Abstract
Background and Objectives: Chronic kidney disease (CKD) and end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) are characterized by persistent inflammation, malnutrition, and immune dysfunction, all of which contribute to poor outcomes in hemodialysis (HD) patients. The C-reactive protein albumin lymphocyte (CALLY) index has been proposed as a novel biomarker that integrates these mechanisms. This study aimed to evaluate the prognostic value of the CALLY index together with established markers, including the C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio (CAR), neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), and monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio (MLR) for all-cause mortality in HD patients. Materials and Methods: This retrospective cohort study was conducted on 106 patients undergoing HD. Demographic, clinical, and laboratory parameters were obtained three months after the effects of HD initiation was reviewed. Results: During a median follow-up of 24.5 months, 29 patients (27.3 percent) died. Non-survivors were significantly older (65.3 vs. 52.5 years, p < 0.001), had a higher prevalence of coronary artery disease (31 percent vs. 2.6 percent, p < 0.001), or shorter dialysis duration (14 vs. 27 months, p < 0.001). They also showed lower hemoglobin (9.2 vs. 10.1 g/dL, p = 0.007), creatinine (5.3 vs. 6.3 mg/dL, p = 0.048), and albumin levels (28 vs. 34 g/L, p = 0.001), as well as a higher MLR (0.329 vs. 0.254, p = 0.014). In multivariate analysis, age, CAR, and NLR independently predicted mortality, explaining 83.8% of the variation. ROC analysis identified age and MLR as significant predictors, with MLR showing a high negative predictive value (83.9%). The CALLY index did not demonstrate independent prognostic value. Conclusions: Age, CAR, NLR, and MLR were independent predictors of mortality in HD patients, whereas the CALLY index was not prognostic in this cohort. Among these markers, MLR may be a practical biomarker with strong negative predictive power. Larger prospective studies are needed to validate these findings.
1. Introduction
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is defined as a form of structural and/or functional kidney damage that has persisted for at least three months [1]. CKD leads to uremia, oxidative stress, infections, dyslipidemia, malnutrition, hypervolemia, dialysis, periodontal diseases, and increased inflammation [2]. Systemic inflammation in end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) is a well-known risk factor for increased mortality in these patients and leads to muscle wasting, vascular calcification, depression, osteoporosis, and frailty [3].
ESKD patients often have poor nutrition; this leads to a decrease in protein and energy reserves, muscle loss, and increased frailty [4]. The presence of malnutrition is a significant predictor of morbidity and mortality in patients with ESKD [5]. Inflammation and malnutrition are complex in CKD/ESKD patients, leading to anorexia and increased fatigue and muscle breakdown, which contributes to muscle atrophy [4,6]. Recent studies have shown that patients receiving hemodialysis (HD) experience a decline in nutritional parameters and a high mortality rate due to malnutrition and inflammation [4,7]. Hypoalbuminemia has been identified as a significant factor associated with an increased risk of mortality, particularly among patients receiving dialysis treatment [8].
Immunometabolic dysregulation is a multifaceted condition involving various cell types, including T cells, B cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells. It is also associated with cytokines, chemokines, and metabolic processes such as oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and inflammation [9,10]. Dysregulation of immune system cells and metabolism negatively impacts HD patients’ morbidity and mortality. In a recent study, a model incorporating neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio (MLR), and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR)-based inflammation scoring systems was employed by Liao et al., and a higher inflammation score was shown to be associated with all-cause mortality in HD patients. Thus, the development of biochemical markers reflecting inflammation, immune status, and nutrition, along with the assessment of HD patients’ prognosis, is essential [11].
