Temporal Validation of a Plasma Diagnosis Approach for Early Alzheimer Disease Diagnosis in a Cognitive Disorder Unit
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. The Derivation Cohort and the Diagnosis Approach
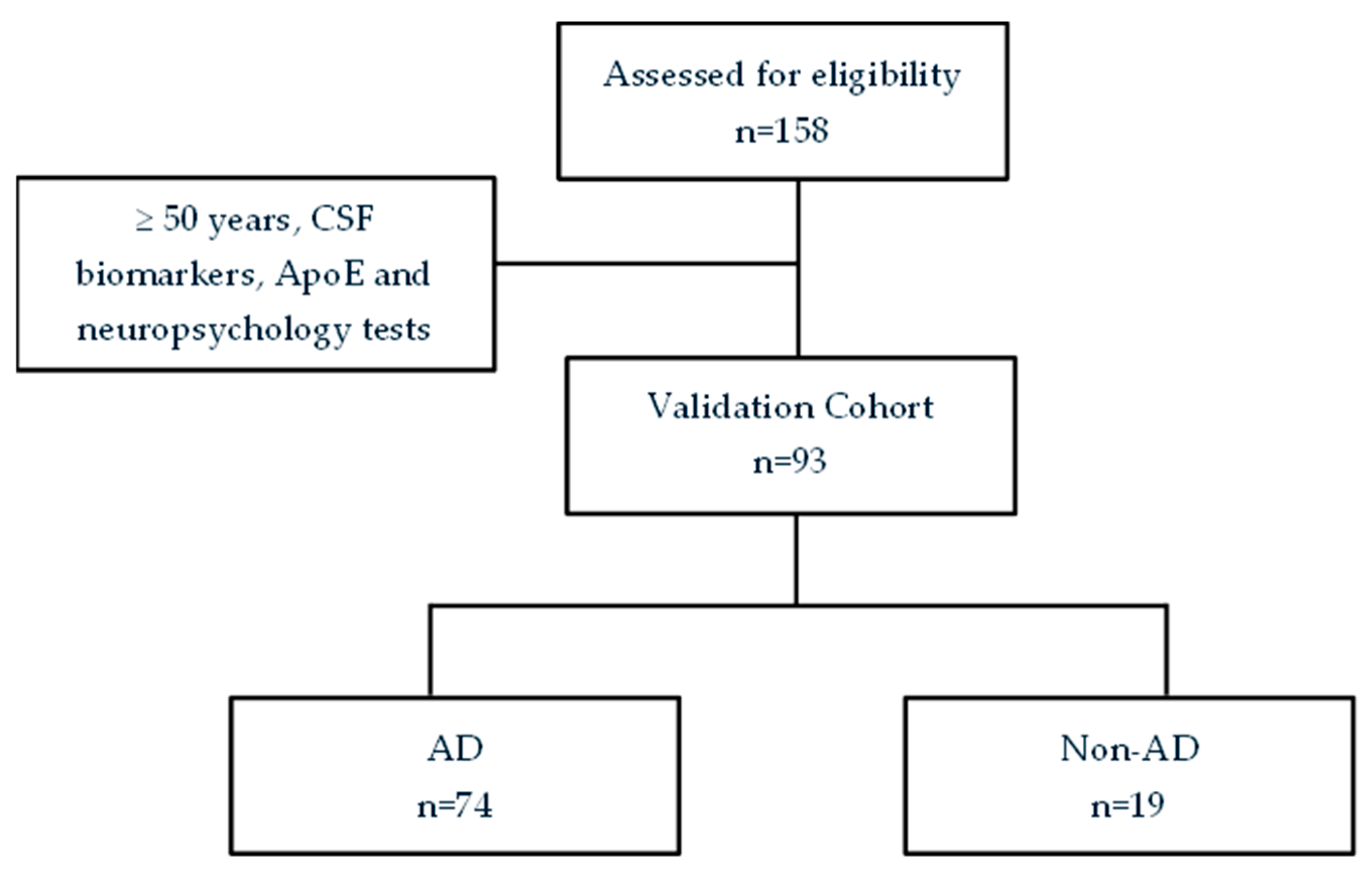
2.2. The Validation Cohort
2.3. Plasma Samples Collection and Determination of Biomarkers
2.4. Apolipoprotein E Genotyping
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participants Description
3.2. Plasma Biomarkers
3.3. CSF, Relationship Between Plasma Biomarkers Levels and Clinical Variables
3.4. Temporal Validation of a Previous AD Diagnosis Model
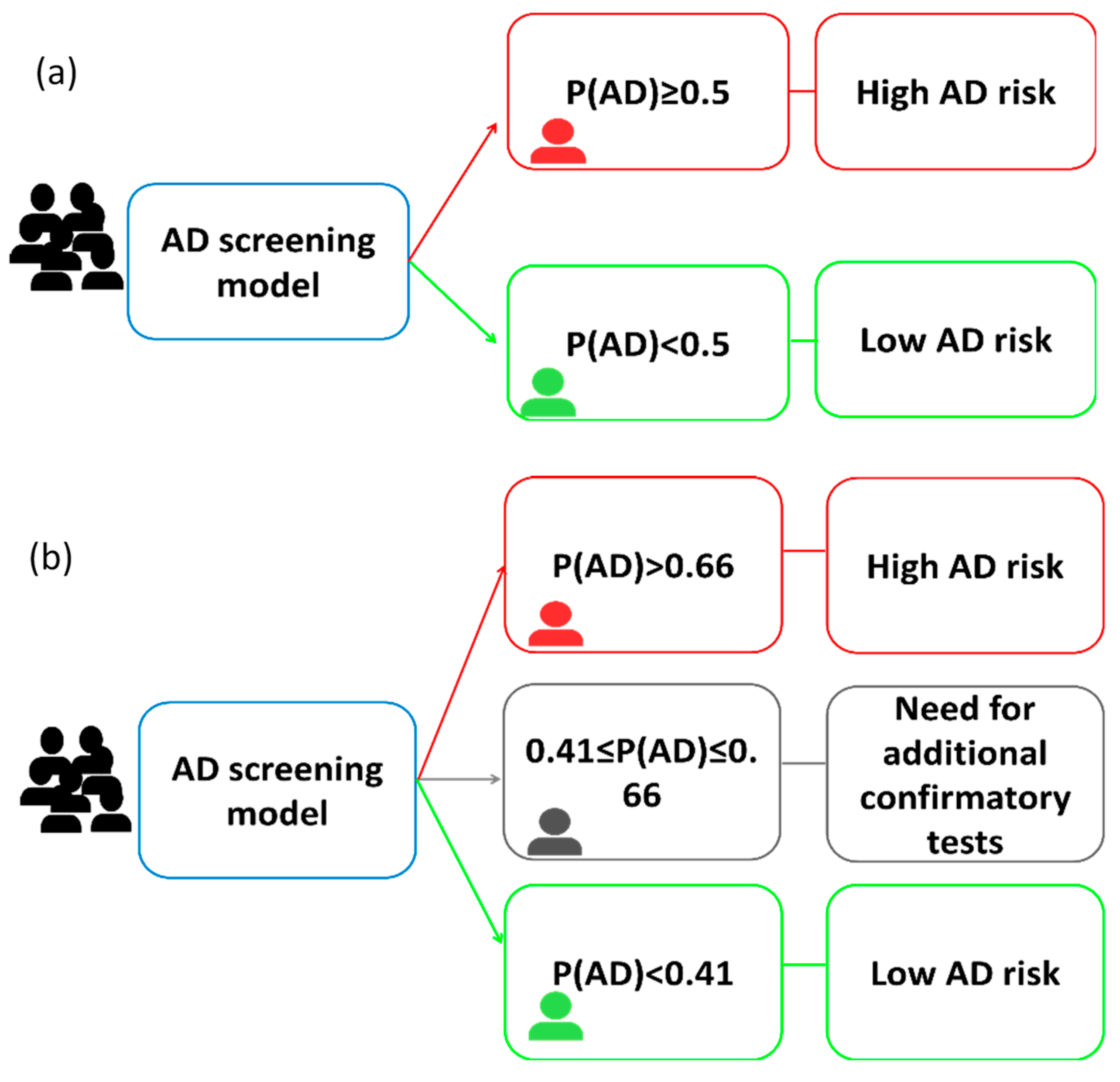
3.4.1. One-Cut-Off Approach
3.4.2. Two-Cut-Off Approach
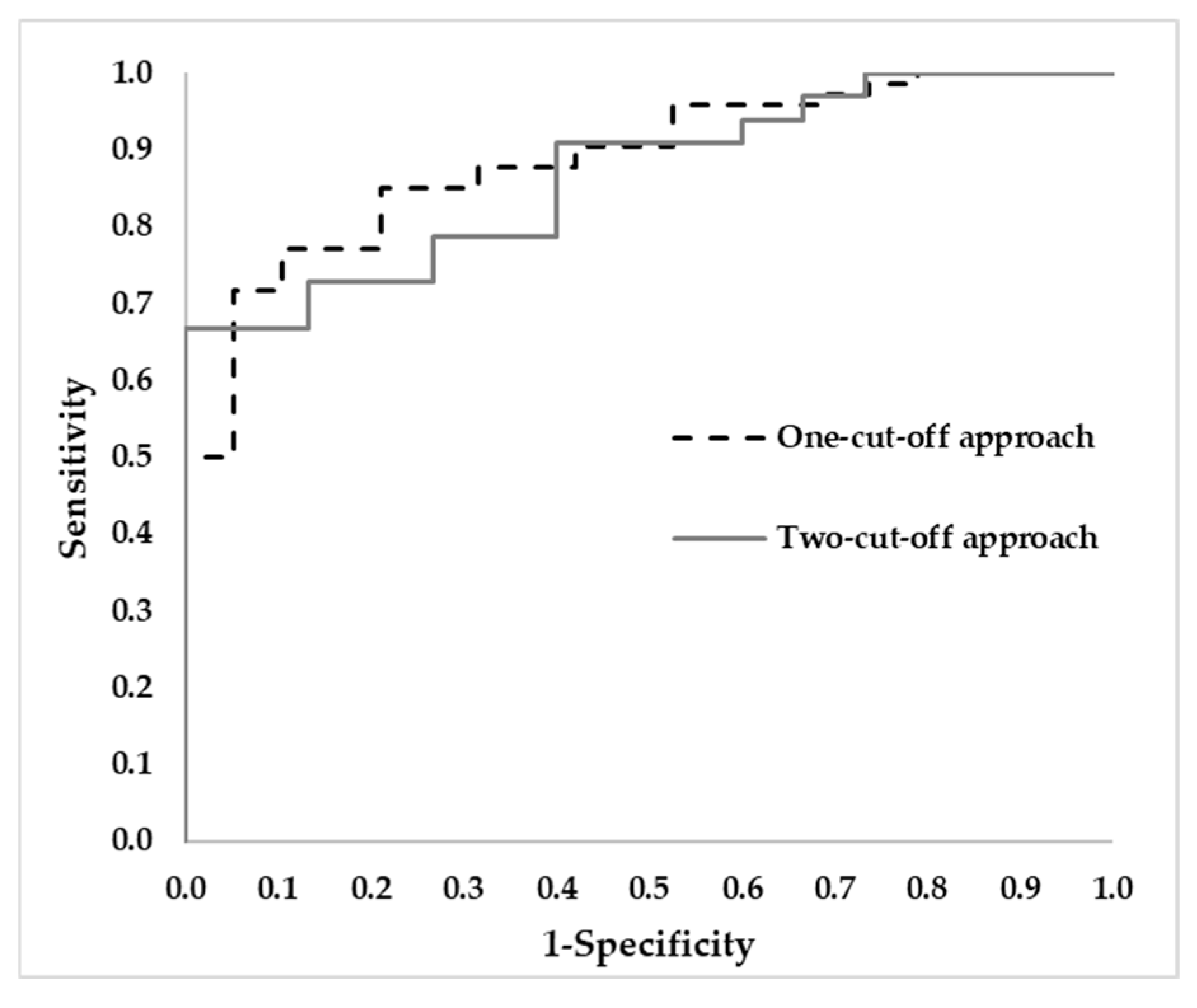
3.4.3. Comparison of Diagnosis Tools
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
List of Abbreviations
| AD | Alzheimer’s Disease |
| Aβ | Amyloid-beta |
| GFAP | Glial fibrillary acidic protein |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal fluid |
| PET | Positron Emission Tomography |
| t-Tau | Total-Tau |
| p-Tau | Phosphorylated Tau |
| NfL | Neurofilament light |
| ADNI | Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative |
| ApoE | Apolipoprotein E |
| BIN1 | Bridging integrator 1 |
| CD2AP | CD2 associated protein |
| CLU | Clusterin |
| INPP5D | Inositol polyphosphate-5-phosphatase D |
| MCI | Mild Cognitive Impairment |
| MACC | Memory Aging and Cognition Centre |
| MAP | Memory & Aging Program |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| CDR | Clinical Dementia Rating |
| MMSE | Mini-Mental State Examination |
| RBANS | Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status |
| FAQ | Functional Activities Questionnaire |
| ADCS-ADL | Alzheimer’s Disease Cooperative Study—Activities of Daily Living |
| GDS | Geriatric Depression Scale |
| PPV | Positive predictive value |
| NPV | Negative predictive value |
| IQR | Inter-quartile range |
| CI | Confidence interval |
References
- Graff-Radford, J.; Yong, K.X.X.; Apostolova, L.G.; Bouwman, F.H.; Carrillo, M.; Dickerson, B.C.; Rabinovici, G.D.; Schott, J.M.; Jones, D.T.; Murray, M.E. New insights into atypical Alzheimer’s disease in the era of biomarkers. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, J.; Apostolova, L.; Rabinovici, G.D.; Atri, A.; Aisen, P.; Greenberg, S.; Hendrix, S.; Selkoe, D.; Weiner, M.; Petersen, R.C.; et al. Lecanemab: Appropriate Use Recommendations. J. Prev. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2023, 10, 362–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurkinen, M.T. Donanemab: Not two without a third. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2023, 32, 1085–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.Y.; Shin, K.Y.; Chang, K.