Prognostic Value of Radiomic Analysis Using Pre- and Post-Treatment 18F-FDG-PET/CT in Patients with Laryngeal Cancer and Hypopharyngeal Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Enrollment
2.2. Acquisition of 18F-FDG PET/CT Imaging
2.3. Feature Extraction Protocols
2.4. Feature Selection and Rad-Score
2.5. Model Construction and Evaluation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Derivation of Rad-Score Formula from Radiomics Features
3.3. Estimating Prognostic Factors for Clinical Characteristics and Rad-Score
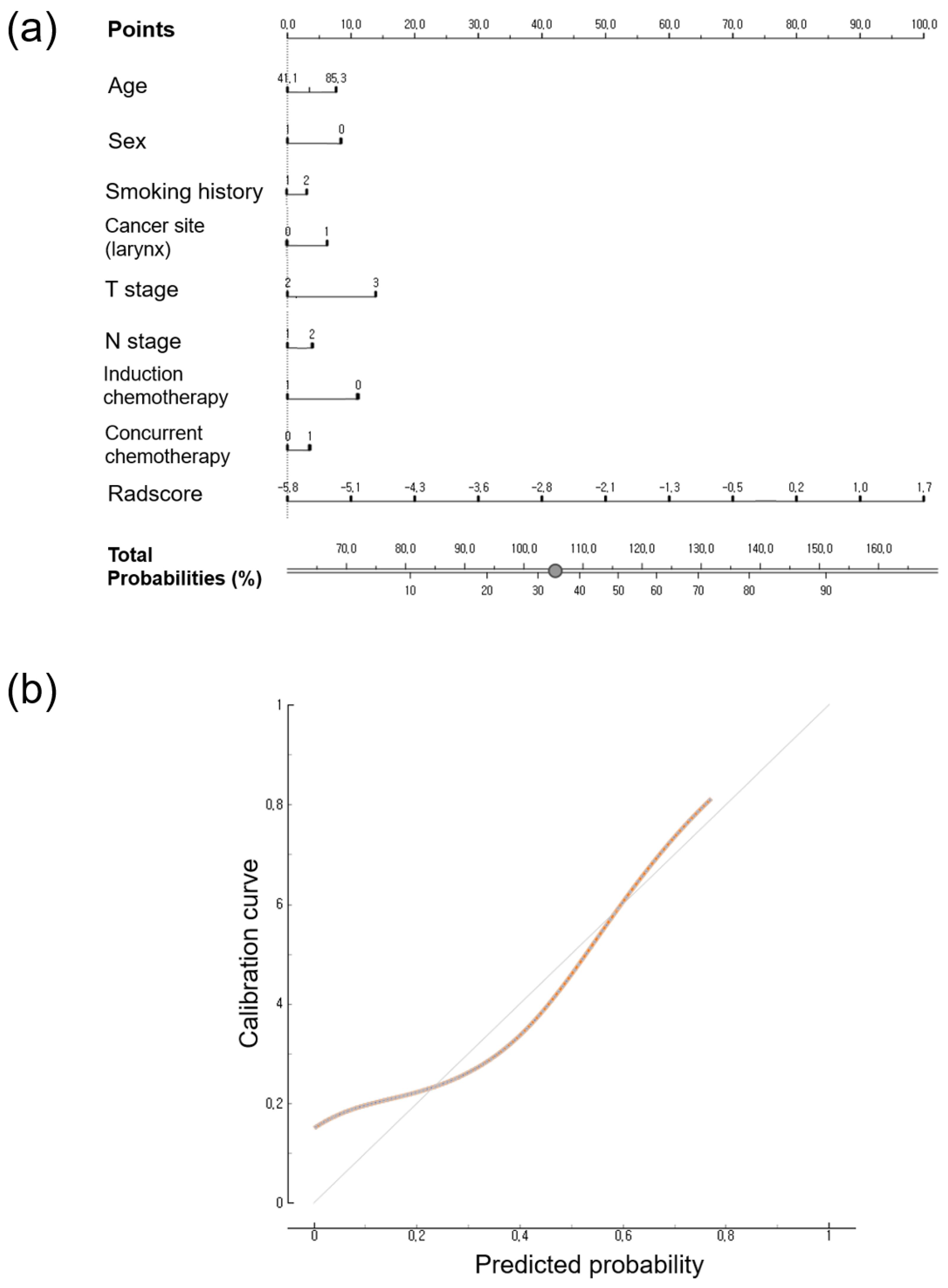
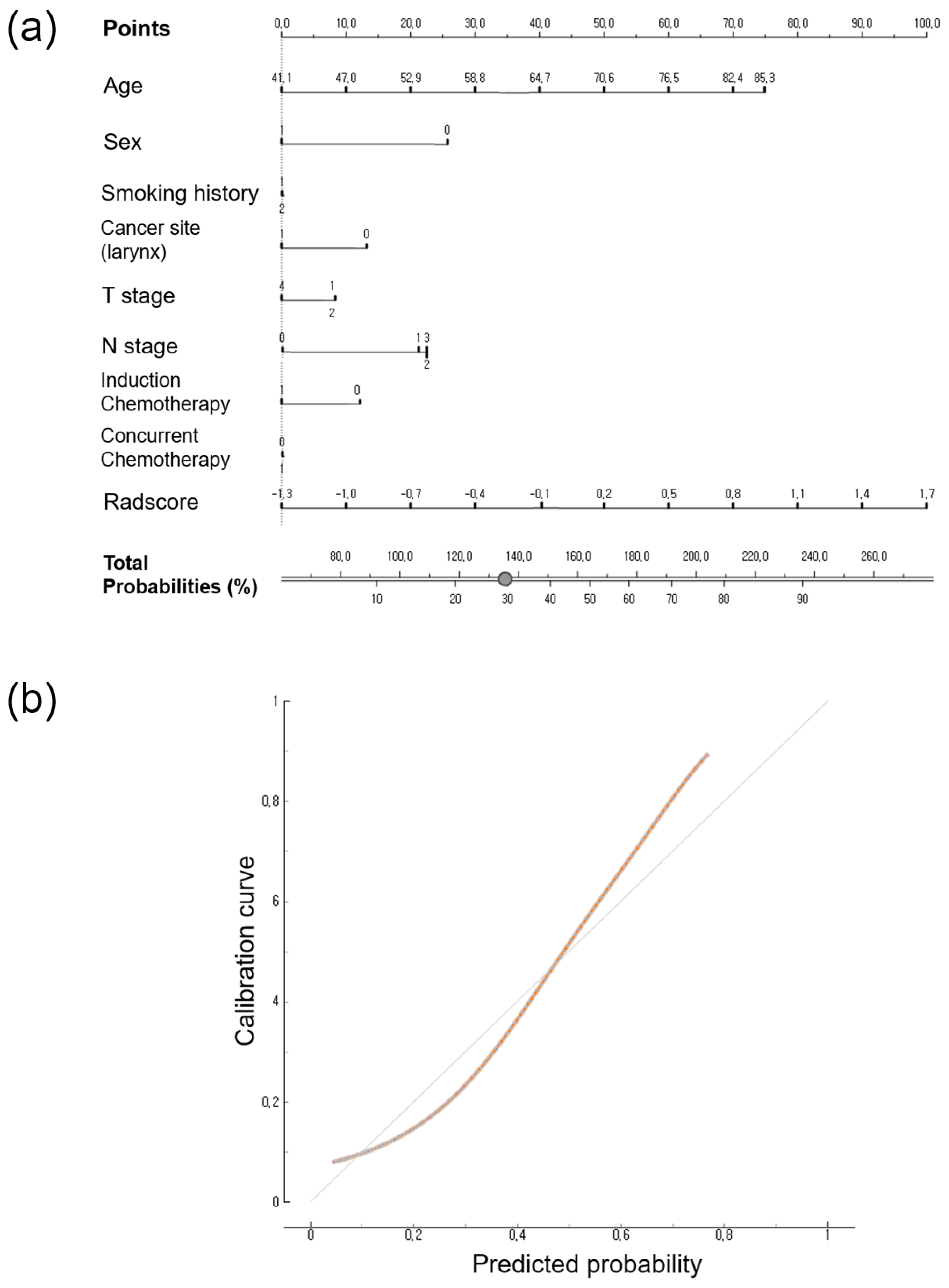
3.4. Calibration Curve and Nomogram
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/laryngeal-and-hypopharyngeal-cancer/about/key-statistics.html (accessed on 3 May 2023).
