Evidence of a Down Syndrome Keratopathy: A Three-Dimensional (3-D) Morphogeometric and Volumetric Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Examination and Measurements
2.4. Clinical and Topographical Classification
2.5. Aim of the Study and Main Outcome Measures
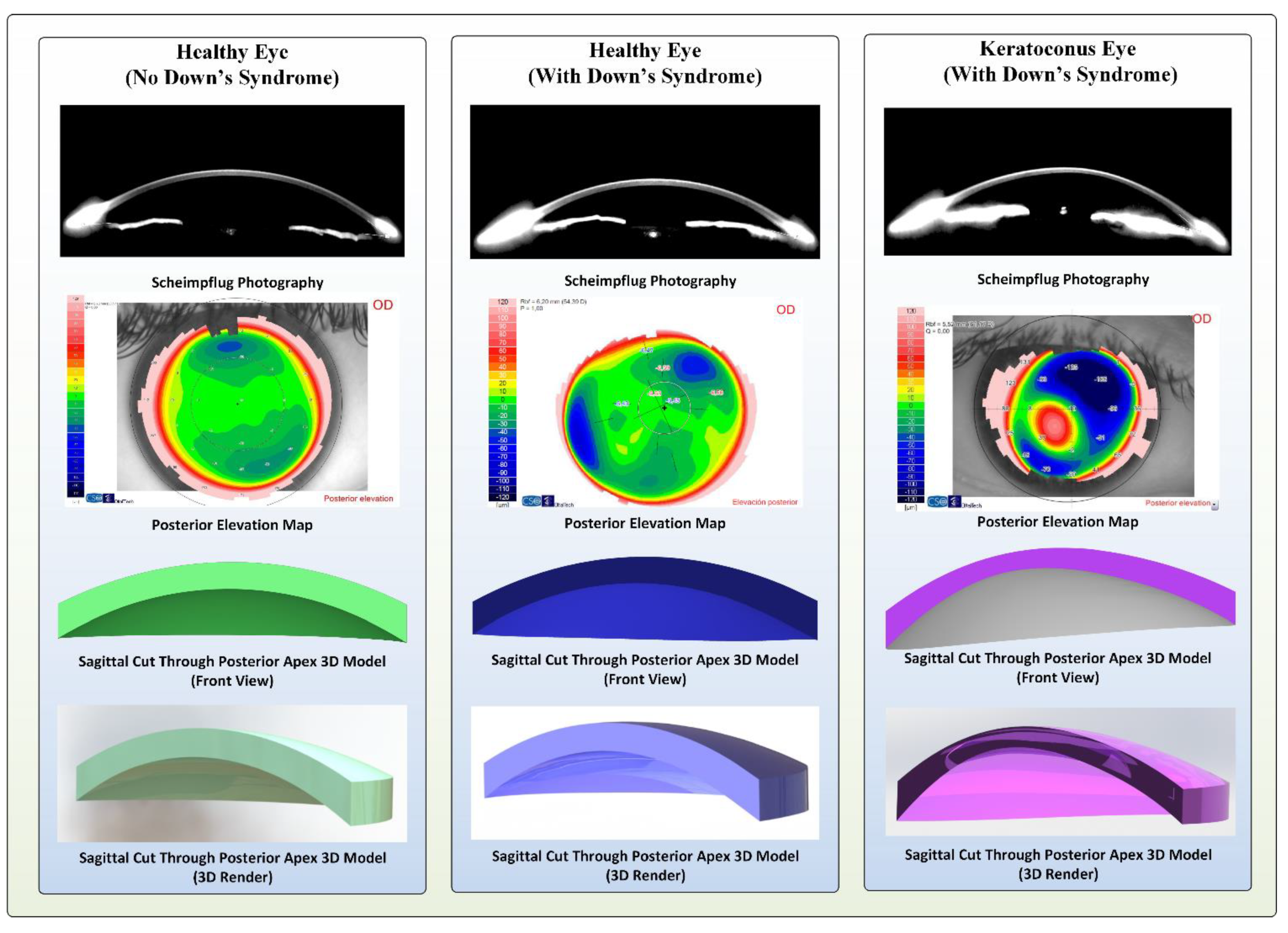
2.6. 3D Corneal Modelling, Morphogeometric and Volumetric Parameters
2.7. Sample Size Calculation
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Control vs. DS Group (Overall) Comparisons
3.1.1. Refractive, Pachymetric and Aberrometric Parameters
3.1.2. 3D Morphogeometric and Volumetric Parameters
3.1.3. Correlations between Corneal Aberrations and Morphogeometric Parameters
3.2. Control, DS with Normal Topography and DS with Abnormal Topography Group Comparisons
3.2.1. Refractive, Pachymetric and Aberrometric Parameters
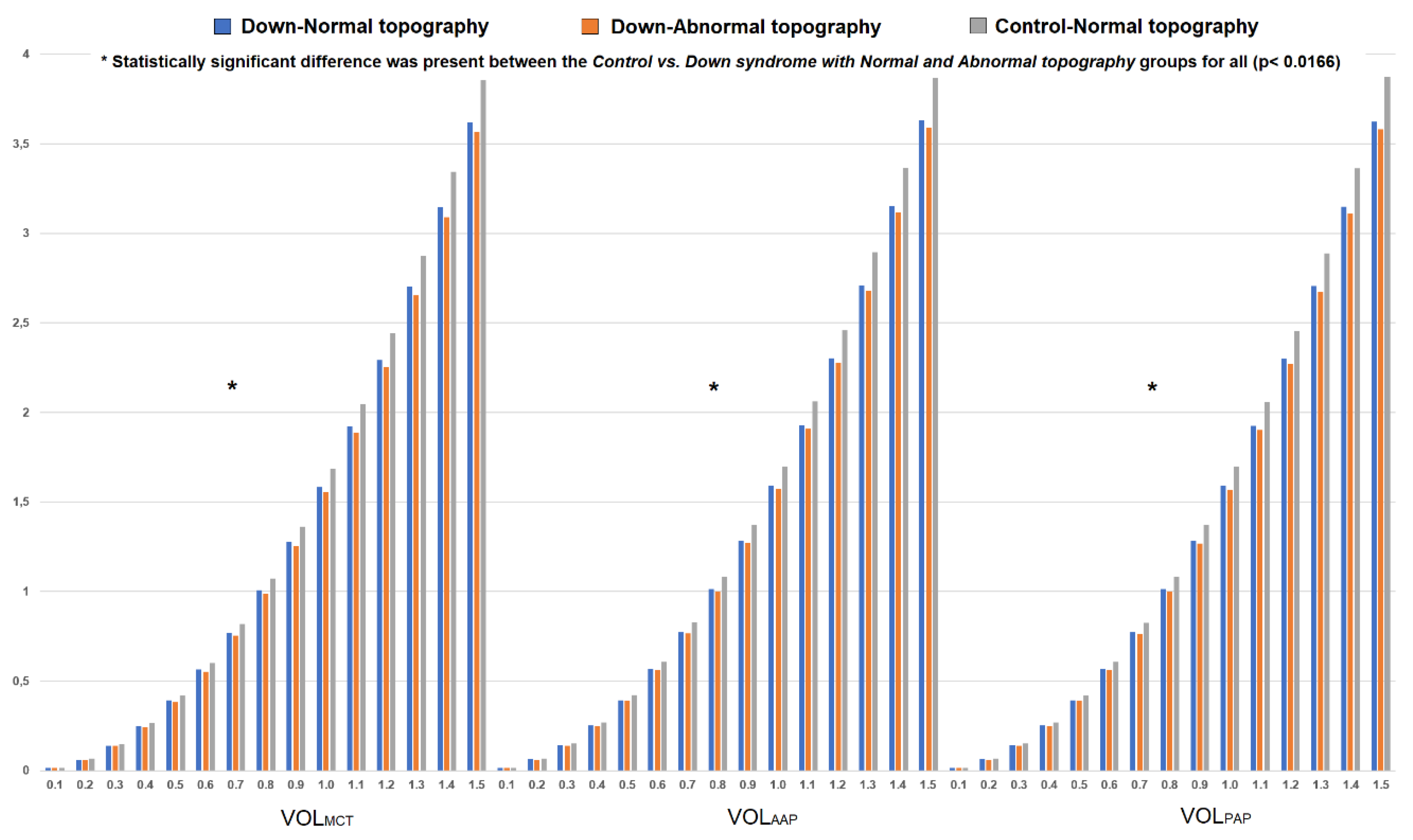
3.2.2. 3D Morphogeometric and Volumetric Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bull, M.J. Down Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2344–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, B.L. Down syndrome and associated congenital malformations. Adv. Down Syndr. Res. 2003, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makateb, A.; Hashemi, H.; Farahi, A.; Mehravaran, S.; Khabazkhoob, M.; Asgari, S. Ocular alignment, media, and eyelid disorders in Down syndrome. Strabismus 2019, 28, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabinowitz, Y.S. Keratoconus. Surv. Ophthalmol. 1998, 42, 297–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alio, J.L.; Vega-Estrada, A.; Sanz, P.; Osman, A.A.; Kamal, A.M.; Mamoon, A.; Soliman, H. Corneal Morphologic Characteristics in Patients With Down Syndrome. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2018, 136, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karousou, E.; Stachtea, X.; Moretto, P.; Viola, M.; Vigetti, D.; D’Angelo, M.L.; Raio, L.; Ghezzi, F.; Pallotti, F.; De Luca, G.; et al. New insights into the pathobiology of Down syndrome—Hyaluronan synthase-2 overexpression is regulated by collagen VIα2 chain. Febs J. 2013, 280, 2418–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udar, N.; Atilano, S.R.; Brown, D.J.; Holguin, B.; Small, K.; Nesburn, A.B.; Kenney, M.C. SOD1: A Candidate Gene for Keratoconus. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saee-Rad, S.; Raoofian, R.; Mahbod, M.; Miraftab, M.; Mojarrad, M.; Asgari, S.; Rezvan, F.; Hashemi, H. Analysis of superoxide dismutase 1, dual-specificity phosphatase 1, and transforming growth factor, beta 1 genes expression in keratoconic and non-keratoconic corneas. Mol. Vis. 2013, 19, 2501. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, A.E.; Hayes, S.; Hardcastle, A.J.; Tuft, S.J. The pathogenesis of keratoconus. Eye 2014, 28, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari, S.; Mehravaran, S.; Fotouhi, A.; Makateb, A.; Hashemi, H. Total corneal refractive power and shape in Down syndrome. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 112067211988359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, L.; Aslankurt, M.; Yüksel, E.; Özdemir, M.; Aksakal, E.; Gümüşalan, Y.; Özdemir, G. Corneal thickness measured by Scheimpflug imaging in children with Down syndrome. J. Am. Assoc. Pediatric Ophthalmol. Strabismus 2013, 17, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asgari, S.; Aghamirsalim, M.; Mehravaran, S.; Hashemi, H. Effect of Down syndrome and keratoconus on corneal density and volume: A triple comparative study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, H.; Makateb, A.; Mehravaran, S.; Fotouhi, A.; Shariati, F.; Asgari, S. Mapping the corneal thickness and volume in patients with Down syndrome: A comparative population-based study. Arq. Bras. Oftalmol. 2020, 83, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vega-Estrada, A.; Fariselli, C.; Alio, J.L. Posterior corneal features in patients with Down syndrome and their relation with keratoconus. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavas-Martínez, F.; Fernández-Pacheco, D.G.; De la Cruz-Sánchez, E.; Nieto Martínez, J.; Fernández Cañavate, F.J.; Vega-Estrada, A.; Plaza-Puche, A.B.; Alió, J.L. Geometrical custom modeling of human cornea in vivo and its use for the diagnosis of corneal ectasia. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavas-Martínez, F.; Bataille, L.; Fernández-Pacheco, D.G.; Cañavate, F.J.F.; Alio, J.L. Keratoconus Detection Based on a New Corneal Volumetric Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavas-Martínez, F.; Bataille, L.; Fernández-Pacheco, D.G.; Cañavate, F.J.F.; Alió, J.L. A new approach to keratoconus detection based on corneal morphogeometric analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toprak, I.; Cavas, F.; Velázquez, J.S.; Alio del Barrio, J.L.; Alio, J.L. Subclinical keratoconus detection with three-dimensional (3-D) morphogeometric and volumetric analysis. Acta Ophthalmol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alifa, R.; Piñero, D.; Velázquez, J.; Alió Del Barrio, J.L.; Cavas, F.; Alió, J.L. Changes in the 3D Corneal Structure and Morphogeometric Properties in Keratoconus after Corneal Collagen Crosslinking. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velázquez, J.S.; Cavas, F.; Piñero, D.P.; Cañavate, F.J.F.; Alio Del Barrio, J.; Alio, J.L. Morphogeometric analysis for characterization of keratoconus considering the spatial localization and projection of apex and minimum corneal thickness point. J. Adv. Res. 2020, 24, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velázquez-Blázquez, J.S.; Fernández-Pacheco, D.G.; del Barrio, J.A.; Alió, J.L.; Cavas-Martínez, F. Efficacy of Morpho-Geometrical Analysis of the Corneal Surfaces in Keratoconus Disease According to Moderate Visual Limitation. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering; Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velázquez, J.S.; Cavas, F.; Alió Del Barrio, J.; Fernández-Pacheco, D.G.; Alió, J. Assessment of the Association between In Vivo Corneal Morphogeometrical Changes and Keratoconus Eyes with Severe Visual Limitation. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 8731626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, H.; Miraftab, M.; Amanzadeh, K.; Seyedian, M.A.; Vinciguerra, R.; Ambrósio, R.; Roberts, C.; Makateb, A.; Vinciguerra, P.; Asgari, S. Keratoconus detection by novel indices in patients with Down syndrome: A cohort population-based study. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 64, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imbornoni, L.M.; Wise, R.E.; Taravella, M.J.; Hickey, F.; McCourt, E.A. Keratoconus and corneal morphology in patients with Down syndrome at a pediatric hospital. J. Am. Assoc. Pediatric Ophthalmol. Strabismus 2020, 24, e140–e141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, D.M.; Gajecka, M. The genetics of keratoconus. Middle East. Afr. J. Ophthalmol. 