A Novel Low-Risk Germline Variant in the SH2 Domain of the SRC Gene Affects Multiple Pathways in Familial Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Samples & Ethical Permissions
2.2. Whole Genome Sequencing and Variant Calling, Annotation and Filtering
2.3. Familial Segregation of the Cancer Predisposing Variant
2.4. Evaluation of the Pathogenicity of Identified Variants Using FCVPPv2
2.5. Confirmation of Familial Segregation by Sanger Sequencing
2.6. Screening of Familial CRC Index Cases and Healthy Individuals by Taqman Assay
2.7. Plasmid Preparation and Cell Culture
2.8. Cell Proliferation Assays
2.9. Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.10. Western Blot
3. Results
3.1. Familial Cancer Variant Prioritization Pipeline Identifies a Novel Germline Variant in SRC Gene
3.2. Confirmation of Familial Segregation and Screening of a Large Cohort of Familial CRC Index Patients and Healthy Individuals
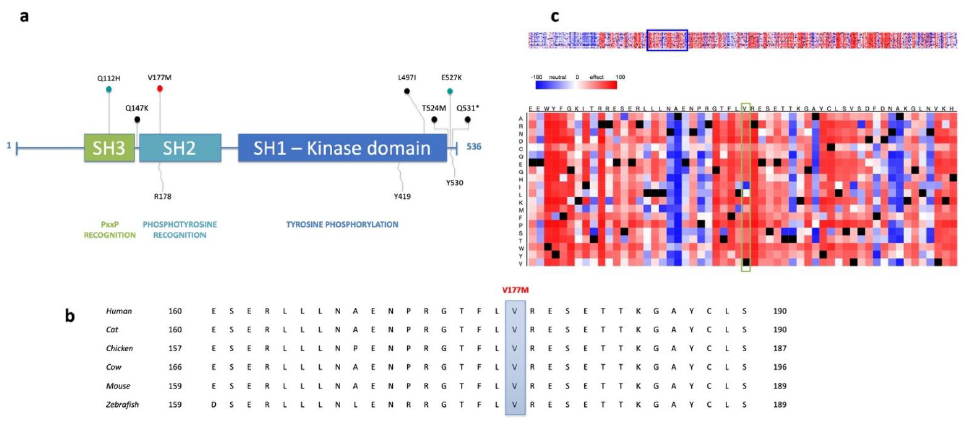
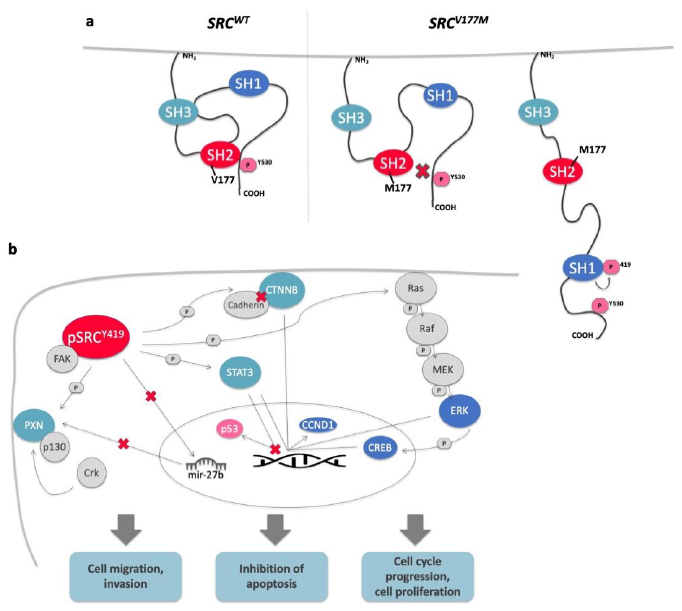
3.3. The Identified Variant Affects the Highly Conserved SH2 Domain of the SRC Protein
3.4. Functional Validation of the Prioritized Variant in SRC Gene
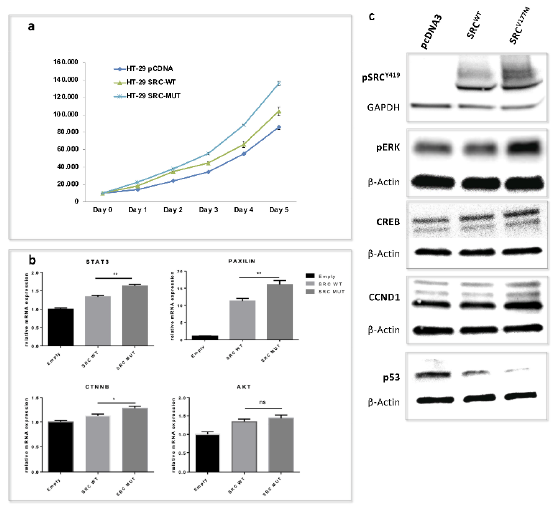
3.4.1. Enhanced Cell Proliferation of SRCV177M Expressing CRC Cells in Vitro
3.4.2. Enhanced STAT3, CTNNB, and PXN Gene Transcription Induced by the SRCV177M Variant
3.4.3. The SRCV177M Variant Leads to Increased SRC Phosphorylation at Y419, a Potential Marker for SRC Activity
3.4.4. The SRCV177M Variant Affects pERK, CREB, CCND1, and p53 Protein Expression
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frank, C.; Fallah, M.; Ji, J.; Sundquist, J.; Hemminki, K. The population impact of familial cancer, a major cause of cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 134, 1899–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weren, R.D.; Ligtenberg, M.J.; Kets, C.M.; De Voer, R.M.; Verwiel, E.T.; Spruijt, L.; van Zelst-Stams, W.A.; Jongmans, M.C.; Gilissen, C.; Hehir-Kwa, J.Y.; et al. A germline homozygous mutation in the base-excision repair gene NTHL1 causes adenomatous polyposis and colorectal cancer. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 668–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuiper, R.P.; Hoogerbrugge, N. NTHL1 defines novel cancer syndrome. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 34069–34070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, H.H.N.; Lai, J.C.W.; Ho, S.L.; Leung, W.K.; Law, W.L.; Lee, J.F.Y.; Chan, A.K.W.; Tsui, W.Y.; Chan, A.S.Y.; Lee, B.C.H.; et al. RNF43 germline and somatic mutation in serrated neoplasia pathway and its association with BRAF mutation. Gut 2016, 66, 1645–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gala, M.K.; Mizukami, Y.; Le, L.P.; Moriichi, K.; Austin, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Lauwers, G.Y.; Bardeesy, N.; Chung, D.C. Germline Mutations in Oncogene-Induced Senescence Pathways Are Associated with Multiple Sessile Serrated Adenomas. