Prevalence of Actionable Exposures to Pharmacogenetic Medications Among Solid Organ Transplant Recipients in a Population-Scale Biobank
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data Sources and Study Population
2.2. Variant Genotyping and Imputation
2.3. PGx Medications and Actionable Exposures
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics and Demographics
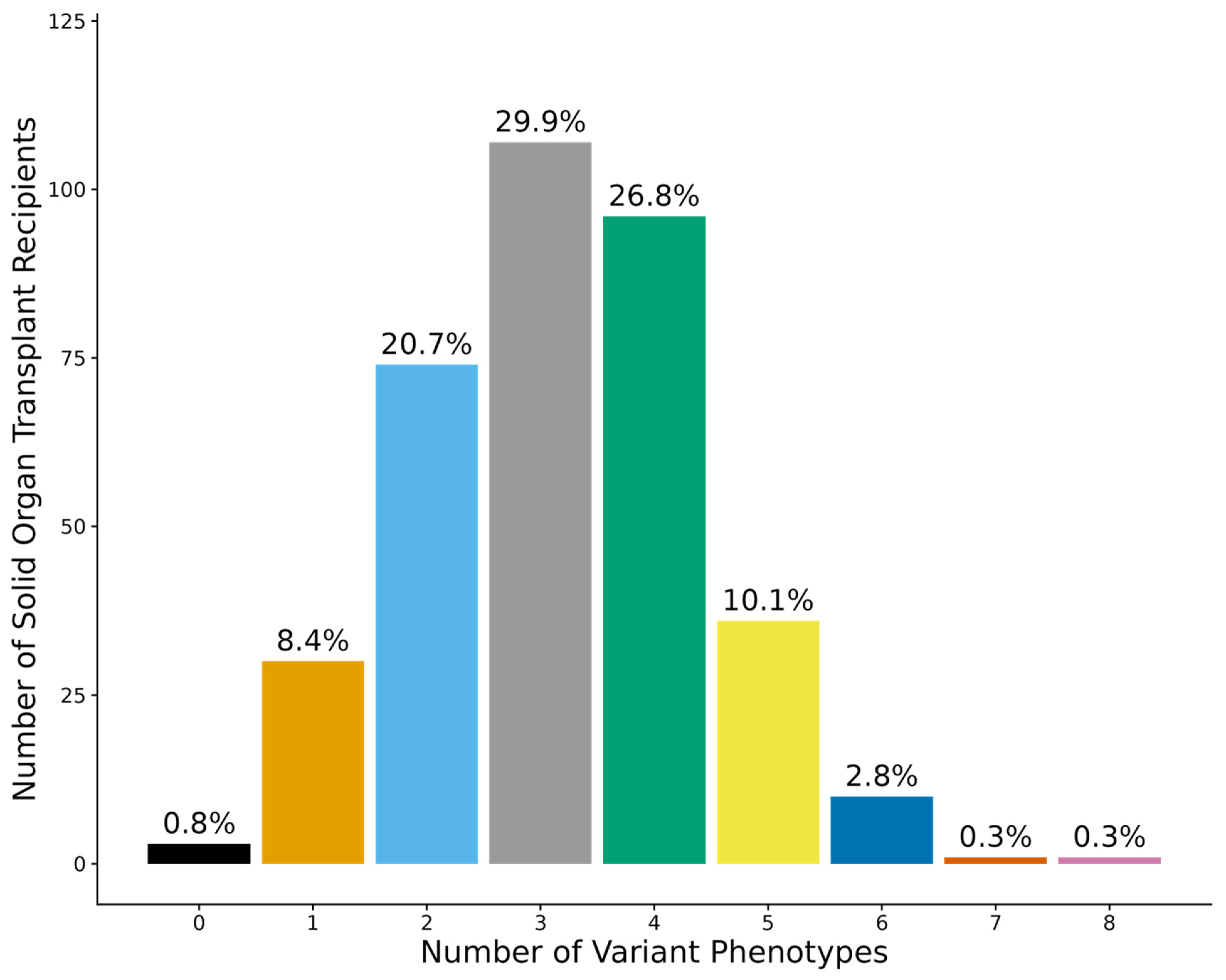
3.2. Diplotypes and Phenotypes
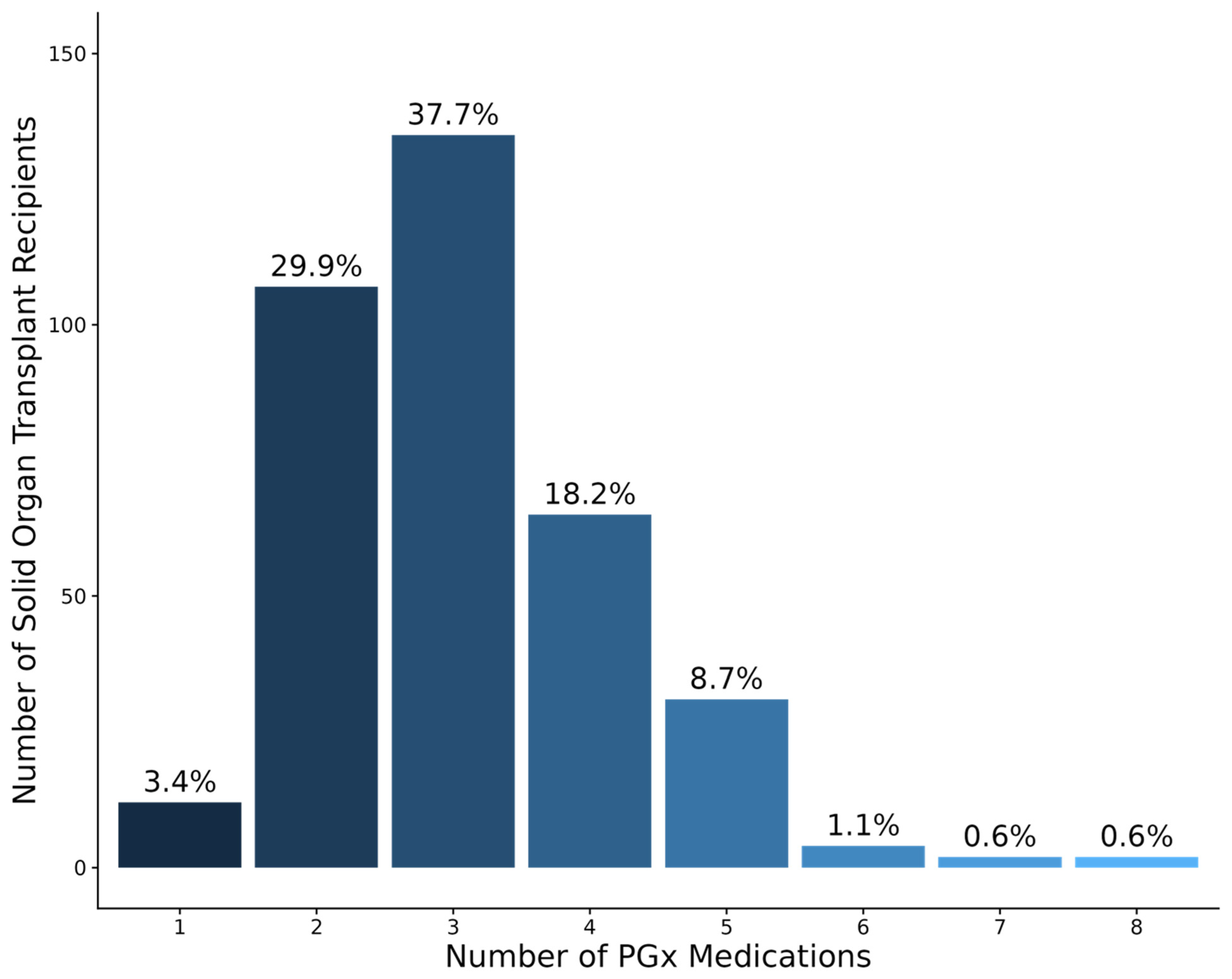
3.3. PGx Medication Characteristics
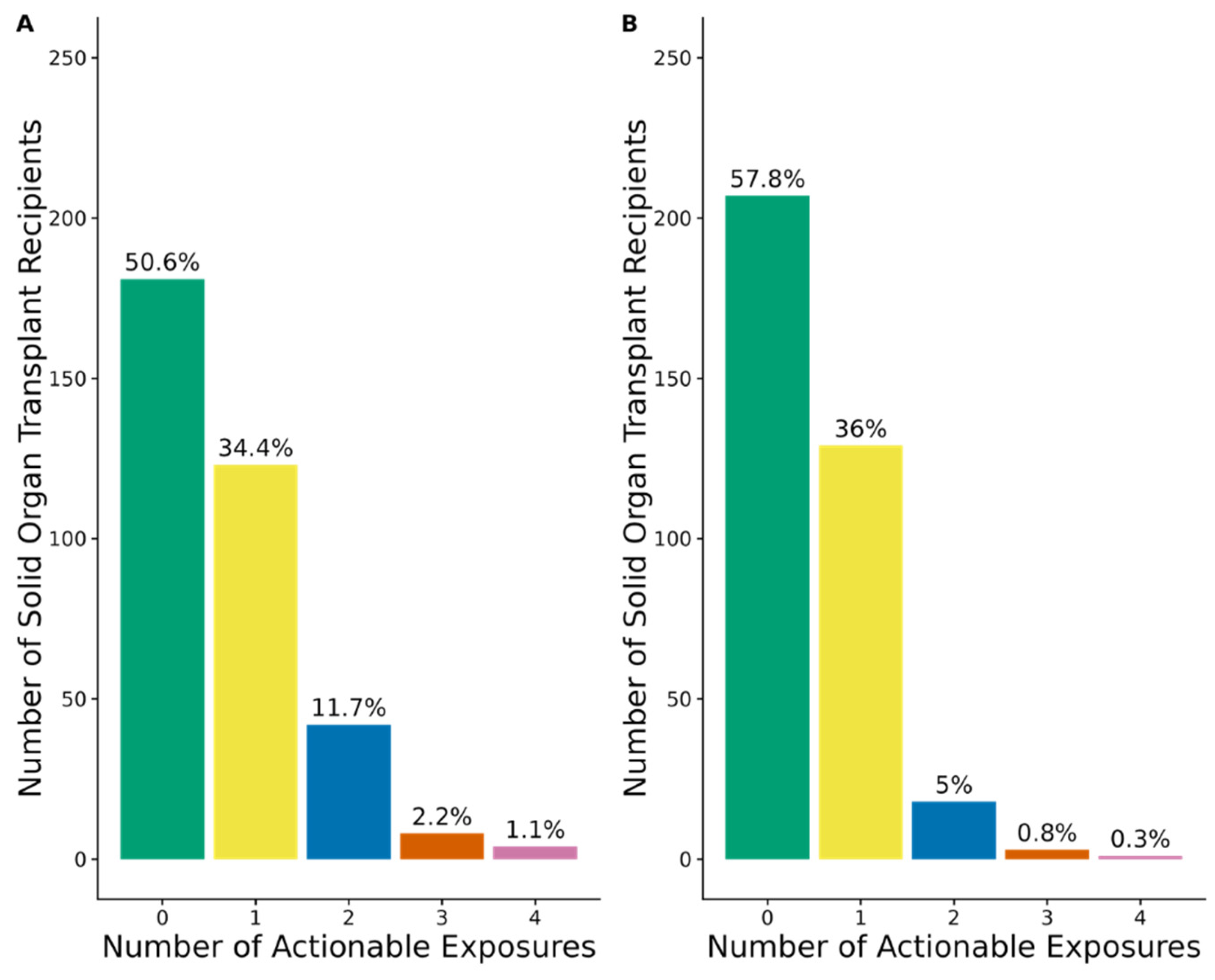
3.4. Actionable Exposures to PGx Medications with Strong, Moderate, or Optional Prescribing Recommendations
3.5. Actionable Exposures to PGx Medications with Strong or Moderate Prescribing Recommendations
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CCPM | Colorado Center for Personalized Medicine |
| CPIC | Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium |
| HDC | Health Data Compass |
| PGx | Pharmacogenetics |
| PPIs | Proton Pump Inhibitors |
| SOT | Solid Organ Transplantation |
| SSRIs | Selective Serotonin reuptake Inhibitors |
References
- Black, C.K.; Termanini, K.M.; Aguirre, O.; Hawksworth, J.S.; Sosin, M. Solid organ transplantation in the 21(st) century. Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 6, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schladt, D.P.; Israni, A.K. OPTN/SRTR 2023 Annual Data Report: Introduction. Am. J. Transplant. 2025, 25, S11–S21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, C.D. Overview of Immunosuppressive Therapy in Solid Organ Transplantation. Anesthesiol. Clin. 2017, 35, 365–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, C.N.; Watson, C.; Barlev, A.; Stevenson, M.; Dharnidharka, V.R. Mean lifetime survival estimates following solid organ transplantation in the US and UK. J. Med. Econ. 2022, 25, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, T.P.; Cherikh, W.S.; Hsich, E.; Lewis, A.; Perch, M.; Kian, S.; Hayes, D., Jr.; Potena, L.; Stehlik, J.; Zuckermann, A.; et al. Graft survival in primary thoracic organ transplant recipients: A special report from the International Thoracic Organ Transplant Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2023, 42, 1321–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomis-Pastor, M.; Roig Mingell, E.; Mirabet Perez, S.; Brossa Loidi, V.; Lopez Lopez, L.; Diaz Bassons, A.; Aretio Pousa, A.; Feliu Ribera, A.; Ferrero-Gregori, A.; Guirado Perich, L.; et al. Multimorbidity and medication complexity: New challenges in heart transplantation. Clin. Transplant. 