Which Is Better in Clinical and Radiological Outcomes for Lumbar Degenerative Disease of Two Segments: MIS-TLIF or OPEN-TLIF?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.2. General Information of Patients
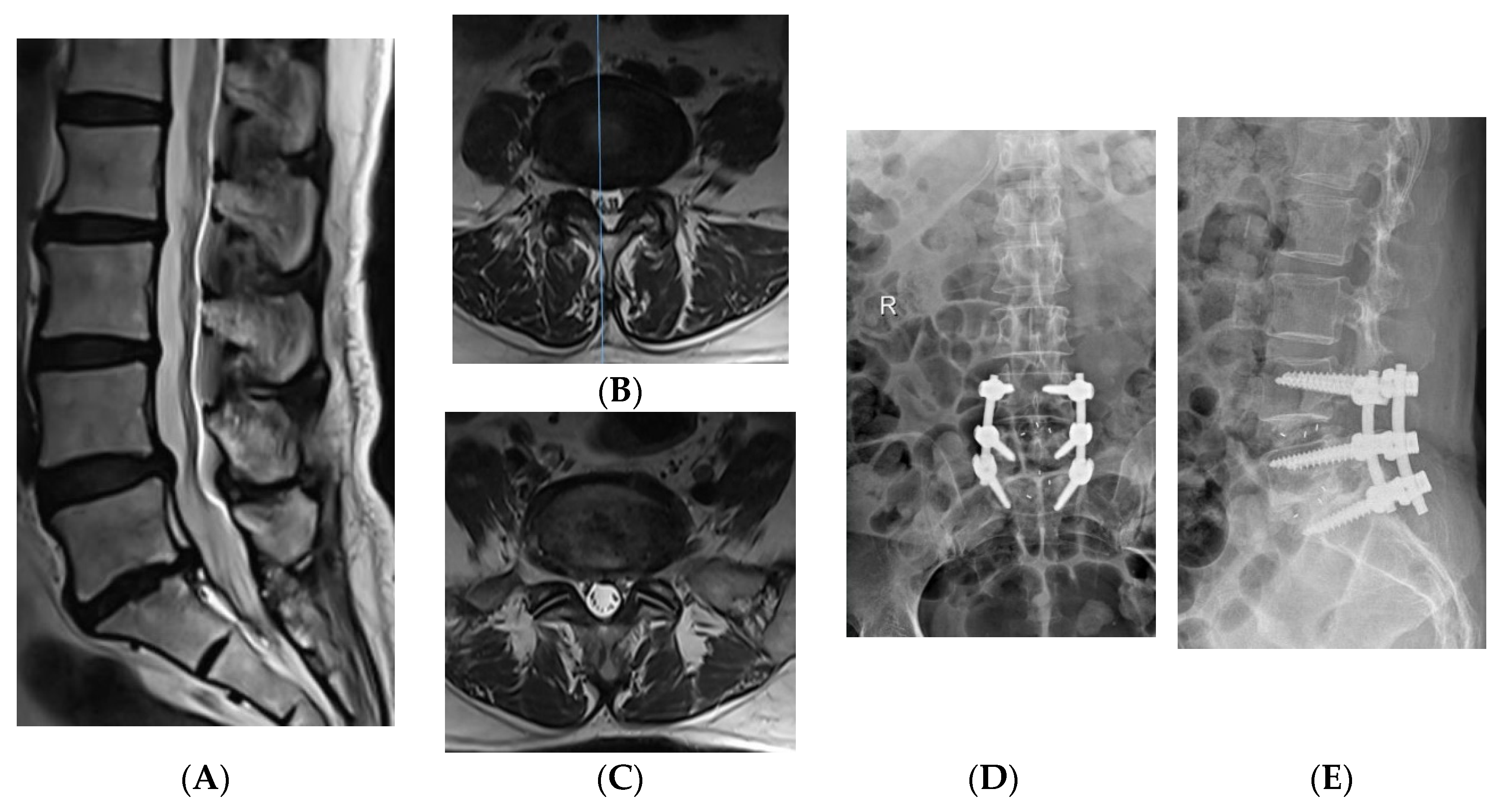
2.3. Surgical Method of OPEN-TLIF
2.4. Surgical Method of MIS-TLIF
2.5. Postoperative Management
2.6. Observational Index
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Surgery Related Information
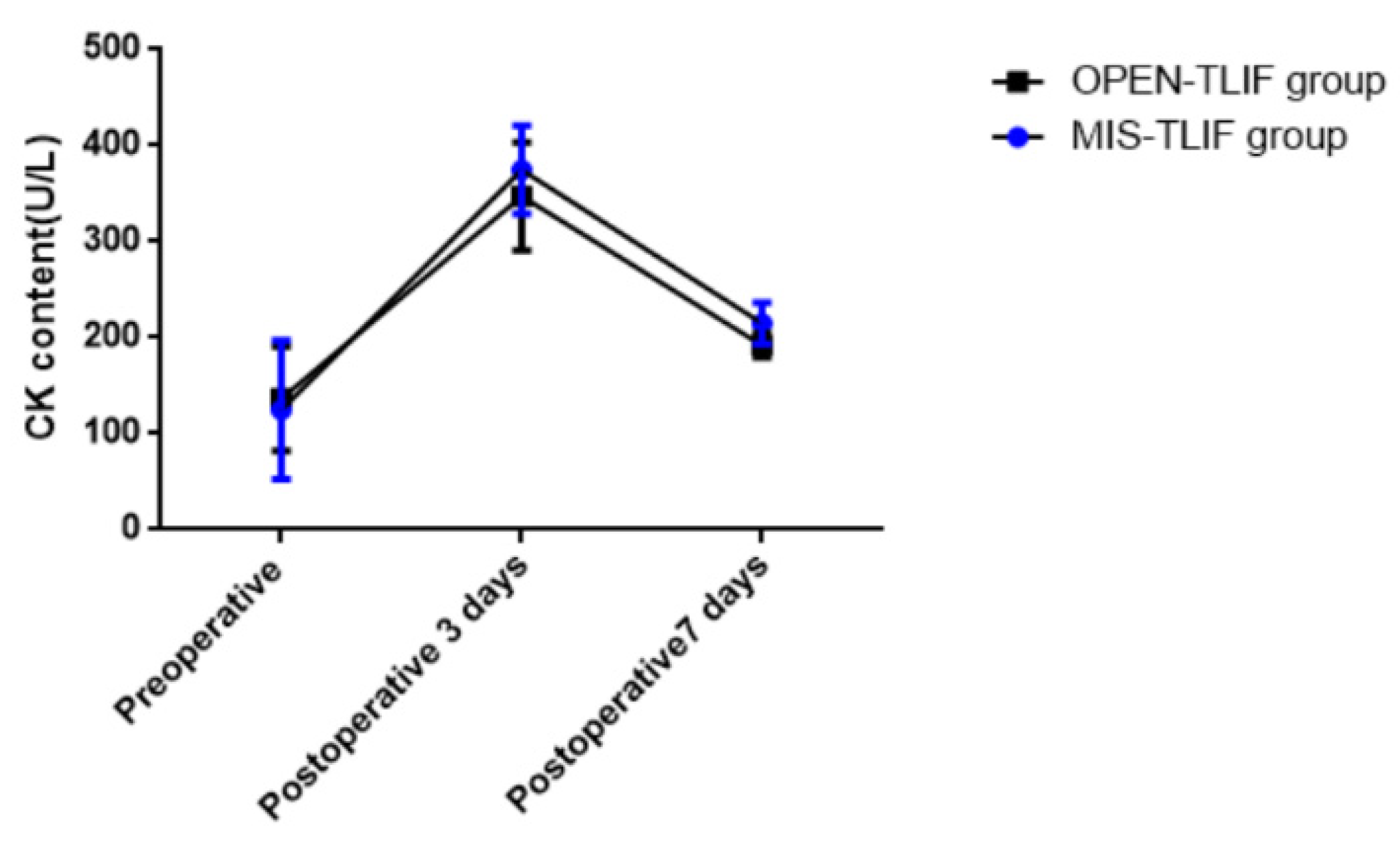
3.2. CK Perioperative Content
3.3. The Change of VAS Score and ODI Index
3.4. The Screws Classified by Rao Grading
3.5. Fusion Level by Bridwell Grading
3.6. Complications
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Bogaert, W.; Tegner, H.; Coppieters, I.; Huysmans, E.; Nijs, J.; Moens, M.; Goudman, L.; Buyl, R.; Lundberg, M. The Predictive Value of Fear Avoidance Beliefs for Outcomes Following Surgery for Lumbar Degenerative Disease: A Systematic Review and Best Evidence Synthesis. Pain Physician 2022, 25, 441–457. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ge, M.; Zhang, Y.; Ying, H.; Feng, C.; Li, Y.; Tian, J.; Zhao, T.; Shao, H.; Huang, Y. Comparison of hidden blood loss and clinical efficacy of percutaneous endoscopic transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion and minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. Int. Orthop. 2022, 46, 2063–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caelers, I.J.M.H.; de Kunder, S.L.; Rijkers, K.; van Hemert, W.L.W.; de Bie, R.A.; Evers, S.M.A.A.; van Santbrink, H. Comparison of (Partial) economic evaluations of transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) versus Posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF) in adults with lumbar spondylolisthesis: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0245963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putzier, M.; Hartwig, T.; Hoff, E.K.; Streitparth, F.; Strube, P. Minimally invasive TLIF leads to increased muscle sparing of the multifidus muscle but not the longissimus muscle compared with conventional PLIF-a prospective randomized clinical trial. Spine J. 2016, 16, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, K.T.; Holly, L.T.; Schwender, J.D. Minimally invasive lumbar fusion. Spine 2003, 28, S26–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonova, O.N.; Cherepanov, E.A.; Krutko, A.V. MIS-TLIF versus O-TLIF for single-level degenerative stenosis: Study protocol for randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e041134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Chu, Z.; Sheng, L.; Qin, R.; Chen, M. Three-year postoperative outcomes between MIS and conventional TLIF in1-segment lumbar disc herniation. Minim Invasive Allied Technol. 