Abstract
Among the more than 60 sources observed in the first two years of operations, IXPE addressed four magnetars, neutron stars believed to host ultra-strong magnetic fields. We report here the main implication coming from IXPE measurements for the physics of magnetars. Polarimetric observations confirmed the expectations of high polarization degrees, up to ≈, values which have not been detected in any other source so far, providing further proof (independent from the P- estimate) that magnetars host indeed ultra-magnetized neutron stars. Polarization measurements also indicate that softer X-rays likely come from surface regions where the overlying atmosphere underwent magnetic condensation. The agreement of the phase-dependent polarization angle with a simple rotating vector model strongly supports the presence of vacuum birefringence around the star.
1. Introduction
Magnetars are observationally identified with two groups of sources, now believed to form a single family: the anomalous X-ray pulsars (AXPs) and the soft gamma repeaters (SGRs). They are a peculiar class of isolated neutron stars (NSs) [1,2,3], with persistent X-ray luminosity of –. Magnetar spectra in the – range are well represented by the superposition of two (or more) thermal components (with temperatures ≈–) or by a thermal component plus a power-law (PL) tail with a photon index of ≈2–4 [4] (see the online magnetar catalog: https://www.physics.mcgill.ca/~pulsar/magnetar/main.html, accessed on 5 June 2024). A hallmark of both SGRs and AXPs is the emission of short bursts of hard X-/soft -rays. In addition, much more energetic “giant flares” have been detected from three SGRs, with (isotropic) luminosity reaching up to . Bursts usually come in bunches, with tens or even hundreds of events grouped in the so-called “burst forests” [2].
In 1992 Duncan and Thompson [5,6] first suggested that SGRs host a strongly magnetized NS (from the name “magnetar”) and that the powerhouse of their activity is their ultra-strong magnetic field (–). Indeed, assuming that the conventional pulsar spin-down model applies, magnetar spin periods (–) and spin-down rates (–) yield dipole fields of ≈–. The internal field is believed to be even stronger, with a “twisted-torus” topology [7,8]. The large toroidal component exerts a stress on the outer crust, deforming it [9] and transferring magnetic helicity to the external field, which, in turn, acquires a “twist”. Supporting currents are needed to sustain the twisted field and the charges flowing along the closed field lines make magnetar magnetospheres optically thick with respect to resonant Compton scattering (RCS) [10]. Repeated scatterings onto the streaming charges produce the power-law tails observed in the soft X-rays [11,12,13].
Despite the RCS paradigm having been successful in interpreting the persistent X-ray emission of magnetar sources, spectral analysis is fairly insensitive to the source geometry and thus fails to provide univocal information about the source properties [14]. On the other hand, magnetar emission is expected to be strongly polarized and polarimetry is bound to add new insights on magnetar physics. In magnetized media, photons propagate in two normal modes, with polarization vectors either parallel (ordinary mode, O) or perpendicular (extraordinary mode, X) to the k-B plane (with being the photon propagation direction [15]). For magnetar-range B-fields, typically exceeding the quantum critical limit (), X-mode photons tend to escape more freely with respect to O-mode ones, because of the much reduced cross sections below the electron cyclotron frequency [11,16,17,18], thus dominating the emitted radiation. However, the observed polarization of photons coming from a sizeable fraction of the NS surface is, in general, severely reduced by geometrical effects. In magnetars, on the other hand, the field is so strong that QED vacuum birefringence forces photons to keep the polarization state they have at emission up to large radii [12,13,19,20,21,22], so that the observed polarization degree is close to that at the surface, see [22,23] for further details.
Until recently, no polarization measurements have been available in X-rays, with the exception of the pioneering observation of the Crab pulsar with the OSO-8 satellite [24,25]. The launch of the joint NASA–Italian Space Agency (ASI) mission IXPE [26] in December 2021 drastically changed the picture, thanks to the large increase in sensitivity provided by its three gas pixel detectors (GPDs). In the following, we present the IXPE observations of four persistent magnetars, the AXPs 4U 0142+61 (Section 2), 1RXS J170849.0−400910 (Section 3), and 1E 2259+586 (Section 5), and from the SGR 1806−20 (Section 4), discussing the main physical implications. Our conclusions are then summarized in Section 6.
