Fetal Growth Restriction: Comparison of Biometric Parameters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Statistical Analysis
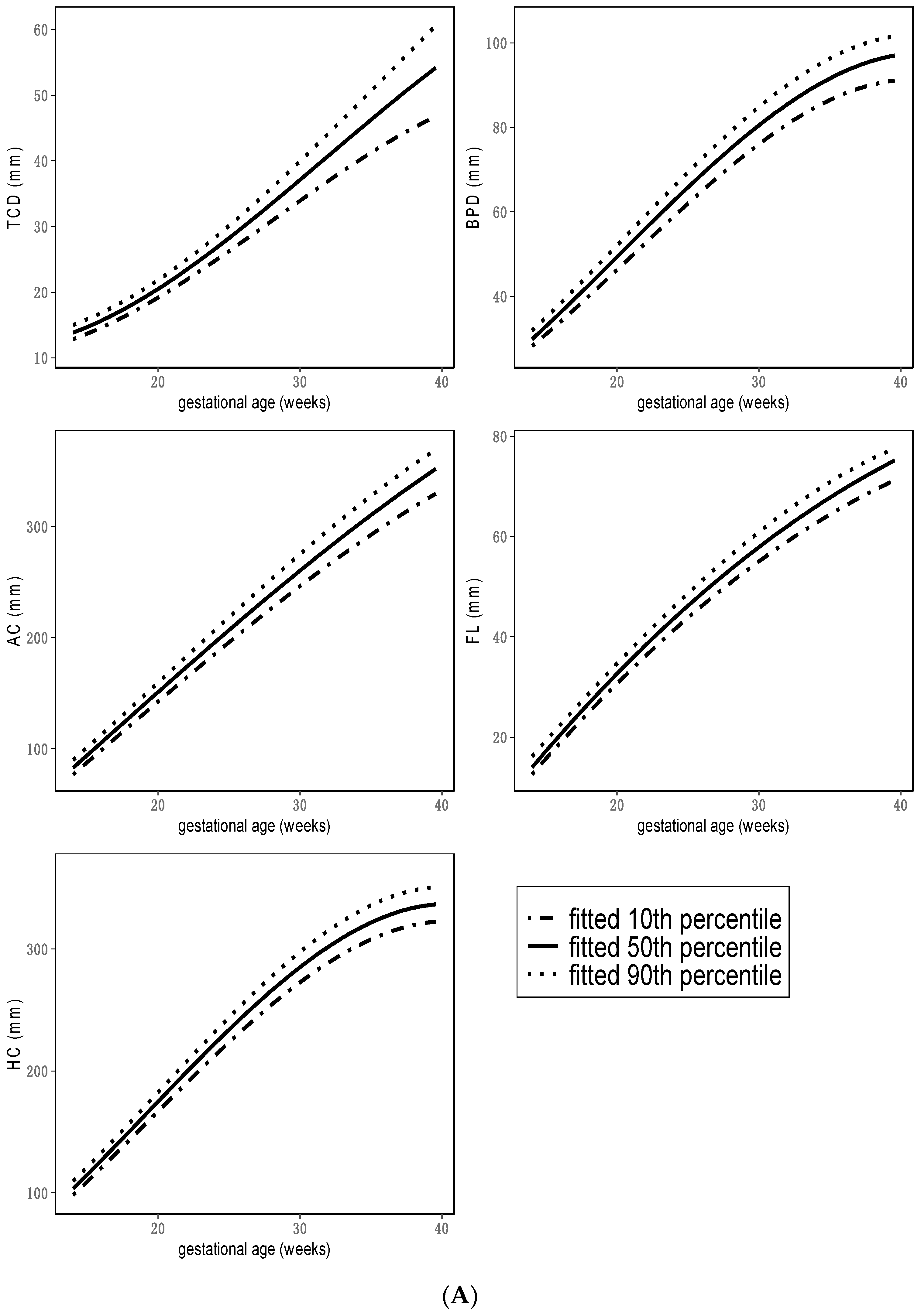
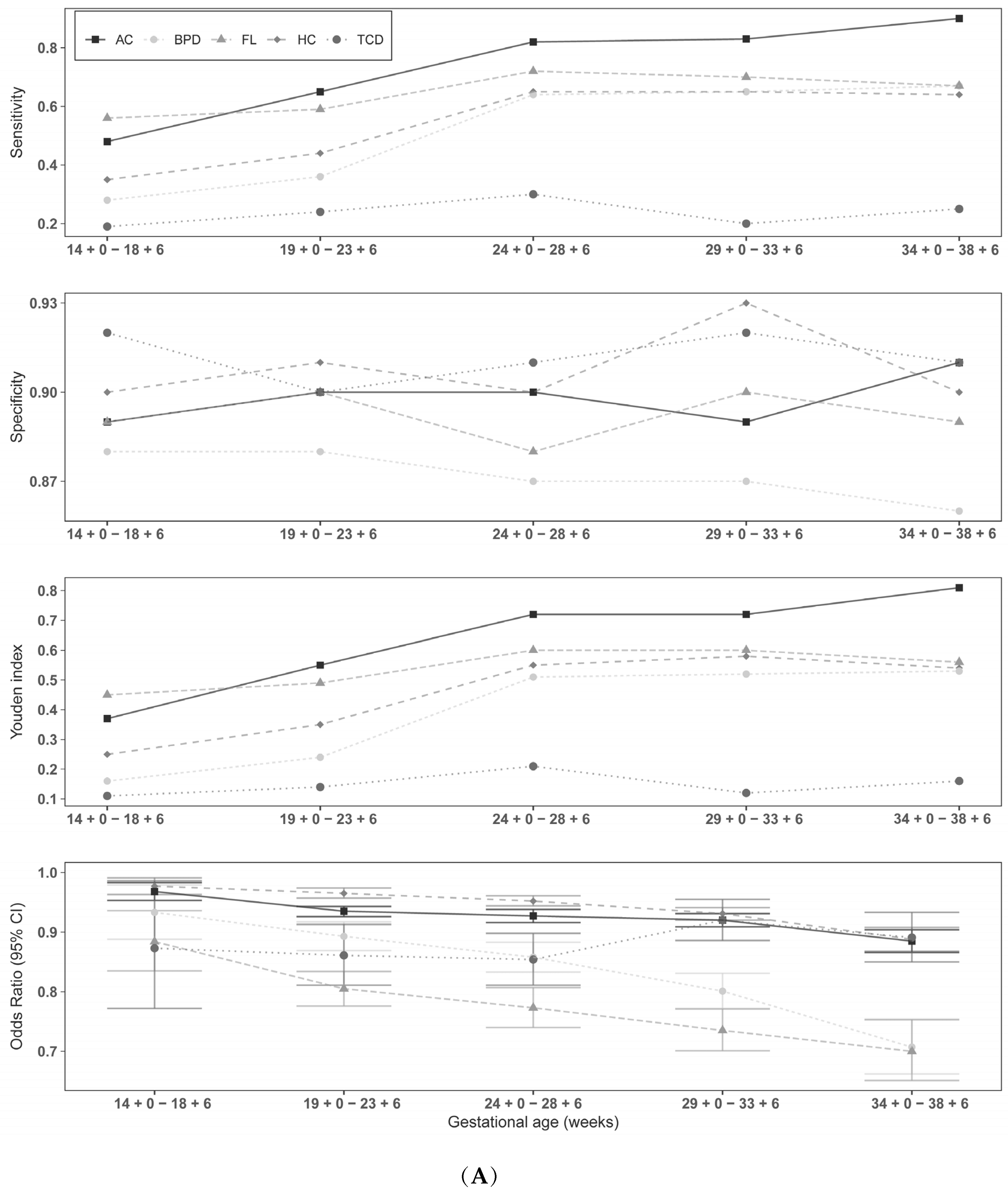
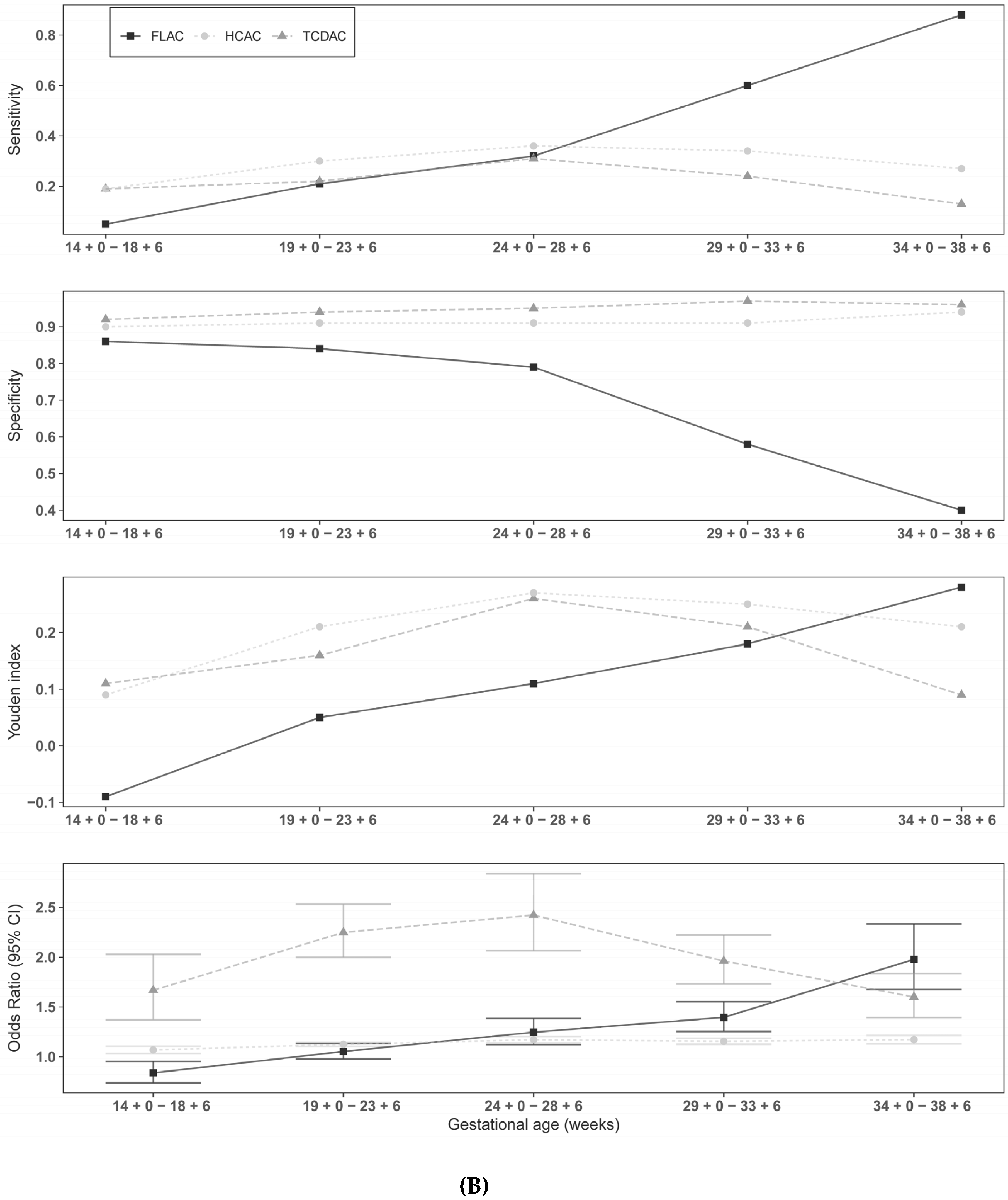
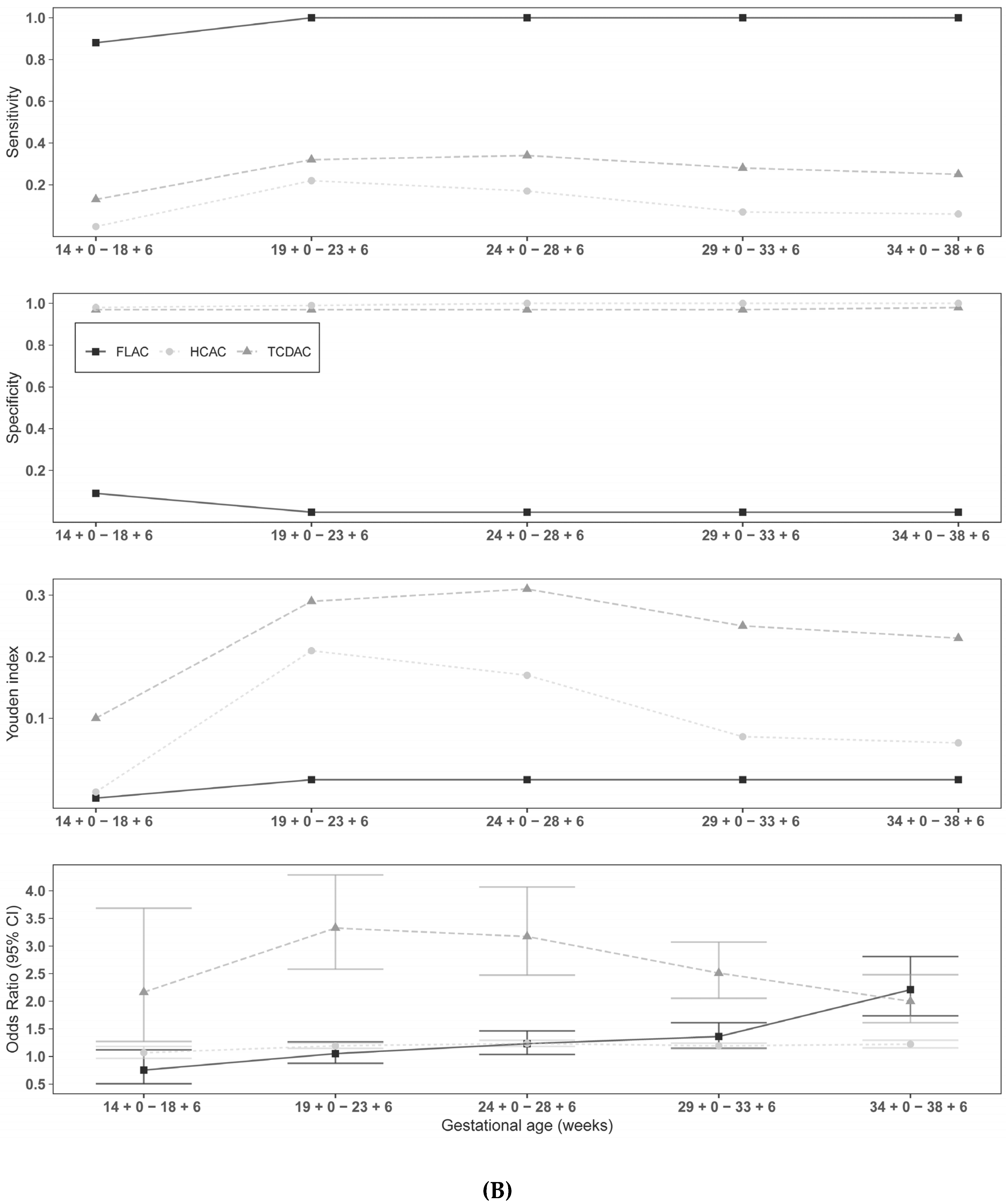
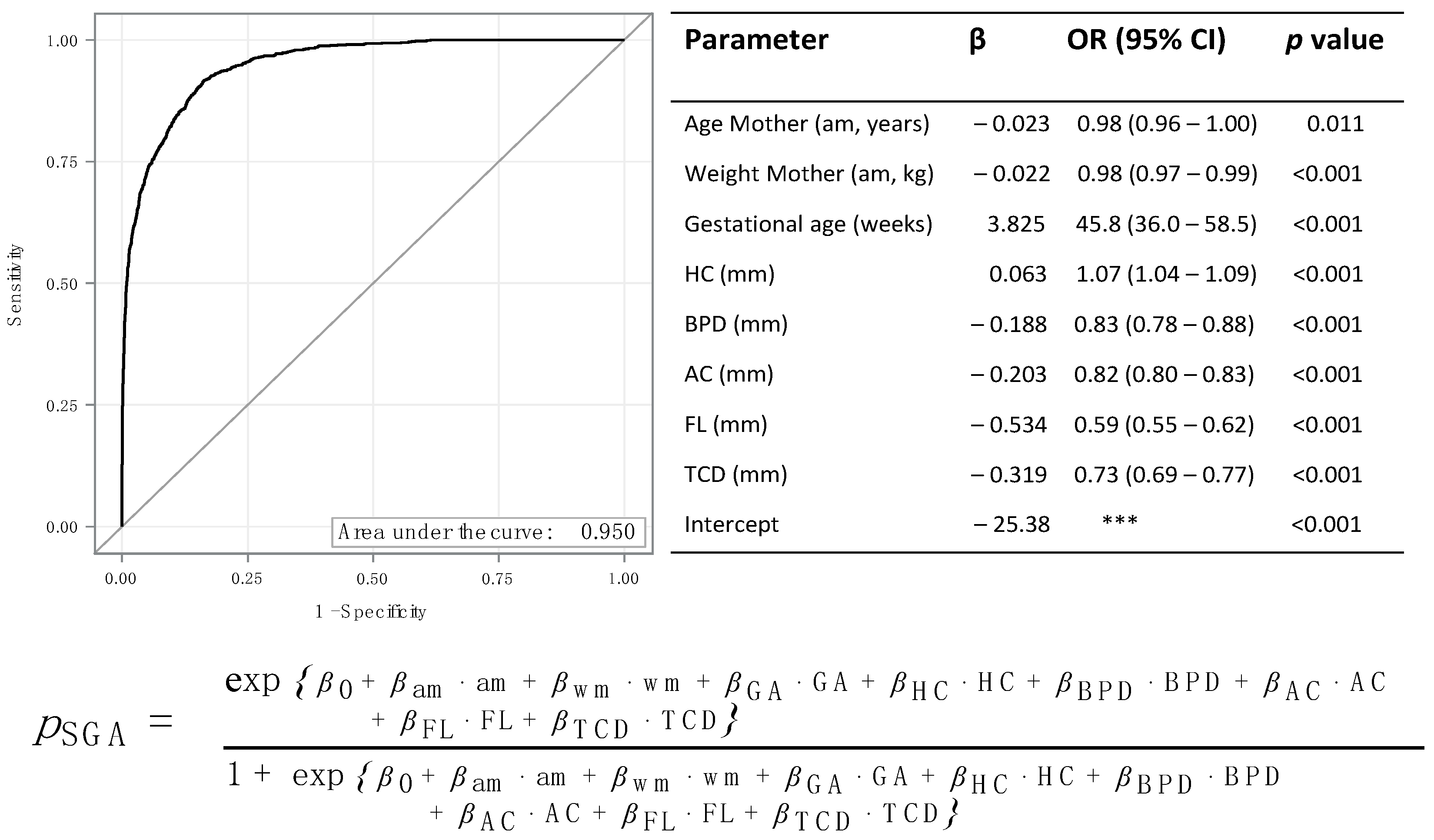
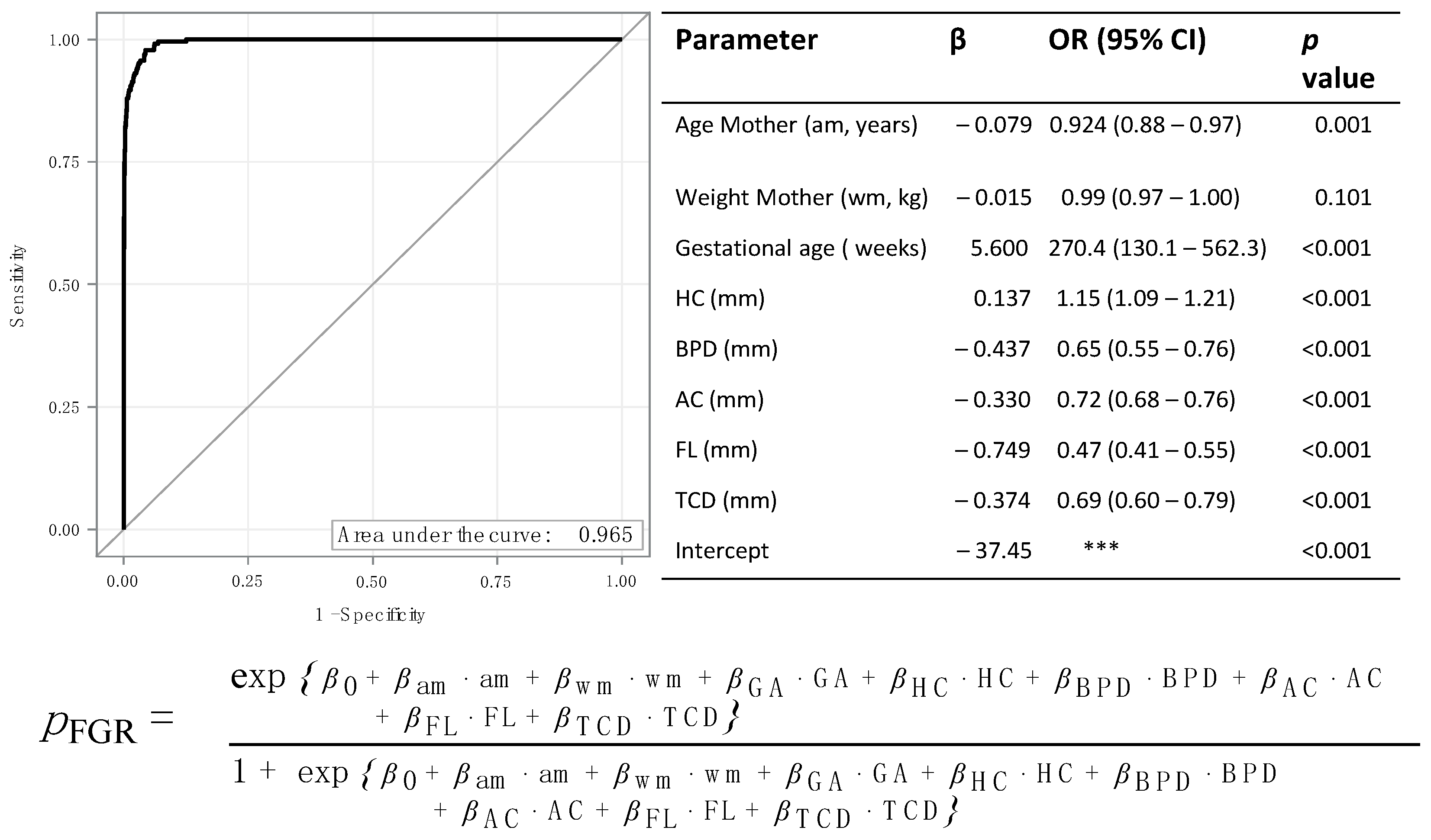
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Albu, A.R.; Anca, A.F.; Horhoianu, V.V.; Horhoianu, I.A. Predictive factors for intrauterine growth restriction. J. Med. Life 2014, 7, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sharma, D.; Shastri, S.; Farahbakhsh, N.; Sharma, P. Intrauterine growth restriction—Part 1. J. Matern. Neonatal Med. 2016, 29, 3977–3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, E.M.; Forouzan, I.; Morgan, M.A. A retrospective analysis of Erb’s palsy cases and their relation to birth weight and trauma at delivery. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 1997, 6, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nohuz, E.; Rivière, O.; Coste, K.; Vendittelli, F. Prenatal identification of small-for-gestational age and risk of neonatal morbidity and stillbirth. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2019, 55, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, S.P.; Beydoun, H.; Chang, E.; Sandlin, A.T.; Dahlke, J.D.; Igwe, E.; Magann, E.F.; Anderson, K.R.; Abuhamad, A.Z.; Ananth, C.V. Prenatal detection of fetal growth restriction in newborns classified as small for gestational age: Correlates and risk of neonatal morbidity. Am. J. Perinatol. 