Delphi Consensus in Otolaryngology: A Systematic Review of Reliability and Reporting Completeness
Abstract
1. Introduction
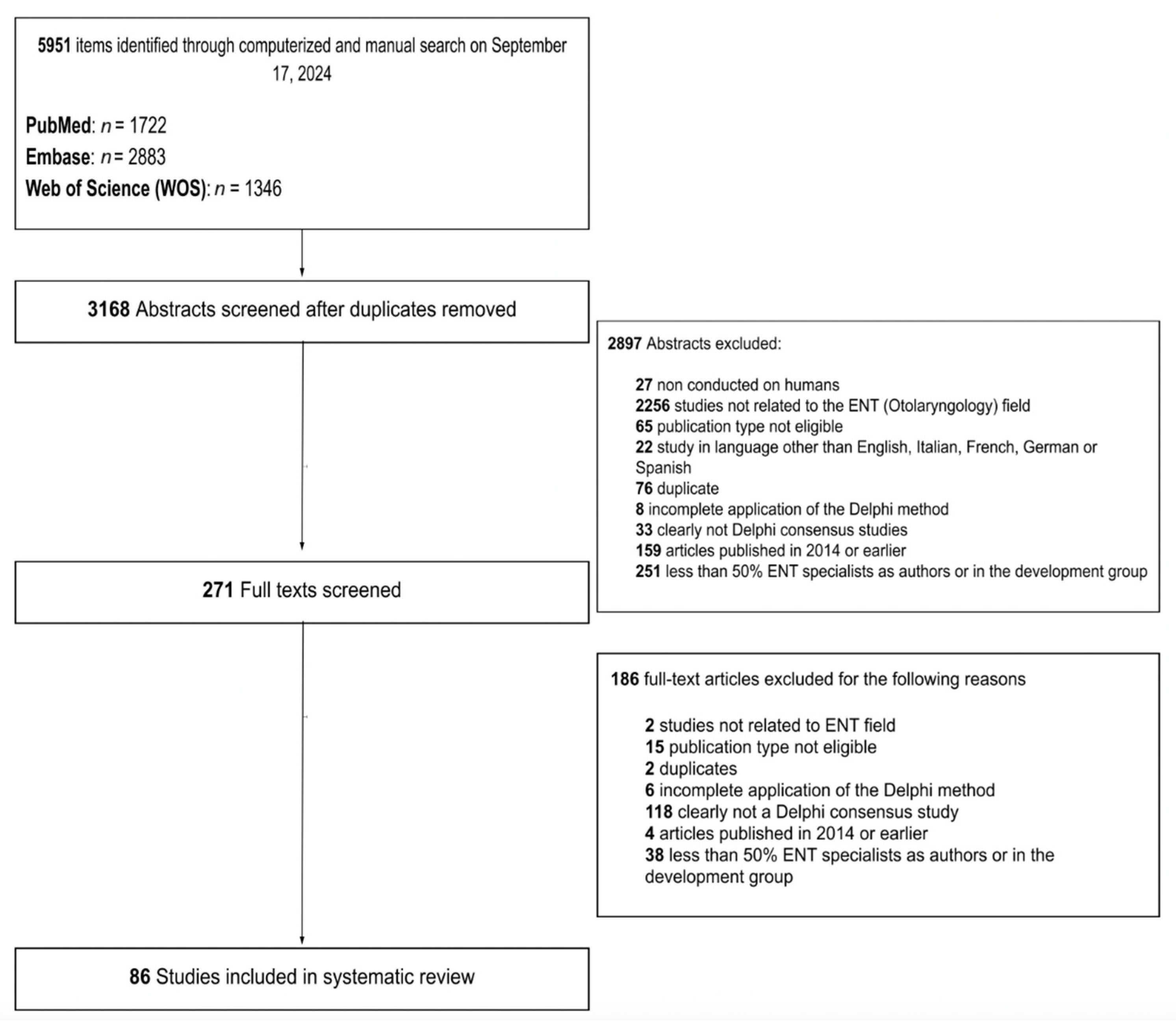
2. Materials and Methods
- -
- Non-human studies;
- -
- Non-otolaryngology-related Delphi topic;
- -
- Papers published in languages other than English, Italian, German, French, or Spanish;
- -
- Conference abstracts;
- -
- Protocol-only papers;
- -
- Studies using mixed consensus techniques or using the DeMet for purposes other than obtaining a clinical consensus (e.g., using Delphi for prioritizing items in a list);
- -
- Studies published before the Rosenfeld development manual appeared in the literature [2];
- -
- Studies lacking an otolaryngologist in the development group or with less than 50% otolaryngologists among panelists.
