Extracranial Hemodynamic Responses to a Noxious Cold Pressor Task Differ Between Persistent Post-Traumatic Headache and Healthy Controls
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
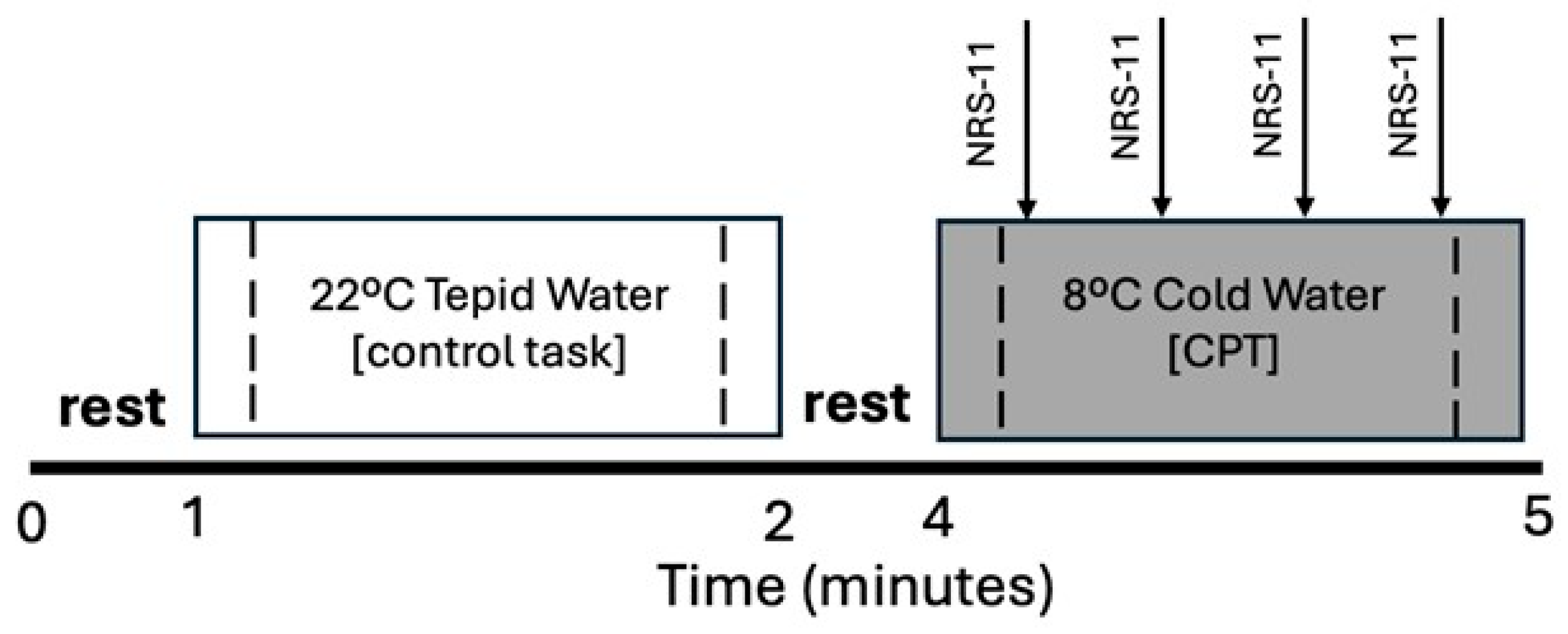
2.2. Procedures
2.3. Data Processing
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Traumatic Brain Injury and Headache Characteristics
3.2. Sociodemographic and Psychologic Characteristics
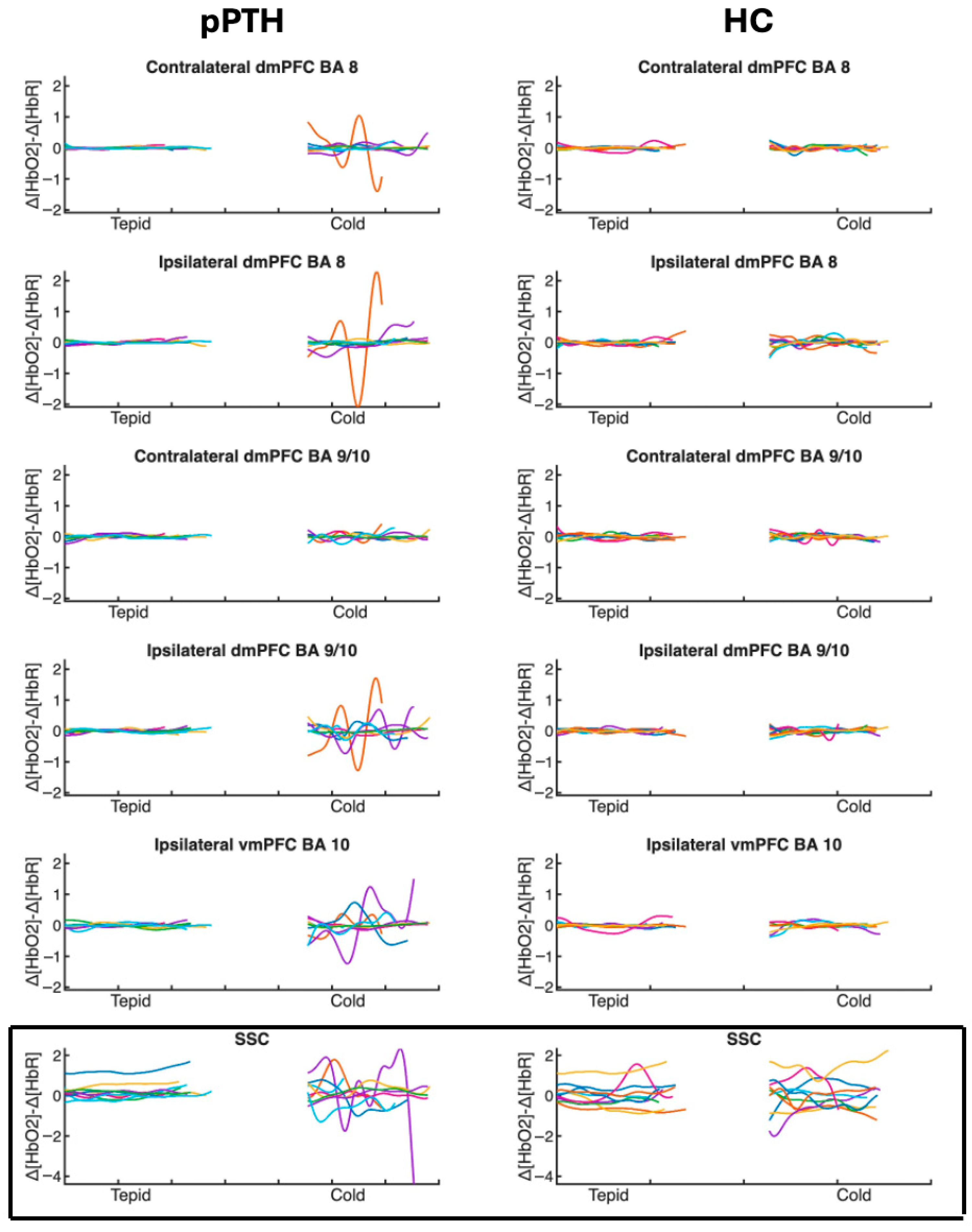
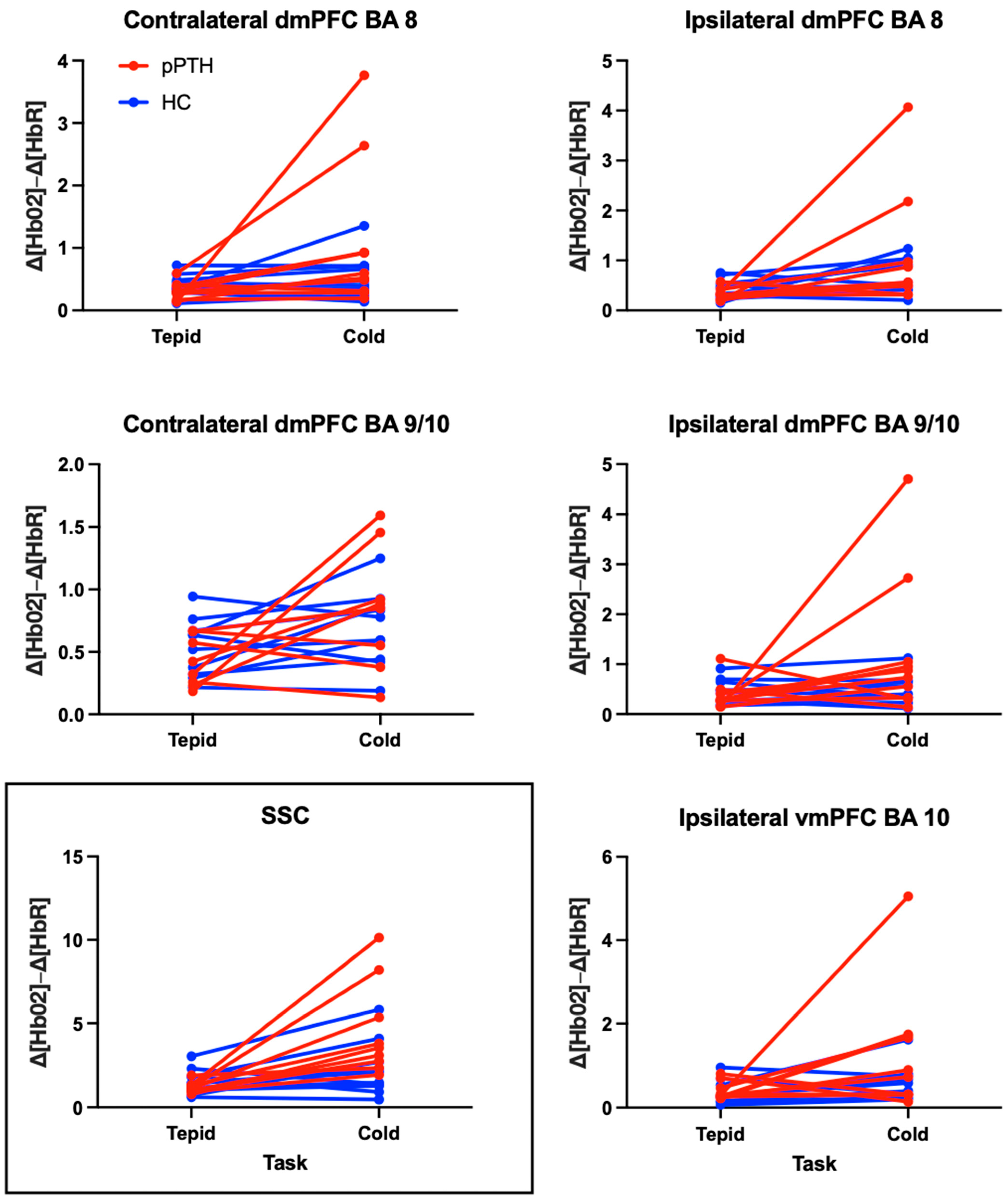
3.3. Peak-to-Peak Hemodynamic Responses
3.4. Evoked Pain Responses
4. Discussion
4.1. Hemodynamic Responses to the Cold Pressor Task Measured by fNIRS
4.2. Role of ANS Regulation on Extracranial Hemodynamic Responses
4.3. Relationship Between Evoked Pain and Intracranial Hemodynamic Responses of the Medial PFC
4.4. Study Limitations and Future Research Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kothari, S.F.; Eggertsen, P.P.; Frederiksen, O.V.; Thastum, M.M.; Svendsen, S.W.; Tuborgh, A.; Næss-Schmidt, E.T.; Rask, C.U.; Schröder, A.; Kasch, H.; et al. Characterization of persistent post-traumatic headache and management strategies in adolescents and young adults following mild traumatic brain injury. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrero Babiloni, A.; Bouferguene, Y.; Exposto, F.G.; Beauregard, R.; Lavigne, G.J.; Moana-Filho, E.J.; Arbour, C. The prevalence of persistent post-traumatic headache in adult civilian traumatic brain injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis on the past 14 years. Pain 2023, 164, 2627–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumkrieger, G.; Chong, C.D.; Ross, K.; Berisha, V.; Schwedt, T.J. Static and dynamic functional connectivity differences between migraine and persistent post-traumatic headache: A resting-state magnetic resonance imaging study. Cephalalgia 2019, 39, 1366–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, C.D.; Peplinski, J.; Berisha, V.; Ross, K.; Schwedt, T.J. Differences in fibertract profiles between patients with migraine and those with persistent post-traumatic headache. Cephalalgia 2019, 39, 1121–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashina, H.; Al-Khazali, H.M.; Iljazi, A.; Ashina, S.; Amin, F.M.; Schytz, H.W. Total tenderness score and pressure pain thresholds in persistent post-traumatic headache attributed to mild traumatic brain injury. J. Headache Pain 2022, 23, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, D.; Gruener, H.; Riabinin, M.; Feingold, Y.; Schreiber, S.; Pick, C.G.; Defrin, R. Different clinical phenotypes of persistent post-traumatic headache exhibit distinct sensory profiles. Cephalalgia 2020, 40, 675–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, X.; Bai, L.; Sun, Y.; Wang, S.; Cao, J.; Sun, C.; Wang, Z.; Xu, H.; Gan, S.; Fan, G.; et al. Disruption of periaqueductal grey-default mode network functional connectivity predicts persistent post-traumatic headache in mild traumatic brain injury. J Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defrin, R.; Riabinin, M.; Feingold, Y.; Schreiber, S.; Pick, C.G. Deficient pain modulatory systems in patients with mild traumatic brain and chronic post-traumatic headache: Implications for its mechanism. J. Neurotrauma 2015, 32, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defrin, R.; Gruener, H.; Schreiber, S.; Pick, C.G. Quantitative somatosensory testing of subjects with chronic post-traumatic headache: Implications on its mechanisms. Eur. J. Pain 2010, 14, 924–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naugle, K.M.; Carey, C.; Evans, E.; Saxe, J.; Overman, R.; White, F.A. The role of deficient pain modulatory systems in the development of persistent post-traumatic headaches following mild traumatic brain injury: An exploratory longitudinal study. J. Headache Pain 2020, 21, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starling, A.J.; Cortez, M.M.; Jarvis, N.R.; Zhang, N.; Porreca, F.; Chong, C.D.; Schwedt, T.J. Cutaneous heat and light-induced pain thresholds in post-traumatic headache attributed to mild traumatic brain injury. Headache 2022, 62, 726–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, L.; Dumkrieger, G.; Chong, C.D.; Ross, K.; Berisha, V.; Schwedt, T.J. Symptoms of Autonomic Dysfunction Among Those With Persistent Posttraumatic Headache Attributed to Mild Traumatic Brain Injury: A Comparison to Migraine and Healthy Controls. Headache 2018, 58, 1397–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, A.R.; Fazalbhoy, A.; Macefield, V.G. Sympathetic Responses to Noxious Stimulation of Muscle and Skin. Front. Neurol. 