2014, 31, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindqvist, P.G.; Molin, J. Does antenatal identification of small-for-gestational age fetuses significantly improve their outcome? Ultrasound Obs. Gynecol. 2005, 25, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitner, Y.; Fattal-Valevski, A.; Geva, R.; Eshel, R.; Toledano-Alhadef, H.; Rotstein, M.; Bassan, H.; Radianu, B.; Bitchonsky, O.; Jaffa, A.J.; et al. Neurodevelopmental outcome of children with intrauterine growth retardation: A longitudinal, 10-Year prospective study. J. Child Neurol. 2007, 22, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehl, S.; Dötsch, J.; Hecher, K.; Schlembach, D.; Schmitz, D.; Stepan, H.; Gembruch, U. Intrauterine Growth Restriction. Guideline of the German Society of Gynecology and Obstetrics. Geburtsh. Frauenheilk. 2017, 77, 1157–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCowan, L.; Figueras, F.; Anderson, N. Evidence-based national guidelines for the management of suspected fetal growth restriction: Comparison, consensus, and controversy. Am. J. Obs. Gynecol. 2018, 218, S855–S868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vinkesteijn, A.; Mulder, P.; Wladimiroff, J. Fetal transverse cerebellar diameter measurements in normal and reduced fetal growth. Ultrasound Obs. Gynecol. 