Polygenic Risk Score and Risk Factors for Gestational Diabetes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Genotype and Phenotype Data
2.3. Procedure for Learning the Polygenic Risk Scores
2.4. Mendelian Randomization
2.5. SNP Annotation
3. Results
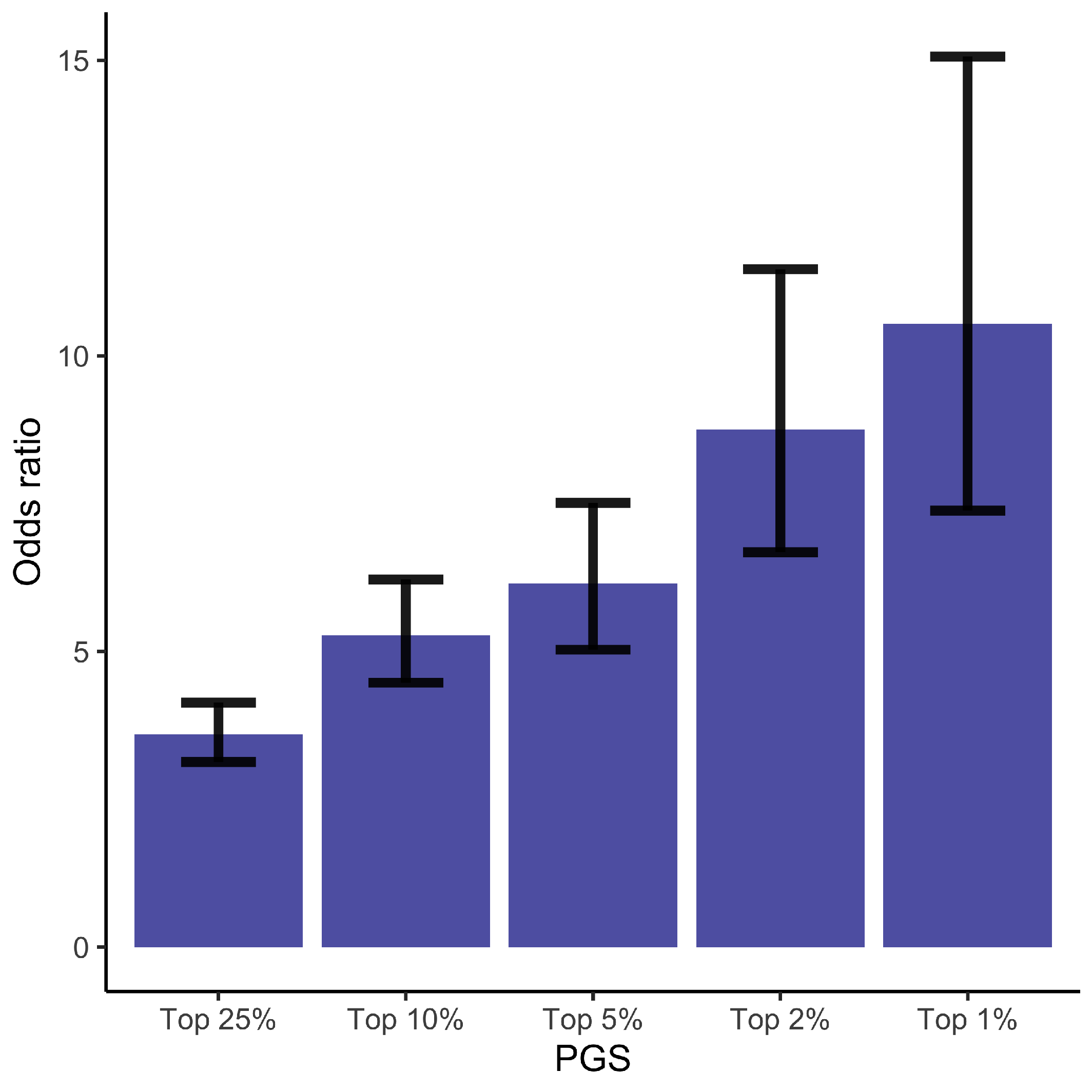
3.1. Polygenic Risk Score
3.2. GDM Risk and BMI
3.3. GDM Risk and Female-Specific Anthropometric Measures
4. Discussion
4.1. Functional Analysis
4.2. Risk Factors for GDM
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McIntyre, H.; Catalano, P.; Zhang, C.; Desoye, G.; Mathiesen, E.R.; Damm, P. Gestational diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2019, 5, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, C. Prevalence of gestational diabetes and risk of progression to type 2 diabetes: A global perspective. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2016, 16, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalfrà, M.G.; Burlina, S.; Del Vescovo, G.G.; Lapolla, A. Genetics and epigenetics: New insight on gestational diabetes mellitus. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 602477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, M.; Liu, Y.; Ronnett, G.V.; Wu, A.; Cox, B.J.; Dai, F.F.; Röst, H.L.; Gunderson, E.P.; Wheeler, M.B. Amino acid and lipid metabolism in post-gestational diabetes and progression to type 2 diabetes: A metabolic profiling study. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaston, A.; Cramp, A. Exercise during pregnancy: A review of patterns and determinants. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2011, 14, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fell, D.B.; Joseph, K.; Armson, B.A.; Dodds, L. The impact of pregnancy on physical activity level. Matern. Child Health J. 2009, 13, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzago, M.; Fraticelli, F.; Stuppia, L.; Vitacolonna, E. Nutrigenetics, epigenetics and gestational diabetes: Consequences in mother and child. Epigenetics 2019, 14, 215–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellmuth, C.; Lindsay, K.L.; Uhl, O.; Buss, C.; Wadhwa, P.D.; Koletzko, B.; Entringer, S. Association of maternal prepregnancy BMI with metabolomic profile across gestation. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Solomon, C.G.; Manson, J.E.; Hu, F.B. A prospective study of pregravid physical activity and sedentary behaviors in relation to the risk for gestational diabetes mellitus. Arch. Intern. Med. 2006, 166, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ning, Y. Effect of dietary and lifestyle factors on the risk of gestational diabetes: Review of epidemiologic evidence. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 94, 1975S–1979S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Bao, W.; Rong, Y.; Yang, H.; Bowers, K.; Yeung, E.; Kiely, M. Genetic variants and the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: A systematic review. Hum. Reprod. Update 2013, 19, 376–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pervjakova, N.; Moen, G.H.; Borges, M.C.; Ferreira, T.; Cook, J.P.; Allard, C.; Beaumont, R.N.; Canouil, M.; Hatem, G.; Heiskala, A.; et al. Multi-ancestry genome-wide association study of gestational diabetes mellitus highlights genetic links with type 2 diabetes. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2022, 00, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powe, C.E.; Kwak, S.H. Genetic studies of gestational diabetes and glucose metabolism in pregnancy. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2020, 20, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powe, C.E.; Nodzenski, M.; Talbot, O.; Allard, C.; Briggs, C.; Leya, M.V.; Perron, P.; Bouchard, L.; Florez, J.C.; Scholtens, D.M.; et al. Genetic determinants of glycemic traits and the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 2018, 67, 2703–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, V.K.; Levinson, R.T.; Adefurin, A.; Kurnik, D.; Collier, S.P.; Conway, D.; Stein, C.M. A genetic risk score that includes common type 2 diabetes risk variants is associated with gestational diabetes. Clin. Endocrinol. 2017, 87, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Chavarro, J.; Olsen, S.; Lin, Y.; Ley, S.H.; Bao, W.; Rawal, S.; Grunnet, L.G.; Thuesen, A.C.B.; Mills, J.L.; et al. Genetic variants of gestational diabetes mellitus: A study of 112 SNPs among 8722 women in two independent populations. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 1758–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, M.; Liu, M.; Zhang, L.; Liang, Z.; Chen, D. An early prediction model for gestational diabetes mellitus based on genetic variants and clinical characteristics in China. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2022, 14, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonzo, T.A. Clinical Prediction Models: A Practical Approach to Development, Validation, and Updating: By Ewout W. Steyerberg. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2009, 170, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keikkala, E.; Mustaniemi, S.; Koivunen, S.; Kinnunen, J.; Viljakainen, M.; Männisto, T.; Ijäs, H.; Pouta, A.; Kaaja, R.; Eriksson, J.G.; et al. Cohort Profile: The Finnish Gestational Diabetes (FinnGeDi) Study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 49, 762–763g. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemani, G.; Zheng, J.; Elsworth, B.; Wade, K.H.; Haberland, V.; Baird, D.; Laurin, C.; Burgess, S.; Bowden, J.; Langdon, R.; et al. The MR-Base platform supports systematic causal inference across the human phenome. eLife 2018, 7, e34408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulc, J.; Sonrel, A.; Mounier, N.; Auwerx, C.; Marouli, E.; Darrous, L.; Draganski, B.; Kilpeläinen, T.O.; Joshi, P.; Loos, R.J.; et al. Composite trait Mendelian randomization reveals distinct metabolic and lifestyle consequences of differences in body shape. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oscanoa, J.; Sivapalan, L.; Gadaleta, E.; Dayem Ullah, A.Z.; Lemoine, N.; Chelala, C. SNPnexus: A web server for functional annotation of human genome sequence variation (2020 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, W185–W192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dayem Ullah, A.Z.; Oscanoa, J.; Wang, J.; Nagano, A.; Lemoine, N.R.; Chelala, C. SNPnexus: Assessing the functional relevance of genetic variation to facilitate the promise of precision medicine. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W109–W113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, K.; Taskesen, E.; van Bochoven, A.; Posthuma, D. Functional mapping and annotation of genetic associations with FUMA. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saltiel, A.R.; Olefsky, J.M. Inflammatory mechanisms linking obesity and metabolic disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellulu, M.S.; Patimah, I.; Khaza’ai, H.; Rahmat, A.; Abed, Y. Obesity and inflammation: The linking mechanism and the complications. Arch. Med. Sci. 2017, 13, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, M.A.; Verweij, N.; van der Harst, P. Associations of combined genetic and lifestyle risks with incident cardiovascular disease and diabetes in the UK Biobank Study. JAMA Cardiol. 