Spinopelvic Motion Evaluation in Patients Undergoing Total Hip Arthroplasty and Patient-Specific Target for Acetabular Cup Placement
Abstract
1. Introduction
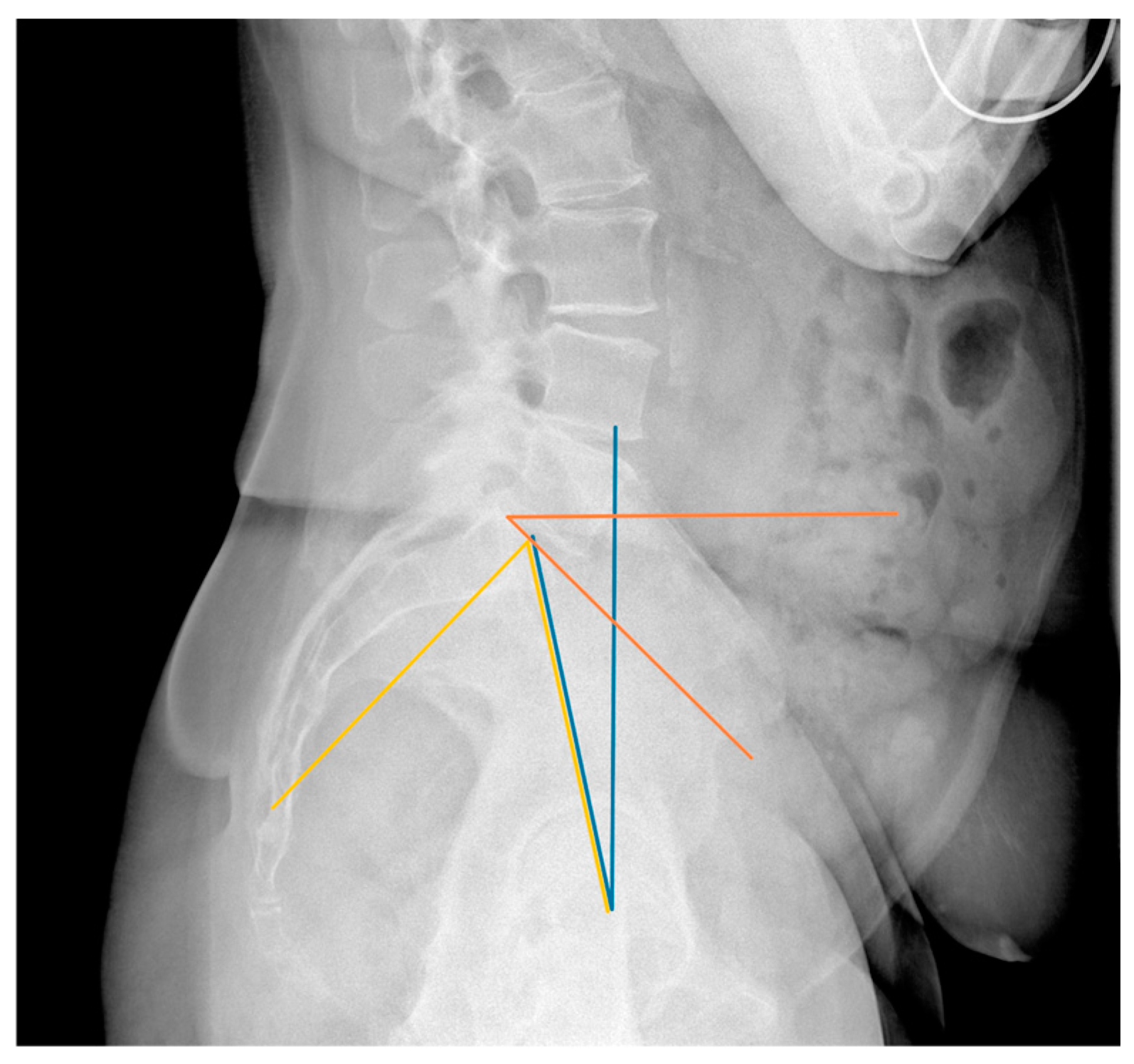
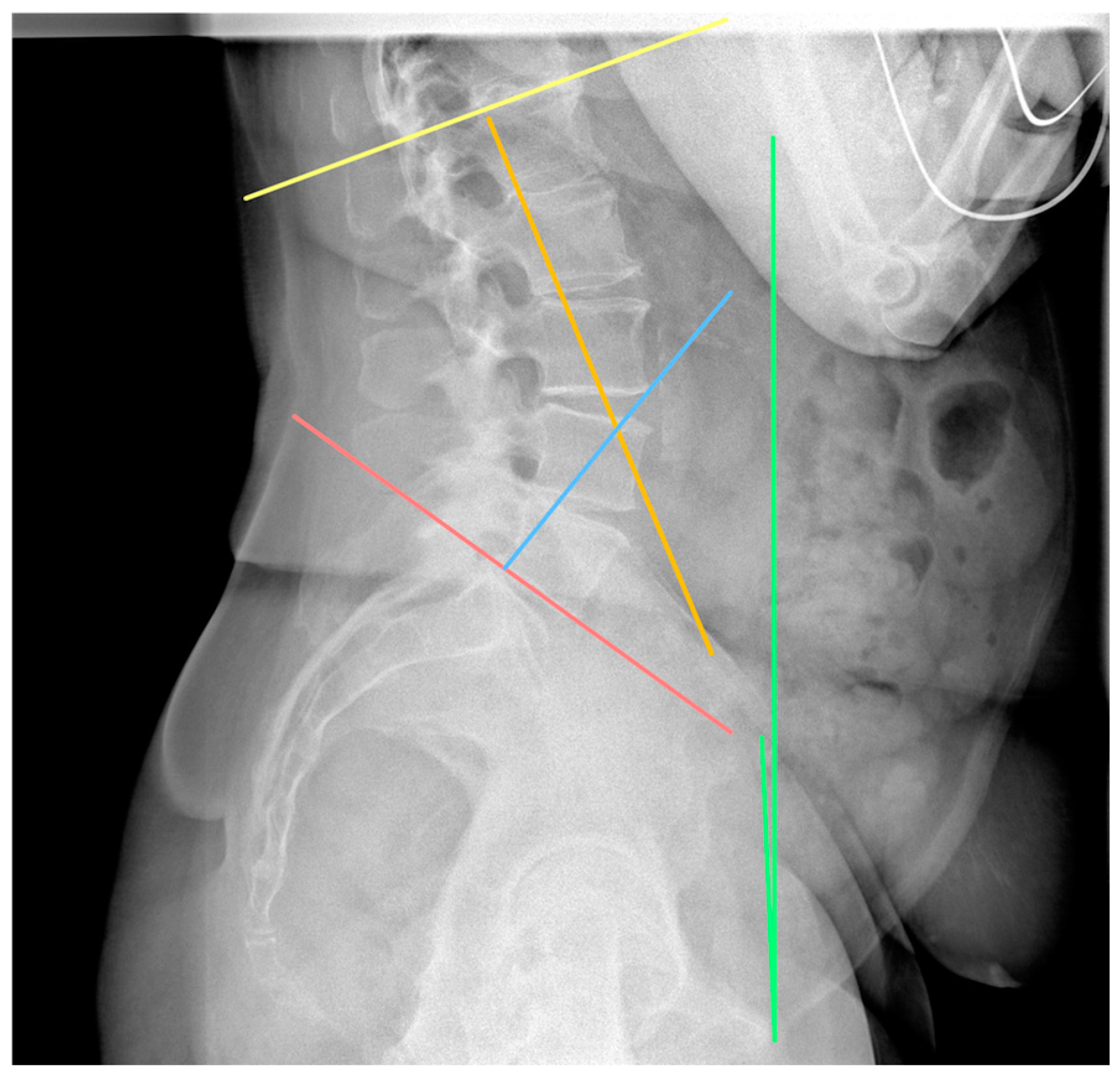
2. Materials and Methods
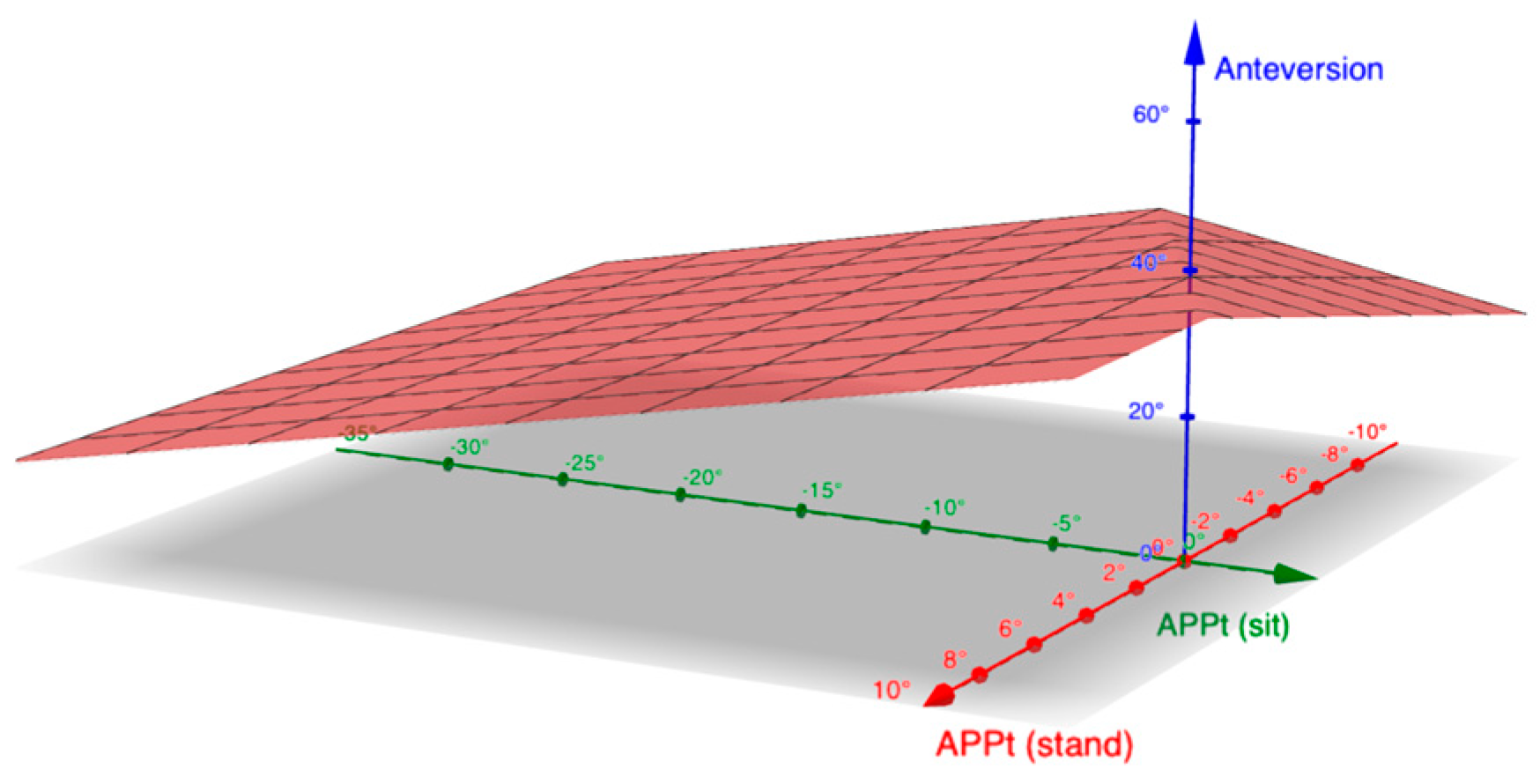
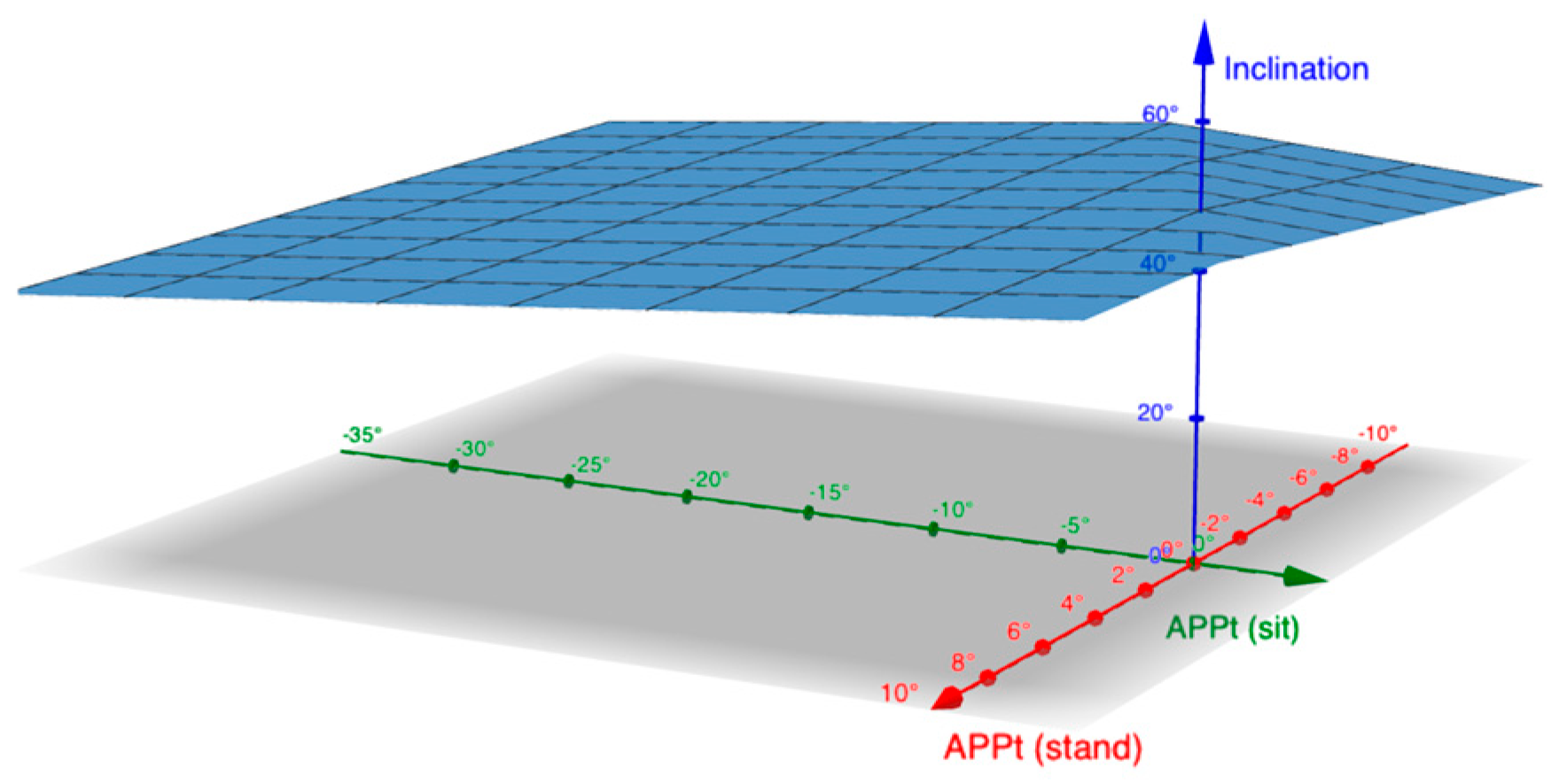
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Galvain, T.; Mantel, J.; Kakade, O.; Board, T.N. Treatment patterns and clinical and economic burden of hip dislocation following primary total hip arthroplasty in England. Bone Jt. J. 2022, 104, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowan, F.E.; Benjamin, B.; Pietrak, J.R.; Haddad, F.S. Prevention of dislocation after total hip arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2018, 33, 1316–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eftekhary, N.; Shimmin, A.; Lazennec, J.Y.; Buckland, A.; Schwarzkopf, R.; Dorr, L.D.; Mayman, D.; Padgett, D.; Vigdorchik, J. A systematic approach to the hip-spine relationship and its applications to total hip arthroplasty. Bone Jt. J. 2019, 101, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazennec, J.Y.; Brusson, A.; Rousseau, M.A. Hip-spine relations and sagittal balance clinical consequences. Eur. Spine J. 2011, 20 (Suppl. 5), 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanawade, V.; Dorr, L.D.; Wan, Z. Predictability of acetabular component angular change with postural shift from standing to sitting position. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2014, 96, 978–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martino, A.; Geraci, G.; Brunello, M.; D’Agostino, C.; Davico, G.; Curreli, C.; Traina, F.; Faldini, C. Hip-spine relationship: Clinical evidence and biomechanical issues. Arch. Orthop. Trauma. Surg. 2024, 144, 1821–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewinnek, G.E.; Lewis, J.L.; Tarr, R.; Compere, C.L.; Zimmerman, J.R. Dislocations after total hip-replacement arthroplasties. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 1978, 60, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grammatopoulos, G.; Falsetto, A.; Sanders, E.; Weishorn, J.; Gill, H.S.; Beaulé, P.E.; Innmann, M.M.; Merle, C. Integrating the Combined Sagittal Index reduces the risk of dislocation following total hip replacement. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2022, 104, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigdorchik, J.M.; Sharma, A.K.; Buckland, A.J.; Elbuluk, A.M.; Eftekhary, N.; Mayman, D.J.; Carroll, K.M.; Jerabek, S.A. 2021 Otto Aufranc Award: A simple Hip-Spine Classification for total hip arthroplasty: Validation and a large multicentre series. Bone Jt. J. 2021, 103 (Supple. B), 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiznia, D.H.; Buchalter, D.B.; Kirby, D.J.; Buckland, A.J.; Long, W.J.; Schwarzkopf, R. Applying the hip-spine relationship in total hip arthroplasty. Hip Int. 2021, 31, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartofilakidis, G.; Stamos, K.; Ioannidis, T.T. Low friction arthroplasty for old untreated congenital dislocation of the hip. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 1988, 70, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legaye, J.; Duval-Beaupère, G.; Hecquet, J.; Marty, C. Pelvic incidence: A fundamental pelvic parameter for three-dimensional regulation of spinal sagittal curves. Eur. Spine J. 1998, 7, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grammatopoulos, G.; Thomas, G.E.; Pandit, H.; Beard, D.J.; Gill, H.S.; Murray, D.W. The effect of orientation of the acetabular component on outcome following total hip arthroplasty with small diameter hard-on-soft bearings. Bone Jt. J. 2015, 97, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babisch, J.W.; Layher, F.; Amiot, L.P. The rationale for tilt-adjusted acetabular cup navigation. