Biased β-Agonists Favoring Gs over β-Arrestin for Individualized Treatment of Obstructive Lung Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
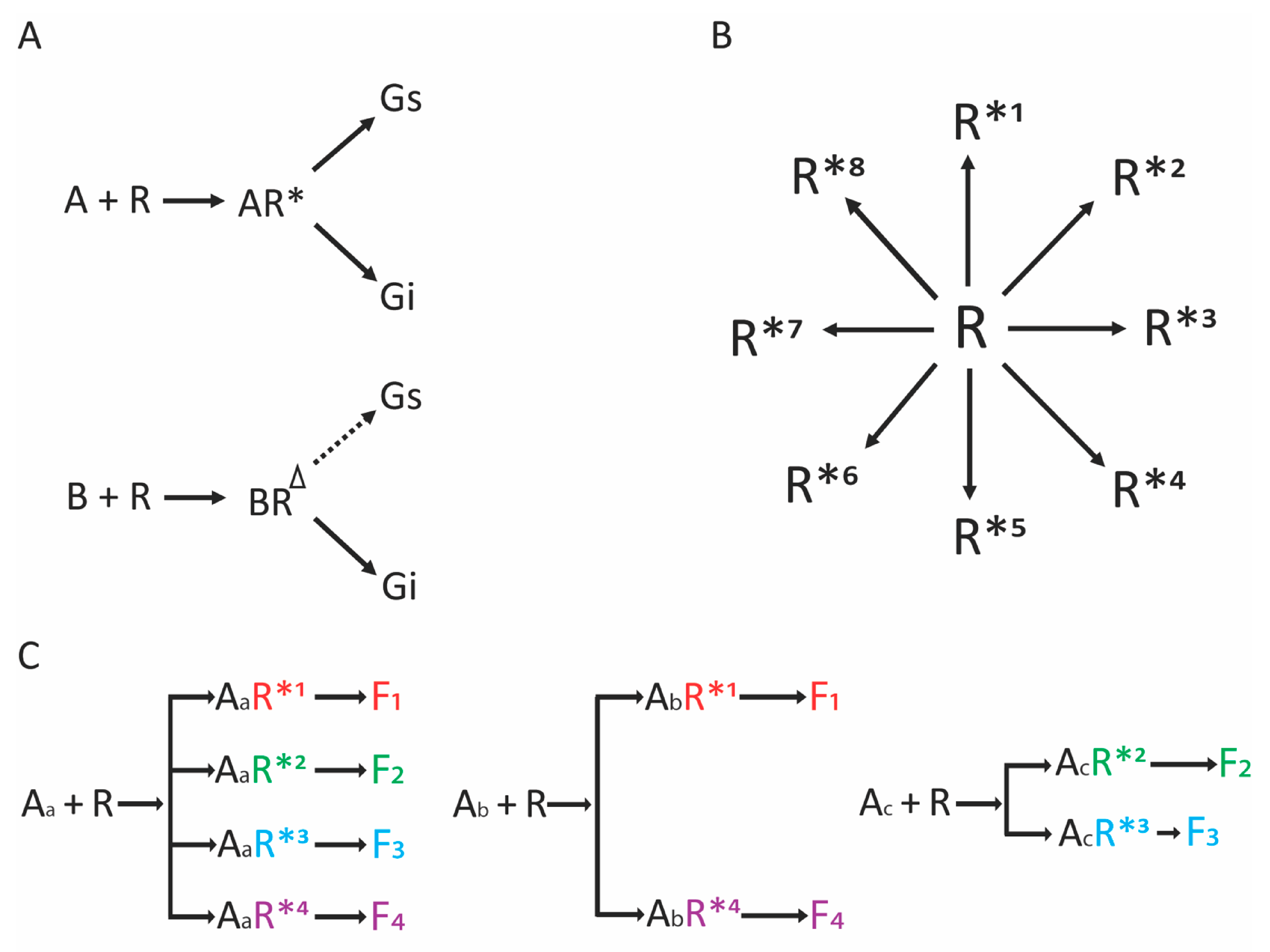
2. Biased Agonist Signaling at GPCRs
3. The Clinical Need for a Gs-Biased β2AR Agonist for Treating Obstructive Lung Disease
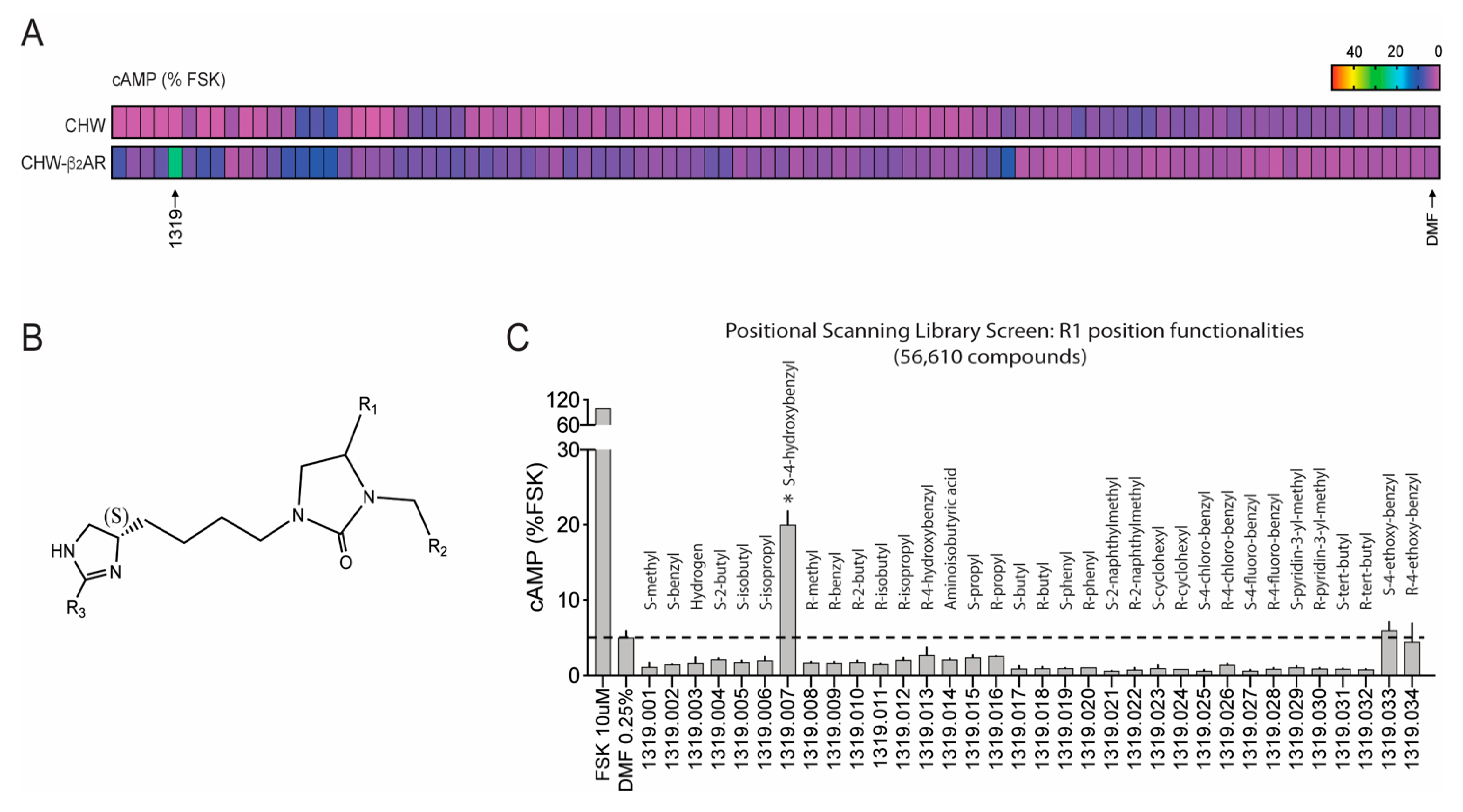
4. Screening Millions of Compounds for Novel β-Agonists with Combinatorial Libraries
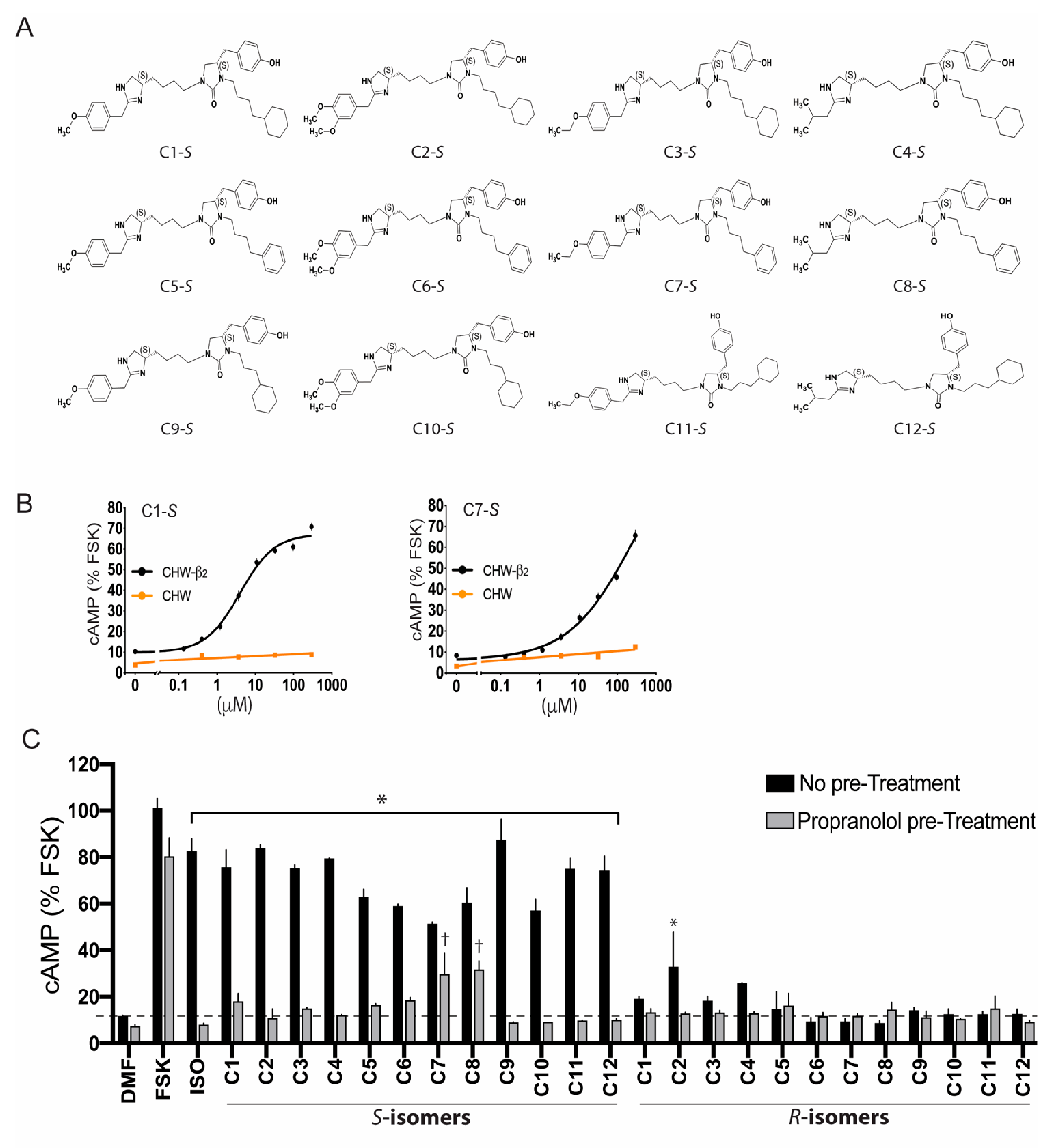
5. Ascertainment of Gs-Biasing with Selected Compounds
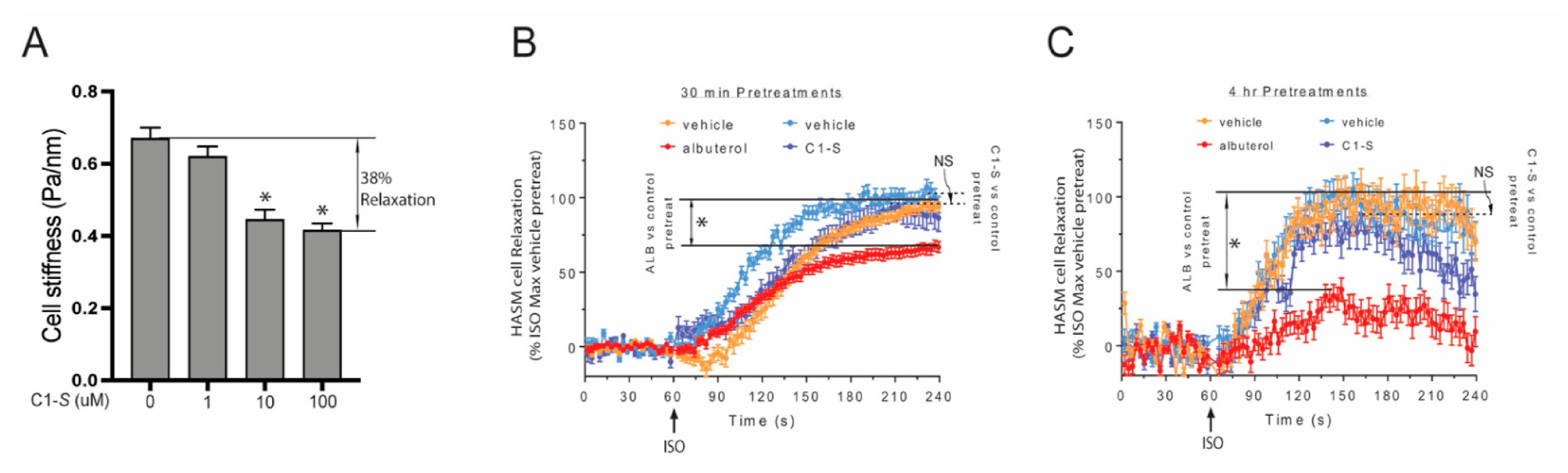
6. The Lack of C1-S Promoted β-Arrestin Interaction Correlates with Absent Physiologic Desensitization of the Human ASM Relaxation Response
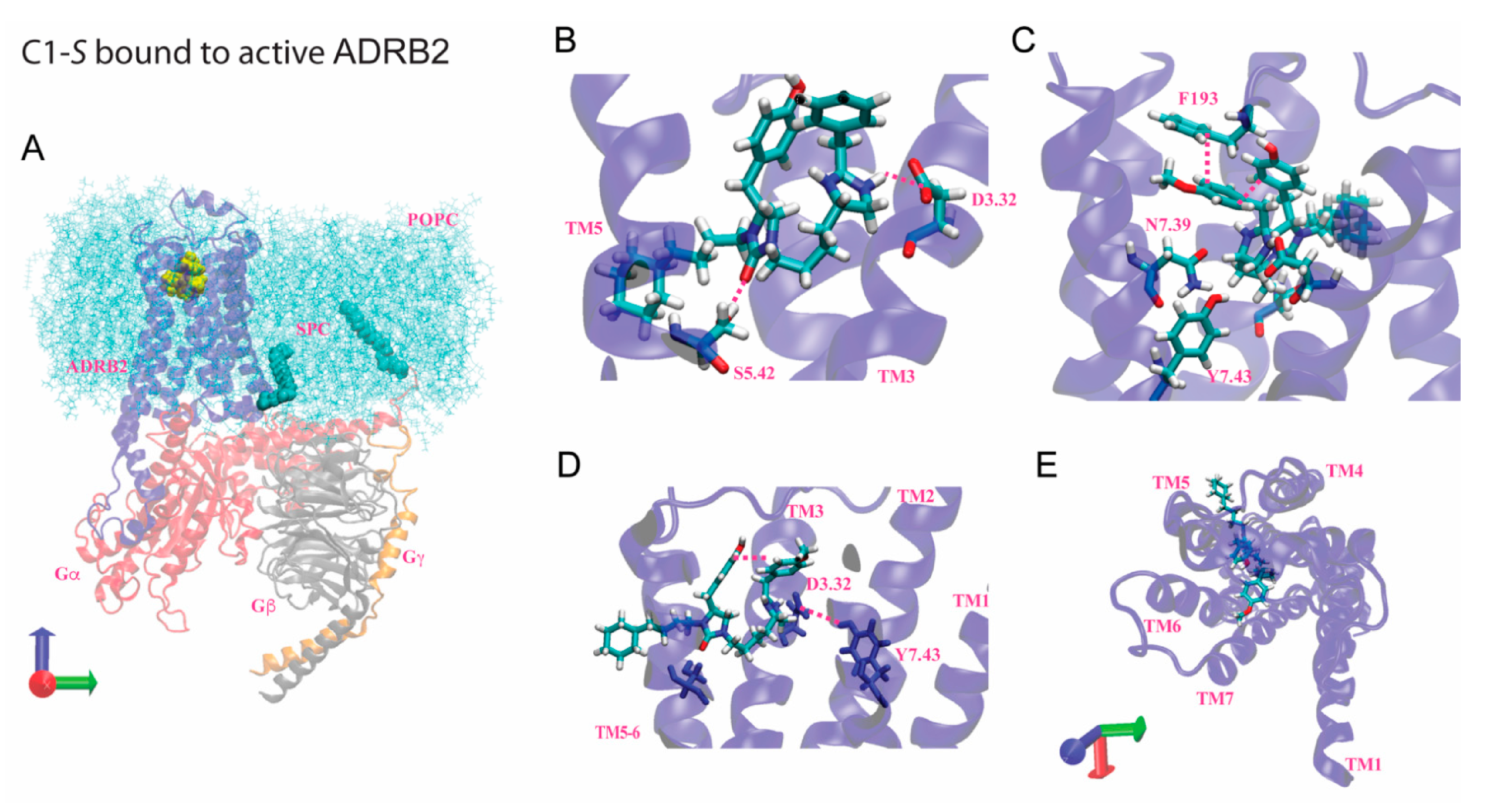
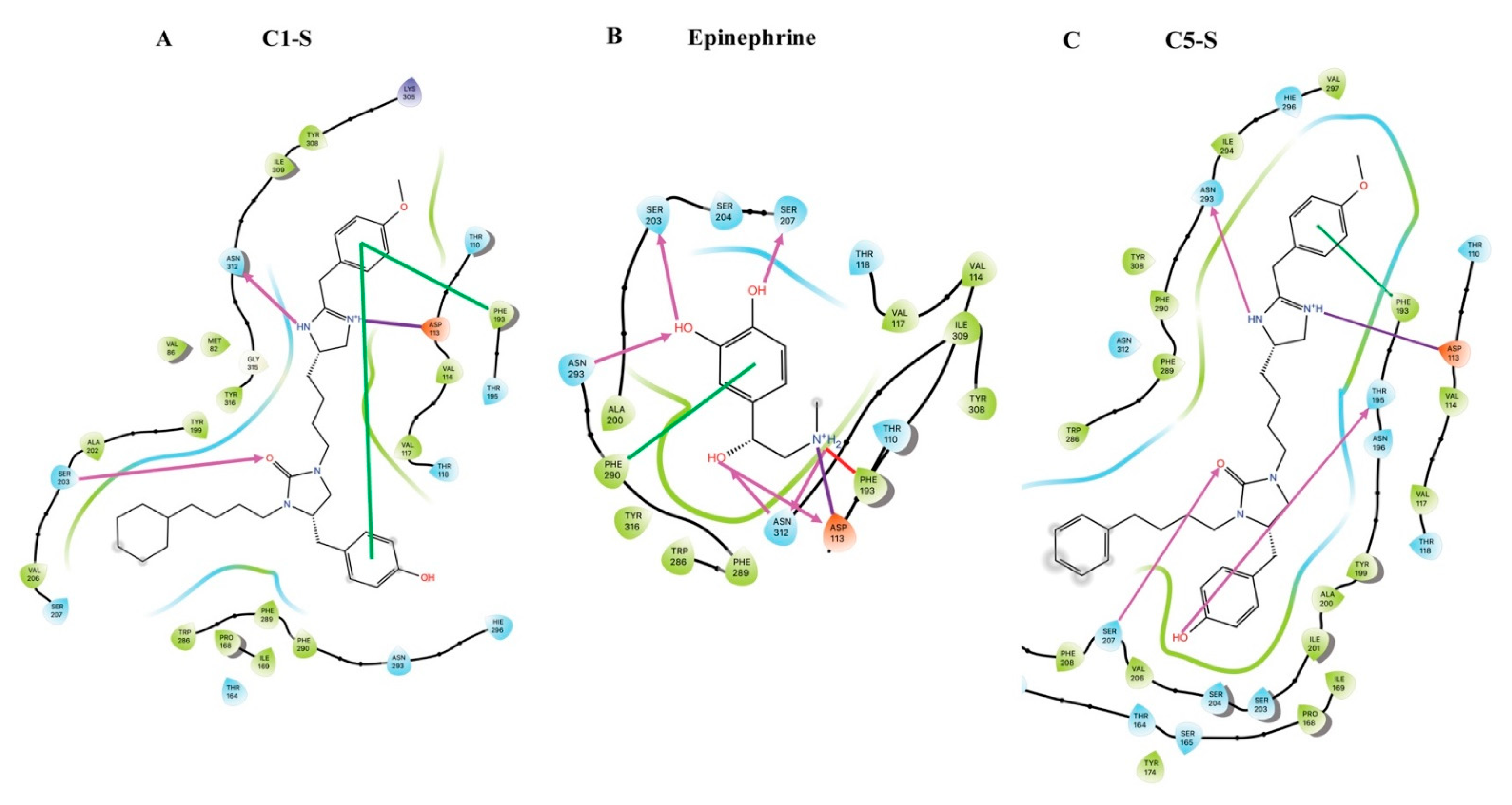
7. Modeling of the Interactions of C1-S, Epinephrine, and C5-S Identifies a Potential Structural Basis of C1-S Biasing
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rajagopal, S.; Shenoy, S.K. GPCR desensitization: Acute and prolonged phases. Cell. Signal. 2018, 41, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eason, M.G.; Kurose, H.; Holt, B.D.; Raymond, J.R.; Liggett, S.B. Simultaneous coupling of a2-adrenergic receptors to two G-proteins with opposing effects: Subtype-selective coupling of a2C10, a2C4 and a2C2 adrenergic receptors to Gi and Gs. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 15795–15801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eason, M.G.; Liggett, S.B. Identification of a Gs coupling domain in the amino-terminus of the third intracellular loop of the a2A-adrenergic receptor: Evidence for distinct structural determinants that confer Gs versus Gi coupling. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 24753–24760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eason, M.G.; Jacinto, M.T.; Liggett, S.B. Contribution of ligand structure to activation of a2AR subtype coupling to Gs. Mol. Pharmacol. 