Relationship between Spatiotemporal Dynamics of the Brain at Rest and Self-Reported Spontaneous Thoughts: An EEG Microstate Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. ARSQ
2.4. EEG Processing
2.5. Microstate Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. EEG Microstates
3.2. Subjective Reports
3.3. Association between Temporal Parameters of Microstates and ARSQ Dimensions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Diessen, E.; Numan, T.; Van Dellen, E.; Van Der Kooi, A.W.; Boersma, M.; Hofman, D.; Van Lutterveld, R.; Van Dijk, B.W.; Van Straaten, E.C.W.; Hillebrand, A.; et al. Opportunities and methodological challenges in EEG and MEG resting state functional brain network research. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 126, 1468–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centeno, M.; Carmichael, D.W. Network connectivity in epilepsy: Resting state fMRI and EEG-fMRI contributions. Front. Neurol. 2014, 5, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, B.J.; Snyder, A.Z.; Zempel, J.M.; Smyth, M.D.; Raichle, M.E. Electrophysiological correlates of the brain’s intrinsic large-scale functional architecture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 16039–16044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Fukunaga, M.; de Zwart, J.A.; Duyn, J.H. Large-scale spontaneous fluctuations and correlations in brain electrical activity observed with magnetoencephalography. Neuroimage 2010, 51, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koenig, T.; Lehmann, D.; Saito, N.; Kuginuki, T.; Kinoshita, T.; Koukkou, M. Decreased functional connectivity of EEG theta-frequency activity in first-episode, neuroleptic-naïve patients with schizophrenia: Preliminary results. Schizophr. Res. 2001, 50, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newson, J.J.; Thiagarajan, T.C. EEG Frequency Bands in Psychiatric Disorders: A Review of Resting State Studies. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, N.W.; Northoff, G. Overview of potential procedural and participant-related confounds for neuroimaging of the resting state. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2013, 38, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bréchet, L.; Ziegler, D.A.; Simon, A.J.; Brunet, D.; Gazzaley, A.; Michel, C.M. Reconfiguration of Electroencephalography Microstate Networks after Breath-Focused, Digital Meditation Training. Brain Connect. 2021, 11, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faber, P.L.; Travis, F.; Milz, P.; Parim, N. EEG microstates during different phases of Transcendental Meditation practice. Cogn. Process. 2017, 18, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milz, P.; Faber, P.L.; Lehmann, D.; Koenig, T.; Kochi, K.; Pascual-Marqui, R.D. The functional significance of EEG microstates-Associations with modalities of thinking. Neuroimage 2016, 125, 643–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitzman, B.A.; Abell, M.; Bartley, S.C.; Erickson, M.A.; Bolbecker, A.R.; Hetrick, W.P. Cognitive manipulation of brain electric microstates. Neuroimage 2017, 146, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diaz, B.A.; Van Der Sluis, S.; Moens, S.; Benjamins, J.S.; Migliorati, F.; Stoffers, D.; Den Braber, A.; Poil, S.-S.; Hardstone, R.; Van ’t Ent, D.; et al. The Amsterdam Resting-State Questionnaire reveals multiple phenotypes of resting-state cognition. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diaz, B.A.; Van Der Sluis, S.; Benjamins, J.S.; Stoffers, D.; Hardstone, R.; Mansvelder, H.D.; Van Someren, E.J.W.; Linkenkaer-Hansen, K. The ARSQ 2.0 reveals age and personality effects on mind-wandering experiences. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diaz, B.A.; Hardstone, R.; Mansvelder, H.D.; Van Someren, E.J.W.; Linkenkaer-Hansen, K. Resting-state subjective experience and EEG biomarkers are associated with sleep-onset latency. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marchetti, A.; Baglio, F.; Costantini, I.; Dipasquale, O.; Savazzi, F.; Nemni, R.; Sangiuliano Intra, F.; Tagliabue, S.; Valle, A.; Massaro, D.; et al. Theory of Mind and the Whole Brain Functional Connectivity: Behavioral and Neural Evidences with the Amsterdam Resting State Questionnaire. Front. Psychol. 2015, 6, 1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pipinis, E.; Melynyte, S.; Koenig, T.; Jarutyte, L.; Linkenkaer-Hansen, K.; Ruksenas, O.; Griskova-Bulanova, I. Association Between Resting-State Microstates and Ratings on the Amsterdam Resting-State Questionnaire. Brain Topogr. 