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2008, 90, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lembeck, B.; Mueller, O.; Reize, P.; Wuelker, N. Pelvic tilt makes acetabular cup navigation inaccurate. Acta Orthop. 2005, 76, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazennec, J.Y.; Rousseau, M.A.; Rangel, A.; Gorin, M.; Belicourt, C.; Brusson, A.; Catonné, Y. Pelvis and total hip arthroplasty acetabular component orientations in sitting and standing positions: Measurements reproductibility with EOS imaging system versus conventional radiographies. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2011, 97, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar, A.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J. Artificial intelligence technology improves the ac-curacy of preoperative planning in primary total hip arthroplasty. Asian J. Surg. 2024, 47, 2999–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernaa, K.; Seppänen, M.; Mäkelä, K.; Saltychev, M. Reliability of sagittal spinopelvic alignment measurements after total hip arthroplasty. Clin. Spine Surg. 2017, 30, E909–E914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, E.I.; Sarpong, N.O.; Steele, J.R.; Davis, E.; Muir, J.M.; Canoles, H.G.; Vigdorchik, J.M. The Hip-spine assessment of a novel surgical planning software provides acetabular component targets that are reliable and in agreement with current clinical recommendations. Arthroplast. Today 2024, 25, 101288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleeman-Forsthuber, L.T.; Elkins, J.M.; Miner, T.M.; Yang, C.C.; Jennings, J.M.; Dennis, D.A. Reliability