IXPE View of BH XRBs during the First 2.5 Years of the Mission
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. IXPE Data Reduction
3. Summary of IXPE Observations of BH XRBs
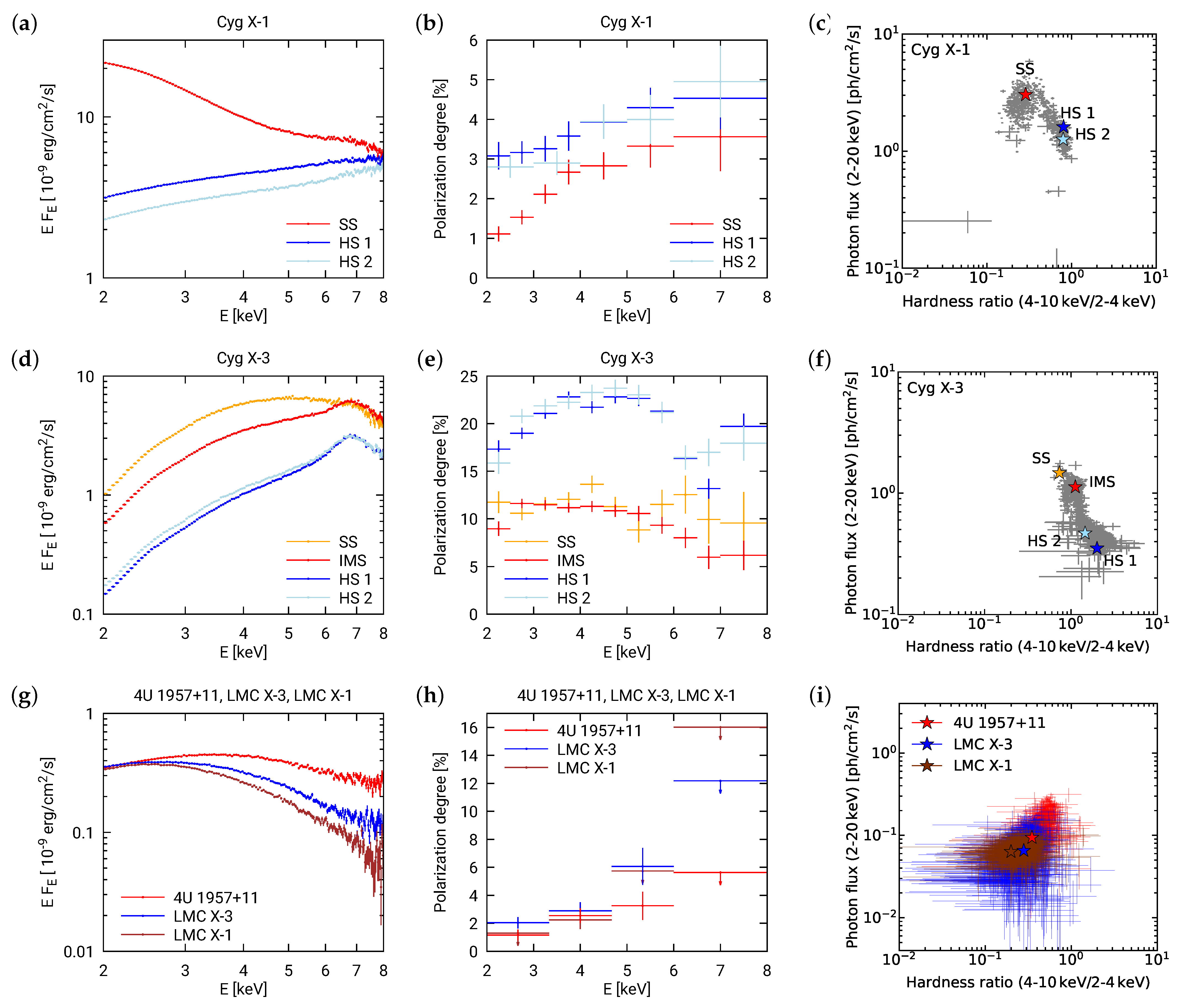
3.1. Cyg X–1
3.2. Cyg X–3
3.3. LMC X–1
3.4. LMC X–3
3.5. 4U 1957+11
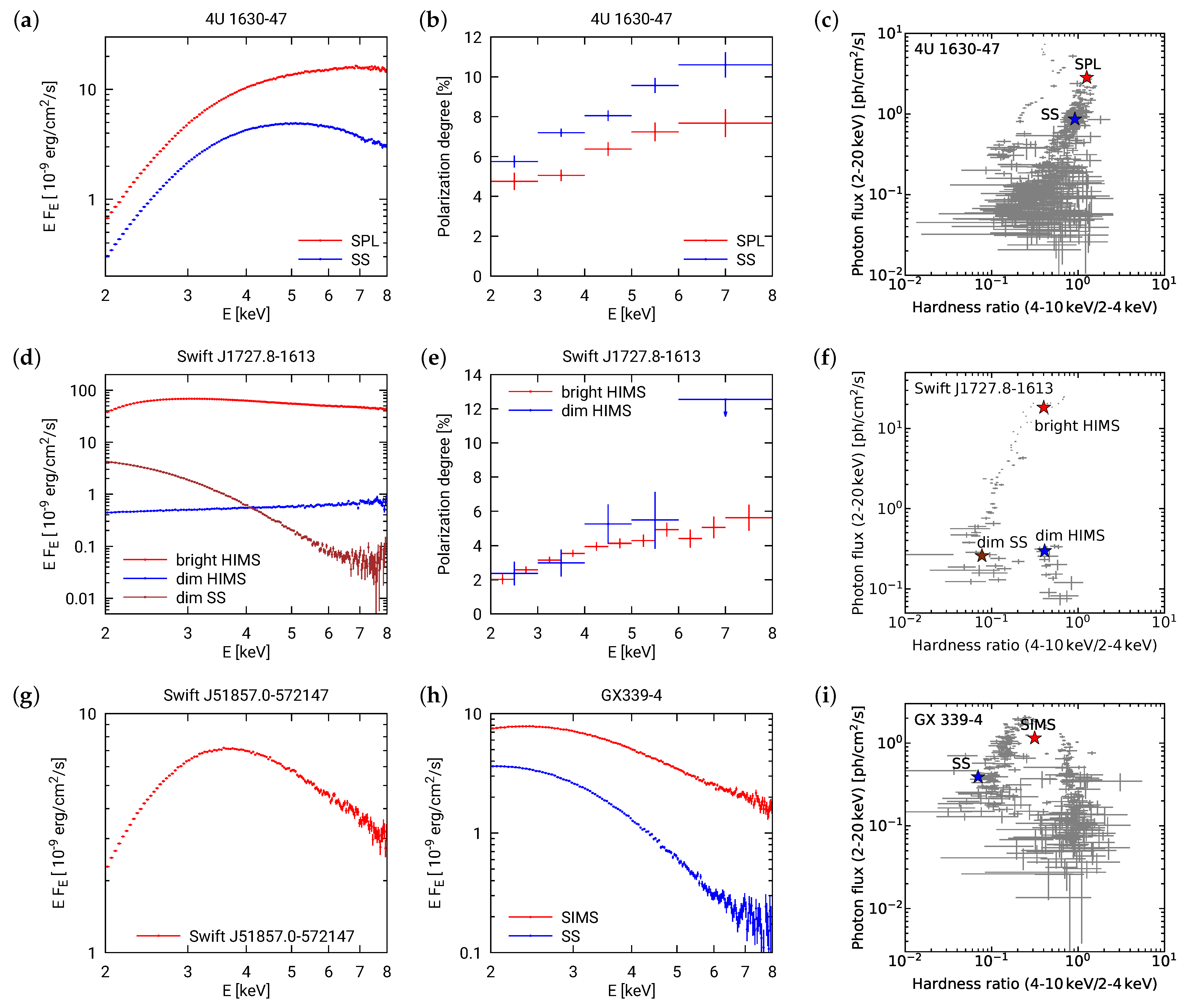
3.6. 4U 1630–47
3.7. Swift J1727.8–1613
3.8. GX 339–4
3.9. Swift J151857.0–572147
3.10. Eastern lobe of SS 433
4. IXPE Achievements in Observations of BH XRBs
4.1. Geometry of Corona
4.2. BH Spin Measurements
4.3. Geometry of the Obscuring Funnel
4.4. Exceptional Case of 4U 1630–47
5. Future Spectropolarimetric Observations of BH XRBs
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NASA | The National Aeronautics and Space Administration |
| ASI | Agenzia Spaziale Italiana |
| HEASARC | High Energy Astrophysics Science Archive Research Center |
| IXPE | Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer |
| OSO | Orbiting Solar Observatory |
| NICER | Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer |
| NuSTAR | Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array |
| XRISM | X-ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission |
| INTEGRAL | INTErnational Gamma-Ray Astrophysics Laboratory |
| MAXI | Monitor of All-sky X-ray Image |
| ATCA | Australia Telescope Compact Array |
| XPoSat | X-ray Polarimeter Satellite |
| POLIX | Polarimeter Instrument in X-rays |
| COSI | Compton Spectrometer and Imager |
| REDSoX | Rocket Experiment Demonstration of a Soft X-ray Polarimeter |
| FoV | Field of view |
| PD | Polarisation degree |
| PA | Polarisation angle |
| GO | General Observer |
| ToO | Target of Opportunity |
| DDT | Director’s Discretionary Time |
| AGN | Active galactic nuclei |
| BH | Black hole |
| XRB | X-ray binary |
| LMXB | Low-mass X-ray binary |
| HMXB | High-mass X-ray binary |
| BHC | Black hole candidate |
| SS | Soft state |
| HS | Hard state |
| SPL | Steep power-law |
| IMS | Intermediate state |
| HIMS | Hard intermediate state |
| SIMS | Soft intermediate state |
| HID | Hardness-intensity diagram |
| TWG | Topical working group |
| 1 | Many of these still lack a proper mass measurement and thus are considered to be black hole candidates (BHC). Their nature is then derived from their spectral and timing characteristics. |
| 2 | Note that for polarisation degree of the order of 1%, the polarised flux is 100 times smaller than the total flux. Furthermore, the polarised flux needs to be measured in the presence of the statistical fluctuations of the unpolarised flux. Polarisation measurements thus need to be several orders of magnitude longer than flux measurements, assuming similar detector efficiencies. Additionally, the Gas Pixel Detector used in IXPE has lower efficiency than a typical CCD chip used in instruments for X-ray spectral observations. |
| 3 | See also the Note on IXPE Statistics prepared by the IXPE team at https://heasarc.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/ixpe/analysis/IXPE_Stats-Advice.pdf accessed on 24 September 2024. |
| 4 | Since the BH XRBs are usually point source objects, the IXPE imaging capabilities have been used only once for these types of targets – for the eastern lobe of SS 433. Note that imaging has been used to its full potential in other extended objects like supernova remnants, pulsar wind nebulae, clouds in Sgr A*, and others. Notwithstanding, imaging capabilities provide a strong background reduction for some of the observed targets that were relatively faint. |
| 5 | See https://heasarc.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/ixpe/archive/ accessed on 24 September 2024. |
| 6 | The ixpecalcarf exits with an error message “The attitude file contains 100.0% of off-axis angle(s) larger than the maximum value in the vignetting CALDB file.” |
| 7 | The best approach would be to use the forward folding method, i.e., fitting a model to all three Stokes parameters. However, this would be too demanding and is beyond the scope of this review, where we seek a simple, uniform approach. When our results are compared with those obtained using the forward folding method, e.g., for Swift J1727.8–1613 in [39], we find excellent agreement well within statistical errors. |
| 8 | To check all the details on the source state, we refer the reader to the original IXPE team papers on these observations. |
| 9 | Note that the SS in Cyg X–1 is not quite like the SS in other BH XRB sources because the Compton component tends to be much stronger, see, e.g., [61]. |
| 10 | Taking the mass accretion rate of g/s and spin , as in [38], gives the accretion rate to be 0.015 in Eddington units. This is an order of magnitude smaller than an accretion rate in a typical SS of other BH XRBs. Note also that, according to [38], the spectrum above 4 keV is dominated by coronal Comptonised radiation and its reflection from the accretion disc, contrary to the typical SS, where the dominance of the thermal emission is much more prominent. |
