The Predictive Value of Red Cell Distribution Width in End-Stage Colorectal Cancers’ 6-Month Palliative Chemotherapy Response—A Single Center’s Experience
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Methods
2.2. Statistical Analysis
2.3. Bioethics Committee
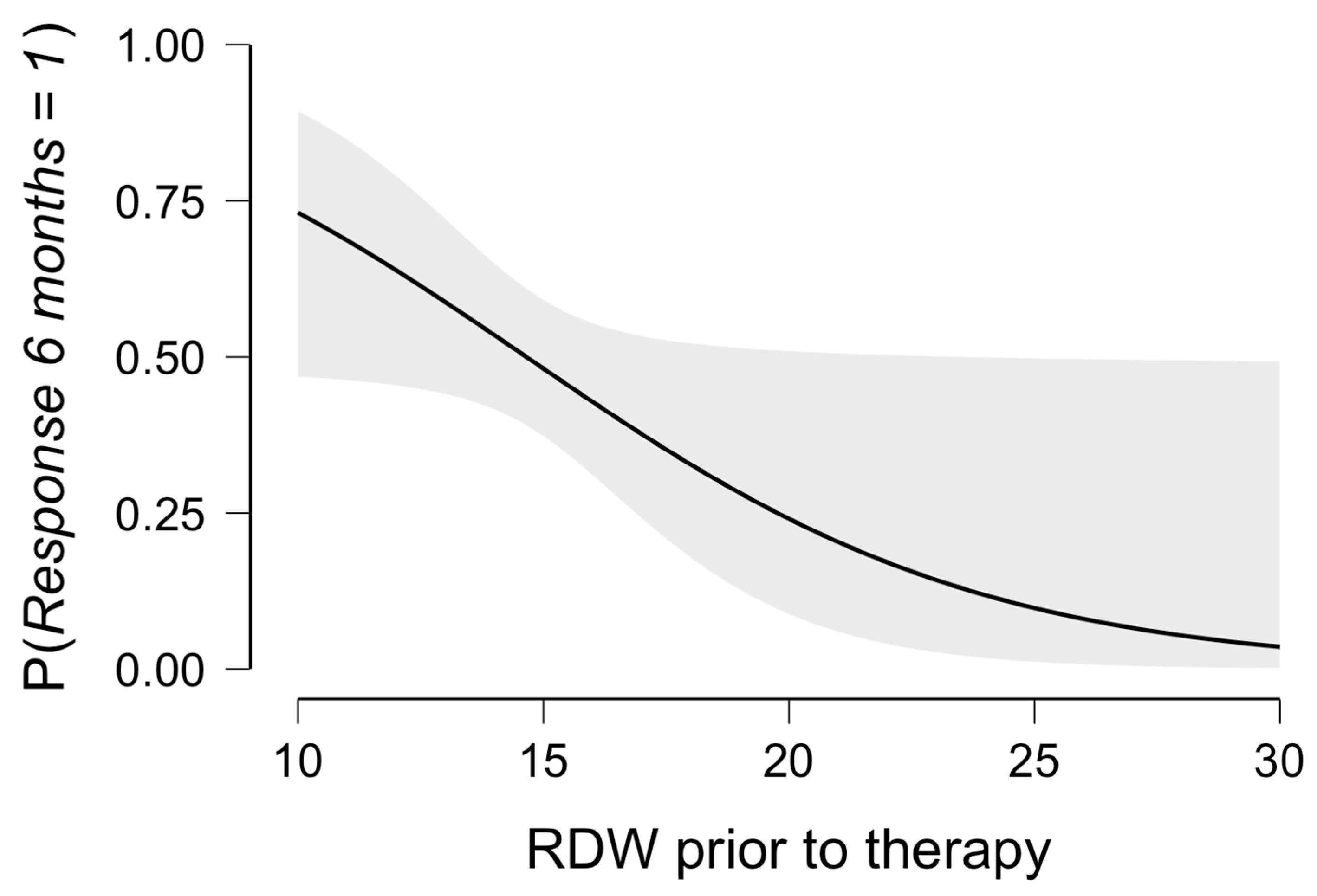
3. Results
3.1. The Multivariable Model for Therapy Response
3.2. Receiver Operating Curve (ROC) for Disease Regression
4. Discussion
Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| a-EGFR | anti-epidermal growth factor receptor |
| AH | arterial hypertension |
| AST | aspartate aminotransferase, |
| BMI | body mass index |
| CI | confidence interval |
| CRC | colorectal cancer |
| CT | computed tomography |
| CTH | chemotherapy |
| DM | diabetes mellitus |
| FH | positive family history for oncological disease |
| GIC | gastrointestinal cancer |
| Hct | hematocrit |
| kg | kilograms |
| M | male |
| MLR | monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio |
| m2 | square meter |
| n | number |
| OR | odds ratio |
| Plt | platelets |
| RDW | red cell distribution width |
| ROC | receiver operating curve |
| y | years |
| Wbc | white blood count |
References
- Arnold, M.; Abnet, C.C.; Neale, R.E.; Vignat, J.; Giovannucci, E.L.; McGlynn, K.A.; Bray, F. Global Burden of 5 Major Types of Gastrointestinal Cancer. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danpanichkul, P.; Suparan, K.; Tothanarungroj, P.; Dejvajara, D.; Rakwong, K.; Pang, Y.; Barba, R.; Thongpiya, J.; Fallon, M.B.; Harnois, D.; et al. Epidemiology of gastrointestinal cancers: A systematic analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Gut 2024, 74, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zheng, R.; Li, J.; Zeng, H.; Li, L.; Chen, R.; Sun, K.; Han, B.; Bray, F.; Wei, W.; et al. Global, regional, and national lifetime risks of developing and dying from gastrointestinal cancers in 185 countries: A population-based systematic analysis of GLOBOCAN. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 9, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mysuru Shivanna, L.; Urooj, A. A Review on Dietary and Non-Dietary Risk Factors Associated with Gastrointestinal Cancer. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2016, 47, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baidoun, F.; Elshiwy, K.; Elkeraie, Y.; Merjaneh, Z.; Khoudari, G.; Sarmini, M.T.; Gad, M.; Al-Husseini, M.; Saad, A. Colorectal Cancer Epidemiology: Recent Trends and Impact on Outcomes. Curr. Drug Targets 2021, 22, 998–1009. [Google Scholar]
- Carbone, F.; Spinelli, A.; Ciardiello, D.; Realis Luc, M.; de Pascale, S.; Bertani, E.; Fazio, N.; Fumagalli Romario, U. Prognosis of early-onset versus late-onset sporadic colorectal cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2025, 215, 115172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sninsky, J.A.; Shore, B.M.; Lupu, G.V.; Crockett, S.D. Risk Factors for Colorectal Polyps and Cancer. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. N. Am. 2022, 32, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, E.; Arnold, M.; Gini, A.; Lorenzoni, V.; Cabasag, C.J.; Laversanne, M.; Vignat, J.; Ferlay, J.; Murphy, N.; Bray, F. Global burden of colorectal cancer in 2020 and 2040: Incidence and mortality estimates from GLOBOCAN. Gut 2023, 72, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osseis, M.; Nehmeh, W.A.; Rassy, N.; Derienne, J.; Noun, R.; Salloum, C.; Rassy, E.; Boussios, S.; Azoulay, D. Surgery for T4 Colorectal Cancer in Older Patients: Determinants of Outcomes. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawla, P.; Sunkara, T.; Barsouk, A. Epidemiology of colorectal cancer: Incidence, mortality, survival, and risk factors. Prz. Gastroenterol. 2019, 14, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, Q.; Tan, A.F.; Loh, C.J.L.; Toh, H.C. Sex differences in cancer and immunotherapy outcomes: The role of androgen receptor. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1416941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufrusine, B.; Di Lisio, C.; Maurizio, A.; Sallese, M.; De Laurenzi, V.; Dainese, E. Influence of food emulsifiers on cellular function and inflammation, a preliminary study. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1197686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, X.K.; Wang, J.B.; Zhao, F.H.; Fan, J.H.; Qiao, Y.L.; Taylor, P.R.; Abnet, C.C. Combined risk factors and risk of upper gastrointestinal cancer mortality in the Linxian general population. Int. J. Cancer 2022, 151, 1462–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grady, W.M.; Yu, M.; Markowitz, S.D. Epigenetic Alterations in the Gastrointestinal Tract: Current and Emerging Use for Biomarkers of Cancer. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 690–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Kawada, K.; Obama, K. Inflammation-Related Biomarkers for the Prediction of Prognosis in Colorectal Cancer Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.; Li, J.; Yao, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Z.; Weng, S. Prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in colorectal cancer liver metastasis: A meta-analysis of results from multivariate analysis. Int. J. Surg. 2022, 107, 106959–106967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuss, J.; Voloboyeva, A.; Polovyj, V.; Yaremkevych, R. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in predicting postoperative complications and prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Pol. Prz. Chir. 2022, 94, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Li, G.L.; Zhu, H.Q.; Yu, J.D.; Chen, Z.P.; Wu, J.Y.; Lin, Z.Y.; Wan, Y.L. The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and lactate dehydrogenase combined in predicting liver metastasis and prognosis of colorectal cancer. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1205897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, Y.; Nishida, T.; Doi, T. Current status of and future prospects for the treatment of unresectable or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Gastric Cancer 2023, 26, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lote, H.; Chau, I. Immunotherapy in Gastrointestinal Cancers. Cancer Treat. Res. 2024, 192, 277–303. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, X.; Madeti, Y.; Cai, J.; Li, W.; Cong, L.; Lu, J.; Mo, L.; Liu, H.; He, S.; Yu, C.; et al. Recent developments in immunotherapy for gastrointestinal tract cancers. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2024, 17, 65–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Cha, Y.; Shin, S.J.; Park, Y.S.; Kang, J.H.; Kim, C.; Lim, S.H.; Kang, M.J.; Kim, J.G.; Hwang, I.G.; et al. Treatment Patterns and Prognosis of Palliative Chemotherapy Combined with Targeting Agents in Patients with Unresectable Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: CHOICE, A Multicenter Longitudinal Observational Study. Anticancer Res. 2024, 44, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koncina, E.; Haan, S.; Rauh, S.; Letellier, E. Prognostic and Predictive Molecular Biomarkers for Colorectal Cancer: Updates and Challenges. Cancers 2020, 12, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanoli, A.; Parente, P.; Fassan, M.; Mastracci, L.; Grillo, F. Gut inflammation and tumorigenesis: Every site has a different tale to tell. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2023, 18, 2169–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denk, D.; Greten, F.R. Inflammation: The incubator of the tumor microenvironment. Trends Cancer 2022, 8, 901–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruch, E.N.; Nagarajan, P.; Gleber-Netto, F.O.; Rao, X.; Xie, T.; Akhter, S.; Adewale, A.; Shajedul, I.; Mattson, B.J.; Ferrarotto, R.; et al. Inflammation induced by tumor-associated nerves promotes resistance to anti-PD-1 therapy in cancer patients and is targetable by interleukin-6 blockade. Biol. Sci. 2023; preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santini, D.; Zeppola, T.; Russano, M.; Citarella, F.; Anesi, C.; Buti, S.; Tucci, M.; Russo, A.; Sergi, M.C.; Adamo, V.; et al. PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoint inhibitors during late stages of life: An ad-hoc analysis from a large multicenter cohort. J. Transl. Med. 2021, 19, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Chang, M.; Chang, H.M.; Chang, F. Expending Role of Microsatellite Instability in Diagnosis and Treatment of Colorectal Cancers. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2017, 48, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Lee, S.; Song, J.H.; Choi, S.; Cho, M.; Kwon, I.G.; Son, T.; Kim, H.I.; Cheong, J.H.; Hyung, W.J.; et al. Prognostic significance of body mass index and prognostic nutritional index in stage II/III gastric cancer. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 46, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, W.X.; Wang, X.; Li, C.; Li, S.; Li, H.; Xu, F.; Chen, J.; Zhao, S.; Li, H. Pretreatment absolute lymphocyte count is an independent predictor for survival outcomes for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients treated with neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy and pembrolizumab: An analysis from a prospective cohort. Thorac. Cancer 2023, 14, 1556–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhao, L.; Li, Q.; Zhu, J.; Yang, H.; Guo, S.; Xi, M. Prediction of Pathologic Response to Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy in Patients with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Incorporating Hematological Biomarkers. Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 53, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koržinek, M.; Ćelap, I.; Fabijanec, M.; Žanić, T.; Ljubičić, N.; Baršić, N.; Verbanac, D.; Barišić, K.; Rajković, M.G. Complete blood count parameters and inflammation-related biomarkers in patients with colorectal carcinoma. Acta Pharm. 