2016, 7, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamotte, G.; Boes, C.J.; Low, P.A.; Coon, E.A. The expanding role of the cold pressor test: A brief history. Clin. Auton. Res. 2021, 31, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.D.; Sackett, J.R.; Schlader, Z.J.; Leddy, J.J. Attenuated Cardiovascular Responses to the Cold Pressor Test in Concussed Collegiate Athletes. J. Athl. Train 2020, 55, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Cesa, S.; Tinelli, E.; Toschi, N.; Di Stefano, G.; Collorone, S.; Aceti, A.; Francia, A.; Cruccu, G.; Truini, A.; Caramia, F. fMRI pain activation in the periaqueductal gray in healthy volunteers during the cold pressor test. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2014, 32, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapotka, M.; Ruz, M.; Salamanca Ballesteros, A.; Ocon Hernandez, O. Cold pressor gel test: A safe alternative to the cold pressor test in fMRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2017, 78, 1464–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.L.; Wagner, J.; Heugel, N.; Sugar, J.; Lee, Y.W.; Conant, L.; Malloy, M.; Heffernan, J.; Quirk, B.; Zinos, A.; et al. Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Its Clinical Application in the Field of Neuroscience: Advances and Future Directions. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masataka, N.; Perlovsky, L.; Hiraki, K. Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) in functional research of prefrontal cortex. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Sobczak, G.; McKay, C.M.; Litovsky, R.Y. Comparing fNIRS signal qualities between approaches with and without short channels. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0244186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.; Li, H.; Li, N.; Zhang, S.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Cai, W. Functional near-infrared spectroscopy as a potential objective evaluation technique in neurocognitive disorders after traumatic brain injury. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 903756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skau, S.; Bunketorp-Kall, L.; Kuhn, H.G.; Johansson, B. Mental Fatigue and Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (fNIRS)—Based Assessment of Cognitive Performance After Mild Traumatic Brain Injury. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.T.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Liu, Y.H.; Cheong, P.L.; Wang, Y.M.; Sun, C.W. Migraine classification by machine learning with functional near-infrared spectroscopy during the mental arithmetic task. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-T.; Li, C.-C.; Liu, Y.-H.; Cheong, P.-L.; Wang, Y.-M.; Sun, C.-W. Migraine Detection in Young Group Based on Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Measurements. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2025, 31, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barati, Z.; Shewokis, P.A.; Izzetoglu, M.; Polikar, R.; Mychaskiw, G.; Pourrezaei, K. Hemodynamic response to repeated noxious cold pressor tests measured by functional near infrared spectroscopy on forehead. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 41, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barati, Z.; Zakeri, I.; Pourrezaei, K. Functional near-infrared spectroscopy study on tonic pain activation by cold pressor test. Neurophotonics 2017, 4, 015004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroe, K.; Schiehser, D.; Parr, A.; Simmons, A.; Hays, W.; Bailey, B.; Shahidi, B. Biological markers of brain network connectivity and pain sensitivity distinguish low coping from high coping Veterans with persistent post-traumatic headache. J. Neurotrauma 2025, 42, 1918–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS) The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 1–211. [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, J.M.; Lucas, S.; Dikmen, S.; Braden, C.A.; Brown, A.W.; Brunner, R.; Diaz-Arrastia, R.; Walker, W.C.; Watanabe, T.K.; Bell, K.R. Natural history of headache after traumatic brain injury. J. Neurotrauma 2011, 28, 1719–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, T.; Roks, G.; de Koning, M.; Scheenen, M.; van der Horn, H.; Plas, G.; Hageman, G.; Schoonman, G.; Spikman, J.; van der Naalt, J. Risk factors and outcomes associated with post-traumatic headache after mild traumatic brain injury. Emerg. Med. J. 2017, 34, 800–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, K.; Bell, K.R.; Ehde, D.M.; Temkin, N.; Dikmen, S.; Williams, R.M.; Dillworth, T.; Hoffman, J.M. Longitudinal Study of Headache Trajectories in the Year After Mild Traumatic Brain Injury: Relation to Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Symptoms. