Periorbital Facial Necrotizing Fasciitis in Adults: A Rare Severe Disease with Complex Diagnosis and Surgical Treatment—A New Case Report and Systematic Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
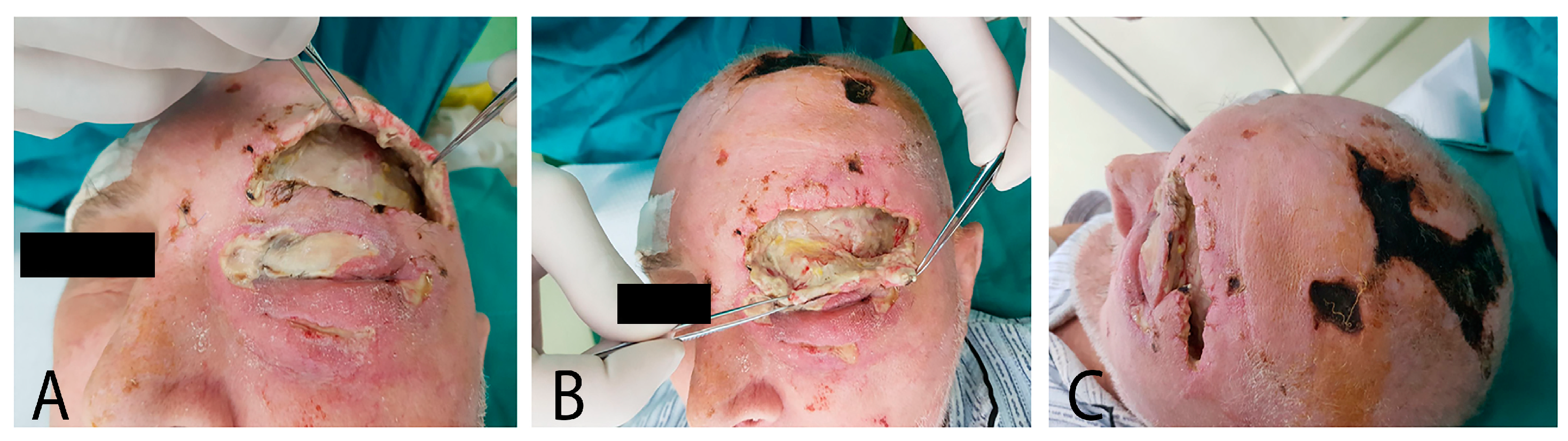
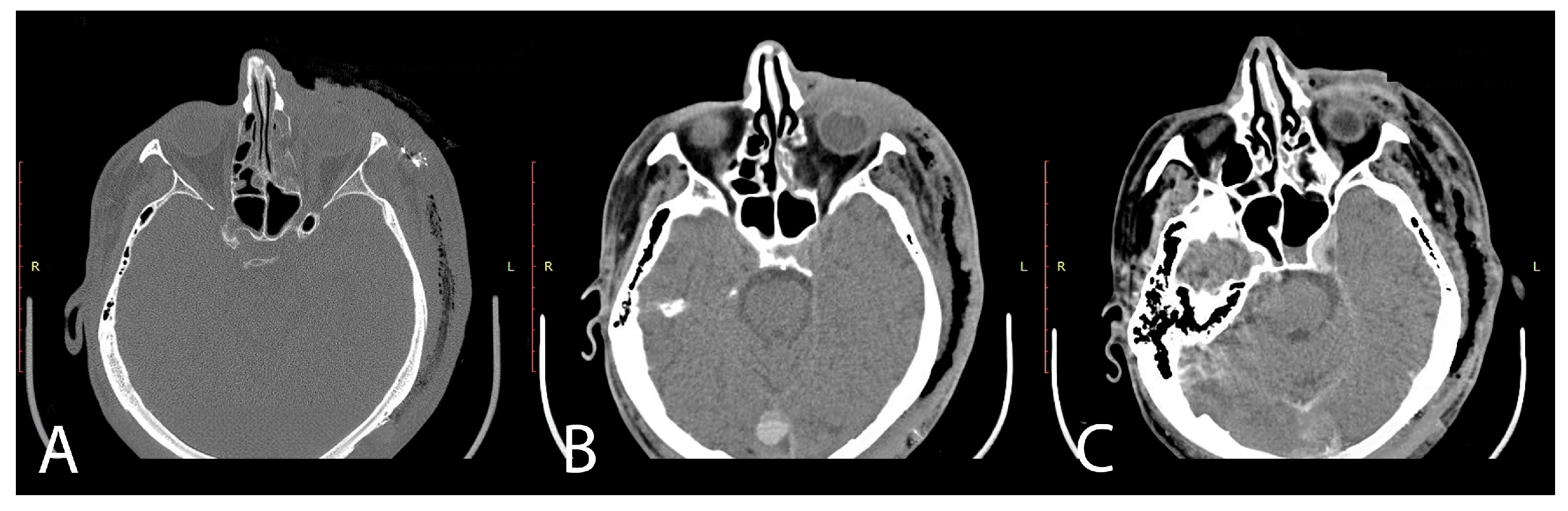
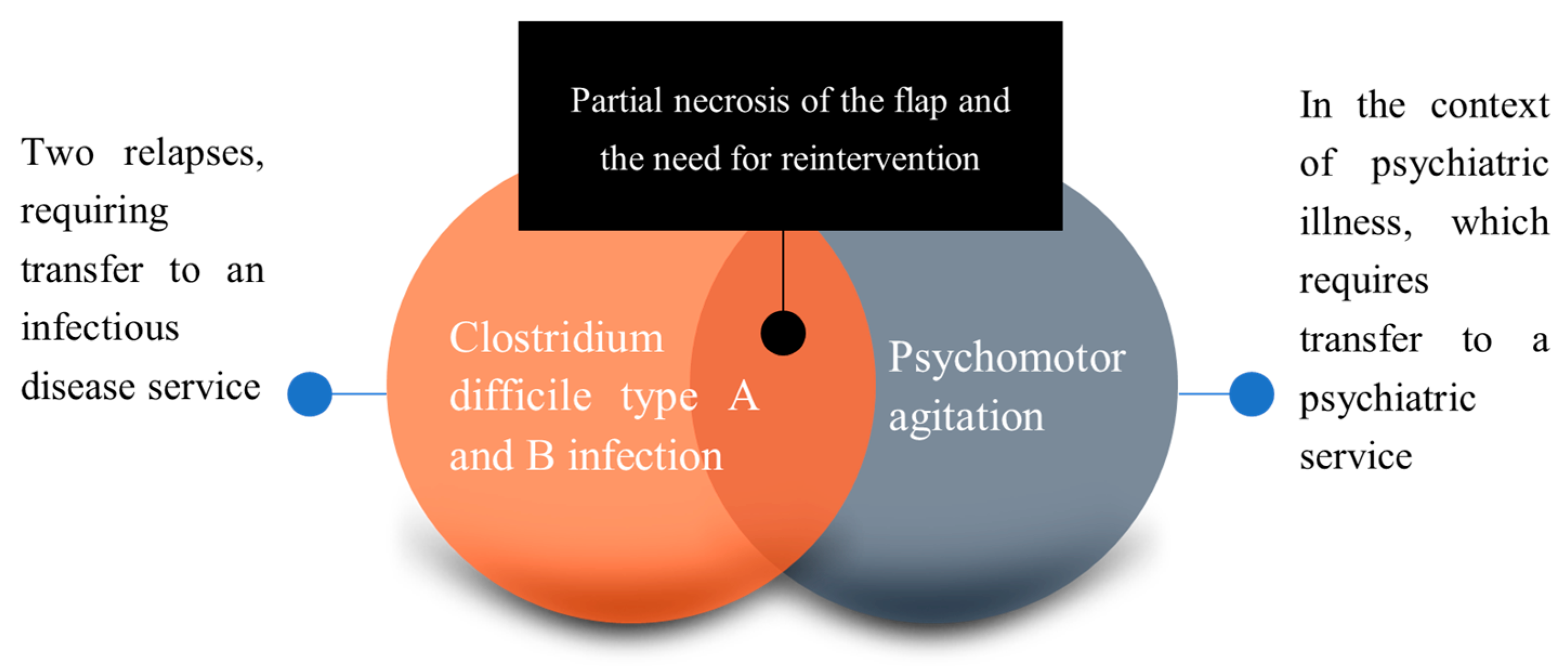
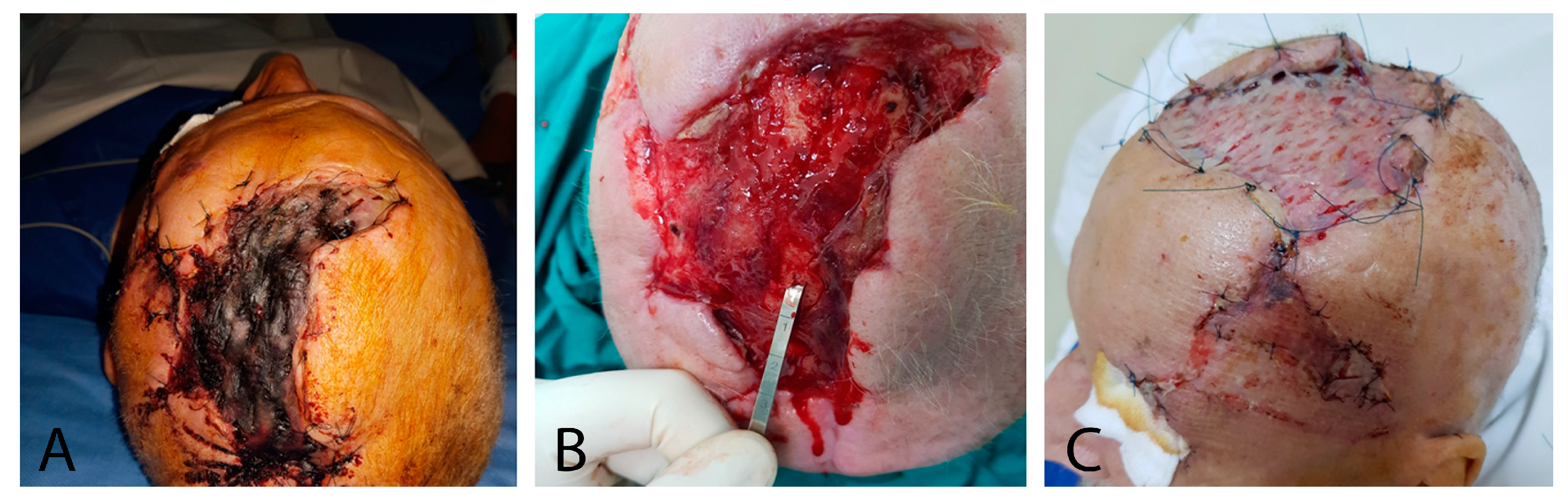
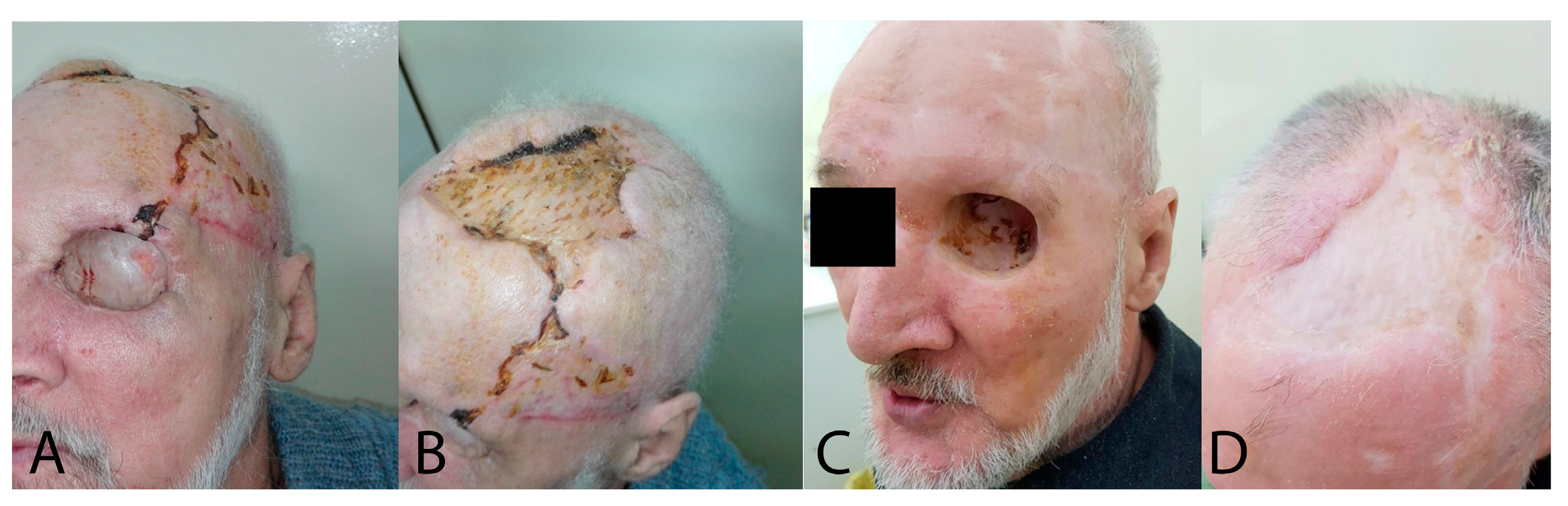
2.1. Case Report
2.2. Systematic Review
3. Results
Systematic Review
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kakimoto, S.; Harada, Y.; Shimizu, T. Periorbital Necrotizing Fasciitis. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2022, 37, 2086–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wladis, E.J. Periorbital Necrotizing Fasciitis. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2022, 67, 1547–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothschild, M.I.; Pacheco, R.R.; Wladis, E.J. Predicting Severity of Periorbital Necrotizing Fasciitis. Orbit 2023, 42, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negi, A.; Amit, K. Facial Necrotizing Fasciitis with Periorbital Involvement. Indian J. Med. Res. 2020, 152 (Suppl. 1), S71–S72. [Google Scholar]
- Hadizamani, Y.; Anastasi, S.; Schori, A.; Lucas, R.; Garweg, J.G.; Hamacher, J. Pathophysiological Considerations in Periorbital Necrotizing Fasciitis: A Case Report. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2023, 31, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, S.Y.; Ahn, J.H. Periorbital Necrotizing Fasciitis Accompanied by Sinusitis and Intracranial Epidural Abscess in an Immunocompetent Patient. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 15, 848–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyirjesy, S.C.; Judd, R.T.; Alfayez, Y.; Lancione, P.; Swendseid, B.; von Windheim, N.; Nogan, S.; Seim, N.B.; VanKoevering, K.K. Use of 3-dimensional Printing at the Point-of-Care to Manage a Complex Wound in Hemifacial Necrotizing Fasciitis: A Case Report. 3D Print Med. 2023, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaur, N.; Rawat, D.; Dhasmana, R.; Lokdarshi, G. Management of Eyelid and Medial Canthus Necrotising Fasciitis Using Laissez-Faire Technique. BMJ Case Rep. 2023, 16, e252462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosenia, A.; Shahlaee, A.; Giese, I.; Winn, B.J. Polymicrobial Odontogenic Periorbital and Orbital Necrotizing Fasciitis (PONF): A Case Report. Am. J. Ophthalmol. Case Rep. 2022, 26, 101439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.W.; Kwak, S.H.; Choi, H.J. Secondary Craniofacial Necrotizing Fasciitis from a Distant Septic Emboli: A Case Report. World J. Clin. Cases 2022, 10, 11630–11637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, R.F.; Hodgson, N. Orbital Necrotizing Fasciitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Fan, K.; Liu, S.; Yu, S. Necrotizing Fasciitis of the Jaw, Neck and Mediastinum Caused by Klebsiella oxytoca and Streptococcus constellatus: A Case Report. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2021, 10, 8431–8436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, A.J.; Tak, N.; Nawathey, N.; Habib, S.A.; Martel, J.B. Treatment of a Rare Case of Orbital Necrotizing Fasciitis Utilizing Negative Pressure Wound Therapy. Cureus 2021, 13, e18682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazıcı, B.; Sabur, H.; Toka, F. Periocular Necrotizing Fasciitis Causing Posterior Orbitopathy and Vision Loss: How to Manage? Turk. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 51, 181–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cecchini, A.; Cox, C.J.; Cecchini, A.A.; Solanki, K.; McSharry, R. Odontogenic Infection Complicated by Cervicofacial Necrotizing Fasciitis in a Healthy Young Female. Cureus 2021, 13, e16835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigby, A.; Sexton, P.; Chengot, P.; Kanatas, A. Necrotizing Fasciitis in the Immediate Post-Operative Period Following Resection and Free Flap Reconstruction for Oral Cancer. Acta Med. 2022, 65, 71–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.K.; Lai, C.C. Concurrent Pseudomonas Periorbital Necrotizing Fasciitis and Endophthalmitis: A Case Report and Literature Review. Pathogens 2021, 10, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, P.Y.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Lin, C.H. Necrotizing Fasciitis of the Entire Head and Neck: Literature Review and Case Report. Biomed. J. 2020, 43, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Chang, Y.J.; Chung, C.H. Klebsiella pneumoniae Necrotizing Fasciitis on the Upper Lip in a Patient with Uncontrolled Diabetes. Arch. Craniofac. Surg. 2020, 21, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, G.A.; Hardy, T.; Campbell, T.G. Bilateral Periorbital Necrotising Fasciitis Associated with Invasive Group A Streptococcus Infection. BMJ Case Rep. 2020, 13, e236800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compton, R.A.; Konstantinou, E.K.; Kapadia, M.K.; Scott, A.R. Optimizing Aesthetics following Surgical Management of Periorbital Necrotizing Fasciitis. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2020, 41, 102668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ting, C.F.; Lam, J.; Anastas, C. Subgaleal Haematoma as a Cause of Periorbital Necrotising Fasciitis: A Case Report. Orbit 2020, 39, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badri, A.A.; Hasheminasab, M.S.; Bolandparva, F. Cervical Necrotizing Fasciitis after Surgery of a Mandibular Fracture. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2020, 31, e541–e542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landeen, K.C.; Mallory, P.W.; Cervenka, B.P. Bilateral Ocular Necrotizing Fasciitis in an Immunosuppressed Patient on Prescription Eye Drops. Cureus 2020, 12, e9129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karan, N.B.; Kose, R.; Kalyoncu, A.; Sekeryapan, B.; Oter, K.; Findik, H.; Yurdakul, C. Fatal Orbital Necrotizing Fasciitis Secondary to Stenotrophomonas Maltophilia Associated Stomatitis. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 120, 260–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haen, P.; Laversanne, S.; Graillon, N.; Foletti, J.M. Facial Necrotising Fasciitis following Rhytidectomy. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 57, 685–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, S.; Lee, B.; Baek, S. A Patient with Periorbital Necrotizing Fasciitis by Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2019, 30, e245–e247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadal, J.; Galatoire, O.; Laouar, K.; Jeanjean, L.; Villain, M.; Audemard, D.; Daien, V. Periorbital Necrotizing Fasciitis without Initial Trauma: A Rare Case Report. J. Fr. Ophtalmol. 2019, 42, e209–e211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sud, R.; Sharma, P.; Garg, G.; Takkar, B.; Khanduja, S. Periorbital Necrotizing Fasciitis due to Klebsiella pneumoniae in an Immunocompetent Patient. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 67, 1721–1722. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Steybe, D.; Voss, P.J.; Ermer, M.A.; Fuessinger, M.A.; Schmelzeisen, R.; Poxleitner, P. Necrotizing Fasciitis as a Complication of Osteonecrosis of the Jaw Related to Oral Bisphosphonate Application in a Patient with Osteoporosis: A Case Report. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 23, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Park, S.I.; Cho, J.T.; Jung, S.N.; Byeon, J.; Seo, B.F. Necrotizing Fasciitis of the Masticator Space with Osteomyelitis of the Mandible in an Edentulous Patient. Arch. Craniofac. Surg. 2019, 20, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffer, Z.N.; Nicholson, C. Bullous Eyelid. BMJ Case Rep. 2018, 2018, bcr2017220962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sondo, K.A.; Diendéré, E.A.; Ouédraogo, M.S.; Ouédraogo, G.A.; Diallo, I.; Zoungrana, J.; Poda, A.; Bognounou, R.; Da, L.; Savadogo, M.; et al. Management of Necrotizing and Non-Necrotic Bacterial Erysipelas of the Face in Tropical Areas: A Series of Four Cases and a Review of the Literature. Med. Sante Trop. 2018, 28, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herdiana, T.R.; Takahashi, Y.; Valencia, M.R.P.; Ana-Magadia, M.G.; Kakizaki, H. Periocular Necrotizing Fasciitis with Toxic Shock Syndrome. Case Rep. Ophthalmol. 2018, 9, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bağli, B.S.; Durgut, O. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy as Adjuvant Therapy in Necrotizing Fasciitis of the Face: Case Report. Undersea Hyperb. Med. 2018, 45, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ţenţ, P.A.; Juncar, M.; Mureșan, O.; Arghir, O.C.; Iliescu, D.M.; Onișor, F. Post-Traumatic Occipital Psoriatic Plaque Complicated by Extensive Necrotizing Fasciitis of the Head and Neck: A Case Report and Literature Review. J. Int. Med. Res. 2018, 46, 3480–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, J.W., 3rd; Pandya, J.K.; Agarwal, S.M.; Gassman, A.A.; Krakauer, M. Negative-Pressure Wound Therapy for Periocular Necrotizing Fasciitis. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2018, 6, e1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deneubourg, D.L.; Zulma, C.; Lejuste, P.; Breton, P. Periorbital Necrotizing Fasciitis Induced by Streptococcus pyogenes: A Case Report and Clarification. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 76, P154.E1–P154.E5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, C.; Hicks, K.; Alexiev, B.; Patel, A.K.; Patel, U.A.; Matsuoka, A.J. Cervicofacial Necrotising Fasciitis by Clindamycin-Resistant and Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in a Young Healthy Man. BMJ Case Rep. 2018, 11, e226975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Year | Reference | Gender and Age | Etiology | Alcohol Use | Associated Pathologies | Symptoms | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2023 | Sarah Nyirjesy et al. [7] | 58, F | Decayed teeth | Unknown | Unknown | Right facial and neck swelling |
| 2 | 2023 | Nripen Gaur et al. [8] | 30, M | Unknown | No | None | Gradual swelling of the right eyelids and adjacent skin |
| 3 | 2022 | Mosenia A et al. [9] | 39, M | Trauma, decayed tooth | Yes | Heavy alcohol use | Left-sided periorbital swelling pain, erythema |
| 4 | 2022 | Da-Woon Lee et al. [10] | 43, M | Hematogenic spread from lung and renal abscesses | No | Diabetes mellitus with insulin | Left hemifacial swelling involving the buccal and submandibular areas, fever |
| 5 | 2022 | Silverman et al. [11] | 21, M | Trauma | Unknown | Unknown | Rigors and right-eye pain and swelling |
