Personalised Advanced Therapies in Parkinson’s Disease: The Role of Non-Motor Symptoms Profile
Abstract
:1. Advanced Parkinson’s Disease: The Clinical Scenario
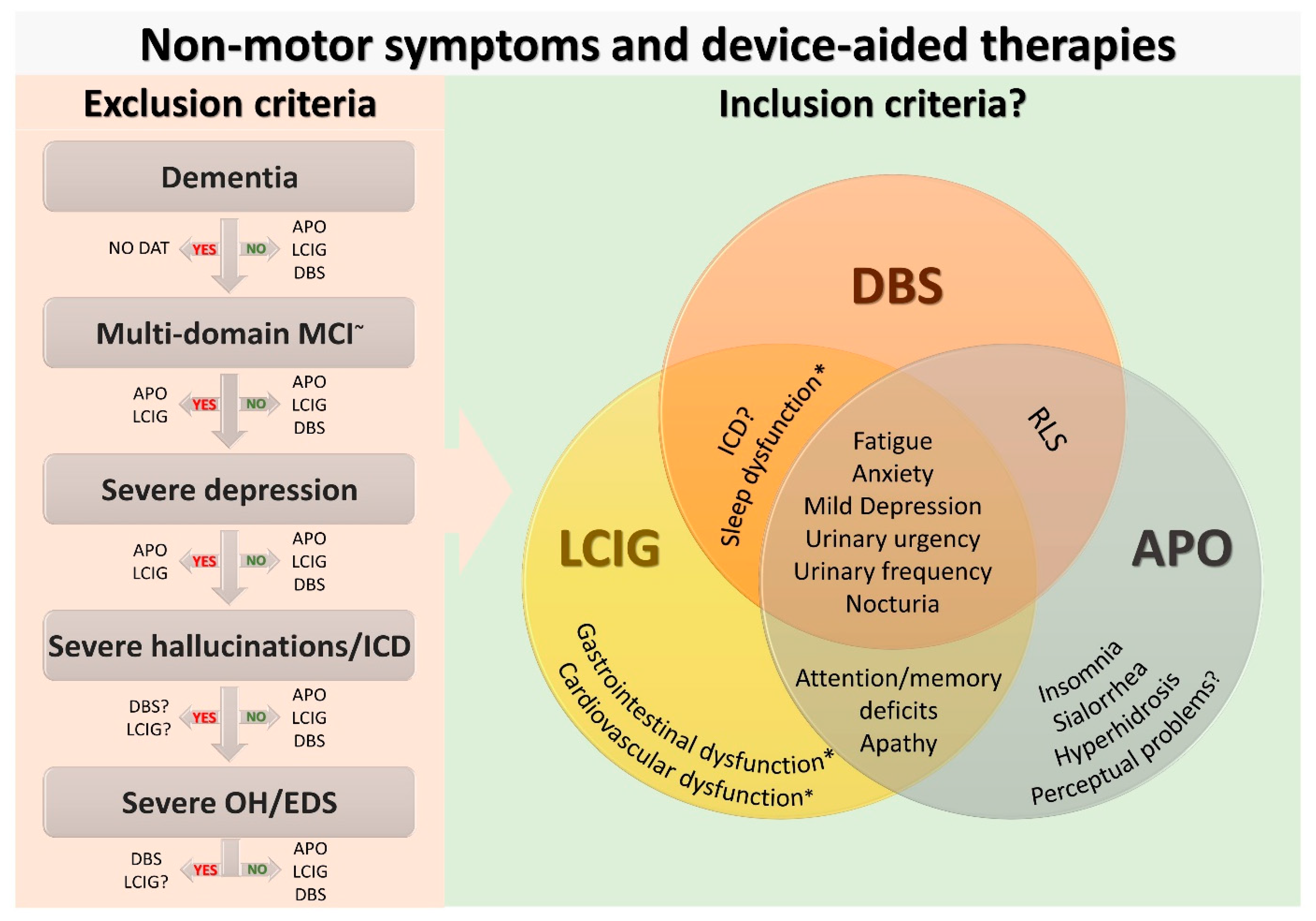
2. Current Use of Non-Motor Symptoms in Device-Aided Therapies Selection
3. Device-Aided Therapies and Differential Effect on Non-Motor Symptoms
3.1. Non-Motor Effects of Deep Brain Stimulation
3.2. Non-Motor Effects of Levodopa-Carbidopa Intestinal Gel Infusion
3.3. Non-Motor Effects of Apomorphine Subcutaneous Infusion
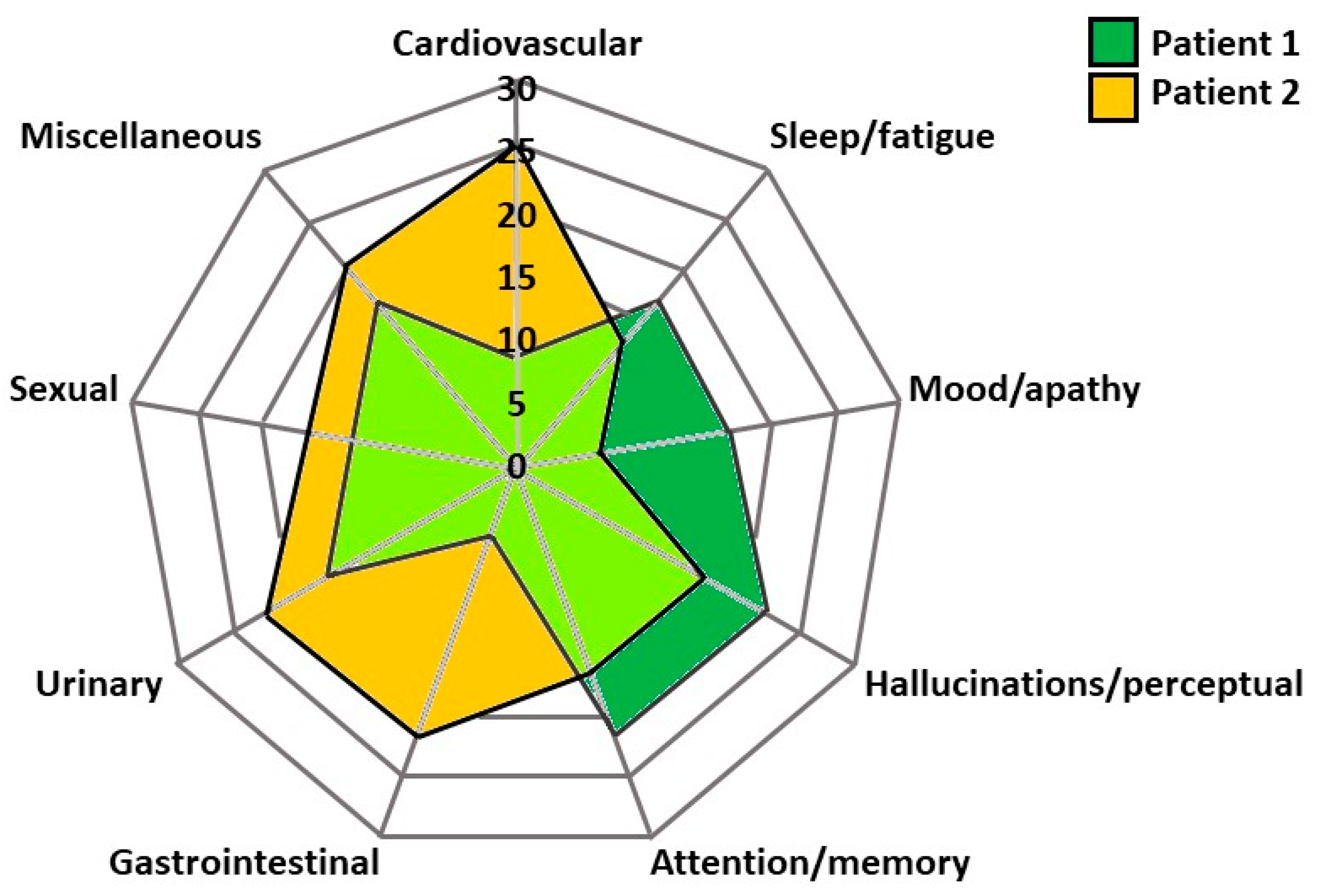
4. Need for Personalised Treatment in Advanced Parkinson’s: Clinical Cases
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Titova, N.; Chaudhuri, K.R. Non-motor Parkinson disease: New concepts and personalised management. Med. J. Aust. 2018, 208, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Titova, N.; Chaudhuri, K.R. Personalized medicine in Parkinson’s disease: Time to be precise. Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray Chaudhuri, K.; Poewe, W.; Brooks, D. Motor and Nonmotor Complications of Levodopa: Phenomenology, Risk Factors, and Imaging Features. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2018, 33, 909–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leta, V.; Jenner, P.; Chaudhuri, K.R.; Antonini, A. Can therapeutic strategies prevent and manage dyskinesia in Parkinson’s disease? An update. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2019, 18, 1203–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapuis, S.; Ouchchane, L.; Metz, O.; Gerbaud, L.; Durif, F. Impact of the motor complications of Parkinson’s disease on the quality of life. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2005, 20, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Politis, M.; Wu, K.; Molloy, S.; Bain, P.G.; Chaudhuri, K.R.; Piccini, P. Parkinson’s disease symptoms: The patient’s perspective. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2010, 25, 1646–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odin, P.; Ray Chaudhuri, K.; Slevin, J.T.; Volkmann, J.; Dietrichs, E.; Martinez-Martin, P.; Krauss, J.K.; Henriksen, T.; Katzenschlager, R.; Antonini, A.; et al. Collective physician perspectives on non-oral medication approaches for the management of clinically relevant unresolved issues in Parkinson’s disease: Consensus from an international survey and discussion program. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2015, 21, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lang, A.E.; Houeto, J.L.; Krack, P.; Kubu, C.; Lyons, K.E.; Moro, E.; Ondo, W.; Pahwa, R.; Poewe, W.; Troster, A.I.; et al. Deep brain stimulation: Preoperative issues. Mov. Disord. 2006, 21 (Suppl. S14), S171–S196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Instiute for Health and Care Excellence. Parkinson’s Disease in Adults [NICE Guideline No. 71]. 2017. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng71 (accessed on 6 August 2021).
- Antonini, A.; Stoessl, A.J.; Kleinman, L.S.; Skalicky, A.M.; Marshall, T.S.; Sail, K.R.; Onuk, K.; Odin, P.L.A. Developing consensus among movement disorder specialists on clinical indicators for identification and management of advanced Parkinson’s disease: A multi-country Delphi-panel approach. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2018, 34, 2063–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, A.; Fung, V.S.C.; Lopiano, L.; Elibol, B.; Smolentseva, I.G.; Seppi, K.; Takáts, A.; Onuk, K.; Parra, J.C.; Bergmann, L.; et al. Characterizing advanced Parkinson’s disease: OBSERVE-PD observational study results of 2615 patients. BMC Neurol. 