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2015, 96, 2000–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorniak, S.L.; Meng, H.; Pollonini, L. Correlation between subcutaneous adipose tissue of the head and body mass index: Implications for functional neuroimaging. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2022, 85, 102997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeussinger, F.B.; Heinzel, S.; Hahn, T.; Schecklmann, M.; Ehlis, A.C.; Fallgatter, A.J. Simulation of near-infrared light absorption considering individual head and prefrontal cortex anatomy: Implications for optical neuroimaging. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maracci, L.M.; Rodrigues, A.S.; Knorst, J.K.; Salbego, R.S.; Ferrazzo, V.A.; Liedke, G.S.; Silva, T.B.; Marquezan, M. Does marital status influence TMD-related chronic pain? A cross-sectional study. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2022, 29, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topping, M.; Fletcher, J. Educational attainment, family background and the emergence of pain gradients in adulthood. Soc. Sci. Med. 2024, 346, 116692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim-Williams, B.; Riley, J.L., 3rd; Williams, A.K.; Fillingim, R.B. A quantitative review of ethnic group differences in experimental pain response: Do biology, psychology, and culture matter? Pain Med. 2012, 13, 522–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortier, C.B.; Amick, M.M.; Grande, L.; McGlynn, S.; Kenna, A.; Morra, L.; Clark, A.; Milberg, W.P.; McGlinchey, R.E. The Boston Assessment of Traumatic Brain Injury-Lifetime (BAT-L) semistructured interview: Evidence of research utility and validity. J. Head Trauma Rehabil. 2014, 29, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Currao, A.; Fonda, J.R.; Beck, B.; Kenna, A.; Fortier, C.B. Diagnostic Accuracy of the Boston Assessment of Traumatic Brain Injury-Lifetime Clinical Interview Compared to Department of Defense Medical Records. Mil. Med. 2023, 188, 3561–3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soble, J.R.; Silva, M.A.; Vanderploeg, R.D.; Curtiss, G.; Belanger, H.G.; Donnell, A.J.; Scott, S.G. Normative Data for the Neurobehavioral Symptom Inventory (NSI) and post-concussion symptom profiles among TBI, PTSD, and nonclinical samples. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2014, 28, 614–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilkonis, P.A.; Choi, S.W.; Reise, S.P.; Stover, A.M.; Riley, W.T.; Cella, D.; Group, P.C. Item banks for measuring emotional distress from the Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System (PROMIS(R)): Depression, anxiety, and anger. Assessment 2011, 18, 263–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.; Barrios, F.; Kopper, B.; Hauptmann, W.; Jones, J.; O’’Neill, E. Factor Structure, Reliability, and Validity of the Pain Catastrophizing Scale. J. Behav. Med. 1997, 20, 589–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosinski, M.; Bayliss, M.S.; Bjorner, J.B.; Ware, J.E.; Garber, W.H.; Batenhorst, A.; Cady, R.; Dahlöf, C.G.H.; Dowson, A.; Tepper, S. A six-item short-form survey for measuring headache impact: The HIT-6. Qual. Life Res. 2003, 12, 963–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Rendas-Baum, R.; Varon, S.F.; Kosinski, M. Validation of the Headache Impact Test (HIT-6) across episodic and chronic migraine. Cephalalgia 2011, 31, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HealthMeasures. Pain Intensity A Brief Guide to the PROMIS Pain Intensity Instrunments; HealthMeasures: Chicago, IL, USA, 2020; Available online: https://www.healthmeasures.net/images/PROMIS/manuals/PROMIS_Pain_Intensity_Scoring_Manual.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Scrivener, C.L.; Reader, A.T. Variability of EEG electrode positions and their underlying brain regions: Visualizing gel artifacts from a simultaneous EEG-fMRI dataset. Brain Behav. 2022, 12, e2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, D.; Lange, G.; Ciccone, D.; Liu, W.; Steffener, J.; Natelson, B. Functional Imaging of Pain in Patients with Primary Fibromyalgia. J. Rheumatol. 2004, 31, 364–378. [Google Scholar]
