The Journey of Acromegaly Towards Treatment: A Single-Center Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
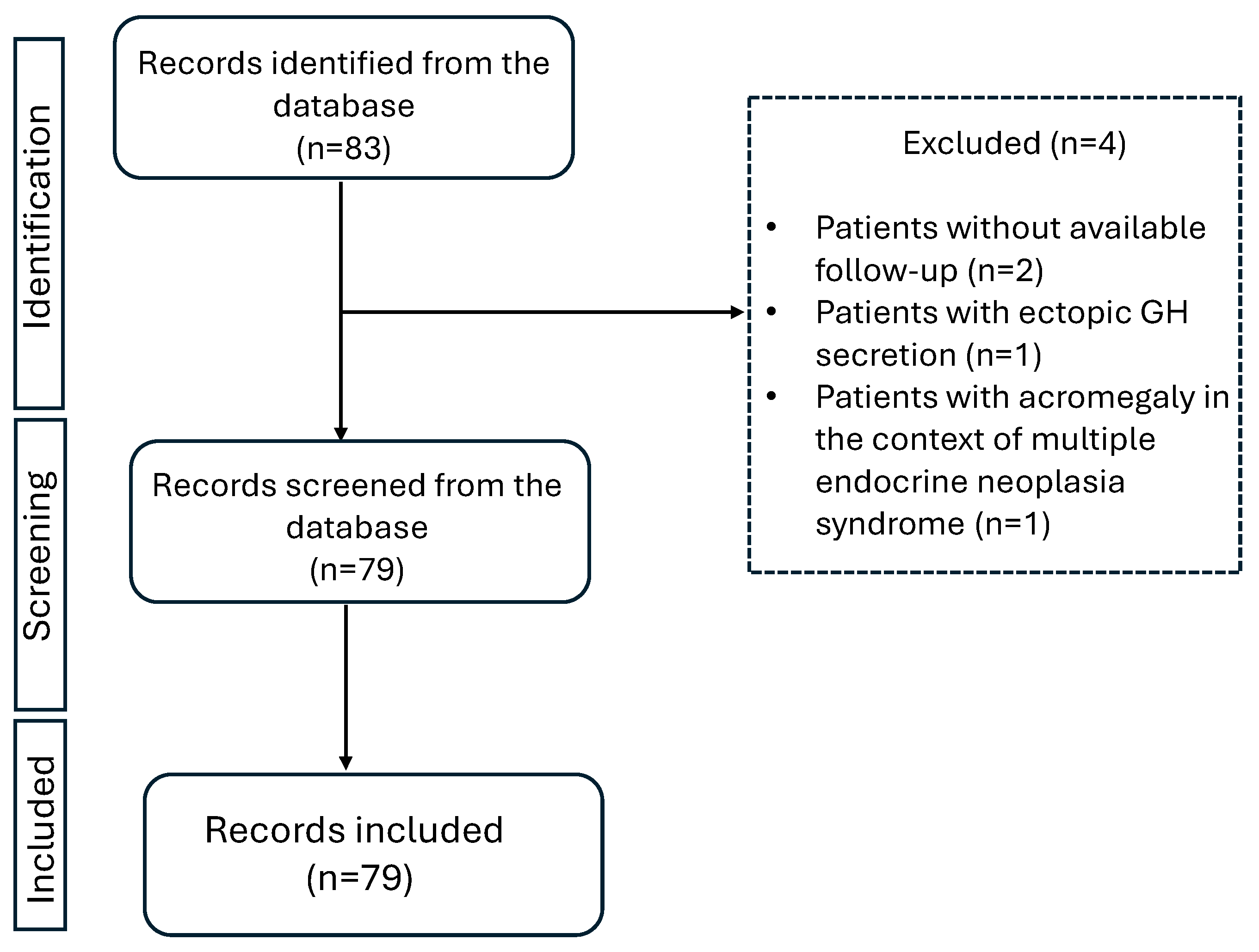
2. Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CT | Computed tomography scan |
| GH | Growth hormone |
| IGF-1 | Insulin-like growth factor-1 |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| mTOR | Mammalian target of rapamycin |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SSAs | Somatostatin analogs |
| SSTR2 | Somatostatin receptor 2 |
| TME | Tumor microenvironment |
| TSS | Transsphenoidal surgery |
| ULN | Upper limit of normal |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
References
- Giustina, A.; Biermasz, N.; Casanueva, F.F.; Fleseriu, M.; Mortini, P.; Strasburger, C.; van der Lely, A.J.; Wass, J.; Melmed, S. Consensus on criteria for acromegaly diagnosis and remission. Pituitary 2024, 27, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Găloiu, S.; Poiană, C. Current therapies and mortality in acromegaly. J. Med. Life 2015, 8, 411–415. [Google Scholar]
- Gadelha, M.R.; Kasuki, L.; Lim, D.S.T.; Fleseriu, M. Systemic complications of acromegaly and the impact of the current treatment landscape: An update. Endocr. Rev. 2019, 40, 268–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolfi, F.; Neves, A.F.; Boguszewski, C.L.; Nunes-Nogueira, V.S. Mortality in acromegaly decreased in the last decade: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 179, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melmed, S.; Bronstein, M.D.; Chanson, P.; Klibanski, A.; Casanueva, F.F.; Wass, J.A.H.; Strasburger, C.J.; Luger, A.; Clemmons, D.R.; Giustina, A. A Consensus Statement on acromegaly therapeutic outcomes. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falch, C.M.; Dupont, A.K.; Olarescu, N.C.; Wiedmann, M.; Dahlberg, D.; Bollerslev, J.; Berg-Johnsen, J.; Heck, A. Long-term control of acromegaly after pituitary surgery in South-Eastern Norway. Acta Neuro-Chir. 2023, 165, 3003–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, B.; Kasuki, L.; Gadelha, M.R. Novel therapies for acromegaly. Endocr. Connect. 2020, 9, R274–R285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirchio, R.; Auriemma, R.S.; Vergura, A.; Pivonello, R.; Colao, A. Investigational drugs for the treatment of acromegaly: New agents to transform therapy. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2024, 33, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, E.; Alexandraki, K.I. The Era of Personalized Treatment in Acromegaly. EC Neurol. 2018, 10, 947–953. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Fleseriu, M. Individualized acromegaly treatment: Is stereotactic radiation therapy changing the paradigm? Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1034576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Didwania, P.; Lehrer, E.J.; Sheehan, D.; Sheehan, K.; Trifiletti, D.M.; Sheehan, J.P. Stereotactic radiosurgery for acromegaly: An international systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical outcomes. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2020, 148, 401–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Mehta, G.U.; Patibandla, M.R.; Lee, C.-C.; Liscak, R.; Kano, H.; Pai, F.