2019, 33, e13682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, B.M.; Libby, A.M.; Metz, K.R.; Page, R.L., 2nd; Ambardekar, A.V.; Lindenfeld, J.; Aquilante, C.L. Evaluating Patient-Level Medication Regimen Complexity Over Time in Heart Transplant Recipients. Ann. Pharmacother. 2016, 50, 926–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marienne, J.; Laville, S.M.; Caillard, P.; Batteux, B.; Gras-Champel, V.; Masmoudi, K.; Choukroun, G.; Liabeuf, S. Evaluation of Changes Over Time in the Drug Burden and Medication Regimen Complexity in ESRD Patients Before and After Renal Transplantation. Kidney Int. Rep. 2021, 6, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roden, D.M.; McLeod, H.L.; Relling, M.V.; Williams, M.S.; Mensah, G.A.; Peterson, J.F.; Van Driest, S.L. Pharmacogenomics. Lancet 2019, 394, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Relling, M.V.; Klein, T.E. CPIC: Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium of the Pharmacogenomics Research Network. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 89, 464–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birdwell, K.A.; Decker, B.; Barbarino, J.M.; Peterson, J.F.; Stein, C.M.; Sadee, W.; Wang, D.; Vinks, A.A.; He, Y.; Swen, J.J.; et al. Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guidelines for CYP3A5 Genotype and Tacrolimus Dosing. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 98, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Relling, M.V.; Schwab, M.; Whirl-Carrillo, M.; Suarez-Kurtz, G.; Pui, C.H.; Stein, C.M.; Moyer, A.M.; Evans, W.E.; Klein, T.E.; Antillon-Klussmann, F.G.; et al. Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline for Thiopurine Dosing Based on TPMT and NUDT15 Genotypes: 2018 Update. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 105, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper-DeHoff, R.M.; Niemi, M.; Ramsey, L.B.; Luzum, J.A.; Tarkiainen, E.K.; Straka, R.J.; Gong, L.; Tuteja, S.; Wilke, R.A.; Wadelius, M.; et al. The Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline for SLCO1B1, ABCG2, and CYP2C9 genotypes and Statin-Associated Musculoskeletal Symptoms. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 111, 1007–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, J.J.; Thomas, C.D.; Barbarino, J.; Desta, Z.; Van Driest, S.L.; El Rouby, N.; Johnson, J.A.; Cavallari, L.H.; Shakhnovich, V.; Thacker, D.L.; et al. Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for CYP2C19 and Proton Pump Inhibitor Dosing. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 109, 1417–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, G.C.; Caudle, K.E.; Whirl-Carrillo, M.; Gordon, R.J.; Hikino, K.; Prows, C.A.; Gaedigk, A.; Agundez, J.; Sadhasivam, S.; Klein, T.E.; et al. Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) guideline for CYP2D6 genotype and use of ondansetron and tropisetron. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 102, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.A.; Caudle, K.E.; Gong, L.; Whirl-Carrillo, M.; Stein, C.M.; Scott, S.A.; Lee, M.T.; Gage, B.F.; Kimmel, S.E.; Perera, M.A.; et al. Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for Pharmacogenetics-Guided Warfarin Dosing: 2017 Update. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 102, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.R.; Luzum, J.A.; Sangkuhl, K.; Gammal, R.S.; Sabatine, M.S.; Stein, C.M.; Kisor, D.F.; Limdi, N.A.; Lee, Y.M.; Scott, S.A.; et al. Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline for CYP2C19 Genotype and Clopidogrel Therapy: 2022 Update. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 112, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriyama, B.; Obeng, A.O.; Barbarino, J.; Penzak, S.R.; Henning, S.A.; Scott, S.A.; Agúndez, J.; Wingard, J.R.; McLeod, H.L.; Klein, T.E.; et al. Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guidelines for CYP2C19 and Voriconazole Therapy. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 102, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crews, K.R.; Monte, A.A.; Huddart, R.; Caudle, K.E.; Kharasch, E.D.; Gaedigk, A.; Dunnenberger, H.M.; Leeder, J.S.; Callaghan, J.T.; Samer, C.F.; et al. Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium Guideline for CYP2D6, OPRM1, and COMT Genotypes and Select Opioid Therapy. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 110, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousman, C.A.; Stevenson, J.M.; Ramsey, L.B.; Sangkuhl, K.; Hicks, J.K.; Strawn, J.R.; Singh, A.B.; Ruaño, G.; Mueller, D.J.; Tsermpini, E.E.; et al. Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for CYP2D6, CYP2C19, CYP2B6, SLC6A4, and HTR2A Genotypes and Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor Antidepressants. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 114, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, J.K.; Sangkuhl, K.; Swen, J.J.; Ellingrod, V.L.; Müller, D.J.; Shimoda, K.; Bishop, J.R.; Kharasch, E.D.; Skaar, T.C.; Gaedigk, A.; et al. Clinical pharmacogenetics implementation consortium guideline (CPIC) for CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 genotypes and dosing of tricyclic antidepressants: 2016 update. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 102, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnes, G.; Lavertu, A.; Sangkuhl, K.; Klein, T.E.; Whirl-Carrillo, M.; Altman, R.B. Pharmacogenetics at Scale: An Analysis of the UK Biobank. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 109, 1528–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Pearson, R.A.; Mohamed, M.E.; Schladt, D.P.; Berglund, D.; Rivers, Z.; Skaar, D.J.; Wu, B.; Guan, W.; van Setten, J.; et al. Pharmacogenomics in kidney transplant recipients and potential for integration into practice. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2020, 45, 1457–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Scherer, S.E.; Bielinski, S.J.; Muzny, D.M.; Jones, L.A.; Black, J.L., 3rd; Moyer, A.M.; Giri, J.; Sharp, R.R.; Matey, E.T.; et al. Implementation of preemptive DNA sequence-based pharmacogenomics testing across a large academic medical center: The Mayo-Baylor RIGHT 10K Study. Genet. Med. 2022, 24, 1062–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.L.; Hsiao, T.H.; Wu, M.F.; Chen, C.H. The Prevalence and Features of Medications with Actionable Pharmacogenomic Biomarkers Prescribed to Kidney Transplant Recipients. Transplant. Proc. 2023, 55, 862–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, A.; Misra, S.; Abdelmalek, M.; Kekic, A.; Kunze, K.; Lim, E.; Jakob, N.; Mour, G.; Keddis, M.T. The Value of Pharmacogenomics for White and Indigenous Americans after Kidney Transplantation. Pharmacy 2023, 11, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aquilante, C.L.; Kao, D.P.; Trinkley, K.E.; Lin, C.T.; Crooks, K.R.; Hearst, E.C.; Hess, S.J.; Kudron, E.L.; Lee, Y.M.; Liko, I.; et al. Clinical implementation of pharmacogenomics via a health system-wide research biobank: The University of Colorado experience. Pharmacogenomics 2020, 21, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiley, L.K.; Shortt, J.A.; Roberts, E.R.; Lowery, J.; Kudron, E.; Lin, M.; Mayer, D.; Wilson, M.; Brunetti, T.M.; Chavan, S.; et al. Building a vertically integrated genomic learning health system: The biobank at the Colorado Center for Personalized Medicine. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2024, 111, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illumina, I.I. Expanded Multi-Ethnic GenotypingArray (MEGAEX). Available online: www.illumina.com/content/dam/illumina-marketing/documents/products/datasheets/mega-ex-data-sheet-370-2015-004.pdf (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Oreschak, K.; Saba, L.M.; Rafaels, N.; Ambardekar, A.V.; Deininger, K.M.; Page, I.R.; Lindenfeld, J.; Aquilante, C.L. Variants in mycophenolate and CMV antiviral drug pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic genes and leukopenia in heart transplant recipients. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2021, 40, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Forer, L.; Schönherr, S.; Sidore, C.; Locke, A.E.; Kwong, A.; Vrieze, S.I.; Chew, E.Y.; Levy, S.; McGue, M.; et al. Next-generation genotype imputation service and methods. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1284–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PGx Gene-Specific Information Tables. Available online: https://www.pharmgkb.org/page/pgxGeneRef (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Caudle, K.E.; Klein, T.E.; Hoffman, J.M.; Muller, D.J.; Whirl-Carrillo, M.; Gong, L.; McDonagh, E.M.; Sangkuhl, K.; Thorn, C.F.; Schwab, M.; et al. Incorporation of pharmacogenomics into routine clinical practice: The Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) guideline development process. Curr. Drug Metab. 2014, 15, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Gelder, T.; Gelinck, A.; Meziyerh, S.; de Vries, A.P.J.; Moes, D. Therapeutic drug monitoring of tacrolimus after kidney transplantation: Trough concentration or area under curve-based monitoring? Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2024. online version of record. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunet, M.; van Gelder, T.; Åsberg, A.; Haufroid, V.; Hesselink, D.A.; Langman, L.; Lemaitre, F.; Marquet, P.; Seger, C.; Shipkova, M.; et al. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Tacrolimus-Personalized Therapy: Second Consensus Report. Ther. Drug Monit. 2019, 41, 261–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, R.L.; Heyrend, C.; Bucher, B.; Brewer, A.; Peterson, C.; May, L.J.; Bonkowsky, J.L. Impact of Pharmacogenomic Testing in Pediatric Heart and Kidney Transplant. Pediatr. Transplant. 2025, 29, e70044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamraz, B.; Shin, J.; Khanna, R.; Van Ziffle, J.; Knowles, S.; Stregowski, S.; Wan, E.; Kamath, R.; Collins, C.; Phunsur, C.; et al. Clinical implementation of preemptive pharmacogenomics testing for personalized medicine at an academic medical center. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2025, 32, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Vnencak-Jones, C.L.; Roland, B.P.; Gatto, C.L.; Mathe, J.L.; Just, S.L.; Peterson, J.F.; Van Driest, S.L.; Weitkamp, A.O. A Tutorial for Pharmacogenomics Implementation Through End-to-End Clinical Decision Support Based on Ten Years of Experience from PREDICT. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 109, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shugg, T.; Tillman, E.M.; Breman, A.M.; Hodge, J.C.; McDonald, C.A.; Ly, R.C.; Rowe, E.J.; Osei, W.; Smith, T.B.; Schwartz, P.H.; et al. Development of a Multifaceted Program for Pharmacogenetics Adoption at an Academic Medical Center: Practical Considerations and Lessons Learned. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2024, 116, 914–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, C.; Crosby, I.; Yip, V.; Maguire, P.; Pirmohamed, M.; Turner, R.M. A Review of the Important Role of CYP2D6 in Pharmacogenomics. Genes 2020, 11, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamba, J.; Hebert, J.M.; Schuetz, E.G.; Klein, T.E.; Altman, R.B. PharmGKB summary: Very important pharmacogene information for CYP3A5. Pharmacogenetics Genom. 2012, 22, 555–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | N = 358 |
|---|---|
| Age at transplant, years | 52.7 ± 13.2 |
| Men | 208 (58.1%) |
| Race | |
| European descent | 291 (81.3%) |
| African American | 17 (4.7%) |
| Asian | 8 (2.2%) |
| American Indian and Alaska native | 3 (0.8%) |
| Other Pacific Islander | 2 (0.6%) |
| Multiple Races | 17 (4.7%) |
| Other | 19 (5.3%) |
| Not reported | 1 (0.3%) |
| Ethnicity | |
| Hispanic | 58 (16.2%) |
| Transplanted Organ | |
| Kidney | 258 (72.1%) |
