Awake Craniotomy for the Excision of a Pediatric Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation for Language Preservation: A Case Description
Abstract
1. Introduction
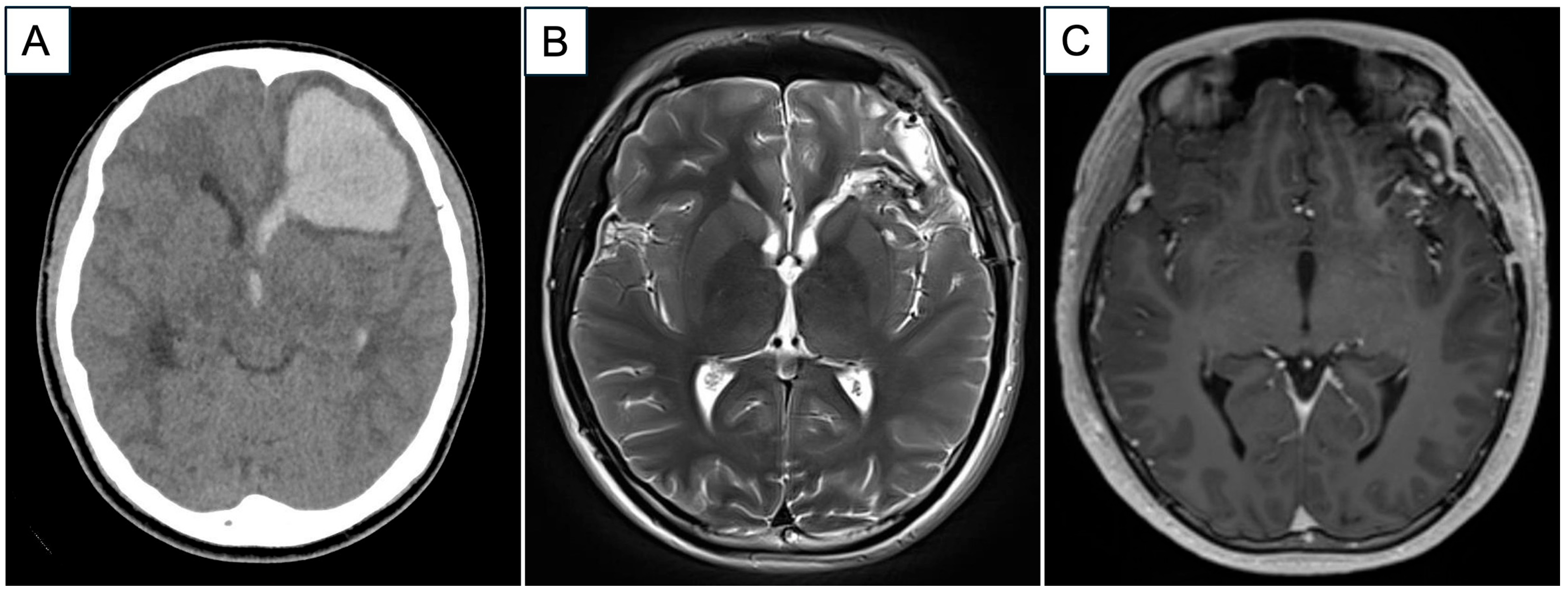
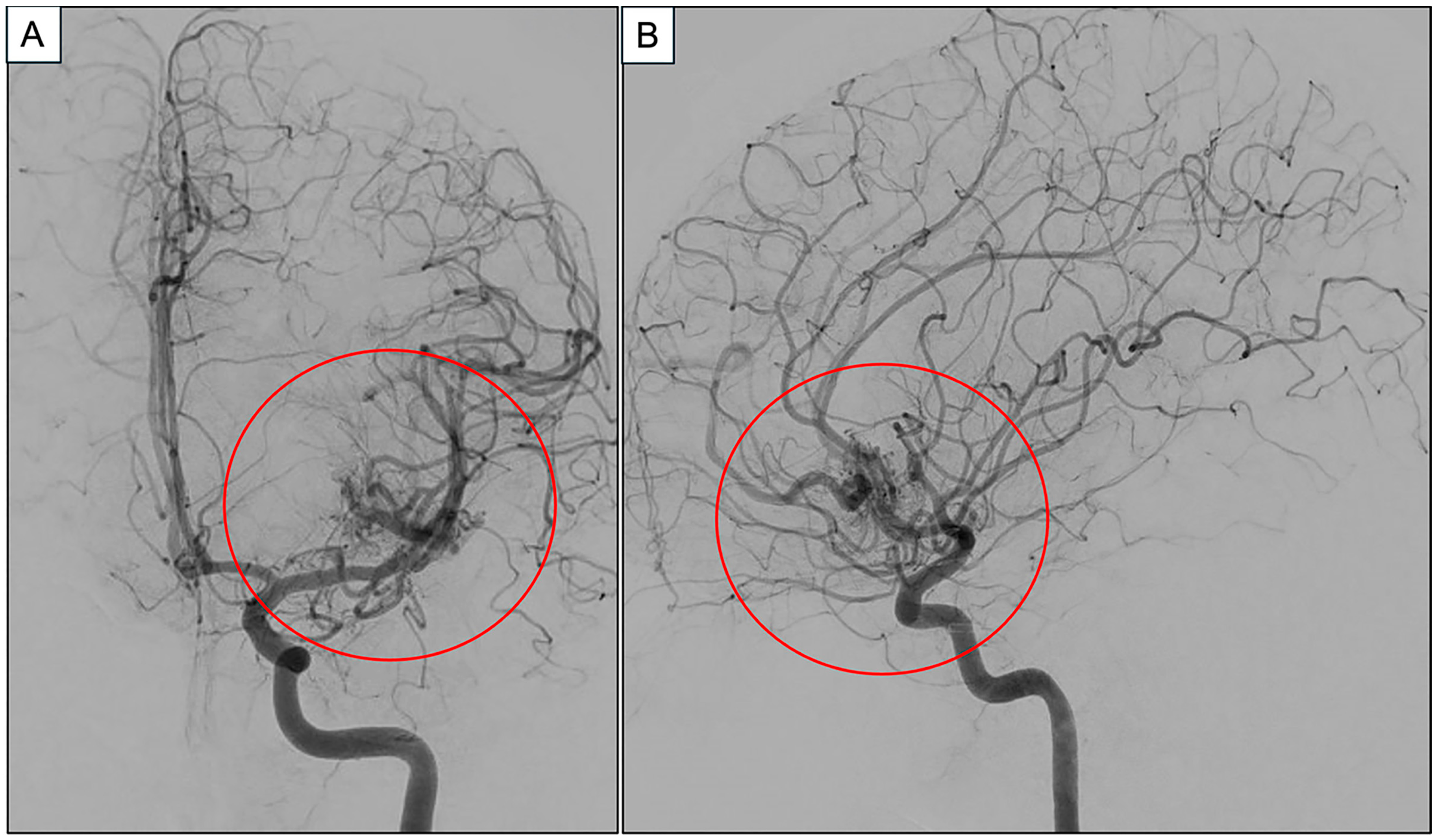
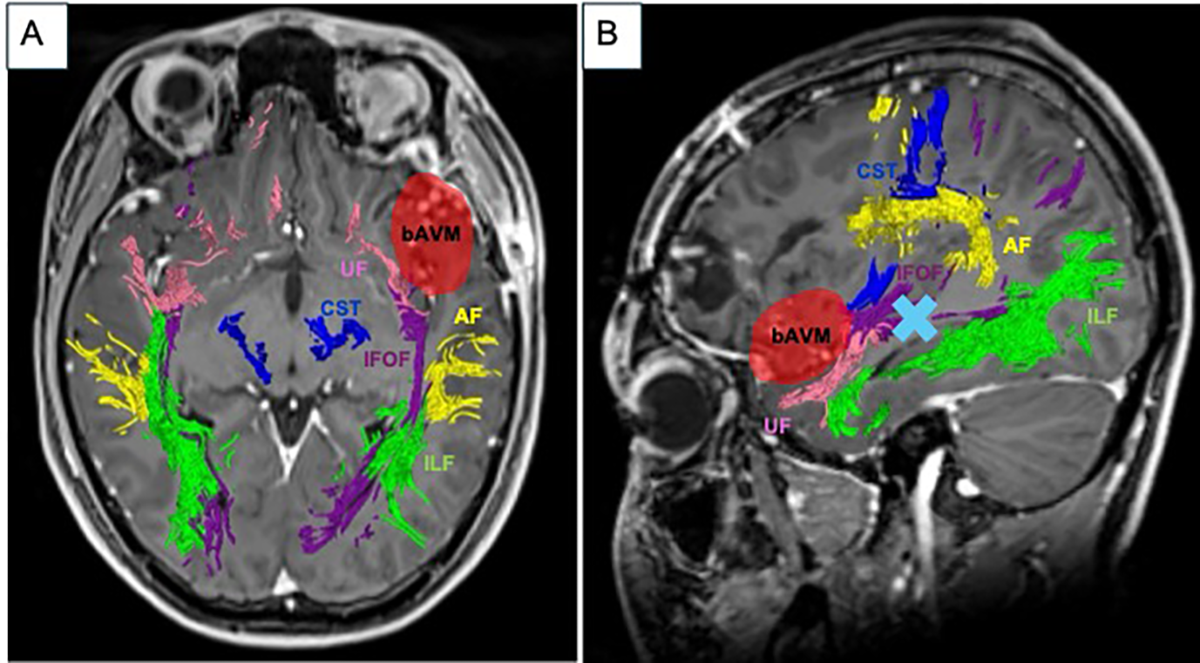
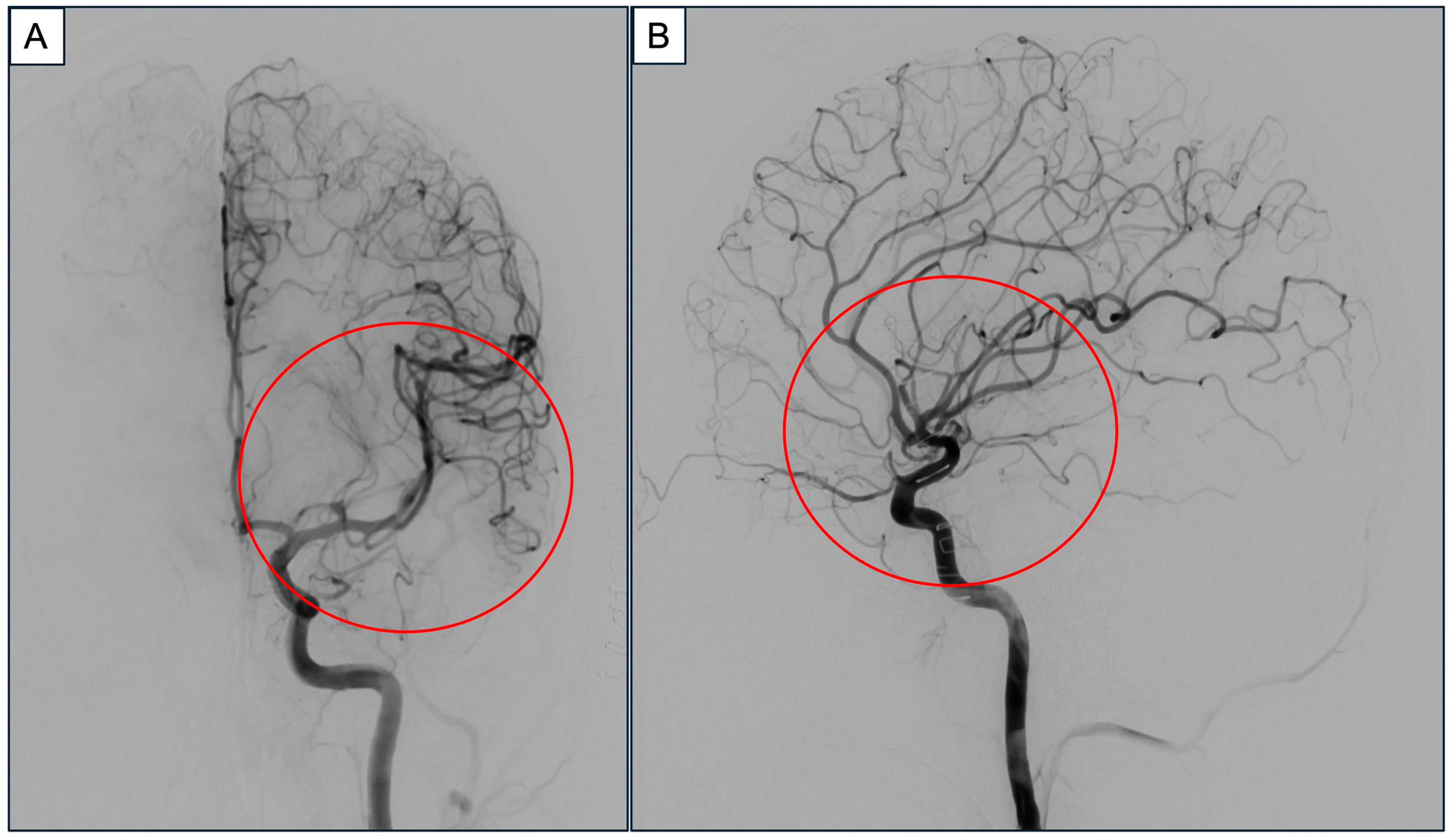
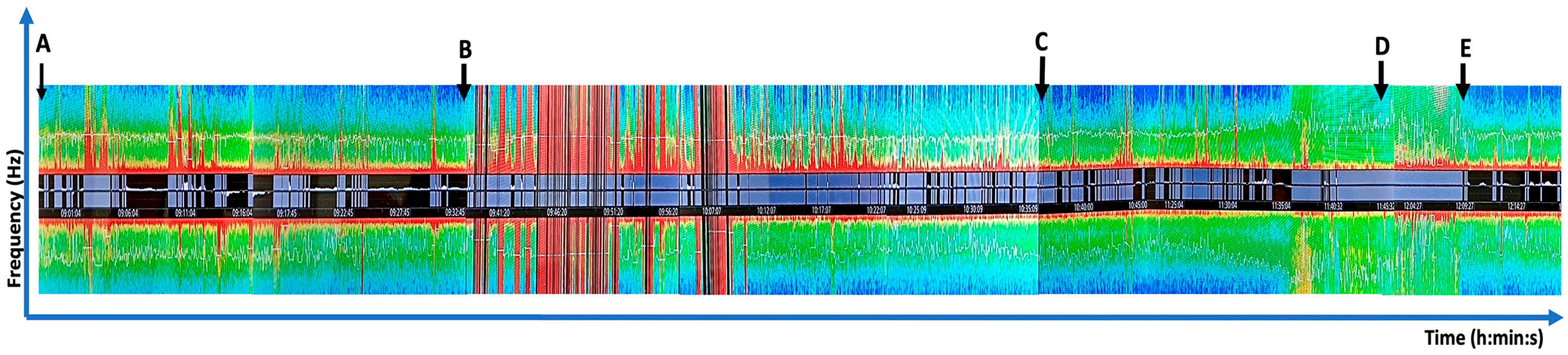
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El-Ghanem, M.; Kass-Hout, T.; Kass-Hout, O.; Alderazi, Y.J.; Amuluru, K.; Al-Mufti, F.; Prestigiacomo, C.J.; Gandhi, C.D. Arteriovenous Malformations in the Pediatric Population: Review of the Existing Literature. Interv. Neurol. 2016, 5, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, R.H. Natural history of intracranial vascular malformations: A review. Neurosurgery 1985, 16, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darsaut, T.E.; Guzman, R.; Marcellus, M.L.; Edwards, M.S.; Tian, L.; Do, H.M.; Chang, S.D.; Levy, R.P.; Adler, J.R.; Marks, M.P.; et al. Management of pediatric intracranial arteriovenous malformations: Experience with multimodality therapy. Neurosurgery 2011, 69, 540–556; discussion 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.Y.; Kim, D.G.; Chung, H.T.; Paek, S.H. Radiosurgery for unruptured cerebral arteriovenous malformations: Long-term seizure outcome. Neurology 2012, 78, 1292–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, B.A.; Du, R. Natural history of cerebral arteriovenous malformations: A meta-analysis. J. Neurosurg. 2013, 118, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Costa, L.; Wallace, M.C.; Ter Brugge, K.G.; O’Kelly, C.; Willinsky, R.A.; Tymianski, M. The natural history and predictive features of hemorrhage from brain arteriovenous malformations. Stroke 2009, 40, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.X.; Cheong, T.M.; Ng, L.P.; Seow, W.T.; Chua, F.H.Z.; Kirollos, R.W.; Low, D.C.Y.; Low, S.Y.Y. Paediatric Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation: Outcomes from a Singapore Children’s Hospital. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2022, 31, 106283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.; Chen, Y.; Yan, D.; Li, R.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, K.; Han, H.