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 520–529.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Briggs, S.; Tomlinson, I. Germline and somatic polymerase epsilon and delta mutations define a new class of hypermutated colorectal and endometrial cancers. J. Pathol. 2013, 230, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palles, C.; Cazier, J.B.; Howarth, K.M.; Domingo, E.; Jones, A.M.; Broderick, P.; Kemp, Z.; Spain, S.L.; Guarino, E.; Salguero, I.; et al. Germline mutations affecting the proofreading domains of POLE and POLD1 predispose to colorectal adenomas and carci-nomas. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valle, L.; de Voer, R.M.; Goldberg, Y.; Sjursen, W.; Försti, A.; Ruiz-Ponte, C.; Caldés, T.; Garré, P.; Olsen, M.F.; Nordling, M.; et al. Update on genetic predisposition to colorectal cancer and polyposis. Mol. Asp. Med. 2019, 69, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasperson, K.W.; Tuohy, T.M.; Neklason, D.W.; Burt, R.W. Hereditary and Familial Colon Cancer. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 2044–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lorans, M.; Dow, E.; Macrae, F.A.; Winship, I.M.; Buchanan, D.D. Update on Hereditary Colorectal Cancer: Improving the Clinical Utility of Multigene Panel Testing. Clin. Color. Cancer 2018, 17, e293–e305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bandapalli, O.R.; Paramasivam, N.; Giangiobbe, S.; Kumar, A.; Benisch, W.; Engert, A.; Witzens-Harig, M.; Schlesner, M.; Hemminki, K.; Försti, A. Whole genome sequencing reveals DICER1 as a candidate predisposing gene in familial Hodgkin lymphoma. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 2076–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, A.; Bandapalli, O.R.; Paramasivam, N.; Giangiobbe, S.; Diquigiovanni, C.; Bonora, E.; Eils, R.; Schlesner, M.; Hemminki, K.; Försti, A. Familial Cancer Variant Prioritization Pipeline version 2 (FCVPPv2) applied to a papillary thyroid cancer family. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srivastava, A.; Kumar, A.; Giangiobbe, S.; Bonora, E.; Hemminki, K.; Forsti, A.; Bandapalli, O.R. Whole Genome Sequencing of Fa-milial Non-Medullary Thyroid Cancer Identifies Germline Alterations in MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathways. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lahiri, D.K.; Schnabel, B. DNA isolation by a rapid method from human blood samples: Effects of MgCl2, EDTA, storage time, and temperature on DNA yield and quality. Biochem. Genet. 1993, 31, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H. A statistical framework for SNP calling, mutation discovery, association mapping and population genetical parameter estimation from sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2987–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rimmer, A.; Phan, H.; Mathieson, I.; Iqbal, Z.; Twigg, S.R.; Consortium, W.G.S.; Wilkie, A.O.; McVean, G.; Lunter, G. Integrating map-ping-, assembly- and haplotype-based approaches for calling variants in clinical sequencing applications. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.; Li, M.; Hakonarson, H. ANNOVAR: Functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genomes Project, C.; Auton, A.; Brooks, L.D.; Durbin, R.M.; Garrison, E.P.; Kang, H.M.; Korbel, J.O.; Marchini, J.L.; McCarthy, S.; McVean, G.A.; et al. A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature 2015, 526, 68–74. [Google Scholar]
- Smigielski, E.M.; Sirotkin, K.; Ward, M.; Sherry, S.T. dbSNP: A database of single nucleotide polymorphisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lek, M.; Karczewski, K.J.; Minikel, E.V.; Samocha, K.E.; Banks, E.; Fennell, T.; O’Donnell-Luria, A.H.; Ware, J.S.; Hill, A.J.; Cummings, B.B.; et al. Analysis of protein-coding genetic variation in 60,706 humans. Nature 2016, 536, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kircher, M.; Witten, D.M.; Jain, P.; O’Roak, B.J.; Cooper, G.M.; Shendure, J. A general framework for estimating the relative patho-genicity of human genetic variants. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cooper, G.M.; Stone, E.A.; Asimenos, G.; Green, E.D.; Batzoglou, S.; Sidow, A. Distribution and intensity of constraint in mammalian genomic sequence. Genome Res. 2005, 15, 901–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siepel, A.; Bejerano, G.; Pedersen, J.S.; Hinrichs, A.S.; Hou, M.; Rosenbloom, K.; Clawson, H.; Spieth, J.; Hillier, L.W.; Richards, S.; et al. Evolutionarily conserved elements in vertebrate, insect, worm, and yeast genomes. Genome Res. 2005, 15, 1034–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petrovski, S.; Wang, Q.; Heinzen, E.L.; Allen, A.S.; Goldstein, D.B. Genic intolerance to functional variation and the interpretation of personal genomes. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, L.D.; Kellis, M. HaploReg: A resource for exploring chromatin states, conservation, and regulatory motif alterations within sets of genetically linked variants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D930–D934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Wu, C.; Li, C.; Boerwinkle, E. dbNSFP v3.0: A One-Stop Database of Functional Predictions and Annotations for Human Nonsynonymous and Splice-Site SNVs. Hum. Mutat. 