Comparison of the Concordance of Allergic Diseases between Monozygotic and Dizygotic Twins: A Cross-Sectional Study Using KoGES HTS Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population and Data Collection
2.2. Participant Selection
2.3. Survey
2.4. Exposure
2.5. Outcome
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kay, A.B. 100 years of ‘Allergy’: Can von Pirquet’s word be rescued? Clin. Exp. Allergy 2006, 36, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, B.R. The allergic march: Can we prevent allergies and asthma? Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2011, 44, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawankar, R.; Canonica, G.W.; Holgate, S.T.; Lockey, R.F.; Blaiss, M. The World Allergy Organization (WAO) White Book on Allergy; World Allergy Organisation: Milwaukee, WI, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Leonardi, A.; Castegnaro, A.; Valerio, A.L.; Lazzarini, D. Epidemiology of allergic conjunctivitis: Clinical appearance and treatment patterns in a population-based study. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 15, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lockett, G.A.; Patil, V.K.; Soto-Ramirez, N.; Ziyab, A.H.; Holloway, J.W.; Karmaus, W. Epigenomics and allergic disease. Epigenomics 2013, 5, 685–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asher, M.I.; Montefort, S.; Bjorksten, B.; Lai, C.K.; Strachan, D.P.; Weiland, S.K.; Williams, H.; Group, I.P.T.S. Worldwide time trends in the prevalence of symptoms of asthma, allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, and eczema in childhood: ISAAC Phases One and Three repeat multicountry cross-sectional surveys. Lancet 2006, 368, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, N.; Ait-Khaled, N.; Beasley, R.; Mallol, J.; Keil, U.; Mitchell, E.; Robertson, C.; Group, I.P.T.S. Worldwide trends in the prevalence of asthma symptoms: Phase III of the International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC). Thorax 2007, 62, 758–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.; Wong, G.W. Environmental Influences and Allergic Diseases in the Asia-Pacific Region: What Will Happen in Next 30 Years? Allergy Asthma. Immunol. Res. 2022, 14, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-S.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.-W.; Hong, S.-C.; Kim, S.-Y.; Lee, K.-H. The Prevalence of Allergic Diseases in Children Living In Jeju. Pard 2012, 22, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrine, N.; Portelli, M.A.; John, C.; Soler Artigas, M.; Bennett, N.; Hall, R.; Lewis, J.; Henry, A.P.; Billington, C.K.; Ahmad, A.; et al. Moderate-to-severe asthma in individuals of European ancestry: A genome-wide association study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paternoster, L.; Standl, M.; Waage, J.; Baurecht, H.; Hotze, M.; Strachan, D.P.; Curtin, J.A.; Bonnelykke, K.; Tian, C.; Takahashi, A.; et al. Multi-ancestry genome-wide association study of 21,000 cases and 95,000 controls identifies new risk loci for atopic dermatitis. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1449–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waage, J.; Standl, M.; Curtin, J.A.; Jessen, L.E.; Thorsen, J.; Tian, C.; Schoettler, N.; The 23andMe Research Team; AAGC Collaborators; Flores, C.; et al. Genome-wide association and HLA fine-mapping studies identify risk loci and genetic pathways underlying allergic rhinitis. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1072–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, W.; Fesinmeyer, M.; Reed, K.; Hampson, L.; Carlsten, C. Family history as a predictor of asthma risk. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2003, 24, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.; Ki, M. Population Attributable Fraction of Helicobacter pylori Infection-Related Gastric Cancer in Korea: A Meta-Analysis. Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 53, 744–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.A.; Ko, S.Y.; Suh, Y.J.; Kim, S.; Park, J.H.; Park, H.R.; Seo, J.; Choi, H.G.; Kang, H.S.; Lim, H.; et al. PIK3CA Mutation as Potential Poor Prognostic Marker in Asian Female Breast Cancer Patients Who Received Adjuvant Chemotherapy. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 2895–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkes, C.H. Twin studies in diabetes mellitus. Diabet. Med. 1997, 14, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, M.F.; Ballestar, E.; Paz, M.F.; Ropero, S.; Setien, F.; Ballestar, M.L.; Heine-Suner, D.; Cigudosa, J.C.; Urioste, M.; Benitez, J.; et al. Epigenetic differences arise during the lifetime of monozygotic twins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 10604–10609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppelman, G.H.; Los, H.; Postma, D.S. Genetic and environment in asthma: The answer of twin studies. Eur. Respir. J. 1999, 13, 2–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, R.; Hesser, L.A.; He, Z.; Zhou, X.; Nadeau, K.C.; Nagler, C.R. Fecal microbiome and metabolome differ in healthy and food-allergic twins. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e141935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Han, B.G.; Ko, G.E.S.g. Cohort Profile: The Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KoGES) Consortium. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Choi, H.G.; Lim, H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, S.J.; Nam, E.S.; Min, K.W.; Park, H.Y.; et al. Comparison of the Concordance of Cardiometabolic Diseases and Physical and Laboratory Examination Findings between Monozygotic and Dizygotic Korean Adult Twins: A Cross-Sectional Study Using KoGES HTS Data. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.G.; Kim, S.Y.; Lim, H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, S.J.; Nam, E.S.; Min, K.W.; Park, H.Y.; Kim, N.Y.; et al. Comparison of Concordance of Peptic Ulcer Disease, Non-Adenomatous Intestinal Polyp, and Gallstone Disease in Korean Monozygotic and Dizygotic Twins: A Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.G.; Kim, S.Y.; Kwon, B.C.; Kang, H.S.; Lim, H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, S.J.; Nam, E.S.; Min, K.W.; et al. Comparison of the Coincidence of Osteoporosis, Fracture, Arthritis Histories, and DEXA T-Score between Monozygotic and Dizygotic Twins: A Cross-Sectional Study Using KoGES HTS Data. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, J.; Cho, S.I.; Lee, K.; Ha, M.; Choi, E.Y.; Choi, J.S.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.; Hong, K.S.; Kim, Y.; et al. Healthy Twin: A twin-family study of Korea--protocols and current status. Twin Res. Hum. Genet. 2006, 9, 844–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.M.; Lee, D.; Lee, M.K.; Lee, K.; Lee, H.J.; Hong, E.J.; Han, B.; Sung, J. Validity of the zygosity questionnaire and characteristics of zygosity-misdiagnosed twin pairs in the Healthy Twin Study of Korea. Twin Res. Hum. Genet. 2010, 13, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopp, R.J.; Bewtra, A.K.; Watt, G.D.; Nair, N.M.; Townley, R.G. Genetic analysis of allergic disease in twins. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1984, 73, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.H.; Wang, J.L.; Chen, H.H.; Hsu, J.Y.; Chao, W.C. Shared prenatal impacts among childhood asthma, allergic rhinitis and atopic dermatitis: A population-based study. Allergy Asthma. Clin. Immunol. 2019, 15, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iweala, O.I.; Nagler, C.R. The Microbiome and Food Allergy. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 37, 377–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crede, R.H.; Carman, C.T.; Whaley, R.D.; Schumacher, I.C. Dissimilar allergic disease in identical twins; a study of psychosomatic aspects. Calif. Med. 1953, 78, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Strachan, D.P.; Wong, H.J.; Spector, T.D. Concordance and interrelationship of atopic diseases and markers of allergic sensitization among adult female twins. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001, 108, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Tsai, H.J.; Hong, X.; Wang, B.; Fang, Y.; Liu, X.; Pongracic, J.A.; Wang, X. Genetic and environmental contributions to allergen sensitization in a Chinese twin study. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2009, 39, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantani, A. The growing genetic links and the early onset of atopic diseases in children stress the unique role of the atopic march: A meta-analysis. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 1999, 9, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaminsky, Z.A.; Tang, T.; Wang, S.C.; Ptak, C.; Oh, G.H.; Wong, A.H.; Feldcamp, L.A.; Virtanen, C.; Halfvarson, J.; Tysk, C.; et al. DNA methylation profiles in monozygotic and dizygotic twins. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVries, A.; Vercelli, D. Epigenetics in allergic diseases. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2015, 27, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogt, G.; Huber, M.; Thiemann, M.; van den Boogaart, G.; Schmitz, O.J.; Schubart, C.D. Production of different phenotypes from the same genotype in the same environment by developmental variation. J. Exp. Biol. 2008, 211, 510–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristics | Total Participants | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monozygotic Twin | Dizygotic Twin | p-Value | ||
| Age (years old, n, %) | 0.004 * | |||
| 20–24 | 6 (0.6) | 0 (0) | ||
| 25–29 | 68 (6.5) | 4 (1.6) | ||
| 30–34 | 362 (34.4) | 87 (35.7) | ||
| 35–39 | 244 (23.2) | 65 (26.6) | ||
| 40–44 | 139 (13.2) | 36 (14.8) | ||
| 45–49 | 131 (12.4) | 20 (8.2) | ||
| 50–54 | 82 (7.8) | 22 (9) | ||
| 55–59 | 14 (1.3) | 10 (4.1) | ||
| 60–64 | 4 (0.4) | 0 (0) | ||
| 65+ | 2 (0.2) | 0 (0) | ||
| Sex (n, %) | 0.015 * | |||
| Males | 386 (36.7) | 110 (45.1) | ||
| Females | 666 (63.3) | 134 (54.9) | ||
| Income (n, %) | 0.984 | |||
| <2 million (won) | 349 (33.2) | 81 (33.2) | ||
| 2 to <3 million (won) | 284 (27.0) | 68 (27.9) | ||
| 3 to <4 million (won) | 214 (20.3) | 50 (20.5) | ||
| ≥4 million (won) | 205 (19.5) | 45 (18.4) | ||
| Education (n, %) | 0.752 | |||
| Under high school | 120 (11.4) | 25 (10.2) | ||
| Graduated from High school | 371 (35.3) | 92 (37.7) | ||
| Commercial college-Dropped out of college | 123 (11.7) | 32 (13.1) | ||
| Graduated from High school | 436 (41.5) | 95 (38.9) | ||
| Marriage (n, %) | 0.325 | |||
| Unmarried | 247 (23.5) | 50 (20.5) | ||
| Married | 738 (70.2) | 173 (70.9) | ||
| Divorced or others | 67 (6.4) | 21 (8.6) | ||
| Physical Activity | ||||
| Hard (hour/1 week, mean, SD) | 3.1 (6.8) | 4.7 (9.7) | 0.013 * | |
| Moderate (hour/1 week, mean, SD) | 5.8 (10.5) | 6.2 (10.2) | 0.606 | |
| Walk (hour/1 week, mean, SD) | 6.1 (9.6) | 6.8 (10.9) | 0.299 | |
| Sit (hour/1 week, mean, SD) | 40.1 (22) | 37.9 (20.7) | 0.153 | |
| Obesity (n, %) | 0.235 | |||
| Underweight (BMI < 18.5) | 27 (2.6) | 5 (2) | ||
| Normal (BMI ≥ 18.5 to <23) | 510 (48.5) | 113 (46.3) | ||
| Overweight (BMI ≥ 23 to <25) | 221 (21) | 68 (27.9) | ||
| Obese I (BMI ≥ 25 to <30) | 262 (24.9) | 52 (21.3) | ||
| Obese II (BMI ≥ 30) | 32 (3) | 6 (2.5) | ||
| Smoking status (n, %) | 0.151 | |||
| Nonsmoker | 691 (65.6) | 145 (59.4) | ||