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, L.; et al. Re-rupture in ruptured brain arteriovenous malformations: A retrospective cohort study based on a nationwide multicenter prospective registry. J. NeuroInterventional Surg. 2024, 16, 1145–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoh, B.L.; Ogilvy, C.S.; Butler, W.E.; Loeffler, J.S.; Putman, C.M.; Chapman, P.H. Multimodality treatment of nongalenic arteriovenous malformations in pediatric patients. Neurosurgery 2000, 47, 346–357; discussion 357–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Rocco, C.; Tamburrini, G.; Rollo, M. Cerebral arteriovenous malformations in children. Acta Neurochir 2000, 142, 145–156; discussion 156–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiris, T.; Sencer, A.; Sahinbas, M.; Sencer, S.; Imer, M.; Izgi, N. Surgical results in pediatric Spetzler-Martin grades I-III intracranial arteriovenous malformations. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2005, 21, 69–74; discussion 75–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Mejia, R.O.; Chennupati, S.K.; Gupta, N.; Fullerton, H.; Young, W.L.; Lawton, M.T. Superior outcomes in children compared with adults after microsurgical resection of brain arteriovenous malformations. J. Neurosurg. 2006, 105, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morshed, R.A.; Young, J.S.; Lee, A.T.; Berger, M.S.; Hervey-Jumper, S.L. Clinical Pearls and Methods for Intraoperative Awake Language Mapping. Neurosurgery 2021, 89, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffau, H. Awake Mapping and Tumor Surgery. In Brain Mapping: From Neural Basis of Cognition to Surgical Applications; Duffau, H., Ed.; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2011; pp. 305–318. [Google Scholar]
- Di Lorenzo, L.; Muccio, F.C. Diffusion tensor imaging magnetic resonance imaging (DTI-MRI) helps to tailor speech therapy: A case report with a short narrative review. NeuroRehabilitation 2023, 53, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, D.P.; McKenna, J.M.; Morin, L.; Ravussin, P. Conscious-sedation analgesia during craniotomy for intractable epilepsy: A review of 354 consecutive cases. Can. J. Anaesth. 