2017, 30, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Portnova, G.V.; Ukraintseva, Y.V.; Liaukovich, K.M.; Martynova, O.V. Association of the retrospective self-report ratings with the dynamics of EEG. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zanesco, A.P.; Denkova, E.; Jha, A.P. Associations between self-reported spontaneous thought and temporal sequences of EEG microstates. Brain Cogn. 2021, 150, 105696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoffers, D.; Diaz, B.A.; Chen, G.; den Braber, A.; van’t Ent, D.; Boomsma, D.I.; Mansvelder, H.D.; de Geus, E.; Van Someren, E.J.; Linkenkaer-Hansen, K. Resting-State fMRI Functional Connectivity Is Associated with Sleepiness, Imagery, and Discontinuity of Mind. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, A.; Pascual-Leone, A.; Farzan, F. Reliability of resting-state microstate features in electroencephalography. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bréchet, L.; Brunet, D.; Birot, G.; Gruetter, R.; Michel, C.M.; Jorge, J. Capturing the spatiotemporal dynamics of self-generated, task-initiated thoughts with EEG and fMRI. Neuroimage 2019, 194, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Custo, A.; Van De Ville, D.; Wells, W.M.; Tomescu, M.I.; Brunet, D.; Michel, C.M. Electroencephalographic Resting-State Networks: Source Localization of Microstates. Brain Connect. 2017, 7, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel, C.M.; Koenig, T. EEG microstates as a tool for studying the temporal dynamics of whole-brain neuronal networks: A review. Neuroimage 2018, 180, 577–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, M.; Baguley, T. Prior approval: The growth of Bayesian methods in psychology. Br. J. Math. Stat. Psychol. 2013, 66, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. EEGLAB: An open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2004, 134, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mullen, T. CleanLine EEGLAB Plugin 2012. Available online: https://www.nitrc.org/projects/cleanline (accessed on 12 October 2021).
- Jung, T.-P.; Makeig, S.; Humphries, C.; Lee, T.-W.; McKeown, M.J.; Iragui, V.; Sejnowski, T.J. Removing electroencephalographic artifacts by blind source separation. Psychophysiology 2000, 37, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin, F.; Pernier, J.; Bertrand, O.; Echallier, J.F. Spherical splines for scalp potential and current density mapping. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1989, 72, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Marqui, R.D.; Michel, C.M.; Lehmann, D. Segmentation of Brain Electrical Activity into Microstates; Model Estimation and Validation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1995, 42, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, T.; Lehmann, D.; Merlo, M.C.G.; Kochi, K.; Hell, D.; Koukkou, M. A deviant EEG brain microstate in acute, neuroleptic-naive schizophrenics at rest. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 1999, 249, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousseeuw, P.J. Silhouettes: A graphical aid to the interpretation and validation of cluster analysis. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 1987, 20, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dinov, M.; Leech, R. Modeling uncertainties in EEG microstates: Analysis of real and imagined motor movements using probabilistic clustering-driven training of probabilistic neural networks. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murray, M.M.; Brunet, D.; Michel, C.M. Topographic ERP analyses: A step-by-step tutorial review. Brain Topogr. 2008, 20, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gschwind, M.; Hardmeier, M.; Van De Ville, D.; Tomescu, M.I.; Penner, I.K.; Naegelin, Y.; Fuhr, P.; Michel, C.M.; Seeck, M. Fluctuations of spontaneous EEG topographies predict disease state in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. NeuroImage Clin. 2016, 12, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, J.; Selker, R.; Marsman, M.; Jamil, T.; Dropmann, D.; Verhagen, J.; Ly, A.; Gronau, Q.F.; Šmíra, M.; Epskamp, S.; et al. JASP: Graphical statistical software for common statistical designs. J. Stat. Softw. 2019, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- JASP Team. JASP (Version 0.14.1) [Computer Software]. 2020. Available online: https://jasp-stats.org/ (accessed on 12 October 2021).