| 6 | 2021 | Ling Jin et al. [12] | 48, M | Peritonsillar abscess | No | Diabetes mellitus with unstable control with insulin | Four-day sore in left throat and half-day dysphagia, and fever, cold, and fatigue without toothache |
| 7 | 2021 | Akshay J Reddy et al. [13] | 44, M | Unknown | Yes | Heavy alcohol use | Swelling, tenderness, and erythema around his right eye, including the right side of his face |
| 8 | 2021 | Bülent Yazıcı et al. [14] | 70, M | Trauma | No | Diabetes mellitus | Afebrile, fatigued, and in distress |
| 9 | 2021 | Amanda Cecchini et al. [15] | 28, F | Dental abscess | No | No | Facial pain and swelling, headache, and vomiting |
| 10 | 2021 | Alice Rigby et al. [16] | 65, F | Surgical carcinoma excision with reconstruction with fibula free flap | No | Type 2 diabetes, coronary artery disease, hyper- tension, hypercholesterolaemia and acid reflux, moderate differentiated squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), | Necrotic skin edges, necrotic muscles including the platysma, strap muscles, sternocleidomastoid, and anterior belly of digastric |
| 11 | 2021 | Yu-Kuei et al. [17] | 62, M | unknown | Yes | hepatitis C and chronic kidney disease after kidney transplantation Under steroids and immunosuppressants, bilateral vitreous hemorrhage and tractional retinal detachment | Periorbital pain and erythematous eyelid swelling |
| 12 | 2020 | Pang-Yun Chou et al. [18] | 44, M | Decayed tooth (molar self-extracted at home) | No | Diabetes mellitus, poor oral hygiene | Progressive left facial necrosis and blurred vision of the left eye, left periorbital pain, swelling, fever, and general malaise |
| 13 | 2020 | Hyeong Seop Kim et al. [19] | 60, F | Bullous lesion in the upper lip | Unknown | Diabetes mellitus and chronic renal failure | Severe pain in the upper lip, cellulitis, upper lip gangrene, and necrosis |
| 14 | 2020 | Aman Negi et al. [4] | 32, M | Trauma to the left side of face | Unknown | Unknown | Swelling, erythema, purulent discharge, fever, and blackish necrotic skin |
| 15 | 2020 | Grace Anne McCabe et al. [20] | 56, F | Unknown | Yes | Hypertension, alcohol excess, and obesity | Periorbital swelling |
| 16 | 2020 | Rebecca A Compton et al. [21] | 44, F | Four days after bathing in a public hot tub | Unknown | None | Periorbital swelling and pain |
| 17 | 2020 | Chloe Ft Ting et al. [22] | 35, F | Trauma, subgaleal hematoma | Yes | Chronic alcohol abuse | Bilateral periorbital pain and swelling, hypotension, tachycardia |
| 18 | 2020 | Amir Ali Badri et al. [23] | 19, M | Trauma, surgery | No | No | Swelling extending from submandibular to suprasternal area, with tender and erythematous skin |
| 19 | 2020 | Landeen Kelly et al. [24] | 58, F | Unknown, immunosuppressed | No | Rheumatoid arthritis (tocilizumab), depression | Erythema, swelling, necrotic eyelids |
| 20 | 2019 | Karan NB et al. [25] | 81, F | Stomatitis | No | right-side facial palsy, diabetes mellitus | Right eyelid edema and diplopia, swelling in the right maxillary area for 7 days in duration |
| 21 | 2019 | Haen P et al. [26] | 57, F | Rhytidectomy | No | None | Inflammation and swelling of the face, with blisters and necrotic lesions |
| 22 | 2019 | Jinhwan Park et al. [27] | 53, F | Unknown | Yes | Diabetus mellitus, chronic hepatitis B, liver cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma | Swelling, erythema |
| 23 | 2019 | Nadal J et al. [28] | 32, F | Unknown | Yes | Breast adenocarcinoma, chronic alcoholism | Right upper eyelid edema, redness and, severe pain |
