Not So Benign: Revisiting Pure Membranous Lupus Nephritis
Abstract
1. The Multiple Facades of Lupus Nephritis
1.1. General Overview
1.2. The Central Role of the Histopathological Classification
1.3. Dynamic Class Switching in Repeat Biopsies
2. Pure Membranous Lupus Nephritis
2.1. Introduction to Pure Membranous Lupus Nephritis
2.2. Clinical Phenotype of Pure Membranous Lupus Nephritis
2.3. Pathogenesis: How Membranous Lupus Nephritis Leads to Kidney Injury
2.4. Towards Precision Medicine: Biomarkers in Membranous Lupus Nephritis
2.5. Long-Term Renal Outcomes in Membranous Lupus Nephritis: Risk Factors and Survival
2.6. Comparative Outcomes: Pure Membranous vs. Proliferative/Mixed Lupus Nephritis
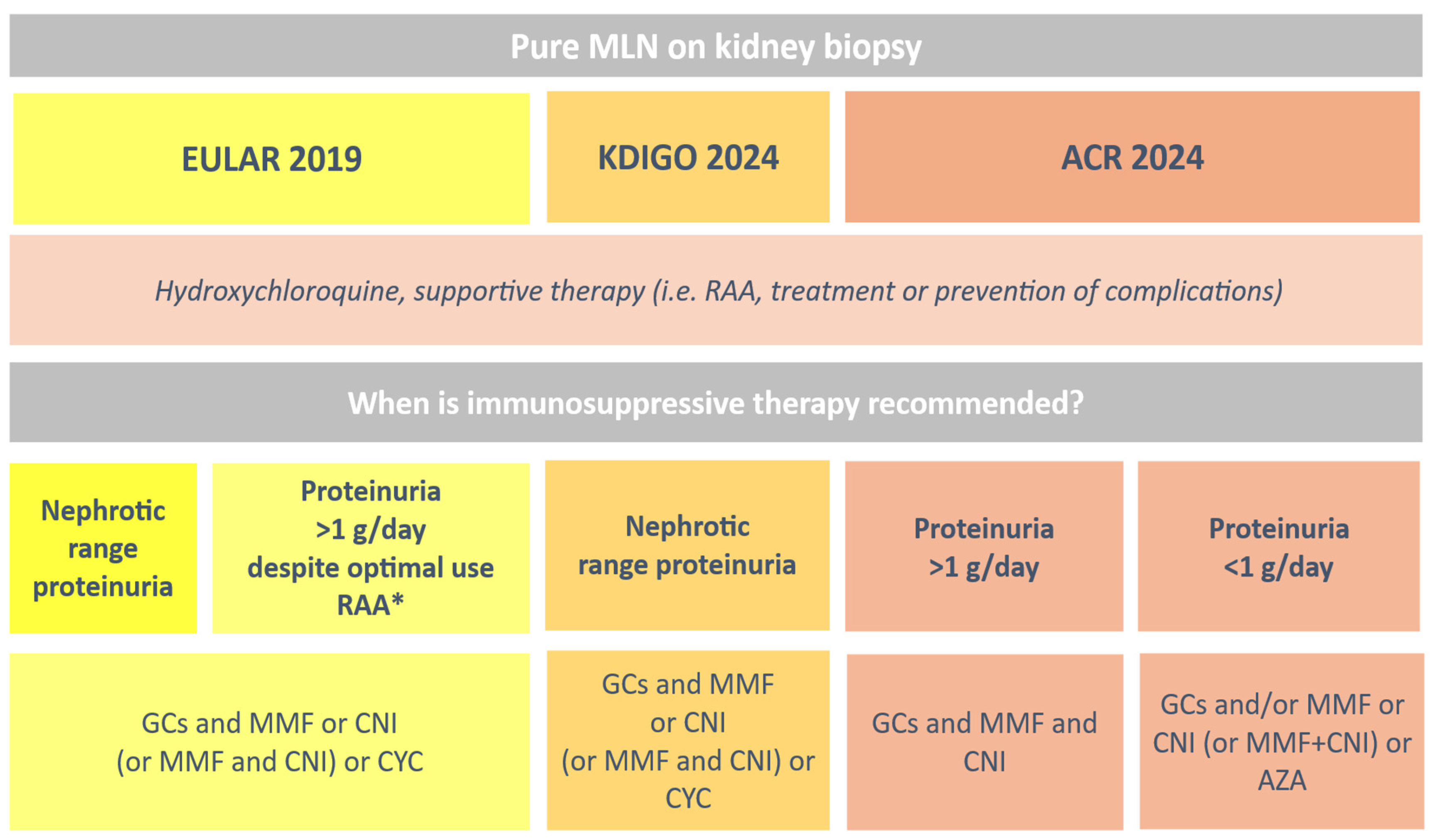
2.7. Therapeutic Strategies for Membranous Lupus Nephritis: From Guidelines to Clinical Practice
3. Current Management and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gensous, N.; Boizard-Moracchini, A.; Lazaro, E.; Richez, C.; Blanco, P. Update on the cellular pathogenesis of lupus. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2021, 33, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, C.C. Towards new avenues in the management of lupus glomerulonephritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, C.C.; Tang, S.S.K. Incidence and predictors of renal disease in Chinese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Am. J. Med. 2004, 117, 791–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanly, J.G.; O’Keeffe, A.G.; Su, L.; Urowitz, M.B.; Romero-Diaz, J.; Gordon, C.; Bae, S.-C.; Bernatsky, S.; Clarke, A.E.; Wallace, D.J.; et al. The frequency and outcome of lupus nephritis: Results from an international inception cohort study. Rheumatology 2016, 55, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, S.V.; Almaani, S.; Brodsky, S.; Rovin, B.H. Update on Lupus Nephritis: Core Curriculum 2020. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 76, 265–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajema, I.M.; Wilhelmus, S.; Alpers, C.E.; Bruijn, J.A.; Colvin, R.B.; Cook, H.T.; D’Agati, V.D.; Ferrario, F.; Haas, M.; Jennette, J.C.; et al. Revision of the ISN/RPS classification for lupus nephritis. Kidney Int. 2018, 93, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroni, G.; Vercelloni, P.G.; Quaglini, S.; Gatto, M.; Gianfreda, D.; Sacchi, L.; Raffiotta, F.; Zen, M.; Costantini, G.; Urban, M.L.; et al. Changing patterns in clinical–histological presentation and renal outcome in lupus nephritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 1318–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovin, B.H.; Caster, D.J.; Cattran, D.C.; Gibson, K.L.; Hogan, J.J.; Moeller, M.J.; Roccatello, D.; Cheung, M.; Wheeler, D.C.; Winkelmayer, W.C.; et al. Management and treatment of glomerular diseases (part 2). Kidney Int. 2019, 95, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatto, M.; Frontini, G.; Calatroni, M.; Reggiani, F.; Depascale, R.; Cruciani, C.; Quaglini, S.; Sacchi, L.; Trezzi, B.; Bonelli, G.D.; et al. Effect of sustained clinical remission on lupus nephritis. Kidney Int. Rep. 2024, 9, 1047–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moroni, G.; Gatto, M.; Tamborini, F.; Quaglini, S.; Radice, F.; Saccon, F.; Frontini, G.; Alberici, F.; Sacchi, L.; Binda, V.; et al. Lack of EULAR/ERA-EDTA response predicts poor renal outcome in lupus nephritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 1077–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petri, M.; Orbai, A.