- Kelter, R. Bayesian alternatives to null hypothesis significance testing in biomedical research: A non-technical introduction to Bayesian inference with JASP. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2020, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dienes, Z. How Bayes factors change scientific practice. J. Math. Psychol. 2016, 72, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dienes, Z. Using Bayes to get the most out of non-significant results. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dienes, Z. Bayesian versus orthodox statistics: Which side are you on? Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2011, 6, 274–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- George Assaf, A.; Tsionas, M. Bayes factors vs. P-values. Tour. Manag. 2018, 67, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wetzels, R.; Wagenmakers, E.J. A default Bayesian hypothesis test for correlations and partial correlations. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2012, 19, 1057–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benjamin, D.J.; Berger, J.O. Three Recommendations for Improving the Use of p-Values. Am. Stat. 2019, 2019, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koenig, T.; Prichep, L.; Lehmann, D.; Sosa, P.V.; Braeker, E.; Kleinlogel, H.; Isenhart, R.; John, E.R. Millisecond by Millisecond, Year by Year: Normative EEG Microstates and Developmental Stages. Neuroimage 2002, 16, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanesco, A.P.; Skwara, A.C.; King, B.G.; Powers, C.; Wineberg, K.; Saron, C.D. Meditation training modulates brain electric microstates and felt states of awareness. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2021, 42, 3228–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’croz-Baron, D.F.; Bréchet, L.; Baker, M.; Karp, T. Auditory and Visual Tasks Influence the Temporal Dynamics of EEG Microstates During Post-encoding Rest. Brain Topogr. 2021, 34, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.; Whitton, A.E.; Deccy, S.; Ironside, M.L.; Rutherford, A.; Beltzer, M.; Sacchet, M.; Pizzagalli, D.A. Abnormalities in electroencephalographic microstates are state and trait markers of major depressive disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 2020, 45, 2030–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damborská, A.; Piguet, C.; Aubry, J.M.; Dayer, A.G.; Michel, C.M.; Berchio, C. Altered Electroencephalographic Resting-State Large-Scale Brain Network Dynamics in Euthymic Bipolar Disorder Patients. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damborská, A.; Tomescu, M.I.; Honzírková, E.; Barteček, R.; Hořínková, J.; Fedorová, S.; Ondruš, Š.; Michel, C.M. EEG resting-state large-scale brain network dynamics are related to depressive symptoms. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jabès, A.; Klencklen, G.; Ruggeri, P.; Michel, C.M.; Banta Lavenex, P.; Lavenex, P. Resting-State EEG Microstates Parallel Age-Related Differences in Allocentric Spatial Working Memory Performance. Brain Topogr. 2021, 34, 442–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, A.; Pascual-Leone, A.; Michel, C.M.; Farzan, F. Microstates in resting-state EEG: Current status and future directions. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2015, 49, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zanesco, A.P.; King, B.G.; Skwara, A.C.; Saron, C.D. Within and between-person correlates of the temporal dynamics of resting EEG microstates. Neuroimage 2020, 211, 116631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britz, J.; Van De Ville, D.; Michel, C.M. BOLD correlates of EEG topography reveal rapid resting-state network dynamics. Neuroimage 2010, 52, 1162–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Xu, J.; Zou, G.; He, Y.; Zou, Q.; Gao, J.H. Reliability and Individual Specificity of EEG Microstate Characteristics. Brain Topogr. 2020, 33, 438–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zappasodi, F.; Perrucci, M.G.; Saggino, A.; Croce, P.; Mercuri, P.; Romanelli, R.; Colom, R.; Ebisch, S.J.H. EEG microstates distinguish between cognitive components of fluid reasoning. Neuroimage 2019, 189, 560–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forkmann, T.; Volz-Sidiropoulou, E.; Helbing, T.; Drüke, B.; Mainz, V.; Rath, D.; Gauggel, S.; Teismann, T. Sense it and use it: Interoceptive accuracy and sensibility in suicide ideators. BMC Psychiatry 2019, 19, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Y.; Van Someren, E.J. Interoception relates to sleep and sleep disorders. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2020, 33, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpraga, S.; Weiland, R.F.; Mansvelder, H.D.; Polderman, T.J.; Begeer, S.; Smit, D.J.; Linkenkaer-Hansen, K. Adults with autism spectrum disorder show atypical patterns of thoughts and feelings during rest. Autism 2021, 136236132199092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Chen, N.-X.; Shen, Y.-Q.; Li, H.-X.; Li, L.; Lu, B.; Zhu, Z.-C.; Fan, Z.; Yan, C.-G. The subsystem mechanism of default mode network underlying rumination: A reproducible neuroimaging study. Neuroimage 2020, 221, 117185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews-Hanna, J.R. The brain’s default network and its adaptive role in internal mentation. Neuroscientist 2012, 18, 251–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Tian, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, K.