1994, 45, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gillis, A.; Gondin, A.B.; Kliewer, A.; Sanchez, J.; Lim, H.D.; Alamein, C.; Manandhar, P.; Santiago, M.; Fritzwanker, S.; Schmiedel, F.; et al. Low intrinsic efficacy for G protein activation can explain the improved side effect profiles of new opioid agonists. Sci. Signal. 2020, 31, eaaz3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staus, D.P.; Wingler, L.M.; Choi, M.; Pani, B.; Manglik, A.; Kruse, A.C.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Sortase ligation enables homogeneous GPCR phosphorylation to reveal diversity in β-arrestin coupling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 3834–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heitzler, D.; Durand, G.; Gallay, N.; Rizk, A.; Ahn, S.; Kim, J.; Violin, J.D.; Dupuy, L.; Gauthier, C.; Piketty, V.; et al. Competing G protein-coupled receptor kinases balance G protein and beta-arrestin signaling. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2012, 8, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewell-Motz, E.A.; Liggett, S.B. G protein-coupled receptor kinase specificity for phosphorylation and desensitization of a2-adrenergic receptor subtypes. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 18082–18087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewell-Motz, E.A.; Small, K.M.; Liggett, S.B. a2A/a2C-adrenergic receptor third loop chimera show that agonist interaction with receptor-subtype backbone establishes G protein-coupled receptor kinase phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 28989–28993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liggett, S.B. Phosphorylation barcoding as a mechanism of directing GPCR signaling. Sci. Signal. 2011, 4, pe36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Tokmakova, A.; Lujan, L.K.; Strzelinski, H.R.; Kim, N.; Najari Beidokhti, M.; Giulianotti, M.A.; Mafi, A.; Woo, J.A.; An, S.S.; et al. Identification and characterization of an atypical Gαs-biased β(2)AR agonist that fails to evoke airway smooth muscle cell tachyphylaxis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser, A.S.; Attwood, M.M.; Rask-Andersen, M.; Schiöth, H.B.; Gloriam, D.E. Trends in GPCR drug discovery: New agents, targets and indications. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 829–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeWire, S.M.; Yamashita, D.S.; Rominger, D.H.; Liu, G.; Cowan, C.L.; Graczyk, T.M.; Chen, X.T.; Pitis, P.M.; Gotchev, D.; Yuan, C.; et al. A G protein-biased ligand at the mu-opioid receptor is potently analgesic with reduced gastrointestinal and respiratory dysfunction compared with morphine. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2013, 344, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viscusi, E.R.; Skobieranda, F.; Soergel, D.G.; Cook, E.; Burt, D.A.; Singla, N. APOLLO-1: A randomized placebo and active-controlled phase III study investigating oliceridine (TRV130), a G protein-biased ligand at the µ-opioid receptor, for management of moderate-to-severe acute pain following bunionectomy. J. Pain Res. 2019, 12, 927–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Violin, J.D.; DeWire, S.M.; Yamashita, D.; Rominger, D.H.; Nguyen, L.; Schiller, K.; Whalen, E.J.; Gowen, M.; Lark, M.W. Selectively engaging beta-arrestins at the angiotensin II type 1 receptor reduces blood pressure and increases cardiac performance. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010, 335, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman-Tancredi, A.; Depoortère, R.Y.; Kleven, M.S.; Kołaczkowski, M.; Zimmer, L. Translating biased agonists from molecules to medications: Serotonin 5-HT(1A) receptor functional selectivity for CNS disorders. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 229, 107937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grove, A.; Lipworth, B.J. Bronchodilator subsensitivity to salbutamol after twice daily salmeterol in asthmatic patients. Lancet 1995, 346, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newnham, D.M.; Grove, A.; McDevitt, D.G.; Lipworth, B.J. Tolerance of bronchodilator and systemic beta-2 adrenoceptor responses after regular twice daily treatment with eformoterol dry powder in asthmatic patients. Eur. Respir. J. 1994, 7, 235s. [Google Scholar]