2000, 15, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reece, E.A.; Goldstein, I.; Pilu, G.; Hobbins, J.C. Fetal cerebellar growth unaffected by intrauterine growth retardation: A new parameter for prenatal diagnosis. Am. J. Obs. Gynecol. 1987, 157, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadlock, F.P.; Deter, R.L.; Harrist, R.B.; Roecker, E.; Park, S.K. A date-independent predictor of intrauterine growth retardation: Femur length/abdominal circumference ratio. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1983, 141, 979–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Campbell, W.A.; Nardi, D.E.; Vintzileos, A.M.; Rodis, J.F.; Turner, G.W.; Egan, J.F. Transverse Cerebellar Diameter/Abdominal Circumference Ratio Throughout Pregnancy: A Gestational Age-Independent Method to Assess Fetal Growth. Am. J. Obs. Gynecol. 1991, 77, 893–896. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, W.J.; Gauthier, D.W.; Goldenberg, B.; Santolaya, J.; Sipos, J.; Cattledge, F. The fetal transverse cerebellar diameter/abdominal circumference ratio: A gestational age-independent method of assessing fetal size. J. Ultrasound Med. 1993, 12, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haller, H.; Petrović, O.; Rukavina, B. Fetal transverse cerebellar diameter/abdominal circumference ratio in assessing fetal size. Int. J. Gynecol Obs. 1995, 50, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongsong, T.; Wanapirak, C.; Thongpadungroj, T. Sonographic diagnosis of intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) by