- Bouhassira, D.; Moisset, X.; Jouet, P.; Duboc, H.; Coffin, B.; Sabate, J.M. Changes in the modulation of spinal pain processing are related to severity in irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2013, 25, 623-e468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Lee, Y.; Lee, S.; Mun, C.W. Evaluation of the effectiveness of pregabalin in alleviating pain associated with fibromyalgia: Using functional magnetic resonance imaging study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, K.B.; Kosek, E.; Petzke, F.; Carville, S.; Fransson, P.; Marcus, H.; Williams, S.C.; Choy, E.; Giesecke, T.; Mainguy, Y.; et al. Evidence of dysfunctional pain inhibition in Fibromyalgia reflected in rACC during provoked pain. Pain 2009, 144, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, A.; Tessitore, A.; Esposito, F.; Marcuccio, L.; Giordano, A.; Conforti, R.; Truini, A.; Paccone, A.; d’Onofrio, F.; Tedeschi, G. Pain processing in patients with migraine: An event-related fMRI study during trigeminal nociceptive stimulation. J. Neurol. 2012, 259, 1903–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derbyshire, S.; Jones, A.; Devani, P.; Friston, K.J.; Feinmann, C.; Harris, M.; Pearce, S.; Watson, J.; Frackowiak, R. Cerebral responses to pain in patients with atypical facial pain measured by positron emission tomography. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1994, 57, 1166–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupers, R.; Lonsdale, M.N.; Aasvang, E.; Kehlet, H. A positron emission tomography study of wind-up pain in chronic postherniotomy pain. Eur. J. Pain 2011, 15, 698.e1–698.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyron, R.; Faillenot, I.; Pomares, F.B.; Le Bars, D.; Garcia-Larrea, L.; Laurent, B. Mechanical allodynia in neuropathic pain. Where are the brain representations located? A positron emission tomography (PET) study. Eur. J. Pain 2013, 17, 1327–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apkarian, A.V.; Thomas, P.; Krauss, B.; Szeverenyi, N. Prefrontal cortical hyperactivity in patients with sympathetically mediated chronic pain. Neurosci. Lett. 2001, 311, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baliki, M.N.; Geha, P.Y.; Fields, H.L.; Apkarian, A.V. Predicting value of pain and analgesia: Nucleus accumbens response to noxious stimuli changes in the presence of chronic pain. Neuron 2010, 66, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moana-Filho, E.J.; Bereiter, D.; Nixdorf, D. Amplified Brain Processing of Dentoalveolar Pressure Stimulus in Persistent Dentoalveolar Pain Disorder Patients. J. Oral Facial Pain Headache 2015, 29, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiramatsu, T.; Nakanishi, K.; Yoshimura, S.; Yoshino, A.; Adachi, N.; Okamoto, Y.; Yamawaki, S.; Ochi, M. The dorsolateral prefrontal network is involved in pain perception in knee osteoarthritis patients. Neurosci. Lett. 2014, 581, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowdle, L.T.; Borckardt, J.J.; Back, S.E.; Morgan, K.; Adams, D.; Madan, A.; Balliet, W.; Hanlon, C.A. Sensitized brain response to acute pain in patients using prescription opiates for chronic pain: A pilot study. Drug. Alcohol. Depend. 2019, 200, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Zhang, J.; Wang, P.; Guo, J.; Zhou, M.; He, L. Functional Alterations of Pain Processing Pathway in Migraine Patients with Cutaneous Allodynia. Pain Med. 2015, 16, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, A.; Esposito, F.; Conte, F.; Fratello, M.; Caiazzo, G.; Marcuccio, L.; Giordano, A.; Tedeschi, G.; Tessitore, A. Functional interictal changes of pain processing in migraine with ictal cutaneous allodynia. Cephalalgia 2017, 37, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, A.; Tessitore, A.; Silvestro, M.; Di Nardo, F.; Trojsi, F.; Del Santo, T.; De Micco, R.; Esposito, F.; Tedeschi, G. Advanced visual network and cerebellar hyperresponsiveness to trigeminal nociception in migraine with aura. J. Headache Pain 2019, 20, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiber, K.L.; Loggia, M.L.; Kim, J.; Cahalan, C.M.; Napadow, V.; Edwards, R.R. Painful After-Sensations in Fibromyalgia are Linked to Catastrophizing and Differences in Brain Response in the Medial Temporal Lobe. J. Pain 2017, 18, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boland, E.G.; Selvarajah, D.; Hunter, M.; Ezaydi, Y.; Tesfaye, S.; Ahmedzai, S.H.; Snowden, J.A.; Wilkinson, I.D. Central pain processing in chronic chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: A functional magnetic resonance imaging study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashima, H.; Ikemura, T.; Hayashi, N. Regional differences in facial skin blood flow responses to the cold pressor and static handgrip tests. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2013, 113, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, I.A.; Dunning, J.; Butts, R.; Cleland, J.A.; Fernandez-de-Las-Penas, C. Psychometric properties of the Numeric Pain Rating Scale and Neck Disability Index in patients with cervicogenic headache. Cephalalgia 2019, 39, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, I.A.; Dunning, J.; Butts, R.; Mourad, F.; Cleland, J. Reliability, construct validity, and responsiveness of the neck disability index and numeric pain rating scale in patients with mechanical neck pain without upper extremity symptoms. Physiother Theory Pr. 2019, 35, 1328–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocsis, L.; Herman, P.; Eke, A. The modified Beer-Lambert law revisited. Phys. Med. Biol. 2006, 51, N91–N98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholkmann, F.; Wolf, M. General equation for the differential pathlength factor of the frontal human head depending on wavelength and age. J. Biomed. Opt. 2013, 18, 105004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, F.; Kranczioch, C. Signal Processing in fNIRS: A Case for the Removal of Systemic Activity for Single Trial Data. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saager, R.B.; Berger, A.J. Direct characterization and removal of interfering absorption trends in two-layer turbid media. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A Opt. Image Sci. Vis. 2005, 22, 1874–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stute, K.; Hudl, N.; Stojan, R.; Voelcker-Rehage, C. Shedding Light on the Effects of Moderate Acute Exercise on Working Memory Performance in Healthy Older Adults: An fNIRS Study. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meissel, K.; Yao, E. Using Cliff’s Delta as a Non-Parametric Effect Size Measure: An Accessible Web App and R Tutorial. Pract. Assess. Res. Eval. 2024, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourshoghi, A.; Zakeri, I.; Pourrezaei, K. Application of functional data analysis in classification and clustering of functional near-infrared spectroscopy signal in response to noxious stimuli. J. Biomed. Opt. 2016, 21, 101411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geissler, C.F.; Frings, C.; Domes, G. The effects of stress on working-memory-related prefrontal processing: An fNIRS study. Stress 2025, 28, 2472067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, V.; Vishwanath, K.; Knauft, K.; Vellen, B.V.; Luebbe, A.; Williams, A. Acute Stress Attenuates Cognitive Flexibility in Males Only: An fNIRS Examination. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Xu, K.; Ding, J.; Gao, J.; Wang, X. Physical Stress Attenuates Cognitive Inhibition: An fNIRS Examination. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2022, 1395, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, J.K.; Schwabe, L. Consistently increased dorsolateral prefrontal cortex activity during the exposure to acute stressors. Cereb. Cortex. 2024, 34, bhae159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazra, S.; Venkataraman, S.; Handa, G.; Yadav, S.L.; Wadhwa, S.; Singh, U.; Kochhar, K.P.; Deepak, K.K.; Sarkar, K. A Cross-Sectional Study on Central Sensitization and Autonomic Changes in Fibromyalgia. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenbaum, D.; Int-Veen, I.; Laicher, H.; Torka, F.; Kroczek, A.; Rubel, J.; Lawyer, G.; Bürger, Z.; Bihlmaier, I.; Storchak, H.; et al. Insights from a laboratory and naturalistic investigation on stress, rumination and frontal brain functioning in MDD: An fNIRS study. Neurobiol. Stress 2021, 15, 100344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pistoia, F.; Salfi, F.; Saporito, G.; Ornello, R.; Frattale, I.; D’Aurizio, G.; Tempesta, D.; Ferrara, M.; Sacco, S. Behavioral and psychological factors in individuals with migraine without psychiatric comorbidities. J. Headache Pain 2022, 23, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaini, S.; Davies, S.; De Francesco, S.; Pelucchi, A.; Rubino, S.; Battaglia, M. Altered pain perception and nociceptive thresholds in major depression and anxiety disorders: A meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2025, 169, 106014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, R.; Jayakaran, P.; Swain, N.; Dassanayake, S.; Tumilty, S.; Mani, R. Relationships Between Psychological, Sleep, and Physical Activity Measures and Somatosensory Function in People With Peripheral Joint Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pain Pract. 