The Correlation between Metformin Use and Incident Dementia in Patients with New-Onset Diabetes Mellitus: A Population-Based Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
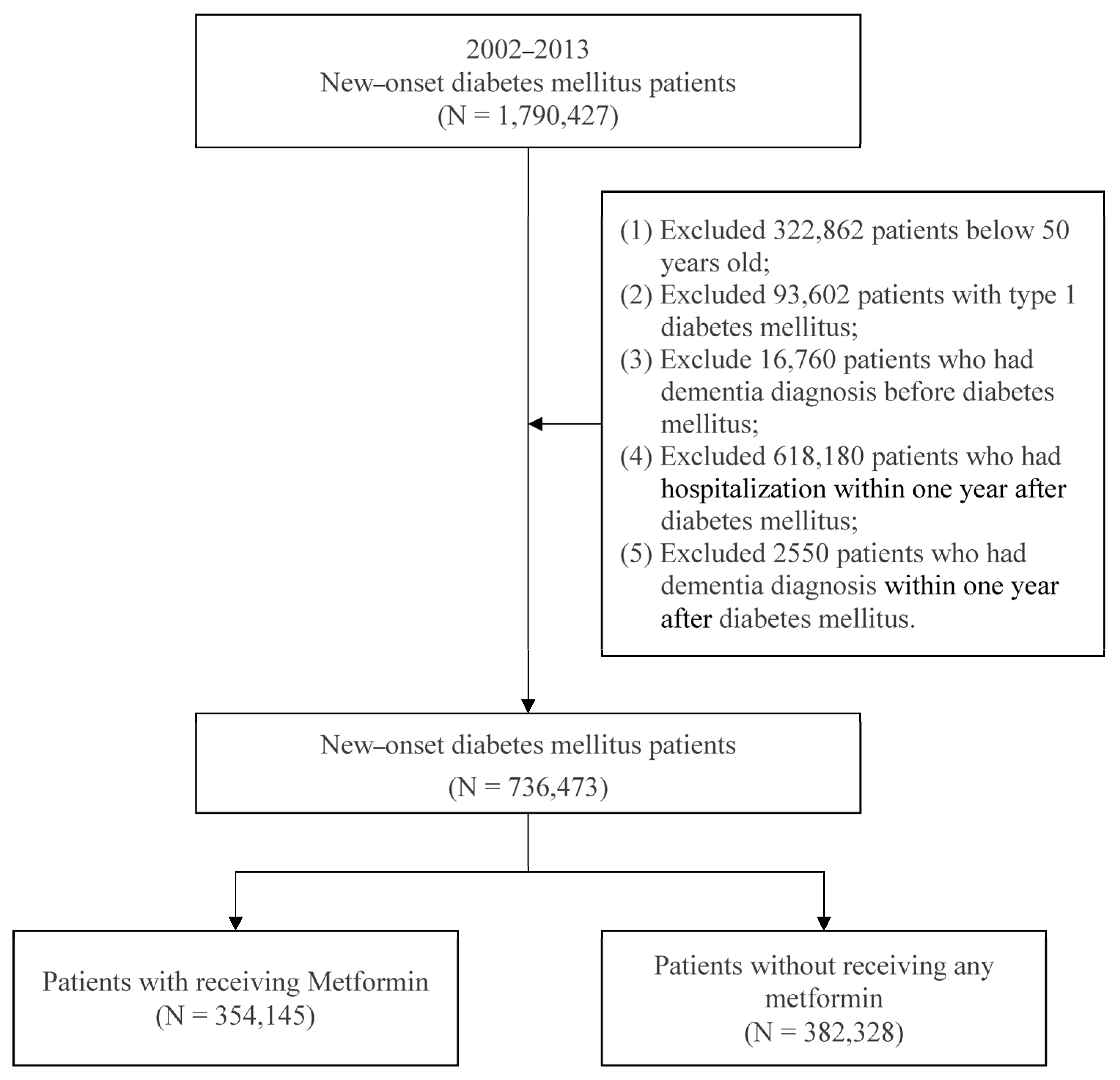
2.2. Study Subjects
2.3. Study Design
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
3.2. Incident Dementia among New-Onset Patients with DM Who Used Metformin
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Erkkinen, M.G.; Kim, M.O.; Geschwind, M.D. Clinical Neurology and Epidemiology of the Major Neurodegenerative Diseases. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect Biol. 2018, 10, a033118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perl, D.P. Neuropathology of Alzheimer’s disease. Mt. Sinai. J. Med. 2010, 77, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bomfim, T.R.; Forny-Germano, L.; Sathler, L.B.; Brito-Moreira, J.; Houzel, J.C.; Decker, H.; Silverman, M.A.; Kazi, H.; Melo, H.M.; McClean, P.L.; et al. An anti-diabetes agent protects the mouse brain from defective insulin signaling caused by Alzheimer’s disease-associated Abeta oligomers. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 1339–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiltunen, M.; Khandelwal, V.K.; Yaluri, N.; Tiilikainen, T.; Tusa, M.; Koivisto, H.; Krzisch, M.; Vepsalainen, S.; Makinen, P.; Kemppainen, S.; et al. Contribution of genetic and dietary insulin resistance to Alzheimer phenotype in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2012, 16, 1206–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talbot, K.; Wang, H.Y.; Kazi, H.; Han, L.Y.; Bakshi, K.P.; Stucky, A.; Fuino, R.L.; Kawaguchi, K.R.; Samoyedny, A.J.; Wilson, R.S.; et al. Demonstrated brain insulin resistance in Alzheimer’s disease patients is associated with IGF-1 resistance, IRS-1 dysregulation, and cognitive decline. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 1316–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.S.S.; Fernandes, C.S.; Vieira, M.N.N.; De Felice, F.G. Insulin Resistance in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Song, D.; Leng, S.X. Link between type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease: From epidemiology to mechanism and treatment. Clin. Interv. Aging 2015, 10, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Liu, S.; Fonseca, V.A.; Thethi, T.K.; Shi, L. Effect of metformin on neurodegenerative disease among elderly adult US veterans with type 2 diabetes mellitus. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e024954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soukas, A.A.; Hao, H.; Wu, L. Metformin as Anti-Aging Therapy: Is It for Everyone? Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 30, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhou, T.; Sun, H.; Edwards, P.; Gao, H.; Yu, F.S.; Qiao, X. Metformin suppresses retinal angiogenesis and inflammation in vitro and in vivo. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, S.; Uniyal, A.; Akhtar, A.; Sah, S.P. Alpha lipoic acid and metformin alleviates experimentally induced insulin resistance and cognitive deficit by modulation of TLR2 signalling. Pharmacol. Rep. 2019, 71, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, J.M.; Stephenson, M.D.; de Courten, B.; Chapman, I.; Bellman, S.M.; Aromataris, E. Metformin Use Associated with Reduced Risk of Dementia in Patients with Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 65, 1225–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orkaby, A.R.; Cho, K.; Cormack, J.; Gagnon, D.R.; Driver, J.A. Metformin vs sulfonylurea use and risk of dementia in US veterans aged >/=65 years with diabetes. Neurology 2017, 89, 1877–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.C.; Wahlqvist, M.L.; Lee, M.S.; Tsai, H.N. Incidence of dementia is increased in type 2 diabetes and reduced by the use of sulfonylureas and metformin. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2011, 24, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herath, P.M.; Cherbuin, N.; Eramudugolla, R.; Anstey, K.J. The Effect of Diabetes Medication on Cognitive Function: Evidence from the PATH Through Life Study. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 7208429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, K.; Wang, R.; Liu, Y.; Kwak, Y.D.; Ma, T.; Thompson, R.C.; Zhao, Y.; Smith, L.; Gasparini, L.; et al. Antidiabetic drug metformin (GlucophageR) increases biogenesis of Alzheimer’s amyloid peptides via up-regulating BACE1 transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3907–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barini, E.; Antico, O.; Zhao, Y.; Asta, F.; Tucci, V.; Catelani, T.; Marotta, R.; Xu, H.; Gasparini, L. Metformin promotes tau aggregation and exacerbates abnormal behavior in a mouse model of tauopathy. Mol. Neurodegener. 2016, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, L.E.; Darling, A.L.; Brown, J.E. Association between metformin and vitamin B12 deficiency in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab. 2016, 42, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imfeld, P.; Bodmer, M.; Jick, S.S.; Meier, C.R. Metformin, other antidiabetic drugs, and risk of Alzheimer’s disease: A population-based case-control study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2012, 60, 916–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, E.M.; Mander, A.G.; Ames, D.; Kotowicz, M.A.; Carne, R.P.; Brodaty, H.; Woodward, M.; Boundy, K.; Ellis, K.A.; Bush, A.I.; et al. Increased risk of cognitive impairment in patients with diabetes is associated with metformin. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 2981–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuan, Y.C.; Huang, K.W.; Lin, C.L.; Hu, C.J.; Kao, C.H. Effects of metformin exposure on neurodegenerative diseases in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 79, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picone, P.; Nuzzo, D.; Caruana, L.; Messina, E.; Barera, A.; Vasto, S.; Di Carlo, M. Metformin increases APP expression and processing via oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction and NF-κB activation: Use of insulin to attenuate metformin’s effect. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1853, 1046–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridhar, G.R.; Lakshmi, G.; Nagamani, G. Emerging links between type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, J.; Choi, D.W.; Kim, K.J.; Cho, S.Y.; Kim, H.; Kim, K.Y.; Koh, Y.; Nam, C.M.; Kim, E. Association of metformin use with Alzheimer’s disease in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: A population-based nested case-control study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 24069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.Y.; Su, C.C.; Shao, S.C.; Sung, S.F.; Lin, S.J.; Kao Yang, Y.H.; Lai, E.C. Taiwan’s National Health Insurance Research Database: Past and future. Clin. Epidemiol. 2019, 11, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.W.; Liao, K.F.; Lin, C.L.; Lin, C.C.; Lin, C.H. Longitudinal data of multimorbidity and polypharmacy in older adults in Taiwan from 2000 to 2013. Biomedicine 2020, 10, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Wu, Y.L.; Sheu, W.H.; Tu, S.T.; Hsu, C.C.; Tai, T.Y. Accountability and utilization of diabetes care from 2005 to 2014 in Taiwan. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2019, 118 (Suppl. S2), S111–S121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimmsmann, T.; Himmel, W. Discrepancies between prescribed and defined daily doses: A matter of patients or drug classes? Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2011, 67, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellington, K. Rosiglitazone/Metformin. Drugs 2005, 65, 1581–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrannini, E. The target of metformin in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1547–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinangeli, C.; Didier, S.; Ahmed, T.; Caillerez, R.; Domise, M.; Laloux, C.; Begard, S.; Carrier, S.; Colin, M.; Marchetti, P.; et al. AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Is Essential for the Maintenance of Energy Levels during Synaptic Activation. iScience 2018, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seixas da Silva, G.S.; Melo, H.M.; Lourenco, M.V.; Lyra, E.S.N.M.; de Carvalho, M.B.; Alves-Leon, S.V.; de Souza, J.M.; Klein, W.L.; da-Silva, W.S.; Ferreira, S.T.; et al. Amyloid-beta oligomers transiently inhibit AMP-activated kinase and cause metabolic defects in hippocampal neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 7395–7406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Li, X.W.; Chen, Z.; Hao, F.; Tao, S.X.; Yu, H.Y.; Cheng, R.; Liu, H. Neuro-Protective Role of Metformin in Patients with Acute Stroke and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus via AMPK/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) Signaling Pathway and Oxidative Stress. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 2186–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Deng, J.; Sheng, W.; Zuo, Z. Metformin attenuates Alzheimer’s disease-like neuropathology in obese, leptin-resistant mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2012, 101, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, W.H.; Nunes, A.K.; Franca, M.E.; Santos, L.A.; Los, D.B.; Rocha, S.W.; Barbosa, K.P.; Rodrigues, G.B.; Peixoto, C.A. Effects of metformin on inflammation and short-term memory in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Brain Res. 2016, 1644, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, S.; Quan, H.; Li, J. Vitamin B12 status in metformin treated patients: Systematic review. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, E.; Mander, A.; Ames, D.; Carne, R.; Sanders, K.; Watters, D. Cognitive impairment and vitamin B12: A review. Int. Psychogeriatr. 2012, 24, 541–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.W.; Leung, C.S.; Leung, C.P.; Cheng, J.N. Association of metformin use with vitamin B12 deficiency in the institutionalized elderly. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2018, 79, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.H.; Lee, C.H.; Cheng, Y.D.; Gau, S.Y.; Tsai, T.H.; Chung, N.J.; Lee, C.Y. Correlation between long-term use of metformin and incidence of NAFLD among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A real-world cohort study. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1027484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.H.; Chang, Y.L.; Gau, S.Y.; Tsai, T.H.; Lee, C.Y. Dose-Response Association of Metformin with Parkinson’s Disease Odds in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattar, D.; Khaliq, F.; Vaney, N.; Madhu, S.V. Is Metformin-Induced Vitamin B12 Deficiency Responsible for Cognitive Decline in Type 2 Diabetes? Indian J. Psychol. Med. 2016, 38, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, S.H.; Ko, S.H.; Ahn, Y.B.; Song, K.H.; Han, K.D.; Park, Y.M.; Ko, S.H.; Kim, H.S. Association of vitamin B12 deficiency and metformin use in patients with type 2 diabetes. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2014, 29, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, T.J.; Tourkmani, A.M.; Abdelhay, O.; Alkhashan, H.I.; Al-Asmari, A.K.; Bin Rsheed, A.M.; Abuhaimed, S.N.; Mohammed, N.; AlRasheed, A.N.; AlHarbi, N.G. The association of metformin use with vitamin B12 deficiency and peripheral neuropathy in Saudi individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damiao, C.P.; Rodrigues, A.O.; Pinheiro, M.F.; Cruz, R.A.F.; Cardoso, G.P.; Taboada, G.F.; Lima, G.A. Prevalence of vitamin B12 deficiency in type 2 diabetic patients using metformin: A cross-sectional study. Sao Paulo Med. J. 2016, 134, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kickstein, E.; Krauss, S.; Thornhill, P.; Rutschow, D.; Zeller, R.; Sharkey, J.; Williamson, R.; Fuchs, M.; Kohler, A.; Glossmann, H.; et al. Biguanide metformin acts on tau phosphorylation via mTOR/protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 21830–21835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafa, D.K.; Ismail, C.A.; Ghareeb, D.A. Differential metformin dose-dependent effects on cognition in rats: Role of Akt. Psychopharmacology 2016, 233, 2513–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, B.A.; Lin, E.; Von Korff, M.; Simon, G.; Ciechanowski, P.; Ludman, E.J.; Everson-Stewart, S.; Kinder, L.; Oliver, M.; Boyko, E.J.; et al. Diabetes complications severity index and risk of mortality, hospitalization, and healthcare utilization. Am. J. Manag. Care 2008, 14, 15–23. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H.Y.; Weiner, J.P.; Richards, T.M.; Bleich, S.N.; Segal, J.B. Validating the adapted Diabetes Complications Severity Index in claims data. Am. J. Manag. Care 2012, 18, 721–726. [Google Scholar]
- Chiu, W.C.; Ho, W.C.; Liao, D.L.; Lin, M.H.; Chiu, C.C.; Su, Y.P.; Chen, P.C.; Health Data Analysis in Taiwan Research Group. Progress of Diabetic Severity and Risk of Dementia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 2899–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LoGiudice, D.; Watson, R. Dementia in older people: An update. Intern. Med. J. 2014, 44, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinstatler, L.; Qi, Y.P.; Williamson, R.S.; Garn, J.V.; Oakley, G.P., Jr. Association of biochemical B(1)(2) deficiency with metformin therapy and vitamin B(1)(2) supplements: The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1999–2006. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorm, A.F. Is depression a risk factor for dementia or cognitive decline? A review. Gerontology 2000, 46, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, M.D.; Katon, W.J.; Lovato, L.C.; Miller, M.E.; Murray, A.M.; Horowitz, K.R.; Bryan, R.N.; Gerstein, H.C.; Marcovina, S.; Akpunonu, B.E.; et al. Association of depression with accelerated cognitive decline among patients with type 2 diabetes in the ACCORD-MIND trial. JAMA Psychiatry 2013, 70, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santabarbara, J.; Lipnicki, D.M.; Olaya, B.; Villagrasa, B.; Bueno-Notivol, J.; Nuez, L.; Lopez-Anton, R.; Gracia-Garcia, P. Does Anxiety Increase the Risk of All-Cause Dementia? An Updated Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knopman, D.S. Dementia and cerebrovascular disease. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2006, 81, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Wei, B.; Tung, T.H.; Tao, P.; Chien, C.W. Association between Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Dementia: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Dis. Extra 2019, 9, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.J. The cytokine network in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 3546–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Sanchez, I.; Rodriguez-Alzueta, E.; Cabrera-Martos, I.; Lopez-Torres, I.; Moreno-Ramirez, M.P.; Valenza, M.C. Cognitive impairment in COPD: A systematic review. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2015, 41, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | Total | Metformin | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Users | Users | p-Value | |||||
| N | % | N | % | N | % | ||
| Total | 736,473 | 100.00 | 354,145 | 51.36 | 382,328 | 48.64 | |
| Gender | |||||||
| Female | 378,225 | 51.36 | 187,099 | 52.83 | 191,126 | 49.99 | <0.001 |
| Male | 358,248 | 48.64 | 167,046 | 47.17 | 191,202 | 50.01 | |
| Age (year) (Mean ± SD) | 62.03 ± 8.76 | 62.90 ± 9.06 | 61.22 ± 8.39 | <0.001 | |||
| 50–64 | 475,964 | 64.63 | 215,283 | 60.79 | 260,681 | 68.18 | |
| 65–74 | 181,583 | 24.66 | 92,699 | 26.18 | 88,884 | 23.25 | |
| 75+ | 78,926 | 10.72 | 46,163 | 13.04 | 32,763 | 8.57 | |
| Income level (NTD) a | <0.001 | ||||||
| ≤21,000 | 381,282 | 51.77 | 187,444 | 52.93 | 193,838 | 50.70 | |
| 21,001–33,000 | 174,995 | 23.76 | 78,427 | 22.15 | 96,568 | 25.26 | |
| ≥33,001 | 180,196 | 24.47 | 88,274 | 24.93 | 91,922 | 24.04 | |
| Urbanization | <0.001 | ||||||
| Level 1 | 203,376 | 27.61 | 103,603 | 29.25 | 99,773 | 26.10 | |
| Level 2 | 238,177 | 32.34 | 113,779 | 32.13 | 124,398 | 32.54 | |
| Level 3 | 114,530 | 15.55 | 52,472 | 14.82 | 62,058 | 16.23 | |
| Level 4 | 103,176 | 14.01 | 48,606 | 13.72 | 54,570 | 14.27 | |
| Level 5 | 17,291 | 2.35 | 8405 | 2.37 | 8886 | 2.32 | |
| Level 6 | 31,369 | 4.26 | 14,398 | 4.07 | 16,971 | 4.44 | |
| Level 7 | 28,554 | 3.88 | 12,882 | 3.64 | 15,672 | 4.10 | |
| DCSI score b | <0.001 | ||||||
| 0 | 447,130 | 60.71 | 211,227 | 59.64 | 235,903 | 61.70 | |
| 1 | 157,532 | 21.39 | 75,610 | 21.35 | 81,922 | 21.43 | |
| 2+ | 131,811 | 17.90 | 67,308 | 19.01 | 64,503 | 16.87 | |
| Hypertension | <0.001 | ||||||
| No | 404,777 | 54.96 | 189,444 | 53.49 | 215,333 | 56.32 | |
| Yes | 331,696 | 45.04 | 164,701 | 46.51 | 166,995 | 43.68 | |
| Hyperlipidemia | <0.001 | ||||||
| No | 579,453 | 78.68 | 265,968 | 75.10 | 313,485 | 81.99 | |
| Yes | 157,020 | 21.32 | 88,177 | 24.90 | 68,843 | 18.01 | |
| Hyperuricemia | <0.001 | ||||||
| No | 730,080 | 99.13 | 350,573 | 98.99 | 379,507 | 99.26 | |
| Yes | 6393 | 0.87 | 3572 | 1.01 | 2821 | 0.74 | |
| Cerebrovascular disease | <0.001 | ||||||
| No | 699,849 | 95.03 | 334,521 | 94.46 | 365,328 | 95.55 | |
| Yes | 36,624 | 4.97 | 19,624 | 5.54 | 17,000 | 4.45 | |
| Coronary artery disease | <0.001 | ||||||
| No | 672,668 | 91.34 | 320,226 | 90.42 | 352,442 | 92.18 | |
| Yes | 63,805 | 8.66 | 33,919 | 9.58 | 29,886 | 7.82 | |
| Arrhythmia | <0.001 | ||||||
| No | 705,090 | 95.74 | 337,005 | 95.16 | 368,085 | 96.27 | |
| Yes | 31,383 | 4.26 | 17,140 | 4.84 | 14,243 | 3.73 | |
| Heart failure | <0.001 | ||||||
| No | 722,542 | 98.11 | 347,017 | 97.99 | 375,525 | 98.22 | |
| Yes | 13,931 | 1.89 | 7128 | 2.01 | 6803 | 1.78 | |
| Anxiety | <0.001 | ||||||
| No | 663,384 | 90.08 | 314,858 | 88.91 | 348,526 | 91.16 | |
| Yes | 73,089 | 9.92 | 39,287 | 11.09 | 33,802 | 8.84 | |
| Depression | <0.001 | ||||||
| No | 732,707 | 99.49 | 352,120 | 99.43 | 380,587 | 99.54 | |
| Yes | 3766 | 0.51 | 2025 | 0.57 | 1741 | 0.46 | |
| COPD b | <0.001 | ||||||
| No | 692,329 | 94.01 | 330,362 | 93.28 | 361,967 | 94.67 | |
| Yes | 44,144 | 5.99 | 23,783 | 6.72 | 20,361 | 5.33 | |
| Chronic kidney disease | <0.001 | ||||||
