Stellar Evolution and Convection in 3D Hydrodynamic Simulations of a Complete Burning Phase
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
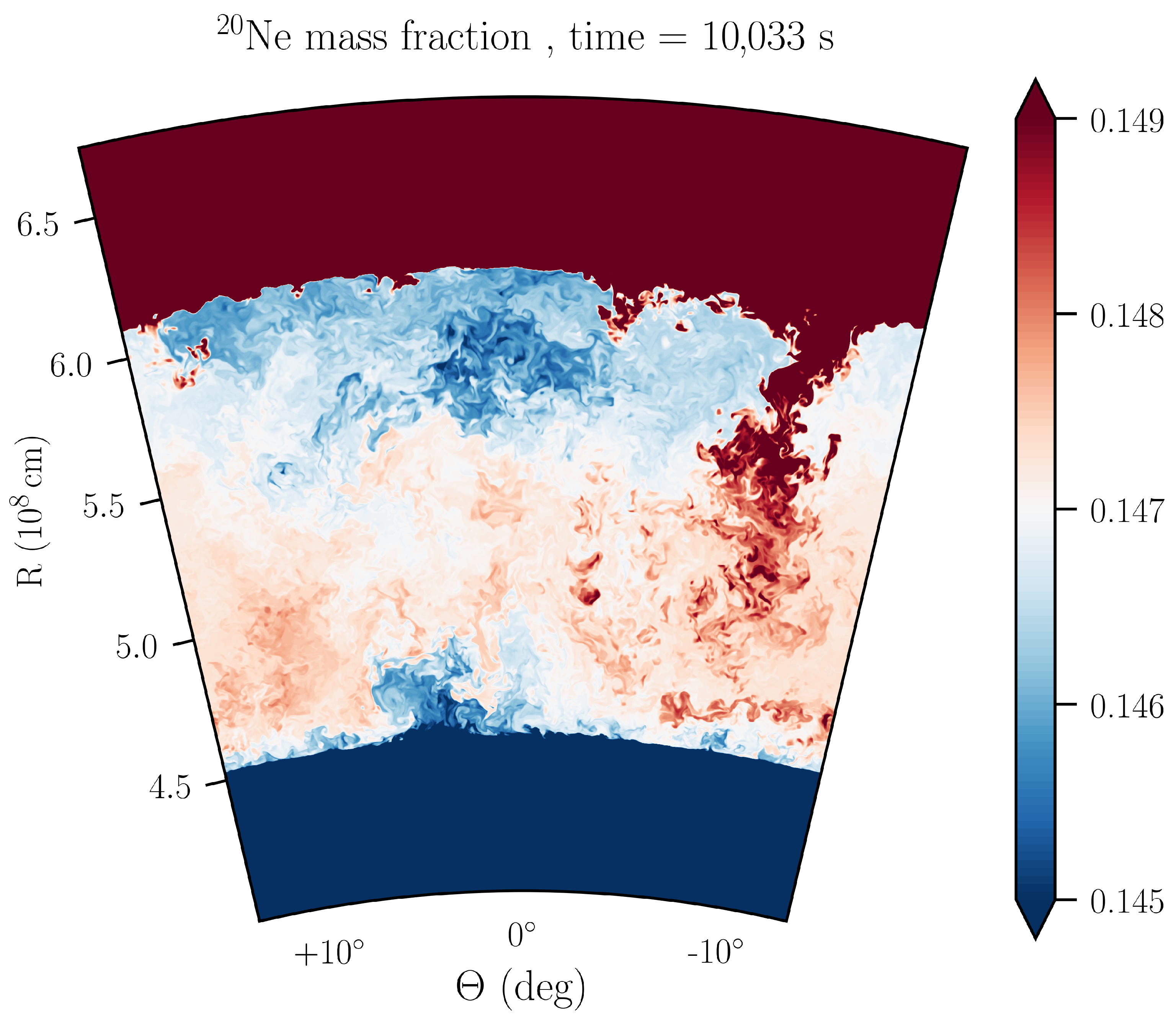
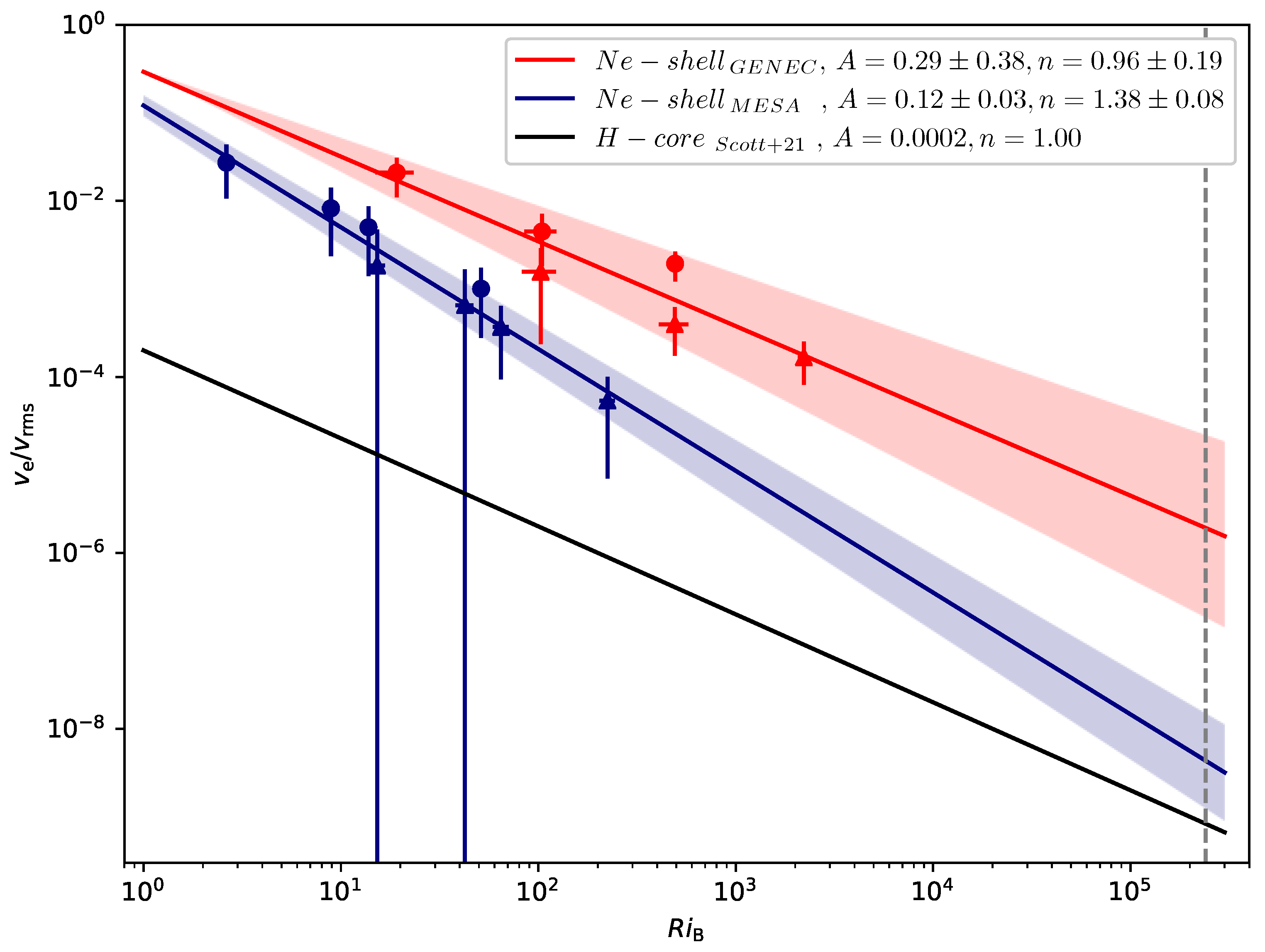
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Böhm-Vitense, E. Über die Wasserstoffkonvektionszone in Sternen verschiedener Effektivtemperaturen und Leuchtkräfte. Z. Astrophys. 1958, 46, 108. [Google Scholar]
- Zahn, J.P. Convective penetration in stellar interiors. Astron. Astrophys. 1991, 252, 179. [Google Scholar]
- Herwig, F.; Bloecker, T.; Schoenberner, D.; El Eid, M. Stellar evolution of low and intermediate-mass stars. IV. Hydrodynamically-based overshoot and nucleosynthesis in AGB stars. Astron. Astrophys. 1997, 324, L81. [Google Scholar]
- Herwig, F.; Freytag, B.; Fuchs, T.; Hansen, J.P.; Hueckstaedt, R.M.; Porter, D.H.; Timmes, F.X.; Woodward, P.R. Convective and Non-Convective Mixing in AGB Stars. Why Galaxies Care About AGB Stars Their Importance Actors Probes ASP Conf. Ser. 2007, 378, 43. [Google Scholar]
- Battino, U.; Pignatari, M.; Ritter, C.; Herwig, F.; Denisenkov, P.; Den Hartogh, J.W.; Trappitsch, R.; Hirschi, R.; Freytag, B.; Thielemann, F.; et al. Application of a Theory and Simulation-based Convective Boundary Mixing Model for AGB Star Evolution and Nucleosynthesis. Astrophys. J. 2016, 827, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battino, U.; Tattersall, A.; Lederer-Woods, C.; Herwig, F.; Denissenkov, P.; Hirschi, R.; Trappitsch, R.; den Hartogh, J.W.; Pignatari, M.; NuGrid Collaboration. NuGrid stellar data set - III. Updated low-mass AGB models and s-process nucleosynthesis with metallicities Z= 0.01, Z = 0.02, and Z = 0.03. