Present and Future of Gravitational Wave Astronomy
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Einstein, A. Naeherungsweise Integration der Feldgleichungen der Gravitation. Sitzungsber. Preuss. Akad. Wiss. 1916, 1, 688. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Abernathy, M.R.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; et al. Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Black Hole Merger. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 061102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitcomb, S. Making LIGO Possible: A Technical History. In Proceedings of the APS April Meeting 2019, Denver, Colorado, 13–16 April 2019; Available online: https://dcc.ligo.org/public/0157/G1802281/001/G1802281-v1.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2022).
- Aasi, J.; Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.; Abernathy, M.R.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; et al. Advanced LIGO. Class. Quantum Grav. 2015, 32, 074001. [Google Scholar]
- Cahillane, C.; Mansell, G. Review of the Advanced LIGO Gravitational Wave Observatories Leading to Observing Run Four. Galaxies 2022, 10, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; et al. GW170817: Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Neutron Star Inspiral. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2017, 119, 161101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acernese, F.A.; Agathos, M.; Agatsuma, K.; Aisa, D.; Allemandou, N.; Allocca, A.; Amarni, J.; Astone, P.; Balestri, G.; Ballardin, G.; et al. Advanced Virgo: A second-generation interferometric gravitational wave detector. Class. Quantum Grav. 2015, 32, 024001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardecchia, I. Detecting Gravitational Waves with Advanced Virgo. Galaxies 2022, 10, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akutsu, T.; Ando, M.; Arai, K.; Arai, Y.; Araki, S.; Araya, A.; Aritomi, N.; Aso, Y.; Bae, S.; Bae, Y.; et al. Overview of KAGRA: Detector design and construction history. Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys. 2021, 2021, 05A101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, H.; Akutsu, T.; Ando, M.; Araya, A.; Aritomi, N.; Asada, H.; Aso, Y.; Bae, S.; Bajpai, R.; Cannon, K.; et al. The Current Status and Future Prospects of KAGRA, the Large-Scale Cryogenic Gravitational Wave Telescope Built in the Kamioka Underground. Galaxies 2022, 10, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dooley, K.L.; Leong, J.R.; Adams, T.; Affeldt, C.; Bisht, A.; Bogan, C.; Degallaix, J.; Gräf, C.; Hild, S.; Hough, J.; et al. GEO 600 and the GEO-HF upgrade program: Successes and challenges. Class. Quantum Grav. 2016, 33, 075009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, R.; Abe, H.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adhikari, N.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adkins, V.K.; Adya, V.B.; Affeldt, C.; Agarwal, D.; et al. First joint observation by the underground gravitational-wave detector, KAGRA, with GEO600. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.01270. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adhikari, N.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; Affeldt, C.; Agarwal, D.; et al. GWTC-3: Compact Binary Coalescences Observed by LIGO and Virgo During the Second Part of the Third Observing Run. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.03606. [Google Scholar]