The long-term exposure of CKD/ESKD and dialysis patients to chronic inflammation, nutritional deficiencies, and dysregulation of the immune system led to the hypothesis that the C-reactive protein–albumin–lymphocyte (CALLY) index score, which is the only marker combining these three pathogenic mechanisms of serum CRP, albumin, and lymphocyte count, could serve as a prognostic tool for mortality in dialysis patients. Incorporating biomarkers like the CALLY index into routine practice may enable precision nephrology by providing patient-specific risk profiles that support individualized treatment intensity, targeted nutritional and anti-inflammatory interventions, and informed modality selection. In our study, we aimed to investigate the role of inflammation, the immune system, and nutritional markers in predicting mortality in hemodialysis patients, focusing on the predictive performance of the C-reactive protein–albumin ratio (CAR), NLR, MLR, and the novel CALLY index (CRP, albumin, and lymphocyte index).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection Criteria and Study Design
This retrospective cohort study was conducted at the SBU Gazi Yasargil Training and Research Hospital, enrolling HD patients between 1 January 2018 and 31 December 2023. The present study followed the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. The research was approved by Health Sciences University, Diyarbakır Gazi Yaşargil Training and Research Hospital Local Ethics Committee, ethical approval code: 2025-317, approval date: 17 January 2025.
The study was conducted with the inclusion of patients aged over 18 years old who had undergone HD treatment for a minimum of three months. We included 106 patients who had been on dialysis. Patients lacking demographic and clinical data, receiving a kidney transplant, patients with concurrent malign tumors, and patients suffering from acute infections were not included in this study.
2.2. Data Collection and Laboratory Assessment
Demographic and clinical data were obtained from electronic medical records, encompassing various parameters, including age, gender, CKD etiology; diabetes mellitus (DM), hypertension (HT), autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease, obstructive disease, glomerulonephritis, hereditary, monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance and coronary artery disease (CAD), dialysis duration, dialysis type, mortality, and relevant laboratory data. It is important to note that the collection of laboratory data was taken for the first time after 3 months of stable HD treatment, with exclusions made for cases of acute infection.
A comprehensive panel of biochemical variables was assessed, including hemoglobin, lymphocytes, neutrophils, platelets, monocytes, C-reactive protein (CRP), albumin, CRP/albumin (CAR), glucose, Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN), creatinine, sodium, potassium, calcium, phosphorus, uric acid, and the NLR, MLR, PLR, and CALLY index. CALLY index = [albumin(g/L) × lymphocytes(109/L)/[C-reactive protein(mg/L) × 10] [12]. NLR, MLR, and PLR were calculated by dividing the number of monocytes and platelets, respectively, by the number of lymphocytes.
2.3. Statistical Analyses
The research data were computerized and evaluated using IBM SPSS 22 (IBM Statistical Package for Social Sciences). The descriptive statistics of the categorical variables were presented as numbers and percentages. The normal distribution of numerical variables was evaluated using the Kolmogorov–Smirnov and Shapiro–Wilk tests. The descriptive statistics of the categorical variables are presented as both absolute numbers and percentages. For the comparison of categorical variables, Pearson’s Chi-square test and Fisher’s exact test were applied using cross-tabulations. To ensure the validity of the results, a statistical technique known as the “Bonferroni Correction” was employed to manage multiple comparisons made within the subgroup tests. In the case of normally distributed numerical variables, mean values and standard deviations were reported as descriptive statistics. Conversely, numerical variables that were not normally distributed were reported as median values (minimum–maximum) in addition to their descriptive statistics. In the two-group analysis, an independent samples t-test was utilized to compare numerical variables with a normal distribution. In the context of a two-group analysis, the “Mann–Whitney U” test was employed to undertake a comparative analysis of numerical variables that were found to be non-normal. The independent risk factors affecting mortality were determined by means of Cox’s proportional hazards regression analysis. Independent variables with p-values less than 0.250 were included in the univariate analysis. In the multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression analysis, the CALLY index, CRP, albumin, and lymphocytes were included in two separate models due to their correlation with each other. Receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was employed to predict mortality. The independent variables that were used to formulate this prediction included sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value. Statistical significance levels were accepted as p < 0.05 and interpreted as p < 0.001.