- Eckel, H.E.; Bradley, P.J. Natural History of Treated and Untreated Hypopharyngeal Cancer. Adv. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 83, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steuer, C.E.; El-Deiry, M.; Parks, J.R.; Higgins, K.A.; Saba, N.F. An update on larynx cancer. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 31–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitajima, K.; Suenaga, Y.; Kanda, T.; Miyawaki, D.; Yoshida, K.; Ejima, Y.; Sasaki, R.; Komatsu, H.; Saito, M.; Otsuki, N.; et al. Prognostic value of FDG PET imaging in patients with laryngeal cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Albano, D.; Dondi, F.; Paderno, A.; Nocivelli, G.; Maddalo, M.; Magrini, S.M.; Nicolai, P.; Maroldi, R.; Giubbini, R.; Bertagna, F. 18F-FDG-PET/CT in laryngeal cancer: Comparison with conventional imaging and prognostic role. Rev. Esp. Med. Nucl. Imagen. Mol. (Engl. Ed.) 2021, 40, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scalco, E.; Rizzo, G. Texture analysis of medical images for radiotherapy applications. Br. J. Radiol. 2017, 90, 20160642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Frood, R.; Brown, P.; Nelstrop, H.; Prestwich, R.; McDermott, G.; Currie, S.; Vaidyanathan, S.; Scarsbrook, A.F. Machine learning-based FDG PET-CT radiomics for outcome prediction in larynx and hypopharynx squamous cell carcinoma. Clin. Radiol. 2021, 76, 78.e9–78.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feliciani, G.; Fioroni, F.; Grassi, E.; Bertolini, M.; Rosca, A.; Timon, G.; Galaverni, M.; Iotti, C.; Versari, A.; Iori, M.; et al. Radiomic Profiling of Head and Neck Cancer: (18)F-FDG PET Texture Analysis as Predictor of Patient Survival. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2018, 2018, 3574310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallieres, M.; Kay-Rivest, E.; Perrin, L.J.; Liem, X.; Furstoss, C.; Aerts, H.; Khaouam, N.; Nguyen-Tan, P.F.; Wang, C.S.; Sultanem, K.; et al. Radiomics strategies for risk assessment of tumour failure in head-and-neck cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Cao, Y.; Diao, W.; Cheng, Y.; Jia, Z.; Peng, X. Radiomics-based prediction of survival in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma based on pre- and post-treatment (18)F-PET/CT. Aging 2020, 12, 14593–14619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guezennec, C.; Robin, P.; Orlhac, F.; Bourhis, D.; Delcroix, O.; Gobel, Y.; Rousset, J.; Schick, U.; Salaun, P.Y.; Abgral, R. Prognostic value of textural indices extracted from pretherapeutic 18-F FDG-PET/CT in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 2019, 41, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ger, R.B.; Zhou, S.; Elgohari, B.; Elhalawani, H.; Mackin, D.M.; Meier, J.G.; Nguyen, C.M.; Anderson, B.M.; Gay, C.; Ning, J.; et al. Radiomics features of the primary tumor fail to improve prediction of overall survival in large cohorts of CT- and PET-imaged head and neck cancer patients. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, J.; Lee, J.; Cheon, M.; Woo, S.K.; Ahn, M.J.; Pyo, H.R.; Choi, Y.S.; Han, J.H.; Choi, J.Y. Predictive Value of (18)F-FDG PET/CT Using Machine Learning for Pathological Response to Neoadjuvant Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy in Patients with Stage III Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, M.; Travaini, L.L.; Ciardo, D.; Garibaldi, C.; Gilardi, L.; Glynne-Jones, R.; Grana, C.M.; Jereczek-Fossa, B.A.; Marvaso, G.; Ronchi, S.; et al. Interim (18)FDG PET/CT during radiochemotherapy in the management of pelvic malignancies: A systematic review. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2017, 113, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldin, A.; Umlauff, L.; Estcourt, L.J.; Collins, G.; Moons, K.G.; Engert, A.; Kobe, C.; von Tresckow, B.; Haque, M.; Foroutan, F.; et al. Interim PET-results for prognosis in adults with Hodgkin lymphoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prognostic factor studies. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 1, CD012643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatt, M.; Tixier, F.; Cheze Le Rest, C.; Pradier, O.; Visvikis, D. Robustness of intratumour (1)(8)F-FDG PET uptake heterogeneity quantification for therapy response prediction in oesophageal carcinoma. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2013, 40, 1662–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, S.; Choi, H.; Paeng, J.C.; Cheon, G.J. Radiomics in Oncological PET/CT: A Methodological Overview. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 53, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camp, R.L.; Dolled-Filhart, M.; Rimm, D.L. X-tile: A new bio-informatics tool for biomarker assessment and outcome-based cut-point optimization. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 7252–7259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiesa-Estomba, C.M.; Echaniz, O.; Larruscain, E.; Gonzalez-Garcia, J.A.; Sistiaga-Suarez, J.A.; Grana, M. Radiomics and Texture Analysis in Laryngeal Cancer. Looking for New Frontiers in Precision Medicine through Imaging Analysis. Cancers 2019, 11, 1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cysouw, M.C.F.; Kramer, G.M.; Schoonmade, L.J.; Boellaard, R.; de Vet, H.C.W.; Hoekstra, O.S. Impact of partial-volume correction in oncological PET studies: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2017, 44, 2105–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, R.M.; Koopman, T.; Noij, D.P.; Pfaehler, E.; Ubelhor, C.; Sharma, S.; Vergeer, M.R.; Leemans, C.R.; Hoekstra, O.S.; Yaqub, M.; et al. Predictive value of quantitative (18)F-FDG-PET radiomics analysis in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. EJNMMI Res. 2020, 10, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Choi, J.Y.; Ahn, Y.C.; Ahn, M.J.; Moon, S.H. The prognostic value of radiomic features from pre- and post-treatment (18)F-FDG PET imaging in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wu, X.; Tian, R.; Ma, H.; Jiang, Z.; Zhao, W.; Cui, G.; Li, M.; Hu, Q.; Yu, X.; et al. MRI-based pre-Radiomics and delta-Radiomics models accurately predict the post-treatment response of rectal adenocarcinoma to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1133008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Liu, H.; Dai, Q.; Yao, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Duan, Q. Treatment Response Prediction Using Ultrasound-Based Pre-, Post-Early, and Delta Radiomics in Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 748008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fave, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, J.; Mackin, D.; Balter, P.; Gomez, D.; Followill, D.; Jones, A.K.; Stingo, F.; Liao, Z.; et al. Delta-radiomics features for the prediction of patient outcomes in non-small cell lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandra, G.; Alexandru, M.; Stefan, C.F.; Petruta-Maria, D.; Gabriel, B.M.; Dragos-Eugen, G.; Teodor, G.M. Blood Group Type Association with Head and Neck Cancer. Hematol. Rep. 2022, 14, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, S.W.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, X.Y.; Jing, Z.H.; Zhao, Z.J.; Zhang, R.H.; Wu, F.P.; Wang, J. Are People with Blood Group O More Susceptible to Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma and Have Worse Survival Rates? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 698113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Li, P.J.; Chen, X.Z.; Hu, W.H. ABO blood group is a predictor of survival in patients with laryngeal cancer. Chin. J. Cancer 2016, 35, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakava, K.; Karelas, I.; Koutrafouris, I.; Damianidis, S.; Stampouloglou, P.; Papadakis, G.; Xenos, A.; Krania, F.; Sarof, P.; Tasopoulos, G.; et al. Relationship between ABO blood groups and head and neck cancer among Greek patients. J. BUON 2016, 21, 594–596. [Google Scholar]
