The IL6-like Cytokine Family: Role and Biomarker Potential in Breast Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The IL6-like Cytokine Family
3. Soluble Receptors and Signalling Modes
4. Shared Cytokine Signalling: Pleiotropy, Redundancy and Specificity
5. The Role of the IL6-like Cytokine Family in BC
5.1. IL6 in BC
5.1.1. Signalling Role in BC
5.1.2. Circulating IL6 Level as a Biomarker
5.2. Other IL6-like Cytokines in BC
5.2.1. IL11
5.2.2. LIF
5.2.3. OSM
5.3. IL6ST as a Biomarker in BC
6. IL6-like Cytokines and Oestrogen Signalling
7. Polymorphisms in gp130/IL6ST-Dependent Signalling
7.1. Polymorphisms in IL6-like Cytokines
7.2. Polymorphisms in Non-Signalling Receptors
7.3. Polymorphisms in Signalling Receptors
7.4. Polymorphisms in Downstream Factors
8. Therapeutic Targeting of gp130/IL6ST Signalling
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duffy, M.J.; Harbeck, N.; Nap, M.; Molina, R.; Nicolini, A.; Senkus, E.; Cardoso, F. Clinical use of biomarkers in breast cancer: Updated guidelines from the European Group on Tumor Markers (EGTM). Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 75, 284–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez-Pérez, C.; Turnbull, A.K.; Dixon, J.M. The evolving role of receptors as predictive biomarkers for metastatic breast cancer. Expert Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2018, 19, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagaraj, G.; Ma, C.X. Clinical Challenges in the Management of Hormone Receptor-Positive, Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer: A Literature Review. Adv. Ther. 2020, 38, 109–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, B.; Hortobagyi, G.N. Current challenges of metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2016, 35, 495–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Li, Q.; Wang, H. Identification of Novel Biomarkers Associated With the Prognosis and Potential Pathogenesis of Breast Cancer via Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 20, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falzone, L.; Grimaldi, M.; Celentano, E.; Augustin, L.S.A.; Libra, M. Identification of Modulated MicroRNAs Associated with Breast Cancer, Diet, and Physical Activity. Cancers 2020, 12, 2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Song, X.; Zhang, L.; Wu, L.; Liu, J. Long non-coding RNAs as novel biomarkers for breast cancer invasion and metastasis. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 1895–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walsh, M.F.; Nathanson, K.L.; Couch, F.J.; Offit, K. Genomic Biomarkers for Breast Cancer Risk. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 882, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bravo, J.; Heath, J.K. New embo members’ review: Receptor recognition by gp130 cytokines. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 2399–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boulay, J.-L.; Paul, W.E. Hematopoietin sub-family classification based on size, gene organization and sequence homology. Curr. Biol. 1993, 3, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprang, S.R.; Bazan, J.F. Cytokine structural taxonomy and mechanisms of receptor engagement: Current opinion in structural biology 1993, 3:815–827. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1993, 3, 815–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbers, C.; Rose-John, S. Dissecting Interleukin-6 Classic- and Trans-Signaling in Inflammation and Cancer. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 1725, pp. 127–140. [Google Scholar]
- Hermanns, H.M. Oncostatin M and interleukin-31: Cytokines, receptors, signal transduction and physiology. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015, 26, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, E.; Corcione, A.; Pistoia, V. The IL-31/IL-31 receptor axis: General features and role in tumor microenvironment. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2017, 102, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rose-John, S. Interleukin-6 Family Cytokines. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2017, 10, a028415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kastelein, R.A.; Hunter, C.A.; Cua, D.J. Discovery and Biology of IL-23 and IL-27: Related but Functionally Distinct Regulators of Inflammation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 25, 221–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murakami, M.; Kamimura, D.; Hirano, T. Pleiotropy and Specificity: Insights from the Interleukin 6 Family of Cytokines. Immunity 2019, 50, 812–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collison, L.W.; Workman, C.J.; Kuo, T.T.; Boyd, K.; Wang, Y.; Vignali, K.M.; Cross, R.; Sehy, D.; Blumberg, R.S.; Vignali, D.A.A. The inhibitory cytokine IL-35 contributes to regulatory T-cell function. Nature 2007, 450, 566–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, S.A.; Jenkins, B.J. Recent insights into targeting the IL-6 cytokine family in inflammatory diseases and cancer. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 773–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; He, C.; Nair, L.; Yeung, J.; Egwuagu, C.E. Interleukin 12 (IL-12) family cytokines: Role in immune pathogenesis and treatment of CNS autoimmune disease. Cytokine 2015, 75, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huising, M.O.; Kruiswijk, C.P.; Flik, G. Phylogeny and evolution of class-I helical cytokines. J. Endocrinol. 2006, 189, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brocker, C.; Thompson, D.; Matsumoto, A.; Nebert, D.W.; Vasiliou, V. Evolutionary divergence and functions of the human interleukin (IL) gene family. Hum. Genom. 2010, 5, 30–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, L.; Vignali, D.A.A. Molecular interactions within the IL-6/IL-12 cytokine/receptor superfamily. Immunol. Res. 2011, 51, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silver, J.S.; Hunter, C.A. gp130 at the nexus of inflammation, autoimmunity, and cancer. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2010, 88, 1145–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heinrich, P.C.; Behrmann, I.; Müller-Newen, G.; Schaper, F.; Graeve, L. Interleukin-6-type cytokine signalling through the gp130/Jak/STAT pathway. Biochem. J. 1998, 334, 297–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Monhasery, N.; Moll, J.; Cuman, C.; Franke, M.; Lamertz, L.; Nitz, R.; Görg, B.; Häussinger, D.; Lokau, J.; Floss, D.M.; et al. Transcytosis of IL-11 and Apical Redirection of gp130 Is Mediated by IL-11α Receptor. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 1067–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knüpfer, H.; Preiss, R. Lack of Knowledge: Breast Cancer and the Soluble Interleukin-6 Receptor. Breast Care 2010, 5, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Metcalfe, R.D.; Putoczki, T.L.; Griffin, M.D.W. Structural Understanding of Interleukin 6 Family Cytokine Signaling and Targeted Therapies: Focus on Interleukin 11. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, L.D.; Howlett, G.J.; Discolo, G.; Yasukawa, K.; Hammacher, A.; Moritz, R.L.; Simpson, R. High affinity interleukin-6 receptor is a hexameric complex consisting of two molecules each of interleukin-6, interleukin-6 receptor, and gp-130. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 23286–23289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulanger, M.J.; Chow, D.-C.; Brevnova, E.E.; Garcia, K.C. Hexameric Structure and Assembly of the Interleukin-6/IL-6 α-Receptor/gp130 Complex. Science 2003, 300, 2101–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paonessa, G.; Graziani, R.; De Serio, A.; Savino, R.; Ciapponi, L.; Lahm, A.; Salvati, A.L.; Toniatti, C.; Ciliberto, G. Two distinct and independent sites on IL-6 trigger gp 130 dimer formation and signalling. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 1942–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grotzinger, J.; Kernebeck, T.; Kallen, K.-J.; Rose-John, S. IL-6 Type Cytokine Receptor Complexes: Hexamer, Tetramer or Both. Biol. Chem. 1999, 380, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, V.A.; Hall, M.A.; Hudson, K.R.; Heath, J.K. Interleukin-11 Signals through the Formation of a Hexameric Receptor Complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 36197–36203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Serio, A.; Graziani, R.; Laufer, R.; Ciliberto, G.; Paonessa, G. In vitro Binding of Ciliary Neurotrophic Factor to its Receptors: Evidence for the Formation of an IL-6-type Hexameric Complex. J. Mol. Biol. 1995, 254, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller-Newen, G. The Cytokine Receptor gp130: Faithfully Promiscuous. Sci. Signal. 2003, 2003, pe40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, V.; Schuster, B.; Schütze, S.; Bussmeyer, I.; Ludwig, A.; Hundhausen, C.; Sadowski, T.; Saftig, P.; Hartmann, D.; Kallen, K.-J.; et al. Cellular Cholesterol Depletion Triggers Shedding of the Human Interleukin-6 Receptor by ADAM10 and ADAM17 (TACE). J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 38829–38839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mülberg, J.; Schooltink, H.; Stoyan, T.; Günther, M.; Graeve, L.; Buse, J.; Mackiewicz, A.; Heinrich, P.C.; Rose-John, S. The soluble interleukin-6 receptor is generated by shedding. Eur. J. Immunol. 1993, 23, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lust, J.A.; Donovan, K.A.; Kline, M.P.; Greipp, P.R.; Kyle, R.A.; Maihle, N.J. Isolation of an mRNA encoding a soluble form of the human interleukin-6 receptor. Cytokine 1992, 4, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose-John, S. The soluble interleukin-6 receptor and related proteins. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 29, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heink, S.; Yogev, N.; Garbers, C.; Herwerth, M.; Aly, L.; Gasperi, C.; Husterer, V.; Croxford, A.L.; Möller-Hackbarth, K.; Bartsch, H.S.; et al. Trans-presentation of IL-6 by dendritic cells is required for the priming of pathogenic TH17 cells. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 18, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chalaris, A.; Garbers, C.; Rabe, B.; Rose-John, S.; Scheller, J. The soluble Interleukin 6 receptor: Generation and role in inflammation and cancer. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 90, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, C.A.; Jones, S.A. IL-6 as a keystone cytokine in health and disease. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Purohit, A.; Wang, D.Y.; Duncan, L.; Ghilchik, M.W.; Reed, M.J. IL-6sR: Release from mcf-7 breast cancer cells and role in regulating peripheral oestrogen synthesis. J. Endocrinol. 1995, 147, R9–R12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillard, J.; Pugnière, M.; Tresca, J.; Mani, J.; Klein, B.; Brochier, J. Interleukin-6 receptor signaling. II. Bio-availability of interleukin-6 in serum. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 1999, 10, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peters, M.; Odenthal, M.; Schirmacher, P.; Blessing, M.; Fattori, E.; Ciliberto, G.; Buschenfelde, K.H.M.Z.; Rose-John, S. Soluble IL-6 receptor leads to a paracrine modulation of the IL-6-induced hepatic acute phase response in double transgenic mice. J. Immunol. 1997, 159, 1474–1481. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Becker, C.; Fantini, M.C.; Schramm, C.; Lehr, H.A.; Wirtz, S.; Nikolaev, A.; Burg, J.; Strand, S.; Kiesslich, R.; Huber, S.; et al. TGF-β Suppresses Tumor Progression in Colon Cancer by Inhibition of IL-6 trans-Signaling. Immunity 2004, 21, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, S.A.; Scheller, J.; Rose-John, S. Therapeutic strategies for the clinical blockade of IL-6/gp130 signaling. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 3375–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lokau, J.; Nitz, R.; Agthe, M.; Monhasery, N.; Aparicio-Siegmund, S.; Schumacher, N.; Wolf, J.; Möller-Hackbarth, K.; Waetzig, G.H.; Grötzinger, J.; et al. Proteolytic Cleavage Governs Interleukin-11 Trans-signaling. Cell Rep. 2016, 14, 1761–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davis, S.; Aldrich, T.H.; Ip, N.Y.; Stahl, N.; Scherer, S.; Farruggella, T.; DiStefano, P.S.; Curtis, R.; Panayotatos, N.; Gascan, H.; et al. Released Form of CNTF Receptor α Component as a Soluble Mediator of CNTF Responses. Science 1993, 259, 1736–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pflanz, S.; Kernebeck, T.; Giese, B.; Herrmann, A.; Pachta-Nick, M.; Stahl, J.; Wollmer, A.; Heinrich, P.C.; Müller-Newen, G.; Grötzinger, J. Signal transducer gp130: Biochemical characterization of the three membrane-proximal extracellular domains and evaluation of their oligomerization potential. Biochem. J. 2001, 356, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Kershaw, N.; Luo, C.S.; Soo, P.; Pocock, M.J.; Czabotar, P.; Hilton, D.; Nicola, N.; Garrett, T.P.J.; Zhang, J.-G. Crystal Structure of the Entire Ectodomain of gp130: Insights into the molecular assembly of the tall cytokine receptor complexes. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 21214–21218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.-G.; Zhang, Y.; Owczarek, C.M.; Ward, L.D.; Moritz, R.L.; Simpson, R.; Yasukawa, K.; Nicola, N. Identification and Characterization of Two Distinct Truncated Forms of gp130 and a Soluble Form of Leukemia Inhibitory Factor Receptor α-Chain in Normal Human Urine and Plasma. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 10798–10805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waetzig, G.H.; Chalaris, A.; Rosenstiel, P.; Suthaus, J.; Holland, C.; Karl, N.; Uriarte, L.V.; Till, A.; Scheller, J.; Grötzinger, J.; et al. N-Linked Glycosylation Is Essential for the Stability but Not the Signaling Function of the Interleukin-6 Signal Transducer Glycoprotein 130. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 1781–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diamant, M.; Rieneck, K.; Mechti, N.; Zhang, X.-G.; Svenson, M.; Bendtzen, K.; Klein, B. Cloning and expression of an alternatively spliced mRNA encoding a soluble form of the human interleukin-6 signal transducer gp1301. FEBS Lett. 1997, 412, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montero-Julian, F.A.; Brailly, H.; Sautès, C.; Joyeux, I.; Dorval, T.; Mosseri, V.; Yasukawa, K.; Wijdenes, J.; Adler, A.; Gorin, I.; et al. Characterization of soluble gp130 released by melanoma cell lines: A polyvalent antagonist of cytokines from the interleukin 6 family. Clin. Cancer Res. 1997, 3, 1443–1451. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Narazaki, M.; Yasukawa, K.; Saito, T.; Ohsugi, Y.; Fukui, H.; Koishihara, Y.; Yancopoulos, G.; Taga, T.; Kishimoto, T. Soluble forms of the interleukin-6 signal-transducing receptor component gp130 in human serum possessing a potential to inhibit signals through membrane-anchored gp130. Blood 1993, 82, 1120–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolf, J.; Waetzig, G.H.; Chalaris, A.; Reinheimer, T.M.; Wege, H.; Rose-John, S.; Garbers, C. Different Soluble Forms of the Interleukin-6 Family Signal Transducer gp130 Fine-tune the Blockade of Interleukin-6 Trans-signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 16186–16196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Müllberg, J.; Oberthür, W.; Lottspeich, F.; Mehl, E.; Dittrich, E.; Graeve, L.; Heinrich, P.C.; Rose-John, S. The soluble human IL-6 receptor. Mutational characterization of the proteolytic cleavage site. J. Immunol. 1994, 152, 4958–4968. [Google Scholar]
- Jostock, T.; Müllberg, J.; Özbek, S.; Atreya, R.; Blinn, G.; Voltz, N.; Fischer, M.; Neurath, M.F.; Rose-John, S. Soluble gp130 is the natural inhibitor of soluble interleukin-6 receptor transsignaling responses. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2001, 268, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabe, B.; Chalaris, A.; May, U.; Waetzig, G.H.; Seegert, D.; Williams, A.S.; Jones, S.A.; Rose-John, S.; Scheller, J. Transgenic blockade of interleukin 6 transsignaling abrogates inflammation. Blood 2008, 111, 1021–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose-John, S.; Heinrich, P.C. Soluble receptors for cytokines and growth factors: Generation and biological function. Biochem. J. 1994, 300, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, P.J.; Nowell, M.A.; Horiuchi, S.; McLoughlin, R.M.; Fielding, C.A.; Grau, S.; Yamamoto, N.; Ehrmann, M.; Rose-John, S.; Williams, A.S.; et al. Functional characterization of a soluble gp130 isoform and its therapeutic capacity in an experimental model of inflammatory arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 1662–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamertz, L.; Rummel, F.; Polz, R.; Baran, P.; Hansen, S.; Waetzig, G.H.; Moll, J.M.; Floss, D.M.; Scheller, J. Soluble gp130 prevents interleukin-6 and interleukin-11 cluster signaling but not intracellular autocrine responses. Sci. Signal. 2018, 11, eaar7388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diveu, C.; Venereau, E.; Froger, J.; Ravon, E.; Grimaud, L.; Rousseau, F.; Chevalier, S.; Gascan, H. Molecular and Functional Characterization of a Soluble Form of Oncostatin M/Interleukin-31 Shared Receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 36673–36682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heaney, M.L.; Golde, D.W. Soluble cytokine receptors. Blood 1996, 87, 847–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Honda, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Cheng, M.; Yasukawa, K.; Suzuki, H.; Saito, T.; Osugi, Y.; Tokunaga, T.; Kishimoto, T. Human soluble IL-6 receptor: Its detection and enhanced release by HIV infection. J. Immunol. 1992, 148, 2175–2180. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Padberg, F.; Feneberg, W.; Schmidt, S.; Schwarz, M.; Körschenhausen, D.; Greenberg, B.D.; Nolde, T.; Müller, N.; Trapmann, H.; König, N.; et al. CSF and serum levels of soluble interleukin-6 receptors (sIL-6R and sgp130), but not of interleukin-6 are altered in multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 1999, 99, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, P.C.; Behrmann, I.; Haan, S.; Hermanns, H.M.; Müller-Newen, G.; Schaper, F. Principles of interleukin (IL)-6-type cytokine signalling and its regulation. Biochem. J. 2003, 374, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bousoik, E.; Aliabadi, H.M. “Do We Know Jack” About JAK? A Closer Look at JAK/STAT Signaling Pathway. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ernst, M.; Jenkins, B. Acquiring signalling specificity from the cytokine receptor gp130. Trends Genet. 2004, 20, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaper, F.; Rose-John, S. Interleukin-6: Biology, signaling and strategies of blockade. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015, 26, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, P.; Grandis, J.R. Stat3 signaling: Anticancer Strategies and Challenges. Mol. Interv. 2011, 11, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schuster, B.; Kovaleva, M.; Sun, Y.; Regenhard, P.; Matthews, V.; Grötzinger, J.; Rose-John, S.; Kallen, K.-J. Signaling of Human Ciliary Neurotrophic Factor (CNTF) Revisited: The interleukin-6 receptor can serve as an α-receptor for CNTF. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 9528–9535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chevalier, S.; Fourcin, M.; Robledo, O.; Wijdenes, J.; Pouplard-Barthelaix, A.; Gascan, H. Interleukin-6 Family of Cytokines Induced Activation of Different Functional Sites Expressed by gp130 Transducing Protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 14764–14772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, Z.-J.; Wijdenes, J.; Zhang, X.-G.; Hallet, M.-M.; Clement, C.; Klein, B. Anti-gp130 transducer monoclonal antibodies specifically inhibiting ciliary neurotrophic factor, interleukin-6, interleukin-11, leukemia inhibitory factor or oncostatin M. J. Immunol. Methods 1996, 190, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, J.; Effenberger, T.; Volpi, E.; Waetzig, G.H.; Bernhardt, M.; Suthaus, J.; Garbers, C.; Rose-John, S.; Floss, D.M.; Scheller, J. Constitutively Active Mutant gp130 Receptor Protein from Inflammatory Hepatocellular Adenoma Is Inhibited by an Anti-gp130 Antibody That Specifically Neutralizes Interleukin 11 Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 13743–13751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbers, C.; Hermanns, H.; Schaper, F.; Müller-Newen, G.; Grötzinger, J.; Rose-John, S.; Scheller, J. Plasticity and cross-talk of interleukin 6-type cytokines. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2012, 23, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, T.; Matsuda, T.; Nakajima, K. Signal transduction through gp130 that is shared among the receptors for the interleukin 6 related cytokine subfamily. Stem Cells 1994, 12, 262–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.E.; O’Keefe, R.A.; Grandis, J.R. Targeting the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling axis in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, N.; Dwarakanath, B.S.; Das, A.; Bhatt, A.N. Role of interleukin-6 in cancer progression and therapeutic resistance. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 11553–11572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candido, S.; Tomasello, B.M.R.; Lavoro, A.; Falzone, L.; Gattuso, G.; Libra, M. Novel Insights into Epigenetic Regulation of IL6 Pathway: In Silico Perspective on Inflammation and Cancer Relationship. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vainer, N.; Dehlendorff, C.; Johansen, J.S. Systematic literature review of IL-6 as a biomarker or treatment target in patients with gastric, bile duct, pancreatic and colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 29820–29841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dranoff, G. Cytokines in cancer pathogenesis and cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, T. IL-6 in inflammation, autoimmunity and cancer. Int. Immunol. 2020, 33, 127–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, L.; Patel, M.R.; Horvath, E.B.; Tawara, K.; Jorcyk, C.L. IL-6 and ovarian cancer: Inflammatory cytokines in promotion of metastasis. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 6685–6693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Omokehinde, T.; Johnson, R.W. GP130 Cytokines in Breast Cancer and Bone. Cancers 2020, 12, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaur, S.; Bansal, Y.; Kumar, R.; Bansal, G. A panoramic review of IL-6: Structure, pathophysiological roles and inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 115327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masjedi, A.; Hashemi, V.; Hojjat-Farsangi, M.; Ghalamfarsa, G.; Azizi, G.; Yousefi, M.; Jadidi-Niaragh, F. The significant role of interleukin-6 and its signaling pathway in the immunopathogenesis and treatment of breast cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 108, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, I.; Pensa, S.; Pannellini, T.; Quaglino, E.; Maritano, D.; Demaria, M.; Voster, A.; Turkson, J.; Cavallo, F.; Watson, C.J.; et al. Constitutively Active Stat3 Enhances Neu-Mediated Migration and Metastasis in Mammary Tumors via Upregulation of Cten. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 2558–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leslie, K.; Gao, S.P.; Berishaj, M.; Podsypanina, K.; Ho, H.; Ivashkiv, L.; Bromberg, J. Differential interleukin-6/Stat3 signaling as a function of cellular context mediates Ras-induced transformation. Breast Cancer Res. 2010, 12, R80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, F.; Ren, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Yang, L.; Han, X.; Chen, Y.; Tong, G.; Yang, G. The crosstalk between STAT3 and p53/RAS signaling controls cancer cell metastasis and cisplatin resistance via the Slug/MAPK/PI3K/AKT-mediated regulation of EMT and autophagy. Oncogenesis 2019, 8, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Knüpfer, H.; Preiss, R. Significance of interleukin-6 (IL-6) in breast cancer (review). Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2006, 102, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danforth, D.N.; Sgagias, M.K. Interleukin-1α and Interleukin-6 Act Additively to Inhibit Growth of MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells in Vitro. Cancer Res. 1993, 53. [Google Scholar]