2. AXP 0142+61
AXP 4U 0142+61, the brightest among the magnetar candidates, was observed by IXPE for a total exposure time of [27]. The long observation time made it possible to derive the spin frequency derivative alongside the rotational frequency , both in agreement, within the errors, with previous estimates [4,28]. The implied dipolar magnetic field is . The spectrum collected by IXPE in the 2– band can be reproduced using two components, which are either two BBs or a single BB plus a high-energy PL tail. The spectral parameters of the latter fit are compatible with those derived from previous analyses of XMM-Newton data [27,29,30].
By integrating over both the rotational phase and photon energy (in the 2– range), a polarization degree and a polarization angle , measured East of the celestial North, were obtained; the result is significant at ≈. The phase-averaged polarization properties, binned into five energy intervals, shows a strong dependence on energy: PD attains a value of at 2–, decreases below the instrumental sensitivity (and so is compatible with zero) at 4–, then increases up to at 6–. Meanwhile, the polarization angle direction suddenly changes from ≈ at low energies (2–) to ≈ at high energies (5–, see Figure 1, left).
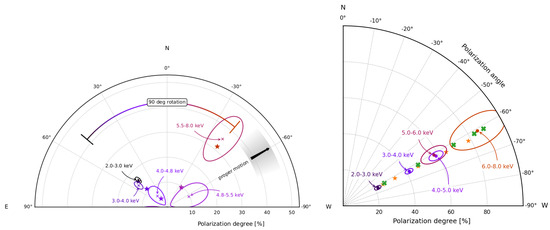
Figure 1.
(Left) PD and PA (crosses with confidence contours) observed by IXPE for the AXP 4U 0142+61, as a function of photon energy and integrated over the rotational phase. Stars mark the simulated values of PD and PA obtained assuming thermal emission from an equatorial belt on the magnetar condensed surface reprocessed by RCS. Figure taken from [27]. (Right) same for the AXP 1RXS J1708. Orange stars and green crosses report the simulated PD and PA for model A and model B, respectively (see text for details). Figure taken from [31].
The polarization level attained at high energies is compatible, within the errors, with the value () one expects if resonantly up-scattered photons dominate the PL tail in the spectrum [10,13,14]. While, according to the RCS scenario, PL photons should be polarized in the X-mode, the swing in the polarization angle points to an excess of O-mode photons at lower energies. O-mode photons are expected to dominate if thermal radiation comes from a magnetically condensed region on the star surface [14], although other possibilities, e.g., an atmosphere heated by back-flowing currents, exist. The results of a numerical simulation based on this picture indeed provide a good representation of the data, as shown in Figure 1, left. The alternative picture, in which low-energy photons are mostly polarized in the X mode while those at higher energies are predominantly O-mode, although possible, is disfavoured, see [27].
The pulse profile of 4U 0142+61 measured by IXPE is double-peaked, in agreement with previous findings [29], and the change polarization degree with phase closely follows that of the counts. This supports the view that the polarization pattern at infinity is directly linked to that at the emission. On the other hand, at variance with both the flux and the polarization degree, the polarization oscillation is quasi-sinusoidal, as observed in pulsars where the phase-dependent polarization direction follows the rotating vector model RVM, see [32,33]
In Equation (1), is the rotational phase and angles and are the inclinations of the observer’s line-of-sight (LOS) and of the magnetic dipole axis with respect to the star’s spin axis, respectively. This relation cannot be assumed to be valid in general for magnetars, due to the fact that the emitting regions on the surface are not necessarily small, as in the case of the emitting caps of pulsars, and because the magnetar external B-field deviates from a purely dipolar topology. Nonetheless, the polarization angle still satisfies Equation (1) if the polarization vectors are fixed at a sufficiently large distance from the star [27], where the magnetic field is nearly dipolar. This can be explained assuming that QED vacuum birefringence is at work. In fact, close to the magnetar surface the ultra-strong magnetic field forces the photon polarization vectors to continuously adapt their direction to that of the field, preserving the surface polarization pattern. At a large distance the field decays and it is not able anymore to keep the photon electric field coupled. This occurs at the polarization limiting radius , a distance of ≈ for a magnetar, large enough to make the magnetic field nearly dipolar.
