Development of Personalized Non-Invasive Ventilation Interfaces for Neonatal and Pediatric Application Using Additive Manufacturing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
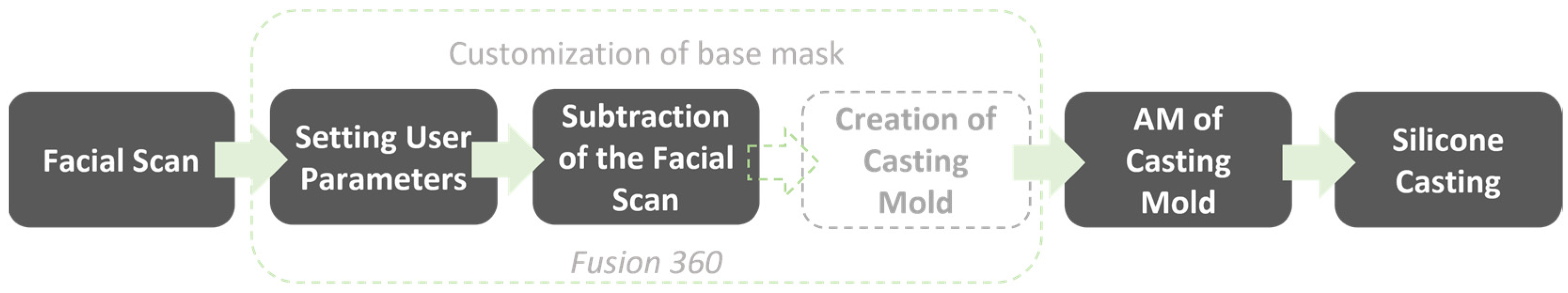
2.1. Design of the Base Mask
2.2. Defining and Modifying Mask Parameters
2.3. User Workflow
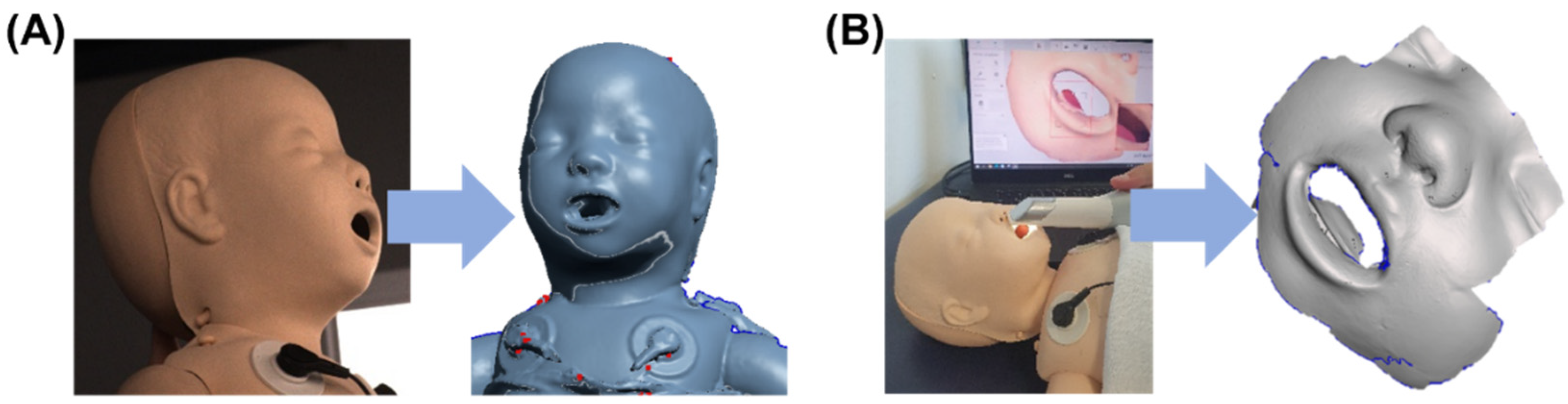
2.4. Patient Data Acquisition and Mask Individualization
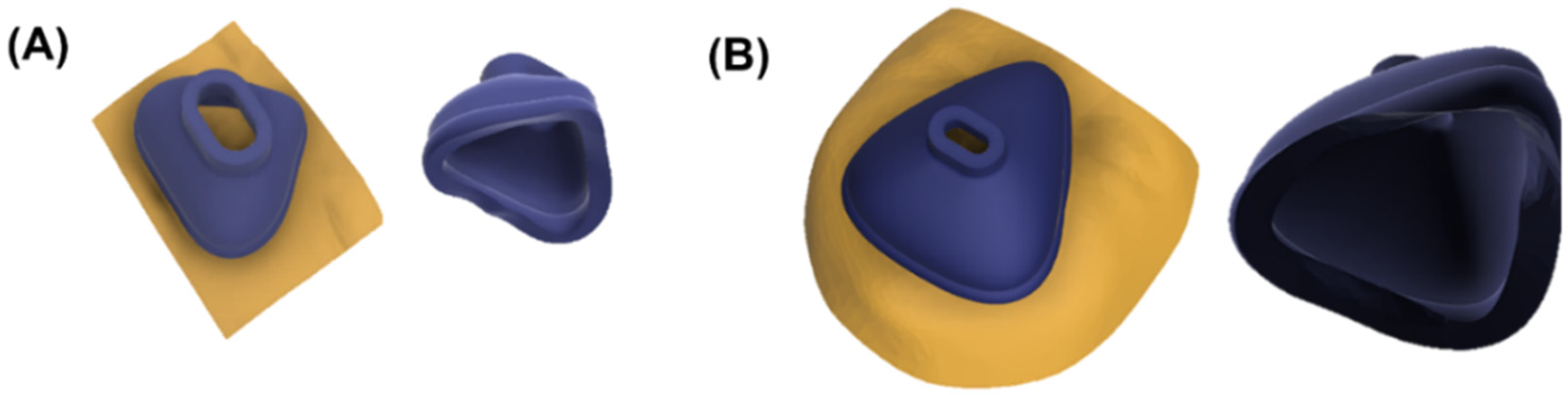
2.5. Design and Manufacturing of the Casting Mold
2.6. Manufacturing of the Silicone Mask
3. Results
3.1. Required Time
3.2. Mask Fit
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison of the Proposed Design to Other Customizable Masks
4.2. Potential of the Workflow
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
6. Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prima, D.M.; Coburn, J.; Hwang, D.; Kelly, J.; Khairuzzaman, A.; Ricles, L. Additively Manufactured Medical Products–The Fda Perspective. 3D Print. Med. 2016, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culmone, C.; Smit, G.; Breedveld, P. Additive manufacturing of medical instruments: A state-of-the-art review. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 27, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.K.; Jin, Y.-A.; Wensman, J.; Shih, A. Additive manufacturing of custom orthoses and prostheses—A review. Addit. Manuf. 2016, 12, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joe, P.S.; Shum, P.C.; Brown, D.W.; Lungu, C.T. A Novel Method for Designing and Fabricating Low-cost Facepiece Prototypes. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2014, 11, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, A.; Galea, K.; No-Cortes, J.; Sammut, E.J.; Alzoubi, E.E.; Attard, N.J. Use of Free Cad Design Software for 3D Printing Individualized Face Masks Based on Face Scans. Int. J. Comput. Dent. 2020, 23, 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Mule, S.T.; Bhusnure, O.; Waghmare, S.; Mali, M.R. Recent Trends, Opportunities and Challenges in 3D Printing Technology for Personalize Medicine. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2020, 10, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singare, S.; Dichen, L.; Bingheng, L.; Yanpu, L.; Zhenyu, G.; Yaxiong, L. Design and Fabrication of Custom Mandible Titanium Tray Based on Rapid Prototyping. Med. Eng. Phys. 2004, 26, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaw, C.