| No | 730,618 | 99.20 | 349,812 | 98.78 | 380,806 | 99.60 | |
| Yes | 5855 | 0.80 | 4333 | 1.22 | 1522 | 0.40 | |
| Obesity | 0.012 | ||||||
| No | 733,254 | 99.56 | 352,668 | 99.58 | 380,586 | 99.54 | |
| Yes | 3219 | 0.44 | 1477 | 0.42 | 1742 | 0.46 | |
| Alcoholism | 0.950 | ||||||
| No | 736,037 | 99.94 | 353,936 | 99.94 | 382,101 | 99.94 | |
| Yes | 436 | 0.06 | 209 | 0.06 | 227 | 0.06 | |
| Variables | Three-Year Follow-Up of Incident Dementia | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Events | Model 1 | Model 2 | ||||||
| N | % | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| Total | 7590 | 1.03 | ||||||
| cDDD of metformin use | ||||||||
| Non-users | 4245 | 1.20 | 1 | |||||
| DDD < 300 | 3312 | 0.88 | 0.92 | 0.88–0.96 | <0.001 | - | - | - |
| DDD 300–500 | 30 | 0.59 | 0.80 | 0.56–1.15 | 0.235 | - | - | - |
| DDD 500+ | 3 | 1.28 | 1.48 | 0.48–4.60 | 0.496 | - | - | - |
| Intensity of metformin use | ||||||||
| Non-users | 4245 | 1.20 | 1 | |||||
| <10 | 2526 | 0.91 | - | - | - | 0.92 | 0.87–0.97 | <0.001 |
| 10~25 | 786 | 0.78 | - | - | - | 0.92 | 0.85–1.00 | 0.037 |
| 25+ | 33 | 0.62 | - | - | - | 0.84 | 0.60–1.18 | 0.317 |
| Gender | ||||||||
| Female | 4115 | 1.09 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Male | 3475 | 0.97 | 0.94 | 0.90–0.98 | 0.006 | 0.94 | 0.90–0.98 | 0.006 |
| Age (year) | ||||||||
| 50–64 | 1145 | 0.24 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 65–74 | 2981 | 1.64 | 6.27 | 5.85–6.72 | <0.001 | 6.27 | 5.85–6.72 | <0.001 |
| 75+ | 3464 | 4.39 | 15.94 | 14.86–17.09 | <0.001 | 15.94 | 14.86–17.09 | <0.001 |
| Income level (NTD) a | ||||||||
| ≤21,000 | 4884 | 1.28 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 21,001–33,000 | 1402 | 0.80 | 0.90 | 0.85–0.96 | <0.001 | 0.90 | 0.85–0.96 | <0.001 |
| ≥33,001 | 1304 | 0.72 | 0.91 | 0.86–0.97 | 0.005 | 0.91 | 0.86–0.97 | 0.005 |
| Urbanization | ||||||||
| Level 1 | 1907 | 0.94 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Level 2 | 2182 | 0.92 | 0.98 | 0.92–1.04 | 0.430 | 0.98 | 0.92–1.04 | 0.429 |
| Level 3 | 1147 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 0.91–1.06 | 0.586 | 0.98 | 0.91–1.05 | 0.584 |
| Level 4 | 1251 | 1.21 | 1.00 | 0.93–1.08 | 0.909 | 1.00 | 0.93–1.08 | 0.911 |
| Level 5 | 281 | 1.63 | 1.07 | 0.95–1.22 | 0.280 | 1.07 | 0.95–1.22 | 0.279 |
| Level 6 | 458 | 1.46 | 1.07 | 0.97–1.19 | 0.202 | 1.07 | 0.97–1.19 | 0.202 |
| Level 7 | 364 | 1.27 | 0.99 | 0.89–1.11 | 0.883 | 0.99 | 0.89–1.11 | 0.884 |
| DCSI score b | ||||||||
| 0 | 3382 | 0.76 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 1 | 1595 | 1.01 | 1.06 | 1.00–1.13 | 0.059 | 1.06 | 1.00–1.13 | 0.059 |
| 2+ | 2613 | 1.98 | 1.44 | 1.35–1.53 | <0.001 | 1.44 | 1.35–1.53 | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | ||||||||
| No | 3239 | 0.80 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 4351 | 1.31 | 0.98 | 0.94–1.03 | 0.529 | 0.98 | 0.94–1.03 | 0.529 |
| Hyperlipidemia | ||||||||
| No | 5976 | 1.03 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 1614 | 1.03 | 0.89 | 0.84–0.94 | <0.001 | 0.89 | 0.84–0.94 | <0.001 |
| Hyperuricemia | ||||||||
| No | 7509 | 1.03 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 81 | 1.27 | 1.05 | 0.84–1.30 | 0.692 | 1.05 | 0.84–1.30 | 0.693 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | ||||||||
| No | 6500 | 0.93 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 1090 | 2.98 | 1.53 | 1.42–1.64 | <0.001 | 1.53 | 1.42–1.64 | <0.001 |
| Coronary artery disease | ||||||||
| No | 6535 | 0.97 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 1055 | 1.65 | 0.91 | 0.84–0.97 | 0.007 | 0.91 | 0.84–0.97 | 0.007 |
| Arrhythmia | ||||||||