1988, 35, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujol, S.; Wells, W.; Pierpaoli, C.; Brun, C.; Gee, J.; Cheng, G.; Vemuri, B.; Commowick, O.; Prima, S.; Stamm, A.; et al. The DTI Challenge: Toward Standardized Evaluation of Diffusion Tensor Imaging Tractography for Neurosurgery. J. Neuroimaging 2015, 25, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffau, H. The dangers of magnetic resonance imaging diffusion tensor tractography in brain surgery. World Neurosurg. 2014, 81, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacko, O.; Lauwers-Cances, V.; Brauge, D.; Sesay, M.; Brenner, A.; Roux, F.E. Awake craniotomy vs surgery under general anesthesia for resection of supratentorial lesions. Neurosurgery 2011, 68, 1192–1198; discussion 1198–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, V.M.; Maddy, K.; Niazi, T.N. Awake Craniotomy in Pediatric Patients: A Meta-analysis of Operative Outcomes. World Neurosurg. 2024, 181, 154–160.e152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhanja, D.; Sciscent, B.Y.; Daggubati, L.C.; Ryan, C.A.; Pahapill, N.K.; Hazard, S.W.; Rizk, E.B. Awake craniotomies in the pediatric population: A systematic review. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2023, 32, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eleveld, D.J.; Colin, P.; Absalom, A.R.; Struys, M. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic model for propofol for broad application in anaesthesia and sedation. Br. J. Anaesth. 2018, 120, 942–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, I.; Bong, C.L.; Chao, J.Y. Intraoperative pediatric electroencephalography monitoring: An updated review. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2024, 77, 289–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purdon, P.L.; Sampson, A.; Pavone, K.J.; Brown, E.N. Clinical Electroencephalography for Anesthesiologists: Part I: Background and Basic Signatures. Anesthesiology 2015, 123, 937–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahangiri, F.R.; Chima, G.S.; Pearson, M.; Jackson, J.; Siddiqui, A.A. Mapping of the Language Cortex. Cureus 2021, 13, e14960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakani, R.; Nair, D.R. Chapter 20—Electrocorticography and Functional Mapping. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Levin, K.H., Chauvel, P., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 160, pp. 313–327. [Google Scholar]
