Abstract
This study aimed to clarify the roles of high-risk human papillomavirus (HR-HPV) infection and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) exon 20 mutations in sinonasal inverted papilloma (IP) and sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma (SNSCC). Samples were collected from 20 cases with IP, 7 with IP and squamous cell carcinoma (IP-SCC), and 20 with SNSCC and examined for HPV infection and EGFR exon 20 mutations. Low- or high-risk HPV DNA was observed in 25% of IP, 57.1% of IP-SCC, and 35% of SNSCC cases. Transcriptionally active HR-HPV infections in IP-SCC and SNSCC, accompanied by p16 overexpression, were observed in 28.5% and 25% of cases, respectively. Heterozygous EGFR exon 20 amino acid insertions (ex20ins), located between amino acids 768–774, were observed in 45% of IP, 28.5% of IP-SCC, and 0% of SNSCC and chronic sinusitis cases. EGFR phosphorylation sites were located at tyrosine (Y) 845, Y1068, Y1086, and Y1197 and induced PI3K/AKT/mTOR activation. The phosphorylation pattern of EGFR with ex20ins resembled that of HPV-related SNSCC and oropharyngeal cancer. The transcriptionally active HR-HPV infection and ex20ins might be responsible for the pathogenesis of IP-SCC cases with different fashions. Since IP-SCC might be a multifactorial disease, further investigation is needed to understand IP-SCC etiology.
1. Introduction
Inverted Schneiderian papilloma (IP) is a benign neoplasm arising in the nasal cavity. Its etiology remains unclear, but several risk factors have been proposed, including human papillomavirus (HPV) infection and chronic inflammation [1,2]. A recent review revealed that 25–40% of cases with sinonasal papilloma have HPV infection [3].
In the clinical setting, IP sometimes accompanies synchronous and metachronous squamous cell carcinoma (IP-SCC). The rate of malignant transformation from IP to SCC has been estimated to be approximately 10% [3,4]. The detailed mechanism of malignant transformation is unclear, but several hypotheses have been proposed. The prevailing view is that high-risk (HR)-HPV infection might play a role; however, several contradictory results have been reported regarding HPV infection [5,6].
The molecular profiles of IP and IP-SCC suggest that mutations in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) exon 20, which promote an active kinase conformation, especially exon 20 insertions (ex20ins), are candidate etiological factors [6,7,8,9,10,11]. EGFR is a transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the ErbB family, which contains EGFR (also known as ErbB1/HER1), ErbB2 (HER2/neu), ErbB3 (HER3), and ErbB4 (HER4). EGFR activation leads to the stimulation of multiple intracellular signaling pathways, including PI3K/AKT and Jak-STAT. High EGFR expression and increased EGFR copy number account for 90% and 21% of cases of head and neck SCC, respectively; however, EGFR mutations are detected in only 1% of head and neck cancer cases [12].
Udager et al. first reported the presence of activating EGFR mutations in 88% of IP and 77% of IP-SCC cases, and this phenomenon might be distinct in IP and IP-malignant transformation among sinonasal squamous tumors [10]. Recent investigations also demonstrated that EGFR mutations, especially ex20ins, are frequently observed in IP and IP-sinonasal SCC (SNSCC) but not in SNSCC without IP lesions [6,13,14,15,16]. The significance of EGFR mutations in the etiology of IP and its malignant transformation remains unclear, especially ex20ins and the downstream phosphorylation targets of ex20ins. On the contrary, approximately 90% of EGFR mutations in NSCLC are observed within the tyrosine kinase domain, and they are the possible genetic mutation targets for treatment. EGFR exon 19 deletions and L858R point mutation in exon 21 are predominant EGFR mutations, representing the favorable response to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). The ex20is has been reported as the subset of driver genes that account for 4% to 9% of NSCLC [17]. Although previous target therapies against the ex20ins in NSCLC were intensively investigated, the response rates and prognosis have been unsatisfactory compared to classical TKIs to other EGFR mutations [17]. Thus, it is important to clarify the status of the ex20ins in sinonasal lesions. Interestingly, several reports have suggested that EGFR mutations and HPV infection are mutually exclusive [6,9,18].
The present study investigated HR-HPV infection and EGFR exon 20 mutations to shed light on their roles in the pathogenesis of IP and IP-SCC.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
Samples were collected from the following patients at our hospital from 2008 to 2021: 20 with IP, 7 with IP-SCC, 20 with SNSCC, and 6 with chronic sinusitis as controls. These patients had no history of previous surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy. SNSCC patients were independent from those with IP-SCC, and the SNSCC samples did not contain any IP part. All specimens were frozen immediately in liquid nitrogen after surgical excision or biopsy and stored at −80 °C until analysis.
This study was conducted with the approval of the Institutional Review Board of the University of Ryukyus (project identification code 156). Written informed consent was obtained from all participants prior to sample collection.
2.2. HPV Infection Analysis
HPV-related tumors for IP, IP-SCC, or SNSCC were defined as being positive for HPV DNA detected by PCR or DNA in situ hybridization (ISH) and p16 overexpression.
2.2.1. Detection of HPV DNA, Measurement of Viral DNA Load, and Physical Status of HPV
Extracted DNA was subjected to PCR using the degenerate consensus primer sets MY09/MY11 and GP5+/GP6+, which were designed to amplify the L1 region, as in previous studies [19,20]. We developed a new quantitative real-time PCR assay system for the E6 and E2 genes of HPV-18, -33, and -52 in addition to HPV-16 [19]. See the Supplementary Materials for details (Table S1).
2.2.2. p16 Immunohistochemistry and ISH with HPV DNA Probes
Immunohistochemistry for p16INK4a expression was performed with a CINTec®p16 Histology Kit (Roche Applied Science, Penzberg, Germany) [19]. The cutoff point for p16 overexpression was defined as diffuse (≥75%) tumor expression with at least moderate (+2/3) staining intensity, according to the 8th edition of the American Joint Committee on Cancer classification [21,22].
Because there were not enough frozen samples for PCR in three patients, DNAs extracted from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) samples were used for PCR analysis; HPV-DNA ISH was used to confirm the presence of HR-HPV infection in these samples. Detailed methods for DNA extraction from FFPE samples are provided in the Supplementary Materials.
ISH of HR-HPV DNA was performed with a GenPoint HPV Biotinylated DNA Probe (Dako; Agilent Technologies, Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA), which can detect HPV-16, -18, -31, -33, -35, -39, -45, -51, -52, -56, -58, -59, and -68 in FFPE sections, as described previously [18].
2.3. EGFR Mutation Analysis
2.3.1. Sanger Sequencing of EGFR Exon 20
PCR was performed with EGFR exon 20-F and 20-R primers (0.24 μM each, Table S1) in a volume of 12.5 μL containing 6.3 μL GoTaq® Green Master Mix (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) and 10 ng genomic DNA. See the Supplementary Materials for details.
2.3.2. Screening of EGFR Phosphorylation Sites
A RayBio Human EGFR Phosphorylation Antibody Array 1 Assay (RayBiotech, Inc., Peachtree Corners, GA, USA) was used to screen specific EGFR phosphorylation sites (Y845, Y922, Y1045, Y1068, Y1086, Y1173, and Y1046/47) in two IP-SCC patients with ex20ins. ErbB2, ErbB3, and ErbB4 phosphorylation were also investigated simultaneously. See the Supplementary Materials for details.