3. AXP 1RXS J170849.0−4009100
Located at an estimated distance of 5– [34], the AXP 1RXS J170849.0−4009100 (hereafter refered to as 1RXS J1708, for short) is the second brightest among persistent magnetars, with unabsorbed flux ≈ [4,35]). Observed with IXPE for a total on source time , it turned out to be the most strongly polarized source discovered so far [31].
The joint analysis of the IXPE data with quasi-simultaneous Swift-XRT [36] and NICER [37] observations led to derive a spin frequency and a frequency derivative , both in agreement with previous estimates [28], which yield a spin-down magnetic field ≈. The pulse profile is essentially single-peaked. Polarization was detected with a high significance: and , measured West of North, after summing over all energies and phases. At variance with 4U 0142+61, the polarization degree monotonically increases with energy, going from at 2– to at 6–, while the polarization angle is constant (see Figure 1, right). As in 4U 0142+61, the PA changes with phase are largely uncorrelated with those of the polarization degree and follow a sinusoidal pattern.
Both a (absorbed) BB+BB and BB+PL decomposition turned out to satisfactorily fit the IXPE spectrum [31]. However, the large polarization degree measured at higher energies, in excess of ∼, clearly does not match the expectations of the twisted magnetosphere model, see e.g., Ref. [14], disfavouring the BB+PL model over the BB+BB one. Zane et al. [31] proposed that the thermal emission comes from two regions on the NS surface, one in the condensed state and the other covered by a magnetized atmosphere. This explains both the low (large) degree of polarization detected at low (high) energies, see again [14], and the thermal spectral decomposition (as suggested by the spectro-polarimetric analysis). The coexistence of different phases follows from the changing the magnetic field and temperature across = the surface of an NS [38]. Numerical simulations were performed assuming two different emission geometries. In the first one (labelled as model A in Figure 1, right), the condensed-surface zone surrounds the star magnetic equator, as in the scenario proposed for 4U 0142+61, while the hotter region covered by the atmosphere is a circular spot located at the pole. In the second one (model B in Figure 1, right), the two emitting regions are both isolated spots with different sizes, located at different magnetic colatitudes. In both cases, IXPE polarization and spectral data are successfully reproduced.
4. SGR 1806−20
SGR 1806−20 appears projected close to the Galactic center, at an estimated distance of ≈ [39]. This source is one of the only three magnetars to date that have been observed to emit a giant flare [40], which turned out to be the brightest. Its persistent emission was observed by IXPE for a exposure, with a simultaneous ≈ pointing by XMM-Newton [41]. Unfortunately, the measurement was performed when the source exhibited an unexpected record-low flux, and the concurrent phase of high solar activity (with the emission of a substantial number of solar flares) resulted in a too low statistical significance for the IXPE measurement.
Despite the fact that the observation was not sufficiently long for deriving the spin-down rate of the source, exploiting the XMM-Newton data, a rotational frequency of was measured, in agreement with recent estimates [42]. The remarkably low source flux made spectral fits to the IXPE counts inconclusive. However, XMM-Newton EPIC data shown that a BB+PL model adequately fit the soft X-ray spectrum, returning parameter values compatible with those published in the literature over the last 10 years.
Given the low counting statistics, the measured (phase- and energy-integrated) polarization degree is not significant and the polarization angle is unconstrained. Nevertheless, a marginally significant was detected in the 4– bin with (East of North). The high background level found at low and high energies, instead, only allowed to place upper limits of (2–) and (5–) at confidence level (see Figure 2, left).