-A. GFAP as a Potential Biomarker for Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cells 2023, 12, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojdała, A.L.; Bellomo, G.; Gaetani, L.; Toja, A.; Chipi, E.; Shan, D.; Chiasserini, D.; Parnetti, L. Trajectories of CSF and plasma biomarkers across Alzheimer’s disease continuum: Disease staging by NF-L, p-tau181, and GFAP. Neurobiol. Dis. 2023, 189, 106356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuzy, A.; Leuzy, A.; Bollack, A.; Pellegrino, D.; Teunissen, C.E.; La Joie, R.; Rabinovici, G.D.; Franzmeier, N.; Johnson, K.; Barkhof, F.; et al. Considerations in the clinical use of amyloid PET and CSF biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2025, 21, e14528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, O.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Dage, J. Blood biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease in clinical practice and trials. Nat. Aging 2023, 3, 506–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Therriault, J.; Janelidze, S.; Benedet, A.L.; Ashton, N.J.; Arranz Martínez, J.; Gonzalez-Escalante, A.; Bellaver, B.; Alcolea, D.; Vrillon, A.; Karim, H.; et al. Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease using plasma biomarkers adjusted to clinical probability. Nat. Aging 2024, 4, 1529–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altuna-Azkargorta, M.; Mendioroz-Iriarte, M. Blood biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurol. (Engl. Ed.) 2021, 36, 704–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Sánchez, L.; Ferré-González, L.; Peña-Bautista, C.; Balaguer, Á.; Amengual, J.L.; Baquero, M.; Cubas, L.; Casanova, B.; Cháfer-Pericás, C. New approach to specific Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis based on plasma biomarkers in a cognitive disorder cohort. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2025, 55, e70034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.; Liu, K.; Fa, W.; Liu, C.; Zhu, M.; Liang, X.; Ren, Y.; Xu, S.; Wang, X.; Tang, S.; et al. Association of polygenic risk scores with Alzheimer’s disease and plasma biomarkers among Chinese older adults: A community-based study. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2024, 20, 6669–6681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson-Hoare, J.; Heslegrave, A.; Leonenko, G.; Fathalla, D.; Bellou, E.; Luckcuck, L.; Marshall, R.; Sims, R.; Morgan, B.P.; Hardy, J.; et al. Plasma biomarkers and genetics in the diagnosis and prediction of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2023, 146, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosun, D.; Veitch, D.; Aisen, P.; Jack, C.R., Jr.; Jagust, W.J.; Petersen, R.C.; Saykin, A.J.; Bollinger, J.; Ovod, V.; Mawuenyega, K.G.; et al. Detection of β-amyloid positivity in Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative participants with demographics, cognition, MRI and plasma biomarkers. Brain Commun. 