2021, 21, 226–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, A.M.; Pacheco-Barrios, K.; Andrade, M.F.; Martinez-Magallanes, D.; Pichardo, E.; Caumo, W.; Fregni, F. Psychological Factors Modulate Quantitative Sensory Testing Measures in Fibromyalgia Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Regression Analysis. Psychosom. Med. 2024, 86, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmert, K.; Breimhorst, M.; Bauermann, T.; Birklein, F.; Rebhorn, C.; Van De Ville, D.; Haller, S. Active pain coping is associated with the response in real-time fMRI neurofeedback during pain. Brain Imaging Behav. 2017, 11, 712–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seminowicz, D.A.; Davis, K.D. Cortical responses to pain in healthy individuals depends on pain catastrophizing. Pain 2006, 120, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulesu, E.; Sambugaro, E.; Torti, T.; Danelli, L.; Ferri, F.; Scialfa, G.; Sberna, M.; Ruggiero, G.M.; Bottini, G.; Sassaroli, S. Neural correlates of worry in generalized anxiety disorder and in normal controls: A functional MRI study. Psychol. Med. 2010, 40, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monkul, E.S.; Silva, L.A.; Narayana, S.; Peluso, M.A.; Zamarripa, F.; Nery, F.G.; Najt, P.; Li, J.; Lancaster, J.L.; Fox, P.T.; et al. Abnormal resting state corticolimbic blood flow in depressed unmedicated patients with major depression: A (15)O-H(2)O PET study. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2012, 33, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.Y.; Zhang, X.X.; Si, C.P.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Bian, H.T.; Zhang, B.W.; Li, X.L.; Yan, Z.R. Prefrontoparietal dysfunction during emotion regulation in anxiety disorder: A meta-analysis of functional magnetic resonance imaging studies. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat 2018, 14, 1183–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waxenbaum, J.A.; Reddy, V.; Varacallo, M.A. Anatomy, Autonomic Nervous System; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539845/ (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Drummond, P.D. Immersion of the hand in ice water releases adrenergic vasoconstrictor tone in the ipsilateral temple. Auton. Neurosci. 2006, 128, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, M.; Gabr, W.; El-Azouni, O.; Enein, A.F. Cardiovascular sympathetic nervous system response to cold pressor test among patients with migraine. Med. Sci. 2019, 24, 26–36. [Google Scholar]
- Drummond, P.D.; Granston, A. Facilitation of extracranial vasodilatation to limb pain in migraine sufferers. Neurology 2003, 61, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Qiu, S.; Zhao, C.; Wang, P.; Yu, S. Heart Rate Variability Analysis in Episodic Migraine: A Cross-Sectional Study. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 647092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saboo, N.; Kacker, S.; Sorout, J. Effects of Cognitive Behavior Therapy on Heart Rate Variability among Medical Students at a Teaching Institution in Jaipur, India. APIK J. Intern. Med. 2025, 13, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amra, B.; Ghadiry, F.; Vaezi, A.; Nematollahy, A.; Radfar, N.; Haghjoo, S.; Penzel, T.; Morin, C.M. Effect of one-shot cognitive behavioral therapy on insomnia and heart rate variability of health care workers at the time of COVID-19 pandemic: A randomized controlled trial. Sleep Breath 2023, 27, 1411–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prados, G.; Miro, E.; Martinez, M.P.; Sanchez, A.I.; Pichot, V.; Medina-Casado, M.; Chouchou, F. Effect of Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy on Nocturnal Autonomic Activity in Patients with Fibromyalgia: A Preliminary Study. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGeary, D.D.; Resick, P.A.; Penzien, D.B.; McGeary, C.A.; Houle, T.T.; Eapen, B.C.; Jaramillo, C.A.; Nabity, P.S.; Reed, D.E., 2nd; Moring, J.C.; et al. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Veterans With Comorbid Posttraumatic Headache and Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Symptoms: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Neurol. 