Longitudinal Study of the Association between General Anesthesia and Increased Risk of Developing Dementia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Korea National Health Insurance Service
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Predictor and Outcome Variables
2.4. Sensitivity Test
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of General Anesthesia on the Incidence of Dementia in Patients Older Than 55 Years
3.2. Hazard Ratios for Dementia in Patients Aged over 55 Years Who Underwent General Anesthesia
3.3. Sensitivity Test for Effect of General Anesthesia on the Incidence of Dementia
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| The Number of Dementia Events | |
|---|---|
| Event | 1015 |
| Non-anesthesia | 775 |
| General anesthesia | 240 |
| Total censored (No event) | 14,485 |
| Non-anesthesia | 11,625 |
| General anesthesia | 2860 |
| Termination of study | 8587 |
| Non-anesthesia | 6446 |
| General anesthesia | 2141 |
| Loss to follow up/Drop-out | 5898 |
| Non-anesthesia | 5179 |
| General anesthesia | 719 |
| Variables | Comparison (n = 18,706) | Dementia (n = 9353) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | 0.929 | ||
| Male | 5239 (28.0%) | 2614 (27.9%) | |
| Female | 13,467 (72.0%) | 6739 (72.1%) | |
| Ages (years) | 1.000 | ||
| 65–74 | 4260 (22.8%) | 2130 (22.8%) | |
| 75–84 | 9310 (49.8%) | 4655 (49.8%) | |
| ≥85 | 5136 (27.5%) | 2568 (27.5%) | |
| Residence | 0.588 | ||
| Seoul | 2562 (13.7%) | 1281 (13.7%) | |
| Second area | 4506 (24.1%) | 2304 (24.6%) | |
| Third area | 11,638 (62.2%) | 5768 (61.7%) | |
| Household income | 0.990 | ||
| Low (0–30%) | 6267 (33.5%) | 3140 (33.6%) | |
| Middle (30–70%) | 4140 (22.1%) | 2064 (22.1%) | |
| High (70–100%) | 8299 (44.4%) | 4149 (44.4%) | |
| Comorbidities | 0.688 | ||
| No | 2697 (14.4%) | 1366 (14.6%) | |
| Yes | 16,009 (85.6%) | 7987 (85.4%) |
References
- Etzioni, D.A.; Liu, J.H.; Maggard, M.A.; Ko, C.Y. The aging population and its impact on the surgery workforce. Ann. Surg. 2003, 238, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, M.; Berger, M.; Eckenhoff, R.G.; Seitz, D.P. General anesthetic and the risk of dementia in elderly patients: Current insights. Clin. Interv. Aging 2014, 9, 1619–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moller, J.T.; Cluitmans, P.; Rasmussen, L.S.; Houx, P.; Rasmussen, H.; Canet, J.; Rabbitt, P.; Jolles, J.; Larsen, K.; Hanning, C.D.; et al. Long-term postoperative cognitive dysfunction in the elderly ISPOCD1 study. ISPOCD investigators. International Study of Post-Operative Cognitive Dysfunction. Lancet 1998, 351, 857–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monk, T.G.; Weldon, B.C.; Garvan, C.W.; Dede, D.E.; van der Aa, M.T.; Heilman, K.M.; Gravenstein, J.S. Predictors of cognitive dysfunction after major noncardiac surgery. Anesthesiology 2008, 108, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eckenhoff, R.G.; Johansson, J.S.; Wei, H.; Carnini, A.; Kang, B.; Wei, W.; Pidikiti, R.; Keller, J.M.; Eckenhoff, M.F. Inhaled anesthetic enhancement of amyloid-beta oligomerization and cytotoxicity. Anesthesiology 2004, 101, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, Y.; Ishiguro, K.; Fujita, S.C. Ether stress-induced Alzheimer-like tau phosphorylation in the normal mouse brain. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Planel, E.; Richter, K.E.; Nolan, C.E.; Finley, J.E.; Liu, L.; Wen, Y.; Krishnamurthy, P.; Herman, M.; Wang, L.; Schachter, J.B.; et al. Anesthesia leads to tau hyperphosphorylation through inhibition of phosphatase activity by hypothermia. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 3090–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bianchi, S.L.; Tran, T.; Liu, C.; Lin, S.; Li, Y.; Keller, J.M.; Eckenhoff, R.G.; Eckenhoff, M.F. Brain and behavior changes in 12-month-old Tg2576 and nontransgenic mice exposed to anesthetics. Neurobiol. Aging 2008, 29, 1002–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bittner, E.A.; Yue, Y.; Xie, Z. Brief review: Anesthetic neurotoxicity in the elderly, cognitive dysfunction and Alzheimer’s disease. Can. J. Anaesth. 2011, 58, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.H.; Jung, H.; Lee, Y.; Sohn, J.H. Surgery Performed Under Propofol Anesthesia Induces Cognitive Impairment and Amyloid Pathology in ApoE4 Knock-In Mouse Model. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 658860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, B.; Moir, R.D.; Xia, W.; Marcantonio, E.R.; Culley, D.J.; Crosby, G.; Tanzi, R.E.; Xie, Z. The common inhalational anesthetic sevoflurane induces apoptosis and increases beta-amyloid protein levels. Arch. Neurol. 2009, 66, 620–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, Y.; Dong, Y.; Wu, X.; Xu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Noron, D.; Tian, M.; Li, S.; Xie, Z. Nitrous Oxide Plus Isoflurane Induces Apoptosis and Increases β-Amyloid Protein Levels. Anesthesiology 2009, 111, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whittington, R.A.; Virág, L.; Marcouiller, F.; Papon, M.A.; El Khoury, N.B.; Julien, C.; Morin, F.; Emala, C.W.; Planel, E. Propofol directly increases tau phosphorylation. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, T.A.; Wolozin, B.; Weiss, K.B.; Bednar, M.M. Assessment of the emergence of Alzheimer’s disease following coronary artery bypass graft surgery or percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2005, 7, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bufill, E.; Bartés, A.; Moral, A.; Casadevall, T.; Codinachs, M.; Zapater, E.; Carles Rovira, J.; Roura, P.; Oliva, R.; Blesa, R. Genetic and environmental factors that may influence in the senile form of Alzheimer’s disease: Nested case control studies. Neurologia 2009, 24, 108–112. [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie, K.; Carrière, I.; Ritchie, C.W.; Berr, C.; Artero, S.; Ancelin, M.L. Designing prevention programmes to reduce incidence of dementia: Prospective cohort study of modifiable risk factors. BMJ 2010, 341, c3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.W.; Lin, C.C.; Chen, K.B.; Kuo, Y.C.; Li, C.Y.; Chung, C.J. Increased risk of dementia in people with previous exposure to general anesthesia: A nationwide population-based case-control study. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2014, 10, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.L.; Yang, C.W.; Tseng, Y.K.; Sun, W.Z.; Wang, J.L.; Wang, S.J.; Oyang, Y.J.; Fuh, J.L. Risk of dementia after anaesthesia and surgery. Br. J. Psychiatry 2014, 204, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amaducci, L.A.; Fratiglioni, L.; Rocca, W.A.; Fieschi, C.; Livrea, P.; Pedone, D.; Bracco, L.; Lippi, A.; Gandolfo, C.; Bino, G.; et al. Risk factors for clinically diagnosed Alzheimer’s disease: A case-control study of an Italian population. Neurology 1986, 36, 922–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Shen, Y.C.; Li, Y.T.; Chen, C.H.; Zhau, Y.W.; Silverman, J.M. A case-control study of Alzheimer’s disease in China. Neurology 1992, 42, 1481–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canadian Study of Health and Aging. The Canadian Study of Health and Aging: Risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease in Canada. Neurology 1994, 44, 2073–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnen, N.; Warner, M.A.; Kokmen, E.; Kurland, L.T. Early and midlife exposure to anesthesia and age of onset of Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Neurosci. 1994, 77, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparini, M.; Vanacore, N.; Schiaffini, C.; Brusa, L.; Panella, M.; Talarico, G.; Bruno, G.; Meco, G.; Lenzi, G.L. A case-control study on Alzheimer’s disease and exposure to anesthesia. Neurol. Sci. 2002, 23, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprung, J.; Jankowski, C.J.; Roberts, R.O.; Weingarten, T.N.; Aguilar, A.L.; Runkle, K.J.; Tucker, A.K.; McLaren, K.C.; Schroeder, D.R.; Hanson, A.C.; et al. Anesthesia and incident dementia: A population-based, nested, case-control study. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2013, 88, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsuda, Y.; Yasunaga, H.; Horiguchi, H.; Ogawa, S.; Kawano, H.; Tanaka, S. Association between dementia and postoperative complications after hip fracture surgery in the elderly: Analysis of 87,654 patients using a national administrative database. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2015, 135, 1511–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello Bowles, E.J.; Larson, E.B.; Pong, R.P.; Walker, R.L.; Anderson, M.L.; Yu, O.; Gray, S.L.; Crane, P.K.; Dublin, S. Anesthesia Exposure and Risk of Dementia and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Prospective Study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2016, 64, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, C.T.; Myung, W.; Lewis, M.; Lee, H.; Kim, S.E.; Lee, K.; Lee, C.; Choi, J.; Kim, H.; Carroll, B.J.; et al. Exposure to General Anesthesia and Risk of Dementia: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 63, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, D.P.; Shah, P.S.; Herrmann, N.; Beyene, J.; Siddiqui, N. Exposure to general anesthesia and risk of Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Geriatr. 2011, 11, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, J.; Dong, Y.; Huang, W.; Bao, M. General anesthesia exposure and risk of dementia: A meta-analysis of epidemiological studies. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 59628–59637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.J.; Choi, G.J.; Kang, H.; Baek, C.W.; Jung, Y.H.; Shin, H.Y.; Park, Y.H.; Woo, Y.C. Relationship between Surgery under General Anesthesia and the Development of Dementia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 3234013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Dong, Y.; Maeda, U.; Alfille, P.; Culley, D.J.; Crosby, G.; Tanzi, R.E. The common inhalation anesthetic isoflurane induces apoptosis and increases amyloid beta protein levels. Anesthesiology 2006, 104, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perucho, J.; Rubio, I.; Casarejos, M.J.; Gomez, A.; Rodriguez-Navarro, J.A.; Solano, R.M.; De Yébenes, J.G.; Mena, M.A. Anesthesia with isoflurane increases amyloid pathology in mice models of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2010, 19, 1245–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Pan, N.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, S.; Guo, W.; Li, H.; Zhou, J.; Liu, G.; Gao, M. Inhaled sevoflurane may promote progression of amnestic mild cognitive impairment: A prospective, randomized parallel-group study. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 345, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprung, J.; Roberts, R.O.; Knopman, D.S.; Olive, D.M.; Gappa, J.L.; Sifuentes, V.L.; Behrend, T.L.; Farmer, J.D.; Weingarten, T.N.; Hanson, A.C.; et al. Association of Mild Cognitive Impairment with Exposure to General Anesthesia for Surgical and Nonsurgical Procedures: A Population-Based Study. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2016, 91, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breteler, M.M.; van Duijn, C.M.; Chandra, V.; Fratiglioni, L.; Graves, A.B.; Heyman, A.; Jorm, A.F.; Kokmen, E.; Kondo, K.; Mortimer, J.A.; et al. Medical history and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease: A collaborative re-analysis of case-control studies. EURODEM Risk Factors Research Group. Int. J. Epidemiol. 1991, 20 (Suppl. 2), S36–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velkers, C.; Berger, M.; Gill, S.S.; Eckenhoff, R.; Stuart, H.; Whitehead, M.; Austin, P.C.; Rochon, P.A.; Seitz, D. Association Between Exposure to General Versus Regional Anesthesia and Risk of Dementia in Older Adults. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2021, 69, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, J.K.; Mungas, D. Risk factor and behavioral differences between vascular and Alzheimer’s dementias: The pathway to end-stage disease. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry Neurol. 1993, 6, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maekawa, K.; Baba, T.; Otomo, S.; Morishita, S.; Tamura, N. Low pre-existing gray matter volume in the medial temporal lobe and white matter lesions are associated with postoperative cognitive dysfunction after cardiac surgery. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kant, I.M.J.; de Bresser, J.; van Montfort, S.J.T.; Slooter, A.J.C.; Hendrikse, J. MRI Markers of Neurodegenerative and Neurovascular Changes in Relation to Postoperative Delirium and Postoperative Cognitive Decline. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2017, 25, 1048–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatano, Y.; Narumoto, J.; Shibata, K.; Matsuoka, T.; Taniguchi, S.; Hata, Y.; Yamada, K.; Yaku, H.; Fukui, K. White-matter hyperintensities predict delirium after cardiac surgery. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2013, 21, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, E.; Tomimoto, H.; Nakao Si, S.; Wakita, H.; Akiguchi, I.; Miyamoto, K.; Shingu, K. Caudoputamen is damaged by hypocapnia during mechanical ventilation in a rat model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. Stroke 2001, 32, 2920–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamamoto, T.; Iwamoto, T.; Kimura, S.; Nakao, S. Persistent isoflurane-induced hypotension causes hippocampal neuronal damage in a rat model of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. J. Anesth. 2018, 32, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, B.; Simone, S.M.; Giovannetti, T.; Floyd, T.F. Cerebral Hypoxia: Its Role in Age-Related Chronic and Acute Cognitive Dysfunction. Anesth. Analg. 2021, 132, 1502–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, S.; Yamamoto, T.; Kimura, S.; Mino, T.; Iwamoto, T. Brain white matter lesions and postoperative cognitive dysfunction: A review. J. Anesth. 2019, 33, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, C.A.; Hardy, J.; Schott, J.M. Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2018, 25, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperling, R.A.; Aisen, P.S.; Beckett, L.A.; Bennett, D.A.; Craft, S.; Fagan, A.M.; Iwatsubo, T.; Jack, C.R., Jr.; Kaye, J.; Montine, T.J.; et al. Toward defining the preclinical stages of Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2011, 7, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bilotta, F.; Doronzio, A.; Stazi, E.; Titi, L.; Fodale, V.; Di Nino, G.; Rosa, G. Postoperative cognitive dysfunction: Toward the Alzheimer’s disease pathomechanism hypothesis. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2010, 22 (Suppl. 3), 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belrose, J.C.; Noppens, R.R. Anesthesiology and cognitive impairment: A narrative review of current clinical literature. BMC Anesthesiol. 2019, 19, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.X.; Mardini, F.; Janik, L.S.; Garrity, S.T.; Li, R.Q.; Bachlani, G.; Eckenhoff, R.G.; Eckenhoff, M.F. Modulation of murine Alzheimer pathogenesis and behavior by surgery. Ann. Surg. 2013, 257, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marcantonio, E.R.; Goldman, L.; Mangione, C.M.; Ludwig, L.E.; Muraca, B.; Haslauer, C.M.; Donaldson, M.C.; Whittemore, A.D.; Sugarbaker, D.J.; Poss, R.; et al. A clinical prediction rule for delirium after elective noncardiac surgery. JAMA 1994, 271, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiner, S.; Silverstein, J.H. Postoperative delirium and cognitive dysfunction. Br. J. Anaesth. 2009, 103 (Suppl. 