of spinopelvic measurements that may influence the cup position in total hip arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2020, 35, 3758–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, N.S.; Jeon, C.H.; Lee, H.D.; Won, S.H. Measurement of spinopelvic parameters on standing lateral lumbar radiographs: Validity and reliability. Clin. Spine Surg. 2017, 30, E119–E123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila-Casademunt, A.; Pellisé, F.; Acaroglu, E.; Pérez-Grueso, F.J.; Martín-Buitrago, M.P.; Sanli, T.; Yakici, S.; de Frutos, A.G.; Matamalas, A.; Sánchez-Márquez, J.M.; et al. The reliability of sagittal pelvic parameters: The effect of lumbosacral instrumentation and measurement experience. Spine 2015, 40, E253–E258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishihara, S.; Sugano, N.; Nishii, T.; Ohzono, K.; Yoshikawa, H. Measurements of pelvic flexion angle using three-dimensional computed tomography. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2003, 411, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.J.; Bendich, I.; Ha, A.S.; Keeney, B.J.; Moschetti, W.E.; Tomek, I.M. A comparison of radiographic outcomes after total hip arthroplasty between the posterior approach and direct anterior approach with intraoperative fluoroscopy. J. Arthroplast. 2017, 32, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhardi, V.J.; Chiu, Y.F.; Sculco, P.K.; Gonzalez Della Valle, A. Accuracy of acetabular cup placement positively correlates with level of training. Int. Orthop. 2021, 45, 2797–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunze, K.N.; Huddleston, H.P.; Romero, J.; Chiu, Y.F.; Jerabek, S.A.; McLawhorn, A.S. Accuracy and precision of acetabular component position does not differ between the anterior and posterior approaches to total hip