2016, 37, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karczewski, K.; Francioli, L.; Tiao, G.; Cummings, B.; Alföldi, J.; Wang, Q.; Collins, R.; Laricchia, K.; Ganna, A.; Birnbaum, D.; et al. Vari-ation across 141,456 human exomes and genomes reveals the spectrum of loss-of-function intolerance across human pro-tein-coding genes. bioRxiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamborero, D.; Rubio-Perez, C.; Deu-Pons, J.; Schroeder, M.P.; Vivancos, A.; Rovira, A.; Tusquets, I.; Albanell, J.; Rodon, J.; Tabernero, J.; et al. Cancer Genome Interpreter annotates the biological and clinical relevance of tumor alterations. Genome Med. 2018, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, M.; Bromberg, Y.; Rost, B. Better prediction of functional effects for sequence variants. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, S1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stelzer, G.; Rosen, N.; Plaschkes, I.; Zimmerman, S.; Twik, M.; Fishilevich, S.; Stein, T.I.; Nudel, R.; Lieder, I.; Mazor, Y.; et al. The GeneCards Suite: From Gene Data Mining to Disease Genome Sequence Analyses. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2016, 54, 1.30.1–1.30.33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marengere, L.E.M.; Pawson, T. Structure and function of SH2 domains. J. Cell Sci. 1994, 1994, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Waksman, G.; Kominos, D.; Robertson, S.C.; Pant, N.; Baltimore, D.; Birge, R.B.; Cowburn, D.; Hanafusa, H.; Mayer, B.J.; Overduin, M.; et al. Crystal structure of the phosphotyrosine recognition domain SH2 of v-src complexed with tyrosine-phosphorylated pep-tides. Nature 1992, 358, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, S.E.; McLaren, W.; Gil, L.; Thormann, A.; Schuilenburg, H.; Sheppard, D.; Parton, A.; Armean, I.M.; Trevanion, S.J.; Flicek, P.; et al. Ensembl variation resources. Database 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turro, E.; Greene, D.; Wijgaerts, A.; Thys, C.; Lentaigne, C.; Bariana, T.K.; Westbury, S.K.; Kelly, A.M.; Selleslag, D.; Stephens, J.C.; et al. A dominant gain-of-function mutation in universal tyrosine kinase SRC causes thrombocytopenia, myelofibrosis, bleeding, and bone pathologies. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 328–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gargalionis, A.N.; Karamouzis, M.V.; Papavassiliou, A.G. The molecular rationale of Src inhibition in colorectal carcinomas. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 134, 2019–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barraclough, J.; Hodgkinson, C.; Hogg, A.; Dive, C.; Welman, A. Increases in c-Yes Expression Level and Activity Promote Motility but Not Proliferation of Human Colorectal Carcinoma Cells. Neoplasia 2007, 9, 745-IN32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiener, J.R.; Windham, T.C.; Estrella, V.C.; Parikh, N.U.; Thall, P.F.; Deavers, M.T.; Bast, R.C.; Mills, G.B.; Gallick, G.E. Activated SRC pro-tein tyrosine kinase is overexpressed in late-stage human ovarian cancers. Gynecol. Oncol. 2003, 88, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wheeler, D.L.; Iida, M.; Dunn, E.F. The Role of Src in Solid Tumors. Oncologist 2009, 14, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonetti, E.; Gesualdi, L.; Scheri, K.C.; DiNicola, S.; Fattore, L.; Masiello, M.G.; Cucina, A.; Mancini, R.; Bizzarri, M.; Ricci, G.; et al. c-Src Recruitment is Involved in c-MET-Mediated Malignant Behaviour of NT2D1 Non-Seminoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahman, N. Realizing the promise of cancer predisposition genes. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 505, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schaller, M.D.; Parsons, J.T. pp125FAK-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of paxillin creates a high-affinity binding site for Crk. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1995, 15, 2635–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feller, S.M. Crk family adaptors–signalling complex formation and biological roles. Oncogene 2001, 20, 6348–6371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lamorte, L.; Rodrigues, S.; Sangwan, V.; Turner, C.E.; Park, M. Crk associates with a multimolecular Paxillin/GIT2/beta-PIX com-plex and promotes Rac-dependent relocalization of Paxillin to focal contacts. Mol. Biol. Cell 2003, 14, 2818–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lesslie, D.P.; Summy, J.M.; Parikh, N.U.; Fan, F.; Trevino, J.G.; Sawyer, T.K.; Metcalf, C.A.; Shakespeare, W.C.; Hicklin, D.J.; Ellis, L.M.; et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 mediates migration of human colorectal carcinoma cells by activation of Src family kinases. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 94, 1710–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, X.; Tay, A.; Guy, G.R.; Tan, Y.H. Activation and association of Stat3 with Src in v-Src-transformed cell lines. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1996, 16, 1595–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bowman, T.; Broome, M.A.; Sinibaldi, D.; Wharton, W.; Pledger, W.J.; Sedivy, J.M.; Irby, R.; Yeatman, T.; Courtneidge, S.A.; Jove, R. Stat3-mediated Myc expression is required for Src transformation and PDGF-induced mitogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 7319–7324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, C.; Meyer, D.; Campbell, G.; Larner, A.; Carter-Su, C.; Schwartz, J.; Jove, R. Enhanced DNA-binding activity of a Stat3-related protein in cells transformed by the Src oncoprotein. Science 1995, 269, 81–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussios, S.; Ozturk, M.A.; Moschetta, M.; Karathanasi, A.; Zakynthinakis-Kyriakou, N.; Katsanos, K.H.; Christodoulou, D.K.; Pavlidis, N. The Developing Story of Predictive Biomarkers in Colorectal Cancer. J. Pers. Med. 2019, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carpenter, R.L.; Lo, H.-W. STAT3 Target Genes Relevant to Human Cancers. Cancers 2014, 6, 897–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niu, G.; Wright, K.L.; Ma, Y.; Wright, G.M.; Huang, M.; Irby, R.; Briggs, J.; Karras, J.; Cress, W.D.; Pardoll, D.; et al. Role of Stat3 in regu-lating p53 expression and function. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 7432–7440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oving, I.M.; Clevers, H.C. Molecular causes of colon cancer. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 32, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, J.A. Cycling to cancer with cyclin D1. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2002, 1, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; ElFiky, A.; Han, M.; Chen, C.; Saif, M.W. The Role of Src in Colon Cancer and Its Therapeutic Implications. Clin. Color. Cancer 2014, 13, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, R.; Kim, O.; Yang, J.; Sato, K.; Eisenmann, K.M.; McCarthy, J.; Chen, H.; Qiu, Y. Regulation of Akt/PKB Activation by Tyrosine Phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 31858–31862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Datta, K.; Bellacosa, A.; Chan, T.O.; Tsichlis, P.N. Akt Is a Direct Target of the Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 30835–30839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Irby, R.B.; Mao, W.; Coppola, D.; Kang, J.; Loubeau, J.M.; Trudeau, W.; Karl, R.; Fujita, D.J.; Jove, R.; Yeatman, T.J. Activating SRC muta-tion in a subset of advanced human colon cancers. Nat. Genet. 1999, 21, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irby, R.B.; Yeatman, T.J. Role of Src expression and activation in human cancer. Oncogene 2000, 19, 5636–5642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
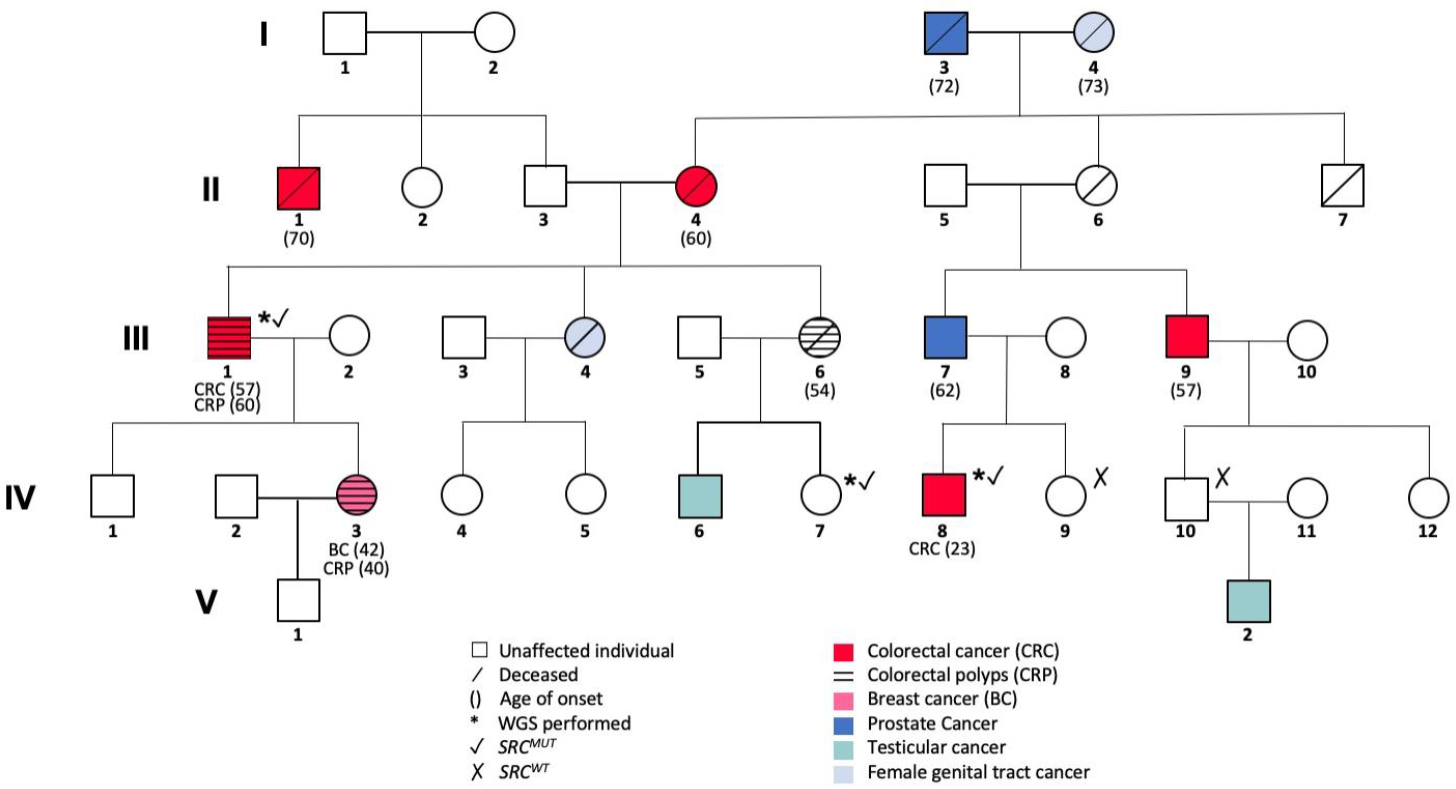
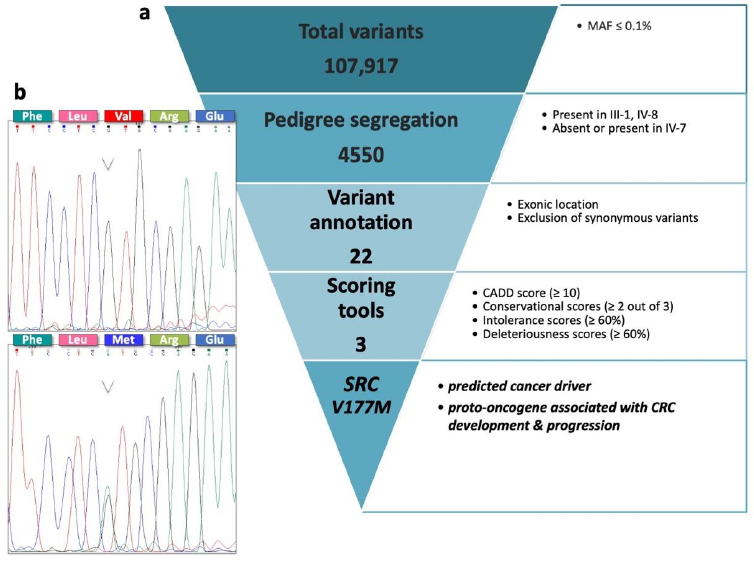