- Morinaga, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Takatsuki, F.; Akiyama, Y.; Taniyama, T.; Matsushima, K.; Onozaki, K. Contribution of IL-6 to the antiproliferative effect of IL-1 and tumor necrosis factor on tumor cell lines. J. Immunol. 1989, 143, 3538–35342. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chiu, J.J.; Sgagias, M.K.; Cowan, K.H. Interleukin 6 acts as a paracrine growth factor in human mammary carcinoma cell lines. Clin. Cancer Res. 1996, 2, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tamm, I.; Cardinale, I.; Krueger, J.; Murphy, J.S.; May, L.T.; Sehgal, P.B. Interleukin 6 decreases cell-cell association and increases motility of ductal breast carcinoma cells. J. Exp. Med. 1989, 170, 1649–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asgeirsson, K.S.; Olafsdottir, K.; Jonasson, J.G.; Ögmundsdóttir, H.M. The effects of il-6 on cell adhesion and e-cadherin expression in breast cancer. Cytokine 1998, 10, 720–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badache, A.; Hynes, N.E. Interleukin 6 inhibits proliferation and, in cooperation with an epidermal growth factor receptor autocrine loop, increases migration of T47D breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.H.; Liu, B.R.; Qu, B.; Xing, H.; Gao, S.L.; Yin, J.M.; Cheng, Y.Q. Silencing STAT3 may inhibit cell growth through regulating signaling pathway, telomerase, cell cycle, apoptosis and angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma: Potential uses for gene therapy. Neoplasma 2011, 58, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Wei, H.; Tian, Z. STAT3-decoy oligodeoxynucleotide inhibits the growth of human lung cancer via down-regulating its target genes. Oncol. Rep. 2007, 17, 1377–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Reske, S.N.; Shen, C. PTEN mutation: Many birds with one stone in tumorigenesis. Anticancer. Res. 2009, 28, 3613–3619. [Google Scholar]
- Trotman, L.C.; Pandolfi, P.P. PTEN and p53: Who will get the upper hand. Cancer Cell 2003, 3, 97–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, W.; Zhou, J.-H.; Broussard, S.R.; Freund, G.G.; Dantzer, R.; Kelley, K.W. Proinflammatory cytokines block growth of breast cancer cells by impairing signals from a growth factor receptor. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 4746–4756. [Google Scholar]
- Studebaker, A.W.; Storci, G.; Werbeck, J.L.; Sansone, P.; Sasser, A.K.; Tavolari, S.; Huang, T.; Chan, M.; Marini, F.C.; Rosol, T.; et al. Fibroblasts Isolated from Common Sites of Breast Cancer Metastasis Enhance Cancer Cell Growth Rates and Invasiveness in an Interleukin-6–Dependent Manner. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 9087–9095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sullivan, N.J.; Sasser, A.K.; Axel, A.E.; Vesuna, F.; Raman, V.; Ramirez, N.; Oberyszyn, T.M.; Hall, B.M. Interleukin-6 induces an epithelial–mesenchymal transition phenotype in human breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2009, 28, 2940–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Selander, K.S.; Li, L.; Watson, L.; Merrell, M.; Dahmen, H.; Heinrich, P.C.; Mü Ller-Newen, G.; Harris, K.W. Inhibition of gp130 Signaling in Breast Cancer Blocks Constitutive Activation of Stat3 and Inhibits in vivo Malignancy. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 6924–6933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arihiro, K.; Oda, H.; Kaneko, M.; Inai, K. Cytokines facilitate chemotactic motility of breast carcinoma cells. Breast Cancer 2000, 7, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Liao, W.; Jian, Y.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ye, L.; Cui, Y.; Wang, B.; Wu, X.; Xiong, Z.; et al. CGI-99 promotes breast cancer metastasis via autocrine interleukin-6 signaling. Oncogene 2017, 36, 3695–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhasselt, B.; Van Damme, J.; Van Larebeke, N.; Put, W.; Bracke, M.; De Potter, C.; Mareel, M. Interleukin-1 is a motility factor for human breast carcinoma cells in vitro: Additive effect with interleukin-6. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 1992, 59, 449–457. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.-M.; Wang, Y.-S.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.-F.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, W.; Chu, D.-K.; Wiedemann, P. Role of PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK in Mediating Hypoxia-Induced Expression of HIF-1 and VEGF in Laser-Induced Rat Choroidal Neovascularization. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 1873–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conze, D.; Weiss, L.; Regen, P.S.; Bhushan, A.; Weaver, D.; Johnson, P.; Rincón, M. Autocrine production of interleukin 6 causes multidrug resistance in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 8851–8858. [Google Scholar]
- Haverty, A.A.; Harmey, J.H.; Redmond, H.; Bouchier-Hayes, D.J. Interleukin-6 Upregulates GP96 Expression in Breast Cancer. J. Surg. Res. 1997, 69, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkaya, H.; Kim, G.-I.; Davis, A.; Malik, F.; Henry, N.L.; Ithimakin, S.; Quraishi, A.A.; Tawakkol, N.; D’Angelo, R.; Paulson, A.; et al. Activation of an IL6 Inflammatory Loop Mediates Trastuzumab Resistance in HER2+ Breast Cancer by Expanding the Cancer Stem Cell Population. Mol. Cell 2012, 47, 570–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garcia-Tuñón, I.; Ricote, M.; Ruiz, A.; Fraile, B.; Paniagua, R.; Royuela, M. IL-6, its receptors and its relationship with bcl-2 and bax proteins in infiltrating and in situ human breast carcinoma. Histopathology 2005, 47, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motallebnezhad, M.; Jadidi-Niaragh, F.; Qamsari, E.S.; Bagheri, S.; Gharibi, T.; Yousefi, M. The immunobiology of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in cancer. Tumor Biol. 2015, 37, 1387–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erez, N.; Glanz, S.; Raz, Y.; Avivi, C.; Barshack, I. Cancer Associated Fibroblasts express pro-inflammatory factors in human breast and ovarian tumors. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 437, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieblein, J.C.; Ball, S.; Hutzen, B.; Sasser, A.K.; Lin, H.-J.; Huang, T.H.; Hall, B.M.; Lin, J. STAT3 can be activated through paracrine signaling in breast epithelial cells. BMC Cancer 2008, 8, 302–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sasser, A.K.; Casneuf, T.; Axel, A.E.; King, P.; Alvarez, J.D.; Werbeck, J.L.; Verhulst, T.; Verstraeten, K.; Hall, B.M. Interleukin-6 is a potential therapeutic target in interleukin-6 dependent, estrogen receptor-α-positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Targets Ther. 2016, 8, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crichton, M.B.; Nichols, J.E.; Zhao, Y.; Bulun, S.E.; Simpson, E.R. Expression of transcripts of interleukin-6 and related cytokines by human breast tumors, breast cancer cells, and adipose stromal cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1996, 118, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivennikov, S.; Karin, M. Autocrine IL-6 Signaling: A Key Event in Tumorigenesis? Cancer Cell 2008, 13, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fisher, D.T.; Appenheimer, M.M.; Evans, S.S. The two faces of IL-6 in the tumor microenvironment. Semin. Immunol. 2014, 26, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lederle, W.; Depner, S.; Schnur, S.; Obermueller, E.; Catone, N.; Just, A.; Fusenig, N.E.; Mueller, M.M. IL-6 promotes malignant growth of skin SCCs by regulating a network of autocrine and paracrine cytokines. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 128, 2803–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, A.R.; Green, V.L.; White, M.C.; Speirs, V. Expression of cytokine messenger RNA in normal and neoplastic human breast tissue: Identification of interleukin-8 as a potential regulatory factor in breast tumours. Int. J. Cancer 1997, 72, 937–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basolo, F.; Conaldi, P.G.; Fiore, L.; Calvo, S.; Toniolo, A. Normal breast epithelial cells produce interleukins 6 and 8 together with tumor-necrosis factor: Defective il6 expression in mammary carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 1993, 55, 926–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karczewska, A.; Nawrocki, S.; Breborowicz, D.; Filas, V.; Mackiewicz, A. Expression of interleukin-6, interleukin-6 receptor, and glycoprotein 130 correlates with good prognoses for patients with breast carcinoma. Cancer 2000, 88, 2061–2071. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Purohit, A.; Ghilchik, M.W.; Walker, M.M.; Duncan, L.; Wang, D.Y.; Singh, A.; Reed, M.J. Aromatase activity and interleukin-6 production by normal and malignant breast tissues. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1995, 80, 3052–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozłowski, L.; Zakrzewska, I.; Tokajuk, P.; Wojtukiewicz, M. Concentration of interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-8 (IL-8) and interleukin-10 (IL-10) in blood serum of breast cancer patients. Rocz. Akad. Med. Bialymst. 2003, 48, 82–84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.J.; Adachi, I. Serum interleukin-6 levels correlate to tumor progression and prognosis in metastatic breast carcinoma. Anticancer. Res. 1999, 19, 1427–1432. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bozcuk, H.; Uslu, G.; Samur, M.; Yıldız, M.; Özben, T.; Özdoğan, M.; Artaç, M.; Altunbaş, H.; Akan, I.; Savaş, B. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-6, and fasting serum insulin correlate with clinical outcome in metastatic breast cancer patients treated with chemotherapy. Cytokine 2004, 27, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, R.; Junius, S.; Benoy, I.; Van Dam, P.; Vermeulen, P.; Van Marck, E.; Huget, P.; Dirix, L.Y. Circulating interleukin-6 predicts survival in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 103, 642–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachelot, T.; Ray-Coquard, I.; Ménétrier-Caux, C.; Rastkha, M.; Duc, A.; Blay, J.-Y. Prognostic value of serum levels of interleukin 6 and of serum and plasma levels of vascular endothelial growth factor in hormone-refractory metastatic breast cancer patients. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 88, 1721–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishimura, R.; Nagao, K.; Miyayama, H.; Matsuda, M.; Baba, K.; Matsuoka, Y.; Yamashita, H.; Fukuda, M.; Mizumoto, T.; Hamamoto, R. An Analysis of Serum Interleukin-6 Levels to Predict Benefits of Medroxyprogesterone Acetate in Advanced or Recurrent Breast Cancer. Oncology 2000, 59, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoe, T.; Lino, Y.; Morishita, Y. Trends of IL-6 and IL-8 levels in patients with recurrent breast cancer: Preliminary report. Breast Cancer 2000, 7, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Gan, Z.; Han, K.; Yao, Y.; Min, D. Interleukin-6 as a Prognostic Marker for Breast Cancer: A Meta-analysis. Tumori J. 2015, 101, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusztai, L.; Mendoza, T.R.; Reuben, J.M.; Martinez, M.M.; Willey, J.S.; Lara, J.; Syed, A.; Fritsche, H.A.; Bruera, E.; Booser, D.; et al. Changes in plasma levels of inflammatory cytokines in response to paclitaxel chemotherapy. Cytokine 2003, 25, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsavaris, N.; Kosmas, C.; Vadiaka, M.; Kanelopoulos, P.; Boulamatsis, D. Immune changes in patients with advanced breast cancer undergoing chemotherapy with taxanes. Br. J. Cancer 2002, 87, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mills, P.J.; Ancoli-Israel, S.; Parker, B.; Natarajan, L.; Hong, S.; Jain, S.; Sadler, G.R.; von Känel, R. Predictors of inflammation in response to anthracycline-based chemotherapy for breast cancer. Brain Behav. Immun. 2008, 22, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, D.-H.; Weaver, M.T.; Park, N.