-Y.; Kosak, M.; Sisterson, N.D.; Martinez-Alvarez, R.; et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for acromegaly: An international multicenter retrospective cohort study. Neurosurgery 2019, 84, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasuki, L.; Gadelha, M.R. Innovative therapeutics in acromegaly. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endo-Crinology Metab. 2022, 36, 101679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Rodriguez, E.; Casanueva, F.F.; Bernabeu, I. Update on prognostic factors in acromegaly: Is a risk score possible? Pituitary 2015, 18, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Chen, W.-L.; Tavakol, S.; Akter, F.; Catalino, M.P.; Guo, X.; Luo, J.; Zeng, A.-L.; Zekelman, L.; Mao, Z.-G.; et al. Predictors of postoperative biochemical remission in acromegaly. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2021, 151, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marazuela, M.; Martínez-Hernandez, R.; Marques-Pamies, M.; Biagetti, B.; Araujo-Castro, M.; Puig-Domingo, M. Predictors of biochemical response to somatostatin receptor ligands in acromegaly. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 38, 101893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandraki, K.I.; Papadimitriou, E.; Mavroeidi, V.; Kyriakopoulos, G.; Xydakis, A.; Papaioannou, T.G.; Kolomodi, D.; Kaltsas, G.A.; Grossman, A.B. Role of receptor profiling for personalized therapy in a patient with a growth hor-mone-secreting macroadenoma resistant to first-generation somatostatin analogues. J. Pers. Med. 2019, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig-Domingo, M.; Resmini, E.; Gomez-Anson, B.; Nicolau, J.; Mora, M.; Palomera, E.; Martí, C.; Halperin, I.; Webb, S.M. Magnetic resonance imaging as a predictor of response to somatostatin analogs in acromegaly after surgical failure. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 4973–4978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig-Domingo, M.; Bernabéu, I.; Picó, A.; Biagetti, B.; Gil, J.; Alvarez-Escolá, C.; Jordà, M.; Marques-Pamies, M.; Soldevila, B.; Gálvez, M.-A.; et al. Pasireotide in the personalized treatment of acromegaly. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 648411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puig Domingo, M. Treatment of acromegaly in the era of personalized and predictive medicine. Clin. Endocrinol. 2015, 83, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.S.T.; Fleseriu, M. Personalized medical treatment of patients with acromegaly: A review. Endocr. Pract. 2022, 28, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiloiro, S.; De Marinis, L. The immune microenviroment in somatotropinomas: From biology to personalized and target therapy. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2023, 24, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosio, M.R.; Gagliardi, I.; Ferreira, A.G.; Bondanelli, M.; Giampietro, A.; Bianchi, A.; De Marinis, L.; Fleseriu, M.; Zatelli, M.C. Acromegaly in the elderly patients. Endocrine 2020, 68, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasagawa, Y.; Hayashi, Y.; Tachibana, O.; Nakagawa, A.; Oishi, M.; Takamura, T.; Iizuka, H.; Nakada, M. Transsphenoidal surgery for elderly patients with acromegaly and its outcomes: Comparison with younger patients. World Neurosurg. 2018, 118, e229–e234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Duan, L.; Yang, S.; Wang, T.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhou, J.; Cui, S.; Pang, C.; Wang, Y.; et al. Biochemical remission, diagnostic delays, and comorbidities of acromegaly in China: A large single-centre retrospective study. Front. Endocrinol. 