- -
- The related otolaryngology subspecialty (if applicable);
- -
- Key elements such as planning, development, and structure according to the Rosenfeld development manual (defining scope, development group, appropriate literature review, modified DeMet implementation, panel inclusion criteria, number of drafting and revision rounds, number of statements, and final results) for a total of 7 items;
- -
- Potential bias elements according to Nasa et al. [7]. (identification of problem area, selection of panel members, anonymity of panelists, controlled feedback, iterative rounds, consensus criteria analysis of consensus, closing criteria, i.e., the criteria which define when the consensus process should be stopped without further rounds, stability) for a total of 9 items;
- -
- Reporting completeness according to the Delphistar protocol (38 items).
3. Results
3.1. Application of Rosenfeld’s Methodology
3.2. Potential Bias Elements
3.3. Application of the DELPHISTAR Reporting Framework
3.3.1. Title and Abstract
3.3.2. Context
3.3.3. Method
3.3.4. Results
3.3.5. Discussion
3.4. Overall Evaluation
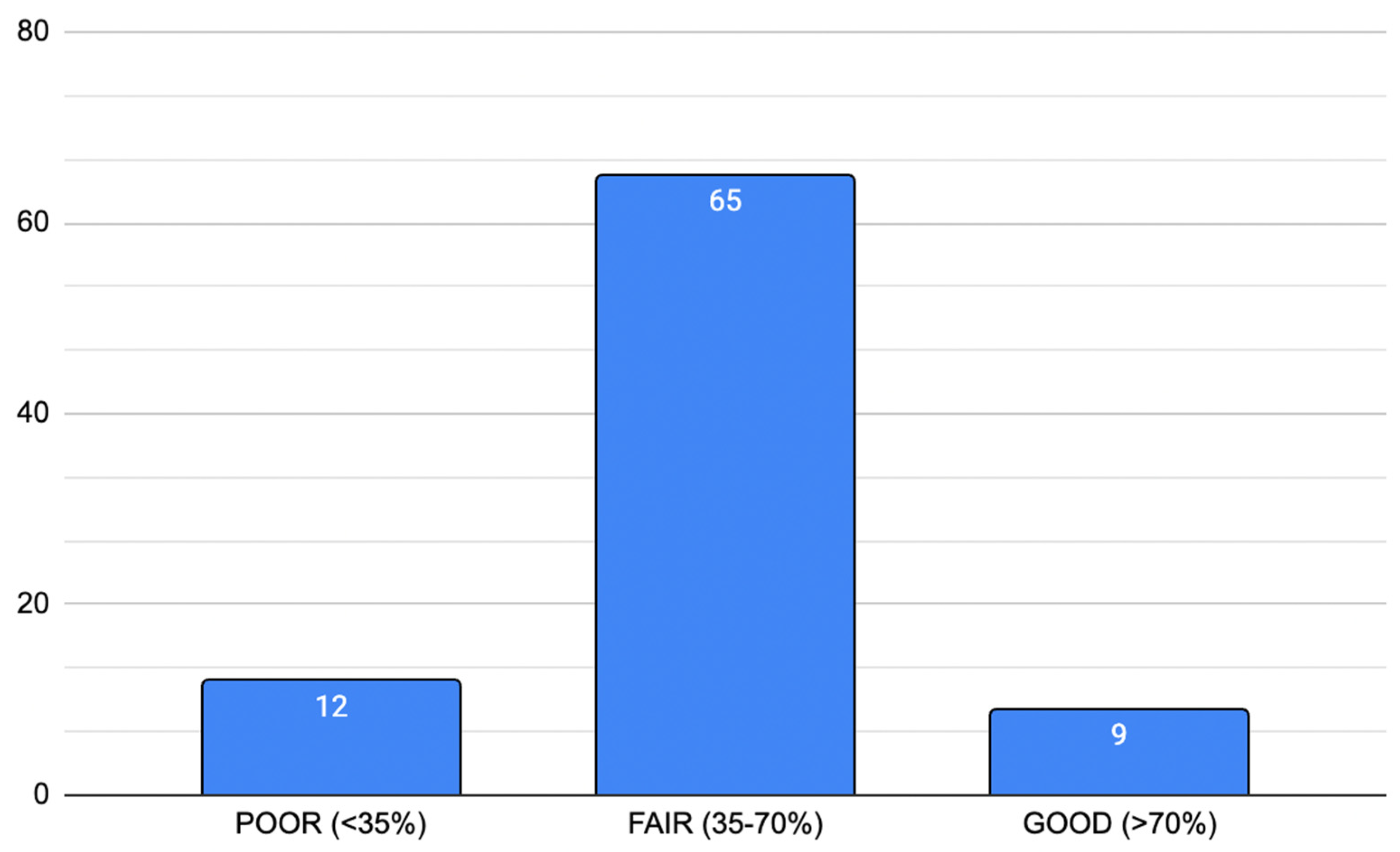
3.4.1. Reliability and Potential Bias According to Nasa et al. [7]
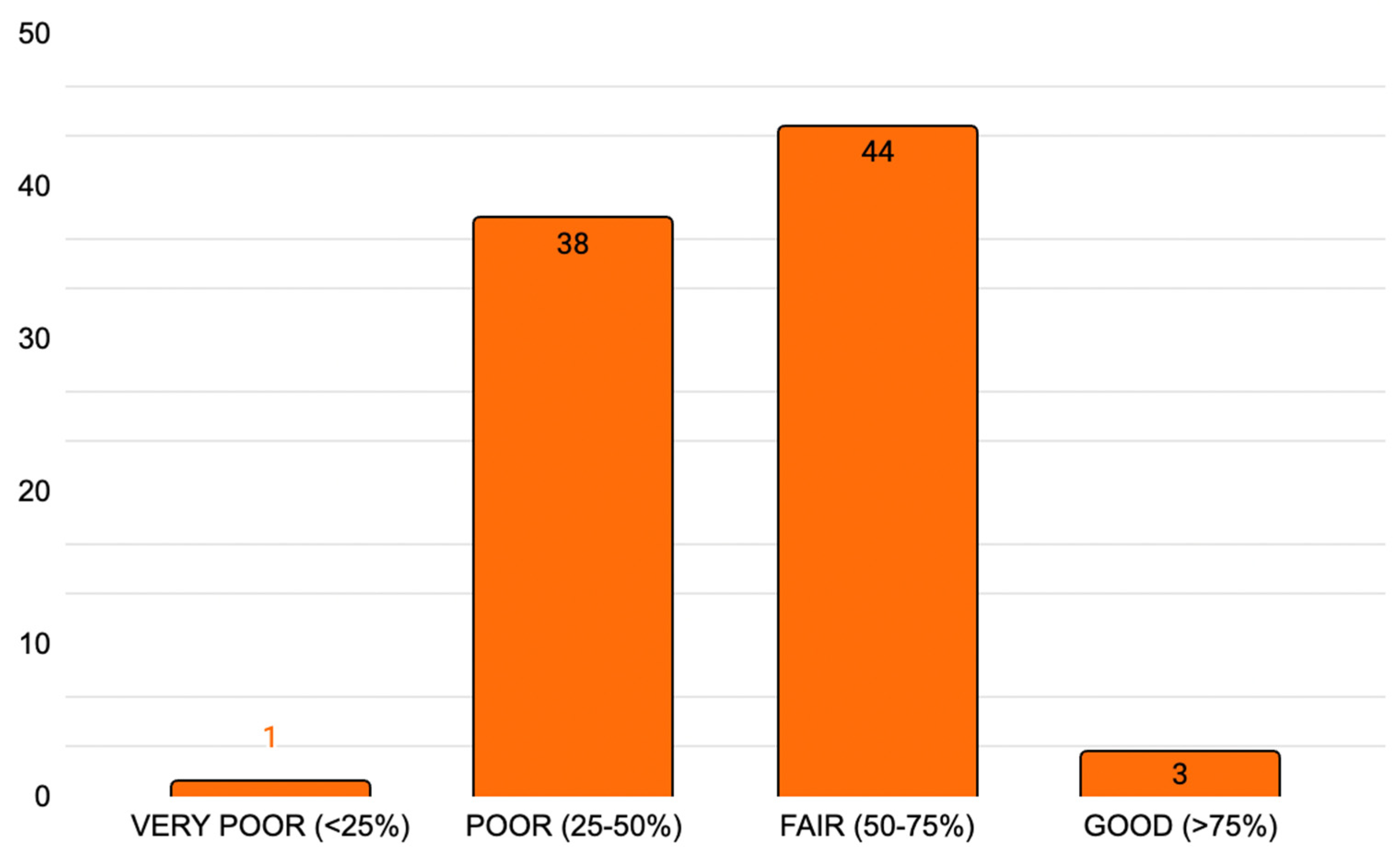
3.4.2. Delphistar Reporting Completeness Score
4. Discussion
- -
- Unclear or incomplete panel selection, often preventing assessment of the adequacy and balance of expertise;
- -
- Absence of predefined consensus thresholds, with criteria sometimes introduced post hoc or without explicit justification;
- -
- Arbitrary or undefined closing criteria, leading to uncertainty about when the Delphi process should conclude;
- -
- Lack of evaluation of response stability, making it difficult to verify whether a genuine consensus was achieved.
