Intracranial Aneurysm Classifier Using Phenotypic Factors: An International Pooled Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Data Collection, Patient and IA Characteristics
2.3. Data Sources
2.4. Data Analysis
2.5. Data Available Statement
3. Results
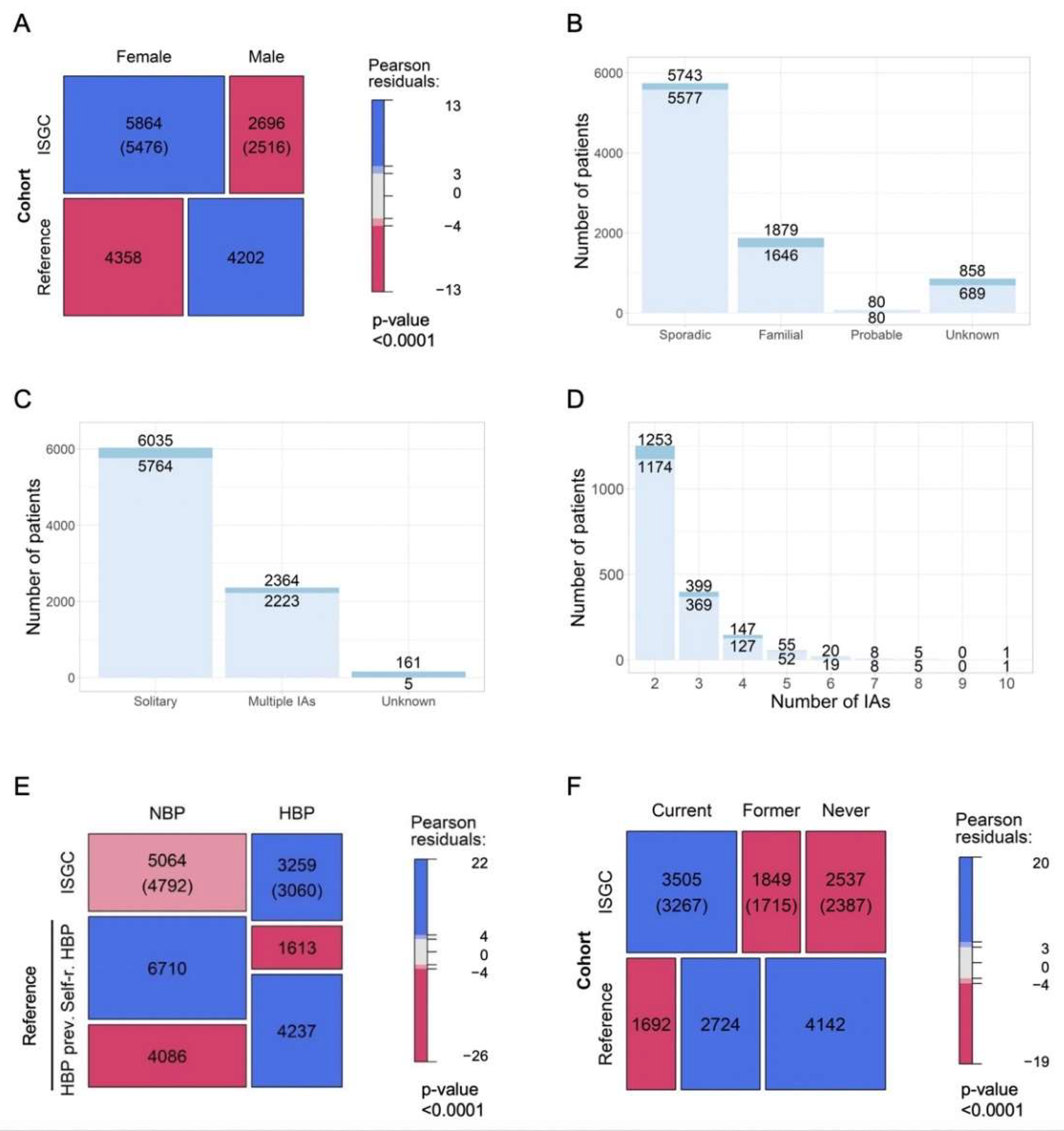
3.1. Characteristics of Whole Cohort
3.2. Patient Characteristics and Likelihood of Being Diagnosed with aSAH
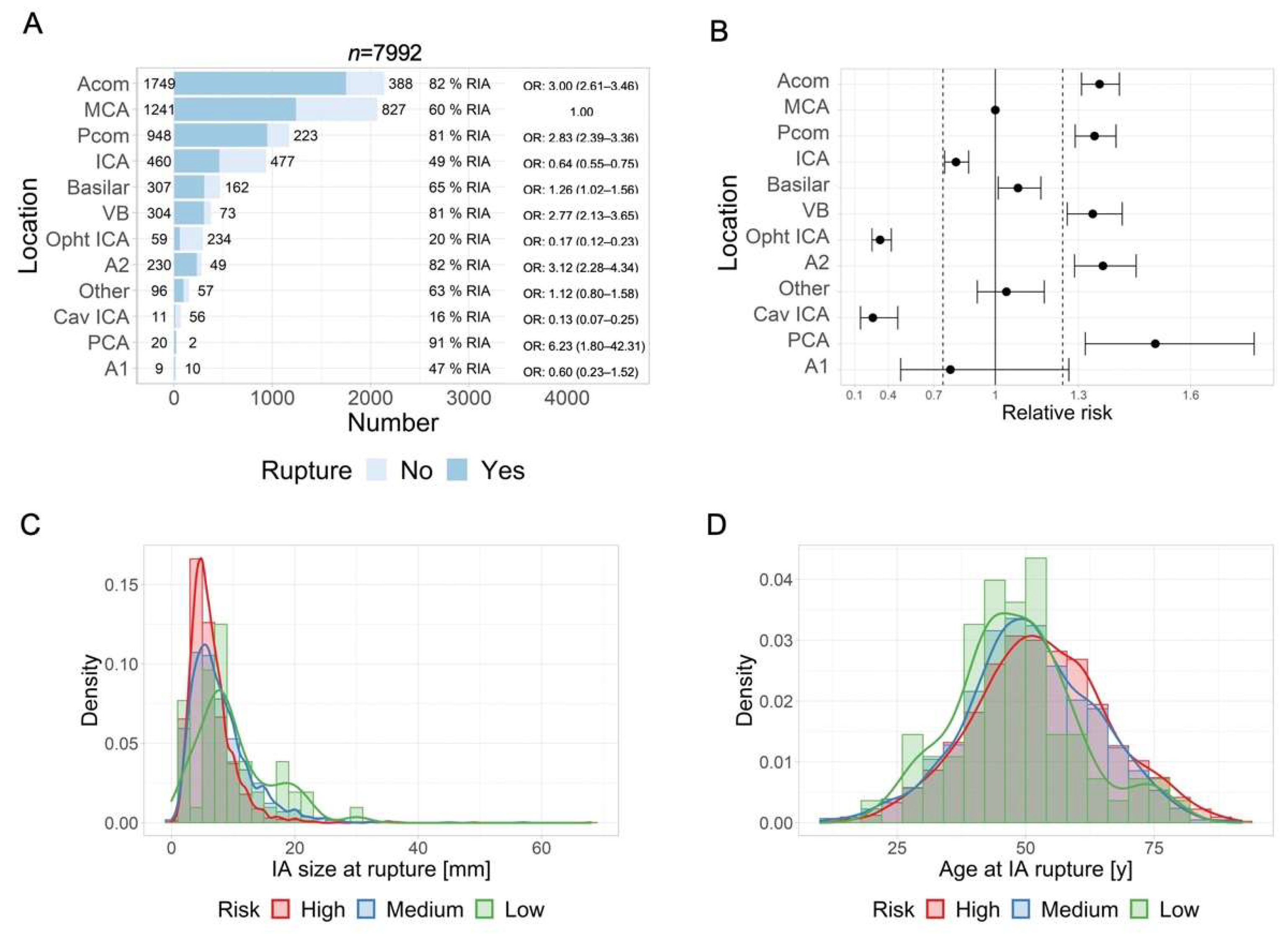
3.3. IA Location and Risk of Rupture
3.4. IA Location and Size at Rupture
3.5. IA Location and Age at Rupture
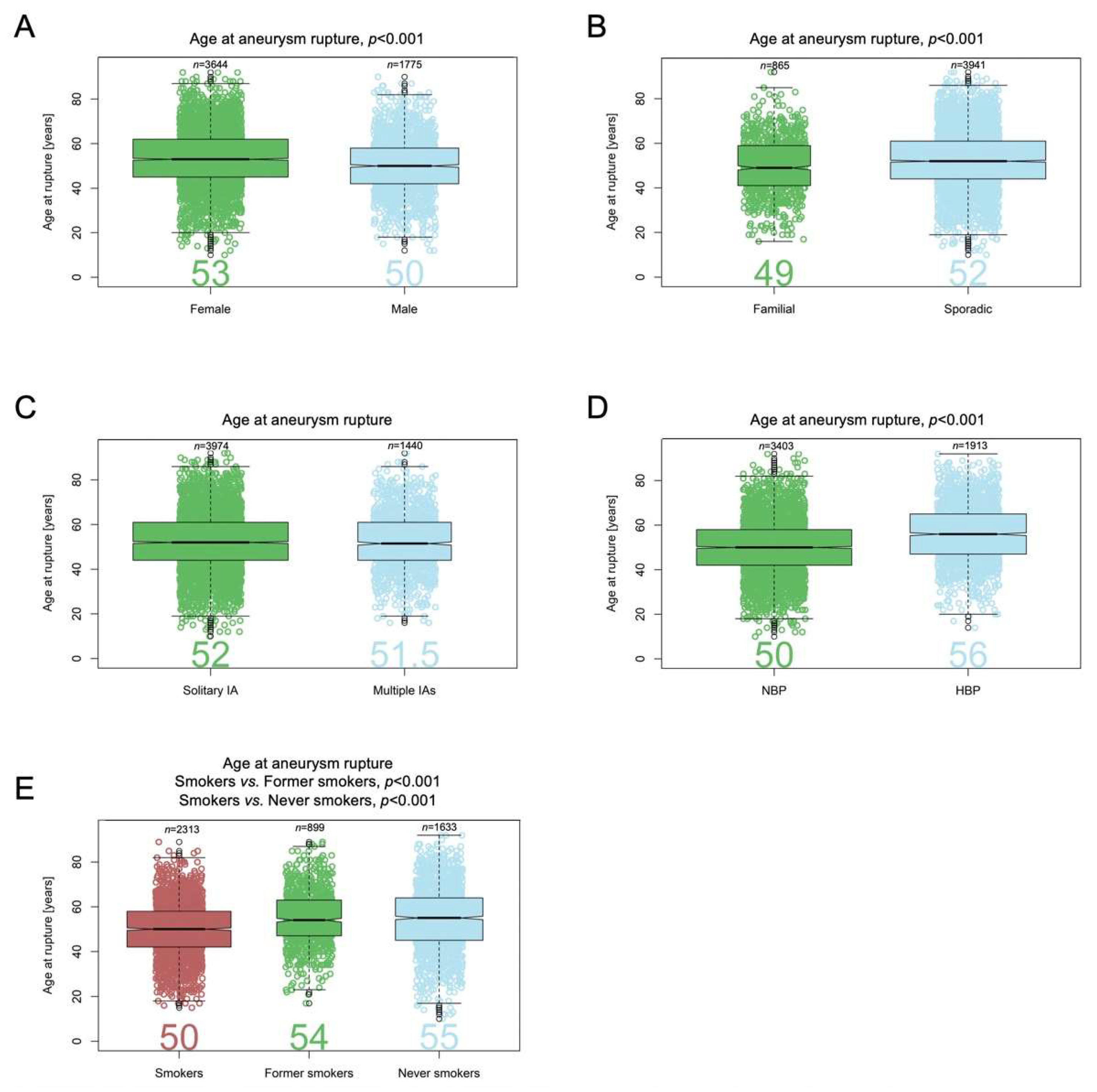
3.6. Patient Age at IA Rupture
3.7. IA Size and Risk of Rupture
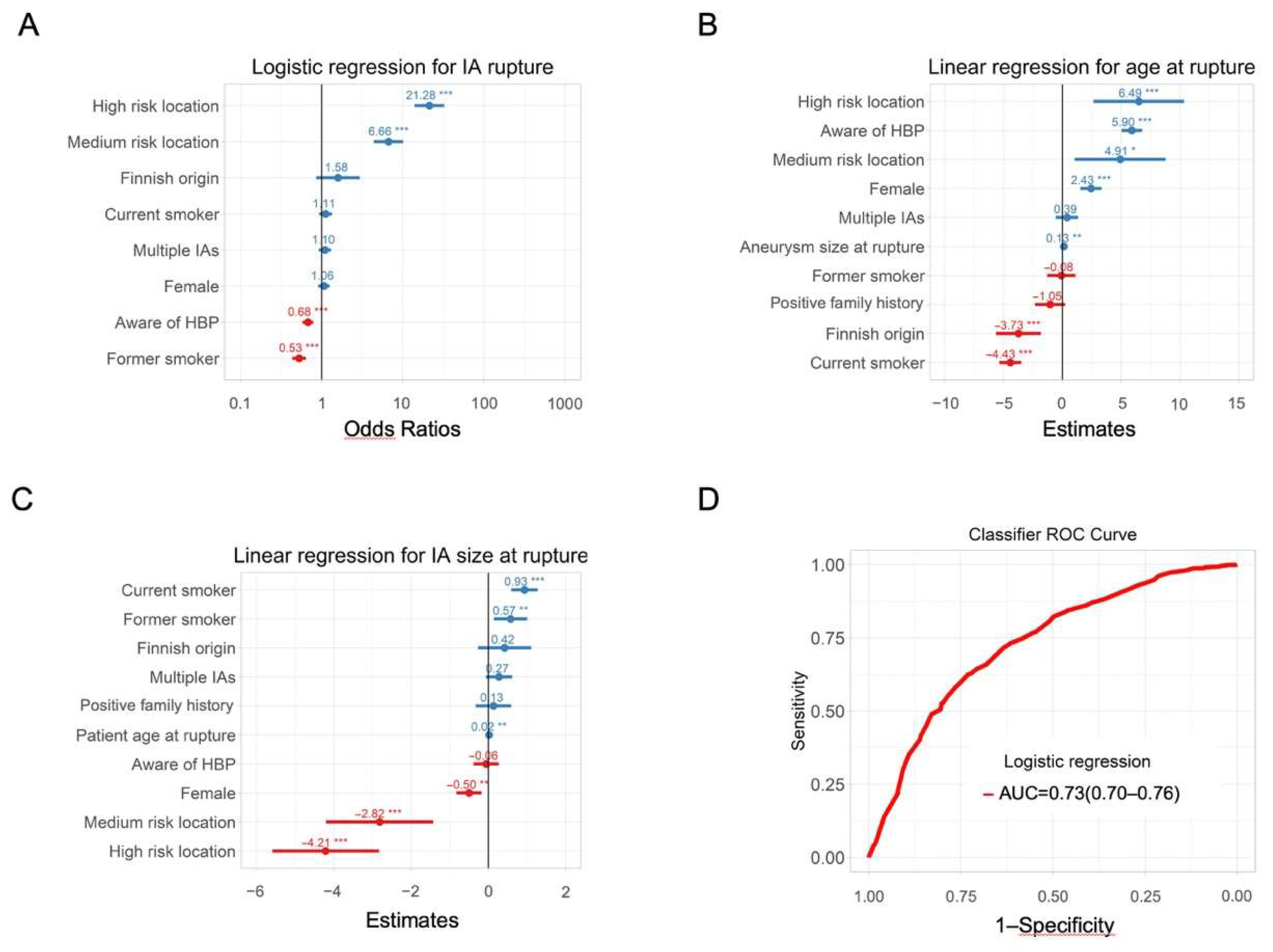
3.8. Classifiers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lawton, M.T.; Vates, G.E. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. New Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schatlo, B.; Fung, C.; Stienen, M.N.; Fathi, A.R.; Fandino, J.; Smoll, N.R.; Zumofen, D.; Daniel, R.T.; Burkhardt, J.K.; Bervini, D.; et