-Y.; Guvendiren, M. Current and emerging applications of 3D printing in medicine. Biofabrication 2017, 9, 024102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallo, L.; Marcianò, A.; Cicciù, M.; Oteri, G. 3D Printing beyond Dentistry during COVID-19 Epidemic: A Technical Note for Producing Connectors to Breathing Devices. Prosthesis 2020, 2, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, C.; Jos, V.S.; Le, T.H.; Lam, K.; Soe, S.; Zlatov, N.; Le, T.P.; Pham, D.T. Medical Reverse Engineering Applications and Methods. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Innovations, Recent Trends and Challenges in Mechatronics, Mechanical Engineering and New High-Tech Products Development, Bucharest, Romania, 23–24 September 2010; pp. 186–196. [Google Scholar]
- Gualdrón, C.-I.L.; Ibarra, E.-R.B.; Bohórquez, A.-P.M.; Bohórquez, I.G. Present and future for technologies to develop patient-specific medical devices: A systematic review approach. Med. Devices 2019, 12, 253–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francoisse, C.A.; Sescleifer, A.M.; King, W.T.; Lin, A.Y. Three-dimensional printing in medicine: A systematic review of pediatric applications. Pediatr. Res. 2021, 89, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Underwood, M.A.; Danielsen, B.; Gilbert, W.M. Cost, Causes and Rates of Rehospitalization of Preterm Infants. J. Perinatol. 2007, 27, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kline-Tilford, A.M.; Sorce, L. Nursing in the Pediatric Intensive Care Unit: Pediatric Noninvasive Ventilation. J. Pediatr. Intensive Care 2015, 4, 121–127. [Google Scholar]
- Mayordomo-Colunga, J.; Pons-Òdena, M.; Medina, A.; Rey, C.; Milesi, C.; Kallio, M.; Wolfler, A.; García-Cuscó, M.; Demirkol, D.; García-López, M.; et al. Non-invasive ventilation practices in children across Europe. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2018, 53, 1107–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedor, K.L. Noninvasive Respiratory Support in Infants and Children. Respir. Care 2017, 62, 699–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Codesal, M.L.; Olmstead, D.L.; MacLean, J.E. Mask interfaces for home non-invasive ventilation in infants and children. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2019, 32, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, A.; Sweeney, L.; Loughlin, R.M. Tracheal Dose Delivery in a Representative Oro Nasal Airway Model of a Newborn (Ronan) across Three Noninvasive Ventilation Interfaces for the Pediatric Population. J. Aerosol Med. Pulm. Drug Deliv. 2016, 29, A10. [Google Scholar]
- Haase, B.; Badinska, A.M.; Koos, B.; Poets, C.F.; Lorenz, L. Do Commonly Available Round Facemasks Fit near-Term and Term Infants? Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2020, 105, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cignacco, E.; Hamers, J.; Van Lingen, R.A.; Stoffel, L.; Büchi, S.; Müller, R.; Schütz, N.; Zimmermann, L.; Nelle, M. Neonatal Procedural Pain Exposure and Pain Management in Ventilated Preterm Infants During the First 14 Days of Life. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2009, 139, 226–232. [Google Scholar]
- Buettiker, V.; Hug, M.I.; Baenziger, O.; Meyer, C.; Frey, B. Advantages and disadvantages of different nasal CPAP systems in newborns. Intensiv. Care Med. 2004, 30, 926–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Tayyab, M.; Farooq, M.A. Comparison of Mask Versus Prong for Delivery of Continuous Airway Pressure in Premature Neonates with Tachypnea in Terms of Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Failure. Natl. Editor. Advis. Board 2020, 31, 92–95. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, D.; Kaur, A.; Farahbakhsh, N.; Agarwal, S. To compare nasal mask with binasal prongs in delivering continuous positive airway pressure for reducing need of invasive ventilation: Randomized controlled trial. J. Matern. Neonatal Med. 2019, 34, 1890–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poets, C.F.; Lim, K.; Marshall, A.; Jackson, H.; Gale, T.J.; Dargaville, A.P. Mask versus nasal prong leak and intermittent hypoxia during continuous positive airway pressure in very preterm infants. Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2020, 106, 81–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visscher, M.O.; White, C.C.; Jones, J.M.; Cahill, T.; Jones, D.C.; Pan, B.S. Face Masks for Noninvasive Ventilation: Fit, Excess Skin Hydration, and Pressure Ulcers. Respir. Care 2015, 60, 1536–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, R.J.; VanKoevering, K.K.; Nasser, H.B.; Kashlan, K.N.; Kline, S.K.; Jensen, D.R.; Edwards, S.P.; Hassan, F.; Schotland, H.M.; Chervin, R.D.; et al. Personalized 3D-Printed Cpap Masks Improve Cpap Effectiveness in Children with Osa and Craniofacial Anomalies. In Proceedings of the Combined Otolaryngology Spring Meetings, Boston, MA, USA, 22–26 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Robin, P. Glossoptosis Due to Atresia and Hypotrophy of the Mandible. Am. J. Dis. Child. 1934, 48, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morice, A.; Soupre, V.; Mitanchez, D.; Renault, F.; Fauroux, B.; Marlin, S.; Leboulanger, N.; Kadlub, N.; Vazquez, M.-P.; Picard, A.; et al. Severity of Retrognathia and Glossoptosis Does Not Predict Respiratory and Feeding Disorders in Pierre Robin Sequence. Front. Pediatr. 2018, 6, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, I.C.W.; Sedaghat, A.R.; McGinley, B.M.; Redett, R.J.; Boss, E.F.; Ishman, S.L. Prevalence and Severity of Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Snoring in Infants with Pierre Robin Sequence. Cleft Palate-Craniofacial J. 2011, 48, 614–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatlach, S.; Maas, C.; Poets, C.F. Birth Prevalence and Initial Treatment of Robin Sequence in Germany: A Prospective Epidemiologic Study. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2014, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, R.M.; Timenetsky, K.T.; Neves, R.C.M.; Shigemichi, L.H.; Kanda, S.S.; Maekawa, C.; Silva, E.; Eid, R.A.C. Adaptation to different noninvasive ventilation masks in critically ill patients. J. Bras. Pneumol. 2013, 39, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pisani, L.; Carlucci, A.; Nava, S. Interfaces for Noninvasive Mechanical Ventilation: Technical Aspects and Efficiency. Minerva Anestesiol. 2012, 78, 1154–1161. [Google Scholar]