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DeMet | Delphi Method |
References
- Khodyakov, D.; Grant, S.; Kroger, J.; Gadwah-Meaden, C.; Motala, A.; Larkin, J. Disciplinary trends in the use of the Delphi method: A bibliometric analysis. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0289009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenfeld, R.M.; Nnacheta, L.C.; Corrigan, M.D. Clinical Consensus Statement Development Manual. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2015, 153, S1–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, L.M.; Jorm, A.F.; Kanowski, L.G.; Kelly, C.M.; Langlands, R.L. Mental health first aid for Indigenous Australians: Using Delphi consensus studies to develop guidelines for culturally appropriate responses to mental health problems. BMC Psychiatry 2009, 9, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jünger, S.; Payne, S.A.; Brine, J.; Radbruch, L.; Brearley, S.G. Guidance on Conducting and REporting DElphi Studies (CREDES) in palliative care: Recommendations based on a methodological systematic review. Palliat. Med. 2017, 31, 684–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattrell, W.T.; Hungin, A.P.; Price, A.; Winchester, C.C.; Tovey, D.; Hughes, E.L.; van Zuuren, E.J.; Goldman, K.; Logullo, P.; Matheis, R.; et al. ACCORD guideline for reporting consensus-based methods in biomedical research and clinical practice: A study protocol. Res. Integr. Peer Rev. 2022, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niederberger, M.; Schifano, J.; Deckert, S.; Hirt, J.; Homberg, A.; Köberich, S.; Kuhn, R.; Rommel, A.; Sonnberger, M.; Network, T.D. Delphi studies in social and health sciences—Recommendations for an interdisciplinary standardized reporting (DELPHISTAR). Results of a Delphi study. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0304651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasa, P.; Jain, R.; Juneja, D. Delphi methodology in healthcare research: How to decide its appropriateness. World, J. Methodol. 2021, 11, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saibene, A.M. Systematic Review Protocol. OSF. Available online: http://osf.io/8cxs7 (accessed on 18 September 2025).