- Hak, J.F.; Boulouis, G.; Kerleroux, B.; Benichi, S.; Stricker, S.; Gariel, F.; Garzelli, L.; Meyer, P.; Kossorotoff, M.; Boddaert, N.; et al. Pediatric brain arteriovenous malformation recurrence: A cohort study, systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2022, 14, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauzier, D.C.; Vellimana, A.K.; Chatterjee, A.R.; Osbun, J.W.; Moran, C.J.; Zipfel, G.J.; Kansagra, A.P. Return of the lesion: A meta-analysis of 1134 angiographically cured pediatric arteriovenous malformations. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2021, 28, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manninen, P.; Contreras, J. Anesthetic considerations for craniotomy in awake patients. Int. Anesthesiol. Clin. 1986, 24, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Fudhaili, A.N.; Al-Busaidi, F.; Madan, Z.M.; Al Issa, M.S.; Al Mamria, M.H.; Al-Saadi, T. Awake Craniotomy Surgery in Pediatrics: A Systematic Review. World Neurosurg. 2023, 179, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisi, G.; Roujeau, T.; Duffau, H. Awake surgery for hemispheric low-grade gliomas: Oncological, functional and methodological differences between pediatric and adult populations. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2016, 32, 1861–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akay, A.; Rükşen, M.; Çetin, H.Y.; Seval, H.Ö.; İşlekel, S. Pediatric Awake Craniotomy for Brain Lesions. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2016, 51, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDowell, M.M.; Ortega Peraza, D.; Abel, T.J. Development and implementation of a novel child life protocol to enhance psychosocial support for pediatric awake craniotomies: Technical note. Neurosurg. Focus 2020, 48, E5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, S.F.; Gujrati, A.; Mubarak, F.; Khan, A.A.; Enam, S.A. Awake resection of a right motor cortex arteriovenous malformation in a pediatric patient: A case report and review of the literature. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2024, 15, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labuschagne, J.; Lee, C.A.; Mutyaba, D.; Mbanje, T.; Sibanda, C. Awake Craniotomy in a Child: Assessment of Eligibility with a Simulated Theatre Experience. Case Rep. Anesthesiol. 