| Lung | 62 (17.3%) |
| Heart | 38 (10.6%) |
| Gene | Phenotype | Genotype/Diplotype/Activity Score | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABCG2 rs2231142 | Normal function Intermediate function Poor function | GG GT TT | 77.7% 21.5% 0.8% |
| CYP2B6 * | Ultrarapid metabolizer Rapid metabolizer Normal metabolizer Intermediate metabolizer Poor metabolizer | *4/*4, *4/*22, *22/*22 *1/*4, *1*22 *1/*1 *1/*6, *1/*9, *1/*18, *4/*6, *6/*22 *6/*6, *6/*9 | 0% 3.9% 48.9% 41.1% 6.1% |
| CYP2C9 * | Normal metabolizer Intermediate metabolizer Poor metabolizer | *1/*1 *1/*2, *1/*3, *1/*8, *1/*11, *2/*2 *2/*3, *3/*3 | 65.4% 32.7% 2.0% |
| CYP2C19 * | Ultrarapid metabolizer Rapid metabolizer Normal metabolizer Intermediate metabolizer Poor metabolizer | *17/*17 *1/*17 *1/*1 *1/*2, *2/*17 *2/*2, *2/*3 | 2.8% 26.0% 45.8% 23.7% 1.7% |
| CYP2C cluster rs12777823 | Normal activity Decreased activity Poor activity | GG GA AA | 73.5% 25.7% 0.8% |
| CYP3A5 * | Normal metabolizer (expressor) Intermediate metabolizer (expressor) Poor metabolizer (non-expressor) | *1/*1 *1/*3, *1/*6 *3/*3, *3/*6, *6/*6 | 2.0% 15.6% 82.4% |
| CYP4F2 rs2108622 | Normal function Intermediate function Poor function | *1/*1 *1/*3 *3/*3 | 53.9% 40.2% 5.9% |
| DPYD * | Normal metabolizer Intermediate metabolizer Poor metabolizer | Activity score: 2 Activity score: 1–1.5 Activity score: 0–0.5 | 95.5% 4.5% 0% |
| SLCO1B1 rs4149056 | Normal function Decreased function Poor function | *1/*1 *1/*5 *5/*5 | 69.0% 27.9% 3.1% |
| NUDT15 * | Normal metabolizer Intermediate metabolizer Poor metabolizer | *1/*1 *1/*3 *3/*3 | 96.1% 3.9% 0% |
| TPMT * | Normal metabolizer Intermediate metabolizer Poor metabolizer | *1/*1 *1/*2, *1/*3A, *1/*3C *3A/*3A | 90.8% 8.9% 0.3% |
| UGT1A1 rs887829 | Normal metabolizer Intermediate metabolizer Poor metabolizer | *1/*1 *1/*80 *80/*80 | 46.9% 41.3% 11.7% |
| VKORC1 rs9923231 | Low warfarin sensitivity Intermediate warfarin sensitivity Warfarin sensitive | GG GA AA | 43.0% 44.7% 12.3% |
| Drug Class or Drug | Number (%) of Patients with at Least One Prescription During the First Six Months Post-Transplant | Number (%) of Patients with at Least One Actionable Exposure to the Medication During the First Six Months Post-Transplant | Actionable Phenotypes and Number (%) of Patients with an Actionable Exposure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Any PPI use | 342 (95.5%) | 54 (15.8%) |
|