2021, 3, fcab008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, B.; Xiao, X.; Yuan, Z.; Guo, L.; Liao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; et al. Associations of risk genes with onset age and plasma biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease: A large case–control study in mainland China. Neuropsychopharmacology 2022, 47, 1121–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebre, R.K.; Graff-Radford, J.; Ramanan, V.K.; Raghavan, S.; Hofrenning, E.I.; Przybelski, S.A.; Nguyen, A.T.; Lesnick, T.G.; Gunter, J.L.; Algeciras-Schimnich, A.; et al. Can integration of Alzheimer’s plasma biomarkers with MRI, cardiovascular, genetics, and lifestyle measures improve cognition prediction? Brain Commun. 2024, 6, fcae300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, A.; Capdevila, M.; Puerta, R.; Arranz, J.; Montrreal, L.; de Rojas, I.; García-González, P.; Olivé, C.; García-Gutiérrez, F.; Sotolongo-Grau, O.; et al. Clinical value of plasma pTau181 to predict Alzheimer’s disease pathology in a large real-world cohort of a memory clinic. eBioMedicine 2024, 108, 105345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, M.A.; Doecke, J.D.; Liew, O.W.; Wong, L.L.; Tan, E.S.J.; Chan, S.P.; Chong, J.R.F.; Cai, Y.; Hilal, S.; Venketasubramanian, N.; et al. Plasma proteomics for cognitive decline and dementia—A Southeast Asian cohort study. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2025, 21, e14577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, M.D.; Britton, K.J.; Joyce, H.E.; Menard, W.; Emrani, S.; Kunicki, Z.J.; Faust, M.A.; Dawson, B.C.; Riddle, M.C.; Huey, E.D.; et al. Clinical application of plasma P-tau217 to assess eligibility for amyloid-lowering immunotherapy in memory clinic patients with early Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2024, 16, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moons, K.G.M.; Altman, D.G.; Reitsma, J.B.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Macaskill, P.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Vickers, A.J.; Ransohoff, D.F.; Collins, G.S. Transparent Reporting of a multivariable prediction model for Individual Prognosis Or Diagnosis (TRIPOD): Explanation and Elaboration. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, W1–W73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Cui, J.; Ge, X.; Tian, Y.; Han, H.; Fan, Z.; Liu, L.; Luo, Y.; Yu, H. Hierarchical multi-class Alzheimer’s disease diagnostic framework using imaging and clinical features. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 935055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charidimou, A.; Boulouis, G.; Frosch, M.P.; Baron, J.C.; Pasi, M.; Albucher, J.F.; Banerjee, G.; Barbato, C.; Bonneville, F.; Brandner, S.; et al. The Boston criteria version 2.0 for cerebral amyloid angiopathy: A multicentre, retrospective, MRI–neuropathology diagnostic accuracy study. Lancet Neurol. 2022, 21, 714–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.R.; Bennett, D.A.; Blennow, K.; Carrillo, M.C.; Dunn, B.; Haeberlein, S.B.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.; Jessen, F.; Karlawish, J.; et al. NIA-AA Research Framework: Toward a biological definition of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2018, 14, 535–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.R.; Andrews, J.S.; Beach, T.G.; Buracchio, T.; Dunn, B.; Graf, A.; Hansson, O.; Ho, C.; Jagust, W.; McDade, E.; et al. Revised criteria for diagnosis and staging of Alzheimer’s disease: Alzheimer’s Association Workgroup. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2024, 20, 5143–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, R.C. Mild Cognitive Impairment. Continuum 2016, 22, 404–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Tseng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, P.; Chiu, H. Diagnostic accuracy of the Clinical Dementia Rating Scale for detecting mild cognitive impairment and dementia: A bivariate meta-analysis. Int. J. Geriat Psychiatry 2021, 36, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoi, K.K.F.; Chan, J.Y.C.; Hirai, H.W.; Wong, S.Y.S.; Kwok, T.C.Y. Cognitive Tests to Detect Dementia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Intern. Med. 2015, 175, 1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, A.J. A meta-analysis of the accuracy of the mini-mental state examination in the detection of dementia and mild cognitive impairment. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2009, 43, 411–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muntal Encinas, S.; Gramunt-Fombuena, N.; Badenes Guia, D.; Casas Hernanz, L.; Aguilar Barbera, M. Traducción y adaptación española de la batería neuropsicológica Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status (RBANS) forma A en una muestra piloto. Neurología 2012, 27, 531–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duff, K.; Humphreys Clark, J.D.; O’Bryant, S.E.; Mold, J.W.; Schiffer, R.B.; Sutker, P.B. Utility of the RBANS in detecting cognitive impairment associated with Alzheimer’s disease: Sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive powers. Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2008, 23, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Ren, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Hou, T.; Liu, K.; Cong, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; et al. The power of the Functional Activities Questionnaire for screening dementia in rural-dwelling older adults at high-risk of cognitive impairment. Psychogeriatrics 2020, 20, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potashman, M.; Pang, M.; Tahir, M.; Shahraz, S.; Dichter, S.; Perneczky, R.; Nolte, S. Psychometric properties of the Alzheimer’s Disease Cooperative Study–Activities of Daily Living for Mild Cognitive Impairment (ADCS-MCI-ADL) scale: A post hoc analysis of the ADCS ADC-008 trial. BMC Geriatr. 2023, 23, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmelee, P.A.; Katz, I.R. Geriatric Depression Scale. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1990, 38, 1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Bautista, C.; Álvarez-Sánchez, L.; Pascual, R.; Moreno, M.J.; Baquero, M.; Cháfer-Pericás, C. Clinical usefulness of cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 53, e13910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Methodological Issues and Strategies in Clinical Research, 4th ed.; American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; pp. 279–284. [Google Scholar]
- De Rino, F.; Rispoli, F.; Zuffi, M.; Matteucci, E.; Gavazzi, A.; Salvatici, M.; Sansico, D.F.; Pollaroli, G.; Drago, L. Assessment of Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers in Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Dementias: A Center-Based Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, B.; Ouyang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Xu, T.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Wan, M.; Xiao, X.; et al. Evaluating the diagnostic performance of six plasma biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative dementias in a large Chinese cohort. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2025, 17, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomucci, G.; Crucitti, C.; Ingannato, A.; Moschini, V.; Bagnoli, S.; Pozzi, F.E.; Marcantelli, E.; Padiglioni, S.; Morinelli, C.; Mazzeo, S.; et al. The two cut-offs approach for plasma p-tau217 in detecting Alzheimer’s disease in subjective cognitive decline and mild cognitive impairment. Alzheimer’s Dement. Diagn. Assess. Dis. Monit. 2025, 17, e70116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, H.K.; Kim, H.K.; Lee, H.S.; Park, M.; Lee, J.H.; Ryu, Y.H.; Cho, H.; Lyoo, C.H. Role of Enlarged Perivascular Space in the Temporal Lobe in Cerebral Amyloidosis. Ann. Neurol. 2023, 93, 965–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.; Lee, E.H.; Yoo, H.; Shin, D.; Kang, H.; Yim, S.; Kim, S.; Kim, K.; Yoon, S.; Zetterberg, H.; et al. Tailoring thresholds for interpreting plasma p-tau217 levels. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarto, J.; Esteller-Gauxax, D.; Guillén, N.; Falgàs, N.; Borrego-Écija, S.; Massons, M.; Fernández-Villullas, G.; González, Y.; Tort-Merino, A.; Bosch, B.; et al. Accuracy and clinical applicability of plasma tau 181 and 217 for Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis in a memory clinic cohort. J. Neurol. 