al. Incidence and Outcome of Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: The Swiss Study on Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (Swiss SOS). Stroke 2021, 52, 344–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Khindi, T.; Macdonald, R.L.; Schweizer, T.A. Cognitive and functional outcome after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke J. Cereb. Circ. 2010, 41, e519–e536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juvela, S.; Poussa, K.; Lehto, H.; Porras, M. Natural history of unruptured intracranial aneurysms: A long-term follow-up study. Stroke 2013, 44, 2414–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiebers, D.O.; Whisnant, J.P.; Huston, J., 3rd; Meissner, I.; Brown, R.D., Jr.; Piepgras, D.G.; Forbes, G.S.; Thielen, K.; Nichols, D.; O’Fallon, W.M.; et al. Unruptured intracranial aneurysms: Natural history, clinical outcome, and risks of surgical and endovascular treatment. Lancet 2003, 362, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greving, J.P.; Wermer, M.J.; Brown, R.D., Jr.; Morita, A.; Juvela, S.; Yonekura, M.; Ishibashi, T.; Torner, J.C.; Nakayama, T.; Rinkel, G.J.; et al. Development of the PHASES score for prediction of risk of rupture of intracranial aneurysms: A pooled analysis of six prospective cohort studies. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, D.; Khoury, J.; Haverbusch, M.M.; Sekar, P.; Flaherty, M.L.; Kleindorfer, D.O.; Kissela, B.M.; Moomaw, C.J.; Deka, R.; Broderick, J.P. Smoking and family history and risk of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurology 2009, 72, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Investigators, U.J.; Morita, A.; Kirino, T.; Hashi, K.; Aoki, N.; Fukuhara, S.; Hashimoto, N.; Nakayama, T.; Sakai, M.; Teramoto, A.; et al. The natural course of unruptured cerebral aneurysms in a Japanese cohort. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2474–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etminan, N.; Beseoglu, K.; Steiger, H.J.; Hanggi, D. The impact of hypertension and nicotine on the size of ruptured intracranial aneurysms. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2011, 82, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tada, Y.; Wada, K.; Shimada, K.; Makino, H.; Liang, E.I.; Murakami, S.; Kudo, M.; Kitazato, K.T.; Nagahiro, S.; Hashimoto, T. Roles of hypertension in the rupture of intracranial aneurysms. Stroke J. Cereb. Circ. 2014, 45, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bijlenga, P.; Ebeling, C.; Jaegersberg, M.; Summers, P.; Rogers, A.; Waterworth, A.; Iavindrasana, J.; Macho, J.; Pereira, V.M.; Bukovics, P.; et al. Risk of rupture of small anterior communicating artery aneurysms is similar to posterior circulation aneurysms. Stroke 2013, 44, 3018–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijlenga, P.; Gondar, R.; Schilling, S.; Morel, S.; Hirsch, S.; Cuony, J.; Corniola, M.V.; Perren, F.; Rufenacht, D.; Schaller, K. PHASES Score for the Management of Intracranial Aneurysm: A Cross-Sectional Population-Based Retrospective Study. Stroke 2017, 48, 2105–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korja, M.; Lehto, H.; Juvela, S. Lifelong rupture risk of intracranial aneurysms depends on risk factors: A prospective Finnish cohort study. Stroke J. Cereb. Circ. 2014, 45, 1958–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wermer, M.J.; Greebe, P.; Algra, A.; Rinkel, G.J. Incidence of recurrent subarachnoid hemorrhage after clipping for ruptured intracranial aneurysms. Stroke J. Cereb. Circ. 2005, 36, 2394–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, M.K.; van der Spek, R.A.A.; van Rheenen, W.; Morel, S.; Bourcier, R.; Hostettler, I.C.; Alg, V.S.; van Eijk, K.R.; Koido, M.; Akiyama, M.; et al. Genome-wide association study of intracranial aneurysms identifies 17 risk loci and genetic overlap with clinical risk factors. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 1303–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission Website. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/health/dyna/echi/datatool (accessed on 4 November 2018).