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 489, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meakin, C.A.; Arnett, D. Turbulent Convection in Stellar Interiors. I. Hydrodynamic Simulation. Astrophys. J. 2007, 667, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzuti, F.; Hirschi, R.; Arnett, W.D.; Georgy, C.; Meakin, C.; Murphy, A.S.; Rauscher, T.; Varma, V. 3D stellar evolution: Hydrodynamic simulations of a complete burning phase in a massive star. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2023, 523, 2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxton, B.; Bildsten, L.; Dotter, A.; Herwig, F.; Lesaffre, P.; Timmes, F. Modules for Experiments in Stellar Astrophysics (MESA). Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2011, 192, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristini, A.; Hirschi, R.; Meakin, C.; Arnett, D.; Georgy, C.; Walkington, I. Dependence of convective boundary mixing on boundary properties and turbulence strength. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 484, 4645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, H.J.S. Turbulent mixing in stratified fluids. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1991, 23, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzuti, F.; Hirschi, R.; Georgy, C.; Arnett, W.D.; Meakin, C.; Murphy, A.S. Realistic 3D hydrodynamics simulations find significant turbulent entrainment in massive stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 515, 4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, L.J.A.; Hirschi, R.; Georgy, C.; Arnett, W.D.; Meakin, C.; Kaiser, E.A.; Ekström, S.; Yusof, N. Convective core entrainment in 1D main sequence stellar models. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 503, 4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgy, C.; Rizzuti, F.; Hirschi, R.; Varma, V.; Arnett, W.D.; Meakin, C.; Mocak, M.; Murphy, A.S.; Rauscher, T. 3D simulations of a neon burning convective shell in a massive star. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2024, 531, 4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzuti, F.; Hirschi, R.; Varma, V.; Arnett, W.D.; Georgy, C.; Meakin, C.; Mocák, M.; Murphy, A.S.; Rauscher, T. Shell mergers in the late stages of massive star evolution: New insight from 3D hydrodynamic simulations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2024, 533, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rizzuti, F.; Hirschi, R.; Varma, V.; Arnett, W.D.; Georgy, C.; Meakin, C.; Mocák, M.; Murphy, A.S.; Rauscher, T. Stellar Evolution and Convection in 3D Hydrodynamic Simulations of a Complete Burning Phase. Galaxies 2024, 12, 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies12060087
Rizzuti F, Hirschi R, Varma V, Arnett WD, Georgy C, Meakin C, Mocák M, Murphy AS, Rauscher T. Stellar Evolution and Convection in 3D Hydrodynamic Simulations of a Complete Burning Phase. Galaxies. 2024; 12(6):87. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies12060087
Chicago/Turabian StyleRizzuti, Federico, Raphael Hirschi, Vishnu Varma, William David Arnett, Cyril Georgy, Casey Meakin, Miroslav Mocák, Alexander StJ. Murphy, and Thomas Rauscher. 2024. "Stellar Evolution and Convection in 3D Hydrodynamic Simulations of a Complete Burning Phase" Galaxies 12, no. 6: 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies12060087
APA StyleRizzuti, F., Hirschi, R., Varma, V., Arnett, W. D., Georgy, C., Meakin, C., Mocák, M., Murphy, A. S., & Rauscher, T. (2024). Stellar Evolution and Convection in 3D Hydrodynamic Simulations of a Complete Burning Phase. Galaxies, 12(6), 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies12060087