| 11 | See https://www.isro.gov.in/XPoSat.html accessed on 24 September 2024. |
References
- Tetarenko, B.E.; Sivakoff, G.R.; Heinke, C.O.; Gladstone, J.C. WATCHDOG: A Comprehensive All-sky Database of Galactic Black Hole X-ray Binaries. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 2016, 222, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corral-Santana, J.M.; Casares, J.; Muñoz-Darias, T.; Bauer, F.E.; Martínez-Pais, I.G.; Russell, D.M. BlackCAT: A catalogue of stellar-mass black holes in X-ray transients. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 587, A61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdziarski, A.A.; Gierliński, M. Radiative Processes, Spectral States and Variability of Black-Hole Binaries. Progr. Theor. Phys. Suppl. 2004, 155, 99–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fender, R.P.; Belloni, T.M.; Gallo, E. Towards a unified model for black hole X-ray binary jets. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2004, 355, 1105–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Done, C. Observational characteristics of accretion onto black holes. arXiv 2010, arXiv:1008.2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakura, N.I.; Sunyaev, R.A. Reprint of 1973A&A....24..337S. Black holes in binary systems. Observational appearance. Astron. Astrophys. 1973, 500, 33–51. [Google Scholar]
- Novikov, I.D.; Thorne, K.S. Astrophysics of black holes. In Proceedings of the Black Holes (Les Astres Occlus), New York, NY, USA; 1973; pp. 343–450. [Google Scholar]
- Maccarone, T.J. Do X-ray binary spectral state transition luminosities vary? Astron. Astrophys. 2003, 409, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClintock, J.E.; Remillard, R.A. Black hole binaries. In Compact Stellar X-ray Sources; Lewin, W.H.G., van der Klis, M., Eds.; Cambridge Astrophysics Series; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006; Volume 39, pp. 157–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, M.J.; Walton, D.J.; Alston, W.; Dauser, T.; Eikenberry, S.; Jiang, Y.F.; Fabian, A.C.; Fuerst, F.; Brightman, M.; Marshall, H.; et al. NuSTAR reveals the hidden nature of SS433. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 506, 1045–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poutanen, J.; Lipunova, G.; Fabrika, S.; Butkevich, A.G.; Abolmasov, P. Supercritically accreting stellar mass black holes as ultraluminous X-ray sources. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2007, 377, 1187–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sądowski, A.; Narayan, R.; McKinney, J.C.; Tchekhovskoy, A. Numerical simulations of super-critical black hole accretion flows in general relativity. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 439, 503–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koljonen, K.I.I.; Tomsick, J.A. The obscured X-ray binaries V404 Cyg, Cyg X–3, V4641 Sgr, and GRS 1915+105. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 639, A13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, K.S.; Chanan, G.A.; Novick, R. The X-ray polarization of the CYG sources. Astrophys. J. 1980, 238, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauvin, M.; Roques, J.P.; Clark, D.J.; Jourdain, E. Polarimetry in the Hard X-Ray Domain with INTEGRAL SPI. Astrophys. J. 2013, 769, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadawale, S.V.; Chattopadhyay, T.; Rao, A.R.; Bhattacharya, D.; Bhalerao, V.B.; Vagshette, N.; Pawar, P.; Sreekumar, S. Hard X-ray polarimetry with Astrosat-CZTI. Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 578, A73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connors, P.A.; Stark, R.F. Observable gravitational effects on polarised radiation coming from near a black hole. Nature 1977, 269, 128–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connors, P.A.; Piran, T.; Stark, R.F. Polarization features of X-ray radiation emitted near black holes. Astrophys. J. 1980, 235, 224–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dovčiak, M.; Muleri, F.; Goosmann, R.W.; Karas, V.; Matt, G. Thermal disc emission from a rotating black hole: X-ray polarization signatures. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 391, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnittman, J.D.; Krolik, J.H. X-ray Polarization from Accreting Black Holes: The Thermal State. Astrophys. J. 2009, 701, 1175–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnittman, J.D.; Krolik, J.H. X-ray Polarization from Accreting Black Holes: Coronal Emission. Astrophys. J. 2010, 712, 908–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczynski, H.; Beheshtipour, B. New Constraints on the Spin of the Black Hole Cygnus X–1 and the Physical Properties of its Accretion Disk Corona. Astrophys. J. 2022, 934, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Dovčiak, M.; Bursa, M.; Karas, V.; Matt, G.; Ursini, F. Investigating the X-ray polarization of lamp-post coronae in BHXRBs. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 515, 2882–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisskopf, M.C.; Soffitta, P.; Baldini, L.; Ramsey, B.D.; O’Dell, S.L.; Romani, R.W.; Matt, G.; Deininger, W.D.; Baumgartner, W.H.; Bellazzini, R.; et al. The Imaging X-Ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE): Pre-Launch. J. Astron. Telesc. Instruments, Syst. 2022, 8, 026002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaaret, P.; Ferrazzoli, R.; Silvestri, S.; Negro, M.; Manfreda, A.; Wu, K.; Costa, E.; Soffitta, P.; Safi-Harb, S.; Poutanen, J.; et al. X-Ray Polarization of the Eastern Lobe of SS 433. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2024, 961, L12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardeen, J.M.; Press, W.H.; Teukolsky, S.A. Rotating Black Holes: Locally Nonrotating Frames, Energy Extraction, and Scalar Synchrotron Radiation. Astrophys. J. 1972, 178, 347–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellinger, A. A Color All-Sky Panorama Image of the Milky Way. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2009, 121, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendreau, K.C.; Arzoumanian, Z.; Okajima, T. The Neutron star Interior Composition ExploreR (NICER): An Explorer mission of opportunity for soft x-ray timing spectroscopy. In Proceedings of the Space Telescopes and Instrumentation 2012: Ultraviolet to Gamma Ray, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1–6 July 2012; Takahashi, T., Murray, S.S., den Herder, J.W.A., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2012; Volume 8443, p. 844313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, F.A.; Craig, W.W.; Christensen, F.E.; Hailey, C.J.; Zhang, W.W.; Boggs, S.E.; Stern, D.; Cook, W.R.; Forster, K.; Giommi, P.; et al. The Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) High-energy X-Ray Mission. Astrophys. J. 2013, 770, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashiro, M.; Maejima, H.; Toda, K.; Kelley, R.; Reichenthal, L.; Hartz, L.; Petre, R.; Williams, B.; Guainazzi, M.; Costantini, E.; et al. Status of x-ray imaging and spectroscopy mission (XRISM). In Proceedings of the Space Telescopes and Instrumentation 2020: Ultraviolet to Gamma Ray, Online, 14–18 December 2020; Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE) Conference Series. den Herder, J.W.A., Nikzad, S., Nakazawa, K., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2020; Volume 11444, p. 1144422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, C.; Courvoisier, T.J.L.; Di Cocco, G.; Gehrels, N.; Giménez, A.; Grebenev, S.; Hermsen, W.; Mas-Hesse, J.M.; Lebrun, F.; Lund, N.; et al. The INTEGRAL mission. Astron. Astrophys. 2003, 411, L1–L6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrels, N.; Chincarini, G.; Giommi, P.; Mason, K.O.; Nousek, J.A.; Wells, A.A.; White, N.E.; Barthelmy, S.D.; Burrows, D.N.; Cominsky, L.R.; et al. The Swift Gamma-Ray Burst Mission. Astrophys. J. 2004, 611, 1005–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, M.; Kawasaki, K.; Ueno, S.; Tomida, H.; Kohama, M.; Suzuki, M.; Adachi, Y.; Ishikawa, M.; Mihara, T.; Sugizaki, M.; et al. The MAXI Mission on the ISS: Science and Instruments for Monitoring All-Sky X-Ray Images. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 2009, 61, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldini, L.; Bucciantini, N.; Lalla, N.D.; Ehlert, S.; Manfreda, A.; Negro, M.; Omodei, N.; Pesce-Rollins, M.; Sgrò, C.; Silvestri, S. ixpeobssim: A simulation and analysis framework for the imaging X-ray polarimetry explorer. SoftwareX 2022, 19, 101194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaud, K.A. XSPEC: The First Ten Years. In Proceedings of the Astronomical Data Analysis Software and Systems V, Tucson, Arizona, 23–25 October 1995; Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference Series. Jacoby, G.H., Barnes, J., Eds.; Astronomical Society of the Pacific: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1996; Volume 101, pp. 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Di Marco, A.; Soffitta, P.; Costa, E.; Ferrazzoli, R.; La Monaca, F.; Rankin, J.; Ratheesh, A.; Xie, F.; Baldini, L.; Del Monte, E.; et al. Handling the Background in IXPE Polarimetric Data. Astron. J. 2023, 165, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczynski, H.; Muleri, F.; Dovčiak, M.; Veledina, A.; Rodriguez Cavero, N.; Svoboda, J.; Ingram, A.; Matt, G.; Garcia, J.A.; Loktev, V.; et al. Polarized x-rays constrain the disk-jet geometry in the black hole x-ray binary Cygnus X–1. Science 2022, 378, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, J.F.; Nathan, E.; Hu, K.; Krawczynski, H.; Dovčiak, M.; Veledina, A.; Muleri, F.; Svoboda, J.; Alabarta, K.; Parra, M.; et al. An IXPE-led X-Ray Spectropolarimetric Campaign on the Soft State of Cygnus X–1: X-Ray Polarimetric Evidence for Strong Gravitational Lensing. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2024, 969, L30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingram, A.; Bollemeijer, N.; Veledina, A.; Dovciak, M.; Poutanen, J.; Egron, E.; Russell, T.D.; Trushkin, S.A.; Negro, M.; Ratheesh, A.; et al. Tracking the X-ray Polarization of the Black Hole Transient Swift J1727.8–1613 during a State Transition. Astrophys. J. 2024, 968, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, J.F.L.; Stewart, B.G. Point and interval estimation of the true unbiased degree of linear polarization in the presence of low signal-to-noise ratios. Astron. Astrophys. 1985, 142, 100–106. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, B.G. Polynomial FITS for Polarization Estimation. Astron. Astrophys. 1991, 246, 280. [Google Scholar]
- Maier, D.; Tenzer, C.; Santangelo, A. Point and Interval Estimation on the Degree and the Angle of Polarization: A Bayesian Approach. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2014, 126, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastroserio, G.; De Marco, B.; Baglio, M.C.; Carotenuto, F.; Fabiani, S.; Russell, T.D.; Capitanio, F.; Cavecchi, Y.; Motta, S.; Russell, D.M.; et al. X-ray and optical polarization aligned with the radio jet ejecta in GX 339–4. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.06856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez Cavero, N. First Year of Stellar-Mass Black Hole Observations with the Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.10371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veledina, A.; Muleri, F.; Poutanen, J.; Podgorný, J.; Dovčiak, M.; Capitanio, F.; Churazov, E.; De Rosa, A.; Di Marco, A.; Forsblom, S.V.; et al. Cygnus X–3 revealed as a Galactic ultraluminous X-ray source by IXPE. Nat. Astron. 2024, 8, 1031–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veledina, A.; Poutanen, J.; Bocharova, A.; Di Marco, A.; Forsblom, S.V.; La Monaca, F.; Podgorny, J.; Tsygankov, S.S.; Zdziarski, A.A.; Ahlberg, V.; et al. Ultrasoft state of microquasar Cygnus X–3: X-ray polarimetry reveals the geometry of astronomical puzzle. Astron. Astrophys. 2024, 688, L27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgorný, J.; Marra, L.; Muleri, F.; Rodriguez Cavero, N.; Ratheesh, A.; Dovčiak, M.; Mikušincová, R.; Brigitte, M.; Steiner, J.F.; Veledina, A.; et al. The first X-ray polarimetric observation of the black hole binary LMC X–1. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svoboda, J.; Dovčiak, M.; Steiner, J.F.; Muleri, F.; Ingram, A.; Yilmaz, A.; Rodriguez Cavero, N.; Marra, L.; Poutanen, J.; Veledina, A.; et al. First X-Ray Polarization Measurement Confirms the Low Black Hole Spin in LMC X–3. Astrophys. J. 2024, 960, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, L.; Brigitte, M.; Rodriguez Cavero, N.; Chun, S.; Steiner, J.F.; Dovčiak, M.; Nowak, M.; Bianchi, S.; Capitanio, F.; Ingram, A.; et al. IXPE observation confirms a high spin value in the accreting black hole 4U 1957+115. Astron. Astrophys. 2024, 684, A95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratheesh, A.; Dovčiak, M.; Krawczynski, H.; Podgorný, J.; Marra, L.; Veledina, A.; Suleimanov, V.; Rodriguez Cavero, N.; Steiner, J.; Svoboda, J.; et al. The high polarisation of the X-rays from the Black Hole X-ray Binary 4U 1630–47 challenges standard thin accretion disc scenario. Astrophys. J. 2024, 964, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez Cavero, N.; Marra, L.; Krawczynski, H.; Dovčiak, M.; Bianchi, S.; Steiner, J.F.; Svoboda, J.; Capitanio, F.; Matt, G.; Negro, M.; et al. The First X-Ray Polarization Observation of the Black Hole X-Ray Binary 4U 1630–47 in the Steep Power-law State. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2023, 958, L8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veledina, A.; Muleri, F.; Dovčiak, M.; Poutanen, J.; Ratheesh, A.; Capitanio, F.; Matt, G.; Soffitta, P.; Tennant, A.F.; Negro, M.; et al. Discovery of X-Ray Polarization from the Black Hole Transient Swift J1727.8–1613. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2023, 958, L16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svoboda, J.; Dovčiak, M.; Steiner, J.F.; Kaaret, P.; Podgorný, J.; Poutanen, J.; Veledina, A.; Muleri, F.; Taverna, R.; Krawczynski, H.; et al. Dramatic Drop in the X-Ray Polarization of Swift J1727.8–1613 in the Soft Spectral State. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2024, 966, L35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgorný, J.; Svoboda, J.; Dovčiak, M.; Veledina, A.; Poutanen, J.; Kaaret, P.; Bianchi, S.; Ingram, A.; Capitanio, F.; Datta, S.R.; et al. Recovery of the X-ray polarisation of Swift J1727.8–1613 after the soft-to-hard spectral transition. Astron. Astrophys. 