2019, 19, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aldred, J.; Anca-Herschkovitsch, M.; Antonini, A.; Bajenaru, O.; Bergmann, L.; Bourgeois, P.; Cubo, E.; Davis, T.L.; Iansek, R.; Kovács, N.; et al. Application of the ‘5-2-1’ screening criteria in advanced Parkinson’s disease: Interim analysis of Duoglobe. Neurodegener. Dis. Manag. 2020, 10, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuepbach, W.M.; Rau, J.; Knudsen, K.; Volkmann, J.; Krack, P.; Timmermann, L.; Halbig, T.D.; Hesekamp, H.; Navarro, S.M.; Meier, N.; et al. Neurostimulation for Parkinson’s disease with early motor complications. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 610–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schuepbach, W.M.M.; Tonder, L.; Schnitzler, A.; Krack, P.; Rau, J.; Hartmann, A.; Halbig, T.D.; Pineau, F.; Falk, A.; Paschen, L.; et al. Quality of life predicts outcome of deep brain stimulation in early Parkinson disease. Neurology 2019, 92, e1109–e1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonini, A.; Robieson, W.Z.; Bergmann, L.; Yegin, A.; Poewe, W. Age/disease duration influence on activities of daily living and quality of life after levodopa-carbidopa intestinal gel in Parkinson’s disease. Neurodegener. Dis. Manag. 2018, 8, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dafsari, H.S.; Reker, P.; Silverdale, M.; Reddy, P.; Pilleri, M.; Martinez-Martin, P.; Rizos, A.; Perrier, E.; Weiß, L.; Ashkan, K.; et al. Subthalamic Stimulation Improves Quality of Life of Patients Aged 61 Years or Older with Short Duration of Parkinson’s Disease. Neuromodulation J. Int. Neuromodulation Soc. 2018, 21, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heald, A.H.; Livingston, M.; Stedman, M.; Wyrko, Z. Higher levels of apomorphine and rotigotine prescribing reduce overall secondary healthcare costs in Parkinson’s disease. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2016, 70, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smilowska, K.; van Wamelen, D.J.; Pietrzykowski, T.; Calvano, A.; Rodriguez-Blazquez, C.; Martinez-Martin, P.; Odin, P.; Chaudhuri, K.R. Cost-Effectiveness of Device-Aided Therapies in Parkinson’s Disease: A Structured Review. J. Parkinson’s Dis. 2021, 11, 475–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schapira, A.H.V.; Chaudhuri, K.R.; Jenner, P. Non-motor features of Parkinson disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 435–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Wamelen, D.J.; Sauerbier, A.; Leta, V.; Rodriguez-Blazquez, C.; Falup-Pecurariu, C.; Rodriguez-Violante, M.; Rizos, A.; Tsuboi, Y.; Metta, V.; Bhidayasiri, R.; et al. Cross-sectional analysis of the Parkinson’s disease Non-motor International Longitudinal Study baseline non-motor characteristics, geographical distribution and impact on quality of life. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storch, A.; Schneider, C.B.; Wolz, M.; Sturwald, Y.; Nebe, A.; Odin, P.; Mahler, A.; Fuchs, G.; Jost, W.H.; Chaudhuri, K.R.; et al. Nonmotor fluctuations in Parkinson disease: Severity and correlation with motor complications. Neurology 2013, 80, 800–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Wamelen, D.J.; Leta, V.; Ray Chaudhuri, K.; Storch, A. Non-motor Fluctuations in Parkinson’s Disease. In Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders; The Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorder Society; in press.
