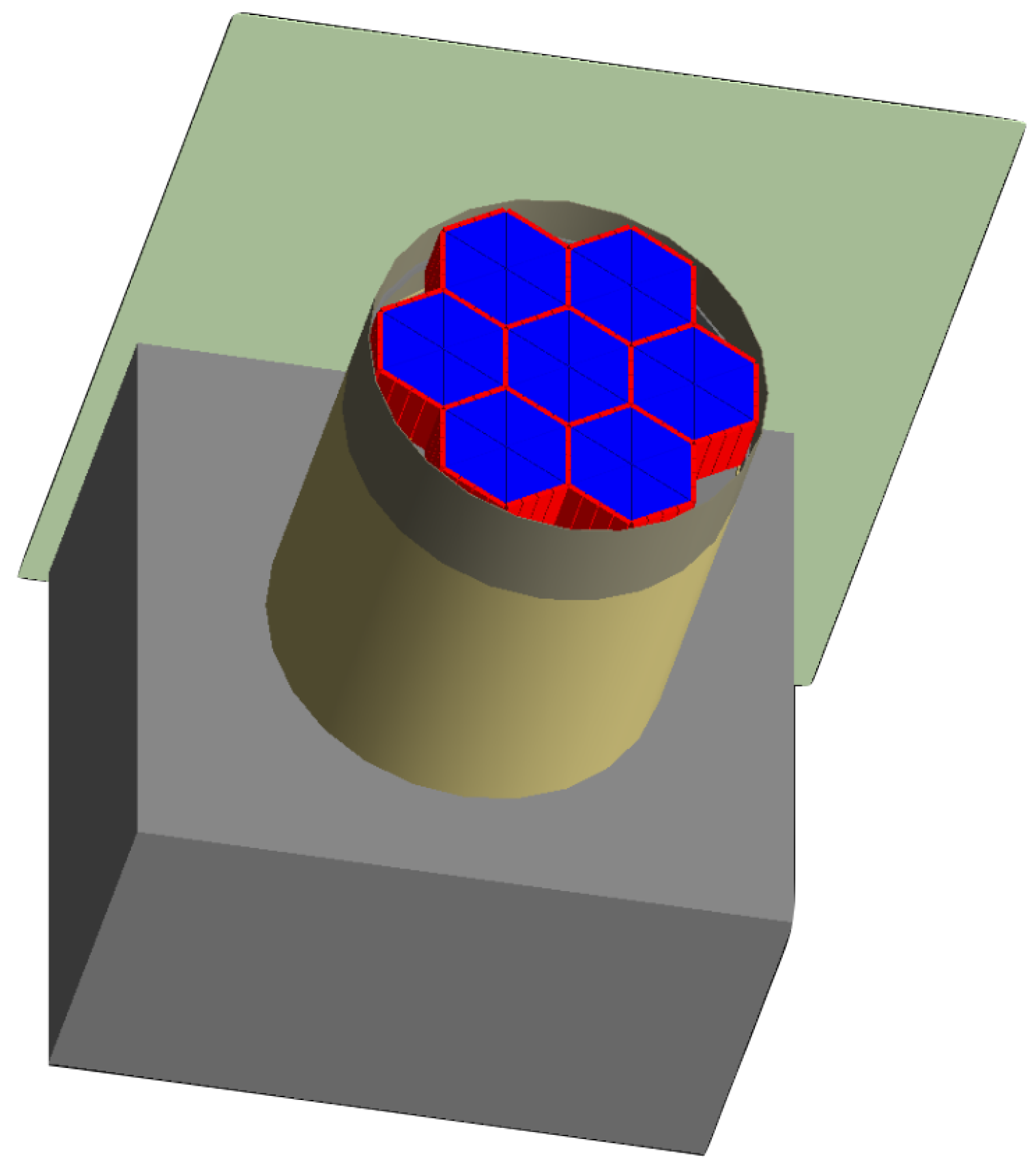
3.1. Geometric Model
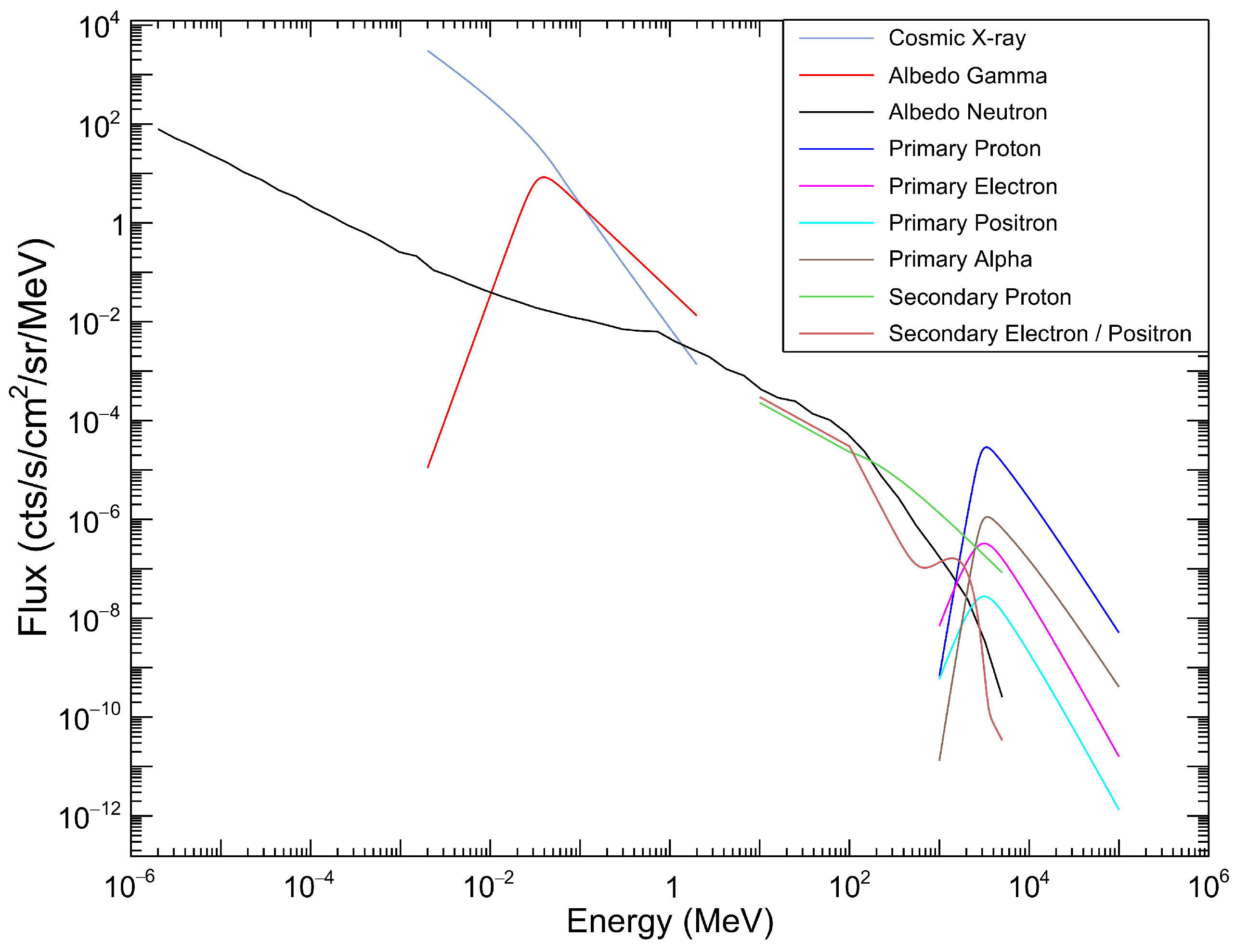
3.2. Space Radiation Environment
3.3. Physics Model for Particle Interactions
3.4. Data Analysis
- All hits must have an energy deposit exceeding the HT.
- At least one hit has an energy deposit above the TT.
- No hit has an energy deposit exceeding the UD.