2.3.3. Western Blot Analysis
The phosphorylation of EGFR and EGFR-related pathway proteins in IP, IP-SCC, SNSCC, and chronic sinusitis with/without ex20ins were examined by western blotting. EGFR, phosphorylated (p)-EGFR (Y845, Y1068, Y1086, and Y1197), Akt, p-Akt (serine [S473]), 4E-BP1, p-4E-BP1 (threonine [T]37/46), STAT3, and p-STAT3 (Y705) were selected based on the RayBio Human EGFR Phosphorylation Antibody Array 1 results. See the Supplementary Materials for details.
2.3.4. Immunohistochemistry for EGFR and p-EGFR
Four-micrometer-thick sections of FFPE samples were deparaffinized in xylene and hydrated in a graded alcohol series. Primary antibodies against EGFR (1:50 dilution, the same antibody used for western blotting) and p-EGFR (Y845, 1:50 dilution, the same antibody used for western blotting) were used. The immunohistochemical reaction was performed with a SAB-PO Kit (Nichirei Bioscience, Tokyo, Japan) [20].
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was conducted with SPSS 25.0 (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Pearson’s χ2-test was used for categorical data, and the Mann–Whitney U-test was used for continuous variables. p-values less than 0.05 were considered significant.
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics (Table 1)
Sixteen (80%) of 20 IP cases had Krouse T3 or T4 stage. Although all cases underwent endoscopic sinus surgery, one (5%) recurred after surgery. In IP-SCC, the chief tumor location was the maxillary sinus (four cases, 57%), and there were four cases (57%) alive without disease. All SNSCC cases were advanced with stage III (36.4%) or stage IV (63.6%), and there were 13 cases (65%) alive without disease. There was no significant difference in the primary tumor site among the three groups.

Table 1.
Patient characteristics.
Table 1.
Patient characteristics.
| Group | Number of Cases (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| IP | n = 20 | |
| Sex | Male/female | 16 (80)/4 (20) |
| Age, median (range) | 57 (33–80) years | |
| Krouse T classification | T1/T2/T3/T4 | 0/4/15/1 |
| Primary tumor site | Maxillary sinus | 14 (70.0) |
| Ethmoid sinus | 5 (25.0) | |
| Sphenoid sinus | 1 (5.0) | |
| Recurrence after surgery | 1 (5%) | |
| IP-SCC | n = 7 | |
| Sex | Male/female | 4/3 |
| Age, median (range) | 57 (46–91) years | |
| Primary tumor site | Maxillary sinus | 4 (57.1) |
| Ethmoid sinus | 2 (28.6) | |
| Sphenoid sinus | 1 (14.3) | |
| Treatment | Surgery + CRT | 2 |
| CRT/RT | 3 | |
| Other | 2 | |
| Prognosis | Alive without disease | 4 |
| Alive with disease | 1 | |
| Dead of disease | 2 | |
| SNSCC | n = 20 | |
| Sex | Male/female | 17 (93.3)/3(6.7) |
| Age, median (range) | 59 (35–81) years | |
| Primary tumor site | Maxillary sinus | 17(85.0) |
| Nasal cavity | 2 (10.0) | |
| Ethmoid sinus | 1 (5.0) | |
| SCC subtype | Poor/moderate/well | 2/11/7 |
| Clinical T classification | T1/T2/T3/T4 | 0/0/7/13 |
| Clinical N classification | N0/N1/N2/N3 | 12/5/3/0 |
| UICC Stage | I/II/III/IV | 0/0/6/14 |
| Treatment | Total maxillectomy | 1 (5.0) |
| CRT/RT | 17 (85.0) | |
| Other | 2 (10.0) | |
| Prognosis | Alive without disease | 13 (65.0) |
| Dead of disease | 6 (30.0) | |
| Intercurrent disease death | 1 (5.0) |
CRT, concurrent chemoradiotherapy; IP, inverted papilloma; RT, radiation therapy; SCC, squamous cell carcinoma; SN, sinonasal; UICC, Union for International Cancer Control (7th edition).
3.2. HPV Infection Analysis
3.2.1. HPV Infection in IP
Of the 20 patients with IP, HPV DNA was detected in 5 samples (25%) by PCR, 3 with HR-HPV (2 HPV-16 and 1 HPV-33), and 2 with low-risk HPV (HPV-6 and -11). However, the viral load could not be determined in the three HR-HPV cases because they were below the detection limit (Table 2).

Table 2.
HPV infection status.
The p16-positive cell rates in IP are shown in Table S2. Twenty-five percent of cases had ≥75% IP cells with p16 immunoreactivity; however, these cases had only weak staining, and there was no case with p16 overexpression (Figure 1A). There was also no significant relationship between p16 immunoreactivity and the presence of HR-HPV DNA (Table 2, Figure 1B). From these findings, no case was judged to have an HPV-related tumor.
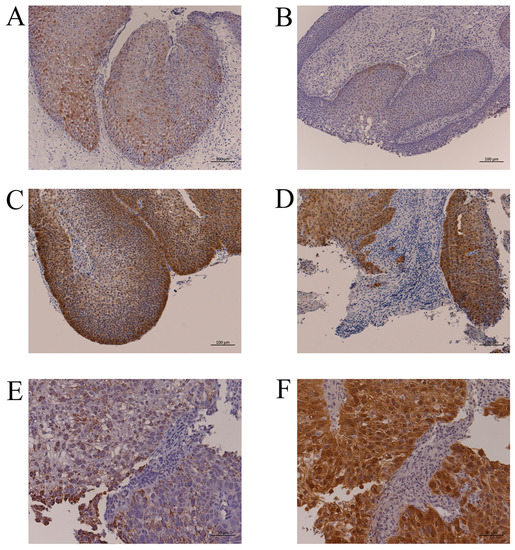
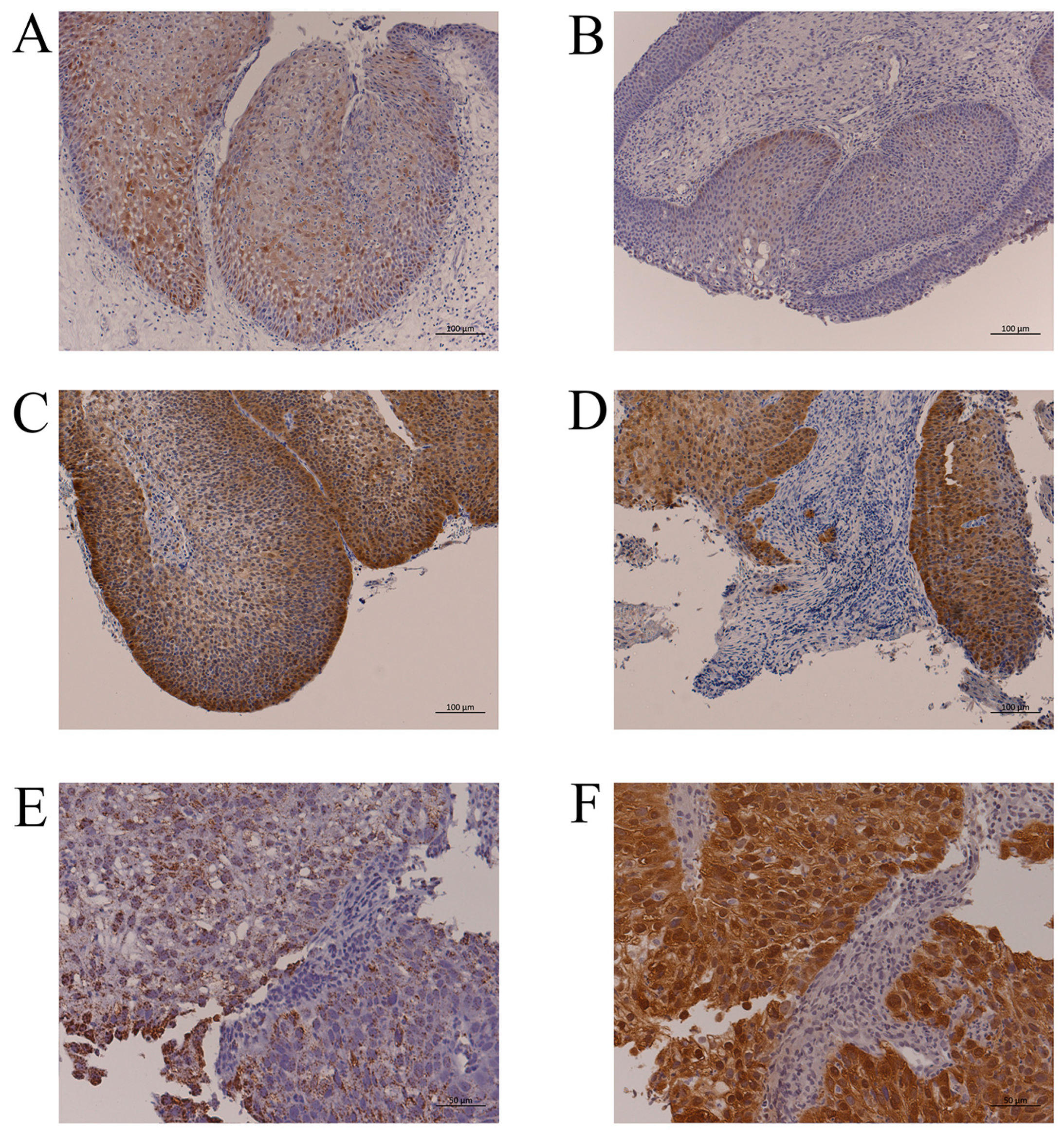
Figure 1.