| 24 | 2019 | Rouli Sud et al. [29] | 52, F | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Bilateral painful lid swelling |
| 25 | 2019 | David Steybe et al. [30] | 77, F | Bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis, tooth extraction | Postmenopausal osteoporosis and type 2 diabetes | Severe, painful swelling affecting the right submandibular and submental region | |
| 26 | 2019 | Jongweon Shin et al. [31] | 79, F | Trauma | Unknown | Hypertension | Right-sided facial swelling |
| 27 | 2018 | Jaffer ZN et al. [32] | 51, F | Unknown | No | Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and Lynch syndrome | Bilateral periorbital swelling |
| 28 | 2018 | Sondo KA et al., review of 4 cases [33] | 1. 43, M 2. 20, F 3. 53, F 4. 44, F | 1. Trauma to zygomatic region 2. Infected boil 3. Micropapule itching of the left cheek 4. A furuncle on the left cheek | 1. No 2. No 3. No 4. No | 1. Diabetes mellitus 2. Drepanocytosis 3. None 4. None | 1. Facial paralysis, lymphadenopaty 2. Pain and edema 3. Edema, facial asymmetry, ulceration of the left cheek covered with a purulent coating and necrotic crusts 4. edema, pain, fever |
| 29 | 2018 | Tri Rejeki Herdiana et al. [34] | 69, F | Left preseptal eyelid infection post surgery | No | Aesthetic upper and lower blepharoplasty on both sides | fever and left eyelid swelling, partial gray-tan discoloration of the involved eyelid of over 3 days’ duration |
| 30 | 2018 | Bekir Selim Bağli et al. [35] | 60, M | Odontogenic infection | No | Unknown | Facial pain and swelling |
| 31 | 2018 | Paul Andrei Ţenţ et al. [36] | 47, F | Trauma | Yes | Heavy alcohol and tobacco use; chronic psoriasis vulgaris | Facial pain and swelling |
| 32 | 2018 | Gillespie et al. [37] | 44, M | ACE inhibitor-induced facial angioedema | Yes | Type 2 diabetes mellitus, primary hypertension, and a history of substance abuse | Tender and swollen eyelid nodule consistent with a hordeolum |
| 33 | 2018 | Deneubourg D et al. [38] | 30, F | Trauma | No | no | Bilateral painful palpebral swelling; palpebral necrosis of the superior and inferior left eyelids, chemosis, redness and facial edema extending to the upper chest and the contralateral eyelids; fever |
| 34 | 2018 | CongRan et al. [39] | 24, M | Removal of an ingrown hair from his chin | No | Emtricitabine/tenofovir for HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis | Fever, as well as facial pain, erythema, and swelling |
| Reference | Empiric Antibiotic Therapy | Isolated Micro-Organism | Definitive Antibiotic Therapy | Multidisciplinary Team | Surgical Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sarah Nyirjesy et al. [7] | Vancomycin, ampicillin-sulbactam, and fluconazole for a planned duration of 4 weeks | Unknown | Vancomycin, ampicillin-sulbactam, and fluconazole | Otolaryngology, Ophtalomology | Surgical debridement, negative-pressure therapy, 3D-printed, patient-specific wound splint, pectoralis muscle flap, split-thickness skin graft, and right paramedian forehead flap |
| Nripen Gaur et al. [8] | Unknown | Gram-positive cocci | Ceftriaxone 1 g 12 hourly and amikacin 400 mg 12 hourly | Unknown | Surgical debridement |
| Mosenia A et al. [9] | Vancomycin and (piperacillin-tazobactam), Clindamycin. | Staphylococcus epidermidis Streptococcus milleri group Staphylococcus lugdunensis. | Ceftriaxone and metronidazole for 7 days | Infectious Disease, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery | Surgical debridement, maxillary antrostomy, ethmoidectomy, and extraction of the infected tooth. Repair with a split-thickness skin graft. |