- Israel, E.; Chinchilli, V.M.; Ford, J.G.; Boushey, H.A.; Cherniack, R.; Craig, T.J.; Deykin, A.; Fagan, J.K.; Fahy, J.V.; Fish, J.; et al. Use of regularly scheduled albuterol treatment in asthma: Genotype-stratified, randomised, placebo-controlled cross-over trial. Lancet 2004, 364, 1505–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, H.; Bish, R.; Walters, J.; Whitehead, F.; Walters, E.H. Salmeterol tachyphylaxis in steroid treated asthmatic subjects. Thorax 1996, 51, 1100–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kalra, S.; Swystun, V.A.; Bhagat, R.; Cockcroft, D.W. Inhaled corticosteroids do not prevent the development of tolerance to the bronchoprotective effect of salmeterol. Chest 1996, 109, 953–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sears, M.R. Role of b-agonists in Asthma Fatalities. In Fatal Asthma; Sheffer, A.L., Ed.; Lung Biology in Health and Disease; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1998; Volume 115, pp. 457–481. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, H.S.; Weiss, S.T.; Bleecker, E.R.; Yancey, S.W.; Dorinsky, P.M. The Salmeterol Multicenter Asthma Research Trial: A comparison of usual pharmacotherapy for asthma or usual pharmacotherapy plus salmeterol. Chest 2006, 129, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grainger, J.; Woodman, K.; Peace, N.; Crane, J.; Burgess, C.; Keane, A.; Beasley, R. Prescribed fenoterol and death from asthma in New Zealand, 1981-7: A further case-control study. Thorax 1991, 46, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salpeter, S.R.; Wall, A.J.; Buckley, N.S. Long-acting beta-agonists with and without inhaled corticosteroids and catastrophic asthma events. Am. J. Med. 2010, 123, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, V.E. Pharmacogenetics of beta2 adrenergic receptor agonists in asthma management. Clin. Genet. 2014, 86, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasti, B.; Liu, S.K.; Xiang, X.D. Role of Epigenetics in the Pathogenesis, Treatment, Prediction, and Cellular Transformation of Asthma. Mediat. Inflamm. 