| Past smoker | 109 (10.4) | 33 (13.5) | ||
| Current smoker | 252 (24.0) | 66 (27.0) | ||
| Frequency of drinking alcohol (n, %) | 0.326 | |||
| Nondrinker | 304 (28.9) | 64 (26.2) | ||
| ≤1 time per month | 238 (22.6) | 46 (18.9) | ||
| 2–4 times per month | 301 (28.6) | 80 (32.8) | ||
| ≥2 times per week | 209 (19.9) | 54 (22.1) | ||
| Sleeping hours (n, %) | 0.388 | |||
| ≤5 h | 54 (5.1) | 16 (6.6) | ||
| 6–7 h | 620 (58.9) | 146 (59.8) | ||
| 8–9 h | 350 (33.3) | 72 (29.5) | ||
| ≥10 h | 28 (2.7) | 10 (4.1) | ||
| Asthma (n, %) | 42 (4.0) | 6 (2.5) | 0.346 | |
| Allergic rhinitis (n, %) | 189 (18.0) | 34 (13.9) | 0.158 | |
| Atopic dermatitis (n, %) | 72 (6.8) | 12 (4.9) | 0.314 | |
| Allergic conjunctivitis (n, %) | 66 (6.3) | 10 (4.1) | 0.227 | |
| Acetaminophen prescription ≥ 3 months (n, %) | 44 (4.2) | 6 (2.5) | 0.268 | |
| Aspirin prescription ≥ 3 months (n, %) | 33 (3.1) | 3 (1.2) | 0.129 | |
| NSAID prescription ≥ 3 months (n, %) | 18 (1.7) | 8 (3.3) | 0.128 | |
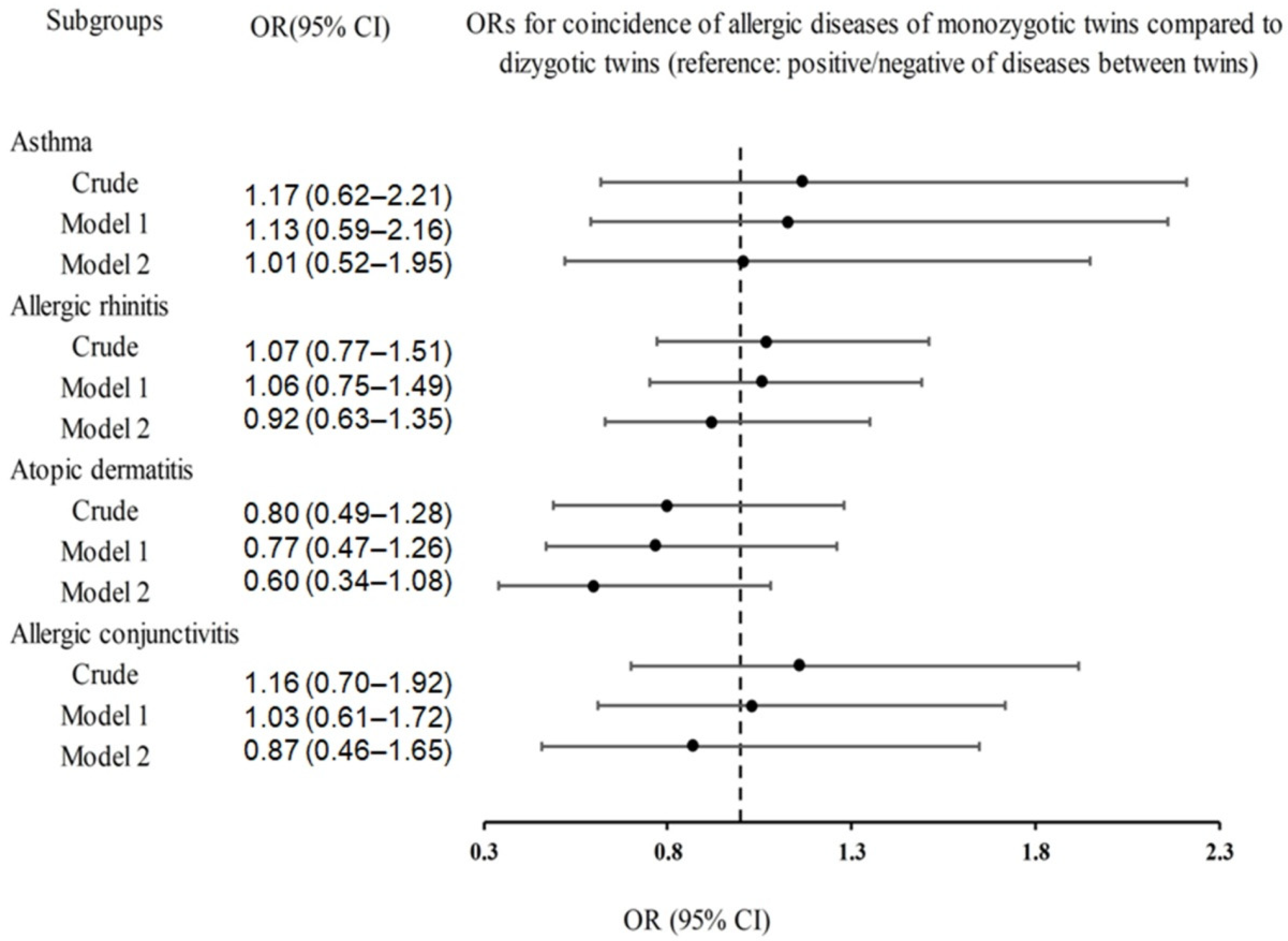
| Coincidence of Diseases | Monozygotic Twin | Dizygotic Twin | Odds Ratios | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | n (%) | Crude | p-Value | Model 1 * | p-Value | Model 2 † | p-Value | ||
| Asthma | |||||||||
| concordant | 992/1052 (94.3) | 232/244 (95.1) | 1.17 (0.62–2.21) | 0.630 | 1.13 (0.59–2.16) | 0.711 | 1.01 (0.52–1.95) | 0.979 | |
| discordant | 60/1052 (5.7) | 12/244 (4.9) | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Allergic rhinitis | |||||||||
| concordant | 815/1052 (77.5) | 192/244 (78.7) | 1.07 (0.77–1.51) | 0.681 | 1.06 (0.75–1.49) | 0.756 | 0.92 (0.63–1.35) | 0.670 | |
| discordant | 237/1052 (22.5) | 52/244 (21.3) | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Atopic dermatitis | |||||||||
| concordant | 968/1052 (92) | 220/244 (90.2) | 0.80 (0.49–1.28) | 0.347 | 0.77 (0.47–1.26) | 0.300 | 0.60 (0.34–1.08) | 0.090 | |
| discordant | 84/1052 (8) | 24/244 (9.8) | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Allergic conjunctivitis | |||||||||
| concordant | 953/1052 (90.6) | 224/244 (91.8) | 1.16 (0.70–1.92) | 0.554 | 1.03 (0.61–1.72) | 0.918 | 0.87 (0.46–1.65) | 0.674 | |
| discordant | 99/1052 (9.4) | 20/244 (8.2) | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
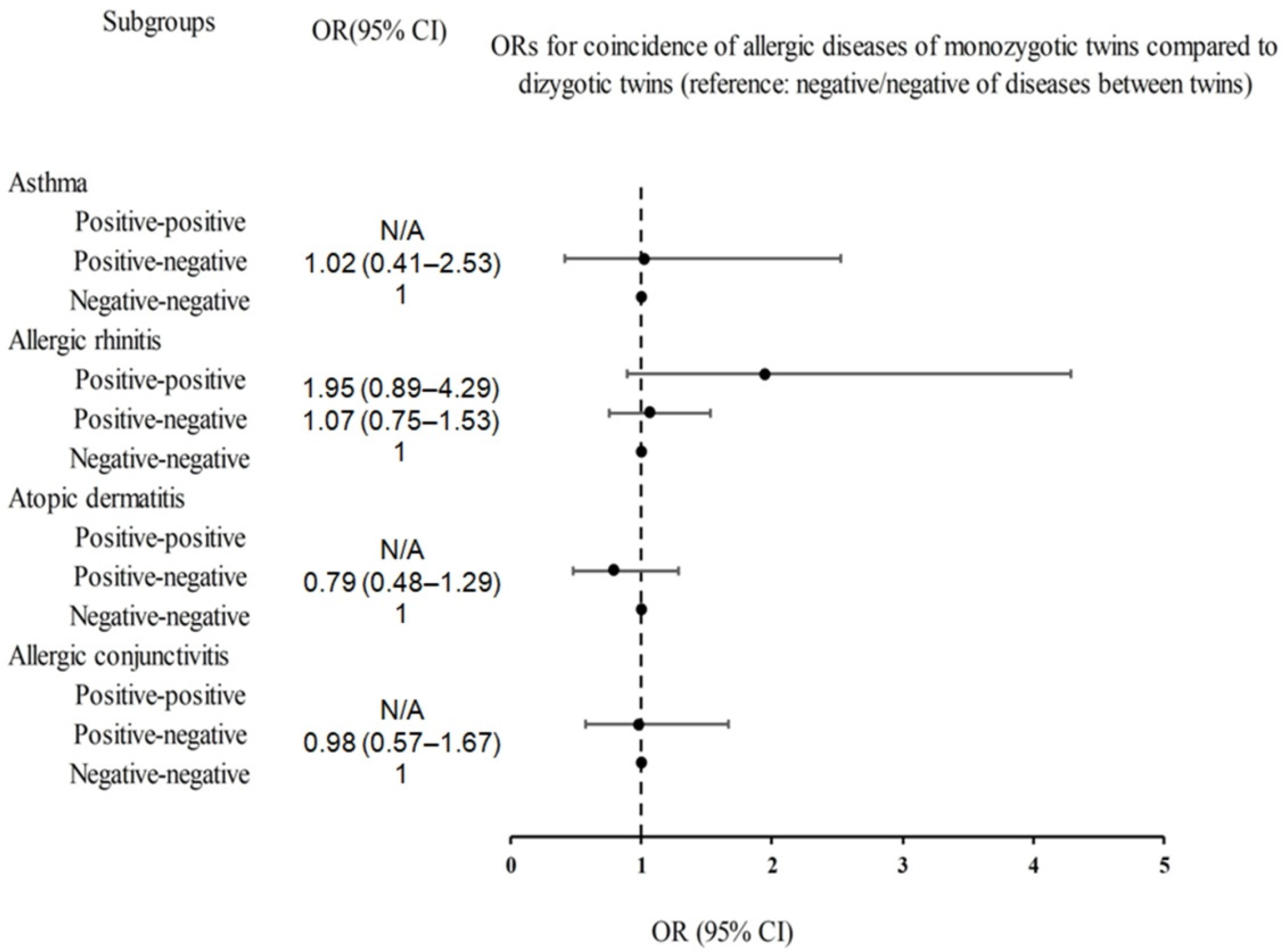
| Concordance of Diseases | Monozygotic Twin | Dizygotic Twin | Odds Ratios (95% CI) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | n (%) | Crude | p-Value | Model 1 * | p-Value | Model 2 † | p-Value | ||
| Asthma | |||||||||
| Positive-positive | 12/1052 (1.1) | 0/244 (0) | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| Positive-negative | 60/1052 (5.7) | 12/244 (4.9) | 1.18 (0.63–2.24) | 0.603 | 1.14 (0.60–2.18) | 0.690 | 1.02 (0.41–2.53) | 0.97 | |