-J.; Smith, B.; McArdle, T.; Carpenter, J. Significant Impairment in Immune Recovery After Cancer Treatment. Nurs. Res. 2009, 58, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oner-Iyidogan, Y.; Oner, P.; Kocak, H.; Lama, A.; Gurdol, F.; Bekpınar, S.; Unur, N.; Özbek-Kır, Z. Evaluation of leukocyte arylsulphatase a, serum interleukin-6 and urinary heparan sulphate following tamoxifen therapy in breast cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2005, 52, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saligan, L.N.; Kim, H.S. A systematic review of the association between immunogenomic markers and cancer-related fatigue. Brain, Behav. Immun. 2012, 26, 830–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bower, J.E.; Ganz, P.A.; Tao, M.L.; Hu, W.; Belin, T.R.; Sepah, S.; Cole, S.; Aziz, N. Inflammatory Biomarkers and Fatigue during Radiation Therapy for Breast and Prostate Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 5534–5540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cameron, B.A.; Bennett, B.; Li, H.; Boyle, F.; Desouza, P.; Wilcken, N.; Friedlander, M.; Goldstein, D.; Lloyd, A.R. Post-cancer fatigue is not associated with immune activation or altered cytokine production. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, 2890–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orre, I.J.; Reinertsen, K.V.; Aukrust, P.; Dahl, A.A.; Fosså, S.D.; Ueland, T.; Murison, R. Higher levels of fatigue are associated with higher CRP levels in disease-free breast cancer survivors. J. Psychosom. Res. 2011, 71, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soygur, H.; Palaoglu, O.; Akarsu, E.S.; Cankurtaran, E.S.; Ozalp, E.; Turhan, L.; Ayhan, I.H. Interleukin-6 levels and HPA axis activation in breast cancer patients with major depressive disorder. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 31, 1242–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musselman, D.L.; Miller, A.H.; Porter, M.R.; Manatunga, A.; Gao, F.; Penna, S.; Pearce, B.D.; Landry, J.; Glover, S.; McDaniel, J.S.; et al. Higher Than Normal Plasma Interleukin-6 Concentrations in Cancer Patients With Depression: Preliminary Findings. Am. J. Psychiatry 2001, 158, 1252–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jehn, C.F.; Flath, B.; Strux, A.; Krebs, M.; Possinger, K.; Pezzutto, A.; Lüftner, D. Influence of age, performance status, cancer activity, and IL-6 on anxiety and depression in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 136, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janelsins, M.C.; Mustian, K.M.; Palesh, O.G.; Mohile, S.G.; Peppone, L.J.; Sprod, L.K.; Heckler, C.E.; Roscoe, J.A.; Katz, A.W.; Williams, J.P.; et al. Differential expression of cytokines in breast cancer patients receiving different chemotherapies: Implications for cognitive impairment research. Support. Care Cancer 2011, 20, 831–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kesler, S.; Janelsins, M.; Koovakkattu, D.; Palesh, O.; Mustian, K.; Morrow, G.; Dhabhar, F.S. Reduced hippocampal volume and verbal memory performance associated with interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha levels in chemotherapy-treated breast cancer survivors. Brain, Behav. Immun. 2013, 30, S109–S116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hudis, C.A.; Subbaramaiah, K.; Morris, P.G.; Dannenberg, A.J. Breast Cancer Risk Reduction: No Pain, No Gain? J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 3436–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heikkila, K.; Harris, R.; Lowe, G.; Rumley, A.; Yarnell, J.; Gallacher, J.; Ben-Shlomo, Y.; Ebrahim, S.; Lawlor, D.A. Associations of circulating C-reactive protein and interleukin-6 with cancer risk: Findings from two prospective cohorts and a meta-analysis. Cancer Causes Control. 2008, 20, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Il’yasova, D.; Colbert, L.H.; Harris, T.B.; Newman, A.B.; Bauer, D.C.; Satterfield, S.; Kritchevsky, S.B. Circulating Levels of Inflammatory Markers and Cancer Risk in the Health Aging and Body Composition Cohort. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2005, 14, 2413–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrews, B.; Shariat, S.F.; Kim, J.-H.; Wheeler, T.M.; Slawin, K.M.; Lerner, S.P. Preoperative plasma levels of interleukin-6 and its soluble receptor predict disease recurrence and survival of patients with bladder cancer. J. Urol. 2002, 167, 1475–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariat, S.F.; Kattan, M.; Traxel, E.; Andrews, B.; Zhu, K.; Wheeler, T.M.; Slawin, K.M. Association of Pre- and Postoperative Plasma Levels of Transforming Growth Factor β1 and Interleukin 6 and Its Soluble Receptor with Prostate Cancer Progression. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 1992–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alexandrakis, M.; Passam, F.; Boula, A.; Christophoridou, A.; Aloizos, G.; Roussou, P.; Kyriakou, D. Relationship between circulating serum soluble interleukin-6 receptor and the angiogenic cytokines basic fibroblast growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor in multiple myeloma. Ann. Hematol. 2003, 82, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stasi, R.; Brunetti, M.; Parma, A.; Di Giulio, C.; Terzoli, E.; Pagano, A. The prognostic value of soluble interleukin-6 receptor in patients with multiple myeloma. Cancer 1998, 82, 1860–1866. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Robak, T.; Wierzbowska, A.; Błasińska-Morawiec, M.; Korycka, A.; Blonski, J.Z. Serum Levels of IL-6 Type Cytokines and Soluble IL-6 Receptors in Active B-Cell Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia and in Cladribine Induced Remission. Mediat. Inflamm. 1999, 8, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soresi, L.G.M.; Antona, A.M.F.; Alessandro, G.M. Interleukin-6 and its soluble receptor in patients with liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 2563–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabłońska, E.; Kiluk, M.; Markiewicz, W.; Piotrowski, L.; Grabowska, Z.; Jabłoński, J. TNF-alpha, IL-6 and their soluble receptor serum levels and secretion by neutrophils in cancer patients. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2001, 49, 63–69. [Google Scholar]
- Kovacs, E. Investigation of interleukin-6 (IL-6), soluble IL-6 receptor (sIL-6R) and soluble gp130 (sgp130) in sera of cancer patients. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2001, 55, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawara, K.; Scott, H.; Emathinger, J.; Wolf, C.; Lajoie, D.; Hedeen, D.; Bond, L.; Montgomery, P.; Jorcyk, C. HIGH expression of OSM and IL-6 are associated with decreased breast cancer survival: Synergistic induction of IL-6 secretion by OSM and IL-1β. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 2068–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lapeire, L.; Hendrix, A.; Lambein, K.; Van Bockstal, M.R.; Braems, G.; Broecke, R.V.D.; Limame, R.; Mestdagh, P.; Vandesompele, J.; Vanhove, C.; et al. Cancer-Associated Adipose Tissue Promotes Breast Cancer Progression by Paracrine Oncostatin M and Jak/STAT3 Signaling. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 6806–6819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tawara, K.; Scott, H.; Emathinger, J.; Ide, A.; Fox, R.; Greiner, D.; LaJoie, D.; Hedeen, D.; Nandakumar, M.; Oler, A.J.; et al. Co-Expression of VEGF and IL-6 Family Cytokines is Associated with Decreased Survival in HER2 Negative Breast Cancer Patients: Subtype-Specific IL-6 Family Cytokine-Mediated VEGF Secretion. Transl. Oncol. 2018, 12, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winship, A.; Van Sinderen, M.; Donoghue, J.; Rainczuk, K.; Dimitriadis, E. Targeting Interleukin-11 Receptor-α Impairs Human Endometrial Cancer Cell Proliferation and Invasion In Vitro and Reduces Tumor Growth and Metastasis In Vivo. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Yang, Q.; Yu, H.; Wu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yue, X.; Liu, Z.; Wu, H.; Haffty, B.G.; et al. LIF promotes tumorigenesis and metastasis of breast cancer through the AKT-mTOR pathway. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 788–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yue, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Hu, W. Leukemia inhibitory factor promotes EMT through STAT3-dependent miR-21 induction. Oncotarget 2015, 7, 3777–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Junk, D.J.; Bryson, B.; Smigiel, J.M.; Parameswaran, N.; Bartel, C.A.; Jackson, M.W. Oncostatin M promotes cancer cell plasticity through cooperative STAT3-SMAD3 signaling. Oncogene 2017, 36, 4001–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cocco, C.; Giuliani, N.; DI Carlo, E.; Ognio, E.; Storti, P.; Abeltino, M.; Sorrentino, C.; Ponzoni, M.; Ribatti, D.; Airoldi, I. Interleukin-27 Acts as Multifunctional Antitumor Agent in Multiple Myeloma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 4188–4197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pan, C.-M.; Wang, M.-L.; Chiou, S.-H.; Chen, H.-Y.; Wu, C.-W. Oncostatin M suppresses metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma by inhibiting SLUG expression through coordination of STATs and PIASs signalings. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 60395–60406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thilakasiri, P.; Huynh, J.; Poh, A.; Tan, C.W.; Nero, T.; Tran, K.; Parslow, A.C.; Afshar-Sterle, S.; Baloyan, D.; Hannan, N.J.; et al. Repurposing the selective estrogen receptor modulator bazedoxifene to suppress gastrointestinal cancer growth. EMBO Mol. Med. 2019, 11, e9539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacroix, M.; Siwek, B.; Marie, P.J.; Body, J.J. Production and regulation of interleukin-11 by breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 1998, 127, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, A.M.; Goss, G.A.; Sutherland, R.L.; Hilton, D.J.; Berndt, M.C.; Nicola, N.A.; Begley, C.G. Expression and function of members of the cytokine receptor superfamily on breast cancer cells. Oncogene 1997, 14, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnstone, C.N.; Chand, A.; Putoczki, T.L.; Ernst, M. Emerging roles for IL-11 signaling in cancer development and progression: Focus on breast cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015, 26, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Putoczki, T.; Wilson, N.; Edwards, K.; McKenzie, B.; Greten, F.; Ernst, M. Interleukin-11 is the dominant IL-6 family cytokine during gastrointestinal 20umourigenesis. Cytokine 2013, 63, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockhorn, J.; Dalton, R.; Nwachukwu, C.; Huang, S.; Prat, A.; Yee, K.; Chang, Y.-F.; Huo, D.; Wen, Y.; Swanson, K.E.; et al. MicroRNA-30c inhibits human breast tumour chemotherapy resistance by regulating TWF1 and IL-11. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Onnis, B.; Fer, N.; Rapisarda, A.; Perez, V.S.; Melillo, G. Autocrine production of IL-11 mediates tumorigenicity in hypoxic cancer cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1615–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, J.E.; Lee, H.-G.; Cho, I.-H.; Chung, D.H.; Yoon, S.-H.; Yang, Y.M.; Lee, J.W.; Choi, S.; Park, J.-W.; Ye, S.-K.; et al. STAT3 is a potential modulator of HIF-1-mediated VEGF expression in human renal carcinoma cells. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1296–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marusyk, A.; Tabassum, D.P.; Altrock, P.; Almendro, V.; Michor, F.; Polyak, K. Non-cell-autonomous driving of tumour growth supports sub-clonal heterogeneity. Nature 2014, 514, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bellido, T.; Borba, V.Z.C.; Roberson, P.; Manolagas, S.C. Activation of the Janus Kinase/STAT (Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription) Signal Transduction Pathway by Interleukin-6-Type Cytokines Promotes Osteoblast Differentiation*. Endocrinology 1997, 138, 3666–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, E.C.; McGregor, N.E.; Poulton, I.J.; Solano, M.; Pompolo, S.; Fernandes, T.J.; Constable, M.J.; Nicholson, G.; Zhang, J.-G.; Nicola, N.; et al. Oncostatin M promotes bone formation independently of resorption when signaling through leukemia inhibitory factor receptor in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walker, E.C.; McGregor, N.E.; Poulton, I.J.; Pompolo, S.; Allan, E.H.; Quinn, J.M.; Gillespie, M.T.; Martin, T.J.; Sims, N.A. Cardiotrophin-1 Is an Osteoclast-Derived Stimulus of Bone Formation Required for Normal Bone Remodeling. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2008, 23, 2025–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Pape, F.; Vargas, G.; Clézardin, P. The role of osteoclasts in breast cancer bone metastasis. J. Bone Oncol. 2016, 5, 93–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Girasole, G.; Passeri, G.; Jilka, R.L.; Manolagas, S.C. Interleukin-11: A new cytokine critical for osteoclast development. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 93, 1516–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sotiriou, C.; Lacroix, M.; Lespagnard, L.; Larsimont, D.; Paesmans, M.; Body, J.-J. Interleukins-6 and -11 expression in primary breast cancer and subsequent development of bone metastases. Cancer Lett. 2001, 169, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, L.; Wang, X.; Dong, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S. Bone metastasis from breast cancer involves elevated IL-11 expression and the gp130/STAT3 pathway. Med Oncol. 2013, 30, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glück, S.; Ross, J.S.; Royce, M.; McKenna, E.F.; Perou, C.; Avisar, E.; Wu, L. TP53 genomics predict higher clinical and pathologic tumor response in operable early-stage breast cancer treated with docetaxel-capecitabine ± trastuzumab. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2011, 132, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finak, G.; Bertos, N.; Pepin, F.; Sadekova, S.; Souleimanova, M.; Zhao, H.; Chen, H.; Omeroglu, G.; Meterissian, S.; Omeroglu, A.; et al. Stromal gene expression predicts clinical outcome in breast cancer. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanavadi, S.; Martin, T.A.; Watkins, G.; Mansel, R.E.; Jiang, W.G. Expression of Interleukin 11 and Its Receptor and Their Prognostic Value in Human Breast Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2006, 13, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desmedt, C.; Piette, F.; Loi, S.; Wang, Y.; Lallemand, F.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Viale, G.; Delorenzi, M.; Zhang, Y.; D’Assignies, M.S.; et al. Strong Time Dependence of the 76-Gene Prognostic Signature for Node-Negative Breast Cancer Patients in the TRANSBIG Multicenter Independent Validation Series. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 3207–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koboldt, D.C.; Fulton, R.S.; McLellan, M.D.; Schmidt, H.; Kalicki-Veizer, J.; McMichael, J.F.; Fulton, L.L.; Dooling, D.J.; Ding, L.; Mardis, E.R.; et al. Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 2012, 490, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Curtis, C.; Shah, S.P.; Chin, S.-F.; Turashvili, G.; Rueda, O.M.; Dunning, M.; Speed, D.; Lynch, A.; Samarajiwa, S.; Yuan, Y.; et al. The genomic and transcriptomic architecture of 2,000 breast tumours reveals novel subgroups. Nature 2012, 486, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, R.K.; Connett, J.; Bailey, W.C.; Casaburi, R.; Cooper, J.A.D.; Criner, G.J.; Curtis, J.; Dransfield, M.T.; Han, M.K.; Lazarus, S.C.; et al. Azithromycin for Prevention of Exacerbations of COPD. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, A.; Hahnfeldt, P.; Maercker, C.; Gröne, H.-J.; Debus, J.; Ansorge, W.; Folkman, J.; Hlatky, L.; Huber, P.E. Endostatin’s Antiangiogenic Signaling Network. Mol. Cell 2004, 13, 649–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrov, Z.; Samal, B.; Lapushin, R.; Kellokumpu-Lehtinen, P.; Sahin, A.A.; Kurzrock, R.; Talpaz, M.; Aggarwal, B.B. Leukemia Inhibitory Factor Binds to Human Breast Cancer Cells and Stimulates Their Proliferation. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 1995, 15, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellokumpu-Lehtinen, P.; Talpaz, M.; Harris, D.; Van, Q.; Kurzrock, R.; Estrov, Z. Leukemia-inhibitory factor stimulates breast, kidney and prostate cancer cell proliferation by paracrine and autocrine pathways. Int. J. Cancer 1996, 66, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.W.; Finger, E.C.; Olcina, M.M.; Vilalta, M.; Aguilera, T.; Miao, Y.; Merkel, A.; Johnson, J.R.; Sterling, J.A.; Wu, J.Y.; et al. Induction of LIFR confers a dormancy phenotype in breast cancer cells disseminated to the bone marrow. Nat. Cell Biol. 2016, 18, 1078–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Douglas, A.M.; Grani, S.L.; Goss, G.A.; Clousion, D.R.; Sulhirland, R.L.; Beflly, C.G. Oncostatin M induces the differentiation of breast cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 1998, 75, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Sun, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, P.; Rezaeian, A.H.; Teruya-Feldstein, J.; Gupta, S.; Liang, H.; Lin, H.-K.; Hung, M.-C.; et al. LIFR is a breast cancer metastasis suppressor upstream of the Hippo-YAP pathway and a prognostic marker. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1511–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeng, H.; Qu, J.; Jin, N.; Xu, J.; Lin, C.; Chen, Y.; Yang, X.; He, X.; Tang, S.; Lan, X.; et al. Feedback Activation of Leukemia Inhibitory Factor Receptor Limits Response to Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors in Breast Cancer. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 459–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, R.S.; Avivar-Valderas, A.; Estrada, Y.; Bragado, P.; Sosa, M.S.; Aguirre-Ghiso, J.A.; Segall, J.E. Dormancy Signatures and Metastasis in Estrogen Receptor Positive and Negative Breast Cancer. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-J.; Qiao, Y.; Xiao, M.M.; Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Lv, W.; Xu, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tan, M.-D.; et al. Opposing Roles of Acetylation and Phosphorylation in LIFR-Dependent Self-Renewal Growth Signaling in Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 933–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iorns, E.; Ward, T.M.; Dean, S.; Jegg, A.; Thomas, D.; Murugaesu, N.; Sims, D.; Mitsopoulos, C.; Fenwick, K.; Kozarewa, I.; et al. Whole genome in vivo RNAi screening identifies the leukemia inhibitory factor receptor as a novel breast tumor suppressor. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 135, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, S.L.; Douglas, A.M.; Goss, G.A.; Begley, C.G. Oncostatin M and Leukemia Inhibitory Factor Regulate the Growth of Normal Human Breast Epithelial Cells. Growth Factors 2001, 19, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franken, N.A.P.; Rodermond, H.M.; Stap, J.; Haveman, J.; Van Bree, C. Clonogenic assay of cells in vitro. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2315–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Spence, M.J.; Wallace, P.M.; Forcier, K.; Hellström, I.; Vestal, R.E. Oncostatin M-specific receptor mediates inhibition of breast cancer cell growth and down-regulation of the c-myc proto-oncogene. Cell Growth Differ. 1997, 8, 667–676. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Ahlborn, T.E.; Kraemer, F.; Liu, J. Oncostatin M–induced growth inhibition and morphological changes of MDA-MB231 breast cancer cells are abolished by blocking the MEK/ERK signaling pathway. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2001, 66, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hadjokas, N.; Mosley, B.; Estrov, Z.; Spence, M.J.; Vestal, R.E. Oncostatin m-specific receptor expression and function in regulating cell proliferation of normal and malignant mammary epithelial cells. Cytokine 1998, 10, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underhill-Day, N.; Heath, J. Oncostatin M (OSM) Cytostasis of Breast Tumor Cells: Characterization of an OSM Receptor β–Specific Kernel. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 10891–10901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jorcyk, C.; Holzer, R.; Ryan, R. Oncostatin M induces cell detachment and enhances the metastatic capacity of T-47D human breast carcinoma cells. Cytokine 2006, 33, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omokehinde, T.; Jotte, A.; Johnson, R.W. gp130 Cytokines Activate Novel Signaling Pathways and Alter Bone Dissemination in ER + Breast Cancer Cells. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2021, 12, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolin, C.; Tawara, K.; Sutherland, C.; Redshaw, J.; Aranda, P.; Moselhy, J.; Anderson, R.; Jorcyk, C.L. Oncostatin M Promotes Mammary Tumor Metastasis to Bone and Osteolytic Bone Degradation. Genes Cancer 2012, 3, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tawara, K.; Bolin, C.; Koncinsky, J.; Kadaba, S.; Covert, H.; Sutherland, C.; Bond, L.; Kronz, J.; Garbow, J.R.; Jorcyk, C.L. OSM potentiates preintravasation events, increases CTC counts, and promotes breast cancer metastasis to the lung. Breast Cancer Res. 2018, 20, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosley, B.; De Imus, C.; Friend, D.; Boiani, N.; Thoma, B.; Park, L.S.; Cosman, D. Dual Oncostatin M (OSM) Receptors. Cloning and characterization of an alternative signaling subunit conferring OSM-specific receptor activation. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 32635–32643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- West, N.; Murphy, L.C.; Watson, P.H. Oncostatin M suppresses oestrogen receptor-α expression and is associated with poor outcome in human breast cancer. Endocrine-Related Cancer 2012, 19, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez-Pérez, C.; Leung, J.; Kay, C.; Meehan, J.; Gray, M.; Dixon, J.; Turnbull, A. The Signal Transducer IL6ST (gp130) as a Predictive and Prognostic Biomarker in Breast Cancer. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontanini, G.; Campani, D.; Roncella, M.; Cecchetti, D.; Calvo, S.; Toniolo, A.; Basolo, F. Expression of Interleukin 6 (IL-6) Correlates with Oestrogen Receptor in Human Breast Carcinoma. Brit J Cancer 1999, 80, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hartman, Z.C.; Yang, X.-Y.; Glass, O.; Lei, G.; Osada, T.; Dave, S.S.; Morse, M.A.; Clay, T.M.; Lyerly, H. HER2 Overexpression Elicits a Proinflammatory IL-6 Autocrine Signaling Loop That Is Critical for Tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 4380–4391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hartman, Z.C.; Poage, G.M.; Hollander, P.D.; Tsimelzon, A.; Hill, J.; Panupinthu, N.; Zhang, Y.; Mazumdar, A.; Hilsenbeck, S.G.; Mills, G.B.; et al. Growth of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells Relies upon Coordinate Autocrine Expression of the Proinflammatory Cytokines IL-6 and IL-8. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 3470–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chavey, C.; Bibeau, F.; Gourgou-Bourgade, S.; Burlinchon, S.; Boissière, F.; Laune, D.; Roques, S.; Lazennec, G. Oestrogen receptor negative breast cancers exhibit high cytokine content. Breast Cancer Res. 2007, 9, R15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dethlefsen, C.; Højfeldt, G.; Hojman, P. The role of intratumoral and systemic IL-6 in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2013, 138, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, H.S.; Kim, Y.A.; Lee, J.S.; Jeon, E.K.; An, H.J.; Sun, D.S.; Ko, Y.H.; Kim, J.S. Soluble Interleukin-6 Receptor is a Prognostic Marker for Relapse-Free Survival in Estrogen Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer. Cancer Investig. 2013, 31, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Purohit, A.; Ghilchik, M.W.; Reed, M.J. The regulation of aromatase activity in breast fibroblasts: The role of interleukin-6 and prostaglandin E 2. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 1999, 6, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Irahara, N.; Miyoshi, Y.; Taguchi, T.; Tamaki, Y.; Noguchi, S. Quantitative analysis ofaromatasemRNA expression derived from various promoters (I.4, I.3, PII and I.7) and its association with expression ofTNF-α,IL-6andCOX-2mRNAs in human breast cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 118, 1915–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, A.; Newman, S.P.; Reed, M.J. The role of cytokines in regulating estrogen synthesis: Implications for the etiology of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2002, 4, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simpson, E.R.; Michael, M.D.; Agarwal, V.R.; Hinshelwood, M.M.; Bulun, S.E.; Zhao, Y. Expression of the CYP19 (aromatase) gene: An unusual case of alternative promoter usage. FASEB J. 1997, 11, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Miguel, F.; Lee, S.O.; Onate, S.A.; Gao, A.C. Stat3 enhances transactivation of steroid hormone receptors. Nucl. Recept. 