4. Results
4.1. Prompt Background
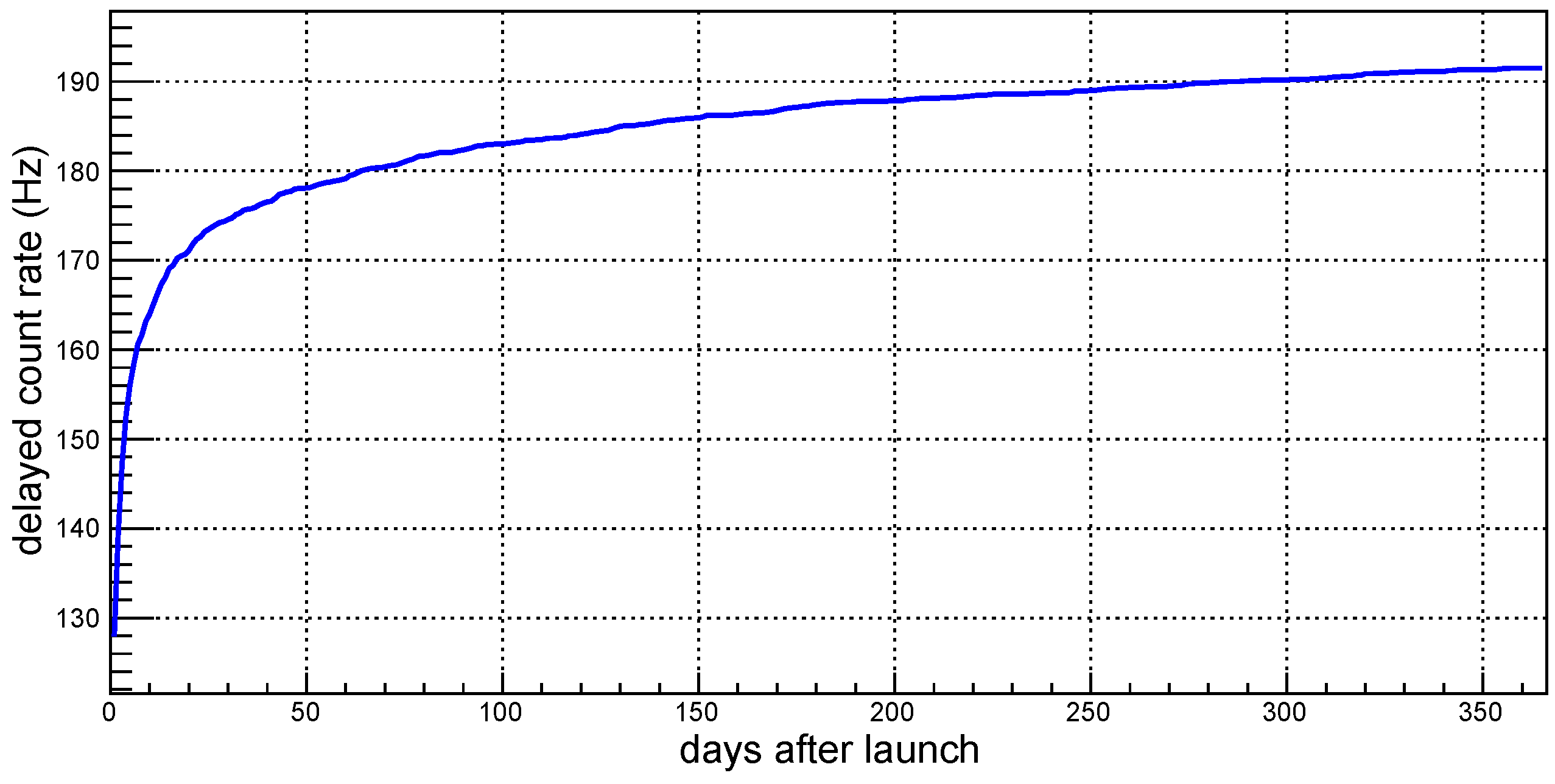
4.2. Delayed Background
4.3. Upper Discriminator Selection
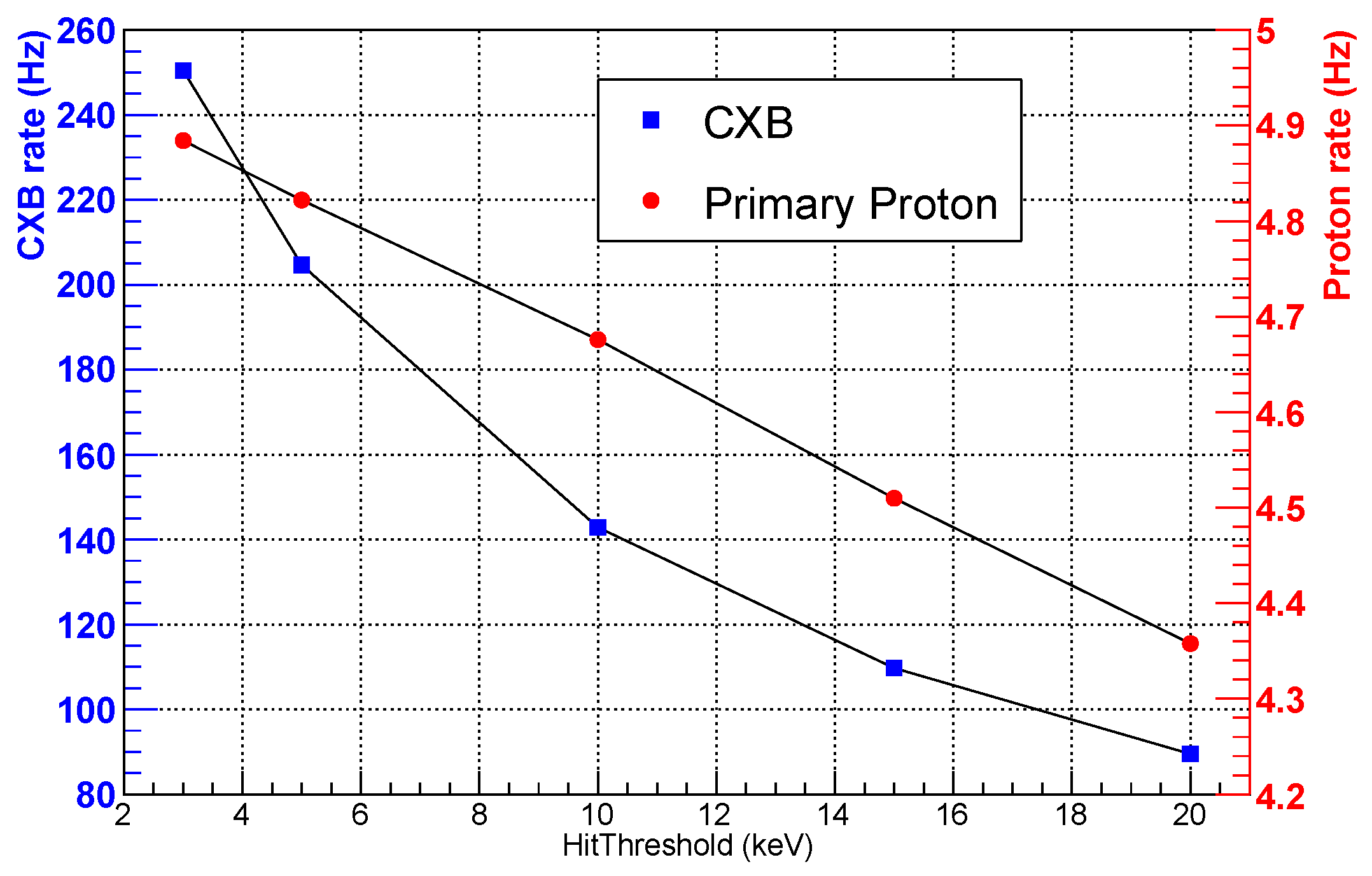
4.4. Hit Threshold
5. Summary
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meszaros, P. Gamma-ray bursts. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2006, 69, 2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woosley, S.E. Gamma-ray bursts from stellar mass accretion disks around black holes. Astrophys. J. 1993, 405, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichler, D.; Livio, M.; Piran, T.; Schramm, D.N. Nucleosynthesis, neutrino bursts and γ-rays from coalescing neutron stars. Nature 1989, 340, 126–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Affeldt, C. Gravitational waves and gamma-rays from a binary neutron star merger: GW170817 and GRB 170817A. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017, 848, L13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waxman, E. Astronomy: New direction for γ-rays. Nature 2003, 423, 388–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, A.J.; Bird, A.J.; Diallo, N.; Ferguson, C.; Lockley, J.J.; Shaw, S.E.; Willis, D.R. The modelling of background noise in astronomical gamma ray telescopes. Space Sci. Rev. 2003, 105, 285–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostinelli, S.; Allison, J.; Amako, K.A.; Apostolakis, J.; Araujo, H.; Arce, P.; Behner, F. GEANT4—A simulation toolkit. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 2003, 506, 250–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Produit, N.; Bao, T.W.; Batsch, T.; Bernasconi, T.; Britvich, I.; Cadoux, F.; Hajdas, W. Design and construction of the POLAR detector. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. A 2018, 877, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneyama, M.; Kataoka, J.; Arimoto, M.; Masuda, T.; Yoshino, M.; Kamada, K.; Usuki, Y. Evaluation of GAGG: Ce scintillators for future space applications. J. Instrum. 2018, 13, P02023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Zhang, J.; Song, L.M.; Xiong, S.L.; Guan, J. Simulation of the in-flight background for HXMT/HE. Astrophys. Space. Sci. 2015, 360, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, T.; Kamae, T.; Godfrey, G.; Handa, T.; Thompson, D.J.; Lauben, D.; Ozaki, M. Cosmic-ray background flux model based on a gamma-ray large area space telescope balloon flight engineering model. Astrophys. J. 2004, 614, 1113–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Band, D.; Matteson, J.; Ford, L.; Schaefer, B.; Palmer, D.; Teegarden, B.; Fishman, G. BATSE observations of gamma-ray burst spectra. I-Spectral diversity. Astrophys. J. 1993, 413, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisskopf, M.C.; Elsner, R.F.; O’Dell, S.L. On understanding the figures of merit for detection and measurement of x-ray polarization. Proc. SPIE 2010, 7732, 77320E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, M.; Eliasson, L.; Iyer, N.K.; Kiss, M.; Kushwah, R.; Larsson, J.; Lundman, C.; Mikhalev, V.; Ryde, F.; Stana, T.A.; et al. SPHiNX—A small satellite GRB polarimetry mission. 2018; in preparation. [Google Scholar]
| 1 | InnoSat System Requirements Document from OHB-Sweden, http://www.snsb.se/Global/Forskare/Utlysningar/InnoSat%20System%20Requirements%20Document_IS-OSE-RS-0001_2C.pdf |
| 2 | FERMIGBRST—Fermi GBM Burst Catalog, which has been used in the performance simulation of SPHiNX, https://heasarc.gsfc.nasa.gov/W3Browse/fermi/fermigbrst.html |
| 3 | |
| 4 |
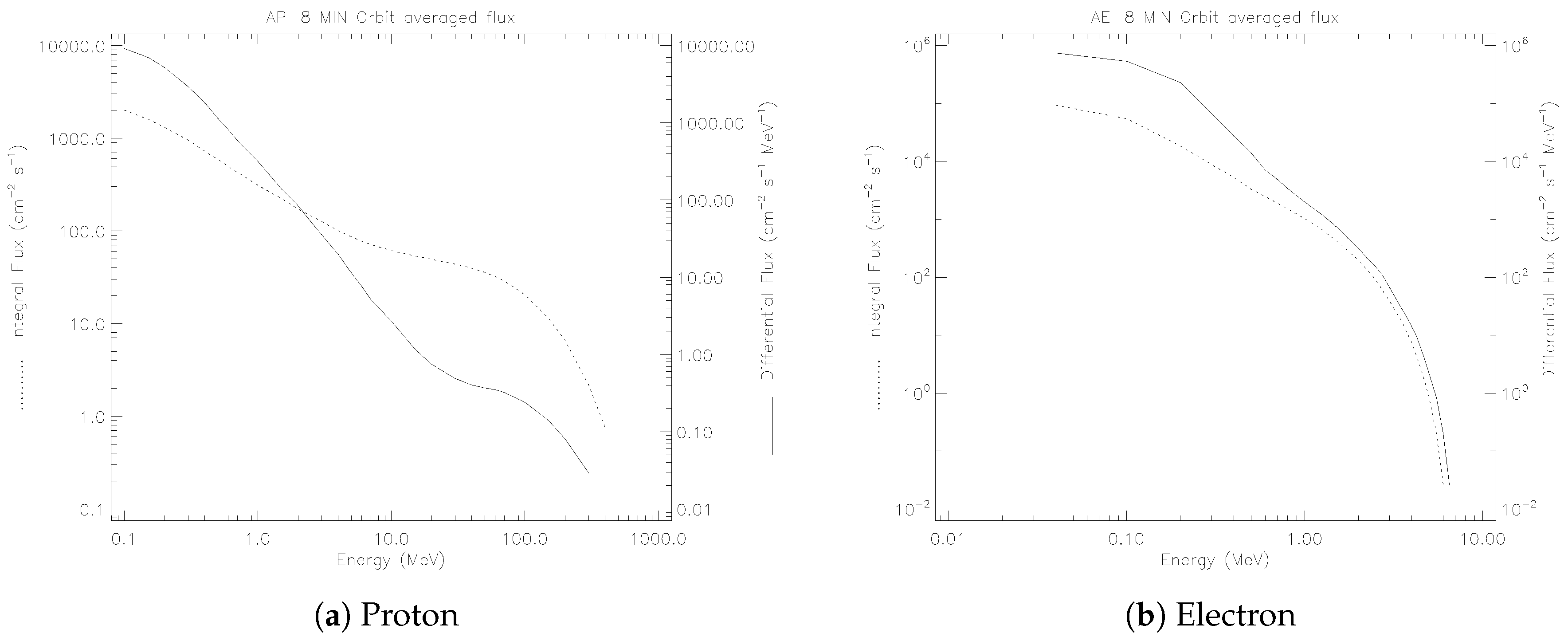
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Field of view | ±60 |
| Energy range | 50–500 keV |
| Effective area | ≥125 cm |
| Energy resolution | ≤30% @ 60 keV |
| Timing resolution | ≤100 ms |
| Parameters | Plastic (keV) | GAGG (keV) |
|---|---|---|
| HT | 5 | 30 |