fetal transverse cerebellar diameter (TCD)/abdominal circumference (AC) ratio. Int. J. Gynecol. Obs. 1999, 66, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellad, M.B.; Dhumale, H.; Pujar, Y.V.; Shravage, J.C.; Sherigar, B.Y.; Durdi, G.S.; Amber, S.S. Fetal Transcerebellar Diameter to Abdominal Circumference Ratio (TCD/AC) in the Assessment of Normal Fetal Growth. J. Ultrasound Obs. Gynecol. 2010, 4, 455–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colley, N.V.; Tremble, J.M.; Henson, G.L.; Cole, T.J. Head circumference/abdominal circumference ratio, ponderal index and fetal malnutrition. Should head circumference/abdominal circumference ratio be abandoned? Br. J. Obs. Gynaecol. 1991, 98, 524–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadlock, F.P.; Harrist, R.B.; Sharman, R.S.; Deter, R.L.; Park, S.K. Estimation of fetal weight with the use of head, body, and femur measurements-A prospective study. Am. J. Obs. Gynecol. 1985, 151, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomon, L.J.; Alfirevic, Z.; Da Silva Costa, F.; Deter, R.L.; Figueras, F.; Ghi, T.A.; Glanc, P.; Khalil, A.; Lee, W.; Napolitano, R.; et al. ISUOG Practice Guidelines: Ultrasound assessment of fetal biometry and growth. Ultrasound Obs. Gynecol. 2019, 53, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordijn, S.J.; Beune, I.M.; Thilaganathan, B.; Papageorghiou, A.; Baschat, A.A.; Baker, P.N.; Silver, R.M.; Wynia, K.; Ganzevoort, W. Consensus definition of fetal growth restriction: A Delphi procedure. Ultrasound Obs. Gynecol. 