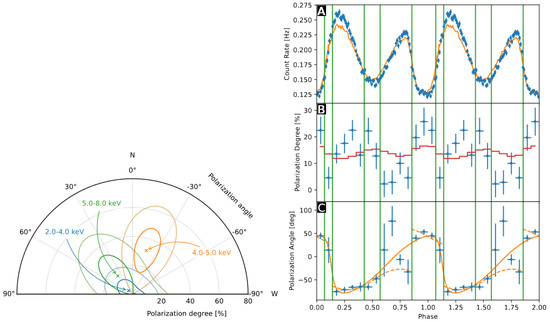
Figure 2.
(Left) PD and PA (crosses with and confidence contours, respectively) measured by IXPE for SGR 1806−20 as a function of the photon energy, by averaging on the rotational phase. Figure taken from [41]. (Right) count rate (panel A) and phase-resolved PD (panel B), and PA (panel C), energy-integrated over the IXPE band (filled circles) for AXP 1E 2259+586. In Panel A, the solid curve marks the –-integrated pulse profile as resulted from a 2014 observation by XMM-Newton [43]. In Panel B, the solid curve marks, instead, the . Finally, in Panel C, the curves show the best RVM fits with (dashed) and without (solid), considering a swing of PA during rotation; the green vertical lines mark the different phase intervals used in the analysis. Figure taken from [44].
5. AXP 1E 2259+586
AXP 1E 2259+586 is the last magnetar observed by IXPE until now. Located at a distance of [45], it was observed with a net exposure time of , with simultaneous data also taken with XMM-Newton and NICER as part of a wider campaign [44].
Both the spin frequency, , and the frequency derivative, , have been obtained from the timing analysis of the joint IXPE, XMM-Newton, and NICER observations. These values allowed for infering a dipolar magnetic field , in excellent agreement the previuous estimates [28].
Although a BB+PL spectral model provides values in agreement with those listed in the McGill catalogue [4], the fit is not entirely satisfactory and was improved by adding an absorption line. The line significance is , and the line energy () and width () agree with those reported in [43], within the errors.
The polarimetric analysis returned a phase-integrated , with = (East of North), integrated over the entire 2– IXPE band. A polarization degree ≈20– is measured at the minimum of the pulse profile. It then approaches ≈0 as the count rate increases towards the primary maximum, rising again to ≈ in the secondary minimum. Finally, the polarization is compatible with zero as the flux increases again towards the secondary maximum. Meanwhile, PA appears to oscillate in phase around ≈ (measured East of North), between the two peaks of the pulse profile, and ≈, in correspondence with the minimum of the light curve (see panels A and B of Figure 2, right).
According to Heyl et al. [44], the peculiar behavior of PD and PA can be related to emission from two spots on the (condensed) NS surface, one of them covered by a plasma loop that acts as a sort of “screen”. Radiation from the spot is (partly) intercepted by the loop at certain rotational phases and scattered/absorbed at the proton cyclotron resonance (see also [43]; a similar explanation was put forward for the absorption feature detected in SGR 0418+5729 [46]). The low polarization degree detected in the rise to the main/secondary pulse peaks is due to O-mode dominated radiation coming directly from the surface, suffering little or no scatterings. On the other hand, when reprocessing by currents in the loop becomes important radiation is expected to be more polarized in the X-mode. This occurs at the main peak and the main dip where PD attains a value of ≈, as indeed predicted by RCS (see panels A and B in Figure 2, right). As noticed for the cases of 4U 0142+61 and 1RXS J1708, also in this case, the polarization angle behavior as a function of the spin phase can be fitted by RVM (see panel C).
6. Discussion and Conclusions
We presented the results of X-ray polarization measurements obtained with IXPE in four persistent magnetar sources. The main findings are summarized below.
- The emission from magnetar targets has been found to be strongly polarized, as expected for radiation propagating in ultra-magnetized environments. In particular, the observed PD turned out to range between ≈15– at 2– to more than at 6– across the four sources that have been investigated.
- In spite of spectral similarities, the differences observed among the polarization patterns of the single sources strongly suggest a different origin for the thermal emission. Photons may come directly from the condensed surface of the neutron star or undergo reprocessing in magnetized atmospheric layers covering the emitting spots. The different scenarios can be well distinguished using X-ray polarimetry, which removes the degeneracy of the spectral analysis alone.