3. Results
The clinical characteristics of patients based on mortality status are presented in Table 1. The median age of the entire patient population was 58 years, and the proportion of female patients was 39.6% (n = 42). With respect to the underlying causes of CKD, DM was the primary etiological factor, accounting for 42.5% of cases, followed by HT, which accounted for 34%. The median follow-up period on dialysis was 24.5 months, with a minimum follow-up period of 4 months and a maximum period of 67 months. The mean age of patients who died was significantly higher than the age of patients who survived (65.3 vs. 52.5 years, p < 0.001). No statistically significant differences were found regarding the etiology of CKD between the study groups (p = 0.210). The rate of CAD was significantly higher in the non-survivor group compared to the survivor group (31% vs. 2.6, p < 0.001). The duration of time on HD was significantly shorter in the non-survivor group compared to the survivor group (14 months vs. 27 months, p < 0.001). Hemoglobin levels were significantly lower in the non-survivor group (9.2 g/dL) compared to the survivor group (10.1 g/dL, p = 0.007). Similarly, creatinine levels were also lower in the non-survivor group (5.3 mg/dL vs. 6.3 mg/dL, p = 0.048). Additionally, albumin levels were lower in the non-survivor group (28 g/dL) compared to the survivor group (34 g/dL, p = 0.001). The MLR was significantly higher in the non-survivor group (0.329 vs. 0.254, p = 0.014).

Table 1.
Clinical characteristics of patients by mortality status.
Cox proportional hazards regression was employed to evaluate risk factors associated with mortality. The results of univariate and multivariate analyses are summarized in Table 2 and Table 3. In the multivariate models, Model 4 was identified as the optimal model, in which age, the CRP/albumin ratio, and the neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio accounted for 83.75% of the variation in mortality. In this model, each one-year increase in age, each unit increase in the CRP/albumin ratio, and each unit increase in the neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio were associated with 1.033-, 1.114-, and 1.049-fold increases in mortality, respectively. The ROC analysis results for the independent variables predicting mortality—including age, CRP/albumin ratio, neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio, and monocyte/lymphocyte ratio—are summarized in Table 4, with the corresponding ROC curves presented in Figure 1a–d.