2003, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Jones, S.A.; Hagood, J.S.; Fuentes, N.L.; Fuller, G.M. STAT3 Acts as a Co-activator of Glucocorticoid Receptor Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 30607–30610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Speirs, V.; Kerin, M.J.J.; Walton, D.S.S.; Newton, C.J.J.; Desai, S.B.B.; Atkin, S.L. Direct activation of oestrogen receptor-alpha by interleukin-6 in primary cultures of breast cancer epithelial cells. Br. J. Cancer 2000, 82, 1312–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat-Nakshatri, P.; Campbell, R.A.; Patel, N.M.; Newton, T.R.; King, A.J.; Marshall, M.S.; Ali, S.; Nakshatri, H. Tumour necrosis factor and PI3-kinase control oestrogen receptor alpha protein level and its transrepression function. Br. J. Cancer 2004, 90, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Classen-Linke, I.; Müller-Newen, G.; Heinrich, P.C.; Beier, H.M.; Von Rango, U. The cytokine receptor gp130 and its soluble form are under hormonal control in human endometrium and decidua. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2004, 10, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhingra, K.; Sahin, A.; Emami, K.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Estrov, Z. Expression of leukemia inhibitory factor and its receptor in breast cancer: A potential autocrine and paracrine growth regulatory mechanism. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 1998, 48, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, C.; Cheng, Z.; Tang, L.; Gao, Y.; Liu, F.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; et al. A mandatory role of nuclear PAK4-LIFR axis in breast-to-bone metastasis of ERα-positive breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2018, 38, 808–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lokau, J.; Garbers, C. Activating mutations of the gp130/JAK/STAT pathway in human diseases. In Advances in Protein Chemistry and Structural Biology; Academic Press Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; Volume 116, pp. 283–309. ISBN 9780128155615. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, A.; Bairwa, N.K.; Ranjan, A.; Gupta, V.; Bamezai, R. Two novel somatic mutations in the human interleukin 6 promoter region in a patient with sporadic breast cancer. Eur. J. Immunogenet. 2003, 30, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.-D.; Di, G.-H.; Fan, L.; Chen, A.-X.; Yang, C.; Shao, Z.-M. Lack of an association between a functional polymorphism in the interleukin-6 gene promoter and breast cancer risk: A meta-analysis involving 25,703 subjects. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2009, 122, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMichele, A.; Gray, R.; Horn, M.; Chen, J.; Aplenc, R.; Vaughan, W.P.; Tallman, M.S. Host Genetic Variants in the Interleukin-6 Promoter Predict Poor Outcome in Patients with Estrogen Receptor-Positive, Node-Positive Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 4184–4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abana, C.O.; Bingham, B.S.; Cho, J.H.; Graves, A.J.; Koyama, T.; Pilarski, R.T.; Chakravarthy, A.B.; Xia, F. IL-6 variant is associated with metastasis in breast cancer patients. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacopetta, B.; Grieu, F.; Joseph, D. The −174 G/C gene polymorphism in interleukin-6 is associated with an aggressive breast cancer phenotype. Br. J. Cancer 2004, 90, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sa-Nguanraksa, D.; Suntiparpluacha, M.; Kulprom, A.; Kummalue, T.; Chuangsuwanich, T.; Avirutnan, P.; O-Charoenrat, P. Association of estrogen receptor alpha and interleukin 6 polymorphisms with lymphovascular invasion, extranodal extension, and lower disease-free survival in thai breast cancer patients. Asian Pacific J. Cancer Prev. 2016, 17, 2935–2940. [Google Scholar]
- Markkula, A.; Simonsson, M.; Ingvar, C.; Rose, C.; Jernström, H. IL6 genotype, tumour ER-status, and treatment predicted disease-free survival in a prospective breast cancer cohort. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slattery, M.L.; Curtin, K.; Baumgartner, R.; Sweeney, C.; Byers, T.; Giuliano, A.R.; Baumgartner, K.B.; Wolff, R.R. IL6, Aspirin, Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs, and Breast Cancer Risk in Women Living in the Southwestern United States. Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers Prev. 2007, 16, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Snoussi, K.; Strosberg, A.D.; Bouaouina, N.; Ahmed, S.B.; Chouchane, L. Genetic variation in pro-inflammatory cytokines (interleukin-1β, interleukin-1α and interleukin-6) associated with the aggressive forms, survival, and relapse prediction of breast carcinoma. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2005, 16, 253–260. [Google Scholar]
- Hefler, L.A.; Grimm, C.; Lantzsch, T.; Lampe, D.; Leodolter, S.; Koelbl, H.; Heinze, G.; Reinthaller, A.; Tong-Cacsire, D.; Tempfer, C.; et al. Interleukin-1 and Interleukin-6 Gene Polymorphisms and the Risk of Breast Cancer in Caucasian Women. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 5718–5721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madeleine, M.M.; Johnson, L.G.; Malkki, M.; Resler, A.J.; Petersdorf, E.W.; McKnight, B.; Malone, K.E. Genetic variation in proinflammatory cytokines IL6, IL6R, TNF-region, and TNFRSF1A and risk of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2011, 129, 887–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balasubramanian, S.P.; Azmy, I.A.F.; Higham, S.E.; Wilson, A.G.; Cross, S.S.; Cox, A.; Brown, N.J.; Reed, M.W. Interleukin gene polymorphisms and breast cancer: A case control study and systematic literature review. BMC Cancer 2006, 6, 188. [Google Scholar]
- Slattery, M.L.; Herrick, J.S.; Torres-Mejia, G.; John, E.M.; Giuliano, A.R.; Hines, L.M.; Stern, M.C.; Baumgartner, K.B.; Presson, A.P.; Wolff, R.K. Genetic variants in interleukin genes are associated with breast cancer risk and survival in a genetically admixed population: The Breast Cancer Health Disparities Study. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 1750–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liao, C.; Hu, S.; Zheng, Z.; Tong, H. Contribution of interaction between genetic variants of interleukin-11 and Helicobacter pylori infection to the susceptibility of gastric cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 7459–7466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, L.H.; Lee, H.-S.; Kim, Y.J.; Jung, J.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, B.L.; Shin, H.D. Identification of novel SNPs in the interleukin 6 receptor gene (IL6R). Hum. Mutat. 2003, 21, 450–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbers, C.; Monhasery, N.; Aparicio-Siegmund, S.; Lokau, J.; Baran, P.; Nowell, M.A.; Jones, S.A.; Rose-John, S.; Scheller, J. The interleukin-6 receptor Asp358Ala single nucleotide polymorphism rs2228145 confers increased proteolytic conversion rates by ADAM proteases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2014, 1842, 1485–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, R.C.; Freitag, D.F.; Cutler, A.; Howson, J.; Rainbow, D.B.; Smyth, D.; Kaptoge, S.; Clarke, P.; Boreham, C.; Coulson, R.M.; et al. Functional IL6R 358Ala Allele Impairs Classical IL-6 Receptor Signaling and Influences Risk of Diverse Inflammatory Diseases. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, N.; Butterworth, A.S.; Hung, J.; Mcquillan, B.M. Interleukin-6 receptor pathways in coronary heart disease: A collaborative meta-analysis of 82 studies. Lancet 2012, 379, 1205–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esparza-Gordillo, J.; Schaarschmidt, H.; Liang, L.; Cookson, W.; Bauerfeind, A.; Lee-Kirsch, M.-A.; Nemat, K.; Henderson, J.; Paternoster, L.; Harper, J.I.; et al. A functional IL-6 receptor (IL6R) variant is a risk factor for persistent atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, S.; Bal, S.K.; Egner, W.; Allen, H.L.; Raza, S.I.; Ma, C.A.; Gürel, M.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, G.; Sabroe, R.A.; et al. Loss of the interleukin-6 receptor causes immunodeficiency, atopy, and abnormal inflammatory responses. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 216, 1986–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Song, N.; Han, S.; Chung, S.; Sung, H.; Lee, J.-Y.; Jung, S.J.; Park, S.K.; Yoo, K.-Y.; Han, W.; et al. The Associations between Immunity-Related Genes and Breast Cancer Prognosis in Korean Women. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Metcalfe, R.D.; Aizel, K.; Zlatic, C.O.; Nguyen, P.M.; Morton, C.; Lio, D.S.-S.; Cheng, H.-C.; Dobson, R.C.J.; Parker, M.; Gooley, P.R.; et al. The structure of the extracellular domains of human interleukin 11α receptor reveals mechanisms of cytokine engagement. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 8285–8301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brischoux-Boucher, E.; Trimouille, A.; Baujat, G.; Goldenberg, A.; Schaefer, E.; Guichard, B.; Hannequin, P.; Paternoster, G.; Baer, S.; Cabrol, C.; et al. IL11RA-related Crouzon-like autosomal recessive craniosynostosis in 10 new patients: Resemblances and differences. Clin. Genet. 2018, 94, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keupp, K.; Li, Y.; Vargel, I.; Hoischen, A.; Richardson, R.; Neveling, K.; Alanay, Y.; Uz, E.; Elcioğlu, N.; Rachwalski, M.; et al. Mutations in the interleukin receptor IL 11 RA cause autosomal recessive Crouzon-like craniosynostosis. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2013, 1, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mars, G.; Windelinckx, A.; Beunen, G.; Delecluse, C.; Lefevre, J.; Thomis, M.A.I. Polymorphisms in the CNTF and CNTF receptor genes are associated with muscle strength in men and women. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 102, 1824–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jenkins, B.; Grail, D.; Nheu, T.; Najdovska, M.; Wang, B.; Waring, P.; Inglese, M.; McLoughlin, R.; Jones, S.A.; Topley, N.; et al. Hyperactivation of Stat3 in gp130 mutant mice promotes gastric hyperproliferation and desensitizes TGF-β signaling. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebouissou, S.; Amessou, M.; Couchy, G.; Poussin, K.; Imbeaud, S.; Pilati, C.; Izard, T.; Balabaud, C.; Bioulac-Sage, P.; Zucman-Rossi, J. Frequent in-frame somatic deletions activate gp130 in inflammatory hepatocellular tumours. Nature 2008, 457, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidt-Arras, D.; Müller, M.; Stevanovic, M.; Horn, S.; Schütt, A.; Bergmann, J.; Wilkens, R.; Lickert, A.; Rose-John, S. Oncogenic deletion mutants of gp130 signal from intracellular compartments. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 127, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwerd, T.; Twigg, S.R.; Aschenbrenner, D.; Manrique, S.; Miller, K.A.; Taylor, I.B.; Capitani, M.; McGowan, S.J.; Sweeney, E.; Weber, A.; et al. A biallelic mutation in IL6ST encoding the GP130 co-receptor causes immunodeficiency and craniosynostosis. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 2547–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arita, K.; South, A.P.; Hans-Filho, G.; Sakuma, T.H.; Lai-Cheong, J.; Clements, S.; Odashiro, M.; Odashiro, D.N.; Hans-Neto, G.; Hans, N.R.; et al. Oncostatin M Receptor-β Mutations Underlie Familial Primary Localized Cutaneous Amyloidosis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 82, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mikelonis, D.; Jorcyk, C.L.; Tawara, K.; Oxford, J.T. Stüve-Wiedemann syndrome: LIFR and associated cytokines in clinical course and etiology. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2014, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Kosfeld, A.; Brand, F.; Weiss, A.