-M.; Alarcón, G.S.; Gordon, C.; Merrill, J.T.; Fortin, P.R.; Bruce, I.N.; Isenberg, D.; Wallace, D.J.; Nived, O.; et al. Derivation and validation of the SLICC classification criteria for SLE. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 2677–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aringer, M.; Costenbader, K.; Daikh, D.; Brinks, R.; Mosca, M.; Ramsey-Goldman, R.; Smolen, J.S.; Wofsy, D.; Boumpas, D.T.; Kamen, D.L.; et al. 2019 EULAR/ACR classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzzo, M.; Kronbichler, A.; Alberici, F.; Bajema, I. Nonlupus full house nephropathy: A systematic review. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2024, 19, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudose, S.; Santoriello, D.; Bomback, A.S.; Stokes, M.B.; D’Agati, V.D.; Markowitz, G.S. Sensitivity and specificity of pathologic findings to diagnose lupus nephritis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 14, 1605–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moroni, G.; Porata, G.; Raffiotta, F.; Quaglini, S.; Frontini, G.; Sacchi, L.; Binda, V.; Calatroni, M.; Reggiani, F.; Banfi, G.; et al. Beyond ISN/RPS classification: Adding chronicity index predicts kidney survival. Kidney360 2022, 3, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weening, J.J.; D’Agati, V.D.; Schwartz, M.M.; Seshan, S.V.; Alpers, C.E.; Appel, G.B.; Balow, J.E.; Bruijn, J.A.; Cook, T.; Ferrario, F.; et al. The classification of glomerulonephritis in SLE revisited. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 15, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churg, J.; Bernstein, J.; Glassock, R.J. Renal Disease: Classification and Atlas of Glomerular Diseases, 2nd ed.; Igaku-Shoin: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Sloan, R.; Schwartz, M.; Korbet, S.; Borok, R. Long-term outcome in systemic lupus erythematosus membranous glomerulonephritis. Lupus Nephritis Collaborative Study Group. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1996, 7, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercadal, L.; Tézenas du Montcel, S.; Nochy, D.; Queffeulou, G.; Piette, J.-C.; Isnard-Bagnis, C.; Martinez, F.; Groupe, T. Factors affecting outcome and prognosis in membranous lupus nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2002, 17, 1771–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colvin, R.B.; Chang, A. Diagnostic Pathology: Kidney Diseases, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Moroni, G.; Quaglini, S.; Gravellone, L.; Gallelli, B.; Leoni, A.; Messa, P.; Sinico, R.A. Membranous nephropathy in systemic lupus erythematosus: Long-term outcome and prognostic factors. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 41, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharouf, F.; Li, Q.; Whittall Garcia, L.P.; Jauhal, A.; Gladman, D.D.; Touma, Z. Short- and long-term outcomes of patients with pure membranous lupus nephritis compared with patients with proliferative disease. Rheumatology 2025, 64, 1912–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparotto, M.; Gatto, M.; Binda, V.; Doria, A.; Moroni, G. Lupus nephritis: Clinical presentations and outcomes in the 21st century. Rheumatology 2020, 59, v39–v51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, B.H.; McMahon, M.A.; Wilkinson, A.; Wallace, W.D.; Daikh, D.I.; FitzGerald, J.D.; Karpouzas, G.A.; Merrill, J.T.; Wallace, D.J.; Yazdany, J.; et al. ACR guidelines for screening, treatment, and management of lupus nephritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2012, 64, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, C.C.; Teng, Y.K.O.; Saxena, R.; Tanaka, Y. Treatment of lupus nephritis: Consensus, evidence and perspectives. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2023, 19, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanouriakis, A.; Kostopoulou, M.; Cheema, K.; Anders, H.J.; Aringer, M.; Bajema, I.; Boletis, J.; Frangou, E.; Houssiau, F.A.; Hollis, J.; et al. 2019 Update of the EULAR/ERA-EDTA recommendations for management of lupus nephritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, S713–S723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerna-López, J.A.; Tejada-Llacsa, P.J.; Valle-Farfán, F.A.d.J.; Alarcón, G.S.; Ugarte-Gil, M.F.; Pimentel-Quiroz, V.R. Rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease-associated hypomyopathic dermatomyositis complicated with pneumomediastinum: A case-based review. Rev. Colomb. Reumatol. 2023, 30, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroni, G.; Depetri, F.; Ponticelli, C. Lupus nephritis: When and how often to biopsy and what does it mean? J. Autoimmun. 2016, 74, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatto, M.; Radice, F.; Saccon, F.; Calatroni, M.; Frontini, G.; Trezzi, B.; Zen, M.; Ghirardello, A.; Tamborini, F.; Binda, V.; et al. Clinical and histological findings at second kidney biopsy predict ESKD in lupus nephritis. Lupus Sci. Med. 2022, 9, e000689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fava, A.; Fenaroli, P.; Rosenberg, A.; Bagnasco, S.; Li, J.; Monroy-Trujillo, J.; Fine, D.; Atta, M.G.; Petri, M. History of proliferative GN predicts ESKD in pure membranous lupus nephritis. Rheumatology 2022, 61, 2483–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Fernández, L.; Otón, T.; Askanase, A.; Carreira, P.; López-Longo, F.J.; Olivé, A.; Rúa-Figueroa, Í.; Narváez, J.; Ruiz-Lucea, E.; Andrés, M.; et al. Pure membranous lupus nephritis: Description of a cohort of 150 patients. Reumatol. Clin. 2019, 15, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, C.C.; Ying, K.Y.; Lau, C.S.; Yim, C.W.; Ng, W.L.; Wong, W.S.; Au, T.C. Treatment of pure membranous lupus nephropathy with prednisone and azathioprine. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2004, 43, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, H.A.; Illei, G.G.; Braun, M.J.; Balow, J.E. Randomized trial of prednisone, cyclophosphamide, and cyclosporine in lupus membranous nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calatroni, M.; Conte, E.; Stella, M.; De Liso, F.; Reggiani, F.; Moroni, G. Clinical and immunological biomarkers can identify proliferative changes in lupus nephritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2025, 27, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glassock, R.J. Prophylactic anticoagulation in nephrotic syndrome: A clinical conundrum. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 2221–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponticelli, C.; Moroni, G.; Fornoni, A. Lupus membranous nephropathy. Glomerular Dis. 2021, 1, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, P.J.; Ochi, R.F.; Schulze, M.; Johnson, R.J.; Campbell, C.; Couser, W.G. Depletion of C6 prevents development of proteinuria in experimental membranous nephropathy in rats. Am. J. Pathol. 1989, 135, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ronco, P.; Plaisier, E.; Debiec, H. Advances in membranous nephropathy. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Sandor, D.G.; Beck, L.H. The role of complement in membranous nephropathy. Semin. Nephrol. 2013, 33, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, D.; Guo, W.-Y.; Wang, F.-M.; Li, Y.-Z.; Song, Y.; Yu, F.; Zhao, M.-H. Complement alternative pathway activation in lupus nephritis. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 353, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkranz, A.R.; Tesar, V. Lupus nephritis and ANCA-associated vasculitis: Towards precision medicine? Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2021, 36, II37–II43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, S.; Milone, A.; Nicoletti, G.F.; Isenberg, D.A.; Ciccia, F. Precision medicine in systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2023, 19, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fava, A.; Buyon, J.; Magder, L.; Hodgin, J.; Rosenberg, A.; Demeke, D.S.; Rao, D.A.; Arazi, A.; Celia, A.I.; Putterman, C.; et al. Urine proteomic signatures of histological class, activity, chronicity, and treatment response in lupus nephritis. JCI Insight 2024, 9, e172569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Xu, H.; Tang, D. Mechanisms of primary membranous nephropathy. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moroni, G.; Quaglini, S.; Radice, A.; Trezzi, B.; Raffiotta, F.; Messa, P.; Sinico, R.A. The value of a panel of autoantibodies for predicting lupus nephritis activity at renal biopsy. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 106904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fava, A.; Wagner, C.A.; Guthridge, C.J.; Kheir, J.; Macwana, S.; DeJager, W.; Gross, T.; Izmirly, P.; Belmont, H.M.; Diamond, B.; et al. Association of autoantibody concentrations with lupus nephritis histologic features and treatment response. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024, 76, 1611–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, Y.; Okawa, H.; Abe, T.; Takeuchi, K.; Kamata, M.; Takeuchi, E.; Suenaga, T.; Iyoda, M.; Takeuchi, Y. Distinction between proliferative and membranous lupus nephritis based on inflammation, NETosis, and glomerular exostosin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Li, S.; Wang, Z.; Ye, S.; Fan, Y.; Peng, W.; Chen, W.; Huang, F.; Tang, R.; Chen, W. Glomerular exostosin positivity and outcomes in membranous lupus nephritis. Kidney Int. Rep. 2024, 9, 1040–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, A.; Casal Moura, M.; Fervenza, F.C.; Nasr, S.H.; Alexander, M.P.; Fidler, M.E.; Herrera Hernandez, L.P.; Zhang, P.; Grande, J.P.; Cornell, L.D.; et al. Exostosin-positive and negative phenotypes in membranous lupus nephritis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavala-Miranda, M.F.; Sobrino-Vargas, A.M.; Hernández-Andrade, A.; Caballero-Malacara, V.; Pérez-Arias, A.A.; Márquez-Macedo, S.E.; Nordmann-Gomes, A.; Navarro-Sánchez, V.; Juárez-Cuevas, B.; Uribe-Uribe, N.O.; et al. Exostosin-1/2 expression and kidney outcomes in lupus nephritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2024, 43, 2533–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yang, F.; Xu, F.; Shi, S.; Zeng, C.; Chen, X.; Miao, Y.; Liu, Z.; et al. Glomerular exostosin as subtype and activity marker of class 5 lupus nephritis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2022, 17, 986–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caza, T.N.; Hassen, S.I.; Kuperman, M.; Sharma, S.G.; Dvanajscak, Z.; Arthur, J.; Edmondson, R.; Storey, A.; Herzog, C.; Kenan, D.J.; et al. Neural cell adhesion molecule 1 as novel autoantigen in membranous lupus nephritis. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Li, S.; Jia, X.; Ye, S.; Fan, Y.; Xiang, W.; Lu, X.; Peng, W.; Chen, W.; Huang, F.; et al. Clinicopathological phenotype and outcomes of NCAM-1+ membranous lupus nephritis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2024, 40, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, E.S.; Ahn, S.M.; Oh, J.S.; Kim, Y.G.; Lee, C.K.; Yoo, B.; Hong, S. Long-term renal outcomes of patients with non-proliferative lupus nephritis. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2023, 38, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejía-Vilet, J.M.; Córdova-Sánchez, B.M.; Uribe-Uribe, N.O.; Correa-Rotter, R. Immunosuppressive treatment for pure membranous lupus nephropathy in Hispanics. Clin. Rheumatol. 2016, 35, 2219–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okpechi, I.G.; Ayodele, O.E.; Jones, E.S.W.; Duffield, M.; Swanepoel, C.R. Outcome of patients with membranous lupus nephritis in South Africa. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 3509–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.O.; Hu, W.X.; Xie, H.L.; Zhang, H.T.; Chen, H.P.; Zeng, C.H.; Liu, Z.H.; Li, L.S. Long-term outcome of Chinese patients with membranous lupus nephropathy. Lupus 2008, 17, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastén, V.R.; Massardo, V.L.; Rosenberg, G.H.; Radrigán, A.F.; Roessler, B.E.; Valdivieso, D.A.; Jacobelli, G.S. Curso clínico de la nefropatía membranosa lúpica pura. Rev. Med. Chil. 2005, 133, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapsia, E.; Marinaki, S.; Michelakis, I.; Liapis, G.; Sfikakis, P.P.; Tektonidou, M.G.; Boletis, J. Long-term outcomes of membranous lupus nephritis from a single-institution cohort. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 809533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, C.; Ying, K.; Yim, C.; Ng, W.; Wong, W. Very long-term outcome of pure lupus membranous nephropathy treated with glucocorticoid and azathioprine. Lupus 2009, 18, 1091–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farinha, F.; Barreira, S.; Couto, M.; Cunha, M.; Fonseca, D.; Freitas, R.; Inês, L.; Luís, M.; Macieira, C.; Prata, A.R.; et al. Risk of chronic kidney disease in 260 patients with lupus nephritis: Analysis of a nationwide multicentre cohort with up to 35 years of follow-up. Rheumatology 2025, 64, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Farinha, F.; Pepper, R.J.; Oliveira, D.G.; McDonnell, T.; Isenberg, D.A.; Rahman, A. Outcomes of membranous and proliferative lupus nephritis: 30 years of follow-up. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 3314–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Stefánsson, B.V.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Chertow, G.M.; Greene, T.; Hou, F.-F.; Mann, J.F.E.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Lindberg, M.; Rossing, P.; et al. Dapagliflozin in patients with chronic kidney disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanouriakis, A.; Kostopoulou, M.; Alunno, A.; Aringer, M.; Bajema, I.; Boletis, J.N.; Cervera, R.; Doria, A.; Gordon, C.; Govoni, M.; et al. 2019 update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of SLE. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovin, B.H.; Ayoub, I.M.; Chan, T.M.; Liu, Z.