Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Therapy Alters the Genomic Profile of Bladder Cancer Cell Line HT-1197
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Justification and Setup
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. PEMF Delivery
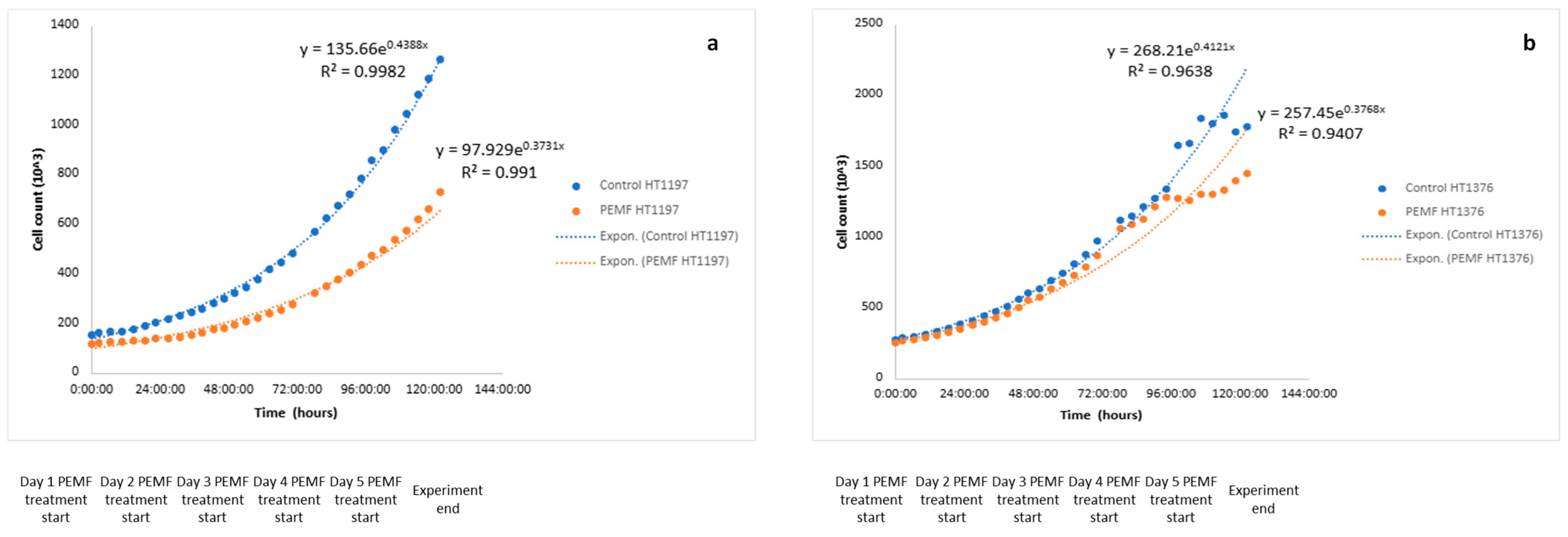
2.4. Growth Curve Determination
2.5. RNA Extraction and nCounter® Tumor Signaling 360™ Analysis
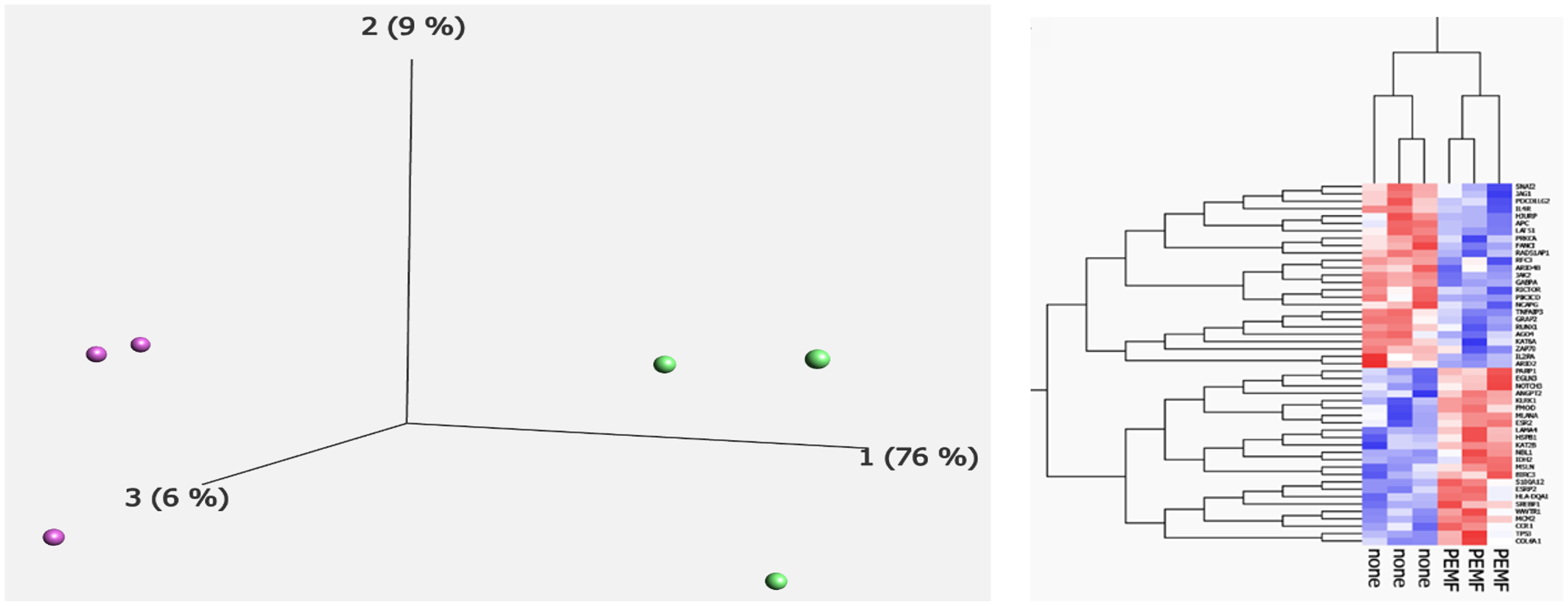
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PEMF | pulsed electromagnetic field therapy |
| mT | MilliTesla |
| RNA | ribonucleic acid |
| DNA | deoxyribonucleic acid |
| Hz | hertz |
| IPA | ingenuity pathway analysis |
| PCA | principal component analysis |
| DETs | differentially expressed transcripts |
| TME | tumor microenvironment |
| PI3K | phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase |
| PTEN | phosphatase and tensin |
References
- Yang, X.; He, H.; Ye, W.; Perry, T.A.; He, C. Effects of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Therapy on Pain, Stiffness, Physical Function, and Quality of Life in Patients with Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trials. Phys. Ther. 2020, 100, 1118–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flatscher, J.; Loriè, E.P.; Mittermayr, R.; Meznik, P.; Slezak, P.; Redl, H.; Slezak, C. Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields (PEMF)—Physiological Response and Its Potential in Trauma Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wade, B. A Review of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) Mechanisms at a Cellular Level: A Rationale for Clinical Use. Am. J. Health Res. 2013, 1, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, D.T.; Ross, C.; Lee, P.; Badlani, G.; Matthews, C.A.; Evans, R.J.; Walker, S.J. Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Therapy for Pain Management in Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome: A Proof-of-Concept Case Series. Urology 2022, 167, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picelli, A.; DI CENSO, R.; Tomasello, S.; Scaturro, D.; Mauro, G.L.; Smania, N.; Filippetti, M. Effects of pulsed electromagnetic fields on bone fractures: A systematic review update. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2024, 60, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceccarelli, G.; Bloise, N.; Mantelli, M.; Gastaldi, G.; Fassina, L.; De Angelis, M.G.C.; Ferrari, D.; Imbriani, M.; Visai, L. A comparative analysis of the in vitro effects of pulsed electromagnetic field treatment on osteogenic differentiation of two different mesenchymal cell lineages. BioRes. Open Access 2013, 2, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Xie, X.; Wu, H.; Wang, X.; Cai, J.; Xu, Z.; E, S. Pulsed electromagnetic therapy in cancer treatment: Progress and outlook. View 2022, 3, 20220029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saginala, K.; Barsouk, A.; Aluru, J.S.; Rawla, P.; Padala, S.A.; Barsouk, A. Epidemiology of Bladder Cancer. Med. Sci. 2020, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandberg, M.; Whitman, W.; Ross, C.; Tsivian, M.; Walker, S.J. Pulsed electromagnetic field therapy’s effect on bladder cancer cell line HT-1376. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42 (Suppl. 4), 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbault, A.; Costa, F.P.; Bottger, B.; Munden, R.F.; Bomholt, F.; Kuster, N.; Pasche, B. Amplitude-modulated electromagnetic fields for the treatment of cancer: Discovery of tumor-specific frequencies and assessment of a novel therapeutic approach. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 28, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasheed, S.; Gardner, M.B.; Rongey, R.W.; Nelson-Rees, W.A.; Arnstein, P. Human Bladder Carcinoma: Characterization of Two New Tumor Cell Lines and Search for Tumor Viruses23. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1977, 58, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cellosaurus HT-1197 [Internet]. Cellosaurus. Available online: https://www.cellosaurus.org/CVCL_1291 (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Holíčková, A.; Roška, J.; Órásová, E.; Bruderová, V.; Palacka, P.; Jurkovičová, D.; Chovanec, M. Response of the Urothelial Carcinoma Cell Lines to Cisplatin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HT-1197 [Internet]. ATCC. Available online: https://www.atcc.org/products/crl-1473 (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Vadalà, M.; Morales-Medina, J.C.; Vallelunga, A.; Palmieri, B.; Laurino, C.; Iannitti, T. Mechanisms and therapeutic effectiveness of pulsed electromagnetic field therapy in oncology. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 3128–3139. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- García-Minguillán, O.; Maestú, C. 30 Hz, Could It Be Part of a Window Frequency for Cellular Response? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colaco, M.; Koslov, D.S.; Keys, T.; Evans, R.J.; Badlani, G.H.; Andersson, K.-E.; Walker, S.J. Correlation of gene expression with bladder capacity in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. J. Urol. 2014, 192, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantelis, P.; Theocharous, G.; Veroutis, D.; Vagena, I.-A.; Polyzou, A.; Thanos, D.-F.; Kyrodimos, E.; Kotsinas, A.; Evangelou, K.; Lagopati, N.; et al. Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields (PEMFs) Trigger Cell Death and Senescence in Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocetti, S.; Beyer, C.; Schade, G.; Egli, M.; Fröhlich, J.; Franco-Obregón, A. Low Intensity and Frequency Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields Selectively Impair Breast Cancer Cell Viability. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72944. [Google Scholar]
- Akbarnejad, Z.; Eskandary, H.; Vergallo, C.; Nematollahi-Mahani, S.N.; Dini, L.; Darvishzadeh-Mahani, F.; Ahmadi, M. Effects of extremely low-frequency pulsed electromagnetic fields (ELF-PEMFs) on glioblastoma cells (U87). Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2017, 36, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, L.; Wei, F.; Lian, Y.; Wu, Y.; Gong, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, J.; Cao, K.; et al. Role of tumor microenvironment in tumorigenesis. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 761–773. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cameron, I.; Sun, L.; Short, N.; Hardman, W.; Williams, C. Daily Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) therapy inhibits tumor angiogenesis via the hypoxia driven pathway: Therapeutic implications. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 287. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, C.L.; Zhou, Y.; McCall, C.E.; Soker, S.; Criswell, T.L. The Use of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field to Modulate Inflammation and Improve Tissue Regeneration: A Review. Bioelectricity 2019, 1, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Calderaro, J.; Rebouissou, S.; de Koning, L.; Masmoudi, A.; Hérault, A.; Dubois, T.; Maille, P.; Soyeux, P.; Sibony, M.; de la Taille, A.; et al. PI3K/AKT pathway activation in bladder carcinogenesis. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 134, 1776–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, S.X.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, A.H.; Yu, W.; Zhang, H.; Lin, T.Y.; Shi, W.; Tepper, C.G.; Henderson, P.T.; Airhart, S.; et al. The Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase Pathway as a Potential Therapeutic Target in Bladder Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 6580–6591. [Google Scholar]
- Sathe, A.; Nawroth, R. Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway in Bladder Cancer. In Urothelial Carcinoma. Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 1655, pp. 335–350. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, A.; Wang, Q.; Lv, X.; Lin, T. Progressive Study on the Non-thermal Effects of Magnetic Field Therapy in Oncology. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 638146. [Google Scholar]