-C.; Kreuzer, M.; Goerk, M.; Martens, H.; Schubert, S.; Schäfer, A.-K.; Riehmer, V.; Hennies, I.; et al. Mutations in the leukemia inhibitory factor receptor (LIFR) gene and Lifr deficiency cause urinary tract malformations. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 1716–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; He, S.Y.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, P. The role of oncostatin M receptor gene polymorphisms in bladder cancer. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 17, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, W.; Luo, Y. The polymorphisms of oncostatin M receptor gene associated with increased risk of lung cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2018, 11, 12421–12428. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, I.K.; Eun, Y.G.; Chung, D.H.; Kwon, K.H.; Kim, D.Y. Association of the Oncostatin M Receptor Gene Polymorphisms with Papillary Thyroid Cancer in the Korean Population. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2011, 4, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkevitch, E.; Durum, S. The promise of Janus kinase inhibitors in the treatment of hematological malignancies. Cytokine 2016, 98, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kralovics, R.; Passamonti, F.; Buser, A.S.; Teo, S.-S.; Tiedt, R.; Passweg, J.R.; Tichelli, A.; Cazzola, M.; Skoda, R.C. A Gain-of-Function Mutation ofJAK2in Myeloproliferative Disorders. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1779–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flex, E.; Petrangeli, V.; Stella, L.; Chiaretti, S.; Hornakova, T.; Knoops, L.; Ariola, C.; Fodale, V.; Clappier, E.; Paoloni, F.; et al. Somatically acquired JAK1 mutations in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, E.G.; Kim, M.S.; Nam, H.K.; Min, C.K.; Lee, S.; Chung, Y.J.; Yoo, N.J.; Lee, S.H. Somatic Mutations of JAK1 and JAK3 in Acute Leukemias and Solid Cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 3716–3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nebral, K.; Denk, D.M.; Attarbaschi, A.; Konig, M.; Mann, G.E.; Haas, O.A.; Strehl, S. Incidence and diversity of PAX5 fusion genes in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2008, 23, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lacronique, V.; Boureux, A.; Della Valle, V.; Poirel, H.; Quang, C.T.; Mauchauffé, M.; Berthou, C.; Lessard, M.; Berger, R.; Ghysdael, J.; et al. A TEL-JAK2 Fusion Protein with Constitutive Kinase Activity in Human Leukemia. Science 1997, 278, 1309–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reiter, A.; Walz, C.; Watmore, A.; Schoch, C.; Blau, I.; Schlegelberger, B.; Berger, U.; Telford, N.; Aruliah, S.; Yin, J.A.; et al. The t(8;9)(p22;p24) Is a Recurrent Abnormality in Chronic and Acute Leukemia that Fuses PCM1 to JAK2. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 2662–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poitras, J.L.; Cin, P.D.; Aster, J.C.; DeAngelo, D.J.; Morton, C.C. NovelSSBP2-JAK2fusion gene resulting from a t(5;9)(q14.1;p24.1) in pre-B acute lymphocytic leukemia. Genes, Chromosom. Cancer 2008, 47, 884–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, Z.; Zheng, H.; Liu, X.; Li, S.; Barber, T.D.; Gong, Z.; Gao, H.; Hao, K.; Willard, M.D.; Xu, J.; et al. Whole-genome sequencing identifies recurrent mutations in hepatocellular carcinoma. Genome Res. 2013, 23, 1422–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pilati, C.; Letouzé, E.; Nault, J.-C.; Imbeaud, S.; Boulai, A.; Calderaro, J.; Poussin, K.; Franconi, A.; Couchy, G.; Morcrette, G.; et al. Genomic Profiling of Hepatocellular Adenomas Reveals Recurrent FRK-Activating Mutations and the Mechanisms of Malignant Transformation. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 428–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lupardus, P.J.; Ultsch, M.; Wallweber, H.; Kohli, P.B.; Johnson, A.R.; Eigenbrot, C. Structure of the pseudokinase-kinase domains from protein kinase TYK2 reveals a mechanism for Janus kinase (JAK) autoinhibition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 8025–8030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waanders, E.; Scheijen, B.; Jongmans, M.C.J.; Venselaar, H.; Van Reijmersdal, S.V.; Van Dijk, A.H.A.; Pastorczak, A.; Weren, R.D.A.; Van Der Schoot, C.E.; Van De Vorst, J.M.; et al. Germline activating TYK2 mutations in pediatric patients with two primary acute lymphoblastic leukemia occurrences. Leukemia 2016, 31, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Velusamy, T.; Kiel, M.J.; Sahasrabuddhe, A.A.; Rolland, D.; Dixon, C.A.; Bailey, N.G.; Betz, B.L.; Brown, N.A.; Hristov, A.C.; Wilcox, R.A.; et al. A novel recurrent NPM1-TYK2 gene fusion in cutaneous CD30-positive lymphoproliferative disorders. Blood 2014, 124, 3768–3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koskela, H.L.M.; Eldfors, S.; Ellonen, P.; Van Adrichem, A.J.; Kuusanmäki, H.; Andersson, E.; Lagström, S.; Clemente, M.J.; Olson, T.; Jalkanen, S.E.; et al. SomaticSTAT3Mutations in Large Granular Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1905–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rajala, H.L.M.; Olson, T.; Clemente, M.J.; Lagström, S.; Ellonen, P.; Lundan, T.; Hamm, D.E.; Zaman, S.A.U.; Marti, J.M.L.; Andersson, E.I.; et al. The analysis of clonal diversity and therapy responses using STAT3 mutations as a molecular marker in large granular lymphocytic leukemia. Haematologica 2014, 100, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sim, S.H.; Kim, S.; Kim, T.M.; Jeon, Y.K.; Nam, S.J.; Ahn, Y.-O.; Keam, B.; Park, H.H.; Kim, D.-W.; Kim, C.W.; et al. Novel JAK3-Activating Mutations in Extranodal NK/T-Cell Lymphoma, Nasal Type. Am. J. Pathol. 2017, 187, 980–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pilati, C.; Amessou, M.; Bihl, M.P.; Balabaud, C.; Van Nhieu, J.T.; Paradis, V.; Nault, J.C.; Izard, T.; Bioulac-Sage, P.; Couchy, G.; et al. Somatic mutations activating STAT3 in human inflammatory hepatocellular adenomas. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 1359–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilati, C.; Zucman-Rossi, J. Mutations leading to constitutive active gp130/JAK1/STAT3 pathway. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015, 26, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchert, M.; Burns, C.J.; Ernst, M. Targeting JAK kinase in solid tumors: Emerging opportunities and challenges. Oncogene 2016, 35, 939–951. [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenblick, A.; Shriki, A.; Galun, E.; Axelrod, J.H.; Daum, H.; Rottenberg, Y.; Hamburger, T.; Mali, B.; Peretz, T. Tissue microarray-based study of patients with lymph node-positive breast cancer shows tyrosine phosphorylation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (tyrosine705-STAT3) is a marker of good prognosis. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2012, 14, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, C.; Pang, A.; Durda, D.; Cheng, H.-C.; Wang, J.H.; Fujita, D.J. Activation of Src in human breast tumor cell lines: Elevated levels of phosphotyrosine phosphatase activity that preferentially recognizes the Src carboxy terminal negative regulatory tyrosine 530. Oncogene 1999, 18, 1227–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schwarz, L.; Fox, E.M.; Balko, J.M.; Garrett, J.T.; Kuba, M.G.; Estrada, M.V.; González-Angulo, A.M.; Mills, G.B.; Red-Brewer, M.; Mayer, I.A.; et al. LYN-activating mutations mediate antiestrogen resistance in estrogen receptor–positive breast cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 5490–5502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia, R.; Bowman, T.L.; Niu, G.; Yu, H.; Minton, S.; Muro-Cacho, C.A.; Cox, C.E.; Falcone, R.; Fairclough, R.; Parsons, S.; et al. Constitutive activation of Stat3 by the Src and JAK tyrosine kinases participates in growth regulation of human breast carcinoma cells. Oncogene 2001, 20, 2499–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, Z.; Yao, Z.; Liu, S.; Tang, H.; Yan, X. An oligonucleotide decoy for Stat3 activates the immune response of macrophages to breast cancer. Immunobiology 2006, 211, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosele, F.; Stefanovska, B.; Lusque, A.; Dien, A.T.; Garberis, I.; Droin, N.; Le Tourneau, C.; Sablin, M.-P.; Lacroix, L.; Enrico, D.; et al. Outcome and molecular landscape of patients with PIK3CA-mutated metastatic breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freitag, C.E.; Mei, P.; Wei, L.; Parwani, A.V.; Li, Z. Genetic alterations and their association with clinicopathologic characteristics in advanced breast carcinomas: Focusing on clinically actionable genetic alterations. Hum. Pathol. 2020, 102, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, S.; Bourne, T.; Meier, C.; Carrington, B.; Gelinas, R.; Henry, A.; Popplewell, A.; Adams, R.; Baker, T.; Rapecki, S.; et al. Discovery and characterization of olokizumab: A humanized antibody targeting interleukin-6 and neutralizing gp130-signaling. mAbs 2014, 6, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heo, T.-H.; Wahler, J.; Suh, N. Potential therapeutic implications of IL-6/IL-6R/gp130-targeting agents in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 15460–15473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rose-John, S. Therapeutic targeting of IL-6 trans-signaling. Cytokine 2021, 144, 155577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasonov, E.; Fatenejad, S.; Feist, E.; Ivanova, M.; Korneva, E.; Krechikova, D.G.; Maslyanskiy, A.L.; Samsonov, M.; Stoilov, R.; Zonova, E.V.; et al. Olokizumab, a monoclonal antibody against interleukin 6, in combination with methotrexate in patients with rheumatoid arthritis inadequately controlled by methotrexate: Efficacy and safety results of a randomised controlled phase III study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandary, F.; Dürr, M.; Budde, K.; Doberer, K.; Reindl-Schwaighofer, R.; Waiser, J.; Wahrmann, M.; Regele, H.; Spittler, A.; Lachmann, N.; et al. Clazakizumab in late antibody-mediated rejection: Study protocol of a randomized controlled pilot trial. Trials 2019, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lacroix, M.; Rousseau, F.; Guilhot, F.; Malinge, P.; Magistrelli, G.; Herren, S.; Jones, S.A.; Jones, G.; Scheller, J.; Lissilaa, R.; et al. Novel Insights into Interleukin 6 (IL-6) Cis- and Trans-signaling Pathways by Differentially Manipulating the Assembly of the IL-6 Signaling Complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 26943–26953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Genovese, M.C.; Fleischmann, R.; Kivitz, A.; Lee, E.-B.; Van Hoogstraten, H.; Kimura, T.; John, G.S.; Mangan, E.K.; Burmester, G.R. Efficacy and safety of sarilumab in combination with csDMARDs or as monotherapy in subpopulations of patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis in three phase III randomized, controlled studies. Arthritis Res. 2020, 22, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.; Burnley, R.J.; Valenzano, C.R.; Qureshi, O.; Doyle, C.; Lumb, S.; Lopez, M.D.C.; Griffin, R.; McMillan, D.; Taylor, R.D.; et al. Discovery of a junctional epitope antibody that stabilizes IL-6 and gp80 protein: Protein interaction and modulates its downstream signaling. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 37716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scheller, J.; Chalaris, A.; Schmidt-Arras, D.; Rose-John, S. The pro- and anti-inflammatory properties of the cytokine interleukin-6. Biochim. Biophys. Mol. Cell Res. 2011, 1813, 878–888. [Google Scholar]