2025, 16, 1526625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila, G.; Luger, A.; van der Lely, A.J.; Neggers, S.J.C.M.M.; Webb, S.M.; Biller, B.M.K.; Valluri, S.; Hey-Hadavi, J. Hypertension in acromegaly in relationship to biochemical control and mortality: Global ACROSTUDY outcomes. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 577173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slagboom, T.N.; de Jong, D.; Bisschop, P.H.; Drent, M.L. Acromegaly: Is earlier diagnosis possible? Exploration of a screening algorithm to select high-risk patients. Endocr. Metab. Sci. 2025, 17, 100223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestron, A.; Webb, S.; Astorga, R.; Benito, P.; Catala, M.; Gaztambide, S.; Gomez, J.; Halperin, I.; Lucas-Morante, T.; Moreno, B.; et al. Epidemiology, clinical characteristics, outcome, morbidity and mortality in acromegaly based on the Spanish Acromegaly Registry (Registro Espanol de Acromegalia, REA). Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2004, 151, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bex, M.; Abs, R.; T’Sjoen, G.; Mockel, J.; Velkeniers, B.; Muermans, K.; Maiter, D. AcroBel–the Belgian registry on acromegaly: A survey of the ‘real-life’outcome in 418 acromegalic subjects. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2007, 157, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöfl, C.; Franz, H.; Grussendorf, M.; Honegger, J.; Jaursch-Hancke, C.; Mayr, B.; Schopohl, J. Long-term outcome in patients with acromegaly: Analysis of 1344 patients from the German Acromegaly Register. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 168, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlett, T.A.; Willis, D.; Walker, G.; Wass, J.A.H.; Trainer, P.J. Control of growth hormone and IGF 1 in patients with acromegaly in the UK: Responses to medical treatment with somatostatin analogues and dopamine agonists. Clin. Endocrinol. 2013, 79, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dal, J.; Skov, B.G.; Andersen, M.S.; Feldt-Rasmussen, U.; Feltoft, C.L.; Karmisholt, J.; Nielsen, E.H.; Dekkers, O.M.; Jørgensen, J.O.L. Sex differences in acromegaly at diagnosis: A nationwide cohort study and meta-analysis of the literature. Clin. Endocrinol. 2021, 94, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrentaki, A.; Paluzzi, A.; Wass, J.A.H.; Karavitaki, N. Epidemiology of acromegaly: Review of population studies. Pituitary 2017, 20, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysoulaki, M.; Daraki, V.; Sfakiotaki, M.; Tzoutzouraki, P.; Floroskoufi, P.; Betsi, G.; Vamvoukaki, R.; Vergou, S.; Michailidis, S.; Maria, M.A.; et al. Epidemiology, clinical presentation, treatment and outcome of acromegaly in the island of crete, greece: Experience of 3 tertiary centers over a four decade period. In Endocrine Abstracts; Bioscientifica: Bristol, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Petersenn, S.; Houchard, A.; Sert, C.; Caron, P.J.; PRIMARYS Study Group. Predictive factors for responses to primary medical treatment with lanreotide autogel 120 mg in acromegaly: Post hoc analyses from the PRIMARYS study. Pituitary 2020, 23, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der LELY, A.J.; Harrls, A.G.; Lamberts, S.W.J. The sensitivity of growth hormone secretion to medical treatment in acromegalic patients: Influence of age and sex. Clin. Endocrinol. 