2017, 26, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, R.; Wu, T.; Liu, H.; Zhou, B.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, X. Minimally invasive versus traditional open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for the treatment of low-grade degenerative spondylolisthesis: A retrospective study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.H.; Liu, G.; Ng, R.; Kumar, N.; Wong, H.K.; Liu, G. Is MIS-TLIF superior to open TLIF in obese patients?: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Spine J. 2018, 27, 1877–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Wu, W.J.; Liang, Y. Comparison between Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion and Conventional Open Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: An Updated Meta-analysis. Chin. Med. J. 2016, 129, 1969–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droeghaag, R.; Hermans, S.M.M.; Caelers, I.J.M.H.; Evers, S.M.A.A.; van Hemert, W.L.W.; van Santbrink, H. Cost-effectiveness of open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (OTLIF) versus minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (MITLIF): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Spine J. 2021, 21, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, N.W.; Parrish, J.M.; Cha, E.D.K.; Lynch, C.P.; Sayari, A.J.; Geoghegan, C.E.; Jadczak, C.N.; Mohan, S.; Singh, K. Validation of PROMIS Physical Function in MIS TLIF: 2-Year Follow-up. Spine 2020, 45, E1516–E1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Jung, B.; Lee, S.H. Instrumented Minimally Invasive Spinal-Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion (MIS-TLIF): Minimum 5-Year Follow-Up With Clinical and Radiologic Outcomes. Clin. Spine Surg. 2018, 31, E302–E309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Ni, H.J.; Zhao, W.; Gu, G.F.; Chen, J.; Zhu, Y.J.; Feng, C.B.; Gong, H.Y.; Fan, Y.S.; He, S.S. Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy via Transforaminal Approach Combined with Interlaminar Approach for L4/5 and L5/S1 Two-Level Disc Herniation. Orthop. Surg. 2021, 13, 979–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridwell, K.H.; Lenke, L.G.; McEnery, K.W.; Baldus, C.; Blanke, K. Anterior fresh frozen structural allografts in the thoracic and lumbar spine. Do they work if combined with posterior fusion and instrumentation in adult patients with kyphosis or anterior column defects? Spine 1995, 20, 1410–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, G.; Brodke, D.S.; Rondina, M.; Bacchus, K.; Dailey, A.T. Inter- and intraobserver reliability of computed tomography in assessment of thoracic pedicle screw placement. Spine 2003, 28, 2527–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Kunder, S.L.; van Kuijk, S.M.J.; Rijkers, K.; Caelers, I.J.M.H.; van Hemert, W.L.W.; de Bie, R.A.; van Santbrink, H. Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) versus posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF) in lumbar spondylolisthesis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Spine J. 2017, 17, 1712–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.N.; Ho, Y.W.; Chu, W.; Chou, W.S.; Cheng, S.H. Effects and Safety of Lumbar Fusion Techniques in Lumbar Spondylolisthesis: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Glob. Spine J. 2022, 12, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Li, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, W.; Guo, L.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, W. A Comparative Study of a New Retractor-Assisted WILTSE TLIF, MIS-TLIF, and Traditional PLIF for Treatment of Single-Level Lumbar Degenerative Diseases. Orthop. Surg. 2022, 14, 1317–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, E.M.S.; El-Hewala, T.A.; Eladawy, A.M.; Sheta, R.A. Does minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (MIS-TLIF) influence functional outcomes and spinopelvic parameters in isthmic spondylolisthesis? J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2022, 17, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.H.; Yeo, W.; Soeharno, H.; Yue, W.M. Learning curve of a complex surgical technique: Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (MIS TLIF). J. Spinal Disord. Tech. 2014, 27, E234–E240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modi, H.N.; Shrestha, U. Comparison of Clinical Outcome and Radiologic Parameters in Open TLIF Versus MIS-TLIF in Single- or Double-Level Lumbar Surgeries. Int. J. Spine Surg. 2021, 15, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkman, R.A.; Wright, A.H.; Khan, I.; Sivaganesan, A. Perioperative Modifications to the Open TLIF Provide Comparable Short-term Outcomes to the MIS-TLIF. Clin. Spine Surg. 2022, 35, E202–E210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Chen, H.; Zhang, K.; Yang, P.; Sun, J.; Mo, J.; Zhou, F.; Yang, H.; Mao, H. O-arm Navigation Combined With Microscope-assisted MIS-TLIF in the Treatment of Lumbar Degenerative Disease. Clin. Spine Surg. 2019, 32, E235–E240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusad, T.; Kundnani, V.; Dutta, S.; Patel, A.; Mehta, G.; Singh, M. Comparative Prospective Study Reporting Intraoperative Parameters, Pedicle Screw Perforation, and Radiation Exposure in Navigation-Guided versus Non-navigated Fluoroscopy-Assisted Minimal Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion. Asian Spine J. 2018, 12, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arif, S.; Brady, Z.; Enchev, Y.; Peev, N.; Encheva, E. Minimising radiation exposure to the surgeon in minimally invasive spine surgeries: A systematic review of 15 studies. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2021, 107, 102795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.S.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, K.H.; Kuh, S.U.; Chin, D.K.; Kim, K.S.; Cho, Y.E. Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with unilateral pedicle screw fixation: Comparison between primary and revision surgery. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 919248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goertz, L.; Stavrinou, P.; Hamisch, C.; Perrech, M.; Czybulka, D.M.; Mehdiani, K.; Timmer, M.; Goldbrunner, R.; Krischek, B. Impact of Obesity on Complication Rates, Clinical Outcomes, and Quality of Life after Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion. J. Neurol. Surg. A Cent. Eur. Neurosurg. 2021, 82, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venier, A.; Croci, D.; Robert, T.; Distefano, D.; Presilla, S.; Scarone, P. Use of Intraoperative Computed Tomography Improves Outcome of Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Single-Center Retrospective Cohort Study. World Neurosurg. 2021, 148, e572–e580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yuan, S.; Tian, Y.; Liu, X. Risk Factors Related to Superior Facet Joint Violation During Lumbar Percutaneous Pedicle Screw Placement in Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion (MIS-TLIF). World Neurosurg. 2020, 139, e716–e723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Mis-TLIF Group (n = 52) | Open-TLIF Group (n = 60) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 64.18 ± 8.17 | 66.24 ± 7.16 | 0.271 |
| Gender (Male/Female) | 28/24 | 34/26 | 0.322 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 32.41 ± 3.87 | 33.74 ± 4.15 | 0.642 |
| Lumbar spondylolisthesis | 18(18/52) | 14(14/60) | 0.196 |
| Operative site | 0.147 | ||
| L3/4 and L4/5 | 16 | 22 | |
| L4/5 and L5/S1 | 36 | 38 |
| Mis-TLIF Group (n = 52) | Open-TLIF Group (n = 60) | Cohen d | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operation time (mins) | 287.74 ± 32.17 | 232.96 ± 42.56 | 1.45 | 0.014 |
| Fluoroscopy | 12.74 ± 2.35 | 7.56 ± 3.21 | 1.84 | 0.032 |
| Amount of bleeding (mL) | 537.62 ± 112.78 | 574.97 ± 134.26 | −0.30 | 0.184 |
| Volume of drainage (mL) | 372.86 ± 165.41 | 354.91 ± 143.92 | 0.12 | 0.081 |
| Bed rest time (days) | 4.50 ± 1.08 | 6.24 ± 1.34 | −1.43 | 0.037 |
| Complications | 0.792 | |||
| CSF leak | 6 | 2 | ||
| Poor wound healing | 0 | 2 | ||
| Numbness | 6 | 4 |