- Samim, D.; Mean, M.; Clair, C.; Marques-Vidal, P. A 10-year observational study on the trends and determinants of smoking status. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, D.; Curjuric, I.; Dratva, J.; Schaffner, E.; Quinto, C.; Rochat, T.; Gaspoz, J.M.; Burdet, L.; Bridevaux, P.O.; Pons, M.; et al. High blood pressure: Prevalence and adherence to guidelines in a population-based cohort. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2016, 146, w14323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joffres, M.; Falaschetti, E.; Gillespie, C.; Robitaille, C.; Loustalot, F.; Poulter, N.; McAlister, F.A.; Johansen, H.; Baclic, O.; Campbell, N. Hypertension prevalence, awareness, treatment and control in national surveys from England, the USA and Canada, and correlation with stroke and ischaemic heart disease mortality: A cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 2013, 3, e003423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- N.C.D. Risk Factor Collaboration. Long-term and recent trends in hypertension awareness, treatment, and control in 12 high-income countries: An analysis of 123 nationally representative surveys. Lancet 2019, 394, 639–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryar, C.D.; Ostchega, Y.; Hales, C.M.; Zhang, G.; Kruszon-Moran, D. Hypertension Prevalence and Control among Adults: United States, 2015–2016; NCHS Data Brief National Center for Health Statistics: Hyattsville, MD, USA, 2017; Volume 289. [Google Scholar]
- Online resource: Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development Stat Web Site. Available online: https://stats.oecd.org (accessed on 4 November 2018).
- Online Resource: The Gallup Organisation. Survey on Tabacco. 2008. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/health/ph_determinants/life_style/Tobacco/Documents/eb_253_en.pdf (accessed on 4 November 2018).
- Asma, S.; Mackay, J.; Song, S.Y.; Zhao, L.; Morton, J.; Palipudi, K.M.; Bettcher, D.; Bhatti, L.; Caixeta, R.; Chandora, R.; et al. The GATS Atlas; CDC Foundation: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Greenland, K.J.R.A.S. Modern Epidemiology; Lippincott-Raven Publishers: London, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Bijlenga, P.; Morel, S.; Hirsch, S.; Schaller, K.; Rufenacht, D. Plea for an international Aneurysm Data Bank: Description and perspectives. Neurosurg Focus 2019, 47, E17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondar, R.; Gautschi, O.P.; Cuony, J.; Perren, F.; Jagersberg, M.; Corniola, M.V.; Schatlo, B.; Molliqaj, G.; Morel, S.; Kulcsar, Z.; et al. Unruptured intracranial aneurysm follow-up and treatment after morphological change is safe: Observational study and systematic review. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2016, 87, 1277–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousseau, O.; Karakachoff, M.; Gaignard, A.; Bellanger, L.; Bijlenga, P.; Constant Dit Beaufils, P.; L’Allinec, V.; Levrier, O.; Aguettaz, P.; Desilles, J.P.; et al. Location of intracranial aneurysms is the main factor associated with rupture in the ICAN population. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2021, 92, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geers, A.J.; Morales, H.G.; Larrabide, I.; Butakoff, C.; Bijlenga, P.; Frangi, A.F. Wall shear stress at the initiation site of cerebral aneurysms. Biomech. Modeling Mechanobiol. 2017, 16, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfano, J.M.; Kolega, J.; Natarajan, S.K.; Xiang, J.; Paluch, R.A.; Levy, E.I.; Siddiqui, A.H.; Meng, H. Intracranial aneurysms occur more frequently at bifurcation sites that typically experience higher hemodynamic stresses. Neurosurgery 2013, 73, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, S.; Shimogonya, Y.; Yonemoto, N.; Group, C.A.S. Differences in Cerebral Aneurysm Rupture Rate According to Arterial Anatomies Depend on the Hemodynamic Environment. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2019, 40, 834–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detmer, F.J.; Mut, F.; Slawski, M.; Hirsch, S.; Bijlenga, P.; Cebral, J.R. Incorporating variability of patient inflow conditions into statistical models for aneurysm rupture assessment. Acta Neurochir. 2020, 162, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulamo, R.; Frosen, J.; Hernesniemi, J.; Niemela, M. Inflammatory changes in the aneurysm wall: A review. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2018, 10, i58–i67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Millan Ruiz, D.; Yilmaz, H.; Dehdashti, A.R.; Alimenti, A.; de Tribolet, N.; Rufenacht, D.A. The perianeurysmal environment: Influence on saccular aneurysm shape and rupture. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2006, 27, 504–512. [Google Scholar]