2022, 79, 746–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, W.Y.; Stohler, C.S.; Herr, D.R. Role of the Prefrontal Cortex in Pain Processing. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 1137–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejl, C.; Burns, C.; Cherry, J.; Bradford, A.; Szabo, Y.Z. Understanding Differences Between Veterans and Civilians on a Range of Biopsychological Domains: Descriptive Report from the MIDUS II Study. J. Veterans Stud. 2023, 9, 203–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, S.A.; Dech, R.T.; Guzik, P.; Neary, J.P. Heart rate variability and implication for sport concussion. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2018, 38, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iser, C.; Arca, K. Headache and Autonomic Dysfunction: A Review. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2022, 22, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, B.E.; Arciero, J.C.; Secomb, T.W. Theoretical model of blood flow autoregulation: Roles of myogenic, shear-dependent, and metabolic responses. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2008, 295, H1572–H1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P. Brief Review Autoregulation of Blood Flow. Circ. Res. 1986, 59, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, M.; Nguyen, T.; Pandey, V.; Zhou, Y.; Pham, H.N.; Bar-Yoseph, R.; Radom-Aizik, S.; Jain, R.; Cooper, D.M.; Khine, M. Respiration rate and volume measurements using wearable strain sensors. NPJ Digit. Med. 2019, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller, D.; Colwell, E.; Low, J.; Orychock, K.; Tobin, M.A.; Simango, B.; Buote, R.; Van Heerden, D.; Luan, H.; Cullen, K.; et al. Reliability and Validity of Commercially Available Wearable Devices for Measuring Steps, Energy Expenditure, and Heart Rate: Systematic Review. JMIR mHealth uHealth 2020, 8, e18694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Yadav, S.; Kumar, A. Blood pressure measurement techniques, standards, technologies, and the latest futuristic wearable cuff-less know-how. Sens. Diagn. 2024, 3, 181–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damoun, N.; Amekran, Y.; Taiek, N.; Hangouche, A.J.E. Heart rate variability measurement and influencing factors: Towards the standardization of methodology. Glob Cardiol. Sci. Pract. 2024, 2024, e202435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Sung, B.; Lin, Y.; Mitas, O. Electrodermal activity measure: A methodological review. Ann. Tour. Res. 2022, 96, 103460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, M.; Schell, A.; Filion, D.; Berntson, G.; Quigley, K.; Lozano, D.; Lorig, T. Autonomic and Somatic Nervous System. In The Handbook of Psychophysiology, 3rd ed.; Berntson, G., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz, J.; Minoshima, S.; Casey, K.L. Keeping pain out of mind: The role of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in pain modulation. Brain 2003, 126, 1079–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stankewitz, A.; Mayr, A.; Irving, S.; Witkovsky, V.; Schulz, E. Pain and the emotional brain: Pain-related cortical processes are better reflected by affective evaluation than by cognitive evaluation. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.; Steele, S.C.; Becerra, L.; Borsook, D. Brodmann area 10: Collating, integrating and high level processing of nociception and pain. Prog. Neurobiol. 2018, 161, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuzuki, D.; Dan, I. Spatial registration for functional near-infrared spectroscopy: From channel position on the scalp to cortical location in individual and group analyses. Neuroimage 2014, 85, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seminowicz, D.A.; Moayedi, M. The Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex in Acute and Chronic Pain. J. Pain 2017, 18, 1027–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borsook, D.; Edwards, R.; Elman, I.; Becerra, L.; Levine, J. Pain and analgesia: The value of salience circuits. Prog. Neurobiol. 2013, 104, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshelh, Z.; Marciszewski, K.K.; Akhter, R.; Di Pietro, F.; Mills, E.P.; Vickers, E.R.; Peck, C.C.; Murray, G.M.; Henderson, L.A. Disruption of default mode network dynamics in acute and chronic pain states. Neuroimage Clin. 2018, 17, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, J.; Jensen, K.; Loiotile, R.; Cheetham, A.; Wey, H.Y.; Tan, Y.; Rosen, B.; Smoller, J.W.; Kaptchuk, T.J.; Gollub, R.L. Functional connectivity of the frontoparietal network predicts cognitive modulation of pain. Pain 2013, 154, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Ridder, D.; Vanneste, S.; Smith, M.; Adhia, D. Pain and the Triple Network Model. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 757241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| NSI (0-88 points) | 36.5 (15.2) |