2024, 686, L12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller-Jones, J.C.A.; Bahramian, A.; Orosz, J.A.; Mandel, I.; Gou, L.; Maccarone, T.J.; Neijssel, C.J.; Zhao, X.; Ziółkowski, J.; Reid, M.J.; et al. Cygnus X-1 contains a 21-solar mass black hole—Implications for massive star winds. Science 2021, 371, 1046–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orosz, J.A.; McClintock, J.E.; Aufdenberg, J.P.; Remillard, R.A.; Reid, M.J.; Narayan, R.; Gou, L. The Mass of the Black Hole in Cygnus X–1. Astrophys. J. 2011, 742, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, L.; McClintock, J.E.; Remillard, R.A.; Steiner, J.F.; Reid, M.J.; Orosz, J.A.; Narayan, R.; Hanke, M.; García, J. Confirmation via the Continuum-fitting Method that the Spin of the Black Hole in Cygnus X–1 Is Extreme. Astrophys. J. 2014, 790, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomsick, J.A.; Nowak, M.A.; Parker, M.; Miller, J.M.; Fabian, A.C.; Harrison, F.A.; Bachetti, M.; Barret, D.; Boggs, S.E.; Christensen, F.E.; et al. The Reflection Component from Cygnus X-1 in the Soft State Measured by NuSTAR and Suzaku. Astrophys. J. 2014, 780, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poutanen, J.; Veledina, A.; Beloborodov, A.M. Polarized X-Rays from Windy Accretion in Cygnus X–1. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2023, 949, L10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dexter, J.; Begelman, M.C. A relativistic outflow model of the X-ray polarization in Cyg X–1. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2024, 528, L157–L160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remillard, R.A.; McClintock, J.E. X-Ray Properties of Black-Hole Binaries. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2006, 44, 49–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dovciak, M.; Steiner, J.F.; Krawczynski, H.; Svoboda, J. First Results of IXPE X-ray Polarization Measurements of Cyg X–1 in its Soft State. Astron. Telegr. 2023, 16084, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Jana, A.; Chang, H.K. X-ray polarization changes with the state transition in Cygnus X–1. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2024, 527, 10837–10843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, M.J.; Miller-Jones, J.C.A. On the Distances to the X-Ray Binaries Cygnus X–3 and GRS 1915+105. Astrophys. J. 2023, 959, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koljonen, K.I.I.; Maccarone, T.J. Gemini/GNIRS infrared spectroscopy of the Wolf-Rayet stellar wind in Cygnus X–3. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 472, 2181–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdziarski, A.A.; Mikolajewska, J.; Belczynski, K. Cyg X–3: A low-mass black hole or a neutron star. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 429, L104–L108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Kerkwijk, M.H.; Charles, P.A.; Geballe, T.R.; King, D.L.; Miley, G.K.; Molnar, L.A.; van den Heuvel, E.P.J.; van der Klis, M.; van Paradijs, J. Infrared helium emission lines from Cygnus X–3 suggesting a Wolf-Rayet star companion. Nature 1992, 355, 703–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martí, J.; Paredes, J.M.; Peracaula, M. The Cygnus X–3 Radio Jets at Arcsecond Scales. Astrophys. J. 2000, 545, 939–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antokhin, I.I.; Cherepashchuk, A.M.; Antokhina, E.A.; Tatarnikov, A.M. Near-IR and X-Ray Variability of Cyg X–3: Evidence for a Compact IR Source and Complex Wind Structures. Astrophys. J. 2022, 926, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrzyński, G.; Graczyk, D.; Gieren, W.; Thompson, I.B.; Pilecki, B.; Udalski, A.; Soszyński, I.; Kozłowski, S.; Konorski, P.; Suchomska, K.; et al. An eclipsing-binary distance to the Large Magellanic Cloud accurate to two per cent. Nature 2013, 495, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orosz, J.A.; Steeghs, D.; McClintock, J.E.; Torres, M.A.P.; Bochkov, I.; Gou, L.; Narayan, R.; Blaschak, M.; Levine, A.M.; Remillard, R.A.; et al. A New Dynamical Model for the Black Hole Binary LMC X–1. Astrophys. J. 2009, 697, 573–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, L.; McClintock, J.E.; Liu, J.; Narayan, R.; Steiner, J.F.; Remillard, R.A.; Orosz, J.A.; Davis, S.W.; Ebisawa, K.; Schlegel, E.M. A DETERMINATION OF THE SPIN OF THE BLACK HOLE PRIMARY IN LMC X–1. Astrophys. J. 2009, 701, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, J.F.; Reis, R.C.; Fabian, A.C.; Remillard, R.A.; McClintock, J.E.; Gou, L.; Cooke, R.; Brenneman, L.W.; Sanders, J.S. A broad iron line in LMC X–1. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 427, 2552–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, S.; Kushwaha, A.; Das, S.; Nandi, A. First detection of X-ray polarization in thermal state of LMC X–3: Spectro-polarimetric study with IXPE. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2024, 527, L76–L81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.; Rawat, D.; Méndez, M. Unveiling the X-ray polarimetric properties of LMC X–3 with IXPE, NICER, and Swift/XRT. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2024, 531, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orosz, J.A.; Steiner, J.F.; McClintock, J.E.; Buxton, M.M.; Bailyn, C.D.; Steeghs, D.; Guberman, A.; Torres, M.A.P. The Mass of the Black Hole in LMC X–3. Astrophys. J. 2014, 794, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, J.F.; McClintock, J.E.; Orosz, J.A.; Remillard, R.A.; Bailyn, C.D.; Kolehmainen, M.; Straub, O. The Low-spin Black Hole in LMC X–3. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2014, 793, L29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, A.; Svoboda, J.; Grinberg, V.; Boorman, P.G.; Bursa, M.; Dovčiak, M. Accretion disc evolution in GRO J1655–40 and LMC X–3 with relativistic and non-relativistic disc models. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2023, 525, 1288–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikusincova, R.; Dovciak, M.; Bursa, M.; Lalla, N.D.; Matt, G.; Svoboda, J.; Taverna, R.; Zhang, W. X-ray polarimetry as a tool to measure the black hole spin in microquasars: Simulations of IXPE capabilities. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2023, 519, 6138–6148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, D.; Garg, A.; Méndez, M. Spectropolarimetric study of 4U 1630-47 in steep power-law state with IXPE and NICER. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2023, 525, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushwaha, A.; Jayasurya, K.M.; Agrawal, V.K.; Nandi, A. IXPE and NICER view of black hole X-ray binary 4U 1630–47: First significant detection of polarized emission in thermal state. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2023, 524, L15–L20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, D.; Garg, A.; Méndez, M. Detection of X-Ray Polarized Emission and Accretion-disk Winds with IXPE and NICER in the Black Hole X-Ray Binary 4U 1630–47. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2023, 949, L43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, A.T.; Krawczynski, H. Impact of the Accretion Disk Thickness on the Polarization of the Thermal Emission from Stellar Mass Black Holes. Astrophys. J. 2023, 957, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaru, R.; Done, C.; Odaka, H. X-ray polarization properties of thermal-radiative disc winds in binary systems. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2024, 527, 7047–7054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratheesh, A.; Matt, G.; Tombesi, F.; Soffitta, P.; Pesce-Rollins, M.; Di Marco, A. Exploring the accretion-ejection geometry of GRS 1915+105 in the obscured state with future X-ray spectro-polarimetry. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 655, A96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennea, J.A.; Swift Team. GRB 230824A is likely a Galactic Transient: Swift J1727.8-1613. GRB Coord. Netw. 2023, 34540, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Negoro, H.; Serino, M.; Nakajima, M.; Kobayashi, K.; Tanaka, M.; Soejima, Y.; Kudo, Y.; Mihara, T.; Kawamuro, T.; Yamada, S.; et al. MAXI/GSC detection of Swift J1727.8-1613 (GRB 230824A). GRB Coord. Netw. 2023, 34544, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Mata Sánchez, D.; Muñoz-Darias, T.; Armas Padilla, M.; Casares, J.; Torres, M.A.P. Evidence for inflows and outflows in the nearby black hole transient Swift J1727.8-162. Astron. Astrophys. 2024, 682, L1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.Q.; Zhang, S.; Shui, Q.C.; Zhang, S.N.; Kong, L.D.; Chen, Y.P.; Wang, P.J.; Ji, L.; Qu, J.L.; Tao, L.; et al. NICER, NuSTAR, and Insight-HXMT Views to the Newly Discovered Black Hole X-Ray Binary Swift J1727.8–1613. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2024, 960, L17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, C.M.; Miller-Jones, J.C.A.; Bahramian, A.; Tingay, S.J.; Prabu, S.; Russell, T.D.; Atri, P.; Carotenuto, F.; Altamirano, D.; Motta, S.E.; et al. Swift J1727.8–1613 has the Largest Resolved Continuous Jet Ever Seen in an X-ray Binary. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2024, 971, L9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.C.; Tao, L.; Li, H.C.; Zhang, S.N.; Feng, H.; Ge, M.Y.; Ji, L.; Wang, Y.N.; Huang, Y.; Ma, X.; et al. The First Polarimetric View on Quasiperiodic Oscillations in a Black Hole X-Ray Binary. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2024, 961, L42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdziarski, A.A.; Ziółkowski, J.; Mikołajewska, J. The X-ray binary GX 339–4/V821 Ara: The distance, inclination, evolutionary status, and mass transfer. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 488, 1026–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.M.; Fabian, A.C.; Reynolds, C.S.; Nowak, M.A.; Homan, J.; Freyberg, M.J.; Ehle, M.; Belloni, T.; Wijnands, R.; van der Klis, M.; et al. Evidence of Black Hole Spin in GX 339-4: XMM-Newton/EPIC-pn and RXTE Spectroscopy of the Very High State. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2004, 606, L131–L134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, J.A.; Steiner, J.F.; McClintock, J.E.; Remillard, R.A.; Grinberg, V.; Dauser, T. X-Ray Reflection Spectroscopy of the Black Hole GX 339-4: Exploring the Hard State with Unprecedented Sensitivity. Astrophys. J. 2015, 813, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludlam, R.M.; Miller, J.M.; Cackett, E.M. Reapproaching the Spin Estimate of GX 339-4. Astrophys. J. 2015, 806, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolehmainen, M.; Done, C.; Díaz Trigo, M. Modelling the high-mass accretion rate spectra of GX 339-4: Black hole spin from reflection? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 416, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, S.; Makishima, K.; Uehara, Y.; Nakazawa, K.; Takahashi, H.; Dotani, T.; Ueda, Y.; Ebisawa, K.; Kubota, A.; Gandhi, P. Is the Black Hole in GX 339-4 Really Spinning Rapidly? Astrophys. J. Lett. 2009, 707, L109–L113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, E.; Corbel, S.; Fender, R.P.; Maccarone, T.J.; Tzioumis, A.K. A transient large-scale relativistic radio jet from GX 339-4. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2004, 347, L52–L56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennea, J.A.; Lien, A.Y.; D’Elia, V.; Melandri, A.; Page, K.L.; Siegel, M.H. Swift J151857.0–572147: Swift detection of a new galactic X-ray transient. Astron. Telegr. 2024, 16500, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Del Santo, M.; Russell, T.D.; Marino, A.; Motta, S. Swift/XRT observation of Swift J151857.0-572147 indicates that the source likely made a transition to the soft state. Astron. Telegr. 2024, 16519, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Burridge, B.J.; Miller-Jones, J.C.A.; Bahramian, A.; Prabu, S.; Carotenuto, F.; Russell, T.D.; Cowie, F.; Fender, R.P. An HI spectroscopic distance constraint on Swift J151857.0-572147. Astron. Telegr. 2024, 16538, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Carotenuto, F.; Russell, T.D. ATCA detection of an extremely bright radio flare from Swift J151857.0-572147. Astron. Telegr. 2024, 16518, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Bardeen, J.M.; Petterson, J.A. The Lense-Thirring Effect and Accretion Disks around Kerr Black Holes. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1975, 195, L65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, S.L.; Lightman, A.P.; Eardley, D.M. A two-temperature accretion disk model for Cygnus X–1: Structure and spectrum. Astrophys. J. 1976, 204, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianolli, V.E.; Kim, D.E.; Bianchi, S.; Agís-González, B.; Madejski, G.; Marin, F.; Marinucci, A.; Matt, G.; Middei, R.; Petrucci, P.O.; et al. Uncovering the geometry of the hot X-ray corona in the Seyfert galaxy NGC 4151 with IXPE. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2023, 523, 4468–4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianolli, V.E.; Bianchi, S.; Kammoun, E.; Gnarini, A.; Marinucci, A.; Ursini, F.; Parra, M.; Tortosa, A.; De Rosa, A.; Kim, D.E.; et al. A second view on the X-ray polarization of NGC 4151 with IXPE. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.17243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingram, A.; Ewing, M.; Marinucci, A.; Tagliacozzo, D.; Rosario, D.J.; Veledina, A.; Kim, D.E.; Marin, F.; Bianchi, S.; Poutanen, J.; et al. The X-ray polarization of the Seyfert 1 galaxy IC 4329A. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2023, 525, 5437–5449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, F.; Gianolli, V.E.; Ingram, A.; Kim, D.E.; Marinucci, A.; Tagliacozzo, D.; Ursini, F. An Examination of the Very First Polarimetric X-ray Observations of Radio-Quiet Active Galactic Nuclei. Galaxies 2024, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirabel, I.F.; Rodriguez, L.F.; Cordier, B.; Paul, J.; Lebrun, F. A double-sided radio jet from the compact Galactic Centre annihilator 1E1740.7-2942. Nature 1992, 358, 215–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursini, F.; Marinucci, A.; Matt, G.; Bianchi, S.; Marin, F.; Marshall, H.L.; Middei, R.; Poutanen, J.; Rogantini, D.; De Rosa, A.; et al. Mapping the circumnuclear regions of the Circinus galaxy with the Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2023, 519, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, F.; Marinucci, A.; Laurenti, M.; Kim, D.E.; Barnouin, T.; Di Marco, A.; Ursini, F.; Bianchi, S.; Ravi, S.; Marshall, H.L.; et al. X-ray polarization measurement of the gold standard of radio- quiet active galactic nuclei: NGC 1068. Astron. Astrophys. 2024, 689, A238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Klis, M. Rapid X-ray Variability. In Compact Stellar X-ray Sources; Cambridge Astrophysics Series; Lewin, W.H.G., van der Klis, M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006; Volume 39, pp. 39–112. [Google Scholar]