2016, 48, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadlock, F.P.; Harrist, R.B.; Martinez-Poyer, J. In Utero Analysis of Fetal Growth: A Sonographic Weight Standard. Radiology 1991, 181, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voigt, M.; Fusch, C.; Olbertz, D.; Hartmann, K.; Rochow, N.; Renken, C.; Schneider, K.T. Analyse des neugeborenenkollektivs der Bundesrepublik Deutschland. Geburtsh. Frauenheilk. 2006, 66, 956–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuhamad, A.; Minton, K.K.; Benson, C.B.; Chudleigh, T.; Crites, L.; Doubilet, P.M.; Driggers, R.; Lee, W.; Mann, K.V.; Perez, J.J.; et al. Obstetric and gynecologic ultrasound curriculum and competency assessment in residency training programs: Consensus report. Am. J. Obs. Gynecol. 2018, 218, 29–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snijders, R.J.M.; Nicolaides, K.H. Fetal biometry at 14-40 weeks’gestation. Ultrasound Obs. Gynecol. 1994, 4, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, W.J.; Gauthier, D.; Ramakrishnan, V.; Sipos, J. Ultrasonographic detection of abnormal fetal growth with the gestational age-independent, transverse cerebellar diameter/abdominal circumference ratio. Am. J. Obs. Gynecol. 1994, 171, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, S.; Thoms, A. Ultrasound Measurement of the Fetal Head To Abdomen Circumference Ratio in the Assessment of Growth Retardation. Br. J. Obs. Gynaecol. 