1992, 37, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenders, N.F.; I McCormack, A.; Ho, K.K.Y. Management of endocrine disease: Does gender matter in the management of acromegaly? Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 182, R67–R82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal, J.; Rosendal, C.; Karmisholt, J.; Feldt-Rasmussen, U.; Andersen, M.S.; Klose, M.; Feltoft, C.; Heck, A.; Nielsen, E.H.; Jørgensen, J.O.L. Sex difference in patients with controlled acromegaly—A multicentre survey. Clin. Endocrinol. 2023, 98, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas-Ramos, D.; Carmichael, J.D.; Cooper, O.; Bonert, V.S.; Gertych, A.; Mamelak, A.N.; Melmed, S. A structural and functional acromegaly classification. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiseljak-Vassiliades, K.; Shafi, S.; Kerr, J.M.; Phang, T.L.; Kleinschmidt-DeMasters, B.K.; Wierman, M.E. Clinical implications of growth hormone–secreting tumor subtypes. Endocrine 2012, 42, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehghani, M.; Davoodi, Z.; Bidari, F.; Moghaddam, A.M.; Khalili, D.; Bahrami-Motlagh, H.; Jamali, E.; Alamdari, S.; Hosseinpanah, F.; Hedayati, M.; et al. Association of different pathologic subtypes of growth hormone producing pituitary adenoma and remission in acromegaly patients: A retrospective cohort study. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2021, 21, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jallad, R.S.; Bronstein, M.D. Acromegaly in the elderly patient. Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 63, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccato, F.; Barbot, M.; Lizzul, L.; Cuccarollo, A.; Selmin, E.; Boschin, I.M.; Daniele, A.; Saller, A.; Occhi, G.; Regazzo, D.; et al. Clinical presentation and management of acromegaly in elderly patients. Hormones 2021, 20, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biagetti, B.; Iglesias, P.; Villar-Taibo, R.; Moure, M.-D.; Paja, M.; Araujo-Castro, M.; Ares, J.; Álvarez-Escola, C.; Vicente, A.; Guivernau, È.Á. Factors associated with therapeutic response in acromegaly diagnosed in the elderly in Spain. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 984877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliardi, I.; Chiloiro, S.; Vallillo, M.; Bondanelli, M.; Volpato, S.; Giampietro, A.; Bianchi, A.; De Marinis, L.; Zatelli, M.C.; Ambrosio, M.R. Multidimensional geriatric evaluation in acromegaly: A comparative cross-sectional study. BMC Geriatr. 2021, 21, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liuzzi, A.; Chiodini, P.; Botalla, L.; Cremascoli, G.; Müller, E.; Silvestrini, F. Decreased plasma growth hormone (GH) levels in acromegalics following CB 154 (2-Br-α-ergocryptine) administration. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1974, 38, 910–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daughaday, W.H. A new treatment for an old disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1985, 313, 1604–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colao, A.; Ferone, D.; Marzullo, P.; Di Sarno, A.; Cerbone, G.; Sarnacchiaro, F.; Cirillo, S.; Merola, B.; Lombardi, G. Effect of different dopaminergic agents in the treatment of acromegaly. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trainer, P.J.; Drake, W.M.; Katznelson, L.; Freda, P.U.; Herman-Bonert, V.; van der Lely, A.; Dimaraki, E.V.; Stewart, P.M.; Friend, K.E.; Vance, M.L.; et al. Treatment of acromegaly with the growth hormone–receptor antagonist pegvisomant. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 1171–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas-Ramos, D.; Fleseriu, M. Pasireotide: A novel treatment for patients with acromegaly. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2016, ume 10, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustina, A.; Chanson, P.; Kleinberg, D.; Bronstein, M.D.; Clemmons, D.R.; Klibanski, A.; van der Lely, A.J.; Strasburger, C.J.; Lamberts, S.W.; Ho, K.K.Y.; et al. Expert consensus document: A consensus on the medical treatment of acromegaly. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2014, 10, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleseriu, M.; Biller, B.M.K.; Freda, P.U.; Gadelha, M.R.; Giustina, A.; Katznelson, L.; Molitch, M.E.; Samson, S.L.; Strasburger, C.J.; van der Lely, A.J.; et al. A Pituitary Society update to acromegaly management guidelines. Pituitary 2021, 24, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogedegbe, O.J.; Cheema, A.Y.; Khan, M.A.; Junaid, S.Z.S.; Erebo, J.K.; Ayirebi-Acquah, E.; Okpara, J.; Bofah, D.; Okon, J.G.; Munir, M.; et al. A comprehensive review of four clinical practice guidelines of acromegaly. Cureus 2022, 14, e28722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giustina, A.; Barkhoudarian, G.; Beckers, A.; Ben-Shlomo, A.; Biermasz, N.; Biller, B.; Boguszewski, C.; Bolanowski, M.; Bollerslev, J.; Bonert, V.; et al. Multidisciplinary management of acromegaly: A consensus. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2020, 21, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustina, A.; Barkan, A.; Beckers, A.; Biermasz, N.; Biller, B.M.K.; Boguszewski, C.; Bolanowski, M.; Bonert, V.; Bronstein, M.D.; Casanueva, F.F.; et al. A consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of acromegaly comorbidities: An update. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, e937–e946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slagboom, T.N.A.; van Bunderen, C.C.; De Vries, R.; Bisschop, P.H.; Drent, M.L. Prevalence of clinical signs, symptoms and comorbidities at diagnosis of acromegaly: A systematic review in accordance with PRISMA guidelines. Pituitary 2023, 26, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padova, G.; Borzì, G.; Incorvaia, L.; Siciliano, G.; Migliorino, V.; Vetri, M.; Tita, P. Prevalence of osteoporosis and vertebral fractures in acromegalic patients. Clin. Cases Miner. Bone Metab. 2011, 8, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Rolla, M.; Jawiarczyk-Przybyłowska, A.; Halupczok-Żyła, J.; Kałużny, M.; Konopka, B.M.; Błoniecka, I.; Zieliński, G.; Bolanowski, M. Complications and comorbidities of acromegaly—Retrospective study in polish center. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 642131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullu, B.E.; Celik, O.; Gazioglu, N.; Kadioglu, P. Thyroid cancer is the most common cancer associated with acromegaly. Pituitary 2010, 13, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzilay, J.; Heatley, G.J.; Cushing, G.W. Benign and malignant tumors in patients with acromegaly. Arch. Intern. Med. 1991, 151, 1629–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaroni, C.; Selice, R.; Benedini, S.; De Menis, E.; Arosio, M.; Ronchi, C.; Gasperi, M.; Manetti, L.; Arnaldi, G.; Polenta, B.; et al. Adrenal morpho-functional alterations in patients with acromegaly. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2008, 31, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifănescu, R.A.; Dal, J. Cancer risk in patients with acromegaly–is extensive screening needed? Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1503633. [Google Scholar]
- Esposito, D.; Ragnarsson, O.; Johannsson, G.; Olsson, D.S. Incidence of benign and malignant tumors in patients with acromegaly is increased: A nationwide population-based study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, 3487–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demarchis, L.; Chiloiro, S.; Giampietro, A.; De Marinis, L.; Bianchi, A.; Fleseriu, M.; Pontecorvi, A. Cancer screening in patients with acromegaly: A plea for a personalized approach and international registries. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2025, 26, 525–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasuki, L.; Maia, B.; Gadelha, M.R. Acromegaly and colorectal neoplasm: An update. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 924952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruchała, M.; Szczepanek-Parulska, E.; Fularz, M.; Woliński, K. Risk of neoplasms in acromegaly [Polish version: Ryzyko rozwoju nowotworów w akromegalii p. 118]. Contemp. Oncol./Współczesna Onkol. 2012, 2, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Jiao, R.; Yang, S.; Wang, Y.; Bai, X.; Zhou, J.; Li, R.; Wang, L.; Yang, H.; Yao, Y.; et al. Incidence and risk factors of cancers in acromegaly: A Chinese single-center retrospective study. Endo-Crine 2023, 82, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzolo, M.; Reimondo, G.; Berchialla, P.; Ferrante, E.; Malchiodi, E.; De Marinis, L.; Pivonello, R.; Grottoli, S.; Losa, M.; Cannavo, S.; et al. Acromegaly is associated with increased cancer risk: A survey in Italy. Endocr.-Relat. Cancer 2017, 24, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killinger, Z.; Kužma, M.; Sterančáková, L.; Payer, J. Osteoarticular changes in acromegaly. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 2012, 839282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustina, A. Acromegaly and bone: An update. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 38, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-González, R.; Royuela, A.; Zamarron, A. Survival following vertebral compression fractures in population over 65 years old. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2023, 35, 1609–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colao, A.; Pivonello, R.; Spinelli, L.; Galderisi, M.; Auriemma, R.S.; Galdiero, M.; Vitale, G.; De Leo, M.; Lombardi, G. A retrospective analysis on biochemical parameters, cardiovascular risk and cardiomyopathy in elderly acromegalic patients. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2007, 30, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiloiro, S.; Giampietro, A.; Gagliardi, I.; Bondanelli, M.; Epifani, V.; Milardi, D.; Ambrosio, M.R.; Zatelli, M.C.; Pontecorvi, A.; De Marinis, L.; et al. Systemic comorbidities of acromegaly in real-life experience: Which difference among young and elderly patients? Endocrine 2023, 80, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Category | Subcategory | Number of Patients (at Diagnosis) | Percentage of Patients | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Female | 43 | 54% | 0.500 1 |