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: Explanation and elaboration. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2009, 62, e1–e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, J.R.; Poetker, D.M.; Aksoy, U.; Allevi, F.; Biglioli, F.; Cha, B.Y.; Chiapasco, M.; Lechien, J.R.; Safadi, A.; Dds, R.S.; et al. Diagnosing odontogenic sinusitis: An international multidisciplinary consensus statement. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2021, 11, 1235–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speyer, R.; Balaguer, M.; Cugy, E.; Devoucoux, C.; Morinière, S.; Soriano, G.; Vérin, E.; Woisard, V. Expert Consensus on Clinical Decision Making in the Disease Trajectory of Oropharyngeal Dysphagia in Adults: An International Delphi Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharpf, J.; Liu, J.C.; Sinclair, C.; Singer, M.; Liddy, W.; Orloff, L.; Steward, D.; Velez, J.B.; Randolph, G.W. Critical Review and Consensus Statement for Neural Monitoring in Otolaryngologic Head, Neck, and Endocrine Surgery. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2021, 166, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saibene, A.M.; Allevi, F.; Ayad, T.; Baudoin, T.; Bernal-Sprekelsen, M.; Briganti, G.; Carrie, S.; Cayé-Thomasen, P.; Saidi, S.D.; Dauby, N.; et al. Appropriateness for SARS-CoV-2 vaccination for otolaryngologist and head and neck surgeons in case of pregnancy, breastfeeding, or childbearing potential: Yo-IFOS and CEORL-HNS joint clinical consensus statement. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2021, 278, 4091–4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saibene, A.M.; Allevi, F.; Calvo-Henriquez, C.; Dauby, N.; Dondossola, D.; Hervochon, R.; Lechien, J.R.; Lobo-Duro, D.; Locatello, L.G.; Maniaci, A.; et al. Comprehensive management of paranasal sinus fungus balls: A Young-IFOS consensus statement. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2022, 13, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiff, E.; Propst, E.J.; Balakrishnan, K.; Johnson, K.; Lounsbury, D.W.; Brenner, M.J.; Tawfik, M.; Workgroup, P.T.E.R.; Yang, C.J. Pediatric Tracheostomy Emergency Readiness Assessment Tool: International Consensus Recommendations. Laryngoscope 2023, 133, 3588–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehanna, H.; Hardman, J.C.; Shenson, J.A.; Abou-Foul, A.K.; Topf, M.C.; AlFalasi, M.; Chan, J.Y.K.; Chaturvedi, P.; Chow, V.L.Y.; Dietz, A.; et al. Recommendations for head and neck surgical oncology practice in a setting of acute severe resource constraint during the COVID-19 pandemic: An international consensus. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, e350–e359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechien, J.R.; Geneid, A.; Bohlender, J.E.; Cantarella, G.; Avellaneda, J.C.; Desuter, G.; Sjogren, E.V.; Finck, C.; Hans, S.; Hess, M.; et al. Consensus for voice quality assessment in clinical practice: Guidelines of the European Laryngological Society and Union of the European Phoniatricians. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2023, 280, 5459–5473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baudouin, R.; Hans, S.; Guiche, M.; Binet, A.; Circiu, M.P.; Crevier-Buchman, L.; Morsomme, D.; Finck, C.; Rutigliano, P.; Rodriguez, A.; et al. Tele-rehabilitation in voice disorders during the pandemic: A consensus paper from the French Society of Phoniatrics and Laryngology. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2022, 280, 2411–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tucci, D.L.; McCoul, E.D.; Rosenfeld, R.M.; Tunkel, D.E.; Batra, P.S.; Chandrasekhar, S.S.; Cordes, S.R.; Eshraghi, A.A.; Kaylie, D.; Lal, D.; et al. Clinical Consensus Statement: Balloon Dilation of the Eustachian Tube. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2019, 161, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-O.; Kim, J.H.; Joo, Y.H.; Kim, S.-Y.; Kim, G.-J.; Kim, H.B.; Hong, H.J.; Park, Y.M.; Chung, E.-J.; Ji, Y.B.; et al. Guideline for the Surgical Management of Locally Invasive Differentiated Thyroid Cancer From the Korean Society of Head and Neck Surgery. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2023, 16, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stack, B.C.; Twining, C.; Rastatter, J.; Angelos, P.; Baloch, Z.; Diercks, G.; Faquin, W.; Kazahaya, K.; Rivkees, S.; Sheyn, T.; et al. Consensus statement by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinology (AACE) and the American Head and Neck Society Endocrine Surgery Section (AHNS-ES) on Pediatric Benign and Malignant Thyroid Surgery. Head Neck 2021, 43, 1027–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Topic | No. of DeMet Consensuses Identified |
|---|---|
| Skull base | 4 |
| Ear | 6 |
| Laryngology | 13 |
| Neuromonitoring | 2 |
| Nose and paranasal sinuses | 15 |
| Head and neck oncology | 13 |
| Sleep/apnea | 2 |
| Pediatric otolaryngology | 17 |