- Aufieri, R.; Picone, S.; Gente, M.; Paolillo, P. 3D Printing in Neonatal Care. Ital. J. Pediatrics 2015, 41, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genta, P.R.; Kaminska, M.; Edwards, B.A.; Ebben, M.R.; Krieger, A.C.; Tamisier, R.; Ye, L.; Weaver, T.E.; Vanderveken, O.M.; Lorenzi-Filho, G. The Importance of Mask Selection on Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Outcomes for Obstructive Sleep Apnea. An Official American Thoracic Society Workshop Report. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2020, 17, 1177–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.Y.; Acharya, D.; Xu, C.; Cheng, B.; Rana, S.; Shimada, K. Custom-Fit Three-Dimensional-Printed BiPAP Mask to Improve Compliance in Patients Requiring Long-Term Noninvasive Ventilatory Support. J. Med. Devices 2018, 12, 031003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Munguia, J.; Hyde, P.; Drinnan, M. Development of a Customized Cpap Mask Using Reverse Engineering and Additive Manufacturing. In Proceedings of the 29th Annual International Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium—An Additive Manufacturing Conference—2018; Austin, TX, USA, 13–15 August 2018; University of Texas at Austin: Austin, TX, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, D.-Y.; Cheng, Y.-L.; Bien, M.-Y.; Lee, H.-C. Development of a Method for Manufacturing Customized Nasal Mask Cushion for Cpap Therapy. Australas. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2015, 38, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sela, M.; Toledo, N.; Honen, Y.; Kimmel, R. Customized Facial Constant Positive Air Pressure (Cpap) Masks. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1609.07049. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.-L.; Chu, J.C. Application of Rapid Tooling to Manufacture Customized Nasal Mask Cushion for Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (Cpap) Devices. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2013, 19, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikama, M.; Nakagami, G.; Noguchi, H.; Mori, T.; Sanada, H. Development of Personalized Fitting Device with 3-Dimensional Solution for Prevention of Niv Oronasal Mask-Related Pressure Ulcers. Respir. Care 2018, 63, 1024–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frassoni, E.; Shankar-Aguilera, S.; Yousef, N.; De Luca, D. Helmet-Delivered Respiratory Support in Neonate with Severe Facial Malformation. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2017, 53, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallem, V.R.; Murki, S. CPAP with Resuscitation Mask in a Neonate with Cleft Lip and Cleft Palate. Indian J. Pediatr. 2018, 85, 582–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza, C.R.M.; De Arruda, J.A.A.; Soares, A.M.; Santos, M.D.O.; De Souza, A.F.; Lanza, L.D.; Moreno, A. Fabrication of a custom pediatric nasal mask for noninvasive ventilation using a maxillofacial elastomer: A straightforward technique. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2018, 121, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limeres, J.; Diz, P.; Vilaboa, C.; Tomás, I.; Feijoo, J.F. Individualized nasal mask fabrication for positive pressure ventilation using dental methods. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2004, 17, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Willox, M.; Metherall, P.; McCarthy, A.D.; Jeays-Ward, K.; Barker, N.; Reed, H.; Elphick, H.E. Custom-Made 3D Printed Masks for Children Using Non-Invasive Ventilation: A Comparison of 3D Scanning Technologies and Specifications for Future Clinical Service Use, Guided by Patient and Professional Experience. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 2020, 44, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, A.; Amirav, I.; Marchand, R.; Olmstead, D.; Majaesic, C.; MacLean, J.E.; Mandhane, P. B25 Interesting Pediatric Cases: 3D Modeled Custom-Made Non-Invasive Positive Pressure Mask in an Infant. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 189, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Amirav, I.; Luder, A.S.; Halamish, A.; Raviv, D.; Kimmel, R.; Waisman, D.; Newhouse, M.T. Design of Aerosol Face Masks for Children Using Computerized 3D Face Analysis. J. Aerosol Med. Pulm. Drug Deliv. 2014, 27, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldovan, C.; Cosma, C.; Berce, P.; Balc, N. Theoretical Analysis and Practical Case Studies of Sla, Polyjet and Fdm Manufacturing Techniques. Acta Tech. Napoc. Ser. 2018, 61, 401–408. [Google Scholar]