2025, 74, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, L.; Yan, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, M.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y. Inflammation and tumor progression: Signaling pathways and targeted intervention. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 263–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virdee, P.S.; Marian, I.R.; Mansouri, A.; Elhussein, L.; Kirtley, S.; Holt, T.; Birks, J. The Full Blood Count Blood Test for Colorectal Cancer Detection: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Critical Appraisal. Cancers 2020, 12, 2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felker, G.M.; Allen, L.A.; Pocock, S.J.; Shaw, L.K.; McMurray, J.J.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Swedberg, K.; Wang, D.; Yusuf, S.; Michelson, E.L.; et al. Red cell distribution width as a novel prognostic marker in heart failure: Data from the CHARM Program and the Duke Databank. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 50, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobieraj, M.; Urbanowicz, T.; Olasińska-Wiśniewska, A.; Gładki, M.; Michalak, M.; Filipiak, K.J.; Węclewska, A.; Bartkowska-Śniatkowska, A.; Tykarski, A.; Bobkowski, W.; et al. Anisocytosis as a possible predictor of low cardiac output syndrome in children undergoing mitral valve surgery. Adv. Med. Sci. 2024, 69, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fava, C.; Cattazzo, F.; Hu, Z.D.; Lippi, G.; Montagnana, M. The role of red blood cell distribution width (RDW) in cardiovascular risk assessment: Useful or hype? Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Hu, S.; Xie, J.; Liu, H.; Li, C. The red blood cell distribution width to albumin ratio was a potential prognostic biomarker for acute respiratory failure: A retrospective study. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2024, 24, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Huang, Z.; Kang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Lu, P.; Lin, Q.; Cai, Z.; Cao, Y.; Zhu, X. Clinical Usefulness and Prognostic Value of Red Cell Distribution Width in Colorectal Cancer. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 9858943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xing, C.; Wei, M.; Wu, H.; Hu, X.; Li, S.; Sun, G.; Zhang, G.; Wu, B.; Zhang, F.; et al. Combining Red Blood Cell Distribution Width (RDW-CV) and CEA Predict Poor Prognosis for Survival Outcomes in Colorectal Cancer. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 1162–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coradduzza, D.; Medici, S.; Chessa, C.; Zinellu, A.; Madonia, M.; Angius, A.; Carru, C.; De Miglio, M.R. Assessing the Predictive Power of the Hemoglobin/Red Cell Distribution Width Ratio in Cancer: A Systematic Review and Future Directions. Medicina 2023, 59, 2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.L.; Zhou, X.; Xiao, D.C. Is red blood cell distribution width a prognostic factor for colorectal cancer? A meta-analysis. Front. Surg. 2022, 9, 945126–945134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fancellu, A.; Zinellu, A.; Mangoni, A.A.; Popova, A.; Galotti, F.; Feo, C.F.; Attene, F.; Cossu, A.; Palmieri, G.; Paliogiannis, P. Red Blood Cell Distribution Width (RDW) Correlates to the Anatomical Location of Colorectal Cancer. Implications for Clinical Use. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2022, 53, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Huang, J.H.; Cong, H. Clinical Value of Routine Biomarkers for Colorectal Patients: A Retrospective Study. Clin. Lab. 2024, 70, 10.7754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casali, P.G.; Blay, J.Y.; Abecassis, N.; Bajpai, J.; Bauer, S.; Biagini, R.; Bielack, S.; Bonvalot, S.; Boukovinas, I.; Bovee, J.V.M.G.; et al. Gastrointestinal stromal tumours: ESMO-EURACAN-GENTURIS Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters | Complete Response (1) n = 2 | Partial Response (2) n = 38 | Stable Disease (3) n = 36 | Disease Progression (4) n = 7 | P 1 vs. 2 | P 1 vs. 3 | P 1 vs. 4 | P 2 vs. 3 | p 2 vs. 4 | P 3 vs. 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic | ||||||||||
| Sex (M (%)) | 1 (50) | 26 (68) | 4 (57) | 6 (60) | 1.000 | 0.249 | 0.417 | <0.001 | 0.488 | 0.745 |
| Age (y) (median (Q1–Q3)) | 69 (68–70) | 68 (62–73) | 71 (65–72) | 72 (69–77) | 0.673 | 0.845 | 0.678 | 0.371 | 0.028 | 0.835 |
| BMI (median (Q1–Q3)) | 26 (25–28) | 26 (24–28) | 25 (22–29) | 25 (23–29) | 0.901 | 0.782 | 0.802 | 0.793 | 0.732 | 0.836 |
| Clinical | ||||||||||
| AH (n (%)) | 2 (100) | 21 (55) | 23 (64) | 5 (71) | 0.499 | 0.538 | 1.000 | 0.486 | 0.174 | 0.294 |
| DM (n (%)) | 0 (0)0 | 9 (23) | 7 (19) | 0 (0) | 0.565 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.780 | 0.433 | 0.675 |
| Nicotine (n (%)) | 0 (0) | 7 (18) | 5 (14) | 0 (0) | 0.688 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.438 | 0.477 | 0.714 |
| FH (n (%)) | 1 (50) | 8 (21) | 6 (17) | 4 (57) | 0.401 | 0.339 | 1.000 | 0.769 | 0.131 | 0.489 |
| Therapy | 1.000 | 0.501 | 1.000 | 0.036 | 0.437 | 0.040 | ||||
| CTH (n (%)) | 1 (50) | 18 (47) | 26 (72) | 2 (29) | ||||||
| CTH-aEFGR (n (%)) | 1 (50) | 20 (53) | 10 (28) | 5 (71) | ||||||
| Metastases | ||||||||||
| Multiple sides (n (%)) | 1(50) | 14 (37) | 14 (39) | 0 (0) | 1.000 | 0.498 | 0.222 | 1.000 | 0.081 | 0.081 |
| including lungs (n (%)) | 0 (0) | 12 (32) | 12 (33) | 3 (43) | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.500 | 1.000 | 0.670 | 0.680 |
| including liver (n (%)) | 2 (100) | 23 (61) | 23 (64) | 2 (29) | 0.519 | 0.538 | 0.167 | 0.814 | 0.214 | 0.110 |
| Surgery prior to therapy (n (%)) | 2 (100) | 24 (63) | 24 (67) | 7 (100) | 0.533 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.811 | 0.081 | 0.163 |
| Parameters | Response Group n = 40 | No Response Group n = 43 | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic | |||
| Sex (M (%)/F (%)) | 27 (63)/13 (37) | 25 (63)/18 (27) | 0.384 |
| Age (years) (median (Q1–Q3) | 68 (63–73) | 70 (64–76) | 0.190 |
| BMI (kg/m2) (median (Q1–Q3) | 26 (24–28) | 26 (24–28) | 0.678 |
| Comorbidities | |||
| Arterial hypertension (n (%)) | 23 (55) | 28 (60) | 0.482 |
| Diabetes mellitus (n (%)) | 9 (25) | 7 (19) | 0.446 |
| Nicotine (n (%)) | 7 (35) | 5 (25) | 0.194 |
| Oncological family history (n (%)) | 9 (25) | 10 (25) | 0.928 |
| Systemic therapy | 0.109 | ||
| CTH (n (%)) | 19 (48) | 28 (65) | |
| CTH-aEFGR (n (%)) | 21 (52) | 15 (35) | |
| Laboratory results prior to therapy | |||
| WBC (109/dL) (median (Q1–Q3)) | 6.93 (5.55–8.74) | 6.93 (5.43–8.57) | 0.544 |