- Spera, M. Compact Binary Coalescences: Astrophysical Processes and Lessons Learned. Galaxies 2022, 10, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepańczyk, M.; Zanolin, M. Gravitational Waves from a Core-Collapse Supernova: Perspectives with detectors in the late 2020s and early 2030s. Galaxies 2022, 10, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccinni, O.J. Status and perspectives of Continuous Gravitational Wave searches. Galaxies 2022, 10, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzini, A.I.; Goncharov, B.; Jenkins, A.C.; Meyers, P.M. Stochastic Gravitational-Wave Backgrounds: Current Detection Efforts and Future Prospects. Galaxies 2022, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adhikari, N.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adya, V.B.; Affeldt, C.; Agarwal, D.; et al. The population of merging compact binaries inferred using gravitational waves through GWTC-3. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.03634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, R.; Abe, H.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adhikari, N.; Adhikari, R.X.; Adkins, V.K.; Adya, V.B.; Affeldt, C.; Agarwal, D.; et al. Tests of General Relativity with GWTC-3. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.06861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, S.; Bhattacharjee, D.; Savage, R.L. Toward Calibration of the Global Network of Gravitational Wave Detectors with Sub-Percent Absolute and Relative Accuracy. Galaxies 2022, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, D.; Walker, M. Detector Characterization and Mitigation of Noise in Ground-Based Gravitational-Wave Interferometers. Galaxies 2022, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajente, G.; Gustafson, E.K.; Reitze, D.H. Precision interferometry for gravitational wave detection: Current status and future trends. In Advances in Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; Chapter 3; Volume 68, pp. 75–148. [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer, S.E.; Mansell, G.L.; McCuller, L. Squeezing in Gravitational Wave Detectors. Galaxies 2022, 10, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trozzo, L.; Badaracco, F. Seismic and Newtonian Noise in the GW Detectors. Galaxies 2022, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, R.X.; Arai, K.; Brooks, A.F.; Wipf, C.; Aguiar, O.; Altin, P.; Barr, B.; Barsotti, L.; Bassiri, R.; Bell, A.; et al. A Cryogenic Silicon Interferometer for Gravitational-wave Detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2001.11173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pace, S.; Mangano, V.; Pierini, L.; Rezaei, A.; Hennig, J.S.; Hennig, M.; Pascucci, D.; Allocca, A.; Tosta e Melo, I.; Nair, V.G.; et al. Research Facilities for Europe?s Next Generation Gravitational-Wave Detector Einstein Telescope. Galaxies 2022, 10, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, E. Cosmic Explorer: A next-generation ground-based gravitational-wave observatory. Galaxies 2022, 10, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danzmann, K.; LISA Study Team. LISA: Laser interferometer space antenna for gravitational wave measurements. Class. Quantum Grav. 1996, 13, A247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, Y.; Shimizu, R.; Ishikawa, T.; Nagano, K.; Iwaguchi, S.; Watanabe, I.; Wu, B.; Yokoyama, S.; Kawamura, S. Optimization of Design Parameters for Gravitational Wave Detector DECIGO Including Fundamental Noises. Galaxies 2022, 10, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
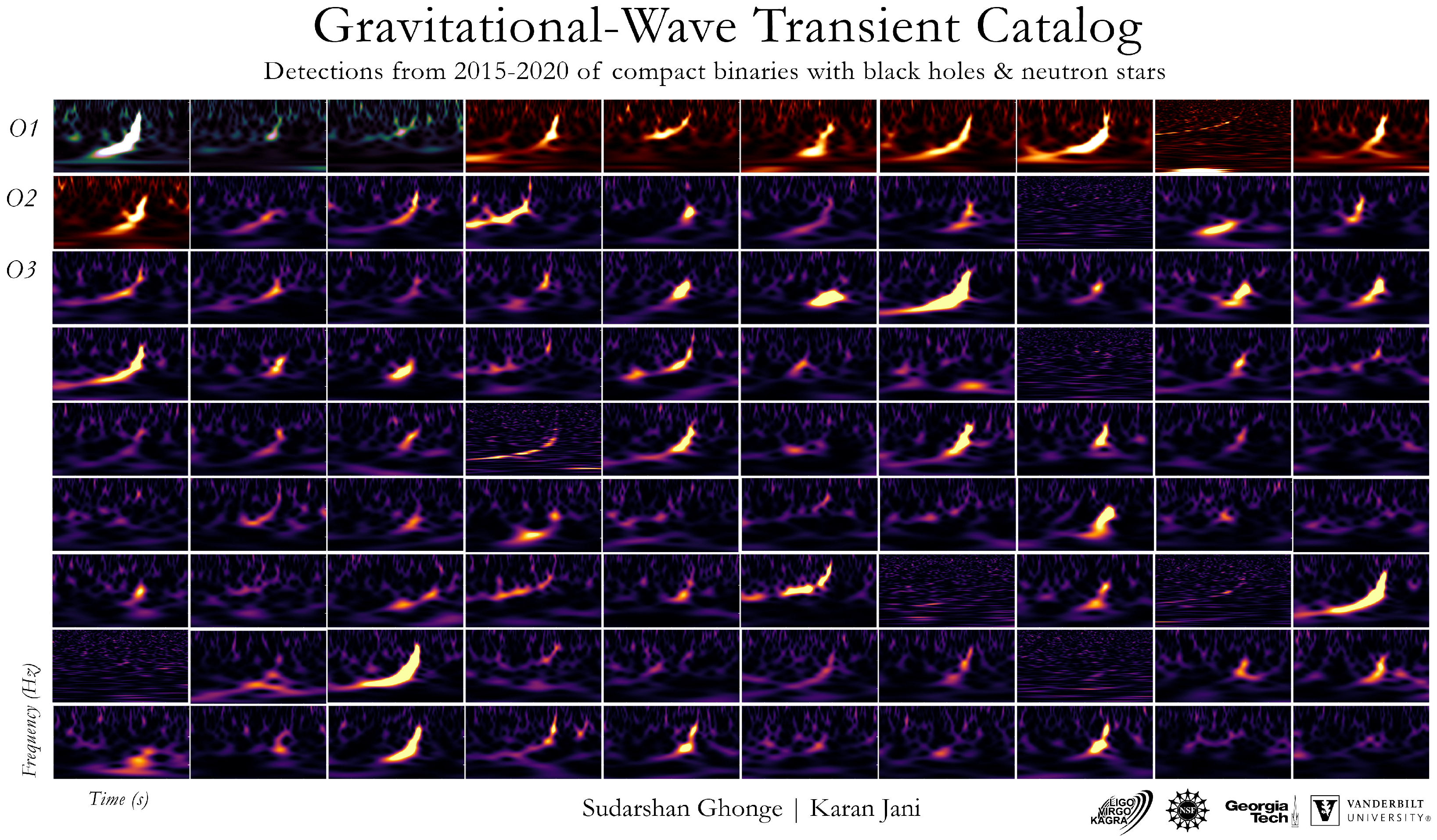
- GWTC-3 Poster. Available online: https://dcc.ligo.org/LIGO-G2102338/public (accessed on 1 June 2022).


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vajente, G. Present and Future of Gravitational Wave Astronomy. Galaxies 2022, 10, 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies10040091
Vajente G. Present and Future of Gravitational Wave Astronomy. Galaxies. 2022; 10(4):91. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies10040091
Chicago/Turabian StyleVajente, Gabriele. 2022. "Present and Future of Gravitational Wave Astronomy" Galaxies 10, no. 4: 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies10040091
APA StyleVajente, G. (2022). Present and Future of Gravitational Wave Astronomy. Galaxies, 10(4), 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies10040091