- Lindgren, A.E.; Koivisto, T.; Bjorkman, J.; von Und Zu Fraunberg, M.; Helin, K.; Jaaskelainen, J.E.; Frosen, J. Irregular Shape of Intracranial Aneurysm Indicates Rupture Risk Irrespective of Size in a Population-Based Cohort. Stroke J. Cereb. Circ. 2016, 47, 1219–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, A.; Castro, V.M.; Ozdemir, Y.H.; Dagen, S.; Yu, S.; Dligach, D.; Finan, S.; Gainer, V.; Shadick, N.A.; Murphy, S.; et al. Association of intracranial aneurysm rupture with smoking duration, intensity, and cessation. Neurology 2017, 89, 1408–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalouhi, N.; Ali, M.S.; Starke, R.M.; Jabbour, P.M.; Tjoumakaris, S.I.; Gonzalez, L.F.; Rosenwasser, R.H.; Koch, W.J.; Dumont, A.S. Cigarette smoke and inflammation: Role in cerebral aneurysm formation and rupture. Mediat. Inflamm 2012, 2012, 271582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schatlo, B.; Gautschi, O.P.; Friedrich, C.M.; Ebeling, C.; Jagersberg, M.; Kulscar, Z.; Pereira, V.M.; Schaller, K.; Bijlenga, P. Association of single and multiple aneurysms with tobacco abuse: An @neurIST risk analysis. Neurosurg. Focus 2019, 47, E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdan, A.; Barnes, J.; Mitchell, P. Subarachnoid hemorrhage and the female sex: Analysis of risk factors, aneurysm characteristics, and outcomes. J. Neurosurg. 2014, 121, 1367–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amenta, P.S.; Medel, R.; Pascale, C.L.; Dumont, A.S. Elucidating Sex Differences in Cerebral Aneurysm Biology and Therapy: The Time Is Now. Hypertension 2016, 68, 312–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wermer, M.J.; van der Schaaf, I.C.; Algra, A.; Rinkel, G.J. Risk of rupture of unruptured intracranial aneurysms in relation to patient and aneurysm characteristics: An updated meta-analysis. Stroke J. Cereb. Circ. 2007, 38, 1404–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algra, A.M.; Klijn, C.J.; Helmerhorst, F.M.; Algra, A.; Rinkel, G.J. Female risk factors for subarachnoid hemorrhage: A systematic review. Neurology 2012, 79, 1230–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, A.I.; Malik, A.A.; Saeed, O.; Defillo, A.; Sherr, G.T.; Suri, M.F. Hormone replacement therapy and the risk of subarachnoid hemorrhage in postmenopausal women. J. Neurosurg. 2016, 124, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, S.; Karol, A.; Graf, V.; Pelli, G.; Richter, H.; Sutter, E.; Braunersreuther, V.; Frosen, J.; Bijlenga, P.; Kwak, B.R.; et al. Sex-related differences in wall remodeling and intraluminal thrombus resolution in a rat saccular aneurysm model. J. Neurosurg. 2019, 134, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morel, S.; Hostettler, I.C.; Spinner, G.R.; Bourcier, R.; Pera, J.; Meling, T.R.; Alg, V.S.; Houlden, H.; Bakker, M.K.; van’t Hof, F.; et al. Intracranial Aneurysm Classifier Using Phenotypic Factors: An International Pooled Analysis. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12091410
Morel S, Hostettler IC, Spinner GR, Bourcier R, Pera J, Meling TR, Alg VS, Houlden H, Bakker MK, van’t Hof F, et al. Intracranial Aneurysm Classifier Using Phenotypic Factors: An International Pooled Analysis. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022; 12(9):1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12091410
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorel, Sandrine, Isabel C. Hostettler, Georg R. Spinner, Romain Bourcier, Joanna Pera, Torstein R. Meling, Varinder S. Alg, Henry Houlden, Mark K. Bakker, Femke van’t Hof, and et al. 2022. "Intracranial Aneurysm Classifier Using Phenotypic Factors: An International Pooled Analysis" Journal of Personalized Medicine 12, no. 9: 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12091410
APA StyleMorel, S., Hostettler, I. C., Spinner, G. R., Bourcier, R., Pera, J., Meling, T. R., Alg, V. S., Houlden, H., Bakker, M. K., van’t Hof, F., Rinkel, G. J. E., Foroud, T., Lai, D., Moomaw, C. J., Worrall, B. B., Caroff, J., Constant-dits-Beaufils, P., Karakachoff, M., Rimbert, A., ... Bijlenga, P. (2022). Intracranial Aneurysm Classifier Using Phenotypic Factors: An International Pooled Analysis. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(9), 1410. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12091410