1977, 84, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilliod, R.A.; Cheng, Y.W.; Snowden, J.M.; Doss, A.E.; Caughey, A.B. The risk of intrauterine fetal death in the small-for-gestational-age fetus. Am. J. Obs. Gynecol. 2012, 207, e1–e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beune, I.M.; Bloomfield, F.H.; Ganzevoort, W.; Embleton, N.D.; Rozance, P.J.; van Wassenaer-Leemhuis, A.G.; Wynia, K.; Gordijn, S.J. Consensus Based Definition of Growth Restriction in the Newborn. J. Pediatrics 2017, 196, 71–76.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, I.; Reece, E.A.; Pilu, G.; Bovicelli, L.; Hobbins, J.C. Cerebellar measurements with ultrasonography in the evaluation of fetal growth and development. Am. J. Obs. Gynecol. 1987, 156, 1065–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baschat, A.A.; Weiner, C.P. Umbilical artery doppler screening for detection of the small fetus in need of antepartum surveillance. Am. J. Obs. Gynecol. 2000, 182, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisz, B.; David, A.L.; Chitty, L.; Peebles, D.; Pandya, P.; Patel, P.; Rodeck, C.H. Association of isolated short femur in the mid-trimester fetus with perinatal outcome. Ultrasound Obs. Gynecol. 2008, 31, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, C.; Agrawal, K.K.; Gandhi, S. Assessment of fetal growth using the ratio of the transverse cerebellar diameter to abdominal circumference. Int. J. Gynecol Obs. 2016, 135, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilmen, G.; Toppare, M.F.; Turhan, N.