Precision Medicine: Technological Impact into Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Decision Making
Abstract
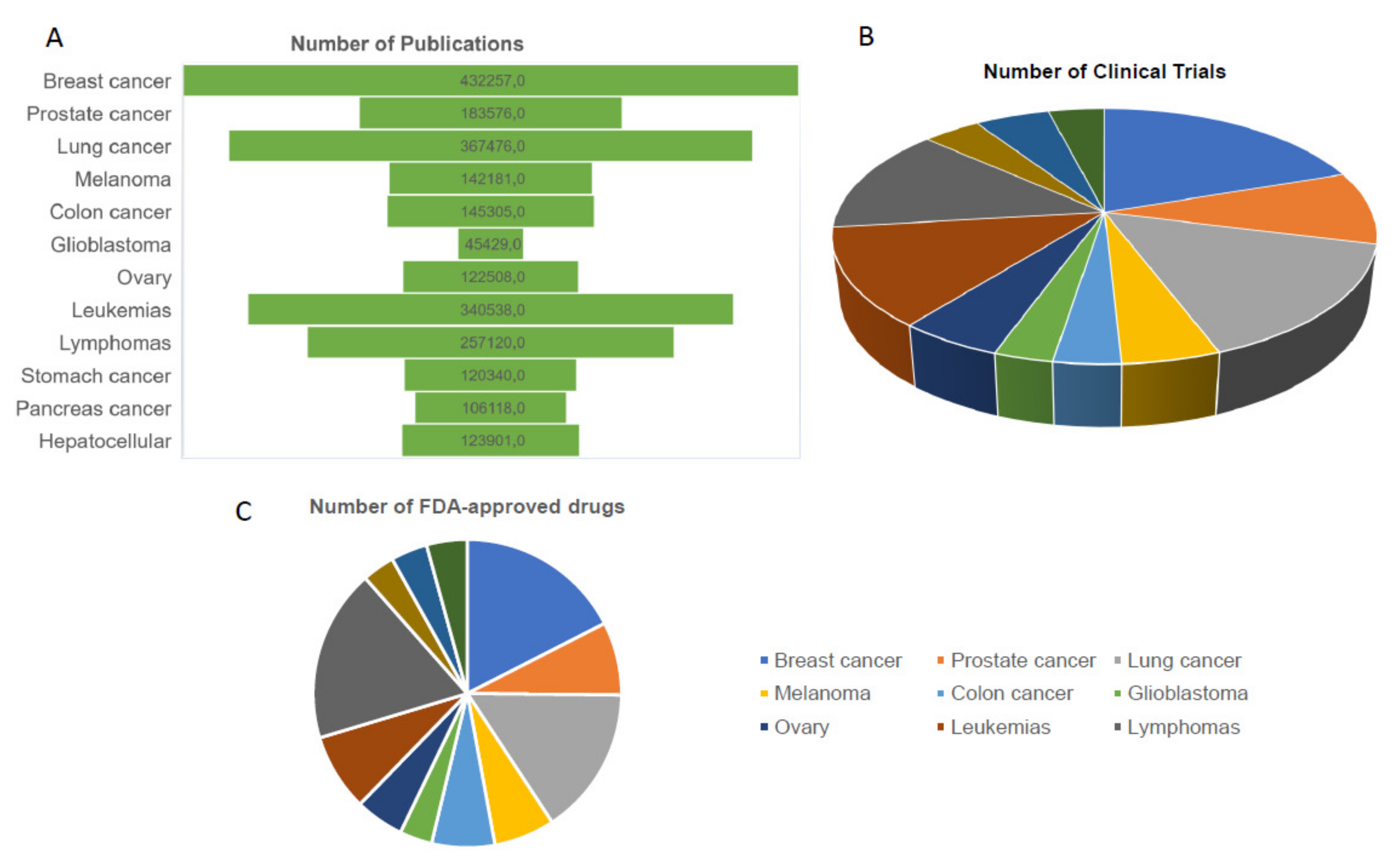
:1. Introduction
2. Technologies and Databases
3. Emerging Concepts from -Omics Data
Breast Tumor Knowledge and Heterogeneity
4. Era of Personalized Medicine
4.1. Targetable Genomic Alteration
4.2. Examples of Molecular Tools Which Are Developed after -Omics Data: Available Tests, Technical Issues and Feasibility
5. Clinically Translatable Promises: Next 10 Years
6. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Breasted, J.H. (Ed.) The Edwin Smith Surgical Papyrus; Special Edition, 1984; The University Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1930. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, S.; Ghoshal, S. The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of Cancer. J. Postgrad. Med. Educ. Res. 2012, 46, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homer. Iliad; Rouse, W.H.D., Translator; A Signet Classic; New American Library: New York, NY, USA, 1966; p. 36. [Google Scholar]
- De Moulin, D. A Short History of Breast Cancer; Martinus Nijhoff: Boston, MA, USA, 1983; pp. 1–107. [Google Scholar]
- Lewison, E.F. The surgical treatment of breast cancer: An historical and collective review. Surgery 1953, 34, 904–953. [Google Scholar]
- Halsted, W.S. The results of operations for the cure of cancer of the breast performed at the Johns Hopkins Hospital from June 1889 to January 1894. Ann. Surg. 1894, 20, 497–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horsley, J.S., III; Horsley, G.W. Twenty years’ experience with prophylactic bilateral oophorectomy in the treatment of carcinoma of the breast. Ann. Surg. 1962, 155, 935–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, E.V.; DeSomber, E.R.; Jungblut, P.W. Estrogen receptors in hormone responsive tissues and tumors. In International Symposium on Endogenous Factors Influencing Host-Tumor Balance; Wissler, R.W., Dao., T.L., Wood, S., Jr., Eds.; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA; London, UK, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Heim, S.; Mitelman, F. Cancer Cytogenetics: Chromosomal and Molecular Genetic Aberrations of Tumor Cells, 4th ed.; Heim, S., Mitelman, F., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Trent, J.M. Cytogenetic and molecular biologic alterations in human breast cancer: A review. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 1985, 5, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pandis, N.; Jin, Y.; Gorunova, L.; Petersson, C.; Bardi, G.; Idvall, I.; Johansson, B.; Ingvar, C.; Mandahl, N.; Mitelman, F.; et al. Chromosome analysis of 97 primary breast carcinomas: Identification of eight karyotypic subgroups. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 1995, 12, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium. Finishing the euchromatic sequence of the human genome. Nature 2004, 431, 931–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöblom, T.; Jones, S.; Wood, L.D.; Parsons, D.W.; Lin, J.; Barber, T.D.; Mandelker, D.; Leary, R.J.; Ptak, J.; Silliman, N.; et al. The consensus coding sequences of human breast and colorectal cancers. Science 2006, 314, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, L.D.; Parsons, D.W.; Jones, S.; Lin, J.; Sjöblom, T.; Leary, R.J.; Shen, D.; Boca, S.; Barber, T.; Ptak, J.; et al. The Genomic Landscapes of Human Breast and Colorectal Cancers. Science 2007, 318, 1108–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ley, T.J.; Mardis, E.R.; Ding, L.; Fulton, B.; McLellan, M.D.; Chen, K.; Dooling, D.; Dunford-Shore, B.H.; McGrath, S.; Hickenbotham, M.; et al. DNA sequencing of a cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukaemia genome. Nature 2008, 456, 66–72. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, S.P.; Morin, R.; Khattra, J.; Prentice, L.; Pugh, T.; Burleigh, A.; Delaney, A.; Gelmon, K.; Guliany, R.; Senz, J.; et al. Mutational evolution in a lobular breast tumour profiled at single nucleotide resolution. Nature 2009, 461, 809–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nik-Zainal, S.; Davies, H.; Staaf, J.; Ramakrishna, M.; Glodzik, D.; Zou, X.; Martincorena, I.; Alexandrov, L.; Martin, S.; Wedge, D.; et al. Landscape of somatic mutations in 560 breast cancer whole-genome sequences. Nature 2016, 534, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perou, C.M.; Sørlie, T.; Eisen, M.B.; Van De Rijn, M.; Jeffrey, S.S.; Rees, C.A.; Pollack, J.R.; Ross, D.T.; Johnsen, H.; Akslen, L.A.; et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 2000, 406, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 2012, 490, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Curtis, C.; Shah, S.P.; Chin, S.-F.; Turashvili, G.; Palacio, O.R.; Dunning, M.; Speed, D.; Lynch, A.; Samarajiwa, S.; Yuan, Y.; et al. The genomic and transcriptomic architecture of 2,000 breast tumours reveals novel subgroups. Nature 2012, 486, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pereira, B.; Chin, S.-F.; Rueda, O.M.; Vollan, H.-K.M.; Provenzano, E.; Bardwell, H.A.; Pugh, M.; Jones, L.; Russell, R.; Sammut, S.-J.; et al. The somatic mutation profiles of 2433 breast cancers refine their genomic and transcriptomic landscapes. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lehmann, B.D.; Bauer, J.A.; Chen, X.; Sanders, M.E.; Chakravarthy, A.B.; Shyr, Y.; Pietenpol, J.A. Identification of human triple-negative breast cancer subtypes and preclinical models for selection of targeted therapies. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2750–2767. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, D.T.; Mitchell, T.N.; Zehir, A.; Shah, R.; Benayed, R.; Syed, A.; Chandramohan, R.; Liu, Z.Y.; Won, H.H.; Scott, S.N.; et al. Memorial Sloan Kettering-Integrated Mutation Profiling of Actionable Cancer Targets (MSK-IMPACT). J. Mol. Diagn. 2015, 17, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehir, A.; Benayed, R.; Shah, R.H.; Syed, A.; Middha, S.; Kim, H.R.; Srinivasan, P.; Gao, J.; Chakravarty, D.; Devlin, S.M.; et al. Mutational landscape of metastatic cancer revealed from prospective clinical sequencing of 10,000 patients. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 703–713. [Google Scholar]
- Zardavas, D.; Maetens, M.; Irrthum, A.; Goulioti, T.T.; Van Engelen, K.; Fumagalli, D.; Salgado, R.; Aftimos, P.; Saini, K.S.; Sotiriou, C.; et al. The AURORA initiative for metastatic breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 1881–1887. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- André, F.; Bachelot, T.; Commo, F.; Campone, M.; Arnedos, M.; Dieras, V.; Lacroix-Triki, M.; Lacroix, L.; Cohen, P.; Gentien, D.; et al. Comparative genomic hybridisation array and DNA sequencing to direct treatment of metastatic breast cancer: A multicentre, prospective trial (SAFIR01/UNICANCER). Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schwaederle, M.; Parker, B.A.; Schwab, R.B.; Daniels, G.A.; Piccioni, D.; Kesari, S.; Helsten, T.L.; Bazhenova, L.A.; Romero, J.; Fanta, P.T.; et al. Precision Oncology: The UC San Diego Moores Cancer Center PREDICT Experience. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bartlett, J.; Sgroi, D.; Treuner, K.; Zhang, Y.; Ahmed, I.; Piper, T.; Salunga, R.; Brachtel, E.; Pirrie, S.; Schnabel, C.; et al. Breast Cancer Index and prediction of benefit from extended endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients treated in the Adjuvant Tamoxifen—To Offer More? (aTTom) trial. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1776–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dubsky, P.; Brase, J.C.; Jakesz, R.; Rudas, M.; Singer, C.F.; Greil, R.; Dietze, O.; Luisser, I.; Klug, E.; Sedivy, R.; et al. The EndoPredict score provides prognostic information on late distant metastases in ER+/HER2− breast cancer patients. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 2959–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Filipits, M.; Dubsky, P.; Rudas, M.; Greil, R.; Balic, M.; Bago-Horvath, Z.; Singer, C.F.; Hlauschek, D.; Brown, K.; Bernhisel, R.; et al. Prediction of Distant Recurrence Using EndoPredict Among Women with ER+, HER2− Node-Positive and Node-Negative Breast Cancer Treated with Endocrine Therapy Only. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3865–3872. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, J.J.; Roth, J.A. The impact of the Oncotype Dx breast cancer assay in clinical practice: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2013, 141, 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Sparano, J.A.; Gray, R.J.; Makower, D.F.; Pritchard, K.I.; Albain, K.S.; Hayes, D.F.; Geyer, C.E.; Dees, E.C.; Perez, E.A.; Olson, J.A.; et al. Prospective Validation of a 21-Gene Expression Assay in Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2005–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparano, J.A.; Gray, R.J.; Makower, D.F.; Pritchard, K.I.; Albain, K.S.; Hayes, D.F.; Geyer, C.E., Jr.; Dees, E.C.; Goetz, M.P.; Olson, J.A.; et al. Adjuvant Chemotherapy Guided by a 21-Gene Expression Assay in Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van’T Veer, L.J.; Dai, H.; Van De Vijver, M.J.; He, Y.D.; Hart, A.A.M.; Mao, M.; Peterse, H.L.; Van Der Kooy, K.; Marton, M.J.; Witteveen, A.T.; et al. Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of breast cancer. Nature 2002, 415, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, S.; Roepman, P.; Veer, L.J.V.; Bernards, R.; De Snoo, F.; Glas, A.M. Biological functions of the genes in the mammaprint breast cancer profile reflect the hallmarks of cancer. Biomark. Insights 2010, 5, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Espinosa, E.; Gamez-Pozo, A.; Sánchez-Navarro, I.; Pinto, A.; Castañeda, C.A.; Ciruelos, E.; Feliú, J.; Vara, J.A.F. The present and future of gene profiling in breast cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2011, 31, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutgers, E.; Piccart-Gebhart, M.J.; Bogaerts, J.; Delaloge, S.; Veer, L.V.T.; Rubio, I.T.; Viale, G.; Thompson, A.M.; Passalacqua, R.; Nitz, U.; et al. The EORTC 10041/BIG 03-04 MINDACT trial is feasible: Results of the pilot phase. Eur. J. Cancer 2011, 47, 2742–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccart, M.; Veer, L.J.V.T.; Poncet, C.; Cardozo, J.M.N.L.; Delaloge, S.; Pierga, J.-Y.; Vuylsteke, P.; Brain, E.; Vrijaldenhoven, S.; A Neijenhuis, P.; et al. 70-gene signature as an aid for treatment decisions in early breast cancer: Updated results of the phase 3 randomised MINDACT trial with an exploratory analysis by age. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J.S.; Mullins, M.; Cheang, M.C.U.; Leung, S.; Voduc, D.; Vickery, T.; Davies, S.; Fauron, C.; He, X.; Hu, Z.; et al. Supervised Risk Predictor of Breast Cancer Based on Intrinsic Subtypes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 1160–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnant, M.; Filipits, M.; Greil, R.; Stoeger, H.; Rudas, M.; Bago-Horvath, Z.; Mlineritsch, B.; Kwasny, W.; Knauer, M.; Singer, C.; et al. Predicting distant recurrence in receptor-positive breast cancer patients with limited clinicopathological risk: Using the PAM50 Risk of Recurrence score in 1478 postmenopausal patients of the ABCSG-8 trial treated with adjuvant endocrine therapy alone. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glück, S.; De Snoo, F.; Peeters, J.; Stork-Sloots, L.; Somlo, G. Molecular subtyping of early-stage breast cancer identifies a group of patients who do not benefit from neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2013, 139, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuerstlein, R.; Kates, R.; Gluz, O.; Grischke, E.