1), i41–i46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cerejeira, J.; Batista, P.; Nogueira, V.; Vaz-Serra, A.; Mukaetova-Ladinska, E.B. The stress response to surgery and postoperative delirium: Evidence of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis hyperresponsiveness and decreased suppression of the gh/igf-1 axis. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry Neurol. 2013, 26, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, J.S.; Park, S.-H.; Shin, S.A.; Kim, K. Cohort Profile: The National Health Insurance Service–National Sample Cohort (NHIS-NSC), South Korea. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

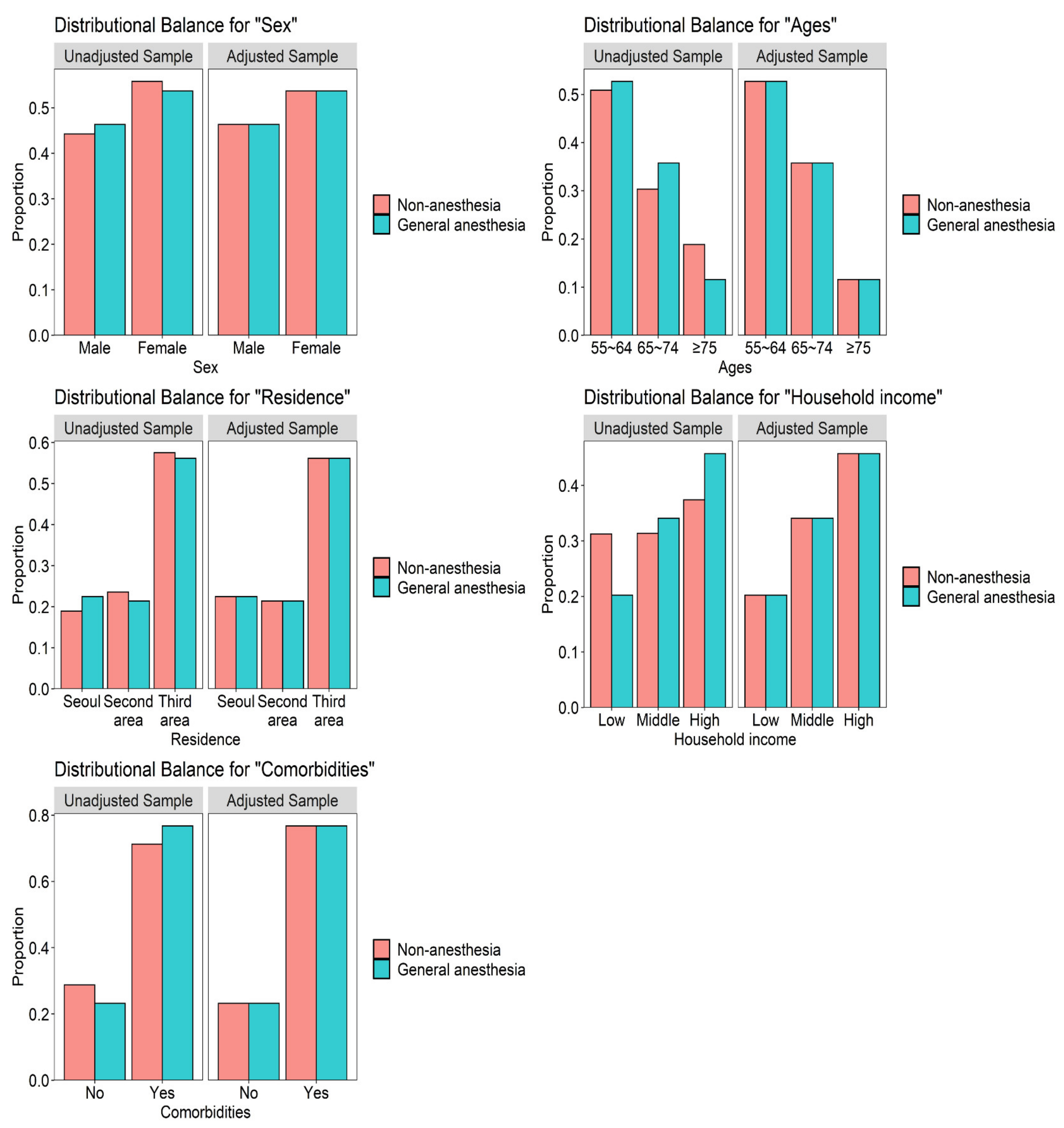


| Variables | Comparison (n = 12,400) | General Anesthesia (n = 3100) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | 1.000 | ||
| Male | 5744 (46.3%) | 1436 (46.3%) | |
| Female | 6656 (53.7%) | 1664 (53.7%) | |
| Ages (years) | 1.000 | ||
| 55–64 | 6532 (52.7%) | 1633 (52.7%) | |
| 65–74 | 4432 (35.7%) | 1108 (35.7%) | |
| ≥75 | 1436 (11.6%) | 359 (11.6%) | |
| Residence | 1.000 | ||
| Seoul | 2784 (22.5%) | 696 (22.5%) | |
| Second area | 2652 (21.4%) | 663 (21.4%) | |
| Third area | 6964 (56.2%) | 1741 (56.2%) | |
| Household income | 1.000 | ||
| Low (0–30%) | 2508 (20.2%) | 627 (20.2%) | |
| Middle (30–70%) | 4224 (34.1%) | 1056 (34.1%) | |
| High (70–100%) | 5668 (45.7%) | 1417 (45.7%) | |
| Comorbidities | 1.000 | ||
| No | 2880 (23.2%) | 720 (23.2%) | |
| Yes | 9520 (76.8%) | 2380 (76.8%) |
| Variables | N | Cases | Incidence | Unadjusted HR (95% CI) | Adjusted HR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | |||||
| Comparison | 12,400 | 775 | 8.8 | 1.00 (ref.) | 1.00 (ref.) |
| General anesthesia | 3100 | 240 | 10.5 | 1.52 (1.30–1.76) *** | 1.36 (1.16–1.58) *** |
| Sex | |||||
| Male | 7180 | 364 | 7.9 | 1.00 (ref.) | 1.00 (ref.) |
| Female | 8320 | 651 | 9.9 | 1.20 (1.05–1.36) ** | 1.16 (1.02–1.32) * |
| Ages (years) | |||||
| 55–64 | 8165 | 275 | 3.9 | 1.00 (ref.) | 1.00 (ref.) |
| 65–74 | 5540 | 554 | 15.4 | 4.25 (3.68–4.91) *** | 3.95 (3.41–4.58) *** |
| ≥75 | 1795 | 186 | 33.3 | 11.63 (9.63–14.05) *** | 10.08 (8.29–12.26) *** |
| Residence | |||||
| Seoul | 3480 | 196 | 7.5 | 1.00 (ref.) | 1.00 (ref.) |
| Second area | 3315 | 224 | 9.8 | 1.36 (1.12–1.65) ** | 1.27 (1.05–1.54) * |
| Third area | 8705 | 595 | 9.6 | 1.31 (1.11–1.54) ** | 1.09 (0.93–1.28) |
| Household income | |||||
| Low (0–30%) | 3135 | 354 | 13.2 | 1.00 (ref.) | 1.00 (ref.) |
| Middle (30–70%) | 5280 | 242 | 6.8 | 0.52 (0.44–0.61) *** | 0.77 (0.65–0.91) ** |
| High (70–100%) | 7085 | 419 | 8.6 | 0.65 (0.56–0.75) *** | 0.78 (0.68–0.91) ** |
| Comorbidities | |||||
| No | 3600 | 90 | 4.8 | 1.00 (ref.) | 1.00 (ref.) |
| Yes | 11,900 | 925 | 10.0 | 1.93 (1.55–2.40) *** | 1.54 (1.24–1.92) *** |
| Sex | Male | Female | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comparison | General Anesthesia | Comparison | General Anesthesia | |
| Dementia | ||||
| Unadjusted HR (95% CI) | 1.00 (ref.) | 1.33 (1.04–1.71) * | 1.00 (ref.) | 1.66 (1.37–2.00) *** |
| Adjusted HR (95% CI) | 1.00 (ref.) | 1.22 (0.95–1.58) | 1.00 (ref.) | 1.44 (1.19–1.75) *** |