- Markoff, S.; Nowak, M.A.; Wilms, J. Going with the Flow: Can the Base of Jets Subsume the Role of Compact Accretion Disk Coronae? Astrophys. J. 2005, 635, 1203–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, E.; Steiner, J.F.; Fabian, A.C.; Cackett, E.M.; Uttley, P.; Remillard, R.A.; Gendreau, K.C.; Arzoumanian, Z.; Altamirano, D.; Eikenberry, S.; et al. The corona contracts in a black-hole transient. Nature 2019, 565, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarr, Q.; Awaki, H.; Baring, M.G.; Bose, R.; De Geronimo, G.; Dowkontt, P.; Errando, M.; Guarino, V.; Hattori, K.; Hayashida, K.; et al. XL-Calibur—A second-generation balloon-borne hard X-ray polarimetry mission. Astropart. Phys. 2021, 126, 102529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, H.; Lowell, A.; Tomsick, J.; Sleator, C.; Zoglauer, A.; Beechert, J.; Boggs, S.; Gulick, H.; Hartmann, D.; Karwin, C.; et al. Soft gamma-ray polarimetry with COSI. In Proceedings of the AAS/High Energy Astrophysics Division, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 13–17 March 2022; Volume 19, p. 204.05. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, H.; Heine, S.; Garner, A.; Masterson, R.; Guenther, M.; Heilmann, R.; Bongiorno, S.; Gullikson, E. The Rocket Experiment Demonstration of a Soft X-ray Polarimeter (REDSoX). In Proceedings of the Multifrequency Behaviour of High Energy Cosmic Sources XIV, Palermo, Italy, 12–17 June 2023; Sissa Medialab srl: Trieste, Italy, 2024; p. 76. [Google Scholar]
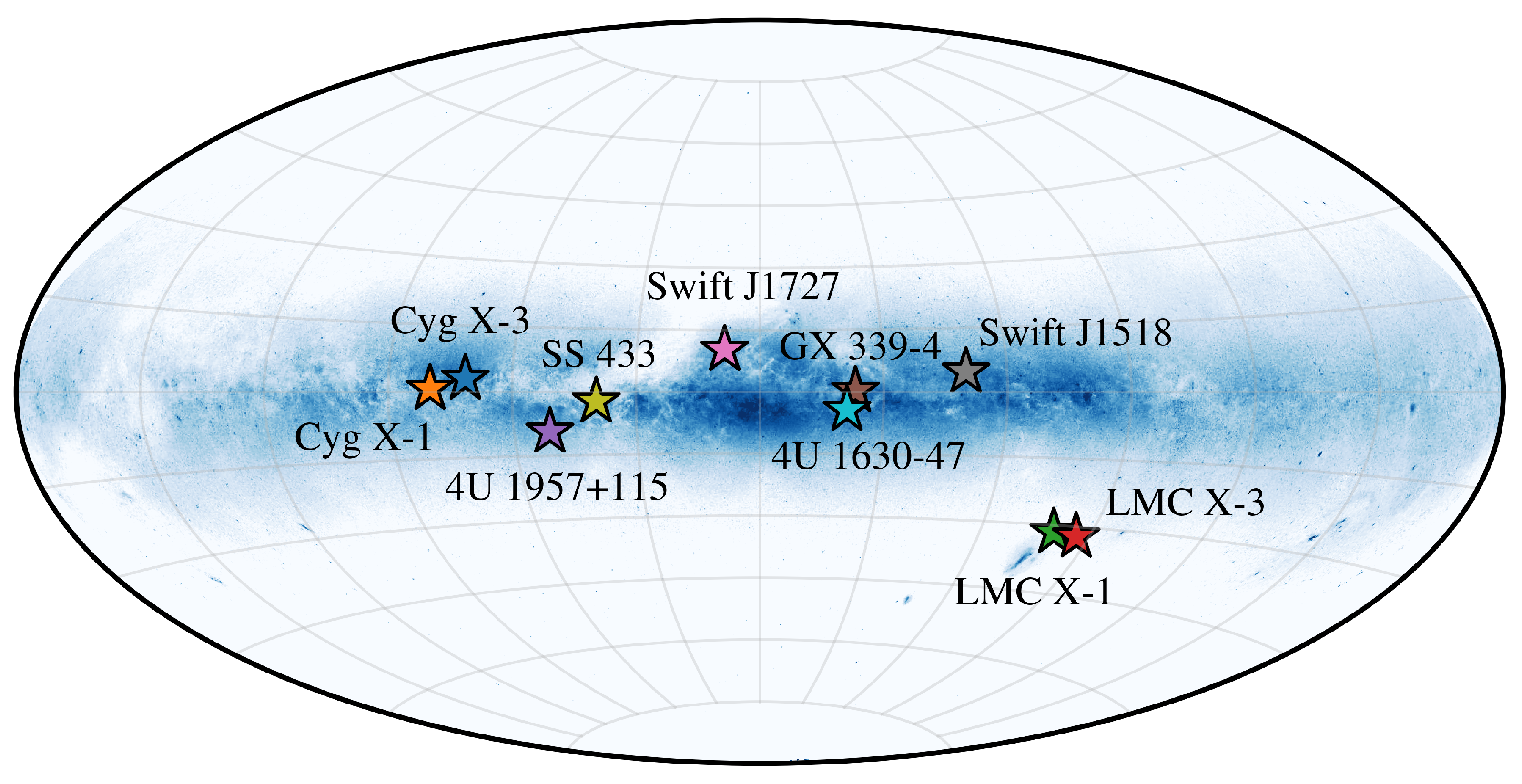
| Object (Object Type) | Observation Date | LIVETIME [ks] | State | Energy Flux a [mCrab] | Polarisation Degree a [%] | Polarisation Angle a [deg] | Ref. b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cyg X–1 c persistentHMXB | 15–21 May 2022 | 242 | HS 1 d | 238 | [37] | ||
| 18–20 June 2022 | 86 | 273 | [37] | ||||
| 2–3 May 2023 | 21 | SS e | 515 | [38] | |||
| 9–10 May 2023 | 31 | 632 | [38] | ||||
| 24–25 May 2023 | 25 | 689 | [38] | ||||
| 13–14 June 2023 | 29 | 677 | [38] | ||||
| 20 June 2023 | 35 | 895 | [38] | ||||
| 12–13 April 2024 | 56 | HS 2 f | 203 | ||||
| 6–7 May 2024 | 54 | 220 | |||||
| 26–27 May 2024 | 58 | 207 | |||||
| 14–15 June 2024 | 56 | 166 | |||||
| Cyg X–3 g persistentHMXB | 14 October–6 November 2022 | 538 | HS 1 | 72 | [45] | ||
| 17–23 November 2023 | 291 | HS 2 | 76 | ||||
| 25–29 December 2022 | 198 | IMS | 192 | [45] | |||
| 2–3 June 2024 | 50 | SS | 268 | [46] | |||
| LMC X–1 persistentHMXB | 19–28 October 2022 | 562 | SS | 14 | — | [47] | |
| LMC X–3 persistentLMXB/HMXB | 7–20 July 2023 | 562 | SS | 16 | [48] | ||
| 4U 1957+11 persistentLMXB | 12–24 May 2023 | 572 | SS | 22 | [49] |
| Object (Object Type) | Observation Date | LIVETIME [ks] | State | Energy Flux a [mCrab] | Polarisation Degree a [%] | Polarisation Angle a [deg] | Ref. b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4U 1630–47 transientLMXB | 23 August 2022–2 September 2022 | 458 | SS | 181 | [50] | ||
| 10–13 March 2023 | 36 102 | SPL c | 389 539 | [51] | |||
| Swift J1727.8–1613 d transientLMXB | 7–8 September 2023 | 19 | bright HIMS e | 3920 | [52] | ||
| 16–17 September 2023 | 37 | 3574 | [39] | ||||
| 27–28 September 2023 | 21 | 3050 | [39] | ||||
| 4 October 2023 | 18 | 3284 | [39] | ||||
| 10 October 2023 | 18 | 2676 | [39] | ||||
| Swift J1727.8–1613 d transientLMXB | 11–12 February 2023 | 67 | dim SS f | 86 | — | [53] | |
| 20–23 February 2023 | 151 | 58 | |||||
| 3–8 April 2023 | 202 | dim HIMS | 32 | [54] | |||
| GX 339–4 g transientLMXB | 14–16 February 2024 | 95 | SIMS | 291 | [43] | ||
| 8–10 March 2024 | 98 | SS | 94 | — | [43] | ||
| Swift J151857.0–572147 transientBHC | 18–20 March 2024 | 96 | SS | 300 | — | García et al., in preparation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dovčiak, M.; Podgorný, J.; Svoboda, J.; Steiner, J.F.; Kaaret, P.; Krawczynski, H.; Ingram, A.; Kravtsov, V.; Marra, L.; Muleri, F.; et al. IXPE View of BH XRBs during the First 2.5 Years of the Mission. Galaxies 2024, 12, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies12050054
Dovčiak M, Podgorný J, Svoboda J, Steiner JF, Kaaret P, Krawczynski H, Ingram A, Kravtsov V, Marra L, Muleri F, et al. IXPE View of BH XRBs during the First 2.5 Years of the Mission. Galaxies. 2024; 12(5):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies12050054
Chicago/Turabian StyleDovčiak, Michal, Jakub Podgorný, Jiří Svoboda, James F. Steiner, Philip Kaaret, Henric Krawczynski, Adam Ingram, Vadim Kravtsov, Lorenzo Marra, Fabio Muleri, and et al. 2024. "IXPE View of BH XRBs during the First 2.5 Years of the Mission" Galaxies 12, no. 5: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies12050054
APA StyleDovčiak, M., Podgorný, J., Svoboda, J., Steiner, J. F., Kaaret, P., Krawczynski, H., Ingram, A., Kravtsov, V., Marra, L., Muleri, F., García, J. A., Mastroserio, G., Mikušincová, R., Ratheesh, A., & Cavero, N. R. (2024). IXPE View of BH XRBs during the First 2.5 Years of the Mission. Galaxies, 12(5), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies12050054