- Rose-John, S. The Soluble Interleukin 6 Receptor: Advanced Therapeutic Options in Inflammation. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 102, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Grande, F.; Garofalo, A.; Neamati, N.; Gu, D.; Liu, H.; Su, G.H.; Zhang, X.; Chin-Sinex, H.; Hanenberg, H.; et al. Discovery of a Novel Orally Active Small-Molecule gp130 Inhibitor for the Treatment of Ovarian Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 937–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, S.-S.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, Y.-H.; Park, K.-Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, J.; Gajulapati, V.; Goo, J.-I.; Singh, S.; et al. A Novel Small-Molecule Inhibitor Targeting the IL-6 Receptor β Subunit, Glycoprotein 130. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.W.; Marquez, C.; Sperberg, R.A.P.; Wu, J.; Bae, W.G.; Huang, P.-S.; Sweet-Cordero, E.A.; Cochran, J.R. Engineering a potent receptor superagonist or antagonist from a novel IL-6 family cytokine ligand. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 14110–14118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Xiao, H.; Lin, L.; Jou, D.; Kumari, V.; Lin, J.; Li, C. Drug Design Targeting Protein–Protein Interactions (PPIs) Using Multiple Ligand Simultaneous Docking (MLSD) and Drug Repositioning: Discovery of Raloxifene and Bazedoxifene as Novel Inhibitors of IL-6/GP130 Interface. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett-Connor, E.; Mosca, L.; Collins, P.; Geiger, M.J.; Grady, D.; Kornitzer, M.; McNabb, M.A.; Wenger, N.K. Effects of Raloxifene on Cardiovascular Events and Breast Cancer in Postmenopausal Women. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gennari, L.; Merlotti, D.; De Paola, V.; Martini, G.; Nuti, R. Bazedoxifene for the prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2008, 4, 1229–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fanning, S.W.; Jeselsohn, R.; Dharmarajan, V.; Mayne, C.G.; Karimi, M.; Buchwalter, G.; Houtman, R.; Toy, W.; Fowler, C.E.; Laine, M.; et al. The SERM/SERD Bazedoxifene Disrupts ESR1 Helix 12 to Overcome Acquired Hormone Resistance in Breast Cancer Cells. Elife 2018, 7, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardell, S.E.; Nelson, E.; Chao, C.A.; McDonnell, D.P. Bazedoxifene Exhibits Antiestrogenic Activity in Animal Models of Tamoxifen-Resistant Breast Cancer: Implications for Treatment of Advanced Disease. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2420–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Cao, Y.; Xiao, H.; Li, C.; Lin, J. Bazedoxifene as a Novel GP130 Inhibitor for Pancreatic Cancer Therapy. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 2609–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, H.; Yan, D.; Wang, Y.; Shi, W.; Liu, T.; Zhao, C.; Huo, S.; Duan, J.; Tao, J.; Zhai, M.; et al. Bazedoxifene exhibits growth suppressive activity by targeting interleukin-6/glycoprotein 130/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 950–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, H.; Bid, H.K.; Chen, X.; Wu, X.; Wei, J.; Bian, Y.; Zhao, C.; Li, H.; Li, C.; Lin, J. Repositioning Bazedoxifene as a novel IL-6/GP130 signaling antagonist for human rhabdomyosarcoma therapy. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, J.; Ma, L.; Lai, Y.-H.; Zhang, R.; Li, H.; Li, C.; Lin, J. Bazedoxifene as a novel GP130 inhibitor for Colon Cancer therapy. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeselsohn, R.; Guo, H.; Rees, R.; Barry, W.T.; Barlett, C.H.; Tung, N.M.; Krop, I.E.; Brown, M.; Winer, E.P. Abstract PD1-05: Results from the phase Ib/II clinical trial of bazedoxifene and palbociclib in hormone receptor positive metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, PD1-05. [Google Scholar]
- Song, D.; Yu, W.; Ren, Y.; Zhu, J.; Wan, C.; Cai, G.; Guo, J.; Zhang, W.; Kong, L. Discovery of bazedoxifene analogues targeting glycoprotein 130. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 199, 112375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, V.O.; Devarajan, E.; Cardó-Vila, M.; Thomas, D.G.; Kleinerman, E.S.; Marchiò, S.; Sidman, R.L.; Pasqualini, R.; Arap, W. BMTP-11 is active in preclinical models of human osteosarcoma and a candidate targeted drug for clinical translation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 8065–8070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cardó-Vila, M.; Marchio, S.; Sato, M.; Staquicini, F.I.; Smith, T.L.; Bronk, J.K.; Yin, G.; Zurita, A.J.; Sun, M.; Behrens, C.; et al. Interleukin-11 Receptor Is a Candidate Target for Ligand-Directed Therapy in Lung Cancer: Analysis of Clinical Samples and BMTP-11 Preclinical Activity. Am. J. Pathol. 2016, 186, 2162–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pasqualini, R.; Millikan, R.E.; Christianson, D.R.; Cardó-Vila, M.; Driessen, W.H.P.; Giordano, R.J.; Hajitou, A.; Hoang, A.G.; Wen, S.; Barnhart, K.F.; et al. Targeting the interleukin-11 receptor α in metastatic prostate cancer: A first-in-man study. Cancer 2015, 121, 2411–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, H.; Herrmann, A.; Reckamp, K.; Zhang, W.; Pal, S.; Hedvat, M.; Zhang, C.; Liang, W.; Scuto, A.; Weng, S.; et al. Antiangiogenic and Antimetastatic Activity of JAK Inhibitor AZD1480. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 6601–6610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hedvat, M.; Huszar, D.; Herrmann, A.; Gozgit, J.M.; Schroeder, A.; Sheehy, A.; Buettner, R.; Proia, D.; Kowolik, C.M.; Xin, H.; et al. The JAK2 Inhibitor AZD1480 Potently Blocks Stat3 Signaling and Oncogenesis in Solid Tumors. Cancer Cell 2009, 16, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tavallai, M.; Booth, L.; Roberts, J.L.; Poklepovic, A.; Dent, P. Rationally Repurposing Ruxolitinib (Jakafi®) as a Solid Tumor Therapeutic. Front. Oncol. 2016, 6, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, A.L.A.; Hirpara, J.L.; Pervaiz, S.; Eu, J.-Q.; Sethi, G.; Goh, B.-C. Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs Do STAT3 inhibitors have potential in the future for cancer therapy. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2017, 26, 883–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.T.; Liu, J.Y. Drugging the “undruggable” DNA-binding domain of STAT3. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 66324–66325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, P.; Turkson, J. Targeting STAT3 in cancer: How successful are we. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2008, 18, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, A.L.; Soo, R.A.; Tan, D.S.; Lee, S.C.; Lim, J.S.; Marban, P.C.; Kong, L.R.; Lee, Y.J.; Wang, L.Z.; Thuya, W.L.; et al. Phase I and biomarker study of OPB-51602, a novel signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) 3 inhibitor, in patients with refractory solid malignancies. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 998–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Zhou, H.; Xu, R.; Zhao, Y.; Chinnaswamy, K.; McEachern, D.; Chen, J.; Yang, C.-Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, M.; et al. A Potent and Selective Small-Molecule Degrader of STAT3 Achieves Complete Tumor Regression In Vivo. Cancer Cell 2019, 36, 498–511.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiquee, K.; Zhang, S.; Guida, W.C.; Blaskovich, M.A.; Greedy, B.; Lawrence, H.R.; Yip, M.L.R.; Jove, R.; McLaughlin, M.M.; Lawrence, N.J.; et al. Selective chemical probe inhibitor of Stat3, identified through structure-based virtual screening, induces antitumor activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7391–7396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jing, N.; Li, Y.; Xiong, W.; Sha, W.; Jing, L.; Tweardy, D.J. G-Quartet Oligonucleotides: A new class of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 inhibitors that suppresses growth of prostate and breast tumors through induction of apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 6603–6609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishdorj, G.; Johnston, J.B.; Gibson, S. Inhibition of Constitutive Activation of STAT3 by Curcurbitacin-I (JSI-124) Sensitized Human B-Leukemia Cells to Apoptosis. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 3302–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, X.; He, L.; Cao, P.; Yu, Q. Eriocalyxin B Inhibits STAT3 Signaling by Covalently Targeting STAT3 and Blocking Phosphorylation and Activation of STAT3. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zinzalla, G.; Haque, M.R.; Basu, B.P.; Anderson, J.; Kaye, S.L.; Haider, S.; Hasan, F.; Antonow, D.; Essex, S.; Rahman, K.M.; et al. A novel small-molecule inhibitor of IL-6 signalling. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 7029–7032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schust, J.; Sperl, B.; Hollis, A.; Mayer, T.; Berg, T. Stattic: A Small-Molecule Inhibitor of STAT3 Activation and Dimerization. Chem. Biol. 2006, 13, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uemura, M.; Trinh, V.A.; Haymaker, C.; Jackson, N.; Kim, D.W.; Allison, J.P.; Sharma, P.; Vence, L.; Bernatchez, C.; Hwu, P.; et al. Selective inhibition of autoimmune exacerbation while preserving the anti-tumor clinical benefit using IL-6 blockade in a patient with advanced melanoma and Crohn’s disease: A case report. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 9, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.T.; Tayar, J.; Trinh, V.A.; Suarez-Almazor, M.; Garcia, S.; Hwu, P.; Johnson, D.H.; Uemura, M.; Diab, A. Successful treatment of arthritis induced by checkpoint inhibitors with tocilizumab: A case series. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 2061–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotz, S.J.; Leino, D.; Szabo, S.; Mangino, J.L.; Turpin, B.K.; Pressey, J.G. Severe cytokine release syndrome in a patient receiving PD-1-directed therapy. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2017, 64, e26642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertucci, F.; Boudin, L.; Finetti, P.; Van Berckelaer, C.; Van Dam, P.; Dirix, L.; Viens, P.; Gonçalves, A.; Ueno, N.T.; Van Laere, S.; et al. Immune landscape of inflammatory breast cancer suggests vulnerability to immune checkpoint inhibitors. OncoImmunology 2021, 10, 1929724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christofi, T.; Baritaki, S.; Falzone, L.; Libra, M.; Zaravinos, A. Current Perspectives in Cancer Immunotherapy. Cancers 2019, 11, 1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jin, K.; Pandey, N.B.; Popel, A.S. Simultaneous blockade of IL-6 and CCL5 signaling for synergistic inhibition of triple-negative breast cancer growth and metastasis. Breast Cancer Res. 2018, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smolen, J.S.; Schoels, M.M.; Nishimoto, N.; Breedveld, F.C.; Burmester, G.R.; Dougados, M.; Emery, P.; Ferraccioli, G.; Gabay, C.; Gibofsky, A.; et al. Consensus statement on blocking the effects of interleukin-6 and in particular by interleukin-6 receptor inhibition in rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory conditions. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

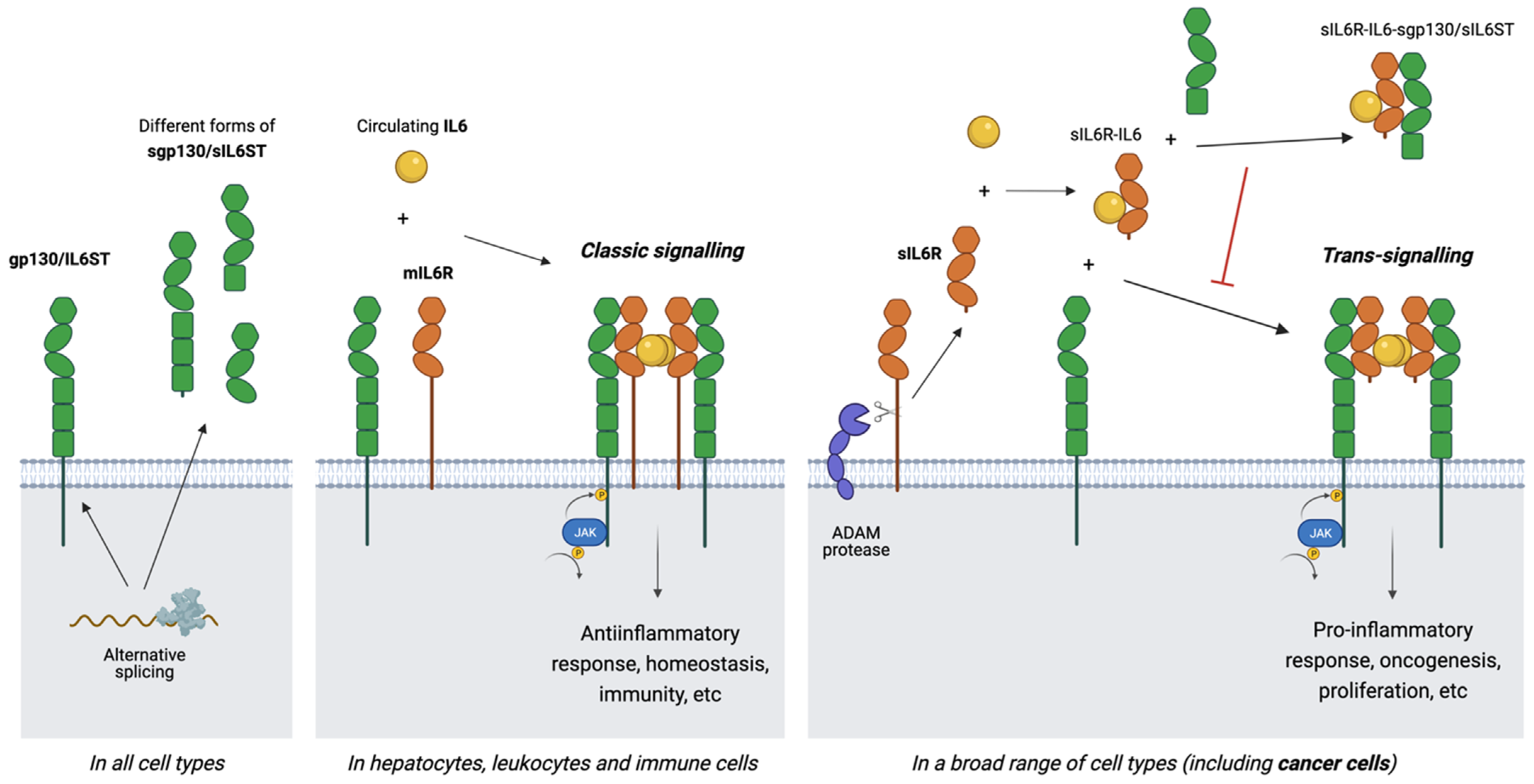
| Cytokine | Site I: Non-Signalling: Receptor | Site II: Signalling Receptor | Site III: Signalling Receptor |
|---|---|---|---|
| IL6 | IL6R (IL6R⍺) | gp130/IL6ST | gp130/IL6ST |
| IL11 | IL11R (IL11R⍺) | gp130/IL6ST | gp130/IL6ST |
| CLC | CNTFR (CNTFR⍺) | gp130/IL6ST | LIFR (LIFRβ) |
| CNTF | CNTFR (CNTFR⍺) | gp130/IL6ST | LIFR (LIFRβ) |
| CT1 | - | gp130/IL6ST | LIFR (LIFRβ) |
| LIF | - | gp130/IL6ST | LIFR (LIFRβ) |
| NPN | - | gp130/IL6ST | - |
| OSM | - | gp130/IL6ST | LIFR (LIFRβ) or OSMR (OSMRβ) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martínez-Pérez, C.; Kay, C.; Meehan, J.; Gray, M.; Dixon, J.M.; Turnbull, A.K. The IL6-like Cytokine Family: Role and Biomarker Potential in Breast Cancer. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11111073
Martínez-Pérez C, Kay C, Meehan J, Gray M, Dixon JM, Turnbull AK. The IL6-like Cytokine Family: Role and Biomarker Potential in Breast Cancer. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(11):1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11111073
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartínez-Pérez, Carlos, Charlene Kay, James Meehan, Mark Gray, J. Michael Dixon, and Arran K. Turnbull. 2021. "The IL6-like Cytokine Family: Role and Biomarker Potential in Breast Cancer" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 11: 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11111073
APA StyleMartínez-Pérez, C., Kay, C., Meehan, J., Gray, M., Dixon, J. M., & Turnbull, A. K. (2021). The IL6-like Cytokine Family: Role and Biomarker Potential in Breast Cancer. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(11), 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11111073