Representative p16 immunohistochemistry and HPV-DNA ISH. (A): IP without HPV infection (IP-2, Table 2). More than 75% of IP cells had p16 immunoreactivity, but the staining intensity was weak. Bar, 100 µm. (B): IP with HPV-16 DNA by PCR (IP-5, Table 2). There were few p16-positive cells despite HPV infection. Bar, 100 µm. (C): p16 overexpression in the IP part of IP-SCC with HPV-18 infection (IP-SCC-3, Table 2). Bar, 100 µm. (D): p16 overexpression in the SCC part of IP-SCC with HPV-18 infection (IP-SCC-3, Table 2). Strong p16 immunoreactivity was observed in SCC and IP. Bar, 100 µm. (E): HPV-DNA ISH of SNSCC with HR-HPV infection (SNSCC-5, Table 2). A positive reaction was observed in all cancer cells. Bar, 50 µm. (F): p16 overexpression in SNSCC with HR-HPV infection (SNSCC-5). Cancer cells showed strong p16 immunoreactivity. Bar, 50 µm.
3.2.2. HPV Infection in IP-SCC
Of the seven patients with IP-SCC, four (57.1%) had HPV DNA: three with HR-HPV (HPV-16, -18, and -33) and one with low-risk HPV (HPV-11). The viral load of IP-SCC-1 (HPV-16) was low (Table 2), and p16 overexpression was not observed in this case. In the IP-SCC group, there were two cases with p16 overexpression (28.5%) who also had HR-HPV DNA by PCR and/or ISH.
The HPV-18-positive case (IP-SCC-3) had a viral load of 2.63 × 103 copies/ng DNA and an E2/E6 ratio of 8.0 × 10−4. In addition, p16 expression was moderate in the IP area (Figure 1C), whereas it was strong in the SCC area (Figure 1D). Thus, two IP-SCC patients (28.5%) were considered to have HPV-related tumors.
3.2.3. HPV Infection in SNSCC
Of the 20 patients with SNSCC, 7 (35%) had HR-HPV DNA (Table 2). Although HPV-16 was detected in SNSCC-7 and -8, their viral loads were relatively low, and they did not overexpress p16. The remaining five HR-HPV-positive cases (SNSCC-2 to -6) also had p16 overexpression. Compared with the cases without p16 overexpression (0.7–1.58 copies/ng DNA), the p16 overexpression cases had a relatively high viral load (1.41 × 102 to 1.63 × 106 copies/ng DNA). All cases with HR-HPV DNA showed integration with an E2/E6 ratio from 0 to 0.83. HPV-DNA ISH and p16 immunohistochemistry demonstrated that viral infection and p16 overexpression occurred in the same cancerous area (Figure 1E,F, SNSCC-5). Thus, HPV-related SNSCC was observed in 5 (25%) of 20 SNSCC cases.
3.3. Mutations in EGFR Exon 20
Heterozygous EGFR ex20ins were observed in nine IP cases (45%), two IP-SCC cases (28%), and zero SNSCC and chronic sinusitis cases (Table 3 and Table S3). A deduced amino acid substitution in EGFR was observed in five IP cases (25%), four IP-SCC cases (57.1%), one SNSCC case (4.5%), and zero chronic sinusitis cases (0%). EGFR ex20ins or substitutions were observed in 10 IP cases (50%), four IP-SCC cases (57.1%), and one SNSCC case (5%) (Table S3). There were significant differences in the frequency of these mutations between the IP and IP-SCC groups and the SNSCC group (p < 0.01, χ2 test).

Table 3.
EGFR mutations and HPV infection in individual patients.
Six different heterozygous EGFR ex20ins were observed in IP (Table 3, Figure S1), which were concentrated in the region encoding amino acids 768–774. Three cases had N771_H773dup, followed by two cases each with D770_N771insGF or H773_V774dup, and one case each with H773_V774insTH or S768_D770dup.
Two of the seven IP-SCC cases (28.6%) were heterozygous for EGFR ex20ins. Interestingly, the same mutation (S768_D770dup) was detected in both IP-SCC cases. Amino acid substitutions were also observed frequently in four of the seven IP-SCC cases (57.1%).