| Gene Name | Chromosomal Position | Exonic Classification | Pedigree Segregation | Allele Frequency | CADD SCORE | Conservational Scores | Deleteriousness Scores * (%) | Intolerance Scores (%) | Amino Acid Change | CGI | Protein Function | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ExAC | gnomAD NFE | GERP++ | PhyloP | PhastCons | ||||||||||
| OGFOD2 | 12-123461223-G-A | nonsyn SNV | III1, IV8 | 6.2 × 10−4 | 7.1 × 10−4 | 24.8 | 5.67 | 6.69 | 1 | 91.67 | 60 | R11Q | PP | Iron ion binding, oxidoreductase activity |
| SRC | 20-36022656-G-A | nonsyn SNV | III1, IV7, IV8 | 1.8 × 10−5 | 3.9 × 10−5 | 26.8 | 4.88 | 6.64 | 1 | 91.67 | 100 | V177M | PD, OG | Embryonic development, gene transcription, cell cycle progression, cell growth, adhesion, migration, transformation apoptosis, immune response |
| ZNF408 | 11-46726628-C-T | stop-gain SNV | III1, IV7, IV8 | 1.1 × 10−4 | 7.2 × 10−5 | 36 | 5.15 | 1.53 | 0.81 | 100 ** | 60 | Q460X | PP | DNA binding protein, highly expressed in retina |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skopelitou, D.; Miao, B.; Srivastava, A.; Kumar, A.; Kuświk, M.; Dymerska, D.; Paramasivam, N.; Schlesner, M.; Lubiński, J.; Hemminki, K.; et al. A Novel Low-Risk Germline Variant in the SH2 Domain of the SRC Gene Affects Multiple Pathways in Familial Colorectal Cancer. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11040262
Skopelitou D, Miao B, Srivastava A, Kumar A, Kuświk M, Dymerska D, Paramasivam N, Schlesner M, Lubiński J, Hemminki K, et al. A Novel Low-Risk Germline Variant in the SH2 Domain of the SRC Gene Affects Multiple Pathways in Familial Colorectal Cancer. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(4):262. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11040262
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkopelitou, Diamanto, Beiping Miao, Aayushi Srivastava, Abhishek Kumar, Magdalena Kuświk, Dagmara Dymerska, Nagarajan Paramasivam, Matthias Schlesner, Jan Lubiński, Kari Hemminki, and et al. 2021. "A Novel Low-Risk Germline Variant in the SH2 Domain of the SRC Gene Affects Multiple Pathways in Familial Colorectal Cancer" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 4: 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11040262
APA StyleSkopelitou, D., Miao, B., Srivastava, A., Kumar, A., Kuświk, M., Dymerska, D., Paramasivam, N., Schlesner, M., Lubiński, J., Hemminki, K., Försti, A., & Bandapalli, O. R. (2021). A Novel Low-Risk Germline Variant in the SH2 Domain of the SRC Gene Affects Multiple Pathways in Familial Colorectal Cancer. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(4), 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11040262