-H.; Mejía-Vilet, J.M.; Floege, J. KDIGO 2024 Clinical Practice Guideline for the management of lupus nephritis. Kidney Int. 2024, 105, S1–S69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sammaritano, L.R.; Askanase, A.; Bermas, B.L.; Dall’Era, M.; Duarte-García, A.; Hiraki, L.T.; Rovin, B.H.; Son, M.B.F.; Alvarado, A.; Aranow, C.; et al. 2024 American College of Rheumatology (ACR) Guideline for the Screening, Treatment, and Management of Lupus Nephritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025, 77, 1115–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radhakrishnan, J.; Moutzouris, D.-A.; Ginzler, E.M.; Solomons, N.; Siempos, I.I.; Appel, G.B. Mycophenolate mofetil and cyclophosphamide as induction therapy for class V lupus nephritis. Kidney Int. 2010, 77, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, D.Y.; Yu, X.; Chen, X.; Lu, F.; Chen, N.; Li, X.; Tang, C.S.; Chan, T.M. 24-month comparison of mycophenolate mofetil and tacrolimus in membranous lupus nephritis. Nephrology 2012, 17, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavarot, N.; Verhelst, D.; Pardon, A.; Caudwell, V.; Mercadal, L.; Sacchi, A.; Leonardi, C.; Le Guern, V.; Karras, A.; Daugas, E. Rituximab alone as induction therapy for membranous lupus nephritis. Medicine 2017, 96, e7429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.; Xing, C.; Fu, P.; Ni, Z.; Chen, J.; Lin, H.; Liu, F.; He, Y.; et al. Multitarget therapy for induction treatment of lupus nephritis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovin, B.H.; Teng, Y.K.O.; Ginzler, E.M.; Arriens, C.; Caster, D.J.; Romero-Diaz, J.; Gibson, K.; Kaplan, J.; Lisk, L.; Navarra, S.; et al. Voclosporin versus placebo for lupus nephritis (AURORA 1): A phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 2070–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furie, R.; Rovin, B.H.; Houssiau, F.; Malvar, A.; Teng, Y.K.O.; Contreras, G.; Amoura, Z.; Yu, X.; Mok, C.-C.; Santiago, M.B.; et al. Two-year randomized controlled trial of belimumab in lupus nephritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1117–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovin, B.H.; Furie, R.; Teng, Y.K.O.; Contreras, G.; Malvar, A.; Yu, X.; Ji, B.; Green, Y.; Gonzalez-Rivera, T.; Bass, D.; et al. Secondary analysis of the Belimumab International Study in lupus nephritis. Kidney Int. 2022, 101, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furie, R.A.; Rovin, B.H.; Garg, J.P.; Santiago, M.B.; Aroca-Martínez, G.; Zuta Santillán, A.E.; Alvarez, D.; Navarro Sandoval, C.; Lila, A.M.; Tumlin, J.A.; et al. Efficacy and safety of obinutuzumab in active lupus nephritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 392, 1471–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panagiotopoulos, A.; Kapsia, E.; Michelakis, I.; Boletis, J.; Marinaki, S.; Sfikakis, P.P.; Tektonidou, M.G. Immunosuppressive discontinuation after renal response in lupus nephritis: Predictors and long-term outcomes. Rheumatology 2025, 64, 1894–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zen, M.; Fuzzi, E.; Loredo Martinez, M.; Depascale, R.; Fredi, M.; Gatto, M.; Larosa, M.; Saccon, F.; Iaccarino, L.; Doria, A. Immunosuppressive therapy withdrawal after remission in lupus nephritis. Rheumatology 2022, 61, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
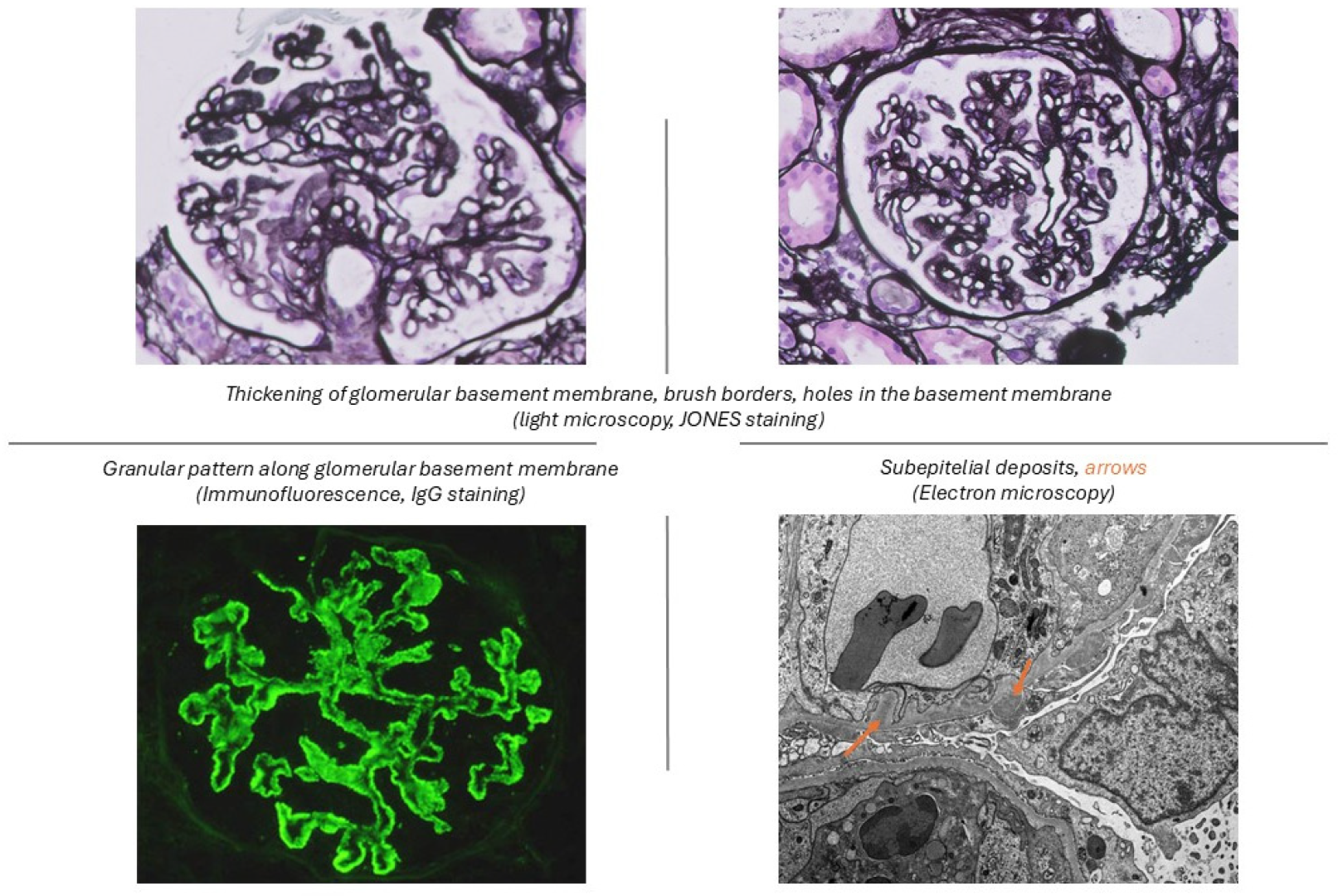
| Class | Name | Definition | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | Minimal mesangial lupus nephritis | Normal by LM with mesangial deposits by IF or EM | May have other features such as podocytopathy or tubulointerstitial disease (beware of unsampled class III). |