Ö.; Öztürk, M.; Işik, S. Transverse cerebellar diameter and transverse cerebellar diameter/abdominal circumference index for assessing fetal growth. Fetal Diagn. Ther. 1996, 11, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, W.A.; Vintzileos, A.M.; Rodis, J.F.; Turner, G.W.; Egan, J.F.; Nardi, D.A. Use of the transverse cerebellar diameter/abdominal circumference ratio in pregnancies at risk for intrauterine growth retardation. J. Clin. Ultrasound 1994, 22, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dashe, J.S.; McIntire, D.D.; Lucas, M.J.; Leveno, K.J. Effects of symmetric and asymmetric fetal growth on pregnancy outcomes. Obs. Gynecol. 2000, 96, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Median (Range) | N (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Examinations | 9292 (100) | ||||
| Maternal characteristics | |||||
| Age, years | 33 (14–50) | ||||
| BMI | 25 (15–65) | ||||
| Fetal characteristics | |||||
| Gender | |||||
| Male | 4765 (51) | ||||
| Female | 4527 (49) | ||||
| Estimated fetal weight, g | 426 (91–4091) | ||||
| Birth weight, g | 3370 (172–4390) | ||||
| AGA | 8231 (89) | ||||
| SGA | 1061 (11) | ||||
| FGR | 255 (24) | ||||
| Subdivision of the gestational age (weeks) | Total | AGA | SGA | FGR | |
| 14 + 0–18 + 6 | 1299 (14) | 1219 (15) | 80 (8) | 8 (3) | |
| 19 + 0–23 + 6 | 4914 (53) | 4517 (55) | 397 (37) | 59 (23) | |
| 24 + 0–28 + 6 | 1221 (13) | 1012 (12) | 209 (20) | 64 (25) | |