- Roh, Y.-G.; Mun, M.-H.; Jeong, M.-S.; Kim, W.-T.; Lee, S.-R.; Chung, J.-W.; Kim, S.I.; Kim, T.N.; Kil Nam, J.; Leem, S.-H. Drug resistance of bladder cancer cells through activation of ABCG2 by FOXM1. BMB Rep. 2018, 51, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Woo, S.-H.; Jung, B.C.; Kim, J.-Y.; Lee, Y.-H.; Kim, Y.S. Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Enhances Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester-induced Death of MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells. Anticancer. Res. 2024, 44, 2407–2415. [Google Scholar]
- Niehans, G.A.; Kratzke, R.A.; Froberg, M.K.; Aeppli, D.M.; Nguyen, P.L.; Geradts, J. G1 checkpoint protein and p53 abnormalities occur in most invasive transitional cell carcinomas of the urinary bladder. Br. J. Cancer 1999, 80, 1175–1184. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Puzio-Kuter, A.M.; Castillo-Martin, M.; Kinkade, C.W.; Wang, X.; Shen, T.H.; Matos, T.; Shen, M.M.; Cordon-Cardo, C.; Abate-Shen, C. Inactivation of p53 and Pten promotes invasive bladder cancer. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stojanovic, M.; Rai, V.; Agrawal, D.K. Effect of Electromagnetic Field on Proliferation and Migration of Fibroblasts and Keratinocytes: Implications in Wound Healing and Regeneration. J. Biotechnol. Biomed. 2024, 7, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stojnev, S.; Krstić, M.; Kokoris, J.Č.; Conić, I.; Petković, I.; Ilić, S.; Milosević-Stevanović, J.; Veličković, L.J. Prognostic Impact of Canonical TGF-β Signaling in Urothelial Bladder Cancer. Medicina 2019, 55, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eder, I.; Stenzl, A.; Hobisch, A.; Cronauer, M.; Bartsch, G.; Klocker, H. Expression of transforming growth factors beta-1, beta 2 and beta 3 in human bladder carcinomas. Br. J. Cancer 1997, 75, 1753–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Selvamurugan, N.; He, Z.; Rifkin, D.; Dabovic, B.; Partridge, N.C. Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Regulates MicroRNA 21 Expression to Activate TGF-β Signaling in Human Bone Marrow Stromal Cells to Enhance Osteoblast Differentiation. Stem Cells Int. 2017, 2017, 2450327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Xu, Z.-B.; Wang, J.-P.; Jiao, Y.; Zhang, B. Rb deficiency accelerates progression of carcinoma of the urinary bladder in vivo and in vitro through inhibiting autophagy and apoptosis. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 50, 1221–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzano, R.G.; Catalan-Latorre, A.; Brugarolas, A. RB1 and TP53 co-mutations correlate strongly with genomic biomarkers of response to immunity checkpoint inhibitors in urothelial bladder cancer. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Grivas, P.; Emamekhoo, H.; Mendiratta, P.; Ali, S.; Hsu, J.; Vasekar, M.; Drabick, J.J.; Pal, S.; Joshi, M. ATM/RB1 mutations predict shorter overall survival in urothelial cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 16891–16898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maffei, M.E. Magnetic Fields and Cancer: Epidemiology, Cellular Biology, and Theranostics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
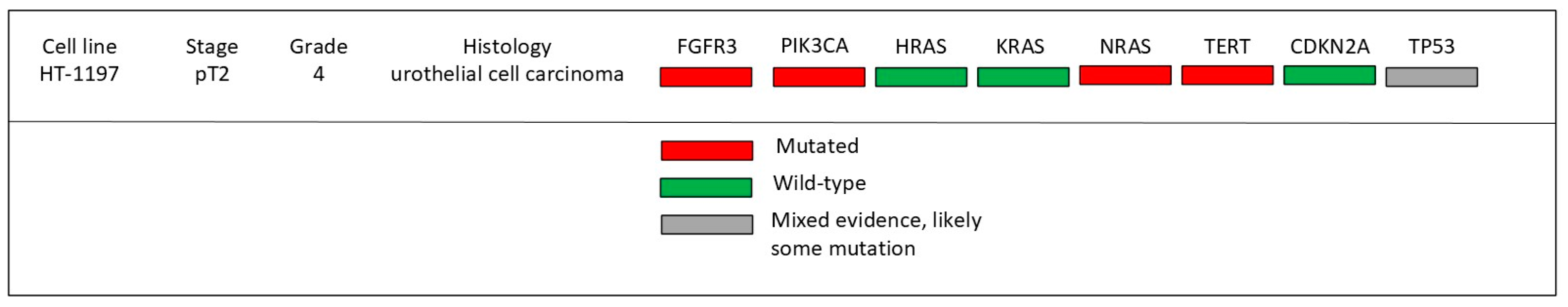




| Gene | Role in Cancer | Log2 Fold Change |
|---|---|---|
| JAK2 | Non-receptor tyrosine kinase: activating mutations implicated in cell proliferation | −0.34 |
| TGFβ2 | Signaling complex: promotility factor in bladder cancer cells | −0.31 |
| PIK3CD | Oncogene: promotes growth factor-independent growth and increases cell invasion and metastasis | −0.22 |
| Rb1 | Tumor suppressor: halts cell cycle, loss of function leads to unregulated cell growth | 0.13 |
| CDKN1A | Cyclin-dependent kinase: target of p53 and activation halts the cell cycle | 0.10 |
| TP53 | Tumor suppressor: loss of function promotes cell division | 0.15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sandberg, M.; Whitman, W.; Bissette, R.; Ross, C.; Tsivian, M.; Walker, S.J. Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Therapy Alters the Genomic Profile of Bladder Cancer Cell Line HT-1197. J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15, 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15040143
Sandberg M, Whitman W, Bissette R, Ross C, Tsivian M, Walker SJ. Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Therapy Alters the Genomic Profile of Bladder Cancer Cell Line HT-1197. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2025; 15(4):143. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15040143
Chicago/Turabian StyleSandberg, Maxwell, Wyatt Whitman, Randall Bissette, Christina Ross, Matvey Tsivian, and Stephen J. Walker. 2025. "Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Therapy Alters the Genomic Profile of Bladder Cancer Cell Line HT-1197" Journal of Personalized Medicine 15, no. 4: 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15040143
APA StyleSandberg, M., Whitman, W., Bissette, R., Ross, C., Tsivian, M., & Walker, S. J. (2025). Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Therapy Alters the Genomic Profile of Bladder Cancer Cell Line HT-1197. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 15(4), 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15040143