Table 2.
Risk factors affecting mortality.

Table 3.
Predictive models for mortality risk.

Table 4.
ROC analysis results for age, CRP/albumin ratio, NLR, and MLR.
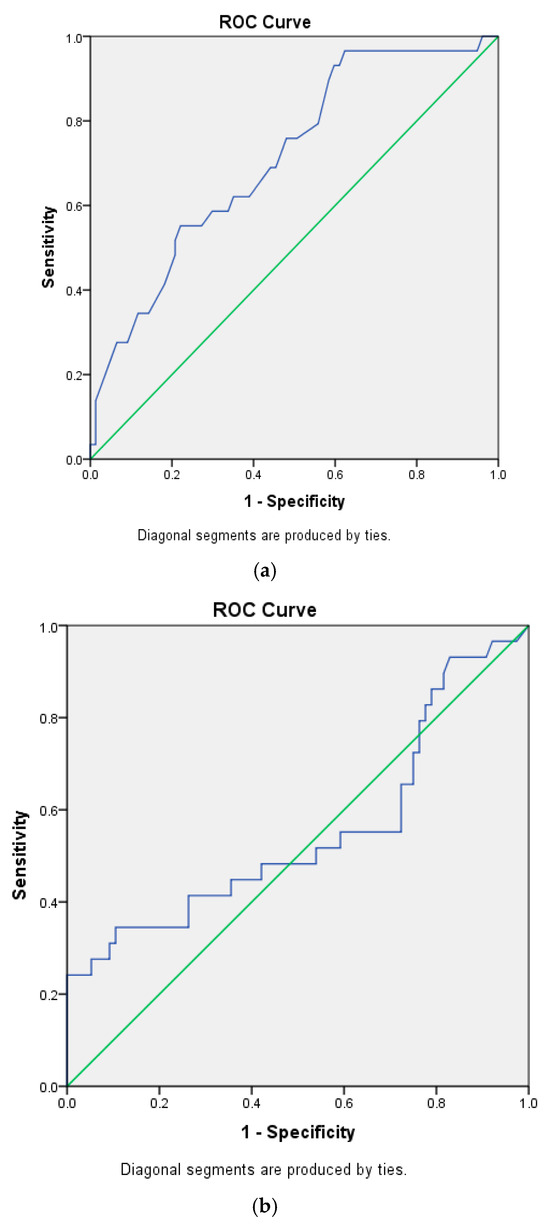
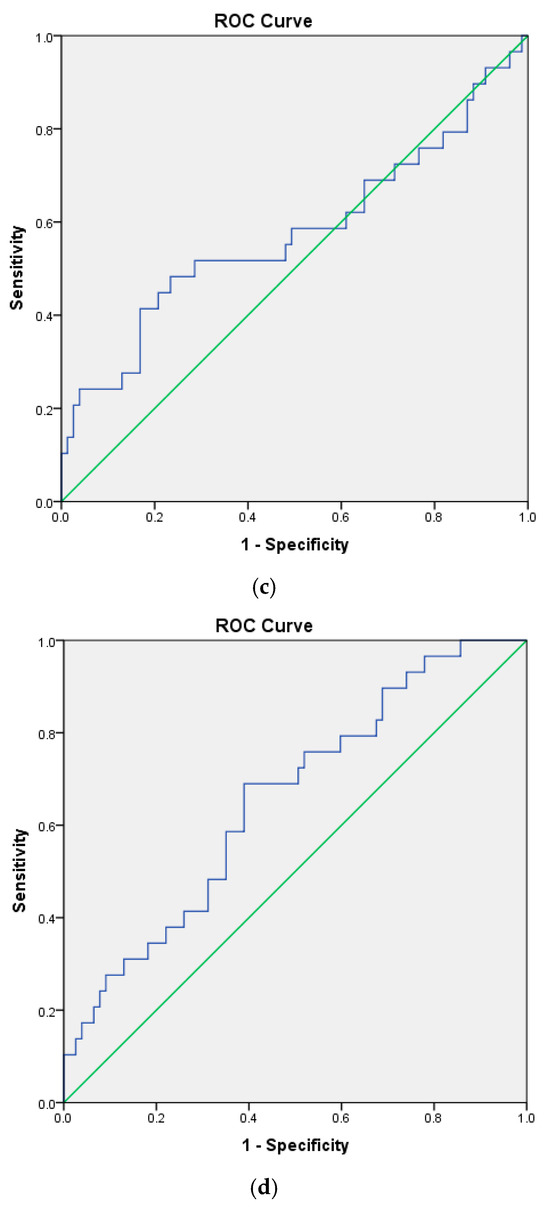
Figure 1.
(a). Receiver-operating curve for age. (b). Receiver-operating curve for CRP/albumin. (c). Receiver-operating curve for NLR. (d). Receiver-operating curve for MLR. Blue for ROC curve, green for diagonal reference line.
ROC analysis identified age and the monocyte/lymphocyte ratio as significant independent predictors of mortality. Age was found to predict mortality with 62.1% sensitivity, 64.9% specificity, 39.5% positive predictive values (PPVs), and 61.5% negative predictive values (NPVs) at a cutoff of 61.5 years, while the monocyte/lymphocyte ratio predicted mortality with 69% sensitivity, 61% specificity, 40% PPVs, and 83.9% NPVs at a cutoff of 0.2866. Overall, both variables demonstrated greater predictive power for the absence of mortality (NPV) than for its occurrence (PPV).
4. Discussion
In this study, we evaluated inflammation, the immune system, and nutritional markers that were considered to be associated with all-cause mortality in hemodialysis patients. A predictive model including age, CAR, and NLR identified mortality with an accuracy of 83.75%. Nevertheless, the newly proposed prognostic index, CALLY, was not superior to conventional inflammation and immune system markers for independently predicting mortality.
DM was the primary etiological factor of CKD in our population, and the prevalence of patients with CAD was notably higher in the non-survivor group. The most common causes of kidney failure across the world are DM and cardiovascular disease, which are the leading causes of morbidity and mortality in CKD patients [13].
In our study, non-survivors were significantly older (mean age: 65.3 years) than survivors (mean age: 52.5 years), with age identified as a predictor of death. This supports the findings of previous studies [14,15]. This observation can be attributed to a confluence of factors in aging dialysis patients, including a higher burden of comorbidities, diminished physiological reserve, malnutrition, uremia and inflammation, an attenuated immune system, impaired executive function and neurophysiological activity, and an increased cardiovascular load [16,17].