- The PA swing detected by IXPE in the case of AXP 4U 0142+61 points towards the presence of photons polarized in the O and X normal modes, which are expected for magnetic fields in excess of . This can be considered as an indirect proof, independent of the P- estimate, that magnetars are indeed neutron stars endowed with ultra-strong magnetic fields. Furthermore, the level of polarization measured at 6– (≈30–) agrees with the predictions of the commonly accepted RCS model. An alternative explanation for the peculiar polarimetric properties of 4U 0142+61 was put forward by Lai [47], who criticized the idea that two phases (gaseous and solid/liquid) can coexist on the surface. He argued, instead, that the polarization angle swing at 4– could arise at the vacuum resonance, due to partial mode conversion in a magnetized atmosphere, although this scenario too is not without problems [48].
- Although a larger polarization degree integrated over both energy and rotational phase would have been required to demonstrate that vacuum birefringence is at work (≳, see [14]), the behavior of the polarization angle as a function of phase observed in three sources is indeed that expected when considering vacuum birefringence effects.
- As the case of the AXP 1E 2259+586 has shown, phase-resolved polarimetry may provide further support to models that rely on the existence of localized magnetic structures, filled with charged particles, from which phase-dependent spectral features originate. Identifying these features with the proton-cyclotron resonance yields an estimate of the magnetic field near the surface of G, confirming the magnetar nature of this source.
X-ray polarimetry performed with the IXPE observatory has proven to be key in enhancing our understanding of (persistent) magnetar emission. In this respect, it is essential to extend observations to lower energy bands (–), where magnetar radiation usually peaks, especially considering future technological advancements. IXPE, however, is still a powerful asset, especially by including in the target list transient magnetars in outburst, which represent the best possibility to provide further evidence of vacuum birefringence effects.
Funding
This research was funded by the Italian Ministry of University and Research (MUR) through grant PRIN 2022LWPEXW.
Data Availability Statement
IXPE data and response functions are available in the HEASARC online data archive https://heasarc.gsfc.nasa.gov/docs/ixpe/archive/ (accessed on 5 June 2024).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Mereghetti, S. The strongest cosmic magnets: Soft gamma-ray repeaters and anomalous X-ray pulsars. Astron. Astrophys. Rev. 2008, 15, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turolla, R.; Zane, S.; Watts, A.L. Magnetars: The physics behind the observations. A review. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2015, 78, 116091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaspi, V.M.; Beloborodov, A.M. Magnetars. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 55, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olausen, S.A.; Kaspi, V.M. The McGill Magnetar Catalog. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2014, 212, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, R.C.; Thompson, C. Formation of Very Strongly Magnetized Neutron Stars: Implications for Gamma-Ray Bursts. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1992, 392, L9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.; Duncan, R.C. The soft gamma repeaters as very strongly magnetized neutron stars—I. Radiative mechanism for outbursts. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1995, 275, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.; Duncan, R.C. The Giant Flare of 1998 August 27 from SGR 1900+14. II. Radiative Mechanism and Physical Constraints on the Source. Astrophys. J. 2001, 561, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braithwaite, J. Axisymmetric magnetic fields in stars: Relative strengths of poloidal and toroidal components. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2009, 397, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perna, R.; Pons, J.A. A Unified Model of the Magnetar and Radio Pulsar Bursting Phenomenology. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2011, 727, L51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.; Lyutikov, M.; Kulkarni, S.R. Electrodynamics of Magnetars: Implication for the Persistent X-ray Emission and Spin-down of the Soft Gamma Repeaters and Anomalous X-ray Pulsars. Astrophys. J. 2002, 574, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobili, L.; Turolla, S.; Zane, S. X-ray spectra from magnetar candidates—I. Monte Carlo simulations in the non-relativistic regime. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 386, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, R.; Davis, S.W. The X-ray Polarization Signature of Quiescent Magnetars: Effect of Magnetospheric Scattering and Vacuum Polarization. Astrophys. J. 2011, 730, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taverna, R.; Muleri, F.; Turolla, R.; Soffitta, P.; Fabiani, S.; Nobili, L. Probing magnetar magnetosphere through X-ray polarization measurements. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 438, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taverna, R.; Turolla, R.; Suleimanov, V.; Potekhin, A.Y.; Zane, S. X-ray spectra and polarization from magnetar candidates. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 492, 5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnedin, Y.N.; Pavlov, G.G. The trasfer equations for normal waves and radiation polarization in an anisotropic medium. Sov. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 1974, 38, 903. [Google Scholar]
- Herold, H. Compton and Thomson scattering in strong magnetic fields. Phys. Rev. D 1979, 19, 2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, J. Scattering of light in a strongly magnetized plasma. Phys. Rev. D 1979, 19, 1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mészáros, P. High-Energy Radiation from Magnetized Neutron Stars; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Heisenberg, W.; Euler, H. Folgerungen aus der Diracschen Theorie des Positrons. Z. Phys. 1936, 98, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyl, J.S.; Shaviv, N.J. Polarization evolution in strong magnetic fields. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2000, 311, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyl, J.S.; Shaviv, N.J. QED and high polarization of the thermal radiation from neutron stars. Phys. Rev. D 2002, 66, 023002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyl, J.S.; Shaviv, N.J.; Lloyd, D. The high-energy polarization-limiting radius of neutron star magnetospheres—I. Slowly rotating neutron stars. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2003, 342, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taverna, R.; Turolla, R.; González-Caniulef, D.; Zane, S.; Muleri, F.; Soffitta, P. Polarization of neutron star surface emission: A systematic analysis. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 454, 3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisskopf, M.C.; Cohen, G.G.; Kestenbaum, H.L.; Long, K.S.; Novick, R.; Wolff, R.S. Measurement of the X-ray polarization of the Crab nebula. Astrophys. J. 1978, 208, L125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisskopf, M.C.; Silver, E.H.; Kestenbaum, H.L.; Long, K.S.; Novick, R. A precision measurement of the X-ray polarization of the Crab Nebula without pulsar contamination. Astrophys. J. 1978, 220, L117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisskopf, M.C.; Soffitta, P.; Baldini, L.; Ramsey, B.D.; O’Dell, S.L.; Romani, R.W.; Matt, G.; Dininger, W.D.; Baumgartner, W.H.; Bellazzini, R.; et al. The Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE): Pre-Launch. J. Astron. Telesc. Instrum. Syst. 2022, 8, 026002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taverna, R.; Turolla, R.; Muleri, F.; Heyl, J.; Zane, S.; Baldini, L.; González-Caniulef, D.; Bachetti, M.; Rankin, J.; Caiazzo, I.; et al. Polarized X-rays from a magnetar. Science 2022, 378, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dib, R.; Kaspi, V.M. 16 yr of RXTE Monitoring of Fiva Anomalous X-ray Pulsars. Astrophys. J. 2014, 784, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, N.; Nichelli, E.; Israel, G.L.; Perna, R.; Oosterbroek, T.; Parmar, A.N.; Turolla, R.; Campana, S.; Stella, L.; Zane, S.; et al. Very deep X-ray observations of the anomalous X-ray pulsar 4U0142+614. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2007, 381, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Hartog, P.R.; Kuiper, L.; Hermsen, W.; Kaspi, V.M.; Dib, R.; Knödlseder, J.; Gavriil, F.P. Detailed high-energy characteristics of AXP 4U 0142+61. Multi-year observations with INTEGRAL, RXTE, XMM-Newton, and ASCA. Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 489, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zane, S.; Taverna, R.; González–Caniulef, D.; Muleri, F.; Turolla, R.; Heyl, J.; Uchiyama, K.; Ng, M.; Tamagawa, T.; Caiazzo, I.; et al. A Strong X-ray Polarization Signal from the Magnetar 1RXS J170849.0–400910. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2023, 944, L27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, V.; Cooke, D.J. Magnetic poles and the polarization structure of pulsar radiation. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1969, 3, 225. [Google Scholar]