| TT | 25 | 30 |
| UD | 600 | 600 |
| Component | One-Hit Rate (Hz) | Two-Hit Rate (Hz) | Higher-Multiplicity Rate (Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CXB | 1270.1 | 195.3 | 37.5 |
| Albedo Gamma | 397.5 | 112.9 | 30.8 |
| Albedo Neutron | 14.3 | 5.1 | 2.7 |
| Primary CRs | 15.5 | 5.3 | 2.9 |
| Secondary CRs | 9.2 | 4.5 | 3.3 |
| Total | 1706.6 | 323.1 | 77.2 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, F.; Pearce, M. A Study of Background Conditions for Sphinx—The Satellite-Borne Gamma-Ray Burst Polarimeter. Galaxies 2018, 6, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies6020050
Xie F, Pearce M. A Study of Background Conditions for Sphinx—The Satellite-Borne Gamma-Ray Burst Polarimeter. Galaxies. 2018; 6(2):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies6020050
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Fei, and Mark Pearce. 2018. "A Study of Background Conditions for Sphinx—The Satellite-Borne Gamma-Ray Burst Polarimeter" Galaxies 6, no. 2: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies6020050
APA StyleXie, F., & Pearce, M. (2018). A Study of Background Conditions for Sphinx—The Satellite-Borne Gamma-Ray Burst Polarimeter. Galaxies, 6(2), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies6020050





