Gene Expression Profiling Provides an Improved Characterization of CD79B-Mutated Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphomas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Mutation Detection Analyses
2.2.1. Mutation Detection of CD79A/B and MYD88
2.2.2. Mutation Detection of TP53
2.3. Multi-Gene Expression Analysis
2.4. TMA and Immunohistochemistry
2.5. Survival Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Information About the DLBCL Patient Population
3.2. Gene Expression Analysis with the PanCancer Pathways Panel
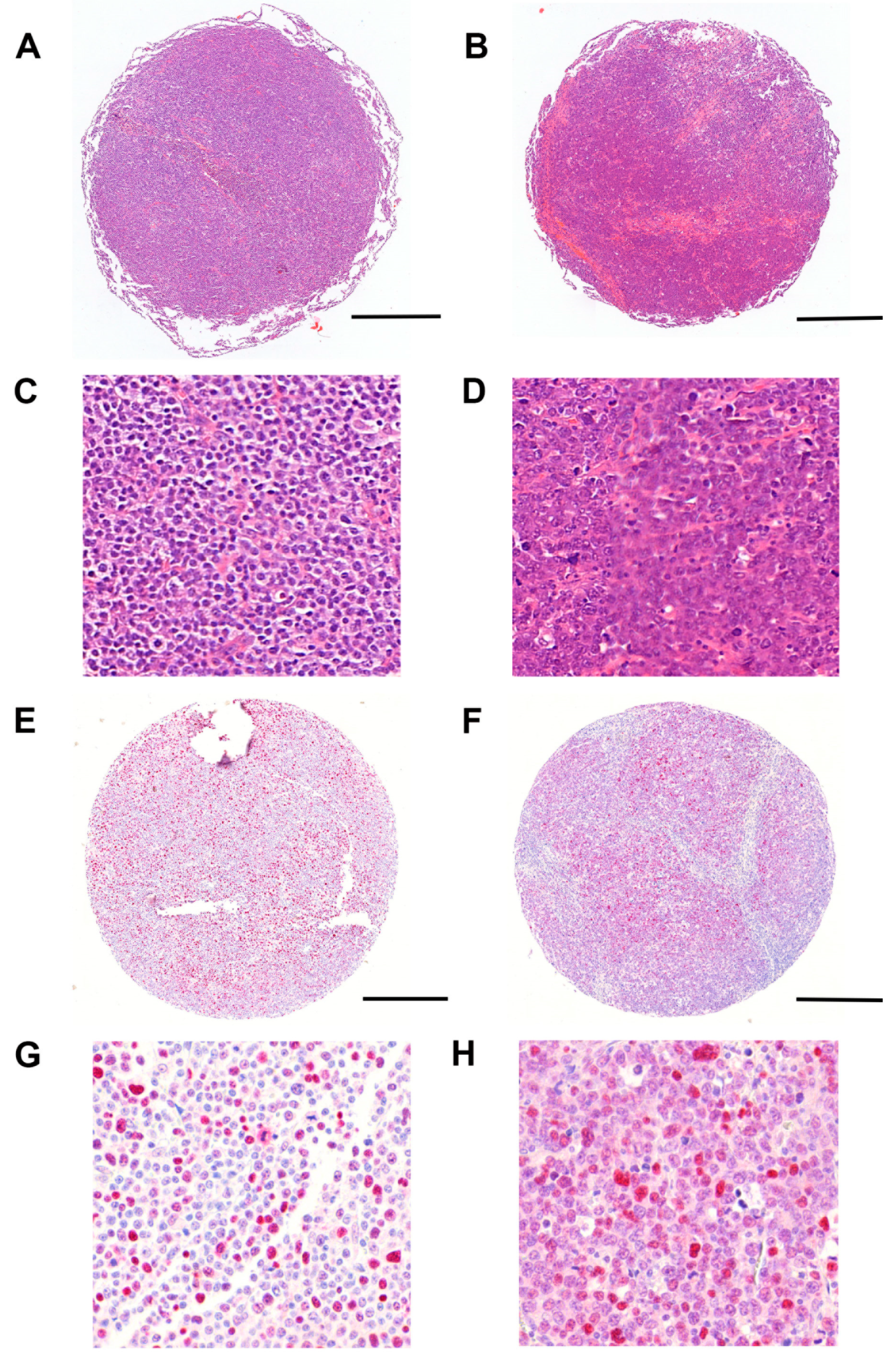
3.3. Immunohistochemical Analysis
3.4. Survival Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pileri, S.A.; Tripodo, C.; Melle, F.; Motta, G.; Tabanelli, V.; Fiori, S.; Vegliante, M.C.; Mazzara, S.; Ciavarella, S.; Derenzini, E. Predictive and Prognostic Molecular Factors in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphomas. Cells 2021, 10, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Xu, Y.; Shen, H.; Jin, J.; Tong, H.; Xie, W. Advances in biology, diagnosis and treatment of DLBCL. Ann. Hematol. 2024, 103, 3315–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehn, L.H.; Salles, G. Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 842–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutmore, N.H.; Krupka, J.A.; Hodson, D.J. Genetic Profiling in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: The Promise and the Challenge. Mod. Pathol. 2023, 36, 100007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurz, K.S.; Ott, M.; Kalmbach, S.; Steinlein, S.; Kalla, C.; Horn, H.; Ott, G.; Staiger, A.M. Large B-Cell Lymphomas in the 5th Edition of the WHO-Classification of Haematolymphoid Neoplasms-Updated Classification and New Concepts. Cancers 2023, 15, 2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berhan, A.; Almaw, A.; Damtie, S.; Solomon, Y. Diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL): Epidemiology, pathophysiology, risk stratification, advancement in diagnostic approaches and prospects: Narrative review. Discov. Oncol. 2025, 16, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaggio, R.; Amador, C.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Attygalle, A.D.; Araujo, I.B.O.; Berti, E.; Bhagat, G.; Borges, A.M.; Boyer, D.; Calaminici, M.; et al. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Lymphoid Neoplasms. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1720–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alig, S.K.; Chapuy, B.; Ennishi, D.; Dunleavy, K.; Hodson, D.J. Evolving molecular classification of aggressive B-cell lymphoma. Histopathology 2025, 86, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.; Dogan, A. Prognostic and Predictive Biomarkers in Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma. Surg. Pathol. Clin. 2019, 12, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, V.N.; Young, R.M.; Schmitz, R.; Jhavar, S.; Xiao, W.; Lim, K.H.; Kohlhammer, H.; Xu, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, H.; et al. Oncogenically active MYD88 mutations in human lymphoma. Nature 2011, 470, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.E.; Ngo, V.N.; Lenz, G.; Tolar, P.; Young, R.M.; Romesser, P.B.; Kohlhammer, H.; Lamy, L.; Zhao, H.; Yang, Y.; et al. Chronic active B-cell-receptor signalling in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Nature 2010, 463, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visco, C.; Tanasi, I.; Quaglia, F.M.; Ferrarini, I.; Fraenza, C.; Krampera, M. Oncogenic Mutations of MYD88 and CD79B in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma and Implications for Clinical Practice. Cancers 2020, 12, 2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Jin, Y.; Chen, X.; Ye, X.; Shen, X.; Lin, M.; Zeng, C.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, J. NF-kappaB in biology and targeted therapy: New insights and translational implications. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.E.; Brown, K.D.; Siebenlist, U.; Staudt, L.M. Constitutive nuclear factor kappaB activity is required for survival of activated B cell-like diffuse large B cell lymphoma cells. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 194, 1861–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frick, M.; Bettstetter, M.; Bertz, S.; Schwarz-Furlan, S.; Hartmann, A.; Richter, T.; Lenze, D.; Hummel, M.; Dreyling, M.; Lenz, G.; et al. Mutational frequencies of CD79B and MYD88 vary greatly between primary testicular DLBCL and gastrointestinal DLBCL. Leuk. Lymphoma 2018, 59, 1260–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, F.; Gonzalez-Rincon, J.; Lavernia, J.; Garcia, J.F.; Martin, P.; Bellas, C.; Piris, M.A.; Pedrosa, L.; Miramon, J.; Gomez-Codina, J.; et al. Mutational profile of primary breast diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 102888–102897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roschewski, M.; Phelan, J.D.; Jaffe, E.S. Primary large B-cell lymphomas of immune-privileged sites. Blood 2024, 144, 2593–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivas-Delgado, A.; Lopez, C.; Clot, G.; Nadeu, F.; Grau, M.; Frigola, G.; Bosch-Schips, J.; Radke, J.; Ishaque, N.; Alcoceba, M.; et al. Testicular large B-cell lymphoma is genetically similar to PCNSL and distinct from nodal DLBCL. Hemasphere 2024, 8, e70024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrader, A.M.R.; Jansen, P.M.; Willemze, R.; Vermeer, M.H.; Cleton-Jansen, A.M.; Somers, S.F.; Veelken, H.; van Eijk, R.; Kraan, W.; Kersten, M.J.; et al. High prevalence of MYD88 and CD79B mutations in intravascular large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2018, 131, 2086–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, R.; Wright, G.W.; Huang, D.W.; Johnson, C.A.; Phelan, J.D.; Wang, J.Q.; Roulland, S.; Kasbekar, M.; Young, R.M.; Shaffer, A.L.; et al. Genetics and Pathogenesis of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1396–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, R.; Fu, D.; Dong, L.; Zhang, M.C.; Shi, Q.; Shi, Z.Y.; Cheng, S.; Wang, L.; Xu, P.P.; Zhao, W.L. Simplified algorithm for genetic subtyping in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, G.W.; Huang, D.W.; Phelan, J.D.; Coulibaly, Z.A.; Roulland, S.; Young, R.M.; Wang, J.Q.; Schmitz, R.; Morin, R.D.; Tang, J.; et al. A Probabilistic Classification Tool for Genetic Subtypes of Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma with Therapeutic Implications. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 551–568.e514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacy, S.E.; Barrans, S.L.; Beer, P.A.; Painter, D.; Smith, A.G.; Roman, E.; Cooke, S.L.; Ruiz, C.; Glover, P.; Van Hoppe, S.J.L.; et al. Targeted sequencing in DLBCL, molecular subtypes, and outcomes: A Haematological Malignancy Research Network report. Blood 2020, 135, 1759–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Zhou, D.; Wang, L.; Zhu, L.; Ye, X. MYD88(L265P) and CD79B double mutations type (MCD type) of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Mechanism, clinical characteristics, and targeted therapy. Ther. Adv. Hematol. 2022, 13, 20406207211072839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.P.; Shen, R.; Shi, Z.Y.; Cheng, S.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Huang, R.; Ma, X.; Wu, X.; et al. The Prognostic Significance of CD79B Mutation in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: A Meta-analysis and Systematic Literature Review. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2022, 22, e1051–e1058.