2020, 2020, 6902075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huguet, L.; Lohkamp, L.N.; Beuriat, P.A.; Desmurget, M.; Bapteste, L.; Szathmari, A.; Mottolese, C.; Di Rocco, F. Psychological aspects of awake brain surgery in children-interests and risks. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2020, 36, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohkamp, L.-N.; Beuriat, P.-A.; Desmurget, M.; Cristofori, I.; Szathmari, A.; Huguet, L.; Di Rocco, F.; Mottolese, C. Awake brain surgery in children—A single-center experience. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2020, 36, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vellinga, R.; Hannivoort, L.N.; Introna, M.; Touw, D.J.; Absalom, A.R.; Eleveld, D.J.; Struys, M. Prospective clinical validation of the Eleveld propofol pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic model in general anaesthesia. Br. J. Anaesth. 2021, 126, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hans, P.; Bonhomme, V.; Born, J.D.; Maertens de Noordhoudt, A.; Brichant, J.F.; Dewandre, P.Y. Target-controlled infusion of propofol and remifentanil combined with bispectral index monitoring for awake craniotomy. Anaesthesia 2000, 55, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T. Anesthetic Technique During Awake Craniotomy-A Case Report. Ann. Case Rep. 2019, 12, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Chauhan, V. Alternate Electrode Placements to Facilitate Frontal Electroencephalography Monitoring in Anesthetized and Critically Ill Patients. J. Neurosurg. Anesthesiol. 2024, 37, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallud, J.; Rigaux-Viode, O.; Corns, R.; Muto, J.; Lopez Lopez, C.; Mellerio, C.; Sauvageon, X.; Dezamis, E. Direct electrical bipolar electrostimulation for functional cortical and subcortical cerebral mapping in awake craniotomy. Practical considerations. Neurochirurgie 2017, 63, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonda, D.; Silverstein, J.W.; Katz, J.; Ellis, J.A.; Boockvar, J.; D’Amico, R. Asleep Speech Mapping Using Orofacial Muscles as Surrogates for Motor Speech in Patients Who Cannot Tolerate Awake Surgery: A Case Series. Cureus 2021, 13, e15861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pechstein, U.; Cedzich, C.; Nadstawek, J.; Schramm, J. Transcranial high-frequency repetitive