| II | Mesangial proliferative lupus nephritis | Purely mesangial hypercellularity by LM with mesangial deposits by IF; may be rare subepithelial or subendothelial deposits by IF or EM (not by LM). | May have other features such as podocytopathy, tubulointerstitial disease (beware of unsampled class III), or thrombotic microangiopathy. |
| III | Focal lupus nephritis | Active or inactive segmental or global endocapillary and/or extracapillary glomerulonephritis by LM in <50% of glomeruli; usually shows subendothelial deposits. | Active (A) & chronic (C) lesions defined in Modified NIH Activity & Chronicity Scoring System; replaces A & C designation. |
| IV | Diffuse lupus nephritis | Active or inactive endocapillary and/or extracapillary glomerulonephritis by LM in ≥50% of glomeruli. | Omitted segmental (S) & global (G) designations due to lack of reproducibility & clinical correlation; A & C lesions as defined in Modified NIH Activity & Chronicity Scoring System. |
| V | Membranous lupus nephritis | Global or segmental granular subepithelial deposits along GBM by LM & IF or EM; if class III or IV is present, needs to be in >50% of capillaries or >50% of glomeruli; ±mesangial alterations. | May occur with class III or IV, which are designated class III/V or class IV/V, respectively. |
| VI | Advanced sclerosing lupus nephritis | ≥90% of glomerular sclerosis without residual activity. | Should be eliminated or reevaluated due to the recognizability of globally sclerotic glomeruli resulting from preceding lupus nephritis active lesions versus nonspecific global sclerosis associated with other factors (i.e., aging, hypertension, or healed TMA lesions). |
| NIH Activity Index | Definition | Score |
|---|---|---|
| Endocapillary hypercellularity (% glomeruli) | None (0), <25% (1+), 25–50% (2+), >50% (3+) of glomeruli | 0–3 |
| Neutrophils/karyorrhexis (% glomeruli) | None (0), <25% (1+), 25–50% (2+), >50% (3+) of glomeruli | 0–3 × 2 |
| Fibrinoid necrosis (% glomeruli) | None (0), <25% (1+), 25–50% (2+), >50% (3+) of glomeruli | 0–3 × 2 |
| Wire loops or hyaline thrombi (% glomeruli) | None (0), <25% (1+), 25–50% (2+), >50% (3+) of glomeruli | 0–3 |
| Cellular or fibrocellular crescents (% glomeruli) | None (0), <25% (1+), 25–50% (2+), >50% (3+) of glomeruli | 0–3 × 2 |
| Interstitial inflammation (% cortex) | None (0), <25% (1+), 25–50% (2+), >50% (3+) of cortex | 0–3 |
| Total (Activity Index): | 0–24 | |
| NIH Chronicity Index | Definition | Score |
| Glomerulosclerosis score, global and/or segmental (% glomeruli) | None (0), <25% (1+), 25–50% (2+), >50% (3+) of glomeruli | 0–3 |
| Fibrous crescents (% glomeruli) | None (0), <25% (1+), 25–50% (2+), >50% (3+) of glomeruli | 0–3 |
| Tubular atrophy (% cortex) | None (0), <25% (1+), 25–50% (2+), >50% (3+) of cortex | 0–3 |
| Interstitial fibrosis (% cortex) | None (0), <25% (1+), 25–50% (2+), >50% (3+) of cortex | 0–3 |
| Total (Chronicity Index): | 0–12 |
| N ° | Kidney Biopsy Histology | Race | Year | Follow-Up (yr) | Main Outcomes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kapsia et al. [59] | 27 | Pure Class V * | Caucasian | 2022 | 4.7 | 22% relapsed, no patient progressed to kidney failure |
| Kang et al. [54] | 50 | Classes V/II + V * (non-proliferative) | Asian | 2022 | 8.6 | At last follow-up: 29% had eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2. Low eGFR levels at 6 months were associated with poor renal outcomes. |
| Silva-Fernandez et al. [31] | 150 | Pure class V * | Caucasian | 2017 | 7.6 | 20% showed impaired eGFR at diagnosis. At last observation: 5% kidney failure, 6% death. |