- Poutanen, J. Relativistic rotating vector model for X-ray millisecond pulsars. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 641, A166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israel, G.L.; Covino, S.; Stella, L.; Campana, S.; Haberl, F.; Mereghetti, S. Further Evidence that 1RXS J170849.0–400910 Is an Anomalous X-ray Pulsar. Astrophys. J. 1999, 518, L107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, N.; Israel, G.L.; Oosterbroek, T.; Campana, S.; Zane, S.; Turolla, R.; Testa, V.; Méndez, M.; Stella, L. X-ray intensity-hardness correlation and deep IR observations of the anomalous X-ray pulsar 1RXS J170849–400910. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2007, 308, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, D.N.; Hill, J.E.; Nousek, J.A.; Kennea, J.A.; Wells, A.; Osborne, J.P.; Abbey, A.F.; Beardmore, A.; Mukerjee, K.; Short, A.D.T.; et al. The Swift X-ray Telescope. Space Sci. Rev. 2005, 120, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzoumanian, Z.; Gendreau, K.C.; Baker, C.L.; Cazeau, T.; Hestnes, P.; Kellogg, J.W.; Kenyon, S.J.; Kozon, R.P.; Liu, K.-C.; Manthripragada, S.S.; et al. The neutron star interior composition explorer (NICER): Mission definition. Proc. SPIE 2014, 9144, 914420. [Google Scholar]
- Potekhin, A.Y.; Pons, J.A.; Page, D. Neutron Stars–Cooling and Transport. Space Sci. Rev. 2015, 191, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibby, J.L.; Crowther, P.A.; Furness, J.P.; Clark, J.S. A downward revision to the distance of the 1806-20 cluster and associated magnetar from Gemini Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 386, L23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, D.M.; Barthelmy, S.; Gehrels, N.; Kippen, R.M.; Cayton, T.; Kouveliotou, C.; Eichler, D.; Wijers, R.A.; Woods, P.M.; Granot, J.; et al. A giant γ-ray flare from the magnetar SGR 1806–20. Nature 2005, 434, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turolla, R.; Taverna, R.; Israel, G.L.; Muleri, F.; Zane, S.; Bachetti, M.; Heyl, J.; Di Marco, A.; Gau, E.; Krawczynski, H.; et al. IXPE and XMM-Newton Observations of the Soft Gamma Repeater SGR 1806–20. Astrophys. J. 2023, 954, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, G.; Baring, M.G.; Kouveliotou, C.; Harding, A.; Donovan, S.; Göǧüş, E.; Kaspi, V.M.; Granot, J. The Sleeping Monster: NuSTAR Observations of SGR 1806–20, 11 Years after the Giant Flare. Astrophys. J. 2017, 851, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzocaro, D.; Tiengo, A.; Mereghetti, S.; Turolla, R.; Esposito, P.; Stella, L.; Zane, S.; Rea, N.; Zelati, F.C.; Israel, G. Detailed X-ray spectroscopy of the magnetar 1E 2259+586. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 626, A39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyl, J.S.; Taverna, R.; Turolla, R.; Israel, G.L.; Ng, M.; Kırmızıbayrak, D.; González-Caniulef, D.; Caiazzo, I.; Zane, S.; Ehlert, S.R.; et al. The detection of polarized X-ray emission from the magnetar 1E 2259+586. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2024, 527, 12219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothes, R.; Foster, T. A Thorough Investigation of the Distance to the Supernova Remnant CTB109 and Its Pulsar AXP J2301+5852. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2012, 746, L4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiengo, A.; Esposito, P.; Mereghetti, S.; Turolla, R.; Nobili, L.; Gastaldello, F.; Götz, D.; Israel, G.L.; Rea, N.; Stella, L.; et al. A variable absoprtion feature in the X-ray spectrum of a magnetar. Nature 2013, 500, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, D. IXPE detection of polarized X-rays from magnetars and photon mode conversion at QED vacuum resonance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.M.E.; Zane, S.; Turolla, R.; Taverna, R. X-ray Polarisation in Magnetar Atmospheres—Effects of Mode Conversion. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2024, 528, 3927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).