-M.; Schem, C.; Thill, M.; Hasmueller, S.; Köhler, A.; Otremba, B.; Griesinger, F.; et al. Strong impact of MammaPrint and BluePrint on treatment decisions in luminal early breast cancer: Results of the WSG-PRIMe study. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 175, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tutt, A.; Wang, A.; Rowland, C.; Gillett, C.; Lau, K.; Chew, K.; Dai, H.; Kwok, S.; Ryder, K.; Shu, H.; et al. Risk estimation of distant metastasis in node-negative, estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer patients using an RT-PCR based prognostic expression signature. BMC Cancer 2008, 8, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Corsinovi, D.; Usai, A.; De Sarlo, M.; Giannaccini, M.; Ori, M. Zebrafish Avatar to Develop Precision Breast Cancer Therapies. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauli, C.; Hopkins, B.D.; Prandi, D.; Shaw, R.; Fedrizzi, T.; Sboner, A.; Sailer, V.; Augello, M.; Puca, L.; Rosati, R.; et al. Personalized In Vitro and In Vivo Cancer Models to Guide Precision Medicine. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 462–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sachs, N.; De Ligt, J.; Kopper, O.; Gogola, E.; Bounova, G.; Weeber, F.; Balgobind, A.V.; Wind, K.; Gracanin, A.; Begthel, H.; et al. A Living Biobank of Breast Cancer Organoids Captures Disease Heterogeneity. Cell 2018, 172, 373–386.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neal, J.T.; Kuo, C.J. Organoids as Models for Neoplastic Transformation. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2016, 11, 199–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachs, N.; Clevers, H. Organoid cultures for the analysis of cancer phenotypes. Curr Opin Genet. Dev. 2014, 24, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampedri, C.; Martínez-Flores, W.A.; Melendez-Zajgla, J. The Use of Zebrafish Xenotransplant Assays to Analyze the Role of lncRNAs in Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 687594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Kantoff, P.W.; Wooster, R.; Farokhzad, O.C. Cancer nanomedicine: Progress, challenges and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 17, 20–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garbayo, E.; Pascual-Gil, S.; Rodríguez-Nogales, C.; Saludas, L.; de Mendoza, A.E.; Blanco-Prieto, M.J. Nanomedicine and drug delivery systems in cancer and regenerative medicine. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 12, e1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hare, J.I.; Lammers, T.; Ashford, M.B.; Puri, S.; Storm, G.; Barry, S.T. Challenges and strategies in anti-cancer nanomedicine development: An industry perspective. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 108, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boulaiz, H.; Alvarez, P.J.; Ramirez, A.; Marchal, J.A.; Prados, J.; Rodríguez-Serrano, F.; Perán, M.; Melguizo, C.; Aranega, A. Nanomedicine: Application Areas and Development Prospects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 3303–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanahan, D. Rethinking the war on cancer. Lancet 2014, 383, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, C.; Sharma, A.R.; Sharma, G.; Doss, C.G.P.; Lee, S.-S. Therapeutic miRNA and siRNA: Moving from Bench to Clinic as Next Generation Medicine. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2017, 8, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dallas, A.; Vlassov, A.V. RNAi: A novel antisense technology and its therapeutic potential. Med. Sci. Monit. 2006, 12, RA67–RA74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Rossi, J.J. Strategies for silencing human disease using RNA interference. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 8, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novobrantseva, T.I.; Akinc, A.; Borodovsky, A.; De Fougerolles, A. Delivering silence: Advancements in developing siRNA therapeutics. Curr. Opin. Drug Discov. Dev. 2008, 11, 217–224. [Google Scholar]