electrical stimulation for recording myogenic motor evoked potentials with the patient under general anesthesia. Neurosurgery 1996, 39, 335–343; discussion 343–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, M.; Jiskoot, L.C.; Papma, J.M. White Matter Tracts of Speech and Language. Semin. Ultrasound CT MRI 2014, 35, 504–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Jing, Y.; Shi, Y.; Mo, H.; Wan, Y.; Zhou, H.; Deng, F. The role of language-related functional brain regions and white matter tracts in network plasticity of post-stroke aphasia. J. Neurol. 2024, 271, 3095–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamberger, M.J.; Miozzo, M.; Schevon, C.A.; Morrison, C.; Carlson, C.; Mehta, A.D.; Klein, G.E.; McKhann, G.M., 2nd; Williams, A.C. Functional differences among stimulation-identified cortical naming sites in the temporal region. Epilepsy Behav. 2016, 60, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkadhi, H.; Kollias, S.S.; Crelier, G.R.; Golay, X.; Hepp-Reymond, M.C.; Valavanis, A. Plasticity of the human motor cortex in patients with arteriovenous malformations: A functional MR imaging study. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2000, 21, 1423–1433. [Google Scholar]
- Lazar, R.M.; Marshall, R.S.; Pile-Spellman, J.; Hacein-Bey, L.; Young, W.L.; Mohr, J.P.; Stein, B.M. Anterior translocation of language in patients with left cerebral arteriovenous malformation. Neurology 1997, 49, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stapleton, C.J.; Walcott, B.P.; Fusco, M.R.; Thomas, A.J.; Ogilvy, C.S. Brain Mapping for Safe Microsurgical Resection of Arteriovenous Malformations in Eloquent Cortex. World Neurosurg. 2015, 83, 1148–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.; Keyoung, H.M.; Dowd, C.F.; Young, W.L.; Lawton, M.T. The effects of diffuseness and deep perforating artery supply on outcomes after microsurgical resection of brain arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery 2007, 60, 638–646; discussion 646–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, G.R.; Heier, L.A.; Patel, P.; Ramakrishna, R.; Magge, R.; Tsiouris, A.J. Diffusion Weighted/Tensor Imaging, Functional MRI and Perfusion Weighted Imaging in Glioblastoma—Foundations and Future. Front. Neurol. 