3.4. Screening of EGFR Phosphorylation Sites
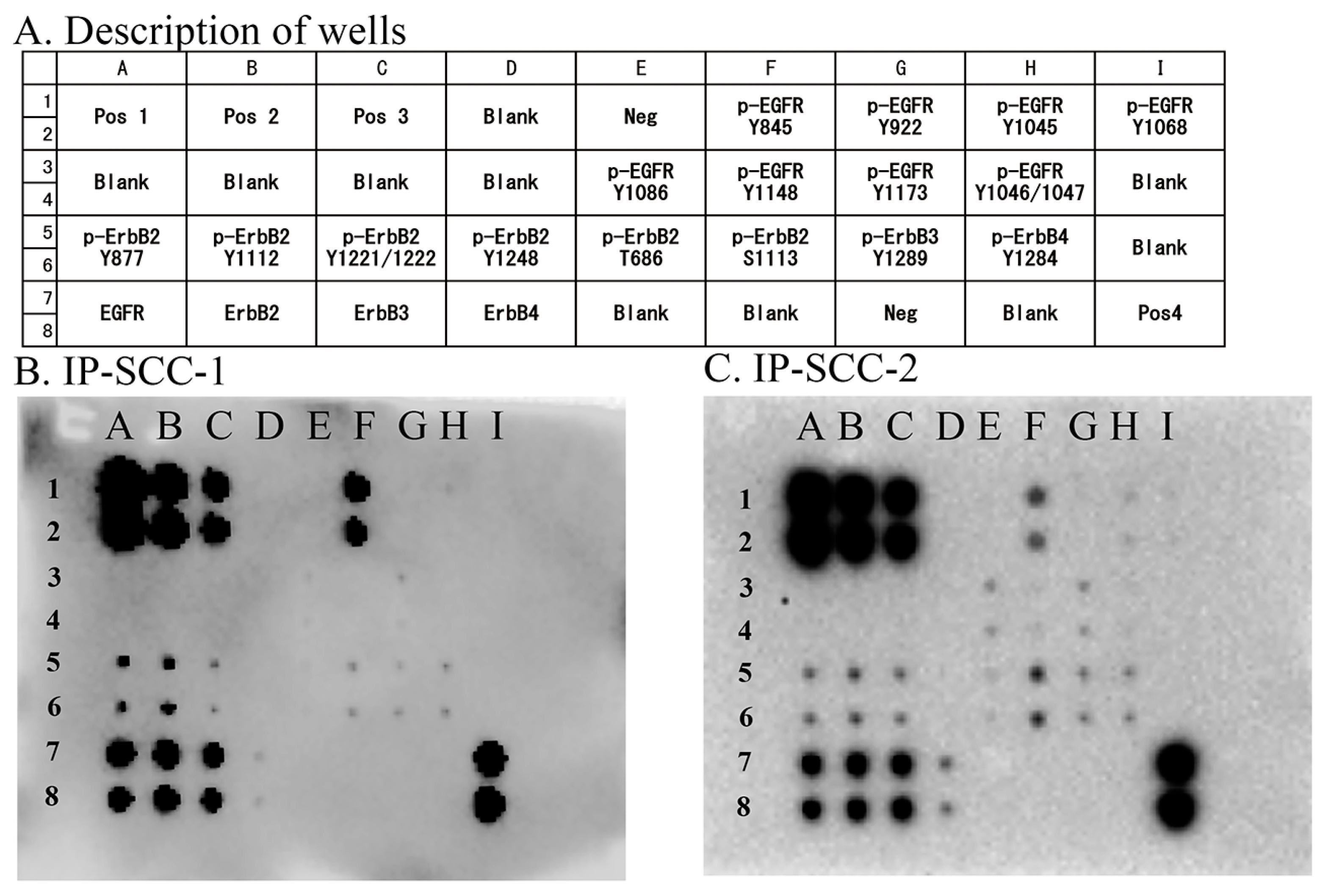
Eight EGFR phosphorylation sites were examined in the two IP-SCC cases carrying S768_D770dup. Of these phosphorylation sites, EGFR Y845 autophosphorylation was extensively observed in both cases (Figure 2). These cases also presented with ErbB2 (Y877, Y1112, Y1221/1222, T686, and S1113), ErbB3 (Y1289), and ErbB4 (Y1284) phosphorylation.
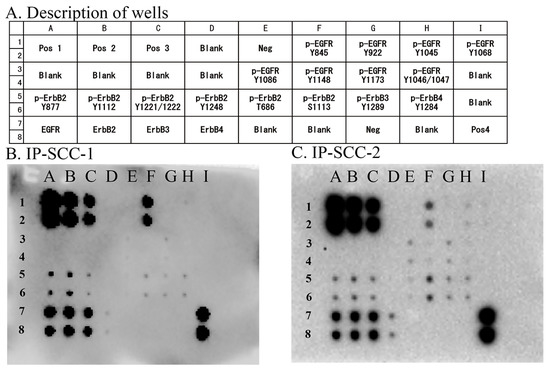
Figure 2.
EGFR phosphorylation sites in IP-SCC. Eight phosphorylation sites in EGFR were investigated using an EGFR Phosphorylation Antibody Array 1 Assay. (A): Description of each well. (B): Results for IP-SCC1. (C): Results for IP-SCC-2. Of the eight sites, Y845 phosphorylation (F1 and F2 wells) was observed in both cases. Neg, negative control; Pos, positive control. Each antibody is spotted in duplicate vertically.
3.5. Western Blot Analysis
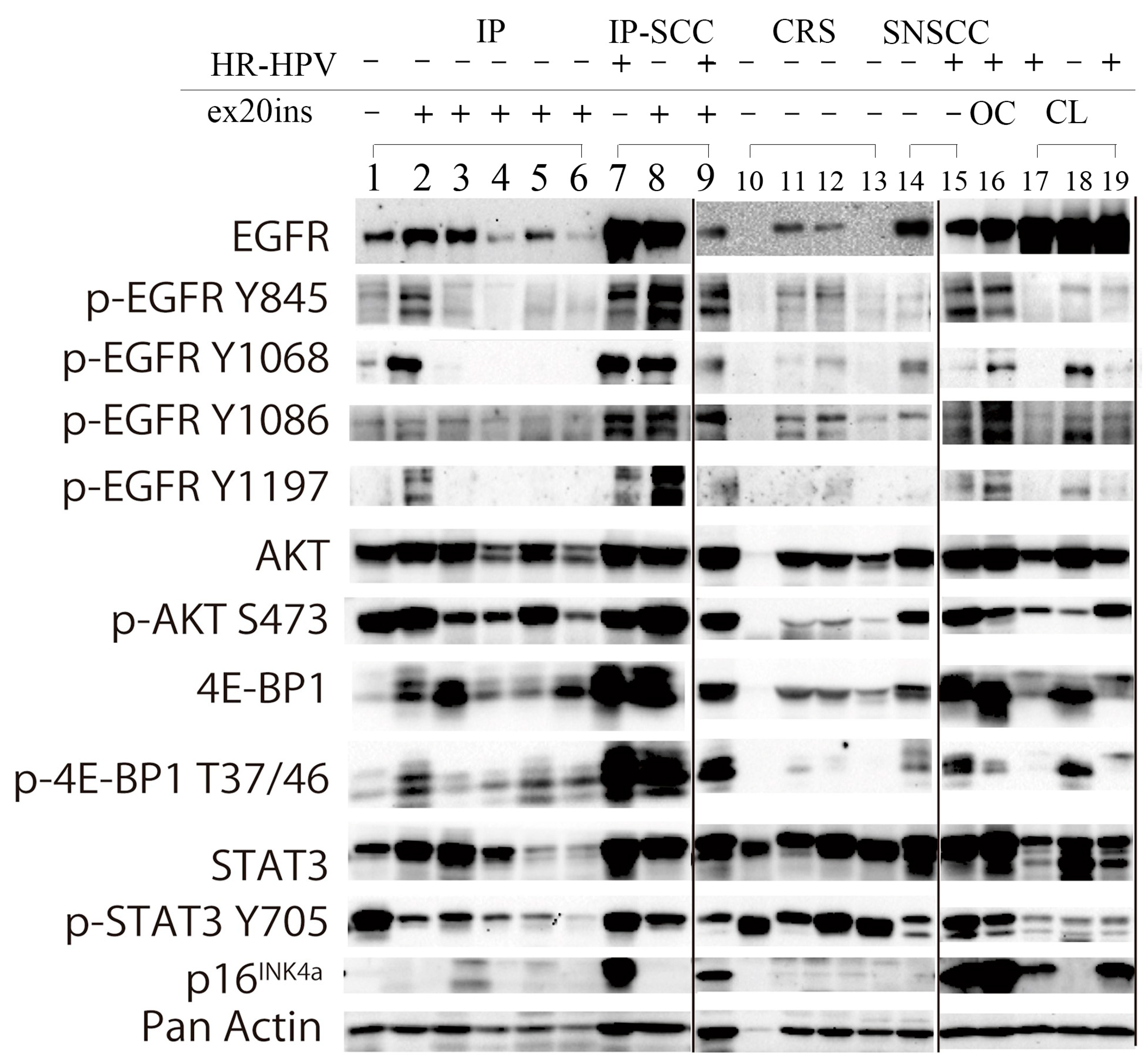
EGFR and the related phosphorylation status of the signaling pathway induced by ex20ins and HR-HPV infection were investigated by western blotting focusing on EGFR, p-EGFR (Y845, Y1068, Y1086, and Y1197), p-Akt (S473), p-4E-BP1 (T37/46), p-STAT3 (Y705), and p16INK4a in IP, IP-SCC, chronic sinusitis, and SNSCC (Figure 3).