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; Wu, L.; Visco, C.; Tai, Y.C.; Tzankov, A.; Liu, W.M.; Montes-Moreno, S.; Dybkaer, K.; Chiu, A.; Orazi, A.; et al. Mutational profile and prognostic significance of TP53 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients treated with R-CHOP: Report from an International DLBCL Rituximab-CHOP Consortium Program Study. Blood 2012, 120, 3986–3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkachenko, A.; Kupcova, K.; Havranek, O. B-Cell Receptor Signaling and Beyond: The Role of Igalpha (CD79a)/Igbeta (CD79b) in Normal and Malignant B Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 25, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, T.; Morimatsu, M.; Oonuma, T.; Shiina, T.; Kitamura, H.; Syuto, B. Transcriptional regulation of the MAIL gene in LPS-stimulated RAW264 mouse macrophages. Gene 2004, 342, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.; Zhang, X.; Edwards, J.P.; Mosser, D.M. NF-kappaB1 (p50) homodimers differentially regulate pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 26041–26050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, P.D.; Pittet, M.J.; Weissleder, R. The chemical biology of IL-12 production via the non-canonical NFkB pathway. RSC Chem. Biol. 2020, 1, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Ramirez, L.M.; Lee, R.L.; Magnuson, N.S.; Bishop, G.A.; Gold, M.R. CD40 signaling in B cells regulates the expression of the Pim-1 kinase via the NF-kappa B pathway. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, W.X.; Edelstein, L.C.; Chen, C.; Bash, J.; Gelinas, C. The prosurvival Bcl-2 homolog Bfl-1/A1 is a direct transcriptional target of NF-kappaB that blocks TNFalpha-induced apoptosis. Genes. Dev. 1999, 13, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogai, H.; Wenzel, S.S.; Hailfinger, S.; Grau, M.; Kaergel, E.; Seitz, V.; Wollert-Wulf, B.; Pfeifer, M.; Wolf, A.; Frick, M.; et al. IkappaB-zeta controls the constitutive NF-kappaB target gene network and survival of ABC DLBCL. Blood 2013, 122, 2242–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beguelin, W.; Sawh, S.; Chambwe, N.; Chan, F.C.; Jiang, Y.; Choo, J.W.; Scott, D.W.; Chalmers, A.; Geng, H.; Tsikitas, L.; et al. IL10 receptor is a novel therapeutic target in DLBCLs. Leukemia 2015, 29, 1684–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, L.T.; Wright, G.; Davis, R.E.; Lenz, G.; Farinha, P.; Dang, L.; Chan, J.W.; Rosenwald, A.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Staudt, L.M. Cooperative signaling through the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 and nuclear factor-kappaB pathways in subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2008, 111, 3701–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Wang, K.B.; Rui, L. STAT3 Activation and Oncogenesis in Lymphoma. Cancers 2019, 12, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.B.; Yu, J.J.; Yu, R.Y.; Mendez, L.M.; Shaknovich, R.; Zhang, Y.; Cattoretti, G.; Ye, B.H. Constitutively activated STAT3 promotes cell proliferation and survival in the activated B-cell subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Blood 2008, 111, 1515–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krappmann, D. Shaping oncogenic NF-kappaB activity in the nucleus. Blood 2013, 122, 2146–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Guan, Q.; Wang, X.; Guo, Y.; Li, L.; Qiu, L.; Qian, Z.; Zhou, S.; et al. PIM1 genetic alterations associated with distinct molecular profiles, phenotypes and drug responses in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Clin. Transl. Med. 2022, 12, e808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, Q.; Luo, H.; Chen, R. Role and mechanism of PIM family in the immune microenvironment of diffuse large B cell lymphoma. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 21, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadevan, D.; Spier, C.; Della Croce, K.; Miller, S.; George, B.; Riley, C.; Warner, S.; Grogan, T.M.; Miller, T.P. Transcript profiling in peripheral T-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified, and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identifies distinct tumor profile signatures. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2005, 4, 1867–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogler, M. BCL2A1: The underdog in the BCL2 family. Cell Death Differ. 2012, 19, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, K.; Morita, M.; Ema, M.; Mimura, J.; Hamada, H.; Fujii, H.; Saijo, Y.; Gotoh, O.; Sogawa, K.; Fujii-Kuriyama, Y. cDNA cloning and tissue-specific expression of a novel basic helix-loop-helix/PAS factor (Arnt2) with close sequence similarity to the aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator (Arnt). Mol. Cell Biol. 1996, 16, 1706–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maltepe, E.; Keith, B.; Arsham, A.M.; Brorson, J.R.; Simon, M.C. The role of ARNT2 in tumor angiogenesis and the neural response to hypoxia. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 273, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, A.L. Hypoxia—A key regulatory factor in tumour growth. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekine, H.; Mimura, J.; Yamamoto, M.; Fujii-Kuriyama, Y. Unique and overlapping transcriptional roles of arylhydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator (Arnt) and Arnt2 in xenobiotic and hypoxic responses. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 37507–37516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, H.; Yao, Y.; Learman, B.S.; Kurozumi, K.; Ishida, J.; Ramakrishnan, S.K.; Overmyer, K.A.; Xue, X.; Cawthorn, W.P.; Reid, M.A.; et al. Induction of WNT11 by hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha regulates cell proliferation, migration and invasion. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landsburg, D.J.; Morrissette, J.J.; Nasta, S.D.; Barta, S.K.; Schuster, S.J.; Svoboda, J.; Chong, E.A.; Bagg, A. TP53 mutations predict for poor outcomes in patients with newly diagnosed aggressive B-cell lymphomas in the current era. Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 7243–7253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenz, T.; Kreuz, M.; Fuge, M.; Klapper, W.; Horn, H.; Staiger, A.M.; Winter, D.; Helfrich, H.; Huellein, J.; Hansmann, M.L.; et al. TP53 mutation and survival in aggressive B cell lymphoma. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 141, 1381–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiappella, A.; Diop, F.; Agostinelli, C.; Novo, M.; Nassi, L.; Evangelista, A.; Ciccone, G.; Di Rocco, A.; Martelli, M.; Melle, F.; et al. Prognostic impact of TP53 mutation in newly diagnosed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients treated in the FIL-DLCL04 trial. Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 196, 1184–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, P.; Zhang, C.; Yang, J.; Gui, L.; He, X.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, S.; Jiang, S.; et al. Prognostic value of BCL2 and TP53 genetic alterations for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients treated with R-CHOP. Cancer Biol. Med. 2021, 19, 893–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Clinical Parameter Overall (n = 48) | Number (%) | |
| CD79 | ||
| CD79B-mutated | 17 (35%) | |
| CD79A-mutated | 0 (0%) | |
| Wild type | 31 (65%) | |
| MYD88 | ||
| Mutated (L265P) | 14 (29%) | |
| Wild type | 32 (67%) | |
| Not informative | 2 (4%) | |
| Maturation | ||
| GCB type | 20 (42%) | |
| Non-GCB type | 26 (54%) | |
| Not informative | 2 (4%) | |
| Location | ||
| Nodal | 17 (35%) | |
| Extranodal | 31 (65%) | |
| Testicular | 13 (42%) | |
| TP53 | ||
| Mutated | 12 (25%) | |
| Wild type | 32 (67%) | |
| Not informative | 4 (8%) | |
| Clinical Parameter | CD79B-Mutated DLBCLs (n = 17) | CD79B Wild Type DLBCLs (n = 31) |