2025, 272, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöll, M.; Verberk, I.M.W.; Del Campo, M.; Delaby, C.; Therriault, J.; Chong, J.R.; Palmqvist, S.; Alcolea, D. Challenges in the practical implementation of blood biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2024, 5, 100630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattsson-Carlgren, N.; Collij, L.E.; Stomrud, E.; Pichet Binette, A.; Ossenkoppele, R.; Smith, R.; Karlsson, L.; Lantero-Rodriguez, J.; Snellman, A.; Strandberg, O.; et al. Plasma Biomarker Strategy for Selecting Patients with Alzheimer Disease for Antiamyloid Immunotherapies. JAMA Neurol. 2024, 81, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmqvist, S.; Janelidze, S.; Quiroz, Y.T.; Zetterberg, H.; Lopera, F.; Stomrud, E.; Su, Y.; Chen, Y.; Serrano, G.E.; Leuzy, A.; et al. Discriminative Accuracy of Plasma Phospho-tau217 for Alzheimer Disease vs Other Neurodegenerative Disorders. JAMA 2020, 324, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therriault, J.; Servaes, S.; Tissot, C.; Rahmouni, N.; Ashton, N.J.; Benedet, A.L.; Karikari, T.K.; Macedo, A.C.; Lussier, F.Z.; Stevenson, J.; et al. Equivalence of plasma p-tau217 with cerebrospinal fluid in the diagnosis of Alzheimers disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2023, 19, 4967–4977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Sánchez, L.; Peña-Bautista, C.; Ferré-González, L.; Balaguer, Á.; Amengual, J.L.; Baquero, M.; Cháfer-Pericás, C. Promising clinical tools for specific Alzheimer disease diagnosis from plasma pTau217 and ApoE genotype in a cognitive disorder unit. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 16316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mielke, M.M.; Fowler, N.R. Alzheimer disease blood biomarkers: Considerations for population-level use. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2024, 20, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Non-AD (n = 19) | AD (n = 74) | p Value | r | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) a | 69.00 (66.00–71.00) | 71 (68.75–74.00) | 0.025 | −0.333 | |
| Gender (female) b | 8 (42.11) | 44 (59.46) | 0.174 | ||
| ApoE Genotype b | ε3/ε3 | 15 (78.95) | 34 (47.22) | 0.011 | |
| ε2/ε3 | 3 (15.79) | 3 (4.17) | |||
| ε2/ε4 | 0 (0.00) | 4 (5.56) | |||
| ε3/ε4 | 1 (5.26) | 28 (38.89) | |||
| ε4/ε4 | 0 (0.00) | 3 (4.17) | |||
| Educational level | Non-formal education | 3 (15.79) | 18 (24.32) | 0.883 | |
| Primary education | 6 (31.58) | 21 (28.38) | |||
| Secondary education | 4 (21.05) | 13 (17.57) | |||
| University education | 6 (31.58) | 22 (29.73) | |||
| CSF Aβ42 a (pg mL−1) | 1279.00 (961.47–1524.00) | 766.00 (599.00–924.00) | <0.001 | 0.666 | |