| Comorbidities | No | Yes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Comparison | General Anesthesia | Comparison | General Anesthesia | |
| Dementia | ||||
| Unadjusted HR (95% CI) | 1.00 (ref.) | 1.43 (0.90–2.28) | 1.00 (ref.) | 1.57 (1.34–1.84) *** |
| Adjusted HR (95% CI) | 1.00 (ref.) | 1.04 (0.64–1.68) | 1.00 (ref.) | 1.39 (1.18–1.64) *** |
| Variables | N | Cases | Incidence | Unadjusted HR (95% CI) | Adjusted HR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alzheimer’s disease | |||||
| Non-anesthesia | 12,400 | 546 | 6.1 | 1.00 (ref.) | 1.00 (ref.) |
| General anesthesia | 3100 | 178 | 7.7 | 1.69 (1.41–2.02) *** | 1.52 (1.27–1.82) *** |
| Vascular dementia | |||||
| Non-anesthesia | 12,400 | 124 | 1.4 | 1.00 (ref.) | 1.00 (ref.) |
| General anesthesia | 3100 | 49 | 2.1 | 1.85 (1.31–2.61) *** | 1.64 (1.15–2.33) ** |
| Comparison (n = 18,706) | Dementia (n = 9353) | |
|---|---|---|
| General anesthesia | ||
| 0 | 16,098 (86.1%) | 7844 (83.9%) |
| 1 | 2147 (11.5%) | 1204 (12.9%) |
| 2 | 361 (1.9%) | 239 (2.6%) |
| 3 | 77 (0.4%) | 50 (0.5%) |
| 4 | 16 (0.1%) | 9 (0.1%) |
| 5 | 4 (0.0%) | 4 (0.0%) |
| 6 | 0 (0.0%) | 2 (0.0%) |
| 7 | 1 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) |
| 8 | 1 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) |
| 9 | 1 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) |
| 13 | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (0.0%) |
| Frequency of General Anesthesia | |
|---|---|
| Mean | |
| Comparison | 0.171 |
| Dementia | 0.205 |
| Standard deviation | |
| Comparison | 0.479 |
| Dementia | 0.538 |
| Levene test | |
| F | 27.327 |
| df (v1; v2) | 1; 28,057 |
| p-value | 0.000 |
| Welch Two Sample t-test | |
| t | −5.029 |
| df | 16,902 |
| p-value | 0.000 |
| 95% confidence interval | −0.046~−0.020 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sohn, J.-H.; Lee, J.J.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, C.; Yu, H.; Kwon, Y.-S.; Kim, D.-K. Longitudinal Study of the Association between General Anesthesia and Increased Risk of Developing Dementia. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1215. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11111215
Sohn J-H, Lee JJ, Lee S-H, Kim C, Yu H, Kwon Y-S, Kim D-K. Longitudinal Study of the Association between General Anesthesia and Increased Risk of Developing Dementia. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(11):1215. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11111215
Chicago/Turabian StyleSohn, Jong-Hee, Jae Jun Lee, Sang-Hwa Lee, Chulho Kim, Hyunjae Yu, Young-Suk Kwon, and Dong-Kyu Kim. 2021. "Longitudinal Study of the Association between General Anesthesia and Increased Risk of Developing Dementia" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 11: 1215. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11111215
APA StyleSohn, J.-H., Lee, J. J., Lee, S.-H., Kim, C., Yu, H., Kwon, Y.-S., & Kim, D.-K. (2021). Longitudinal Study of the Association between General Anesthesia and Increased Risk of Developing Dementia. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(11), 1215. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11111215