- Ray Chaudhuri, K.; Rojo, J.M.; Schapira, A.H.; Brooks, D.J.; Stocchi, F.; Odin, P.; Antonini, A.; Brown, R.G.; Martinez-Martin, P. A proposal for a comprehensive grading of Parkinson’s disease severity combining motor and non-motor assessments: Meeting an unmet need. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dafsari, H.S.; Ray-Chaudhuri, K.; Mahlstedt, P.; Sachse, L.; Steffen, J.K.; Petry-Schmelzer, J.N.; Dembek, T.A.; Reker, P.; Barbe, M.T.; Visser-Vandewalle, V.; et al. Beneficial effects of bilateral subthalamic stimulation on alexithymia in Parkinson’s disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2019, 26, 222-e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, F.; Djamshidian, A.; Seppi, K.; Poewe, W. Apomorphine for Parkinson’s Disease: Efficacy and Safety of Current and New Formulations. CNS Drugs 2019, 33, 905–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinez-Martin, P.; Reddy, P.; Katzenschlager, R.; Antonini, A.; Todorova, A.; Odin, P.; Henriksen, T.; Martin, A.; Calandrella, D.; Rizos, A.; et al. EuroInf: A multicenter comparative observational study of apomorphine and levodopa infusion in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dafsari, H.S.; Martinez-Martin, P.; Rizos, A.; Trost, M.; Dos Santos Ghilardi, M.G.; Reddy, P.; Sauerbier, A.; Petry-Schmelzer, J.N.; Kramberger, M.; Borgemeester, R.W.K.; et al. EuroInf 2: Subthalamic stimulation, apomorphine, and levodopa infusion in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2019, 34, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deuschl, G.; Schade-Brittinger, C.; Krack, P.; Volkmann, J.; Schafer, H.; Botzel, K.; Daniels, C.; Deutschlander, A.; Dillmann, U.; Eisner, W.; et al. A randomized trial of deep-brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 896–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Antonini, A.; Poewe, W.; Chaudhuri, K.R.; Jech, R.; Pickut, B.; Pirtosek, Z.; Szasz, J.; Valldeoriola, F.; Winkler, C.; Bergmann, L.; et al. Levodopa-carbidopa intestinal gel in advanced Parkinson’s: Final results of the GLORIA registry. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2017, 45, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shalash, A.; Alexoudi, A.; Knudsen, K.; Volkmann, J.; Mehdorn, M.; Deuschl, G. The impact of age and disease duration on the long term outcome of neurostimulation of the subthalamic nucleus. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2014, 20, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Fabregues, O.; Dot, J.; Abu-Suboh, M.; Hernández-Vara, J.; Ferré, A.; Romero, O.; Ibarria, M.; Seoane, J.L.; Raguer, N.; Puiggros, C.; et al. Long-term safety and effectiveness of levodopa-carbidopa intestinal gel infusion. Brain Behav. 2017, 7, e00758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietz, K.; Hagell, P.; Odin, P. Subcutaneous apomorphine in late stage Parkinson’s disease: A long term follow up. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1998, 65, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Regidor, I.; Benita, V.; Del Álamo de Pedro, M.; Ley, L.; Martinez Castrillo, J.C. Duodenal Levodopa Infusion for Long-Term Deep Brain Stimulation-Refractory Symptoms in Advanced Parkinson Disease. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2017, 40, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Murgai, A.; Naranian, T.; Jog, M.; Fasano, A. Levodopa-carbidopa intestinal gel therapy after deep brain stimulation. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2018, 33, 334–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkouzi, A.; Ramirez-Zamora, A.; Zeilman, P.; Barabas, M.; Eisinger, R.S.; Malaty, I.A.; Okun, M.S.; Almeida, L. Rescue levodopa-carbidopa intestinal gel (LCIG) therapy in Parkinson’s disease patients with suboptimal response to deep brain stimulation. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2019, 6, 1989–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bautista, J.M.P.; Oyama, G.; Nuermaimaiti, M.; Sekimoto, S.; Sasaki, F.; Hatano, T.; Nishioka, K.; Ito, M.; Umemura, A.; Ishibashi, Y.; et al. Rescue Levodopa/Carbidopa Intestinal Gel for Secondary Deep Brain Stimulation Failure. J. Mov. Disord. 