| No | 7014 | 0.99 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 576 | 1.84 | 1.01 | 0.93–1.11 | 0.785 | 1.01 | 0.93–1.11 | 0.784 |
| Heart failure | ||||||||
| No | 7253 | 1.00 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 337 | 2.42 | 0.95 | 0.85–1.07 | 0.379 | 0.95 | 0.85–1.07 | 0.379 |
| Anxiety | ||||||||
| No | 6331 | 0.95 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 1259 | 1.72 | 1.50 | 1.41–1.59 | <0.001 | 1.50 | 1.41–1.59 | <0.001 |
| Depression | ||||||||
| No | 7496 | 1.02 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 94 | 2.50 | 1.76 | 1.43–2.16 | <0.001 | 1.76 | 1.43–2.16 | <0.001 |
| COPD b | ||||||||
| No | 6723 | 0.97 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 867 | 1.96 | 1.11 | 1.03–1.20 | 0.004 | 1.11 | 1.03–1.20 | 0.004 |
| Chronic kidney disease | ||||||||
| No | 7455 | 1.02 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 135 | 2.31 | 0.99 | 0.83–1.18 | 0.927 | 0.99 | 0.83–1.18 | 0.927 |
| Obesity | ||||||||
| No | 7573 | 1.03 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 17 | 0.53 | 0.75 | 0.47–1.21 | 0.237 | 0.75 | 0.47–1.21 | 0.238 |
| Alcoholism | ||||||||
| No | 7583 | 1.03 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 7 | 1.61 | 2.47 | 1.18–5.20 | 0.017 | 2.47 | 1.18–5.19 | 0.017 |
| Variables | Five-Year Follow-Up of Incident Dementia | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Events | Model 1 | Model 2 | ||||||
| N | % | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| Total | 15,989 | 2.17 | ||||||
| cDDD of metformin use | ||||||||
| Non-users | 8801 | 2.49 | 1 | |||||
| DDD < 300 | 7111 | 1.89 | 0.94 | 0.91–0.97 | <0.001 | - | - | - |
| DDD 300–500 | 70 | 1.37 | 0.88 | 0.70–1.12 | 0.304 | - | - | - |
| DDD 500+ | 7 | 2.98 | 1.61 | 0.77–3.38 | 0.207 | - | - | - |
| Intensity of metformin use | ||||||||
| Non-users | 8801 | 2.49 | 1 | |||||
| <10 | 5409 | 1.96 | - | - | - | 0.94 | 0.91–0.97 | <0.001 |
| 10~25 | 1702 | 1.70 | - | - | - | 0.95 | 0.90–1.00 | 0.035 |
| 25+ | 77 | 1.44 | - | - | - | 0.92 | 0.74–1.15 | 0.477 |
| Gender | ||||||||
| Female | 8811 | 2.33 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Male | 7178 | 2.00 | 0.90 | 0.88–0.93 | <0.001 | 0.90 | 0.88–0.93 | <0.001 |
| Age (year) | ||||||||
| 50–64 | 2657 | 0.56 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 65–74 | 6487 | 3.57 | 5.88 | 5.62–6.16 | <0.001 | 5.88 | 5.62–6.16 | <0.001 |
| 75+ | 6845 | 8.67 | 13.92 | 13.28–14.59 | <0.001 | 13.92 | 13.28–14.60 | <0.001 |
| Income level (NTD) a | ||||||||
| ≤21,000 | 10,557 | 2.77 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 21,001–33,000 | 2692 | 1.54 | 0.78 | 0.75–0.82 | <0.001 | 0.78 | 0.75–0.82 | <0.001 |
| ≥33,001 | 2740 | 1.52 | 0.87 | 0.84–0.91 | <0.001 | 0.87 | 0.84–0.91 | <0.001 |
| Urbanization | ||||||||
| Level 1 | 3915 | 1.93 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Level 2 | 4633 | 1.95 | 1.01 | 0.97–1.05 | 0.731 | 1.01 | 0.97–1.05 | 0.733 |
| Level 3 | 2397 | 2.09 | 1.00 | 0.95–1.05 | 0.997 | 1.00 | 0.95–1.05 | 0.994 |
| Level 4 | 2720 | 2.64 | 1.07 | 1.02–1.13 | 0.006 | 1.07 | 1.02–1.13 | 0.007 |
| Level 5 | 572 | 3.31 | 1.08 | 0.99–1.18 | 0.091 | 1.08 | 0.99–1.18 | 0.090 |
| Level 6 | 972 | 3.10 | 1.12 | 1.04–1.20 | 0.003 | 1.12 | 1.04–1.20 | 0.003 |
| Level 7 | 780 | 2.73 | 1.05 | 0.97–1.13 | 0.264 | 1.05 | 0.97–1.13 | 0.263 |
| DCSI score b | ||||||||
| 0 | 7311 | 1.64 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| 1 | 3510 | 2.23 | 1.09 | 1.04–1.13 | <0.001 | 1.09 | 1.04–1.13 | <0.001 |
| 2+ | 5168 | 3.92 | 1.38 | 1.32–1.44 | <0.001 | 1.38 | 1.32–1.44 | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | ||||||||