| CSF Aβ40 a | 12,854.00 (8811.00–14,831.50) | 14,756.50 (12,112.50–17,514.25) | 0.039 | 0.375 | |
| CSF Aβ42/Aβ40 a | 0.112 (0.101–0.115) | 0.053 (0.045–0.059) | <0.001 | 1.000 | |
| CSF p-Tau181 a (pg mL−1) | 37.00 (27.00–44.00) | 89.00 (63.00–121.00) | <0.001 | 0.953 | |
| CSF t-Tau a (pg mL−1) | 263.00 (164.00–313.00) | 567.00 (439.50–762.50) | <0.001 | 0.808 | |
| CSF t-Tau/Aβ42 a | 0.23 (0.18–0.28) | 0.77 (0.55–1.03) | <0.001 | 0.985 | |
| CSF NfL a (pg mL−1) | 725.86 (460.79–869.50) | 956.40 (794.00–1212.98) | 0.001 | 0.584 | |
| AT classification b | A+T+ | 0 (0.00) | 44 (75.86) | <0.001 | |
| A-T- | 19 (100.00) | 0 (0.00) | |||
| A+T- | 0 (0.00) | 14 (24.14) | |||
| A-T+ | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | |||
| CDR sum of boxes a (score) | 0.50 (0.00–3.00) | 2.00 (1.00–3.00) | 0.110 | 0.237 | |
| CDR_GS b (score) | 0 | 7 (36.84) | 10 (13.51) | 0.005 | |
| 0.5 | 10 (52.63) | 63 (85.14) | |||
| 1 | 2 (10.53) | 1 (1.35) | |||
| MMSE a (score) | 27.00 (24.00–28.00) | 26.00 (23.00–28.00) | 0.407 | 0.123 | |
| RBANS_A a (score) | 91.00 (76.50–97.75) | 72.00 (60.00–88.00) | 0.007 | 0.412 | |
| RBANS_L a (score) | 89.00 (874.00–93.50) | 79.00 (64.00–93.00) | 0.167 | 0.210 | |
| RBANS_IM a (score) | 85.00 (74.25–97.75) | 69.00 (61.00–83.00) | 0.003 | 0.460 | |
| RBANS_V/C a (score) | 88.00 (71.25–98.25) | 81.00 (71.25–92.00) | 0.436 | 0.119 | |
| RBANS_DM a (score) | 99.00 (87.50–103.50) | 64.00 (55.00–86.25) | <0.001 | 0.610 | |
| GDS a (score) | 17.00 (7.00–19.00) | 9.00 (6.00–14.00) | 0.048 | 0.298 | |
| ADCS-ADL-MCI a (score) | 44.00 (38.00–47.00) | 44.00 (39.00–47.00) | 0.858 | 0.027 | |
| FAQ a (score) | 1.00 (0.00–5.00) | 3.50 (0.00–7.00) | 0.077 | 0.287 | |
| Non-AD (n = 19) | AD (n = 74) | p Value | r | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma p-Tau181 a (pg mL−1) | 13.00 (9.00–17.00) | 29.00 (20.00–37.00) | <0.001 | 0.733 |
| Plasma Aβ42/Aβ40 a | 0.042 (0.038–0.047) | 0.039 (0.036–0.043) | 0.046 | 0.297 |
| Plasma GFAP a (pg mL−1) | 115.00 (78.00–185.00) | 194.50 (140.75–280.50) | <0.001 | 0.481 |
| Plasma p-Tau181 (pg mL−1) | Plasma Aβ42/Aβ40 (pg mL−1) | Plasma GFAP (pg mL−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CDR_GS (score) | 0.362 * (p < 0.001) | −0.256 * (0.013) | 0.324 * (0.002) |
| CDR sum of boxes (score) | 0.354 * (0.001) | −0.283 * (0.006) | 0.330 * (0.001) |
| MMSE (score) | −0.280 * (0.007) | 0.219 * (0.035) | −0.354 * (0.001) |
| RBANS_MI (score) | −0.325 * (0.002) | 0.134 (0.202) | −0.265 * (0.011) |
| RBANS_VC (score) | −0.221 * (0.035) | 0.128 (0.224) | −0.165 (0.116) |
| RBANS_L (score) | −0.205 (0.052) | 0.219 * (0.036) | −0.329 * (0.001) |
| RBANS_A (score) | −0.174 (0.099) | 0.139 (0.187) | −0.224 * (0.032) |
| RBANS_MR (score) | −0.455 * (p < 0.001) | 0.296 * (0.004) | −0.402 * (p < 0.001) |