- Franchini, M.; Liumbruno, G.M.; Lippi, G. The prognostic value of ABO blood group in cancer patients. Blood Transfus. 2016, 14, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner-Wasik, M.; Nelson, A.D.; Choi, W.; Arai, Y.; Faulhaber, P.F.; Kang, P.; Almeida, F.D.; Xiao, Y.; Ohri, N.; Brockway, K.D.; et al. What is the best way to contour lung tumors on PET scans? Multiobserver validation of a gradient-based method using a NSCLC digital PET phantom. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 82, 1164–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daisne, J.F.; Sibomana, M.; Bol, A.; Doumont, T.; Lonneux, M.; Gregoire, V. Tri-dimensional automatic segmentation of PET volumes based on measured source-to-background ratios: Influence of reconstruction algorithms. Radiother. Oncol. 2003, 69, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, N.M.; Lin, C.Y.; Liao, C.T.; Tsan, D.L.; Ng, S.H.; Yen, T.C. The added values of (18)F-FDG PET/CT in differentiating cancer recurrence and osteoradionecrosis of mandible in patients with treated oral squamous cell carcinoma. EJNMMI Res. 2023, 13, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, C.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.; Lim, C.W.; Kim, Z.; Woo, S.K.; Park, S.B.; Park, J.M. Development and External Validation of (18)F-FDG PET-Based Radiomic Model for Predicting Pathologic Complete Response after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Qiu, Q.; Fu, J.; Cui, K.; Chen, X.; Xing, L.; Sun, X. Stage-Specific PET Radiomic Prediction Model for the Histological Subtype Classification of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2021, 13, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Chen, C.J.; Hsu, W.L.; Chang, S.M.; Huang, Y.F.; Tyan, Y.C. Prognostic Significance of Metabolic Parameters and Textural Features on (18)F-FDG PET/CT in Invasive Ductal Carcinoma of Breast. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.; Park, S.; Bang, J.I.; Kim, E.K.; Lee, H.Y. Metabolic Radiomics for Pretreatment (18)F-FDG PET/CT to Characterize Locally Advanced Breast Cancer: Histopathologic Characteristics, Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy, and Prognosis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | All Patients (n = 91) | Training Set (n = 61) | Validation Set (n = 30) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean age, y | 62.50 ± 10.00 | 61.34 ± 9.55 | 65.00 ± 10.70 | 0.103 |
| Sex (M:F) | 0.798 | |||
| Male | 84 | 56 | 28 | |
| Female | 7 | 5 | 2 | |
| Smoking history | 0.349 | |||
| Ex/current smoker | 77 | 53 | 24 | |
| Never smoked | 11 | 6 | 5 | |
| N/A | 3 | |||
| Cancer site | 0.924 | |||
| Larynx | 57 | 38 | 19 | |
| Hypopharynx | 34 | 23 | 11 | |
| Concurrent chemoradiotherapy | 0.201 | |||
| Yes | 57 | 41 | 16 | |
| No | 34 | 20 | 14 | |
| Induction chemotherapy | 0.984 | |||
| Yes | 6 | 4 | 2 | |
| No | 85 | 57 | 28 | |
| T stage | 0.317 | |||
| T1 | 20 | 11 | 9 | |
| T2 | 41 | 28 | 13 | |
| T3 | 18 | 14 | 4 | |
| T4 | 12 | 8 | 4 | |
| N stage | 0.575 | |||
| N0 | 47 | 30 | 17 | |
| N1 | 17 | 16 | 1 | |
| N2 | 26 | 15 | 11 | |
| N3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Mean a PFS, mo | 59.30 ± 40.32 | 61.15 ± 38.85 | 55.53 ± 43.59 | 0.535 |