2018, 8, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, M.; Maesawa, S.; Motomura, K.; Futamura, M.; Hayashi, Y.; Koba, I.; Wakabayashi, T. Intraoperative subcortical mapping of a language-associated deep frontal tract connecting the superior frontal gyrus to Broca’s area in the dominant hemisphere of patients with glioma. J. Neurosurg. JNS 2015, 122, 1390–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kierońska-Siwak, S.; Słoniewski, P. The usefulness and limitations of diffusion tensor imaging -a review study. Eur. J. Transl. Clin. Med. 2019, 2, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitnikov, A.R.; Grigoryan, Y.A.; Mishnyakova, L.P. Awake craniotomy without sedation in treatment of patients with lesional epilepsy. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2018, 9, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soldozy, S.; Akyeampong, D.K.; Barquin, D.L.; Norat, P.; Yağmurlu, K.; Sokolowski, J.D.; Sharifi, K.A.; Tvrdik, P.; Park, M.S.; Kalani, M.Y.S. Systematic Review of Functional Mapping and Cortical Reorganization in the Setting of Arteriovenous Malformations, Redefining Anatomical Eloquence. Front. Surg. 2020, 7, 514247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouchtouris, N.; Jabbour, P.M.; Starke, R.M.; Hasan, D.M.; Zanaty, M.; Theofanis, T.; Ding, D.; Tjoumakaris, S.I.; Dumont, A.S.; Ghobrial, G.M.; et al. Biology of cerebral arteriovenous malformations with a focus on inflammation. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2015, 35, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulmer, J.L.; Hacein-Bey, L.; Mathews, V.P.; Mueller, W.M.; DeYoe, E.A.; Prost, R.W.; Meyer, G.A.; Krouwer, H.G.; Schmainda, K.M. Lesion-induced pseudo-dominance at functional magnetic resonance imaging: Implications for preoperative assessments. Neurosurgery 2004, 55, 569–579; discussion 580–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrader, L.M. Direct Cortical Stimulation to Localize Sensory, Motor and Language Function. In Handbook of Clinical Neurophysiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; Volume 8, pp. 150–162. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, E.; Calandra, C.; Geralemou, S.; Page, C.; Davis, R.; Andraous, W.; Mikell, C. The Stony Brook awake craniotomy protocol: A technical note. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 67, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, M.N.; Shahin, M.N.; Stevens, I.; Calvert, J.; Colgan, D.D.; Vega, M.; Collins, K. Pediatric Awake Craniotomy: An Educational Review. Paediatr. Anaesth. 2025, 35, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Gittleman, H.; Farah, P.; Ondracek, A.; Chen, Y.; Wolinsky, Y.; Stroup, N.E.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS statistical report: Primary brain and central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2006-2010. Neuro Oncol. 2013, 15 (Suppl. 2), ii1–ii56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsy, A.A.; Ng, W.H. Awake craniotomy using electromagnetic navigation technology without rigid pin fixation. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2015, 22, 1827–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Long, M.; Thiaghu, C.; Cheong, T.M.; Kirollos, R.W.; Han, J.; Ng, L.P.; Low, S.Y.Y. Awake Craniotomy for the Excision of a Pediatric Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation for Language Preservation: A Case Description. J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15, 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15070319
Long M, Thiaghu C, Cheong TM, Kirollos RW, Han J, Ng LP, Low SYY. Awake Craniotomy for the Excision of a Pediatric Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation for Language Preservation: A Case Description. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2025; 15(7):319. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15070319
Chicago/Turabian StyleLong, Melody, C. Thiaghu, Tien Meng Cheong, Ramez W. Kirollos, Julian Han, Lee Ping Ng, and Sharon Y. Y. Low. 2025. "Awake Craniotomy for the Excision of a Pediatric Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation for Language Preservation: A Case Description" Journal of Personalized Medicine 15, no. 7: 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15070319
APA StyleLong, M., Thiaghu, C., Cheong, T. M., Kirollos, R. W., Han, J., Ng, L. P., & Low, S. Y. Y. (2025). Awake Craniotomy for the Excision of a Pediatric Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation for Language Preservation: A Case Description. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 15(7), 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15070319