2020, 13, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sesar, Á.; Fernández-Pajarín, G.; Ares, B.; Relova, J.L.; Arán, E.; Rivas, M.T.; Gelabert-González, M.; Castro, A. Continuous subcutaneous apomorphine in advanced Parkinson’s disease patients treated with deep brain stimulation. J. Neurol. 2019, 266, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulroy, E.; Leta, V.; Zrinzo, L.; Foltynie, T.; Chaudhuri, K.R.; Limousin, P. Successful Treatment of Levodopa/Carbidopa Intestinal Gel Associated “Biphasic-like” Dyskinesia with Pallidal Deep Brain Stimulation. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2021, 8, 273–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xie, A. Improvement of Subthalamic Nucleus Deep Brain Stimulation in Sleeping Symptoms in Parkinson’s Disease: A Meta-Analysis. Parkinsons Dis. 2019, 2019, 6280896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellini, G.; Best, L.A.; Brechany, U.; Mills, R.; Pavese, N. Clinical Impact of Deep Brain Stimulation on the Autonomic System in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2020, 7, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartmill, T.; Skvarc, D.; Bittar, R.; McGillivray, J.; Berk, M.; Byrne, L.K. Deep Brain Stimulation of the Subthalamic Nucleus in Parkinson’s Disease: A Meta-Analysis of Mood Effects. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalloni, F.; Debove, I.; Lachenmayer, M.L.; Krack, P.; Pollo, C.; Schuepbach, W.M.M.; Bassetti, C.L.A.; Bargiotas, P. A case series and systematic review of rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder outcome after deep brain stimulation in Parkinson’s disease. Sleep Med. 2021, 77, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwary, A.; Mohite, D.; Omole, J.A.; Bhatti, K.S.; Khan, S. Is Deep Brain Stimulation Associated With Detrimental Effects on Cognitive Functions in Patients of Parkinson’s Disease? A Systematic Review. Cureus 2020, 12, e9688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jost, S.T.; Ray Chaudhuri, K.; Ashkan, K.; Loehrer, P.A.; Silverdale, M.; Rizos, A.; Evans, J.; Petry-Schmelzer, J.N.; Barbe, M.T.; Sauerbier, A.; et al. Subthalamic Stimulation Improves Quality of Sleep in Parkinson Disease: A 36-Month Controlled Study. J. Parkinson’s Dis. 2021, 11, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dafsari, H.S.; Ray-Chaudhuri, K.; Ashkan, K.; Sachse, L.; Mahlstedt, P.; Silverdale, M.; Rizos, A.; Strack, M.; Jost, S.T.; Reker, P.; et al. Beneficial effect of 24-month bilateral subthalamic stimulation on quality of sleep in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. 2020, 267, 1830–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baumann-Vogel, H.; Imbach, L.L.; Surucu, O.; Stieglitz, L.; Waldvogel, D.; Baumann, C.R.; Werth, E. The Impact of Subthalamic Deep Brain Stimulation on Sleep-Wake Behavior: A Prospective Electrophysiological Study in 50 Parkinson Patients. Sleep 2017, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irmen, F.; Horn, A.; Mosley, P.; Perry, A.; Petry-Schmelzer, J.N.; Dafsari, H.S.; Barbe, M.; Visser-Vandewalle, V.; Schneider, G.H.; Li, N.; et al. Left Prefrontal Connectivity Links Subthalamic Stimulation with Depressive Symptoms. Ann. Neurol. 2020, 87, 962–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petry-Schmelzer, J.N.; Krause, M.; Dembek, T.A.; Horn, A.; Evans, J.; Ashkan, K.; Rizos, A.; Silverdale, M.; Schumacher, W.; Sack, C.; et al. Non-motor outcomes depend on location of neurostimulation in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 2019, 142, 3592–3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dafsari, H.S.; Dos Santos Ghilardi, M.G.; Visser-Vandewalle, V.; Rizos, A.; Ashkan, K.; Silverdale, M.; Evans, J.; Martinez, R.C.R.; Cury, R.G.; Jost, S.T.; et al. Beneficial nonmotor effects of subthalamic and pallidal neurostimulation in Parkinson’s disease. Brain Stimul. 2020, 13, 1697–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Little, S.; Brown, P. What brain signals are suitable for feedback control of deep brain stimulation in Parkinson’s disease? Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1265, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florin, E.; Dafsari, H.S.; Reck, C.; Barbe, M.T.; Pauls, K.A.; Maarouf, M.; Sturm, V.; Fink, G.R.; Timmermann, L. Modulation of local field potential power of the subthalamic nucleus during isometric force generation in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience 2013, 240, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbach, L.L.; Baumann-Vogel, H.; Baumann, C.R.; Surucu, O.; Hermsdorfer, J.; Sarnthein, J. Adaptive grip force is modulated by subthalamic beta activity in Parkinson’s disease patients. Neuroimage Clin. 2015, 9, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoang, K.B.; Cassar, I.R.; Grill, W.M.; Turner, D.A. Biomarkers and Stimulation Algorithms for Adaptive Brain Stimulation. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jost, S.T.; Visser-Vandewalle, V.; Rizos, A.; Loehrer, P.A.; Silverdale, M.; Evans, J.; Samuel, M.; Petry-Schmelzer, J.N.; Sauerbier, A.; Gronostay, A.; et al. Non-motor predictors of 36-month quality of life after subthalamic stimulation in Parkinson disease. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2021, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirdefeldt, K.; Odin, P.; Nyholm, D. Levodopa-Carbidopa Intestinal Gel in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review. CNS Drugs 2016, 30, 381–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, N.; Simuni, T. Infusion Therapies for Parkinson’s Disease. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2020, 20, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonini, A.; Odin, P.; Pahwa, R.; Aldred, J.; Alobaidi, A.; Jalundhwala, Y.J.; Kukreja, P.; Bergmann, L.; Inguva, S.; Bao, Y.; et al. The Long-Term Impact of Levodopa/Carbidopa Intestinal Gel on ‘Off’-time in Patients with Advanced Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review. Adv. Ther. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honig, H.; Antonini, A.; Martinez-Martin, P.; Forgacs, I.; Faye, G.C.; Fox, T.; Fox, K.; Mancini, F.; Canesi, M.; Odin, P.; et al. Intrajejunal levodopa infusion in Parkinson’s disease: A pilot multicenter study of effects on nonmotor symptoms and quality of life. Mov. Disord. 2009, 24, 1468–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray Chaudhuri, K.; Antonini, A.; Robieson, W.Z.; Sanchez-Soliño, O.; Bergmann, L.; Poewe, W. Burden of non-motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease patients predicts improvement in quality of life during treatment with levodopa-carbidopa intestinal gel. Eur. J. Neurol. 2019, 26, 581-e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzenschlager, R.; Poewe, W.; Rascol, O.; Trenkwalder, C.; Deuschl, G.; Chaudhuri, K.R.; Henriksen, T.; van Laar, T.; Spivey, K.; Vel, S.; et al. Apomorphine subcutaneous infusion in patients with Parkinson’s disease with persistent motor fluctuations (TOLEDO): A multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorova, A.; Ray Chaudhuri, K. Subcutaneous apomorphine and non-motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2013, 19, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa-Grilo, M.; Qamar, M.A.; Evans, A.; Chaudhuri, K.R. The efficacy of apomorphine—A non-motor perspective. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2016, 33 (Suppl. S1), S28–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martinez-Martin, P.; Reddy, P.; Antonini, A.; Henriksen, T.; Katzenschlager, R.; Odin, P.; Todorova, A.; Naidu, Y.; Tluk, S.; Chandiramani, C.; et al. Chronic subcutaneous infusion therapy with apomorphine in advanced Parkinson’s disease compared to conventional therapy: A real life study of non motor effect. J. Parkinson’s Dis. 2011, 1, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ellis, C.; Lemmens, G.; Parkes, J.D.; Abbott, R.J.; Pye, I.F.; Leigh, P.N.; Chaudhuri, K.R. Use of apomorphine in parkinsonian patients with neuropsychiatric complications to oral treatment. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 1997, 3, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drapier, S.; Gillioz, A.S.; Leray, E.; Péron, J.; Rouaud, T.; Marchand, A.; Vérin, M. Apomorphine infusion in advanced Parkinson’s patients with subthalamic stimulation contraindications. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2012, 18, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himeno, E.; Ohyagi, Y.; Ma, L.; Nakamura, N.; Miyoshi, K.; Sakae, N.; Motomura, K.; Soejima, N.; Yamasaki, R.; Hashimoto, T.; et al. Apomorphine treatment in Alzheimer mice promoting amyloid-β degradation. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 69, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonini, A.; Isaias, I.U.; Rodolfi, G.; Landi, A.; Natuzzi, F.; Siri, C.; Pezzoli, G. A 5-year prospective assessment of advanced Parkinson disease patients treated with subcutaneous apomorphine infusion or deep brain stimulation. J. Neurol. 2011, 258, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouwyn, J.P.; Derrey, S.; Lefaucheur, R.; Fetter, D.; Rouille, A.; Le Goff, F.; Maltête, D. Age Limits for Deep Brain Stimulation of Subthalamic Nuclei in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Parkinson’s Dis. 2016, 6, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, V.; Carrabba, G.; Rampini, P.; Locatelli, M. Short term surgical complications after subthalamic deep brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease: Does old age matter? BMC Geriatr. 2015, 15, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dryden, M.; Baguneid, M.; Eckmann, C.; Corman, S.; Stephens, J.; Solem, C.; Li, J.; Charbonneau, C.; Baillon-Plot, N.; Haider, S. Pathophysiology and burden of infection in patients with diabetes mellitus and peripheral vascular disease: Focus on skin and soft-tissue infections. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Off. Publ. Eur. Soc. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21 (Suppl. S2), S27–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marshall, T.; Pugh, A.; Fairchild, A.; Hass, S. Patient Preferences for Device-Aided Treatments Indicated for Advanced Parkinson Disease. Value Health J. Int. Soc. Pharm. Outcomes Res. 2017, 20, 1383–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, J.C.; Lewis, A. Weight in Parkinson’s Disease: Phenotypical Significance. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2017, 134, 891–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titova, N.; Ray Chaudhuri, K. Intrajejunal levodopa infusion therapy for Parkinson’s disease: Practical and pragmatic tips for successful maintenance of therapy. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2017, 17, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senek, M.; Nielsen, E.I.; Nyholm, D. Levodopa-entacapone-carbidopa intestinal gel in Parkinson’s disease: A randomized crossover study. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2017, 32, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leta, V.; van Wamelen, D.J.; Sauerbier, A.; Jones, S.; Parry, M.; Rizos, A.; Chaudhuri, K.R. Opicapone and Levodopa-Carbidopa Intestinal Gel Infusion: The Way Forward Towards Cost Savings for Healthcare Systems? J. Parkinson’s Dis. 2020, 10, 1535–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leta, V.; Dafsari, H.S.; Sauerbier, A.; Metta, V.; Titova, N.; Timmermann, L.; Ashkan, K.; Samuel, M.; Pekkonen, E.; Odin, P.; et al. Personalised Advanced Therapies in Parkinson’s Disease: The Role of Non-Motor Symptoms Profile. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 773. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11080773
Leta V, Dafsari HS, Sauerbier A, Metta V, Titova N, Timmermann L, Ashkan K, Samuel M, Pekkonen E, Odin P, et al. Personalised Advanced Therapies in Parkinson’s Disease: The Role of Non-Motor Symptoms Profile. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(8):773. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11080773
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeta, Valentina, Haidar S. Dafsari, Anna Sauerbier, Vinod Metta, Nataliya Titova, Lars Timmermann, Keyoumars Ashkan, Michael Samuel, Eero Pekkonen, Per Odin, and et al. 2021. "Personalised Advanced Therapies in Parkinson’s Disease: The Role of Non-Motor Symptoms Profile" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 8: 773. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11080773
APA StyleLeta, V., Dafsari, H. S., Sauerbier, A., Metta, V., Titova, N., Timmermann, L., Ashkan, K., Samuel, M., Pekkonen, E., Odin, P., Antonini, A., Martinez-Martin, P., Parry, M., van Wamelen, D. J., & Ray Chaudhuri, K. (2021). Personalised Advanced Therapies in Parkinson’s Disease: The Role of Non-Motor Symptoms Profile. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(8), 773. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11080773