- Ngamcherdtrakul, W.; Yantasee, W. siRNA therapeutics for breast cancer: Recent efforts in targeting metastasis, drug resistance, and immune evasion. Transl. Res. 2019, 214, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, M.J.; Mitra, R.; McArthur, M.J.; Baze, W.; Barnhart, K.; Wu, S.; Rodriguez-Aguayo, C.; Zhang, X.; Coleman, R.L.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; et al. Preclinical Mammalian Safety Studies of EPHARNA (DOPC Nanoliposomal EphA2-Targeted siRNA). Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 1114–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adams, D.; Gonzalez-Duarte, A.; O’Riordan, W.D.; Yang, C.-C.; Ueda, M.; Kristen, A.V.; Tournev, I.; Schmidt, H.H.; Coelho, T.; Berk, J.L.; et al. Patisiran, an RNAi Therapeutic, for Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanasty, R.L.; A Whitehead, K.; Vegas, A.J.; Anderson, D.G. Action and Reaction: The Biological Response to siRNA and Its Delivery Vehicles. Mol. Ther. 2012, 20, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guaragna, A.; Chiaviello, A.; Paolella, C.; D’Alonzo, D.; Palumbo, G.; Palumbo, G. Synthesis and Evaluation of Folate-Based Chlorambucil Delivery Systems for Tumor-Targeted Chemotherapy. Bioconj. Chem. 2011, 23, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, M.E.; Zuckerman, J.E.; Choi, C.H.J.; Seligson, D.; Tolcher, A.; Alabi, C.A.; Yen, Y.; Heidel, J.D.; Ribas, A. Evidence of RNAi in humans from systemically administered siRNA via targeted nanoparticles. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 464, 1067–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampen, K.R. Membrane Proteins: The Key Players of a Cancer Cell. J. Membr. Biol. 2011, 242, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosedělová, L.; Nekulová, M.; Zahradníková, M.; Faktor, J.; Vojtěšek, B.; Hernychová, L. Importance of Membrane Proteins in the Treatment of Tumor Diseases and the Possibilities of Their Further Study. Klin. Onkol. 2018, 31, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, Y.S.; Moresco, J.J.; Tu, P.G.; Yates, J.R.; Nardulli, A.M. Plasma Membrane Proteomics of Human Breast Cancer Cell Lines Identifies Potential Targets for Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peoples, G.E.; Gurney, J.M.; Hueman, M.T.; Woll, M.M.; Ryan, G.B.; Storrer, C.E.; Fisher, C.; Shriver, C.D.; Ioannides, C.G.; Ponniah, S. Clinical Trial Results of a HER2/neu (E75) Vaccine to Prevent Recurrence in High-Risk Breast Cancer Patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 7536–7545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, C.-J.; Ning, Y.-L.; Han, Y.-S.; Min, H.-Y.; Ye, H.; Zhu, Y.-L.; Qian, K.-Q. Autologous dendritic cell vaccine for estrogen receptor (ER)/progestin receptor (PR) double-negative breast cancer. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2012, 61, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzoi, M.; Romano, E.; Piccart, M. Immunotherapy for early breast cancer: Yoo soon, too superficial, or just right? Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Database | Accesion Link | Main Features |
|---|---|---|
| The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) | https://portal.gdc.cancer.gov/ (accessed on 11 October 2021) | Largest database of molecularly characterized over 20,000 primary cancer and matched normal samples spanning 33 cancer types. |
| ICGC Data Portal | https://dcc.icgc.org/ (accessed on 11 October 2021) | The ICGC Data Portal provides many tools for visualizing, querying, and downloading cancer data. |