2021, 2021, 9412929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.C.; Mihlbachler, K.A.; Brunnett, A.C.; Liggett, S.B. Targeted transgenesis reveals discrete attenuator functions of GRK and PKA in airway beta2-adrenergic receptor physiologic signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 15007–15012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dooley, C.T.; Ny, P.; Bidlack, J.M.; Houghten, R.A. Selective ligands for the mu, delta, and kappa opioid receptors identified from a single mixture based tetrapeptide positional scanning combinatorial library. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 18848–18856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Maida, L.E.; Santos, R.G.; Welmaker, G.S.; LaVoi, T.M.; Nefzi, A.; Yu, Y.; Houghten, R.A.; Toll, L.; et al. Scaffold ranking and positional scanning utilized in the discovery of nAChR-selective compounds suitable for optimization studies. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 10103–10117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghten, R.A.; Pinilla, C.; Giulianotti, M.A.; Appel, J.R.; Dooley, C.T.; Nefzi, A.; Ostresh, J.M.; Yu, Y.; Maggiora, G.M.; Medina-Franco, J.L.; et al. Strategies for the use of mixture-based synthetic combinatorial libraries: Scaffold ranking, direct testing in vivo, and enhanced deconvolution by computational methods. J. Comb. Chem. 2008, 10, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.G.; Appel, J.R.; Giulianotti, M.A.; Edwards, B.S.; Sklar, L.A.; Houghten, R.A.; Pinilla, C. The mathematics of a successful deconvolution: A quantitative assessment of mixture-based combinatorial libraries screened against two formylpeptide receptors. Molecules 2013, 18, 6408–6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, J.A.; Liu, T.; Fang, C.C.; Castaño, M.A.; Kee, T.; Yrigoin, K.; Yan, Y.; Cazzaro, S.; Matlack, J.; Wang, X.; et al. β-Arrestin2 oligomers impair the clearance of pathological tau and increase tau aggregates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 5006–5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, J.A.; Yan, Y.; Kee, T.R.; Cazzaro, S.; McGill