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J. Biomarkers for Prediction of Schizophrenia: Insights from Resting-State EEG Microstates. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 213078–213093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellante, F.; Ferri, F.; Baroni, G.; Croce, P.; Migliorati, D.; Pettoruso, M.; De Berardis, D.; Martinotti, G.; Zappasodi, F.; Giannantonio, M. Di Euthymic bipolar disorder patients and EEG microstates: A neural signature of their abnormal self experience? J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 272, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiller, B.; Koenig, T.; Heinrichs, M. Oxytocin modulates the temporal dynamics of resting EEG networks. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schönbrodt, F.D.; Perugini, M. At what sample size do correlations stabilize? J. Res. Pers. 2013, 47, 609–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomescu, M.I.; Rihs, T.A.; Rochas, V.; Hardmeier, M.; Britz, J.; Allali, G.; Fuhr, P.; Eliez, S.; Michel, C.M. From swing to cane: Sex differences of EEG resting-state temporal patterns during maturation and aging. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2018, 31, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
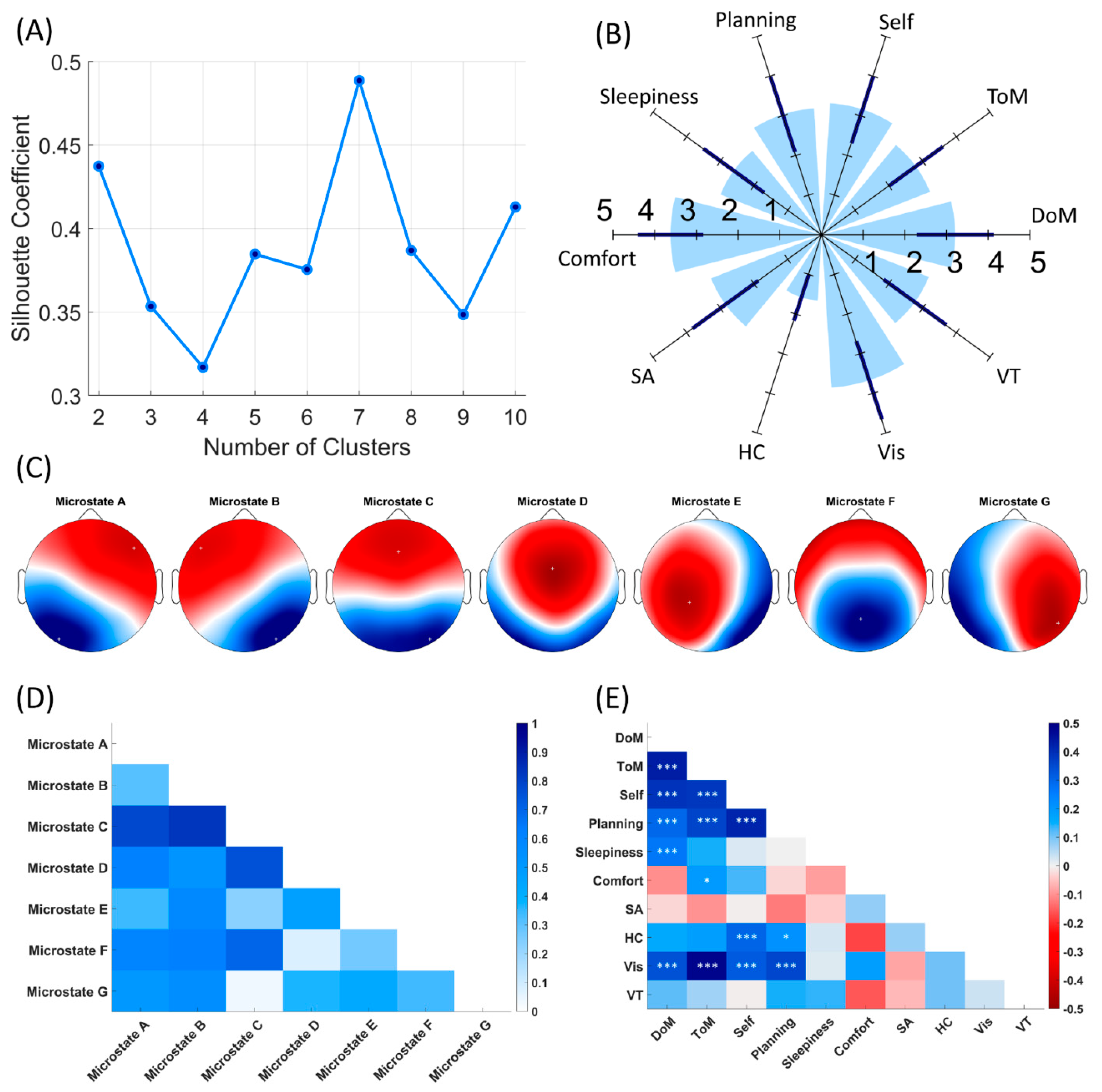
| Duration (ms) | Occurrence (Hz) | Coverage (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MS A | 43.361 (±8.26) | 3.6 (±0.95) | 15.13 (±4) |
| MS B | 45.337 (±9.25) | 3.8 (±0.89) | 16.93 (±4.2) |
| MS C | 52.505 (±14.18) | 4.5 (±0.83) | 22.91 (±6.5) |
| MS D | 40.909 (±7.16) | 3.44 (±1) | 13.82 (±3.9) |
| MS E | 36.718 (±6.31) | 2.62 (±0.73) | 9.43 (±2.4) |
| MS F | 39.589 (±7.34) | 3.22 (±0.99) | 12.56 (±4) |
| MS G | 36.056 (±5.81) | 2.65 (±0.81) | 9.31 (±2.5) |
| DoM | ToM | Self | Planning | Sleep | Comfort | SA | Health | Visual | Verbal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microstate A | Dur | r = −0.020 BF10 = 0.093 | r = 0.029 BF10 = 0.097 | r = −0.119 BF10 = 0.352 | r = −0.008 BF10 = 0.090 | r = −0.005 BF10 = 0.089 | r = 0.134 BF10 = 0.512 | r = 0.034 BF10 = 0.100 | r = −0.018 BF10 = 0.092 | r = 0.023 BF10 = 0.099 | r = −0.037 BF10 = 0.102 |
| Occ | r = 0.012 BF10 = 0.090 | r = 0.051 BF10 = 0.115 | r = 0.096 BF10 = 0.220 | r = −0.038 BF10 = 0.103 | r = 0.111 BF10 = 0.294 | r = −0.082 BF10 = 0.172 | r = −0.019 BF10 = 0.092 | r = 0.028 BF10 = 0.096 | r = 0.062 BF10 = 0.129 | r = 0.035 BF10 = 0.100 | |
| Cov | r = −0.009 BF10 = 0.090 | r = 0.056 BF10 = 0.121 | r = 0.010 BF10 = 0.090 | r = −0.055 BF10 = 0.119 | r = 0.097 BF10 = 0.223 | r = 0.002 BF10 = 0.089 | r = −0.005 BF10 = 0.089 | r = 0.050 BF10 = 0.114 | r = 0.056 BF10 = 0.120 | r = 0.030 BF10 = 0.097 | |