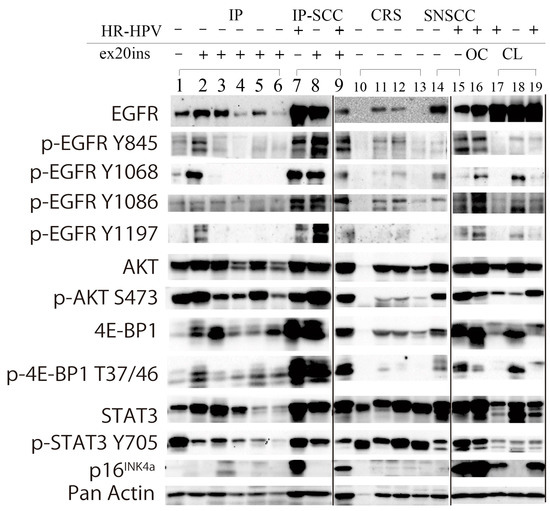
Figure 3.
Western blot analysis of IP, IP-SCC, SNSCC, and chronic rhinosinusitis cases. EGFR and the related phosphorylation status of the signaling pathway induced by ex20ins and transcriptionally active HR-HPV infection (HR-HPV) were investigated by western blotting in IP (lanes 1–6), IP-SCC (lanes 7–9), chronic sinusitis (lanes 10–13), and SNSCC (lanes 14 and 15) cases. EGFR was expressed in all IP, IP-SCC, and SNSCC cases, and two of four sinusitis samples. AKT and 4E-BP1 were expressed in all IP, IP-SCC, SNSCC, and chronic sinusitis cases. The transcriptionally active HR-HPV-positive clinical samples (lanes 7, 9, 15, and 16) also demonstrated high p-EGFR, p-AKT, and p-4E-BP1 levels, regardless of ex20ins status. Lane 1: IP-19. Lane 2: IP-6 with S768_D770dup. Lane 3: IP-2 with D770_N771insGF. Lane 4: IP-1 with N771_H773dup. Lane 5: IP-7 with H773_V774insTH. Lane 6: IP-5 with H773_V774dup and HPV-16 DNA. Lane 7: IP-SCC-3 with HPV-18 DNA. Lane 8: IP-SCC-2 with S768_D770dup. Lane 9: IP-SCC-1 with S768_D770dup and HPV-16 DNA. Lane 10: chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS)-2. Lane 11: CRS-3. Lane 12: CRS-4. Lane 13: CRS-5. Lane 14: SNSCC-12 without ex20ins or HR-HPV DNA. Lane 15: SNSCC-2 with HPV-16 DNA. Lane 16: oropharyngeal carcinoma with HPV-16 DNA. Lane 17: UMSCC-47 cell line (a gift from Professor Thomas E. Carey, University of Michigan) derived from tongue carcinoma with HPV-16. Lane 18: SAS cell line (National Institute of Biomedical Innovation JCRB Cell Bank, Osaka, Japan) derived from tongue carcinoma without HPV infection. Lane 19: CaSki cell line (European Collection of Authenticated Cell Cultures, Salisbury, UK) derived from cervical cancer with HPV-16.
EGFR was expressed in all IP, IP-SCC, and SNSCC cases. Of the four EGFR phosphorylation sites, Y845 and Y1068 were robustly phosphorylated in IP-9 (lane 2) and IP-SCC-1 and -2 (lanes 8 and 9), who had S768_D770dup. IP-SCC-3 (lane 7), who had HR-HPV infection without ex20ins, demonstrated a similar EGFR phosphorylation pattern as cases with ex20ins. For ex20ins, only cases with S768_D770dup showed high p-EGFR levels (lanes 2, 8, and 9). IP cases without ex20ins (lane 1) had low p-EGFR and p-4E-BP1 levels but high p-AKT and p-STAT3 levels.
AKT (S473) was highly phosphorylated in all IP, IP-SCC, and SNSCC cases, regardless of HR-HPV infection and ex20ins status. 4E-BP1 (T37/46) was phosphorylated in all IP, IP-SCC, and SNSCC cases. p-4E-BP1 levels were much higher in IP-SCC (lanes 7–9) cases than in SNSCC and oropharyngeal carcinoma with HR-HPV infection cases. p-4E-BP1 levels were higher in IP with ex20ins cases than in IP without ex20ins (lane 1) and chronic sinusitis cases. STAT3 was expressed in all samples examined, while it was weakly expressed in IP-5 and IP-9 with H773_V774dup and H773_V774insTH, respectively. STAT3 (Y705) was similarly phosphorylated, and p-STAT3 levels were lower in IP cases than in chronic sinusitis cases.
HR-HPV-positive samples (lanes 7, 9, 15, and 16 in Figure 3) showed robust p16 expression in western blotting. The EGFR phosphorylation pattern of the HR-HPV-positive samples resembled that of the samples with ex20ins (lanes 2 and 8).