arthroplasty with robotic assistance: A matched-pair analysis. Arthroplast. Today 2022, 18, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foissey, C.; Batailler, C.; Coulomb, R.; Giebaly, D.E.; Coulin, B.; Lustig, S.; Kouyoumdjian, P. Image-based robotic-assisted total hip arthroplasty through direct anterior approach allows a better orientation of the acetabular cup and a better restitution of the centre of rotation than a conventional procedure. Int. Orthop. 2023, 47, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodner, R.J. The functional mechanics of the acetabular component in total hip arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2022, 37, 2199–2207.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckmann, N.; McKnight, B.; Stefl, M.; Trasolini, N.A.; Ike, H.; Dorr, L.D. Late dislocation following total hip arthroplasty: Spinopelvic imbalance as a causative factor. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2018, 100, 1845–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Cizmic, Z.; Dennis, D.A.; Kreuzer, S.W.; Miranda, M.A.; Vigdorchik, J.M. Low dislocation rates with the use of patient specific “Safe zones” in total hip arthroplasty. J. Orthop. 2021, 27, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Mean | SD | |
|---|---|---|
| PI | 51.0 | 13.1 |
| SS | 35.0 | 10.3 |
| PT | 16.0 | 13.3 |
| APPtstand | −3.4 | 12.0 |
| APPtsit | −30.7 | 15.3 |
| ΔAPPt (APPtstand − APPtsit) | 27.3 | 13.4 |
| LL | 39.5 | 11.3 |
| PI | SS | PT | APPtstand | APPtsit | LL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rater 1 (consultant) (ICC value) | 0.91 | 0.83 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.82 | 0.94 |
| Rater 1 (consultant) 95% CI | 0.82–0.96 | 0.67–0.92 | 0.95–0.99 | 0.97–0.99 | 0.63–0.92 | 0.89–0.97 |