| Da-Woon Lee et al. [10] | Meropenem 1 g every 8 h and levofloxacin 750 mg per day | K. pneumoniae | Cefotaxime + Ceftriaxona 2 g/d | Infectious Disease, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery | Surgical debridement and decompression |
| Silverman et al. [11] | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Surgical debridement |
| Ling Jin et al. [12] | Vancomycin, piperacillin sulbactam, and ornidazole | Klebsiella oxytoca Streptococcus constellatus Candida albicans and candida guilliermondii) | Meropenem Tigecycline Fluconazole | Infectious Disease, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery | Negative-pressure drain tube, surgical debridement |
| Akshay J Reddy et al. [13] | Unknown | Streptococcus pyogenes | Unknown | Infectious Disease, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Maxillofacial Surgery, ICU | Surgical debridement and wound negative-pressure therapy |
| Bülent Yazıcı et al. [14] | Ampicillin-sulbactam (6 g/day, intravenous) Ciprofloxacin (1200 mg/day, intravenous | Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcusparasanguinis, Enterobacter cloacae | Unknown | Ophtalmology, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery | Surgical debridement. Upper and lower eyelid reconstructions with skin grafts. |
| Amanda Cecchini et al. [15] | 900 mg intravenous (IV) clindamycin, IV vancomycin | Streptococcus anginosus, group F streptococcus, Eikenella corrodens, Prevotella, and Bacteroides species | A two-week course of linezolid and clindamycin | Oral Surgery and Otolaryngology | Surgical debridement |
| Alice Rigby et al. [16] | Teicoplanin, clindamycin, aztreonam, and gentamicin | Gram-negative anaerobes, including veillonella parvula, pseudomonasaeruginosa | Teicoplanin, clindamycin, ciprofloxacin | Department of Oncology | Surgical debridement, pedicle flap (pectoralis major) |
| Yu-Kuei et al. [17] | 400 mg intravenous teicoplanin every other day and 2000 mg ceftriaxone once a day | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 2000 mg ceftazidimeonce a day | Ophtalmology | Surgical debridement and anterior orbitotomy |
| Pang-Yun Chou et al. [18] | Oxacilin Ceftazidim | Pseudomonas aeruginosa and S. aureus Klebsiella pneumoniae | Vancomycin imipenem/cilastatin. | Maxillofacial Surgery, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery | Surgical debridement. Left medial thigh meshed split-thickness skin graft. |
| Hyeong Seop Kim et al. [19] | Unknown | Klebsiella pneumoniaeMethicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) | Ceftriaxone and metronidazole | Department of Dermatology | Surgical debdridement, Abbe flap |
| Aman Negi et al. [4] | Unknown | Group A beta-haemolytic streptococci | Intravenous penicillin G and clindamycin | Department of General Surgery | Surgical debridement and intermediate-thickness skin grafting |
| Grace Anne McCabe et al. [20] | Unknown | Group A Streptococcus (GAS). | Vancomycin, benzylpenicillin, meropenemandclindamycin | Ophthalmology and Plastic Surgery | Surgical debridement, full-thickness skin graft |
| Rebecca A Compton et al. [21] | Unknown | Group A Streptococcus | Unknown | Ophtalmology | Surgical debridement. Reconstructed with full-thickness grafts |
| Chloe Ft Ting et al. [22] | IV flucloxacillin, clindamycin | S. pyogenes, methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) | Penicillin and clindamycin, cephalexin | Ophthalmology, Infectious Diseases Services | Surgical debridement, full-thickness skin graft |