| Male | 36 | 46% | ||
| Age group | 17–39 | 30 | 38% | <0.001 2 |
| 40–59 | 37 | 47% | ||
| ≥60 | 12 | 15% | ||
| Outcome | Remission | 67 | 85% | <0.001 1 |
| Non remission | 12 | 15% | ||
| Surgery | No surgery | 11 | 14% | <0.001 2 |
| One surgery | 57 | 73% | ||
| Two surgeries | 10 | 13% | ||
| Medical agents | One agent | 36 | 67% | <0.001 2 |
| Two agents | 14 | 26% | ||
| Three agents | 4 | 7% | ||
| Monotherapy | *SSAs | 32 | 90.3% | <0.001 1 |
| Dopamine agonists | 3 | 9.7% | ||
| Pegvisomant | 1 | 3% | ||
| Radiotherapy | No | 63 | 82% | <0.001 1 |
| Yes | 14 | 18% | ||
| Adenoma size | Microadenoma | 8 | 12% | <0.001 1 |
| Macroadenoma | 58 | 88% | ||
| Granulation | Dense | 14 | 47% | 1.000 1 |
| Sparse | 16 | 53% | ||
| Type 2 diabetes 3 | No | 42 | 59% | 0.154 1 |
| Yes | 29 (3) | 41% | ||
| Hyperlipidemia 4 | No | 36 | 51% | 1.00 1 |
| Yes | 35 (4) | 49% | ||
| Hypertension 5 | No | 38 | 53% | 0.724 1 |
| Yes | 34 (2) | 47% | ||
| Cardiovascular disease 6 | No | 43 | 60% | 0.125 1 |
| Yes | 29 (2) | 40% | ||
| Cardiovascular disease | Valvular lesions | 19 | 26% | - |
| Ischemic disease | 4 (2) | 5.5% | ||
| Hypertrophy | 6 | 8% | ||
| Diastolic dysfunction | 13 (1) | 18% | ||
| Systolic dysfunction | 3 | 4% | ||
| Hepatic steatosis 7 | No | 28 (0) | 58% | 0.312 1 |
| Yes | 20 (0) | 42% | ||
| Bone disease | No | 29 | 56% | 0.488 1 |
| Yes | 23 (2) | 44% | ||
| Osteopenia/Osteoporosis 8 | - | 12/11 (2) | 23%/21% | - |
| Neoplasia Before or at the Time of Acromegaly Diagnosis | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Benign | Malignant | ||
| Neoplasia | Number of patients (percentage) | Neoplasia | Number of patients (percentage) |
| Thyroid nodules | 7 (10%) | Papillary thyroid carcinoma | 1 (1.4%) |
| Colon tubular adenoma, polyp | 1 (1.3%), 2 (2.6%) | Bladder carcinoma | 1 (1.4%) |
| Ovarian teratoma | 1 (1.3%) | Breast cancer | 1 (1.4%) |
| Lipoma | 1 (1.3%) | - | - |
| Endometrial hyperplasia | 1 (1.3%) | - | - |
| Cervix polyp; vocal cord polyp | 1 (1.3%), 1 (1.3%) | - | - |
| Neoplasia after the time of acromegaly diagnosis | |||
| Benign | Malignant | ||
| Neoplasia | Number of patients (percentage) | Neoplasia | Number of patients (percentage) |
| Thyroid nodules | 26 (34%) | Papillary thyroid carcinoma | 3 (3.9%) |
| Colon adenoma; polyp | 6 (8%), 8 (10.5%) | Breast cancer | 3 (3.9%) |
| Adrenal adenoma–hyperplasia | 13 (17%) | Kidney cancer | 2 (2.6%) |
| Meningioma | 2 (2.6%) | Prostate cancer | 1 (1.3%) |
| Bladder papilloma | 1 (1.3%) | Urothelial cancer | 1 (1.3%) |
| Esophagus papilloma | 1 (1.3%) | Colon cancer | 1 (1.3%) |
| Uterine fibromyoma | 1 (1.3%) | Melanoma | 1 (1.3%) |
| Other (pancreatic lesion, kidney mass, or ECL hyperplasia) | 3 (3.9%) | Duodenal neuroendocrine tumor | 1 (1.3%) |
| - | - | Paraganglioma | 1 (1.3%) |
| Category | Subcategory | Group A (<60 yrs) | Group B (≥60 yrs) | OR (CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Female | 37 (55%) | 6 (50%) | 1.233 (0.361–4.219) | 0.738 1 |
| Male | 30 (45%) | 6 (50%) | |||
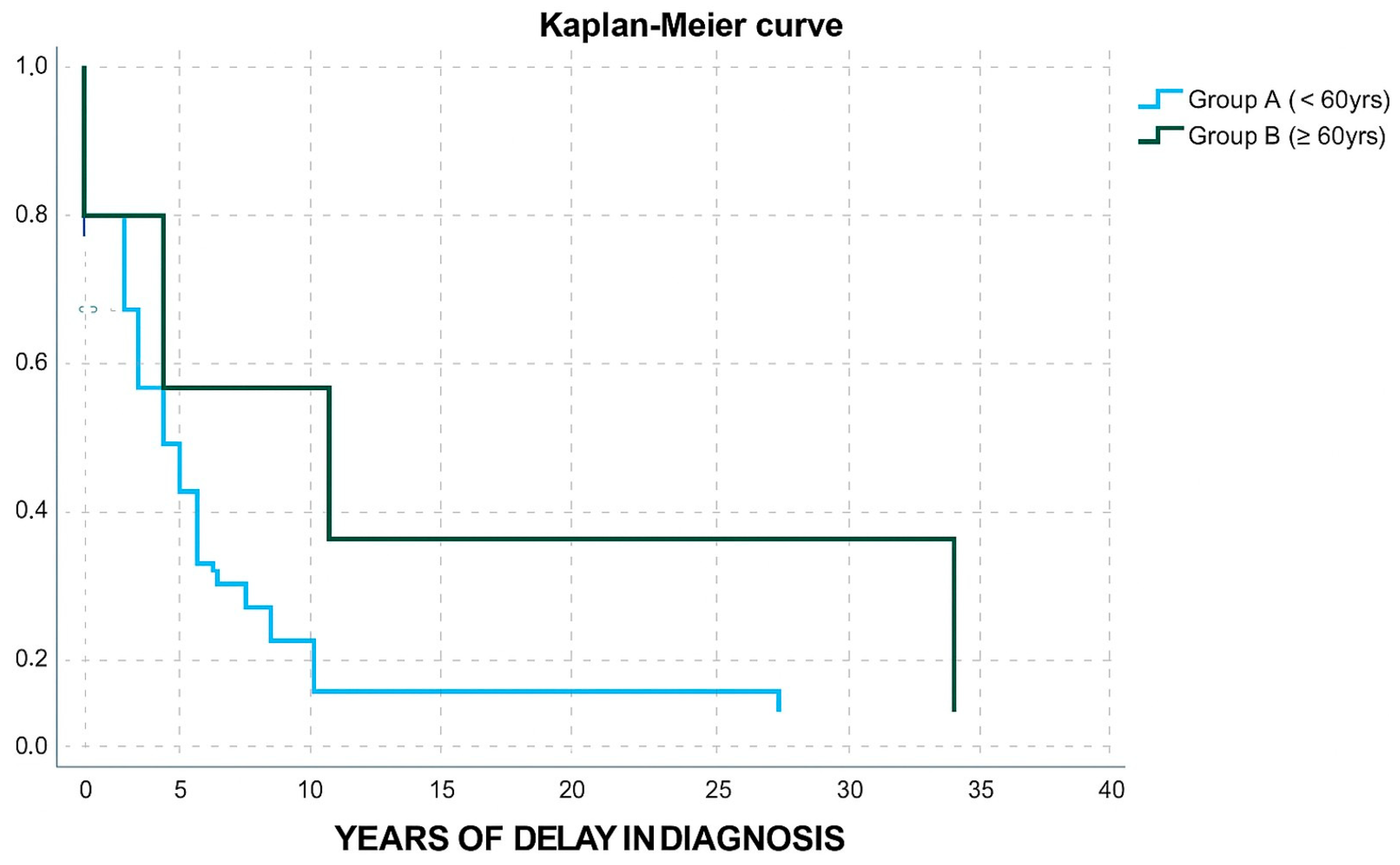
| Diagnosis age; mean ± SD | - | 41 ± 10 | 65 ± 5 | - | <0.001 2 |
| IGF-1/ULN ratio; mean ± SD/median | - | 2.6 ± 1/2.3 | 3.5 ± 2/3 | - | 0.434 2 |