| No | 6976 | 1.72 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 9013 | 2.72 | 0.97 | 0.94–1.01 | 0.112 | 0.97 | 0.94–1.01 | 0.112 |
| Hyperlipidemia | ||||||||
| No | 12,577 | 2.17 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 3412 | 2.17 | 0.91 | 0.87–0.94 | <0.001 | 0.91 | 0.87–0.94 | <0.001 |
| Hyperuricemia | ||||||||
| No | 15,821 | 2.17 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 168 | 2.63 | 1.05 | 0.91–1.23 | 0.498 | 1.05 | 0.91–1.23 | 0.499 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | ||||||||
| No | 13,905 | 1.99 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 2084 | 5.69 | 1.45 | 1.38–1.52 | <0.001 | 1.45 | 1.38–1.52 | <0.001 |
| Coronary artery disease | ||||||||
| No | 13,744 | 2.04 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 2245 | 3.52 | 0.95 | 0.91–1.00 | 0.049 | 0.95 | 0.91–1.00 | 0.049 |
| Arrhythmia | ||||||||
| No | 14,787 | 2.10 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 1202 | 3.83 | 1.05 | 0.99–1.11 | 0.129 | 1.05 | 0.99–1.11 | 0.129 |
| Heart failure | ||||||||
| No | 15,331 | 2.12 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 658 | 4.72 | 0.93 | 0.85–1.01 | 0.071 | 0.93 | 0.85–1.01 | 0.071 |
| Anxiety | ||||||||
| No | 13,457 | 2.03 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 2532 | 3.46 | 1.44 | 1.38–1.50 | <0.001 | 1.44 | 1.38–1.50 | <0.001 |
| Depression | ||||||||
| No | 15,820 | 2.16 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 169 | 4.49 | 1.58 | 1.35–1.84 | <0.001 | 1.58 | 1.35–1.84 | <0.001 |
| COPD b | ||||||||
| No | 14,266 | 2.06 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 1723 | 3.90 | 1.08 | 1.02–1.13 | 0.004 | 1.08 | 1.02–1.13 | 0.004 |
| Chronic kidney disease | ||||||||
| No | 15,745 | 2.16 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 244 | 4.17 | 0.92 | 0.81–1.05 | 0.194 | 0.92 | 0.81–1.05 | 0.195 |
| Obesity | ||||||||
| No | 15,943 | 2.17 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 46 | 1.43 | 0.94 | 0.71–1.26 | 0.699 | 0.95 | 0.71–1.26 | 0.701 |
| Alcoholism | ||||||||
| No | 15,979 | 2.17 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Yes | 10 | 2.29 | 1.69 | 0.91–3.14 | 0.098 | 1.69 | 0.91–3.14 | 0.098 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, K.-H.; Tsai, Y.-F.; Lee, C.B.; Gau, S.-Y.; Tsai, T.-H.; Chung, N.-J.; Lee, C.-Y. The Correlation between Metformin Use and Incident Dementia in Patients with New-Onset Diabetes Mellitus: A Population-Based Study. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 738. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13050738
Huang K-H, Tsai Y-F, Lee CB, Gau S-Y, Tsai T-H, Chung N-J, Lee C-Y. The Correlation between Metformin Use and Incident Dementia in Patients with New-Onset Diabetes Mellitus: A Population-Based Study. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2023; 13(5):738. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13050738
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Kuang-Hua, Ya-Fang Tsai, Chiachi Bonnie Lee, Shuo-Yan Gau, Tung-Han Tsai, Ning-Jen Chung, and Chien-Ying Lee. 2023. "The Correlation between Metformin Use and Incident Dementia in Patients with New-Onset Diabetes Mellitus: A Population-Based Study" Journal of Personalized Medicine 13, no. 5: 738. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13050738
APA StyleHuang, K.-H., Tsai, Y.-F., Lee, C. B., Gau, S.-Y., Tsai, T.-H., Chung, N.-J., & Lee, C.-Y. (2023). The Correlation between Metformin Use and Incident Dementia in Patients with New-Onset Diabetes Mellitus: A Population-Based Study. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 13(5), 738. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13050738