| GFP | r = −0.016 BF10 = 0.091 | r = 0.040 BF10 = 0.104 | r = −0.066 BF10 = 0.137 | r = −0.039 BF10 = 0.103 | r = −0.015 BF10 = 0.091 | r = 0.115 BF10 = 0.324 | r = 0.001 BF10 = 0.089 | r = −0.027 BF10 = 0.096 | r = 0.037 BF10 = 0.102 | r = −0.060 BF10 = 0.127 | |
| Microstate B | Dur | r = −0.028 BF10 = 0.096 | r = 0.028 BF10 = 0.096 | r = −0.054 BF10 = 0.119 | r = 0.052 BF10 = 0.116 | r = −0.101 BF10 = 0.242 | r = 0.182 BF10 = 2.339 | r = −0.004 BF10 = 0.089 | r = −0.063 BF10 = 0.131 | r = 0.012 BF10 = 0.090 | r = −0.016 BF10 = 0.091 |
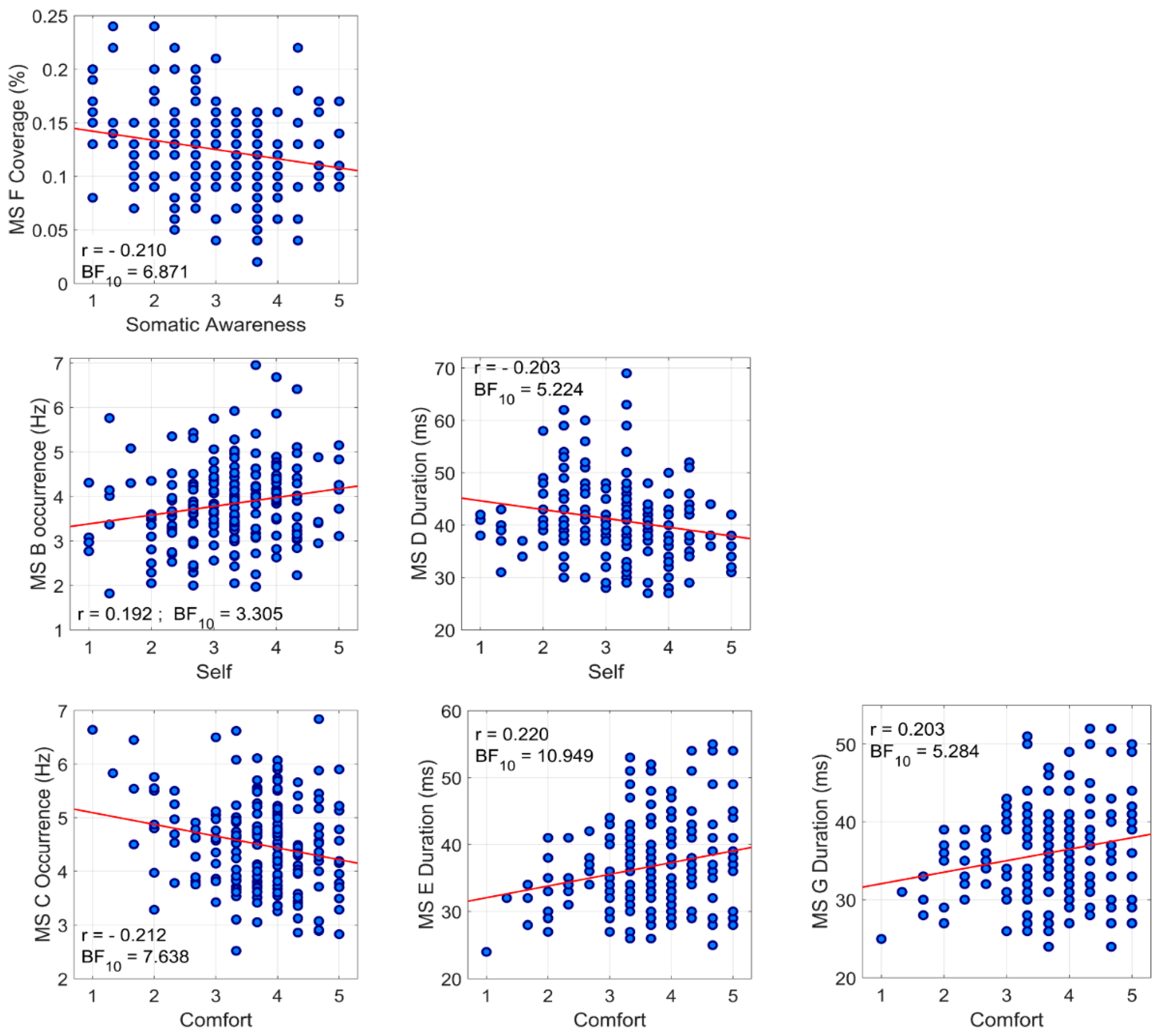
| Occ | r = 0.068 BF10 = 0.139 | r = −0.017 BF10 = 0.092 | r = 0.192 BF10 = 3.305 | r = 0.083 BF10 = 0.173 | r = −0.038 BF10 = 0.103 | r = −0.117 BF10 = 0.337 | r = 0.024 BF10 = 0.094 | r = 0.044 BF10 = 0.107 | r = −0.003 BF10 = 0.089 | r = 0.062 BF10 = 0.130 | |
| Cov | r = 0.038 BF10 = 0.103 | r = 0.008 BF10 = 0.090 | r = 0.130 BF10 = 0.464 | r = 0.111 BF10 = 0.295 | r = −0.121 BF10 = 0.372 | r = 0.048 BF10 = 0.111 | r = −0.001 BF10 = 0.089 | r = 0.004 BF10 = 0.089 | r = 0.006 BF10 = 0.090 | r = 0.058 BF10 = 0.123 | |
| GFP | r = −0.019 BF10 = 0.092 | r = 0.040 BF10 = 0.104 | r = −0.058 BF10 = 0.124 | r = −0.019 BF10 = 0.092 | r = −0.041 BF10 = 0.105 | r = 0.128 BF10 = 0.442 | r = 0.008 BF10 = 0.090 | r = −0.034 BF10 = 0.099 | r = 0.039 BF10 = 0.104 | r = −0.076 BF10 = 0.155 | |
| Microstate C | Dur | r = −0.070 BF10 = 0.141 | r = −0.028 BF10 = 0.096 | r = −0.124 BF10 = 0.398 | r = −0.063 BF10 = 0.131 | r = −0.003 BF10 = 0.089 | r = 0.106 BF10 = 0.266 | r = 0.008 BF10 = 0.090 | r = −0.050 BF10 = 0.113 | r = −0.045 BF10 = 0.109 | r = −0.067 BF10 = 0.138 |
| Occ | r = 0.004 BF10 = 0.089 | r = −0.028 BF10 = 0.096 | r = 0.093 BF10 = 0.205 | r = −0.042 BF10 = 0.106 | r = 0.074 BF10 = 0.151 | r = −0.212 BF10 = 7.638 | r = −0.021 BF10 = 0.093 | r = 0.034 BF10 = 0.100 | r = −0.023 BF10 = 0.094 | r = −0.006 BF10 = 0.089 | |
| Cov | r = −0.056 BF10 = 0.120 | r = −0.046 BF10 = 0.109 | r = −0.059 BF10 = 0.125 | r = −0.100 BF10 = 0.237 | r = 0.027 BF10 = 0.096 | r = −0.037 BF10 = 0.102 | r = −0.007 BF10 = 0.090 | r = −0.011 BF10 = 0.090 | r = −0.047 BF10 = 0.110 | r = −0.063 BF10 = 0.130 | |
| GFP | r = −0.023 BF10 = 0.094 | r = 0.035 BF10 = 0.101 | r = −0.070 BF10 = 0.144 | r = −0.038 BF10 = 0.103 | r = −0.030 BF10 = 0.097 | r = 0.112 BF10 = 0.302 | r = 0.009 BF10 = 0.090 | r = −0.032 BF10 = 0.099 | r = −0.033 BF10 = 0.99 | r = −0.081 BF10 = 0.169 | |
| Microstate D | Dur | r = 0.069 BF10 = 0.141 | r = −0.034 BF10 = 0.100 | r = −0.203 BF10 = 5.224 | r = −0.037 BF10 = 0.102 | r = −0.101 BF10 = 0.239 | r = 0.177 BF10 = 1.939 | r = 0.103 BF10 = 0.247 | r = −0.067 BF10 = 0.138 | r = −0.041 BF10 = 0.105 | r = −0.048 BF10 = 0.111 |