| Thyroid | 9 |
| Other | 5 |
| Reliability Score According to Nasa et al. [7]. | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Identification of problem area | 2 Selection of panel members | 3 Anonymity of panelists | 4 Controlled feedback | 5 Iterative rounds | 6 Consensus criteria | 7 Analysis of consensus | 8 Closing criteria | 9 Stability * |
| 1/9 | 1/9 | 1/9 | 1/9 | 1/9 | 1/9 | 1/9 | 1/9 | 1/9 |
| Total = 9/9 * | ||||||||
| Reliability (% of total) | Poor: score < 35% | n = 12 | ||||||
| Fair: score 35–70% | n = 65 | |||||||
| Good: score > 70% | n = 9 | |||||||
| DELPHISTAR Completeness Score | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1 Title and abstract | Identification as a Delphi procedure in the title; Identification as a Delphi procedure in the abstract; Structured abstract | Tot: 3/38 |
| 2 Context | Formal: information about the sources of funding *; the team of authors and/or researchers; method consulting; the project background; the study protocol | Tot: 5/38 |
| Content: justification of the chosen method (Delphi procedure) to answer the research question; aim of the Delphi procedure (e.g., consensus, forecasting) | Tot: 2/38 | |
| 3 Method | Body and integration of knowledge: Identification and elucidation of relevant expertise, spheres of experience, and perspectives; handling of knowledge, expertise and perspectives which are missing or have been deliberately not integrated; basic definition of expert | Tot: 3/38 |
| Delphi variations: Identification of the type of Delphi procedure and potential modifications; justification of the Delphi variation and modifications *, including during the Delphi process, if applicable * | Tot: 2/38 | |
| Sample of experts: Selection criteria; Identification of the experts; Information about recruitment and any subsequent recruitment of experts | Tot: 3/38 | |
| Survey: Elucidation of the content development for the questionnaire; Description of the questionnaire | Tot: 2/38 | |
| Delphi rounds: Number of rounds; Information about the aims of the individual Delphi rounds; Disclosure and justification of the criterion for discontinuation | Tot: 3/38 | |
| Feedback: Information about what data was reported back per round; Information on how the results of the previous round were fed back to the experts surveyed; Information on whether feedback was differentiated by specific groups; Information about how dissent and unclear results were handled | Tot: 4/38 | |
| Data analysis: Disclosure of the quantitative and qualitative analytical strategy; Definition and measurement of consensus; Information on group-specific analysis or weighting of experts | Tot: 3/38 | |
| 4 Results | Delphi process: Illustration of the Delphi process; Information about special aspects during the Delphi process; Number of experts per round (both invited and participating) | Tot: 3/38 |
| Results: Presentation of the results for each Delphi round and the final results | Tot: 1/38 | |
| 5 Discussion | Quality of findings: Highlighting the findings from the Delphi study; Validity of the results; Reliability of the results; Reflection on potential limitations | Tot: 4/38 |
| Total = 38/38 * | ||
| Completeness (% of total) | Very poor: score < 25%; | n = 1 |
| Poor: score 25–50%; | n = 38 | |
| Fair: score 50–75%; | n = 44 | |
| Good: score > 70% | n = 3 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Urbanelli, A.; Pugliese, G.; Bolis, E.; Coccapani, M.; Corti, M.G.; D’Angelo, B.; Lancieri, A.; Maggi, L.; Maniaci, A.; Lechien, J.R.; et al. Delphi Consensus in Otolaryngology: A Systematic Review of Reliability and Reporting Completeness. J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15, 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15120567
Urbanelli A, Pugliese G, Bolis E, Coccapani M, Corti MG, D’Angelo B, Lancieri A, Maggi L, Maniaci A, Lechien JR, et al. Delphi Consensus in Otolaryngology: A Systematic Review of Reliability and Reporting Completeness. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2025; 15(12):567. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15120567
Chicago/Turabian StyleUrbanelli, Anastasia, Giorgia Pugliese, Elisa Bolis, Matilde Coccapani, Martina Gemma Corti, Barbara D’Angelo, Anna Lancieri, Laura Maggi, Antonino Maniaci, Jerome R. Lechien, and et al. 2025. "Delphi Consensus in Otolaryngology: A Systematic Review of Reliability and Reporting Completeness" Journal of Personalized Medicine 15, no. 12: 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15120567
APA StyleUrbanelli, A., Pugliese, G., Bolis, E., Coccapani, M., Corti, M. G., D’Angelo, B., Lancieri, A., Maggi, L., Maniaci, A., Lechien, J. R., & Saibene, A. M. (2025). Delphi Consensus in Otolaryngology: A Systematic Review of Reliability and Reporting Completeness. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 15(12), 567. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15120567