| Low Back Pain VAS Score | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Operation | Postoperative 1 Week | Postoperative 3 Months | Postoperative 12 Months | |
| MIS-TLIF | 5.78 ± 2.12 | 2.03 ± 1.43 a | 1.69 ± 0.72 | 1.19 ± 0.75 |
| OPEN-TLIF | 5.22 ± 3.37 | 3.11 ± 1.04 | 1.42 ± 0.46 | 1.08 ± 0.82 |
| Cohen d | 0.20 | −0.86 | 0.45 | 0.14 |
| p value | 0.432 | 0.012 | 0.067 | 0.081 |
| Leg Pain VAS Score | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Operation | Postoperative 1 Week | Postoperative 3 Months | Postoperative 12 Months | |
| MIS-TLIF | 7.35 ± 1.15 | 2.46 ± 0.75 | 1.34 ± 0.87 | 1.04 ± 0.59 |
| OPEN-TLIF | 8.04 ± 2.01 | 2.45 ± 1.25 | 1.67 ± 0.43 | 1.15 ± 0.64 |
| Cohen d | −0.42 | 0.01 | −0.48 | −0.18 |
| p value | 0.134 | 0.237 | 0.073 | 0.126 |
| ODI (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Operation | Postoperative 1 Week | Postoperative 3 Months | Postoperative 12 Months | |
| MIS-TLIF | 76.17 ± 6.63 | 13.71 ± 2.38 | 12.26 ± 3.54 | 12.46 ± 4.31 |
| OPEN-TLIF | 68.42 ± 7.47 | 16.24 ± 3.12 | 15.17 ± 2.46 | 14.14 ± 3.37 |
| Cohen d | 1.11 | −0.91 | −0.95 | −0.43 |
| p value | 0.243 | 0.176 | 0.102 | 0.065 |
| OPEN-TLIF Group (n = 360) | MIS-TLIF Group (n = 312) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| A type screw | 0.312 | ||
| A0 screw | 151 | 124 | |
| A1 screw | 23 | 27 | |
| A2 screw | 6 | 5 | |
| B type screw | 0.021 | ||
| B0 screw | 107 | 121 | |
| B1 screw | 41 | 31 | |
| B2 screw | 32 | 4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, W.; Yang, G.; Wang, H.; Wu, X.; Ma, H.; Zhang, K.; Gao, Y. Which Is Better in Clinical and Radiological Outcomes for Lumbar Degenerative Disease of Two Segments: MIS-TLIF or OPEN-TLIF? J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12121977
Hu W, Yang G, Wang H, Wu X, Ma H, Zhang K, Gao Y. Which Is Better in Clinical and Radiological Outcomes for Lumbar Degenerative Disease of Two Segments: MIS-TLIF or OPEN-TLIF? Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022; 12(12):1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12121977
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Weiran, Guang Yang, Hongqiang Wang, Xiaonan Wu, Haohao Ma, Kai Zhang, and Yanzheng Gao. 2022. "Which Is Better in Clinical and Radiological Outcomes for Lumbar Degenerative Disease of Two Segments: MIS-TLIF or OPEN-TLIF?" Journal of Personalized Medicine 12, no. 12: 1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12121977
APA StyleHu, W., Yang, G., Wang, H., Wu, X., Ma, H., Zhang, K., & Gao, Y. (2022). Which Is Better in Clinical and Radiological Outcomes for Lumbar Degenerative Disease of Two Segments: MIS-TLIF or OPEN-TLIF? Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(12), 1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12121977