| Occ | r = −0.009 BF10 = 0.090 | r = −0.054 BF10 = 0.119 | r = 0.008 BF10 = 0.090 | r = −0.088 BF10 = 0.189 | r = 0.094 BF10 = 0.210 | r = −0.128 BF10 = 0.438 | r = 0.135 BF10 = 0.531 | r = 0.054 BF10 = 0.118 | r = 0.024 BF10 = 0.094 | r = 0.037 BF10 = 0.102 | |
| Cov | r = −0.057 BF10 = 0.122 | r = −0.078 BF10 = 0.160 | r = −0.115 BF10 = 0.322 | r = −0.100 BF10 = 0.234 | r = 0.024 BF10 = 0.094 | r = −0.031 BF10 = 0.098 | r = 0.158 BF10 = 1.034 | r = 0.026 BF10 = 0.095 | r = −0.053 BF10 = 0.117 | r = 0.020 BF10 = 0.093 | |
| GFP | r = −0.015 BF10 = 0.091 | r = 0.026 BF10 = 0.095 | r = −0.093 BF10 = 0.206 | r = −0.043 BF10 = 0.107 | r = −0.024 BF10 = 0.094 | r = 0.121 BF10 = 0.371 | r = 0.039 BF10 = 0.103 | r = −0.041 BF10 = 0.105 | r = 0.033 BF10 = 0.099 | r = −0.076 BF10 = 0.155 | |
| Microstate E | Dur | r = −0.040 BF10 = 0.104 | r = 0.016 BF10 = 0.091 | r = −0.116 BF10 = 0.328 | r = 0.043 BF10 = 0.107 | r = −0.108 BF10 = 0.279 | r = 0.220 BF10 = 10.95 | r = 0.056 BF10 = 0.121 | r = −0.083 BF10 = 0.172 | r = 0.011 BF10 = 0.090 | r = −0.045 BF10 = 0.108 |
| Occ | r = 0.025 BF10 = 0.095 | r = −0.015 BF10 = 0.091 | r = 0.116 BF10 = 0.329 | r = 0.015 BF10 = 0.091 | r = −0.110 BF10 = 0.090 | r = −0.081 BF10 = 0.167 | r = 0.034 BF10 = 0.099 | r = 0.030 BF10 = 0.097 | r = 0.026 BF10 = 0.095 | r = 0.008 BF10 = 0.090 | |
| Cov | r = 0.015 BF10 = 0.091 | r = −0.030 BF10 = 0.097 | r = 0.030 BF10 = 0.097 | r = 0.037 BF10 = 0.102 | r = −0.110 BF10 = 0.289 | r = 0.052 BF10 = 0.116 | r = 0.067 BF10 = 0.137 | r = −0.027 BF10 = 0.096 | r = 0.020 BF10 = 0.093 | r = 0.001 BF10 = 0.089 | |
| GFP | r = −0.015 BF10 = 0.091 | r = 0.037 BF10 = 0.102 | r = −0.066 BF10 = 0.137 | r = −0.016 BF10 = 0.092 | r = −0.034 BF10 = 0.100 | r = 0.135 BF10 = 0.530 | r = 0.021 BF10 = 0.093 | r = −0.040 BF10 = 0.104 | r = 0.040 BF10 = 0.104 | r = −0.077 BF10 = 0.158 | |
| Microstate F | Dur | r = −0.038 BF10 = 0.103 | r = 0.014 BF10 = 0.091 | r = −0.134 BF10 = 0.507 | r = 0.088 BF10 = 0.188 | r = −0.030 BF10 = 0.097 | r = 0.121 BF10 = 0.374 | r = −0.101 BF10 = 0.241 | r = −0.093 BF10 = 0.205 | r = −0.009 BF10 = 0.090 | r = −0.022 BF10 = 0.093 |
| Occ | r = 0.051 BF10 = 0.115 | r = 0.029 BF10 = 0.097 | r = 0.071 BF10 = 0.145 | r = 0.119 BF10 = 0.352 | r = 0.082 BF10 = 0.172 | r = −0.111 BF10 = 0.294 | r = −0.140 BF10 = 0.607 | r = −0.026 BF10 = 0.095 | r = 0.026 BF10 = 0.092 | r = −0.018 BF10 = 0.092 | |
| Cov | r = 0.035 BF10 = 0.100 | r = 0.041 BF10 = 0.105 | r = −0.016 BF10 = 0.092 | r = 0.146 BF10 = 0.710 | r = 0.043 BF10 = 0.107 | r = −0.036 BF10 = 0.101 | r = −0.210 BF10 = 6.871 | r = −0.064 BF10 = 0.132 | r = 0.019 BF10 = 0.092 | r = −0.031 BF10 = 0.098 | |