3.6. EGFR and p-EGFR (Y845) Immunohistochemistry
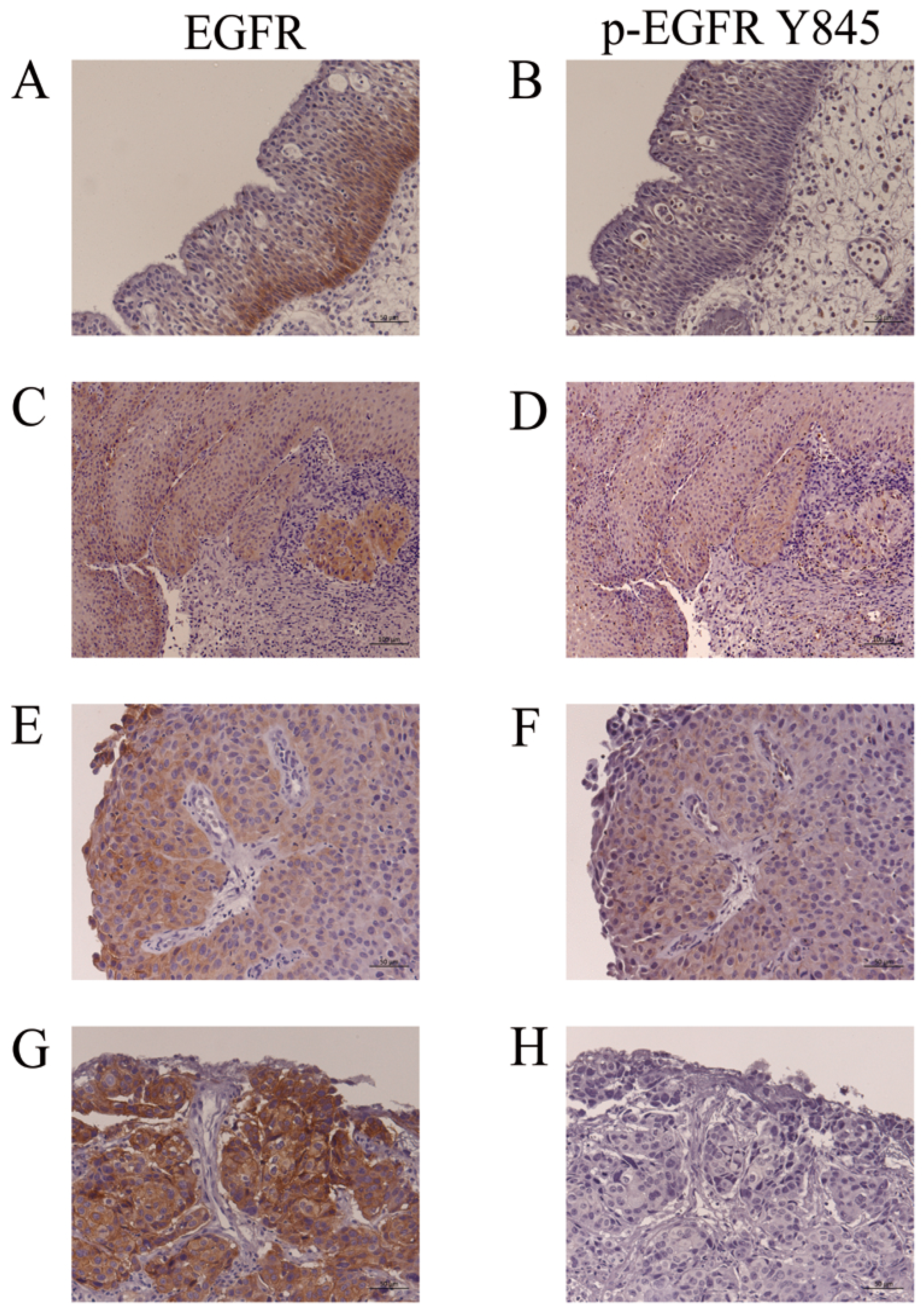
Representative findings of EGFR and p-EGFR (Y845) immunohistochemistry in IP (IP-19, Table 3), IP-SCC (IP-SCC-2, Table 3) and SNSCC (SNSCC-17, Table 3) cases are shown in Figure 4. EGFR expression was usually observed in the basal cell layer of IP (Figure 4A); however, p-EGFR (Y845) was not noted in IP (Figure 4B). IP-SCC cases with S768_D770dup showed EGFR and p-EGFR (Y845) immunoreactivity in the IP and SCC parts (Figure 4C–F). The SNSCC case with neither HR-HPV infection nor ex20ins demonstrated strong EGFR expression (Figure 4G) but not p-EGFR (Y845) (Figure 4H). These findings were consistent with the western blotting results.
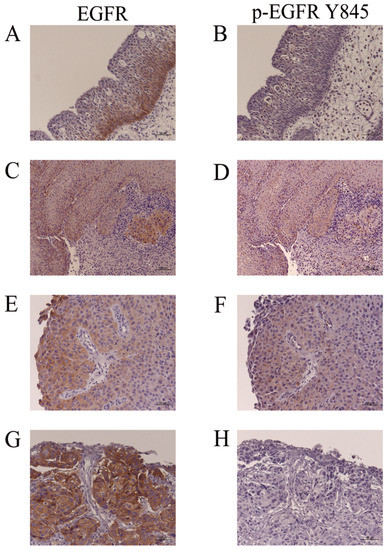
Figure 4.
Immunohistochemistry for EGFR and p-EGFR (Y845). (A,B): IP-19. EGFR, but not p-EGFR (Y845), was detected in the basal cell layers of IP. (C,D): The IP part of IP-SCC-2 with S768_D770dup. (E,F): SCC part of IP-SCC-2 with S768_D770dup. EGFR and p-EGFR (Y845) were detected in the IP and SCC parts of IP-SCC-2. (G,H): SCC without HPV infection (SNSCC-12). There was intense EGFR staining (G) but none for p-EGFR (Y845) (H). Bar, 100 µm.
4. Discussion
This study aimed to shed light on IP and IP-SCC in view of HR-HPV infection and EGFR exon 20 mutations.
HPV infection was observed in 25% of IP cases, 57.1% of IP-SCC cases, and 35% of SNSCC cases by PCR analysis. Because HPV was not transcriptionally active and had a low viral load in IP, it is still controversial whether HPV DNA is involved in the etiology of IP. On the contrary, HR-HPV infection in IP-SCC and SNSCC accompanied by p16 overexpression was observed in 28.5% and 25% of cases, respectively, suggesting that HR-HPV infection is a crucial factor in sinonasal cancer, consistent with previous studies [14,23,24].
Regarding the impact of HPV type, HPV-16 was the primary type, followed by HPV-33 and HPV-18. The observed HPV types were consistent with the HR-HPV types detected in oropharyngeal carcinoma in our institution [22]. Information on viral load in head and neck cancers is limited. In our previous study of oropharyngeal carcinoma, the viral loads of HPV-16-positive samples ranged from 0.24 to 2.69 × 105 copies/ng DNA (mean 3.49 × 104 and median 3.1 × 102 copies/ng DNA) [25]. In the present study, the viral loads of HPV-16 and -33 in IP-SCC and SNSCC ranged from 0.7 to 1.63 × 106 copies/ng DNA. Although the sample number was limited, the viral loads in IP-SCC and SNSCC were not significantly different from those in oropharyngeal carcinoma. The results for p16 overexpression and HPV viral load suggest a subgroup of HPV-related lesions in IP-SCC and SNSCC.
EGFR ex20ins are heterogeneous but comprise mainly in-frame insertions and duplications that cluster between amino acids 762 and 774 [26]. The amino acids changed by ex20ins in the present study were located in the tyrosine kinase domain, which contains the C-helix and the loop following the C-helix. These ex20ins result in the internal rotation of the C-helix, thereby promoting the constitutive activation of EGFR [26]. Qin et al. reported that 2.24% of non-small cell lung cancer cases had unique ex20ins, with A767_V769dup (25.1%) and S768_D770dup (17.6%) as the most prevalent [27]. ex20ins resulting in amino acid changes were observed in up to 50% of IP cases and 57% of IP-SCC cases, and ex20ins were identified only in IP and IP-SCC cases. The most common subtype of ex20ins was S768_D770dup in the IP-SCC group. Although ex20ins are not common in sinonasal cancer (6.15%) [26], IP-SCC has a high incidence of ex20ins (30–90%) compared with other cancers [6,10,28]. In the present study, ex20ins were observed frequently in the IP group, suggesting that they are involved in the etiology of IP.