| Lymphocyte (109/dL) (median (Q1–Q3)) | 1.39 (1.11–1.73) | 1.36 (1.18–1.63) | 0.913 |
| Neutrophil (109/dL) (median (Q1–Q3)) | 4.52 (3.68–6.58) | 4.52 (3.41–6.01) | 0.678 |
| Monocyte (109/dL) (median (Q1–Q3)) | 0.55 (0.40–0.67) | 0.51 (0.43–0.67) | 0.898 |
| MLR (median (Q1–Q3)) | 0.39 (0.25–0.53) | 0.41 (0.27–0.49) | 0.888 |
| Hb median (mmol/L) (median (Q1–Q3)) | 12.9 (11.7–13.9) | 12.9 (11.6–13.5) | 0.457 |
| Hct (%) (median (Q1–Q3)) | 40 (37–42) | 39 (35–42) | 0.297 |
| Plt (109/dL) (median (Q1–Q3)) | 249 (209–311) | 266 (215–296) | 0.719 |
| RDW (%) (median (Q1–Q3)) | 13.8 (13.2–15.5) | 14.9 (13.9–16.2) | 0.007 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) (median (Q1–Q3)) | 0.9 (0.8–1.0) | 0.9 (0.7–1.0) | 0.975 |
| AST (IU/L) (median (Q1–Q3)) | 22 (18–29) | 21 (16–26) | 0.167 |
| Metastases | |||
| Multiple sides (n (%)) | 16 () | 14 () | 0.487 |
| including lungs (n (%)) | 12 () | 15 () | 0.641 |
| including liver (n (%)) | 31 () | 25 () | 0.062 |
| Surgery prior to therapy (n(%)) | 30 | 31 () | 0.770 |
| Parameters | Univariable Model | Multivariable Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p | OR | 95% CI | p | |
| Demographic | ||||||
| Sex (male) | 1.40 | 0.61–3.67 | 0.379 | |||
| Age | 0.97 | 0.93–1.02 | 0.270 | |||
| BMI | 1.03 | 0.44–3.09 | 0.395 | |||
| Clinical | ||||||
| Arterial hypertension | 0.73 | 0.30–1.80 | 0.477 | |||
| Diabetes mellitus | 1.49 | 0.50–4.48 | 0.474 | |||
| Nicotine | 1.91 | 0.57–6.44 | 0.297 | |||
| Oncological family history | 0.98 | 0.34–2.81 | 0.963 | |||
| Surgery prior to systemic therapy | 1.16 | 0.44–3.09 | 0.764 | |||
| Therapy | ||||||
| CTH therapy | 0.49 | 0.20–1.17 | 0.108 | |||
| Laboratory results prior to therapy | 0.81 | 0.65–1.00 | 0.049 | |||
| MLR | 1.20 | 0.87–1.14 | 0.874 | |||
| RDW | 0.80 | 0.61–1.00 | 0.040 | |||
| Hb | 1.18 | 0.89–1.58 | 0.254 | |||
| Creatinine | 0.67 | 0.08–5.50 | 0.701 | |||
| AST | 1.01 | 0.99–1.03 | 0.431 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jankowski, M.; Bratos, K.; Wawer, J.; Urbanowicz, T. The Predictive Value of Red Cell Distribution Width in End-Stage Colorectal Cancers’ 6-Month Palliative Chemotherapy Response—A Single Center’s Experience. J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15, 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15080359
Jankowski M, Bratos K, Wawer J, Urbanowicz T. The Predictive Value of Red Cell Distribution Width in End-Stage Colorectal Cancers’ 6-Month Palliative Chemotherapy Response—A Single Center’s Experience. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2025; 15(8):359. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15080359
Chicago/Turabian StyleJankowski, Maciej, Krystyna Bratos, Joanna Wawer, and Tomasz Urbanowicz. 2025. "The Predictive Value of Red Cell Distribution Width in End-Stage Colorectal Cancers’ 6-Month Palliative Chemotherapy Response—A Single Center’s Experience" Journal of Personalized Medicine 15, no. 8: 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15080359
APA StyleJankowski, M., Bratos, K., Wawer, J., & Urbanowicz, T. (2025). The Predictive Value of Red Cell Distribution Width in End-Stage Colorectal Cancers’ 6-Month Palliative Chemotherapy Response—A Single Center’s Experience. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 15(8), 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15080359