Percy, K.C.; Wang, X.; Liu, T.; Liggett, S.B.; Kang, D.E. β-arrestin1 promotes tauopathy by transducing GPCR signaling, disrupting microtubules and autophagy. Life Sci. Alliance 2022, 5, e202101183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajagopal, S.; Ahn, S.; Rominger, D.H.; Gowen-MacDonald, W.; Lam, C.M.; Dewire, S.M.; Violin, J.D.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Quantifying ligand bias at seven-transmembrane receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2011, 80, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisler, J.W.; DeWire, S.M.; Whalen, E.J.; Violin, J.D.; Drake, M.T.; Ahn, S.; Shenoy, S.K.; Lefkowitz, R.J. A unique mechanism of beta-blocker action: Carvedilol stimulates beta-arrestin signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 16657–16662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, R.H.J.; DiBerto, J.F.; English, J.G.; Glaudin, A.M.; Krumm, B.E.; Slocum, S.T.; Che, T.; Gavin, A.C.; McCorvy, J.D.; Roth, B.L.; et al. TRUPATH, an open-source biosensor platform for interrogating the GPCR transducerome. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2020, 16, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, S.K.; Drake, M.T.; Nelson, C.D.; Houtz, D.A.; Xiao, K.; Madabushi, S.; Reiter, E.; Premont, R.T.; Lichtarge, O.; Lefkowitz, R.J. beta-arrestin-dependent, G protein-independent ERK1/2 activation by the beta2 adrenergic receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 1261–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenakin, T. Biased Receptor Signaling in Drug Discovery. Pharmacol. Rev. 2019, 71, 267–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, D.A.; Wang, W.C.; McIlmoyle, E.L.; Robinett, K.S.; Schillinger, R.M.; An, S.S.; Sham, J.S.; Liggett, S.B. Bitter taste receptors on airway smooth muscle bronchodilate by localized calcium signaling and reverse obstruction. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 1299–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.S.; Fabry, B.; Trepat, X.; Wang, N.; Fredberg, J.J. Do biophysical properties of the airway smooth muscle in culture predict airway hyperresponsiveness? Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2006, 35, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafi, A.; Kim, S.K.; Goddard, W.A., 3rd. Mechanism of β-arrestin recruitment by the μ-opioid G protein-coupled receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 16346–16355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mafi, A.; Kim, S.K.; Goddard, W.A., 3rd. The atomistic level structure for the activated human kappa-opioid receptor bound to the full Gi protein and the MP1104 agonist. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 5836–5843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.K.; Riley, L.; Abrol, R.; Jacobson, K.A.; Goddard, W.A., 3rd. Predicted structures of agonist and antagonist bound complexes of adenosine A3 receptor. Proteins 2011, 79, 1878–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goddard, W.A., 3rd; Kim, S.K.; Li, Y.; Trzaskowski, B.; Griffith, A.R.; Abrol, R. Predicted 3D structures for adenosine receptors bound to ligands: Comparison to the crystal structure. J. Struct. Biol. 2010, 170, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.Y.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, D.; Liggett, S.B.; Goddard, W.A., 3rd. Structures and Agonist Binding Sites of Bitter Taste Receptor TAS2R5 Complexed with Gi Protein and Validated against Experiment. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 9293–9300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J.; Han, S.K.; Vaidehi, N.; Wendel, J.; Kekenes-Huskey, P.; Goddard, W.A., 3rd. Prediction of the 3D structure of FMRF-amide neuropeptides bound to the mouse MrgC11 GPCR and experimental validation. Chembiochem 2007, 8, 1527–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, J.A.; Weinstein, H. [19] Integrated methods for the construction of three-dimensional models and computational probing of structure-function relations in G protein-coupled receptors. In Methods in Neurosciences; Sealfon, S.C., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1995; Volume 25, pp. 366–428. [Google Scholar]