| Negative-negative | 980/1052 (93.2) | 232/244 (95.1) | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Allergic rhinitis | |||||||||
| Positive-positive | 70/1052 (6.7) | 8/244 (3.3) | 2.16 (1.02–4.57) | 0.044 * | 2.14 (1.00–4.57) | 0.049* | 1.95 (0.89–4.29) | 0.097 | |
| Positive-negative | 237/1052 (22.5) | 52/244 (21.3) | 1.13 (0.80–1.58) | 0.496 | 1.11 (0.79–1.57) | 0.557 | 1.07 (0.75–1.53) | 0.697 | |
| Negative-negative | 745/1052 (70.8) | 184/244 (75.4) | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Atopic dermatitis | |||||||||
| Positive-positive | 30/1052 (2.9) | 0/244 (0) | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| Positive-negative | 84/1052 (8) | 24/244 (9.8) | 0.82 (0.51–1.32) | 0.417 | 0.80 (0.49–1.31) | 0.375 | 0.79 (0.48–1.29) | 0.514 | |
| Negative-negative | 938/1052 (89.2) | 220/244 (90.2) | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| Allergic conjunctivitis | |||||||||
| Positive-positive | 16/1052 (1.5) | 0/244 (0) | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| Positive-negative | 99/1052 (9.4) | 20/244 (8.2) | 1.18 (0.72–1.96) | 0.511 | 1.05 (0.63–1.76) | 0.854 | 0.98 (0.57–1.67) | 0.927 | |
| Negative-negative | 937/1052 (89.1) | 224/244 (91.8) | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, E.J.; Kim, J.-H.; Choi, H.G.; Kang, H.S.; Lim, H.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, S.-J.; Nam, E.S.; Park, H.Y.; Kim, N.Y.; et al. Comparison of the Concordance of Allergic Diseases between Monozygotic and Dizygotic Twins: A Cross-Sectional Study Using KoGES HTS Data. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 721. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13050721
Lee EJ, Kim J-H, Choi HG, Kang HS, Lim H, Kim JH, Cho S-J, Nam ES, Park HY, Kim NY, et al. Comparison of the Concordance of Allergic Diseases between Monozygotic and Dizygotic Twins: A Cross-Sectional Study Using KoGES HTS Data. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2023; 13(5):721. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13050721
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Eun Jae, Joo-Hee Kim, Hyo Geun Choi, Ho Suk Kang, Hyun Lim, Ji Hee Kim, Seong-Jin Cho, Eun Sook Nam, Ha Young Park, Nan Young Kim, and et al. 2023. "Comparison of the Concordance of Allergic Diseases between Monozygotic and Dizygotic Twins: A Cross-Sectional Study Using KoGES HTS Data" Journal of Personalized Medicine 13, no. 5: 721. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13050721
APA StyleLee, E. J., Kim, J.-H., Choi, H. G., Kang, H. S., Lim, H., Kim, J. H., Cho, S.-J., Nam, E. S., Park, H. Y., Kim, N. Y., & Kwon, M. J. (2023). Comparison of the Concordance of Allergic Diseases between Monozygotic and Dizygotic Twins: A Cross-Sectional Study Using KoGES HTS Data. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 13(5), 721. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13050721