| 29 + 0–33 + 6 | 1212 (13) | 978 (12) | 234 (22) | 75 (29) | |
| 34 + 0–38 + 6 | 631 (7) | 494 (6) | 137 (13) | 48 (19) | |
| ≥ 39 + 0 | 15 (0) | 11 (0) | 4 (0) | 1 (0) | |
| GA ultrasound, weeks | 21 (14–40) | ||||
| GA delivery, weeks | 39 (19–43) | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marchand, C.; Köppe, J.; Köster, H.A.; Oelmeier, K.; Schmitz, R.; Steinhard, J.; Fruscalzo, A.; Kubiak, K. Fetal Growth Restriction: Comparison of Biometric Parameters. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12071125
Marchand C, Köppe J, Köster HA, Oelmeier K, Schmitz R, Steinhard J, Fruscalzo A, Kubiak K. Fetal Growth Restriction: Comparison of Biometric Parameters. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022; 12(7):1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12071125
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarchand, Carolin, Jeanette Köppe, Helen Ann Köster, Kathrin Oelmeier, Ralf Schmitz, Johannes Steinhard, Arrigo Fruscalzo, and Karol Kubiak. 2022. "Fetal Growth Restriction: Comparison of Biometric Parameters" Journal of Personalized Medicine 12, no. 7: 1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12071125
APA StyleMarchand, C., Köppe, J., Köster, H. A., Oelmeier, K., Schmitz, R., Steinhard, J., Fruscalzo, A., & Kubiak, K. (2022). Fetal Growth Restriction: Comparison of Biometric Parameters. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(7), 1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12071125