Y845 is an Src-induced transphosphorylation site on EGFR, which is located in an activation loop that influences kinase activity and is also recognized as a key residue for the oncogenic properties of EGFR [29]. When EGF binds to the extracellular domain of EGFR, the regulatory C-helix rotates from an outward to an inward orientation, leading to the constitutive activation of EGFR [30]. ex20ins has been considered to promote C-helix rotation by pushing the α-C helix, resulting in a conformational change of EGFR in the absence of EGF binding [17,30]. In the present study, ex20ins was located between amino acids 768 and 774 and may induce continuous EGFR activation without ligand binding. The active conformation of the tyrosine kinase domain leads to the autophosphorylation of tyrosine residues (including Y703, Y920, Y992, Y1045, Y1068, Y1086, Y1148, and Y1173) in the intracellular C-terminal tail of EGFR [31]. Autophosphorylation of Y1068 and Y1197 has been reported in ex20ins cases [10,32], which was also observed in our series. However, the most prominent phosphorylation site was Y845 in IP-SCC cases with S768_D770dup. Y845 in EGFR is similarly located in the activation segment of the kinase domain but has distinctive features. Y845 phosphorylation is not mediated by EGFR autophosphorylation but is co-mediated by c-Src [33]. c-Src binds to EGFR and phosphorylates its tyrosine residues to induce cell transformation and carcinogenesis [34]. The conformational change of the kinase domain induced by S768_D770dup allows c-Src access to Y845, which may lead to EGFR phosphorylation (Figure 2 and Figure 3) [35]. The present report is the first to demonstrate Y845 phosphorylation in IP and IP-SCC cases with EGFR ex20ins. In addition, HPV-related tumors, IP-SCC-3, SNSCC-2, and oropharyngeal carcinoma showed Y845 phosphorylation despite the lack of ex20ins. Although the cause of Y845 phosphorylation in HPV-related carcinomas remains unclear, it might be due to carcinogenesis induced by HPV infection.
In the present study, active HR-HPV infection was observed in 28.5% of IP-SCC and 25% of SNSCC but not in IP and sinusitis, while sinusitis samples were different from the nasal mucosa in the healthy subjects. On the contrary, ex20ins was observed in 45% of IP, 28.5% of IP-SCC, and 0% of SNSCC and sinusitis. IP and IP-SCC are diagnosed by histological findings. Thus, these phenomena reflect that IP-SCC might be a multifactorial disease. The active HR-HPV infection and ex20ins might be responsible for the pathogenesis of half of IP-SCC cases from the present results. Although case numbers were limited, patients with active HR-HPV infection did not have ex20ins, except for one IP-SCC case (IP-SCC-1 in Table 3). The finding is in accordance with the previous reports [6,9,17]. Further investigation is needed to understand IP-SCC etiology fully, including the roles of HR-HPV and EGFR mutations.
5. Conclusions
HPV infection status and EGFR ex20ins were investigated in IP, IP-SCC, and SNSCC. HR-HPV infection in IP was observed with a low viral load and was not transcriptionally active. On the contrary, IP-SCC and SNSCC had transcriptionally active infections with high viral load. These results suggest that HPV integration may occur during persistent infection in IP and eventually induce malignant transformation to IP-SCC. EGFR ex20ins was frequently detected in IP and IP-SCC but not in SNSCC and chronic sinusitis. Since EGFR ex20ins in IP and IP-SCC induced EGFR phosphorylation and activated the PI3K/AKT/mTOR activation, IP and IP-SCC might have a different etiology from SNSCC. The present report is the first to demonstrate EGFR Y845 phosphorylation in IP and IP-SCC cases with EGFR ex20ins. Patients with active HR-HPV infection did not have ex20ins, except for one IP-SCC case. Since IP-SCC is histologically determined, further investigation is needed to fully understand IP-SCC etiology.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/jpm13040657/s1: Figure S1. Localization of EGFR ex20ins between amino acids 768 and 774 in IP and IP-SCC; Table S1. Primers used for HPV infection analysis and Sanger sequencing of EGFR exon 20; Table S2. Relationship between p16 immunoreactivity and HR-HPV in IP; and Table S3. EGFR amino acid insertions/duplications and substitutions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.I., M.S. and H.H.; methodology, T.I., N.H., J.K. and H.H.; software, T.I.; validation, M.S., H.M. and H.H.; formal analysis, T.I. and M.S.; investigation, T.I., N.H., J.K., N.K. and S.K.; resources, N.K., H.K., S.K., S.A., N.H., J.K. and H.M.; data curation, M.S. and H.H.; writing—original draft preparation, H.H.; writing—review and editing, M.S. and T.I.; visualization, M.S.; project administration, M.S.; funding acquisition, H.H., T.I. and M.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (KAKENHI Grant Numbers 20K097581, 21K09635, and 21K09585) to H.H., T.I., and M.S., respectively, and by a GSK Japan Research Grant 2021 to T.I.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the University of Ryukyu (protocol code 156, 23 February 2017) and conducted in accordance with the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the present study have not been made publicly available. However, data can be made available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We thank Yoshihisa Kobayashi, Division of Molecular Pathology, National Cancer Center Research Institute, Tokyo, Japan, for valuable suggestions regarding the manuscript. We also thank Meiko Shiroma and Yukari Matsuda, Ryukyu Society, for the Promotion of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology, for administrative assistance related to this investigation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- McCormick, J.P.; Suh, J.D.; Lee, J.T.; Wells, C.; Wang, M.B. Role of high-risk HPV detected by PCR in malignant sinonasal inverted papilloma: A meta-analysis. Laryngoscope 2022, 132, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.J.; Noel, J.E. Etiology of sinonasal inverted papilloma: A narrative review. World J. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2017, 3, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syrjänen, S.; Syrjänen, K. Hpv-associated benign squamous cell papillomas in the upper aero-digestive tract and their malignant potential. Viruses 2021, 13, 1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Re, M.; Gioacchini, F.M.; Bajraktari, A.; Tomasetti, M.; Kaleci, S.; Rubini, C.; Bertini, A.; Magliulo, G.; Pasquini, E. Malignant transformation of sinonasal inverted papilloma and related genetic alterations: A systematic review. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 274, 2991–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasumatsu, R.; Jiromaru, R.; Hongo, T.; Uchi, R.; Wakasaki, T.; Matsuo, M.; Taura, M.; Nakagawa, T. A clinical analysis of sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma: A comparison of de novo squamous cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma arising from inverted papilloma. Acta Otolaryngol. 2020, 140, 706–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongo, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Jiromaru, R.; Nozaki, Y.; Yasumatsu, R.; Hashimoto, K.; Yoneda, R.; Sugii, A.; Taguchi, K.; Masuda, M.; et al. Clinicopathologic significance of EGFR mutation and HPV infection in sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2021, 45, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasukawa, S.; Kano, S.; Hatakeyama, H.; Nakamaru, Y.; Takagi, D.; Mizumachi, T.; Suzuki, M.; Suzuki, T.; Nakazono, A.; Tanaka, S.; et al. Genetic mutation analysis of the malignant transformation of sinonasal inverted papilloma by targeted amplicon sequencing. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 23, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udager, A.M.; McHugh, J.B.; Betz, B.L.; Montone, K.T.; Livolsi, V.A.; Seethala, R.R.; Yakirevich, E.; Iwenofu, O.H.; Perez-Ordonez, B.; DuRoss, K.E.; et al. Activating KRAS mutations are characteristic of oncocytic sinonasal papilloma and associated sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Pathol. 