| Amir Ali Badri et al. [23] | Unknown | Staphylococcusaureus | Vancomycin and meropenem | Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery | Surgical debridement, deltopectoral flap |
| Landeen Kelly et al. [24] | Unknown | Streptococcus pyogenes, MRSA | Penicillin, vancomycin | Ophtalmology, Otolaryngology | Surgical debridement |
| Karan NB et al. [25] | Ciprofloxacin Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole | S. maltophilia | Unknown | Maxillofacial Surgery, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Infectious Disease | Surgical debridement, enucleation of the right eye. Microsurgical rectus abdominis myocutaneous (TRAM) flap reconstruction. |
| Haen P et al. [26] | Unknown | Group A streptococcus | Unknown | Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery | Surgical debridement, bilateral orbitotomy, functional endoscopic sinus surgery |
| Jinhwan Park et al. [27] | Tazime (Ceftazidime, 1 g/8 h), vancomycin 1 g/24 h, Clindamycin 600 mg/8 h | K. pneumoniae | Ceftazidime | Opthalmology | Surgical debridement, endoscopic sinus surgery, transverse abdominis myocutaneusflap |
| Nadal J et al. [28] | Tazocillin 1 g × 3/day, Vancomycine 30 mg/kg/day and Clindamycine 600 mg × 3/day intravenously | Group A strep- tococcus | Unknown | Opthalmology | Surgical debridement |
| Rouli Sud et al. [29] | Amikacin | Gram-negative bacilli, Kleibsella pneumoniae | Amikacin | Ophtalmology | Surgical debridement |
| David Steybe et al. [30] | Penicillin (10 Mio. IU once a day) and metronidazole (500 mg twice a day) | Prevotella nigrescens resistant to penicillin but sensitive to metronidazole | Cefuroxime (1.5 g twice a day) andmetronidazole (500 mg twice a day) | Oral and MaxillofacialSurgery | Surgical debridement, surgical resection of the necrotic bone, reconstruction plate was inserted for stabilization of the mandible |
| Jongweon Shin et al. [31] | Ceftazidime and clindamycin | Group A beta-hemolytic Streptoccus | Ceftriaxone and clindamycin | Infectious Disease Department | Surgical debridement |
| Jaffer ZN et al. [32] | piperacillin–tazobactam 4.5 g intravenously every 8 h and vancomycin 1500 mg intravenously every 12 h, clindamycin 900 mg | Group A Streptococcus (Streptococcus pyogenes) | 5 days of intravenous piperacillin–tazobactam | Ophtalmology, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Intensive Care Unit | Surgical debridement healing; granulation tissue with oculoplastic follow-up |
| Sondo KA et al., review of 4 cases [33] | 1. Ceftriaxone 2 g/day 2. Amoxicilline-acide clavulanique 1 g/8 h and gentamicine 160 mg/day 3. Oxaciline 4. Unknown | 1. Non-groupable Streptococcus 2. Staphylococcus aureus 3. S. epidermidis 4. Blood cultures negative | 1. Ceftriaxone 2 g/day, gentamicine 160 mg/day 2. Amoxicilline 6 g/day and ciprofloxacine 1 g/day 3. Amoxicilline—acide clavulanique 4. Amoxicilline—acide clavulanique 1g/8h | Infectious Disease | Surgical debridement |
| Tri Rejeki Herdiana et al. [34] | Flomoxefsodium, 1.8 g/day of intravenous clindamycin, 6 g/day of ampicillin, and 1.2 g/day of vancomycin | Streptococcus pyogenes | 1.8 g/day of intravenous clindamycin, 6 g/day of ampicillin, oral levofloxacin | Oculoplastic specialist, intensivist, infection disease specialist, endocrinologist, and dermatologist | Surgical debridement, skin graft, and local skin flaps |