- Junk, S. Fusion 360—Kurz Und Bündig; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Unkovskiy, A.; Spintzyk, S.; Brom, J.; Huettig, F.; Keutel, C. Direct 3D printing of silicone facial prostheses: A preliminary experience in digital workflow. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2018, 120, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luis, E.; Pan, H.M.; Sing, S.L.; Bastola, A.K.; Goh, G.D.; Goh, G.L.; Tan, H.K.J.; Bajpai, R.; Song, J.; Yeong, W.Y. Silicone 3D Printing: Process Optimization, Product Biocompatibility, and Reliability of Silicone Meniscus Implants. 3D Print. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 6, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhakeyev, A.; Leung, D.Y.C.; Xuan, J. Go-Modified Flexible Polymer Nanocomposites Fabricated Via 3D Stereolithography. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2019, 13, 736–743. [Google Scholar]
- Nold, J.; Metzger, M.C.; Schwarz, S.; Wesemann, C.; Wemken, G.; Pieralli, S.; Kernen, F.; Weingart, J.; Schirmeister, C.G.; Schumann, S.; et al. Air seal performance of personalized and statistically shaped 3D-printed face masks compared with market-available surgical and FFP2 masks. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta-Cheng, C.; Yi-Wen, C.; Yen-Shan, C.; Kuo, Y. A Cloud Information Platform for 3D Printing Rehabilitation Devices. Adv. Technol. Innov. 2019, 4, 73–83. [Google Scholar]
- Netzel, T. En Iso 17510: 2020: Schlafapnoe-Atemtherapie-Masken Und Anwendungszubehör; Beuth Verlag: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]

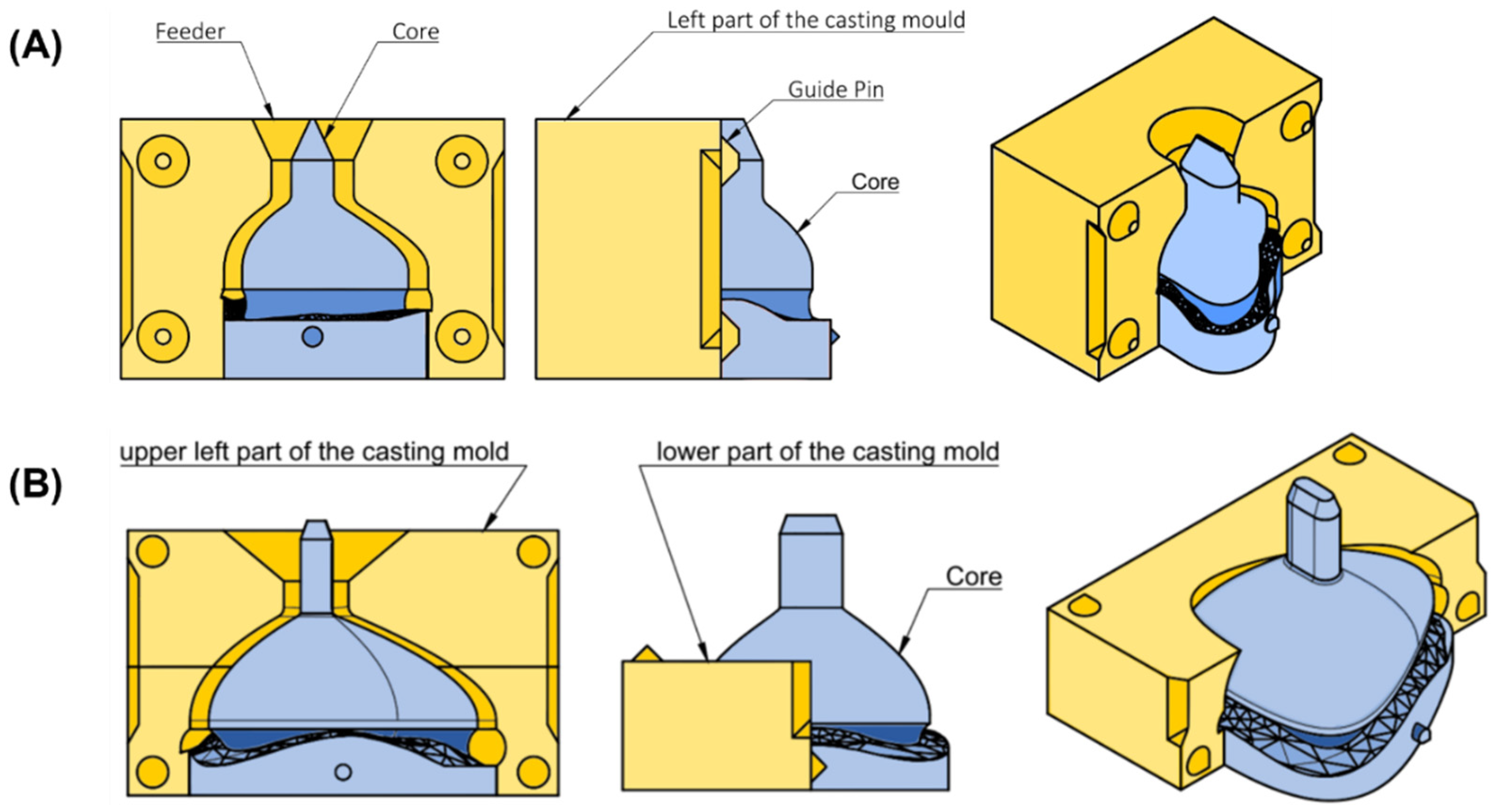
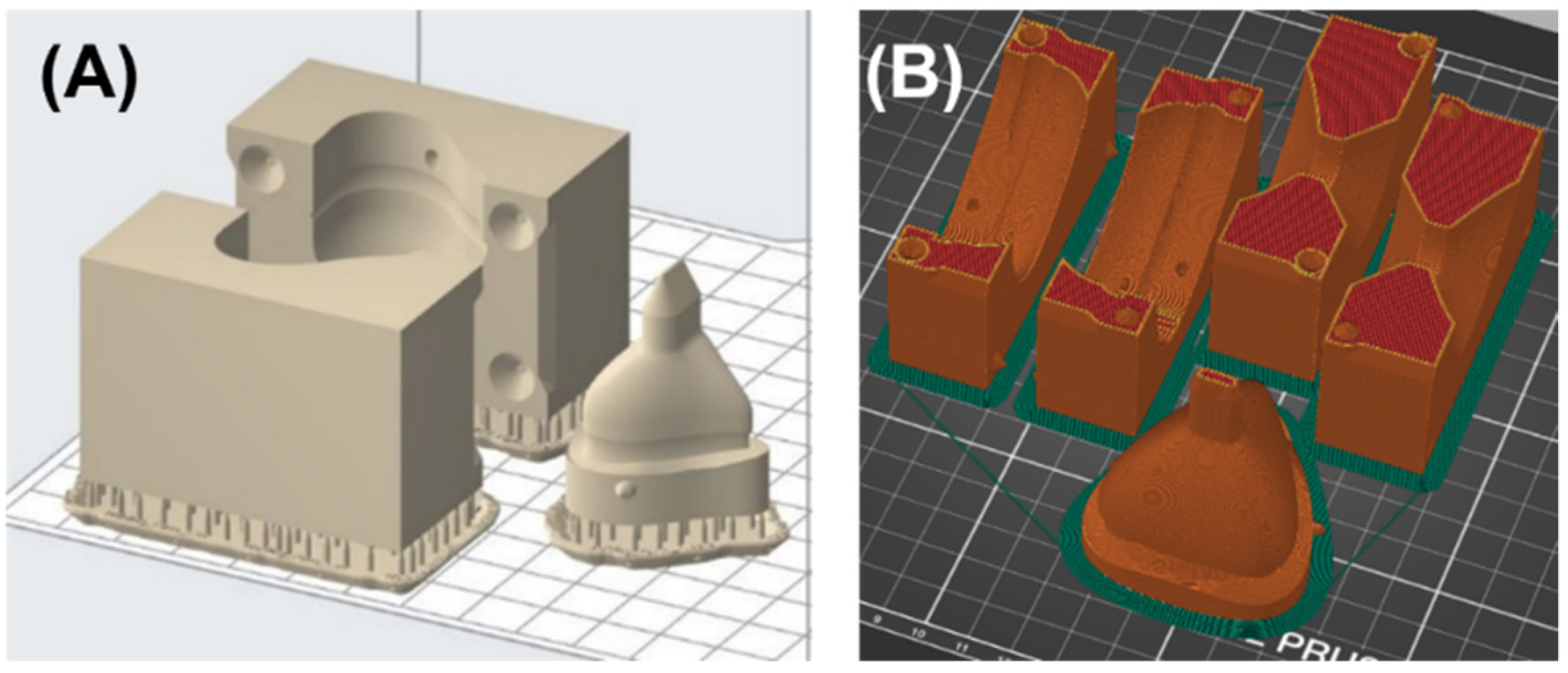
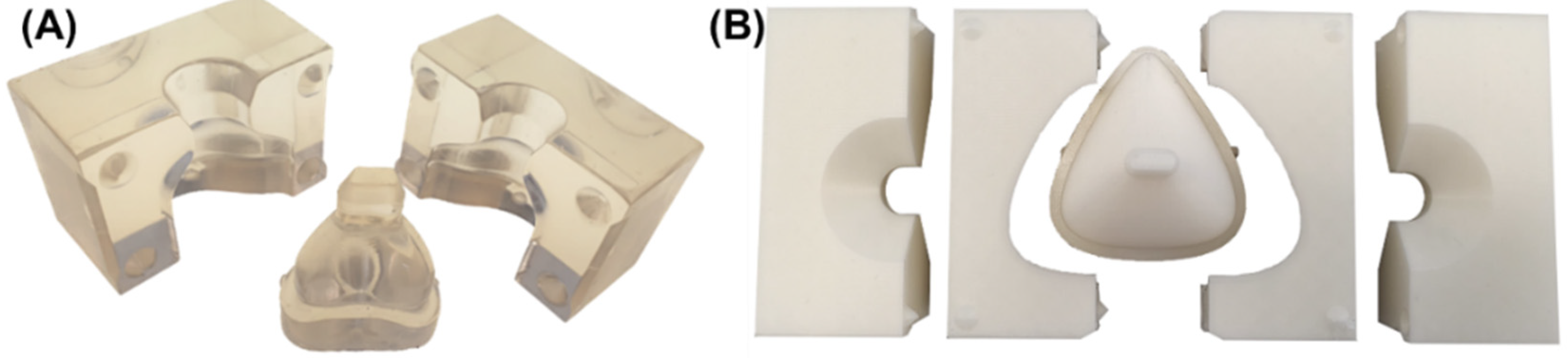
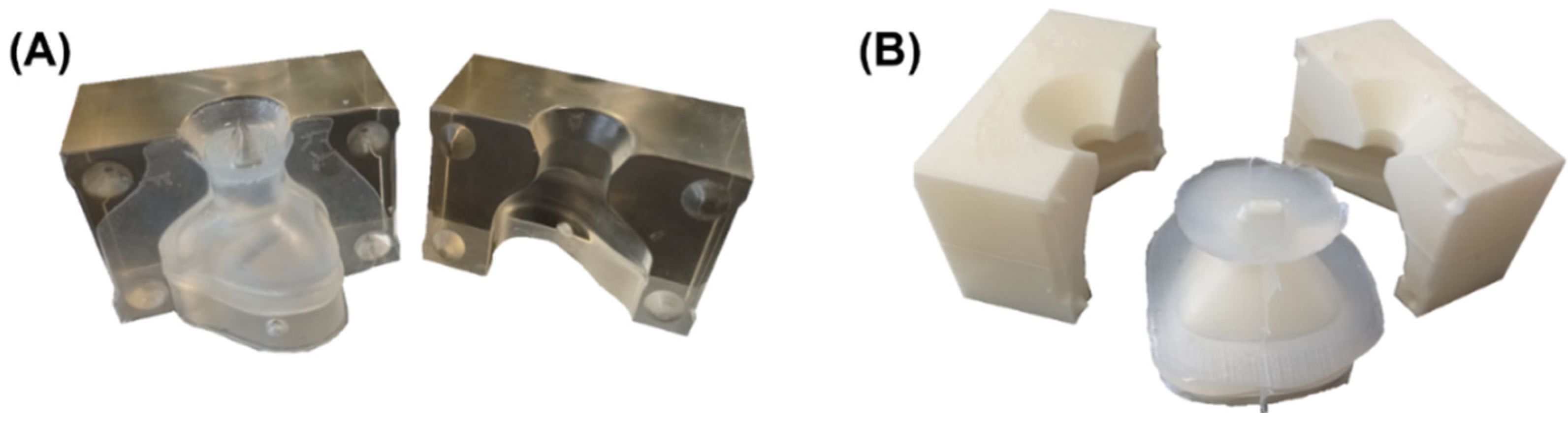
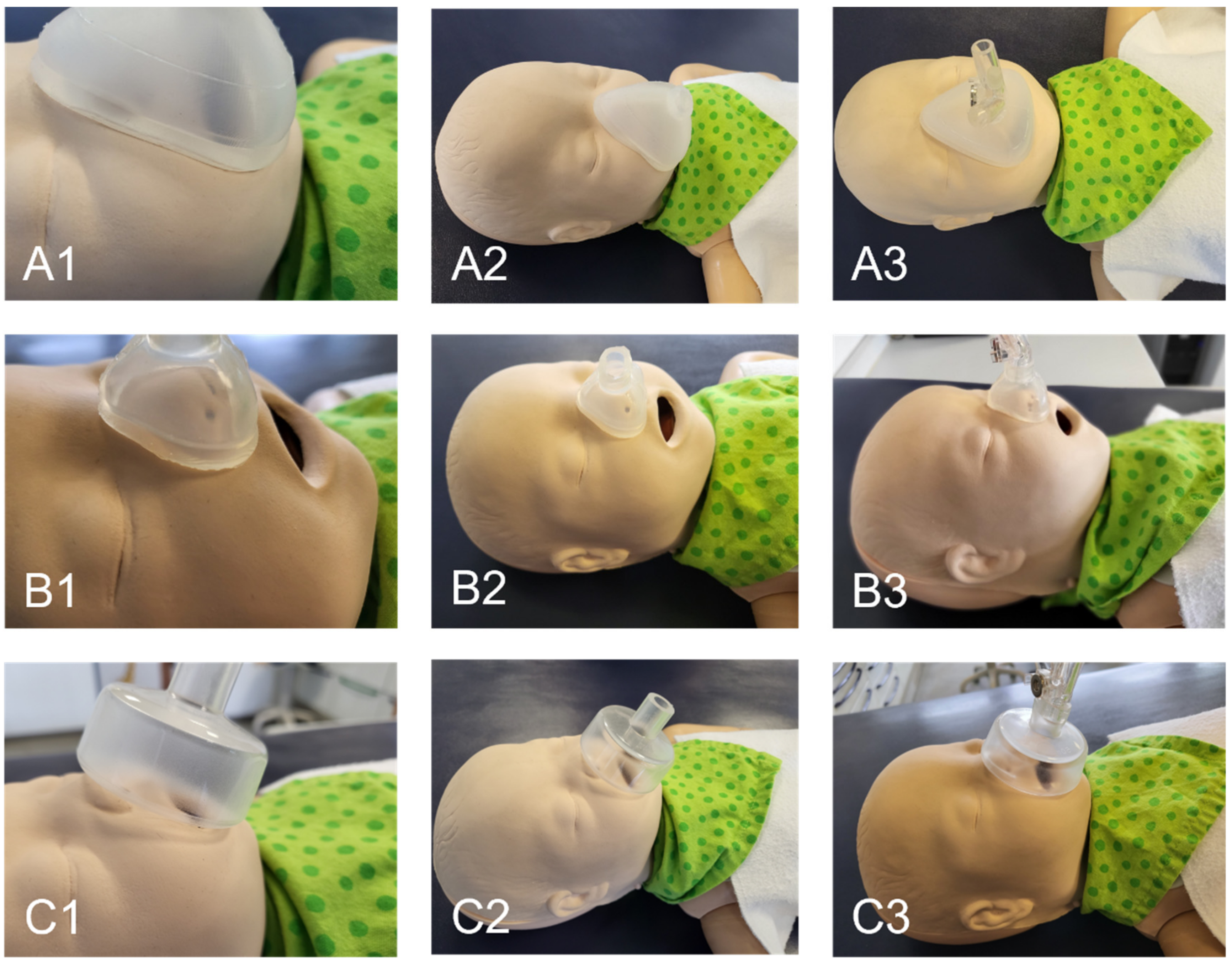
| NIV Interface | Nasal Mask | Oronasal Mask | Prong |
|---|---|---|---|
 |  |  | |
| Advantages |
|
|
|
| Disadvantages |
|
|
|
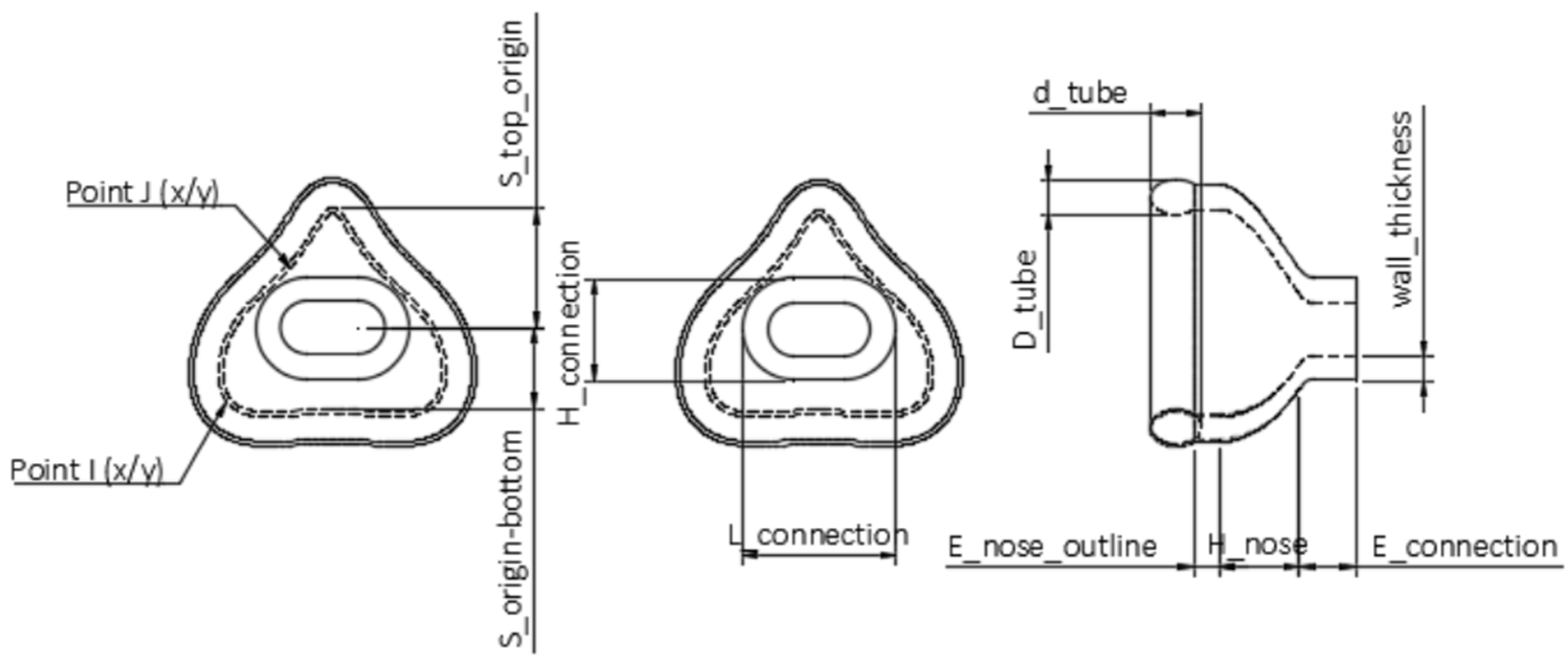
| Fixed Parameter | Abbreviation | Standard Value |
|---|---|---|
| Height of connection | H_connection | 12 mm |
| Length of connection | L_connection | 18 mm |
| Wall thickness | wall_thickness | 2.5 mm |
| Height of extrusion of connection | E_connection | 6 mm |
| Customizable parameter | Abbreviation | |
| Height of the nose | H_nose | |
| Space between the top of the nose outline and the origin | S_top_origin | |
| Space between the bottom of the nose outline and the origin (0/0/0) | S_bottom_origin | |
| x-coordinate of point I | I_X | |