2011, 18, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsack, J.D.; Benoit, J.S.; Kollbaum, P.S.; Anderson, H.A. Application of Topographical Keratoconus Detection Metrics to Eyes of Individuals with Down Syndrome. Optom Vis. Sci 2019, 96, 664–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables (Mean ± SD) | Control Group Normal Topography (n = 58) | Down Syndrome Normal Topography (n = 18) | Down Syndrome Abnormal Topography (n = 25) | Down Syndrome Group Total (n = 43) | 3-Group Comparison * p | Pairwise Comparisons ** p | Down vs. Control Group Comparison *** p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 26.9 ± 10.1 | 17.7 ± 8.1 | 29.0 ± 11.0 | 24.3 ± 11.3 | 0.002 | a, c (0.004, 0.002) | 0.224 (S) |
| Gender (F/M) | 30/28 | 11/7 | 13/12 | 24/19 | 0.773 (chi square) | - | 0.693 (C) |
| Sphere (dioptres) | −0.74 ± 3.80 | 0.18 ± 5.31 | 0.10 ± 4.03 | 0.13 ± 4.56 | 0.095 | - | 0.085 (M) |
| Cylinder (dioptres) | −0.58 ± 0.62 | −1.23 ± 0.84 | −2.03 ± 1.04 | −1.69 ± 1.03 | <0.0001 | b (<0.0001) | <0.0001 (M) |
| Spherical equivalent (dioptres) | −1.03 ± 3.78 | −0.43 ± 5.25 | −0.91 ± 4.00 | −0.70 ± 4.52 | 0.199 | - | 0.120 (M) |
| High-order aberrations (HOAs) RMS (μm) | 0.40 ± 0.10 | 0.63 ± 0.41 | 1.64 ± 1.24 | 1.22 ± 1.10 | <0.0001 | a, b, c (0.011, <0.0001, 0.006) | <0.0001 (M) |
| Coma RMS (μm) | 0.26 ± 0.10 | 0.39 ± 0.16 | 0.98 ± 1.17 | 0.73 ± 0.94 | <0.0001 | b (<0.0001) | <0.0001 (M) |
| Spherical RMS (μm) | 0.21 ± 0.05 | 0.15 ± 0.19 | 0.002 ± 0.67 | 0.06 ± 0.52 | 0.004 | b (0.004) | 0.001 (M) |
| 8-mm Q value | −0.21 ± 0.18 | −0.42 ± 0.10 | −0.53 ± 0.30 | −0.49 ± 0.24 | <0.0001 | a, b (<0.0001 both) | <0.0001 (M) |
| Central corneal thickness (μm) | 544.2 ± 32.5 | 502.5 ± 24.8 | 491.5 ± 33.4 | 500.8 ± 29.5 | <0.0001 | a, b (0.001, <0.0001) | <0.0001 (S) |
| Variables (Mean ± SD) | Control Group Normal Topography (n = 58) | Down Syndrome Normal Topography (n = 18) | Down Syndrome Abnormal Topography (n = 25) | Down Syndrome Group Total (n = 43) | 3-Group Comparison * p | Pairwise Comparisons ** p | Down vs. Control Group Comparison *** p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dapexant (mm) | 0 | 0.003 ± 0.008 | 0.009 ± 0.010 | 0.007 ± 0.010 | <0.0001 | a, b (<0.0001 both) | <0.0001 (M) |
| Dapexpost (mm) | 0.071 ± 0.021 | 0.061 ± 0.038 | 0.086 ± 0.053 | 0.076 ± 0.048 | 0.058 | - | 0.406 (M) |
| Dmctant (mm) | 0.841 ± 0.243 | 1.268 ± 0.856 | 1.585 ± 1.156 | 1.453 ± 1.042 | 0.007 | b (0.009) | 0.002 (M) |
| Dmctpost (mm) | 0.772 ± 0.236 | 1.187 ± 0.842 | 1.499 ± 1.121 | 1.368 ± 1.015 | 0.005 | b (0.006) | 0.002 (M) |