| 260 (72.6%) | 43 (16.5%) |
|
| 86 (24.0%) | 11 (12.8%) |
|
| 8 (2.2%) | 2 (25%) |
|
| Tacrolimus | 310 (86.6%) | 55 (17.7%) |
|
| Any statin use | 214 (59.8%) | 46 (21.5%) |
|
| 128 (35.8%) | 36 (28.1%) |
|
| 79 (22.1%) | 1 (1.3%) |
|
| 26 (7.3%) | 7 (26.9%) |
|
| 12 (3.4%) | 2 (16.7%) |
|
| Azathioprine | 65 (18.2%) | 9 (13.8%) |
|
| Warfarin | 47 (13.1%) | 42 (89.4%) |
|
| Any SSRI use | 41 (11.5%) | 22 (53.7%) |
|
| 22 (6.1%) | 14 (63.6%) |
|
| 9 (2.5%) | 6 (66.7%) |
|
| 19 (5.3%) | 8 (42.1%) |
|
| Voriconazole | 17 (4.7%) | 8 (47.1%) |
|
| Clopidogrel | 5 (1.4%) | 1 (20%) |
|
| Hydantoins | 1 (0.3%) | 1 (100%) |
|
| 1 (0.3%) | 1 (100%) |
|
| 1 (0.3%) | 1 (100%) |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Radwan, A.; Deininger, K.M.; Ambardekar, A.V.; Anderson, H.D.; Rafaels, N.; Saba, L.M.; The Colorado Center for Personalized Medicine; Aquilante, C.L. Prevalence of Actionable Exposures to Pharmacogenetic Medications Among Solid Organ Transplant Recipients in a Population-Scale Biobank. J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15, 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050185
Radwan A, Deininger KM, Ambardekar AV, Anderson HD, Rafaels N, Saba LM, The Colorado Center for Personalized Medicine, Aquilante CL. Prevalence of Actionable Exposures to Pharmacogenetic Medications Among Solid Organ Transplant Recipients in a Population-Scale Biobank. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2025; 15(5):185. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050185
Chicago/Turabian StyleRadwan, Alaa, Kimberly M. Deininger, Amrut V. Ambardekar, Heather D. Anderson, Nicholas Rafaels, Laura M. Saba, The Colorado Center for Personalized Medicine, and Christina L. Aquilante. 2025. "Prevalence of Actionable Exposures to Pharmacogenetic Medications Among Solid Organ Transplant Recipients in a Population-Scale Biobank" Journal of Personalized Medicine 15, no. 5: 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050185
APA StyleRadwan, A., Deininger, K. M., Ambardekar, A. V., Anderson, H. D., Rafaels, N., Saba, L. M., The Colorado Center for Personalized Medicine, & Aquilante, C. L. (2025). Prevalence of Actionable Exposures to Pharmacogenetic Medications Among Solid Organ Transplant Recipients in a Population-Scale Biobank. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 15(5), 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050185