| Mean b OS, mo | 72.10 ± 35.51 | 74.22 ± 33.27 | 67.78 ± 39.93 | 0.420 |
| Variables | Hazard Ratio (95%CI) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 1.0245 | (0.974–1.077) | 0.347 |
| Sex (F/M) | 0.6419 | (0.086–4.790) | 0.666 |
| Smoking history (ex/current smoker/never smoked) | 1.8968 | (0.551–6.534) | 0.310 |
| T2 | 0.5173 | (0.145–1.847) | 0.310 |
| T3 | 1.6504 | (0.495–5.503) | 0.415 |
| T4 | 0.9511 | (0.213–4.256) | 0.948 |
| N1 | 0.6646 | (0.208–2.123) | 0.490 |
| N2 | 1.5761 | (0.597–4.162) | 0.359 |
| Induction chemotherapy (yes/no) | 0.6609 | (0.089–4.932) | 0.686 |
| Concurrent chemotherapy (yes/no) | 1.5537 | (0.568–4.250) | 0.391 |
| Cancer type (hypopharyngeal cancer/laryngeal cancer) | 1.4726 | (0.623–3.481) | 0.378 |
| Rad-score | 2.1509 | (1.100–4.207) | 0.025 |
| Variables | Hazard Ratio (95%CI) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 1.1162 | (1.041–1.197) | 0.002 |
| Sex (F/M) | 1.36 × 10−8 | (0–Inf) | 0.998 |
| Smoking history (ex/current smoker/never smoked) | 0.9612 | (0.123–7.504) | 0.970 |
| T2 | 0.7856 | (0.186–3.316) | 0.743 |
| T3 | 2.3993 | (0.589–9.779) | 0.222 |
| T4 | 1.1261 | (0.187–6.790) | 0.897 |
| N1 | 1.1485 | (0.335–3.938) | 0.826 |
| N2 | 1.6463 | (0.520–5.208) | 0.396 |
| Induction chemotherapy (yes/no) | 1.0813 | (0.143–8.198) | 0.940 |
| Concurrent chemotherapy (yes/no) | 1.2448 | (0.429–3.610) | 0.687 |
| Cancer type (hypopharyngeal cancer/laryngeal cancer) | 0.7829 | (0.271–2.260) | 0.651 |
| Rad-score | 33.885 | (2.891–397.175) | 0.005 |
| Model | C-Index (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|
| Training Set | Validation Set | |
| Clinical model | 0.758 (0.629 to 0.860) | 0.895 (0.724 to 0.977) |
| Clinical + Radiomics model | 0.802 (0.678 to 0.894) | 0.889 (0.717 to 0.975) |
| Model | C-Index (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|
| Training Set | Validation Set | |
| Clinical model | 0.791 (0.665 to 0.886) | 0.916 (0.752 to 0.986) |
| Clinical + Radiomics model | 0.860 (0.745 to 0.937) | 0.958 (0.811 to 0.998) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, J.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Woo, S.-K.; Moon, J.E.; Lim, C.H.; Park, S.B.; Seo, S.; Ahn, Y.C.; Ahn, M.-J.; Moon, S.H.; et al. Prognostic Value of Radiomic Analysis Using Pre- and Post-Treatment 18F-FDG-PET/CT in Patients with Laryngeal Cancer and Hypopharyngeal Cancer. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14010071
Choi JH, Choi JY, Woo S-K, Moon JE, Lim CH, Park SB, Seo S, Ahn YC, Ahn M-J, Moon SH, et al. Prognostic Value of Radiomic Analysis Using Pre- and Post-Treatment 18F-FDG-PET/CT in Patients with Laryngeal Cancer and Hypopharyngeal Cancer. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2024; 14(1):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14010071
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Joon Ho, Joon Young Choi, Sang-Keun Woo, Ji Eun Moon, Chae Hong Lim, Soo Bin Park, Seongho Seo, Yong Chan Ahn, Myung-Ju Ahn, Seung Hwan Moon, and et al. 2024. "Prognostic Value of Radiomic Analysis Using Pre- and Post-Treatment 18F-FDG-PET/CT in Patients with Laryngeal Cancer and Hypopharyngeal Cancer" Journal of Personalized Medicine 14, no. 1: 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14010071
APA StyleChoi, J. H., Choi, J. Y., Woo, S.-K., Moon, J. E., Lim, C. H., Park, S. B., Seo, S., Ahn, Y. C., Ahn, M.-J., Moon, S. H., & Park, J. M. (2024). Prognostic Value of Radiomic Analysis Using Pre- and Post-Treatment 18F-FDG-PET/CT in Patients with Laryngeal Cancer and Hypopharyngeal Cancer. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 14(1), 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14010071