| Adenoma size | Microadenoma | 6 (11%) | 2 (18%) | 0.551 (0.096–3.174) | 0.505 1 |
| Macroadenoma | 49 (89%) | 9 (82%) | |||
| Granulation | Dense | 13 (46%) | 1 (50%) | 0.867 (0.049–15.279) | 0.922 1 |
| Sparse | 15 (54%) | 1 (50%) | |||
| Outcome | Remission | 58 (87%) | 9 (75%) | 2.148 (0.487–9.469) | 0.312 1 |
| Non remission | 9 (13) | 3 (25%) | |||
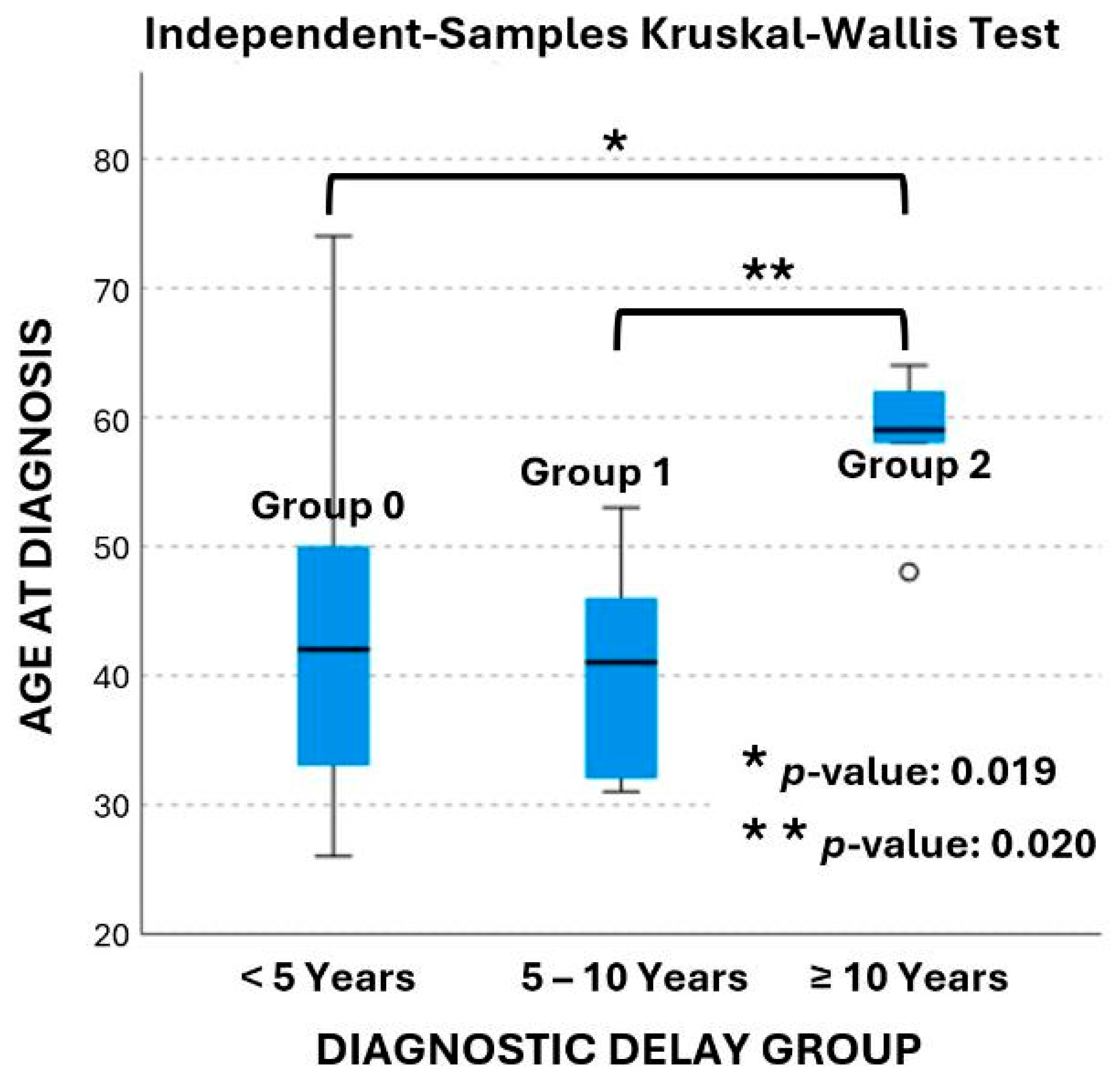
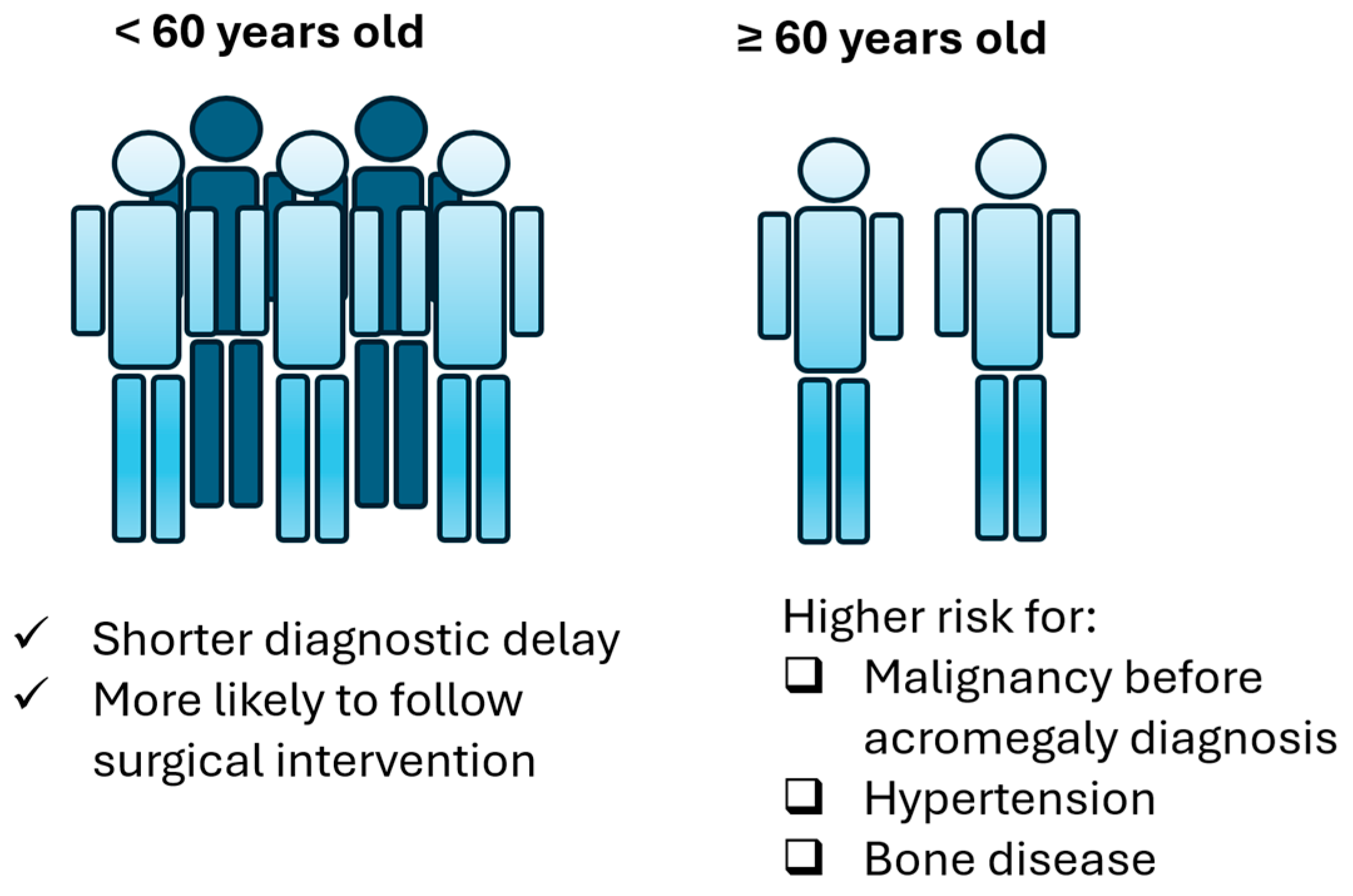
| Diagnostic delay group | 0 (<5 years) | 26 (66.7%) | 2 (50%) | 12 (1.219–118.1) 3 | 0.033 1 |
| 1 (5–10 years) | 10 (25.6%) | 0 | |||
| 2 (≥10 years) | 3 (7.7%) | 2 (50%) | |||
| Surgery | No surgery | 4 (6%) | 7 (58%) | 0.046 (0.01–0.213) 4 | <0.001 1 |
| 1 surgery | 52 (79%) | 5 (42%) | |||
| 2 surgeries | 10 (15%) | 0 | |||
| Medical agents | One agent | 29 (64%) | 7 (78%) | 0.518 (0.096–2.795) 5 | 0.444 1 |
| 2 agents | 13 (29%) | 1 (11%) | |||
| 3 agents | 3 (7) | 1 (11%) | |||
| Radiotherapy | No | 52 (80%) | 11 (92%) | 0.364 (0.043–3.077) | 0.353 1 |
| Yes | 13 (20%) | 1 (8%) | |||
| Cardiovascular disease | - | 22 (36%) | 7 (64%) | 3.102 (0.816–11.789) | 0.096 |
| Type 2 diabetes | - | 23 (38%) | 6 (54.5%) | 1.93 (0.528–7.054) | 0.320 |
| Hyperlipidemia | - | 29 (48%) | 6 (54.5%) | 1.283 (0.353–4.661) | 0.705 |
| Hypertension | - | 25 (41%) | 9 (82%) | 6.48 (1.289–32.578) | 0.023 |
| Hepatic steatosis | - | 18 (46%) | 2 (18%) | 0.333 (0.061–1.812) | 0.203 |
| Bone disease | - | 16 (36%) | 7 (87.5%) | 12.25 (1.38–108.744) | 0.025 |
| Osteopenia | - | 8 (18%) | 4 (50%) | 4.5 (0.924–21.925) | 0.063 |
| Osteoporosis | - | 8 (18%) | 3 (37.5%) | 2.7 (0.532–13.691) | 0.230 |
| Variable | Exp (B) | 95% CI for Exp (B) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender (male vs. female) | 1.233 | 0.361–4.219 | 0.738 |
| Age at diagnosis | 1.016 | 0.95–1.087 | 0.647 |
| IGF-1/ULN ratio at diagnosis | 1.717 | 0.903–3.264 | 0.099 |
| Adenoma size | 1.286 | 0.141–11.75 | 0.824 |
| Granulation type (sparse vs. dense) | 1.385 | 0.196–9.768 | 0.744 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Chalmantzi, V.; Vlachou, S.; Chondrogianni, M.E.; Panagaki, M.; Spyroglou, A.; Tsoli, M.; Kassi, E.; Kaltsas, G.; Alexandraki, K.I. The Journey of Acromegaly Towards Treatment: A Single-Center Study. J. Pers. Med. 2026, 16, 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm16020085
Chalmantzi V, Vlachou S, Chondrogianni ME, Panagaki M, Spyroglou A, Tsoli M, Kassi E, Kaltsas G, Alexandraki KI. The Journey of Acromegaly Towards Treatment: A Single-Center Study. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2026; 16(2):85. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm16020085
Chicago/Turabian StyleChalmantzi, Varvara, Sophia Vlachou, Maria Eleni Chondrogianni, Maria Panagaki, Ariadni Spyroglou, Marina Tsoli, Eva Kassi, Gregory Kaltsas, and Krystallenia I. Alexandraki. 2026. "The Journey of Acromegaly Towards Treatment: A Single-Center Study" Journal of Personalized Medicine 16, no. 2: 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm16020085
APA StyleChalmantzi, V., Vlachou, S., Chondrogianni, M. E., Panagaki, M., Spyroglou, A., Tsoli, M., Kassi, E., Kaltsas, G., & Alexandraki, K. I. (2026). The Journey of Acromegaly Towards Treatment: A Single-Center Study. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 16(2), 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm16020085