| Aant (mm2) | 43.09 ± 0.15 | 43.52 ± 0.17 | 43.41 ± 0.30 | 43.46 ± 0.25 | <0.0001 | a, b (<0.0001 both) | <0.0001 (S) |
| Apost (mm2) | 44.24 ± 0.30 | 44.68 ± 0.37 | 44.54 ± 0.46 | 44.60 ± 0.42 | <0.0001 | a, b (<0.0001, 0.013) | <0.0001 (M) |
| Atot (mm2) | 103.75 ± 1.22 | 103.55 ± 1.60 | 103.17 ± 1.46 | 103.33 ± 1.51 | 0.240 | - | 0.121 (S) |
| Aapexant (mm2) | 0 | 4.00 ± 0.26 | 3.96 ± 0.32 | 3.98 ± 0.29 | <0.0001 | a, b (<0.0001 both) | <0.0001 (S) |
| Aapexpost (mm2) | 4.27 ± 0.28 | 3.99 ± 0.26 | 3.95 ± 0.29 | 3.97 ± 0.27 | <0.0001 | a, b (0.003, <0.0001) | <0.0001 (S) |
| Amctpost (mm2) | 4.26 ± 0.27 | 3.97 ± 0.26 | 3.92 ± 0.29 | 3.94 ± 0.28 | <0.0001 | a, b (0.001, <0.0001) | <0.0001 (S) |
| Cx (mm) | 0.041 ± 0.015 | 0.008 ± 0.038 | −0.013 ± 0.052 | −0.004 ± 0.048 | <0.0001 | a, b (0.01, <0.0001) | <0.0001 (S) |
| Cy (mm) | 0.034 ± 0.025 | 0.033 ± 0.041 | 0.011 ± 0.048 | 0.020 ± 0.041 | 0.056 | - | 0.044 (S) |
| Cz (mm) | 0.767 ± 0.023 | 0.787 ± 0.026 | 0.782 ± 0.031 | 0.784 ± 0.029 | 0.008 | a (0.0160) | 0.024 (M) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Toprak, I.; Cavas, F.; Vega, A.; Velázquez, J.S.; Alio del Barrio, J.L.; Alio, J.L. Evidence of a Down Syndrome Keratopathy: A Three-Dimensional (3-D) Morphogeometric and Volumetric Analysis. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11020082
Toprak I, Cavas F, Vega A, Velázquez JS, Alio del Barrio JL, Alio JL. Evidence of a Down Syndrome Keratopathy: A Three-Dimensional (3-D) Morphogeometric and Volumetric Analysis. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(2):82. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11020082
Chicago/Turabian StyleToprak, Ibrahim, Francisco Cavas, Alfredo Vega, José S. Velázquez, Jorge L. Alio del Barrio, and Jorge L. Alio. 2021. "Evidence of a Down Syndrome Keratopathy: A Three-Dimensional (3-D) Morphogeometric and Volumetric Analysis" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 2: 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11020082
APA StyleToprak, I., Cavas, F., Vega, A., Velázquez, J. S., Alio del Barrio, J. L., & Alio, J. L. (2021). Evidence of a Down Syndrome Keratopathy: A Three-Dimensional (3-D) Morphogeometric and Volumetric Analysis. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(2), 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11020082