| FAQ (score) | 0.271 * (0.013) | −0.325 * (0.002) | 0.204 (0.061) |
| ADCS-ADL-MCI (score) | −0.109 (0.303) | 0.047 (0.654) | −0.089 (0.399) |
| GDS (score) | −0.225 * (0.031) | 0.163 (0.119) | −0.137 (0.190) |
| CSF Aβ42 (pg mL-1) | −0.390 * (0.001) | 0.108 (0.353) | −0.091 (0.434) |
| CSF t-Tau (pg mL−1) | 0.493 * (p < 0.001) | −0.256 * (0.021) | 0.402 * (p < 0.001) |
| CSF p-Tau181 (pg mL−1) | 0.582 * (p < 0.001) | −0.314 * (0.006) | 0.448 * (p < 0.001) |
| CSF Aβ40 (pg mL−1) | 0.162 (0.213) | −0.149 (0.251) | 0.208 (0.108) |
| CSF Aβ42/Aβ40 | −0.500 * (p < 0.001) | 0.286 * (0.025) | −0.275 * (0.032) |
| CSF NfL (pg mL−1) | 0.258 * (0.047) | −0.487 * (p < 0.001) | 0.399 * (0.002) |
| CSF t-Tau/Aβ42 | 0.597 (p < 0.001) | −0.303 * (0.008) | 0.360 * (0.001) |
| Diagnosis Index | One-Cut-Off Approach | Two-Cut-Off Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Cut-off values | 0.5 | 0.41–0.66 |
| AUC | 0.888 | 0.867 |
| PPV (CI 95%) | 96.5% (88.1−99.0%) | 100.0% (85.1–100%) |
| NPV (CI 95%) | 47.2% (32.0–63.0%) | 57.7% (38.9–74.5%) |
| Sensitivity (CI 95%) | 74.3% (63.3–82.9%) | 66.7% (49.6–80.2%) |
| Specificity (CI 95%) | 89.5% (68.6–97.1%) | 99.9% (79.5–100%) |
| Accuracy (%) | 77.4% (67.9–84.7%) | 77.1% (63.4–86.7%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martí-Navia, A.; López, A.; Álvarez-Sánchez, L.; Ferré-González, L.; Balaguer, A.; Baquero, M.; Cháfer-Pericás, C. Temporal Validation of a Plasma Diagnosis Approach for Early Alzheimer Disease Diagnosis in a Cognitive Disorder Unit. J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15, 475. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15100475
Martí-Navia A, López A, Álvarez-Sánchez L, Ferré-González L, Balaguer A, Baquero M, Cháfer-Pericás C. Temporal Validation of a Plasma Diagnosis Approach for Early Alzheimer Disease Diagnosis in a Cognitive Disorder Unit. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2025; 15(10):475. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15100475
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartí-Navia, Aleix, Alejandro López, Lourdes Álvarez-Sánchez, Laura Ferré-González, Angel Balaguer, Miguel Baquero, and Consuelo Cháfer-Pericás. 2025. "Temporal Validation of a Plasma Diagnosis Approach for Early Alzheimer Disease Diagnosis in a Cognitive Disorder Unit" Journal of Personalized Medicine 15, no. 10: 475. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15100475
APA StyleMartí-Navia, A., López, A., Álvarez-Sánchez, L., Ferré-González, L., Balaguer, A., Baquero, M., & Cháfer-Pericás, C. (2025). Temporal Validation of a Plasma Diagnosis Approach for Early Alzheimer Disease Diagnosis in a Cognitive Disorder Unit. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 15(10), 475. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15100475