2018, 3, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, E.; Glymour, M.M.; Holmes, M.V.; Kang, H.; Morrison, J.; Munafò, M.R.; Palmer, T.; Schooling, C.M.; Wallace, C.; Zhao, Q.; et al. Mendelian randomization. Nat. Rev. Methods Prim. 2022, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Mendola, P.; Albert, P.S.; Bao, W.; Hinkle, S.N.; Tsai, M.Y.; Zhang, C. Insulin-like growth factor axis and gestational diabetes mellitus: A longitudinal study in a multiracial cohort. Diabetes 2016, 65, 3495–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konuma, T.; Okada, Y. Statistical genetics and polygenic risk score for precision medicine. Inflamm. Regen. 2021, 41, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Term | Estimate | Std. Error | Statistic | p Value | Overlapped Gene | Nearest Upstream Gene | Nearest Downstream Gene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs10830963 | 0.267 | 0.046 | 5.834 | MTNR1B | |||
| rs6959526 | 0.378 | 0.081 | 4.671 | MGAM | |||
| rs34075917 | 0.205 | 0.045 | 4.54 | CTC-419K13.1 | ENC1 | ||
| rs7903146 | 0.204 | 0.046 | 4.45 | TCF7L2 | |||
| rs11257655 | 0.209 | 0.050 | 4.186 | RN7SL232P | RN7SL198P | ||
| rs4746822 | 0.190 | 0.046 | 4.123 | RP11-227H15.4; HKDC1 | |||
| rs79953201 | 0.583 | 0.144 | 4.037 | HAPLN1 | |||
| rs34882181 | −0.149 | 0.042 | −3.512 | PTPRD | |||
| rs535447438 | −0.155 | 0.046 | −3.355 | LPHN2 | |||
| rs141240229 | 0.318 | 0.096 | 3.296 | 0.001 | EEF1A1P9 | AC004066.2 | |
| rs116847631 | 0.202 | 0.062 | 3.279 | 0.001 | PGR | ||
| rs7957197 | −0.180 | 0.058 | −3.127 | 0.0018 | OASL | ||
| rs116966095 | 0.258 | 0.085 | 3.04 | 0.0024 | CFDP1 | ||
| rs62603092 | −0.248 | 0.082 | −3.014 | 0.0026 | RP11-274K13.5 | snoU13 | |
| rs2866307 | −0.145 | 0.049 | −2.939 | 0.0033 | RP11-168E17.1 | RNU6-578P | |
| rs7743373 | −0.152 | 0.052 | −2.902 | 0.0037 | RP3-435K13.1 | RP3-455E7.1 | |
| rs340874 | 0.123 | 0.043 | 2.846 | 0.0044 | PROX1-AS1; PROX1 | ||
| rs62052363 | 0.251 | 0.092 | 2.735 | 0.0062 | PKD1L2 | ||
| rs568927434 | 0.134 | 0.049 | 2.734 | 0.0063 | SPP1 | ||
| rs4376068 | 0.121 | 0.045 | 2.712 | 0.0067 | IGF2BP2 | ||
| rs62170385 | 0.270 | 0.102 | 2.64 | 0.0083 | ARHGAP15 | ||
| rs174550 | −0.120 | 0.046 | −2.588 | 0.0096 | FADS2; FADS1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perišić, M.M.; Vladimir, K.; Karpov, S.; Štorga, M.; Mostashari, A.; Khanin, R. Polygenic Risk Score and Risk Factors for Gestational Diabetes. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1381. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12091381
Perišić MM, Vladimir K, Karpov S, Štorga M, Mostashari A, Khanin R. Polygenic Risk Score and Risk Factors for Gestational Diabetes. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022; 12(9):1381. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12091381
Chicago/Turabian StylePerišić, Marija Majda, Klemo Vladimir, Sarah Karpov, Mario Štorga, Ali Mostashari, and Raya Khanin. 2022. "Polygenic Risk Score and Risk Factors for Gestational Diabetes" Journal of Personalized Medicine 12, no. 9: 1381. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12091381
APA StylePerišić, M. M., Vladimir, K., Karpov, S., Štorga, M., Mostashari, A., & Khanin, R. (2022). Polygenic Risk Score and Risk Factors for Gestational Diabetes. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(9), 1381. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12091381