- Masureel, M.; Zou, Y.; Picard, L.P.; van der Westhuizen, E.; Mahoney, J.P.; Rodrigues, J.; Mildorf, T.J.; Dror, R.O.; Shaw, D.E.; Bouvier, M.; et al. Structural insights into binding specificity, efficacy and bias of a beta2AR partial agonist. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2018, 14, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippolito, M.; De Pascali, F.; Inoue, A.; Benovic, J.L. Phenylalanine 193 in Extracellular Loop 2 of the β (2)-Adrenergic Receptor Coordinates β-Arrestin Interaction. Mol. Pharmacol. 2022, 101, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedabadi, M.; Ghahremani, M.H.; Albert, P.R. Biased signaling of G protein coupled receptors (GPCRs): Molecular determinants of GPCR/transducer selectivity and therapeutic potential. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 200, 148–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tokmakova, A.; Kim, D.; Goddard, W.A., III; Liggett, S.B. Biased β-Agonists Favoring Gs over β-Arrestin for Individualized Treatment of Obstructive Lung Disease. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12030331
Tokmakova A, Kim D, Goddard WA III, Liggett SB. Biased β-Agonists Favoring Gs over β-Arrestin for Individualized Treatment of Obstructive Lung Disease. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022; 12(3):331. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12030331
Chicago/Turabian StyleTokmakova, Alina, Donghwa Kim, William A. Goddard, III, and Stephen B. Liggett. 2022. "Biased β-Agonists Favoring Gs over β-Arrestin for Individualized Treatment of Obstructive Lung Disease" Journal of Personalized Medicine 12, no. 3: 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12030331
APA StyleTokmakova, A., Kim, D., Goddard, W. A., III, & Liggett, S. B. (2022). Biased β-Agonists Favoring Gs over β-Arrestin for Individualized Treatment of Obstructive Lung Disease. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(3), 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12030331