| cBioPortal | www.cbioportal.org (accessed on 11 October 2021) | Graphical summaries; gene alteration; processed data; visualization. |
| UALCAN | http://ualcan.path.uab.edu/ (accessed on 11 October 2021) | Graphical summaries; processed data; visualization. |
| The human cancer metastasis database | hcmdb.i-sanger.com/index (accessed on 11 October 2021) | Integrated database designed to store and analyze large scale expression data of cancer metastasis. |
| Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia | https://portals.broadinstitute.org/ccle (accessed on 11 October 2021) | Project for large-scale genetic characterization of ~1000 cancer cell lines. |
| MET500 | https://met500.path.med.umich.edu/ (accessed on 11 October 2021) | Website for the MET500 metastatic cancer cohort: View aberrations in and interactions among gene sets and view the aberrations in a tumor sample, prioritized by their annotations. |
| COSMIC | http://cancer.sanger.ac.uk (accessed on 11 October 2021) | COSMIC, the Catalogue Of Somatic Mutations In Cancer, is the world’s largest and most comprehensive resource for exploring the impact of somatic mutations in human cancer. |
| MethyCancer | http://methycancer.psych.ac.cn (accessed on 11 October 2021) | Relationship among DNA methylation, gene expression and cancer. |
| SomamiR | http://compbio.uthsc.edu/SomamiR/ (accessed on 11 October 2021) | Correlation between somatic mutation and microRNA; genome-wide displaying. |
| UCSC Cancer Genomics Browser | https://genome-cancer.soe.ucsc.edu/ (accessed on 11 October 2021) | Clinical information; gene expression; copy number variation; visualization. |
| GDSC | http://www.cancerrxgene.org (accessedon 11 October 2021) | Drug sensitivity information; drug response information. |
| cansar | https://cansar.icr.ac.uk/ (accessed on 11 October 2021) | Multidisciplinary information; drug discovery. |
| NONCODE | http://www.noncode.org/ (accessed on 11 October 2021) | Data about ncRNAs; lncRNAs; up-to-date and comprehensive resource. |
| GEO DatSets | https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gds (accessed on 11 October 2021) | This database stores curated gene expression DataSets, as well as original Series and Platform records in the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) repository. |
| Proteomics DB | https://www.proteomicsdb.org/ (accessed on 11 October 2021) | Repository of proteomics data, including 87 projects and 826 experiments. |
| The Humans Protein Atlas | https://www.proteinatlas.org/ (accessed on 11 October 2021) | The Human Protein Atlas was initiated in 2003 with the aim to map all the human proteins in cells, tissues and organs using an integration of various omics technologies, including antibody-based imaging, mass spectrometry-based proteomics, transcriptomics and systems biology. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tilli, T.M. Precision Medicine: Technological Impact into Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Decision Making. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11121348
Tilli TM. Precision Medicine: Technological Impact into Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Decision Making. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(12):1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11121348
Chicago/Turabian StyleTilli, Tatiana Martins. 2021. "Precision Medicine: Technological Impact into Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Decision Making" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 12: 1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11121348
APA StyleTilli, T. M. (2021). Precision Medicine: Technological Impact into Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Decision Making. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(12), 1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11121348