2016, 239, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udager, A.M.; McHugh, J.B.; Goudsmit, C.M.; Weigelin, H.C.; Lim, M.S.; Elenitoba-Johnson, K.S.J.; Betz, B.L.; Carey, T.E.; Brown, N.A. Human papillomavirus (HPV) and somatic EGFR mutations are essential, mutually exclusive oncogenic mechanisms for inverted sinonasal papillomas and associated sinonasal squamous cell carcinomas. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udager, A.M.; Rolland, D.C.M.; McHugh, J.B.; Betz, B.L.; Murga-Zamalloa, C.; Carey, T.E.; Marentette, L.J.; Hermsen, M.A.; DuRoss, K.E.; Lim, M.S.; et al. High-frequency targetable EGFR mutations in sinonasal squamous cell carcinomas arising from inverted sinonasal papilloma. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 2600–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchi, R.; Jiromaru, R.; Yasumatsu, R.; Yamamoto, H.; Hongo, T.; Manako, T.; Sato, K.; Hashimoto, K.; Wakasaki, T.; Matsuo, M.; et al. Genomic sequencing of cancer-related genes in sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma and coexisting inverted papilloma. Anticancer Res. 2021, 41, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, R.; Gatalica, Z.; Knezetic, J.; Reddy, S.; Nathan, C.A.; Javadi, N.; Teknos, T. Molecular profiling of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 2016, 38 (Suppl. 1), E1625–E1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahnane, N.; Ottini, G.; Turri-Zanoni, M.; Furlan, D.; Battaglia, P.; Karligkiotis, A.; Albeni, C.; Cerutti, R.; Mura, E.; Chiaravalli, A.M.; et al. Comprehensive analysis of HPV infection, EGFR exon 20 mutations and line1 hypomethylation as risk factors for malignant transformation of sinonasal-inverted papilloma to squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 1313–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabal, V.N.; Menendez, M.; Vivanco, B.; Potes-Ares, S.; Riobello, C.; Suarez-Fernandez, L.; Garcia-Marin, R.; Blanco-Lorenzo, V.; Lopez, F.; Alvarez-Marcos, C.; et al. EGFR mutation and HPV infection in sinonasal inverted papilloma and squamous cell carcinoma. Rhinology 2020, 58, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, E.; Nishikawa, D.; Hanai, N.; Hasegawa, Y.; Yatabe, Y. Sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma and EGFR mutations: A molecular footprint of a benign lesion. Histopathology 2018, 73, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Li, H.; Hu, L.; Zhou, J.; Zhai, C.; Wang, D.; Sun, X. EGFR and KRAS mutations in Chinese patients with sinonasal inverted papilloma and oncocytic papilloma. Histopathology 2019, 75, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meador, C.B.; Sequist, L.V.; Piotrowska, Z. Targeting EGFR exon 20 insertions in non-small cell lung cancer: Recent advances and clinical updates. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 2145–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrad, M.; Stelow, E.B.; Bishop, J.A.; Wang, X.; Haynes, W.; Oliver, D.; Chernock, R.D.; Lewis, J.S., Jr. Transcriptionally active HPV and targetable EGFR mutations in sinonasal inverted papilloma: An association between low-risk HPV, condylomatous morphology, and cancer risk? Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2020, 44, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikegami, T.; Uehara, T.; Deng, Z.; Kondo, S.; Maeda, H.; Kiyuna, A.; Agena, S.; Hirakawa, H.; Yamashita, Y.; Ganaha, A.; et al. Detection of human papillomavirus in branchial cleft cysts. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 1571–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikegami, T.; Hirakawa, H.; Tsukahara, N.; Murakami, A.; Kise, N.; Kiyuna, A.; Kosugi, T.; Agena, S.; Kinjyo, H.; Hasegawa, N.; et al. Coordinated expression of hpv-6 genes with predominant e4 and e5 expression in laryngeal papilloma. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doescher, J.; Veit, J.A.; Hoffmann, T.K. The 8th edition of the AJCC cancer staging manual: Updates in otorhinolaryngology, head and neck surgery. HNO 2017, 65, 956–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, Y.; Ikegami, T.; Hirakawa, H.; Uehara, T.; Deng, Z.; Agena, S.; Uezato, J.; Kondo, S.; Kiyuna, A.; Maeda, H.; et al. Staging and prognosis of oropharyngeal carcinoma according to the 8th edition of the American joint committee on cancer staging manual in human papillomavirus infection. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 276, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, Y.; Hasegawa, M.; Deng, Z.; Maeda, H.; Kondo, S.; Kyuna, A.; Matayoshi, S.; Agena, S.; Uehara, T.; Kouzaki, H.; et al. Human papillomavirus infection and immunohistochemical expression of cell cycle proteins pRB, p53, and p16(INK4a) in sinonasal diseases. Infect. Agents Cancer 2015, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepp, W.H.; Farzal, Z.; Kimple, A.J.; Ebert, C.S., Jr.; Senior, B.A.; Zanation, A.M.; Thorp, B.D. Hpv in the malignant transformation of sinonasal inverted papillomas: A meta-analysis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2021, 11, 1461–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.; Hasegawa, M.; Kiyuna, A.; Matayoshi, S.; Uehara, T.; Agena, S.; Yamashita, Y.; Ogawa, K.; Maeda, H.; Suzuki, M. Viral load, physical status, and E6/E7 mRNA expression of human papillomavirus in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 2013, 35, 800–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedlaender, A.; Subbiah, V.; Russo, A.; Banna, G.L.; Malapelle, U.; Rolfo, C.; Addeo, A. EGFR and HER2 exon 20 insertions in solid tumors: From biology to treatment. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 19, 51–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Jian, H.; Tong, X.; Wu, X.; Wang, F.; Shao, Y.W.; Zhao, X. Variability of EGFR exon 20 insertions in 24 468 Chinese lung cancer patients and their divergent responses to EGFR inhibitors. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 14, 1695–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskilsson, E.; Røsland, G.V.; Solecki, G.; Wang, Q.; Harter, P.N.; Graziani, G.; Verhaak, R.G.W.; Winkler, F.; Bjerkvig, R.; Miletic, H. Egfr heterogeneity and implications for therapeutic intervention in glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 2018, 20, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.L.; Chen, X.R.; Lan, A.; Hsu, Y.L.; Wu, P.S.; Hung, P.F.; Hung, C.L.; Pan, S.H. N-glycosylated GPNMB ligand independently activates mutated EGFR signaling and promotes metastasis in NSCLC. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 1911–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyse, S.; Huang, P.H. Targeting EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations in non-small cell lung cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2019, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wee, P.; Wang, Z. Epidermal growth factor receptor cell proliferation signaling pathways. Cancers 2017, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, Z.; Kannan, N. Altered conformational landscape and dimerization dependency underpins the activation of EGFR by alphac-beta4 loop insertion mutations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E8162–E8171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belli, S.; Esposito, D.; Servetto, A.; Pesapane, A.; Formisano, L.; Bianco, R. C-src and EGFR inhibition in molecular cancer therapy: What else can we improve? Cancers 2020, 12, 1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maa, M.C.; Leu, T.H.; McCarley, D.J.; Schatzman, R.C.; Parsons, S.J. Potentiation of epidermal growth factor receptor-mediated oncogenesis by c-src: Implications for the etiology of multiple human cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 6981–6985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, K.-I. Cellular functions regulated by phosphorylation of EGFR on tyr845. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 10761–10790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).