| Rater 2 (resident) (ICC value) | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.98 | 0.82 | 0.93 | 0.91 |
| Rater 2 (resident) 95% CI | 0.93–0.98 | 0.90–0.97 | 0.95–0.99 | 0.65–0.92 | 0.85–0.97 | 0.80–0.92 |
| PI | SS | PT | APPtstand | APPtsit | LL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICC value | 0.91 | 0.83 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.82 | 0.94 |
| 95% CI | 0.82–0.96 | 0.67–0.92 | 0.95–0.99 | 0.97–0.99 | 0.63–0.92 | 0.89–0.97 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koutalos, A.A.; Gkekas, N.K.; Akrivos, V.; Stefanou, N.; Karachalios, T. Spinopelvic Motion Evaluation in Patients Undergoing Total Hip Arthroplasty and Patient-Specific Target for Acetabular Cup Placement. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14121161
Koutalos AA, Gkekas NK, Akrivos V, Stefanou N, Karachalios T. Spinopelvic Motion Evaluation in Patients Undergoing Total Hip Arthroplasty and Patient-Specific Target for Acetabular Cup Placement. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2024; 14(12):1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14121161
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoutalos, Antonios A., Nifon K. Gkekas, Vasileios Akrivos, Nikolaos Stefanou, and Theofilos Karachalios. 2024. "Spinopelvic Motion Evaluation in Patients Undergoing Total Hip Arthroplasty and Patient-Specific Target for Acetabular Cup Placement" Journal of Personalized Medicine 14, no. 12: 1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14121161
APA StyleKoutalos, A. A., Gkekas, N. K., Akrivos, V., Stefanou, N., & Karachalios, T. (2024). Spinopelvic Motion Evaluation in Patients Undergoing Total Hip Arthroplasty and Patient-Specific Target for Acetabular Cup Placement. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 14(12), 1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14121161