Inflammation, immune dysfunction, and malnutrition are interrelated processes that frequently coexist in HD patients. Chronic inflammation in HD can impair immune competence, while malnutrition itself further exacerbates immune deficiency and predisposes to infections. Protein–energy wasting (PEW) is a frequent complication in this population and has been associated with increased mortality [18]. Persistent exposure to uremic toxins and systemic inflammation accelerates PEW by reducing oral intake, promoting catabolism, and contributing to muscle wasting [19]. Serum albumin, the most abundant protein synthesized in the liver, is a well-established marker of both nutritional and inflammatory status [20]. Beyond maintaining plasma oncotic pressure, albumin exerts antioxidant effects by scavenging free radicals and contributes to vascular permeability and acid–base homeostasis [20]. Hypoalbuminemia may result from malnutrition in the general population, but in CKD patients, it often reflects a combination of reduced nutrient intake, chronic inflammation, increased catabolism, impaired anabolism, and dialysis-associated protein loss [21]. In a recent study by Lai KJ et al., lower serum albumin levels were independently associated with higher mortality rates in dialysis patients [22]. In line with the previous literature, our findings demonstrated that HD patients who died had significantly lower albumin levels compared with survivors. In addition, our multivariate analyses showed that the C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio was a strong and independent predictor of mortality. Recent data from a cohort of 787 HD patients indicated that an elevated CAR was significantly associated with increased mortality risk within the first six months of dialysis [23]. Another study also supported CAR as a reliable prognostic biomarker in this setting [24]. The observed relationship between CAR and adverse outcomes in ESKD is likely attributable to the combined effects of chronic inflammation, malnutrition, and accelerated atherosclerosis. It is noteworthy that up to half of HD patients develop a protein–energy deficiency. The underlying mechanisms behind this are multifactorial and include poor dietary intake, dietary restrictions, chronic inflammation, oxidative stress, nutrient loss through urine or dialysate, decreased anabolic hormones, increased catabolic drive, metabolic acidosis, sarcopenia, and age-related functional decline [25]. These overlapping pathways reinforce the clinical relevance of nutritional and inflammatory markers such as albumin and CAR in the risk stratification of HD patients.
In CKD, inflammation contributes to complications through several mechanisms, including increased skeletal muscle protein degradation, reduced muscle protein synthesis, and enhanced insulin resistance [26]. Atherosclerosis is a frequent complication in ESKD and is driven by inflammation, malnutrition, and heightened oxidative stress [27]. These processes result in abnormalities in lipid and lipoprotein metabolism as well as endothelial dysfunction. HD patients with elevated serum CRP and reduced albumin levels are often described as having malnutrition–inflammation–atherosclerosis syndrome, which highlights the association between these factors and the progression of advanced atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease [28]. Given that both inflammation and malnutrition are independently associated with increased mortality, the CAR serves as a valuable biomarker for assessing the combined impact of malnutrition and inflammation on mortality risk in HD patients. In our study, the combination of CRP and albumin expressed as CAR provided a more sensitive predictor of mortality than either CRP or albumin alone.
In our study, we identified the NLR as a strong and independent predictor of mortality in HD patients. The NLR is a well-recognized biomarker of systemic inflammation [29]. Neutrophils play a crucial role in innate immune defense and exert regulatory effects on adaptive immunity, serving as the principal effector cells in systemic inflammatory response syndrome [29]. Lymphocytes, another key component of the immune system, are responsible for both protection against external infections and recognition within the immune system [30]. Thus, the NLR integrates the innate immune response, largely mediated by neutrophils, with the adaptive immune response, mediated by lymphocytes [31]. Several studies have demonstrated that an elevated NLR is an independent risk factor for mortality in HD patients [29,32]. Consistent with these findings, our results confirmed the NLR as a significant predictor of mortality. As an inexpensive and easily measurable marker of systemic inflammation, the NLR reflects both the intensity of a patient’s pro-inflammatory state, through increased neutrophil counts, and the degree of immunosuppression, through reduced lymphocyte counts. Although we were unable to establish a clear cutoff value based on ROC curve analysis, multivariate analyses revealed that higher NLR values were significantly associated with increased mortality.