| GFP | r = −0.006 BF10 = 0.089 | r = 0.051 BF10 = 0.115 | r = −0.064 BF10 = 0.133 | r = 0.005 BF10 = 0.089 | r = −0.011 BF10 = 0.090 | r = 0.103 BF10 = 0.252 | r = −0.034 BF10 = 0.100 | r = −0.044 BF10 = 0.108 | r = 0.045 BF10 = 0.108 | r = −0.081 BF10 = 0.169 | |
| Microstate G | Dur | r = −0.024 BF10 = 0.094 | r = 0.018 BF10 = 0.092 | r = −0.114 BF10 = 0.315 | r = 0.025 BF10 = 0.095 | r = −0.090 BF10 = 0.195 | r = 0.203 BF10 = 5.284 | r = 0.030 BF10 = 0.097 | r = −0.039 BF10 = 0.104 | r < 0.001 BF10 = 0.089 | r = −0.029 BF10 = 0.097 |
| Occ | r = 0.075 BF10 = 0.153 | r = 0.023 BF10 = 0.094 | r = 0.139 BF10 = 0.580 | r = 0.011 BF10 = 0.090 | r = 0.046 BF10 = 0.109 | r = −0.068 BF10 = 0.140 | r = 0.055 BF10 = 0.120 | r = 0.044 BF10 = 0.108 | r = 0.024 BF10 = 0.094 | r = 0.060 BF10 = 0.126 | |
| Cov | r = 0.083 BF10 = 0.174 | r = 0.042 BF10 = 0.106 | r = 0.096 BF10 = 0.217 | r = 0.041 BF10 = 0.105 | r = −0.023 BF10 = 0.094 | r = 0.047 BF10 = 0.110 | r = 0.068 BF10 = 0.140 | r = 0.042 BF10 = 0.105 | r = 0.021 BF10 = 0.093 | r = 0.074 BF10 = 0.151 | |
| GFP | r = −0.010 BF10 = 0.090 | r = 0.047 BF10 = 0.110 | r = −0.052 BF10 = 0.116 | r = −0.015 BF10 = 0.091 | r = −0.024 BF10 = 0.094 | r = 0.135 BF10 = 0.523 | r = 0.017 BF10 = 0.092 | r = −0.030 BF10 = 0.097 | r = 0.044 BF10 = 0.108 | r = −0.058 BF10 = 0.123 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tarailis, P.; Šimkutė, D.; Koenig, T.; Griškova-Bulanova, I. Relationship between Spatiotemporal Dynamics of the Brain at Rest and Self-Reported Spontaneous Thoughts: An EEG Microstate Approach. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11111216
Tarailis P, Šimkutė D, Koenig T, Griškova-Bulanova I. Relationship between Spatiotemporal Dynamics of the Brain at Rest and Self-Reported Spontaneous Thoughts: An EEG Microstate Approach. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(11):1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11111216
Chicago/Turabian StyleTarailis, Povilas, Dovilė Šimkutė, Thomas Koenig, and Inga Griškova-Bulanova. 2021. "Relationship between Spatiotemporal Dynamics of the Brain at Rest and Self-Reported Spontaneous Thoughts: An EEG Microstate Approach" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 11: 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11111216
APA StyleTarailis, P., Šimkutė, D., Koenig, T., & Griškova-Bulanova, I. (2021). Relationship between Spatiotemporal Dynamics of the Brain at Rest and Self-Reported Spontaneous Thoughts: An EEG Microstate Approach. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(11), 1216. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11111216