| Bekir Selim Bağli et al. [35] | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown | Department of Underwater and Hyperbaric Medicine, Department of Otorhinolaryngology | Surgical debridement and hyperbaric oxygen (HBO2) therapy |
| Paul Andrei Ţenţ et al. [36] | Colistin 3 million IU/8 h Vancomycin 1000 mg, Imipenem 500 mg, and Metronidazole 500 mg | Staphylococcus epidermidis Klebsiella sp. Acinetobacter sp. | Colistin administered as an intravenous injection of 3 million IU every 8 h in association with the previous antibiotics | Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery; Plastic Surgery Department | Surgical debridement, flaps (pedicled trapezius musculocutaneous and rotated scalp flaps), and two free skin grafts |
| Gillespie et al. [37] | Vancomycin, piperacillin/tazobactam, clindamycin, and steroid, clindamycin, meropenem, and micafungin | S. pyogenes | Vancomycin, piperacillin/tazobactam, clindamycin, and steroid | Plastic Surgery Department, Ophtalmology | Surgical debridement, NPWT for 2 weeks, bilateral upper lid full-thickness skin grafting. NPWT was continued for 6 days after skin graft placement with dressing changes every 2 days. |
| Deneubourg D et al. [38] | 1 g of intravenous amoxicillin and clavulanic acid, piperacillin-tazobactam, gentamicin and clindamycin | Group A beta- haemolytic streptococcus (Stresptococcus pyogenes) | Oral clindamycin (1800 mg in 3 takes) and amoxicillin 9 g per day from day 4 today 10, 12 g a day from day 11 today 25) and followed by oral amoxicillin (6 g per day from day 26 to 41) | Stomatology Maxillofacial and Plastic Surgery, Infectious Disease | Surgical debridement, full-thickness skin graft |
| CongRan et al. [39] | Unknown | Clindamycin-resistant and methicillin-resistant strain of Staphylococcus aureus | Unknown | Otolaryngology | Surgical debridement |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pertea, M.; Fotea, M.-C.; Luca, S.; Moraru, D.C.; Filip, A.; Olinici-Temelie, D.; Lunca, S.; Carp, A.C.; Grosu, O.-M.; Amarandei, A.; et al. Periorbital Facial Necrotizing Fasciitis in Adults: A Rare Severe Disease with Complex Diagnosis and Surgical Treatment—A New Case Report and Systematic Review. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13111612
Pertea M, Fotea M-C, Luca S, Moraru DC, Filip A, Olinici-Temelie D, Lunca S, Carp AC, Grosu O-M, Amarandei A, et al. Periorbital Facial Necrotizing Fasciitis in Adults: A Rare Severe Disease with Complex Diagnosis and Surgical Treatment—A New Case Report and Systematic Review. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2023; 13(11):1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13111612
Chicago/Turabian StylePertea, Mihaela, Madalina-Cristina Fotea, Stefana Luca, Dan Cristian Moraru, Alexandru Filip, Doinita Olinici-Temelie, Sorinel Lunca, Adrian Claudiu Carp, Oxana-Madalina Grosu, Alexandru Amarandei, and et al. 2023. "Periorbital Facial Necrotizing Fasciitis in Adults: A Rare Severe Disease with Complex Diagnosis and Surgical Treatment—A New Case Report and Systematic Review" Journal of Personalized Medicine 13, no. 11: 1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13111612
APA StylePertea, M., Fotea, M.-C., Luca, S., Moraru, D. C., Filip, A., Olinici-Temelie, D., Lunca, S., Carp, A. C., Grosu, O.-M., Amarandei, A., & Veliceasa, B. (2023). Periorbital Facial Necrotizing Fasciitis in Adults: A Rare Severe Disease with Complex Diagnosis and Surgical Treatment—A New Case Report and Systematic Review. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 13(11), 1612. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13111612