| Mejia et al. [55] | 60 | Pure Class V * | Caucasian | 2016 | 4.3 | 38.3% showed impaired eGFR at diagnosis; at last observation: 3.3% kidney failure, 5% death. |
| Okpechi et al. [56] | 42 | Pure Class V * | African American | 2012 | NA | 26.2% of patients reached the composite endpoint (death, end-stage renal failure, or persistent doubling of serum creatinine). |
| Sun et al. [57] | 100 | Pure Class V * | Asian | 2008 | 6.4 | 29.9% relapsed, 21 patients re-biopsied after 33 months: 8 (38.1%) transformed (5 patients transformed to class V + class IV, 2 patients in class V + III, and 1 patient in class VI). Patient survival at 5 and 10 years: 98%. Renal survival at 5 and 10 years: 96.1% and 92.7% |
| Pasten et al. [58] | 33 | Va/Vb ° | Caucasian | 2005 | 5.3 | At last observation: 33% death, 25% had CrCl < 15 mL/min at 5 years |
| Mok et al. [32,60] | 38 | Va/Vb ° | Asian | 2004 and 2009 (long term outcome study) | 7.5 and 12 | 2004: 67% complete remission, 19% renal flares, 13% had Cr/Cl decline by 20%. 2009: no patient progressed to kidney failure |
| Mercadal et al. [19] | 66 | Va/Vb ° | 48% Caucasian, 47% African American | 2002 | 6.9 | 49% relapsed; renal survival at 5 and at 10 years: 97%, and 88%; kidney failure rate: 9%. |
| N ° | Comparison | Pure Membranous | Mixed Classes | Pure Proliferative | Race | Year | Follow-Up (yr) | Main Outcomes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kharouf et al. [22] | 215 | Class V vs. Classes III or IV vs. classes VII + V/IV + V * | 51 | 44 | 120 | Australian | 2024 | 8 | No differences in complete renal response, proteinuria recovery. PLN vs. pMLN/mixed LN: trend towards worse long-term outcomes |
| Farinha et al. [61] | 260 | Class V vs. Classes III or IV * | 47 | (10 ^) | 203 | Caucasian | 2024 | 8 | pMLN: lower creatinine at onset PLN: low C3–C4, higher anti-DNA positivity. At last observation: CKD: 17% PLN vs. 7% pMLN; ESKD: 4% vs. 2%, mortality: 7% vs. 2% |
| Moroni et al. [21] | 103 | Class V vs. Classes III + V/IV + V * | 67 | 36 | NA | Caucasian | 2012 | 13 | Mixed classes: more frequent nephrotic syndrome at onset, low C3-C4, anti-DNA positivity, higher activity-chronicity indexes. No differences in remission (94.5 vs. 94.0%) and kidney survival (85.8 vs. 86.0%) at 10 years between groups |
| Sloan et al. [18] | 79 | WHO Va/Vb vs. Vc/Vd ° | 36 | 43 | NA | American | 1996 | 4 | Va/Vb better prognosis than Vc/Vd: 10-y renal survival 72% Va/Vb vs. 20–49% Vc/Vd |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uzzo, M.; Calatroni, M.; Moroni, G.L. Not So Benign: Revisiting Pure Membranous Lupus Nephritis. J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15, 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15120580
Uzzo M, Calatroni M, Moroni GL. Not So Benign: Revisiting Pure Membranous Lupus Nephritis. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2025; 15(12):580. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15120580
Chicago/Turabian StyleUzzo, Martina, Marta Calatroni, and Gabriella Luisa Moroni. 2025. "Not So Benign: Revisiting Pure Membranous Lupus Nephritis" Journal of Personalized Medicine 15, no. 12: 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15120580
APA StyleUzzo, M., Calatroni, M., & Moroni, G. L. (2025). Not So Benign: Revisiting Pure Membranous Lupus Nephritis. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 15(12), 580. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15120580