| BAT-L (0–60 points) | 5.9 (2.6) |
| Number of lifetime TBIs a | 3.5 (4.8) |
| Time since TBI b (months) | 143.8 (92.7) |
| TBI severity grade b, n (%) | |
| Mild | |
| Grade I | 1 (10) |
| Grade II | 6 (60) |
| Grade III | 2 (20) |
| Moderate | 1 (10) |
| LOC b, n (%) | 7 (70) |
| AMS b, n (%) | 9 (90) |
| Mechanism of injury b, n (%) | |
| Blast | 2 (20) |
| Blunt | 8 (80) |
| TBI sustained during Combat/Deployment TBI, n (%) | 8 (80) |
| Headache Characteristics | |
| Onset of headache after TBI b, n (%) | |
| Acute (≤7 days) | 3 (30) |
| Delayed (>7 days) | 7 (70) |
| HIT-6 (36–78 points) | 57.3 (10.0) |
| PROMIS headache intensity (T-score) | 58.2 (7.6) |
| pPTH Group | HC Group | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sociodemographic Characteristics | |||
| Sex, n (%) | 1.000 | ||
| Male | 9 (90) | 9 (90) | |
| Female | 1 (10) | 1 (10) | |
| Age | 0.968 | ||
| Mean (+/− SD), years | 39.8 (11.0) | 39.6 (11.0) | |
| BMI | 0.520 | ||
| Mean (+/− SD), kg/m2 | 28.8 (3.2) | 29.0 (2.3) | |
| Ethnicity/Race, n (%) | 0.867 | ||
| Non-Hispanic White | 5 (50) | 7 (70) | |
| Non-Hispanic Black | 2 (20) | 1 (10) | |
| Hispanic White | 3 (30) | 2 (20) | |
| Education, n (%) | 0.339 | ||
| High school diploma or less | 1 (10) | 2 (20) | |
| Some college | 5 (50) | 2 (20) | |
| Bachelor’s degree or higher | 4 (40) | 6 (60) | |
| Marital status, n (%) | 0.223 | ||
| Married or partnered | 7 (70) | 7 (70) | |
| Single | 1 (10) | 3 (30) | |
| Divorced | 2 (20) | 0 (0) | |
| Psychological Characteristics | |||
| PROMIS Anxiety (T-score) | 61.1 (4.9) | 47.0 (7.4) | 0.001 |
| PROMIS Depression (T-score) | 56.0 (6.1) | 41.3 (4.1) | <0.001 |
| PCS (0–52 points) | 16.3 (10.1) | 1.6 (3.4) | <0.001 |
| Cont. dmPFC BA 8 | lps. dmPFC BA 8 | Cont. dmPFC BA 9/10 | lps. dmPFC BA 9/10 | lps. vmPFC BA 10 | SSC | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed Effects | β | CI | p | β | CI | p | β | CI | p | β | CI | p | β | CI | p | β | CI | p |
| Evoked Pain | 0.16 | (0.01, 0.31) | 0.184 | 0.22 | (0.09, 0.35) | 0.031 | 0.19 | (0.06, 0.33) | 0.069 | 0.27 | (0.11, 0.42) | 0.031 | 0.21 | (0.01, 0.41) | 0.184 | 0.12 | (−0.01, 0.25) | 0.224 |
| Task | −0.34 | (−1.02, 0.33) | 0.554 | −0.13 | (−0.73, 0.47) | 0.78 | −0.35 | (−0.95, 0.24) | 0.554 | −0.78 | (−1.49, −0.06) | 0.184 | 0.06 | (−0.80, 0.92) | 0.936 | −0.10 | (−0.64, 0.42) | 0.797 |
| Group | −0.29 | (−0.84, 0.25) | 0.554 | −0.21 | (−0.66, 0.25) | 0.554 | −0.26 | (−0.73, 0.21) | 0.554 | −0.24 | (−0.79, 0.30) | 0.554 | 0.24 | (−0.42, 0.90) | 0.597 | −0.20 | (−0.65, 0.25) | 0.554 |
| Task × Group | 0.67 | (−0.05, 1.38) | 0.224 | 0.33 | (−0.32, 0.98) | 0.554 | 0.27 | (−0.39, 0.91) | 0.563 | 0.71 | (−0.06, 1.49) | 0.224 | −0.03 | (−0.98, 0.91) | 0.946 | 0.95 | (0.41, 1.48) | 0.031 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Parr, A.W.; Berry, D.B.; Shahidi, B.; Schiehser, D.M.; Monroe, K.S. Extracranial Hemodynamic Responses to a Noxious Cold Pressor Task Differ Between Persistent Post-Traumatic Headache and Healthy Controls. J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15, 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15120593
Parr AW, Berry DB, Shahidi B, Schiehser DM, Monroe KS. Extracranial Hemodynamic Responses to a Noxious Cold Pressor Task Differ Between Persistent Post-Traumatic Headache and Healthy Controls. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2025; 15(12):593. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15120593
Chicago/Turabian StyleParr, Aaron W., David B. Berry, Bahar Shahidi, Dawn M. Schiehser, and Katrina S. Monroe. 2025. "Extracranial Hemodynamic Responses to a Noxious Cold Pressor Task Differ Between Persistent Post-Traumatic Headache and Healthy Controls" Journal of Personalized Medicine 15, no. 12: 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15120593
APA StyleParr, A. W., Berry, D. B., Shahidi, B., Schiehser, D. M., & Monroe, K. S. (2025). Extracranial Hemodynamic Responses to a Noxious Cold Pressor Task Differ Between Persistent Post-Traumatic Headache and Healthy Controls. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 15(12), 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15120593