In our study, higher MLR values were associated with an increased risk of death, whereas lower MLR values strongly predicted improved survival. MLR is a novel biomarker that, similar to NLR, reflects both innate and adaptive immune pathways and can be easily calculated from routine blood parameters [33]. Recent studies have also demonstrated that MLR is a strong predictor of cardiovascular mortality in patients undergoing HD and peritoneal dialysis [34,35]. In our cohort, elevated MLR likely reflected a predominance of pro-inflammatory responses accompanied by a reduced immunosuppressive capacity within the immune system. These findings suggest that MLR may serve as a valuable biomarker for mortality prediction in HD patients. Notably, the high negative predictive value observed in our study indicates that patients with lower MLR values are more likely to have favorable survival outcomes.
The CALLY index, derived from serum CRP, albumin, and lymphocyte count, is a novel biomarker that reflects inflammation, nutritional status, and immune function. Previous studies have demonstrated its prognostic value as an independent factor in various malignancies [36,37]. Recently, Huang J. et al. reported for the first time, through multivariate analysis, a correlation between the CALLY index and all-cause mortality in HD patients [14]. In our study, we compared the CALLY index between survivors and non-survivors; however, we did not observe a significant difference between the two groups. Although the CALLY index has emerged as a prognostic indicator in the context of malignancy and inflammatory diseases, this association was not evident in our cohort. This discrepancy may be explained by the relatively small sample size, the limited follow-up duration, or the possibility that the prognostic strength of the CALLY index is restricted in the CKD population. Therefore, large-scale prospective studies are warranted to clarify the prognostic utility of the CALLY index in predicting mortality among patients with renal failure.
However, this study has several limitations. First, it was a retrospective analysis of a relatively small sample size. Second, we only collected CRP, lymphocyte count, and albumin levels on the third month after starting dialysis, without analyzing any dynamic changes or their impact on prognosis.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we compared inflammation, the immune system, and nutritional markers affecting mortality in hemodialysis (HD) patients. Using a model consisting of age, CAR, and NLR, we predicted mortality with an accuracy of 83.75%. We found that the novel biomarker CALLY index was not superior to traditional markers in HD patients. The high negative predictive value of MLR indicated that patients with low MLR had better survival outcomes. In conclusion, CAR, NLR, and MLR emerged as reliable and practical markers for predicting mortality in HD patients, whereas the prognostic value of the CALLY index requires validation in larger, prospective studies.
Author Contributions
U.C.: Conceptualization; Data curation; Formal analysis; Investigation; Methodology; Project administration; Resources; Software; Supervision; Validation; Visualization; Roles/Writing—original draft; and Writing—review and editing. N.S.: Conceptualization; Data curation—review and editing. S.A.: Conceptualization; Data curation; Formal analysis, O.M.: Conceptualization; Data curation; Formal analysis; Investigation; Methodology; Project administration; Resources; Software; Supervision; Validation; Visualization; Roles/Writing—original draft; and Writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The present study followed the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. The research was approved by Health Sciences University, Diyarbakır Gazi Yaşargil Training and Research Hospital Local Ethics Committee, ethical approval code: 2025-317, approval date: 17 January 2025.
Informed Consent Statement
The requirement for written informed consent was waived by the ethics committee due to the retrospective nature of the study.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ketteler, M.; Block, G.A.; Evenepoel, P.; Fukagawa, M.; Herzog, C.A.; McCann, L.; Moe, S.M.; Shroff, R.; Tonelli, M.A.; Toussaint, N.D.; et al. Executive summary of the 2017 KDIGO Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD) Guideline Update: What’s changed and why it matters. Kidney Int. 2017, 92, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadatane, S.P.; Satariano, M.; Massey, M.; Mongan, K.; Raina, R. The Role of Inflammation in CKD. Cells 2023, 12, 1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooman, J.P.; Dekker, M.J.; Usvyat, L.A.; Kotanko, P.; van der Sande, F.M.; Schalkwijk, C.G.; Shiels, P.G.; Stenvinkel, P. Inflammation and premature aging in advanced chronic kidney disease. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2017, 313, F938–F950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, R.M.; Ghobry, L.; Wassef, O.; Rhee, C.M.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. A Practical Approach to Nutrition, Protein-Energy Wasting, Sarcopenia, and Cachexia in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Blood Purif. 2020, 49, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herselman, M.; Esau, N.; Kruger, J.M.; Labadarios, D.; Moosa, M.R. Relationship between serum protein and mortality in adults on long-term hemodialysis: Exhaustive review and meta-analysis. Nutrition 2010, 26, 10–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Hoedt, C.H.; Bots, M.L.; Grooteman, M.P.; van der Weerd, N.C.; Penne, E.L.; Mazairac, A.H.; Levesque, R.; Blankestijn, P.J.; Nubé, M.J.; ter Wee, P.M.; et al. Clinical predictors of decline in nutritional parameters over time in ESRD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 9, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, J.; Mitra, N.; Kanetsky, P.A.; Devaney, J.; Wing, M.R.; Reilly, M.; Shah, V.O.; Balakrishnan, V.S.; Guzman, N.J.; Girndt, M.; et al. Association between albuminuria, kidney function, and inflammatory biomarker profile in CKD in CRIC. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 7, 1938–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kistler, B.M.; Moore, L.W.; Benner, D.; Biruete, A.; Boaz, M.; Brunori, G.; Chen, J.; Drechsler, C.; Guebre-Egziabher, F.; Hensley, M.K.; et al. The International Society of Renal Nutrition and Metabolism Commentary on the National Kidney Foundation and Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics KDOQI Clinical Practice Guideline for Nutrition in Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Ren. Nutr. 2021, 31, 116–120.e111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matz, A.J.; Qu, L.; Karlinsey, K.; Zhou, B. MicroRNA-regulated B cells in obesity. Immunometabolism 2022, 4, e00005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso, P.J.; Andrade-Oliveira, V.; Câmara, N.O.S. Targeting immune cell metabolism in kidney diseases. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2021, 17, 465–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.; Wei, D.; Sun, C.; Yang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Liu, X. Prognostic value of the combination of neutrophil-to-lymhocyte ratio, monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio on mortality in patients on maintenance hemodialysis. BMC Nephrol. 2022, 8, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, H.; Tani, M.; Komeda, K.; Nomi, T.; Matsushima, H.; Tanaka, S.; Ueno, M.; Nakai, T.; Maehira, H.; Mori, H.; et al. Superiority of CRP-albumin-lymphocyte index (CALLY index) as a non-invasive prognostic biomarker after hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma. HPB 2022, 24, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahr, A.J.; Molitch, M.E. Management of Diabetes Mellitus in Patients With CKD: Core Curriculum 2022. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2022, 79, 728–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Hao, J.; Luo, H.; Chen, L.; Luo, H.; Liu, H.; Xu, Y.; Wang, P. Construction of a C-reactive protein-albumin-lymphocyte index-based prediction model for all-cause mortality in patients on maintenance hemodialysis. Ren. Fail. 2025, 47, 2444396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selen, T.; Ulusal Okyay, G.; Ayerden Ebinç, F.; Merhametsiz, Ö.; Şahin, H.; Aylı, M.D. Does Control Nutritional Status (CONUT) Score Predict Early and Long-Term Mortality at the Initiation of Maintenance Hemodialysis? Int. J. Gen. Med. 2025, 18, 3775–3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Tian, R.; Ye, P.; Luo, Y. Frailty in Older Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis and Its Association with All-Cause Mortality: A Prospective Cohort Study. Clin. Interv. Aging 2022, 17, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, G.C.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Ng, J.K.; Tian, N.; Burns, A.; Chow, K.M.; Szeto, C.C.; Li, P.K. Frailty in patients on dialysis. Kidney Int. 2024, 106, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, T.; Khor, B.H.; Sahathevan, S.; Kaur, D.; Latifi, E.; Afroz, M.; Mitali, E.J.; Tashkandi, B.; Begum, N.A.S.; Kashem, T.S.; et al. Protein Energy Wasting in a Cohort of Maintenance Hemodialysis Patients in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graterol Torres, F.; Molina, M.; Soler-Majoral, J.; Romero-González, G.; Rodríguez Chitiva, N.; Troya-Saborido, M.; Socias Rullan, G.; Burgos, E.; Paúl Martínez, J.; Urrutia Jou, M.; et al. Evolving Concepts on Inflammatory Biomarkers and Malnutrition in Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.Y.; Liou, S.Y.; Kuo, W.W.; Wu, H.C.; Chang, Y.L.; Chen, T.S. Chemiluminescence analysis of antioxidant capacity for serum albumin isolated from healthy or uremic volunteers. Luminescence 2016, 31, 1474–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatino, A.; Regolisti, G.; Karupaiah, T.; Sahathevan, S.; Sadu Singh, B.K.; Khor, B.H.; Salhab, N.; Karavetian, M.; Cupisti, A.; Fiaccadori, E. Protein-energy wasting and nutritional supplementation in patients with end-stage renal disease on hemodialysis. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.J.; Hsieh, Y.P.; Chiu, P.F.; Lin, P.R. Association of Albumin and Globulin with Mortality Risk in Incident Peritoneal Dialysis Patients. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sant’Ana, M.; Gameiro, J.; Costa, C.; Branco, C.; Marques da Silva, B.; Peres, N.; Cardoso, A.; Abrantes, A.M.; Fonseca, J.A.; Outerelo, C.; et al. C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio and six-month mortality in incident hemodialysis patients. Ren. Fail. 2023, 45, 2182615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wang, G.; Yin, X.; Liu, W.; Huang, H.; Li, D. Inflammatory and nutritional indices for overall survival in Hemodialysis patients: A multicenter cohort study. BMC Nephrol. 2025, 26, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodebo, B.T.; Shah, A.; Kopple, J.D. Is it Important to Prevent and Treat Protein-Energy Wasting in Chronic Kidney Disease and Chronic Dialysis Patients? J. Ren. Nutr. 2018, 28, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, J.L. Insulin resistance and muscle metabolism in chronic kidney disease. ISRN Endocrinol. 2013, 2013, 329606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nusair, M.B.; Rajpurohit, N.; Alpert, M.A. Chronic Inflammation and Coronary Atherosclerosis in Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease. Cardiorenal Med. 2012, 2, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parhi, K.K.; Vijayasamundeeswari, C.K.; Kanchan, R.K.; Ghosh, S.; Ronald, P.J.; Periasamy, P. Association of Serum Albumin and C-Reactive Protein with Outcomes in ESRD Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis at a Tertiary Care Center in Salem, Tamil Nadu. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2024, 16, S4540–S4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Yang, F.; Xu, Y.; Feng, C.; Zhao, Y. The regulatory roles of neutrophils in adaptive immunity. Cell Commun. Signal. 2019, 17, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonacera, A.; Stancanelli, B.; Colaci, M.; Malatino, L. Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio: An Emerging Marker of the Relationships between the Immune System and Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Graubard, B.I.; Rabkin, C.S.; Engels, E.A. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and mortality in the United States general population. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Li, C.; Ge, J.; Li, Z.; Cao, L.; Fan, W.; Peng, Y.; Li, Q. Serum ferritin and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predict all-cause mortality in patients receiving maintenance hemodialysis: A prospective study. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2024, 11, 1366753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Han, F. Association of monocyte to lymphocyte ratio with length of stay in intensive care unit in neonatal apnea modified by treatment. Transl. Pediatr. 2025, 14, 1073–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, F.; Chen, R.; Cao, X.; Shen, B.; Liu, Z.; Tan, X.; Ding, X.; Zou, J. Monocyte/lymphocyte ratio as a better predictor of cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in hemodialysis patients: A prospective cohort study. Hemodial. Int. 2018, 22, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Zhan, X.; Wang, N.; Peng, F.; Feng, X.; Wu, X. Monocyte/Lymphocyte Ratio and Cardiovascular Disease Mortality in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients. Mediat. Inflamm. 2020, 2020, 9852507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, K.; Tsunematsu, M.; Tanji, Y.; Ishizaki, S.; Akaoka, M.; Haruki, K.; Uwagawa, T.; Onda, S.; Matsumoto, M.; Ikegami, T. Impact of C-reactive protein-albumin-lymphocyte (CALLY) index on prognosis after hepatectomy for colorectal liver metastasis. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 47, 101911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Shi, J.; Xie, H.; Liu, X.; Ruan, G.; Lin, S.; Ge, Y.; Liu, C.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, X.; et al. Superiority of CRP-albumin-lymphocyte index as a prognostic biomarker for patients with gastric cancer. Nutrition 2023, 116, 112191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).