| y-coordinate of point I | I_Y | |
| x-coordinate of point J | J_Y | |
| coordinate of point J | J_X | |
| Height of extrusion of nose outline | E_nose_outline | |
| Width of the tube | D_tube | |
| Height of the tube | d_tube | |
| Workflow | Time Required | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal Mask | Oronasal Mask | |||
| SLA | FFF | SLA | FFF | |
| Preparatory scan * | 10 min | 12 min | ||
| Creating mask and casting mold * | 8 min | 10 min | ||
| AM of casting mold | 4 h 15 min | 8 h 12 min | 6 h 45 min | 15 h 38 min |
| Postprocessing of the mold * | 1 h | 1 min | 1 h | 1 min |
| Casting the silicone * | 10 min | 2 × 10 min | ||
| Curing the silicone | 15 min | 15 min | ||
| Postprocessing the nasal mask * | 4 min | 4 min | ||
| In total * Hands-on time | 6 h 2 min 1 h 32 min | 9 h 33 min | 8 h 46 min 1 h 46 min | 16 h 40 min 47 min |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bockstedte, M.; Xepapadeas, A.B.; Spintzyk, S.; Poets, C.F.; Koos, B.; Aretxabaleta, M. Development of Personalized Non-Invasive Ventilation Interfaces for Neonatal and Pediatric Application Using Additive Manufacturing. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12040604
Bockstedte M, Xepapadeas AB, Spintzyk S, Poets CF, Koos B, Aretxabaleta M. Development of Personalized Non-Invasive Ventilation Interfaces for Neonatal and Pediatric Application Using Additive Manufacturing. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022; 12(4):604. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12040604
Chicago/Turabian StyleBockstedte, Marit, Alexander B. Xepapadeas, Sebastian Spintzyk, Christian F. Poets, Bernd Koos, and Maite Aretxabaleta. 2022. "Development of Personalized Non-Invasive Ventilation Interfaces for Neonatal and Pediatric Application Using Additive Manufacturing" Journal of Personalized Medicine 12, no. 4: 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12040604
APA StyleBockstedte, M., Xepapadeas, A. B., Spintzyk, S., Poets, C. F., Koos, B., & Aretxabaleta, M. (2022). Development of Personalized Non-Invasive Ventilation Interfaces for Neonatal and Pediatric Application Using Additive Manufacturing. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(4), 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12040604