| Number (%) | Number (%) | |
| MYD88 | ||
| Mutated (L265P) | 12 (71%) | 2 (6%) |
| Wild type | 4 (23%) | 28 (90%) |
| Not informative | 1 (6%) | 1 (3%) |
| Maturation | ||
| GCB type | 3 (18%) | 17 (55%) |
| Non-GCB type | 13 (76%) | 13 (42%) |
| Not informative | 1 (6%) | 1 (3%) |
| Location | ||
| Testicular | 10 (59%) | 3 (10%) |
| Non-testicular | 7 (41%) | 28 (90%) |
| Gene | Description | Fold Change | Adj. p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| ARNT2 | aryl-hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator 2 | 4.78 | 0.0001 |
| WNT11 | wingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 11 | 3.04 | 0.0072 |
| GZMB | granzyme B (granzyme 2, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated serine esterase 1) | 2.89 | 0.0046 |
| IL10 | interleukin 10 | 2.70 | 0.0024 |
| IL12A | interleukin 12A (natural killer cell stimulatory factor 1, cytotoxic lymphocyte maturation factor 1) | 2.62 | 0.0003 |
| NFKBIZ | nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor, zeta | 2.61 | 0.0001 |
| RASGRF1 | Ras protein-specific guanine nucleotide-releasing factor 1 | 2.48 | 0.0011 |
| IL7 | interleukin 7 | 2.15 | 0.0001 |
| PIM1 | pim-1 oncogene | 2.11 | 0.0002 |
| RUNX1T1 | runt-related transcription factor 1; translocated to, 1 (cyclin D-related) | 2.00 | 0.0406 |
| CARD11 | caspase recruitment domain family, member 11 | 1.96 | 0.0034 |
| BCL2A1 | BCL2-related protein A1 | 1.77 | 0.0307 |
| STAT3 | signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (acute-phase response factor) | 1.76 | 0.0001 |
| HSP90B1 | heat shock protein 90 kDa beta (Grp94), member 1 | 1.76 | 0.003 |
| MLLT4 | myeloid/lymphoid or mixed-lineage leukemia (trithorax homolog, Drosophila); translocated to, 4 | 1.62 | 0.0032 |
| RUNX1 | runt-related transcription factor 1 | 1.59 | 0.0005 |
| CD14 | CD14 molecule | 1.57 | 0.034 |
| BID | BH3 interacting domain death agonist | 1.54 | 0.0054 |
| TP53 | tumor protein p53 | 1.37 | 0.022 |
| NFKB1 | nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 1 | 1.25 | 0.0352 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grossmann, L.; Jagla, W.; Bettstetter, M.; Bertz, S.; Schwarz-Furlan, S.; Richter, T.; Dechow, T.; Decker, T.; Dreyling, M.; Sotlar, K.; et al. Gene Expression Profiling Provides an Improved Characterization of CD79B-Mutated Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphomas. J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15, 548. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15110548
Grossmann L, Jagla W, Bettstetter M, Bertz S, Schwarz-Furlan S, Richter T, Dechow T, Decker T, Dreyling M, Sotlar K, et al. Gene Expression Profiling Provides an Improved Characterization of CD79B-Mutated Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphomas. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2025; 15(11):548. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15110548
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrossmann, Luis, Wolfgang Jagla, Marcus Bettstetter, Simone Bertz, Stephan Schwarz-Furlan, Thomas Richter, Tobias Dechow, Thomas Decker, Martin Dreyling, Karl Sotlar, and et al. 2025. "Gene Expression Profiling Provides an Improved Characterization of CD79B-Mutated Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphomas" Journal of Personalized Medicine 15, no. 11: 548. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15110548
APA StyleGrossmann, L., Jagla, W., Bettstetter, M., Bertz, S., Schwarz-Furlan, S., Richter, T., Dechow, T., Decker, T., Dreyling, M., Sotlar, K., Bartsch, H., Hartmann, A., Honecker, J., & Gaumann, A. (2025). Gene Expression Profiling Provides an Improved Characterization of CD79B-Mutated Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphomas. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 15(11), 548. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15110548







