Effect of Nephrology Care on Mortality in Incident Dialysis Patients: A Population-Based Cohort Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
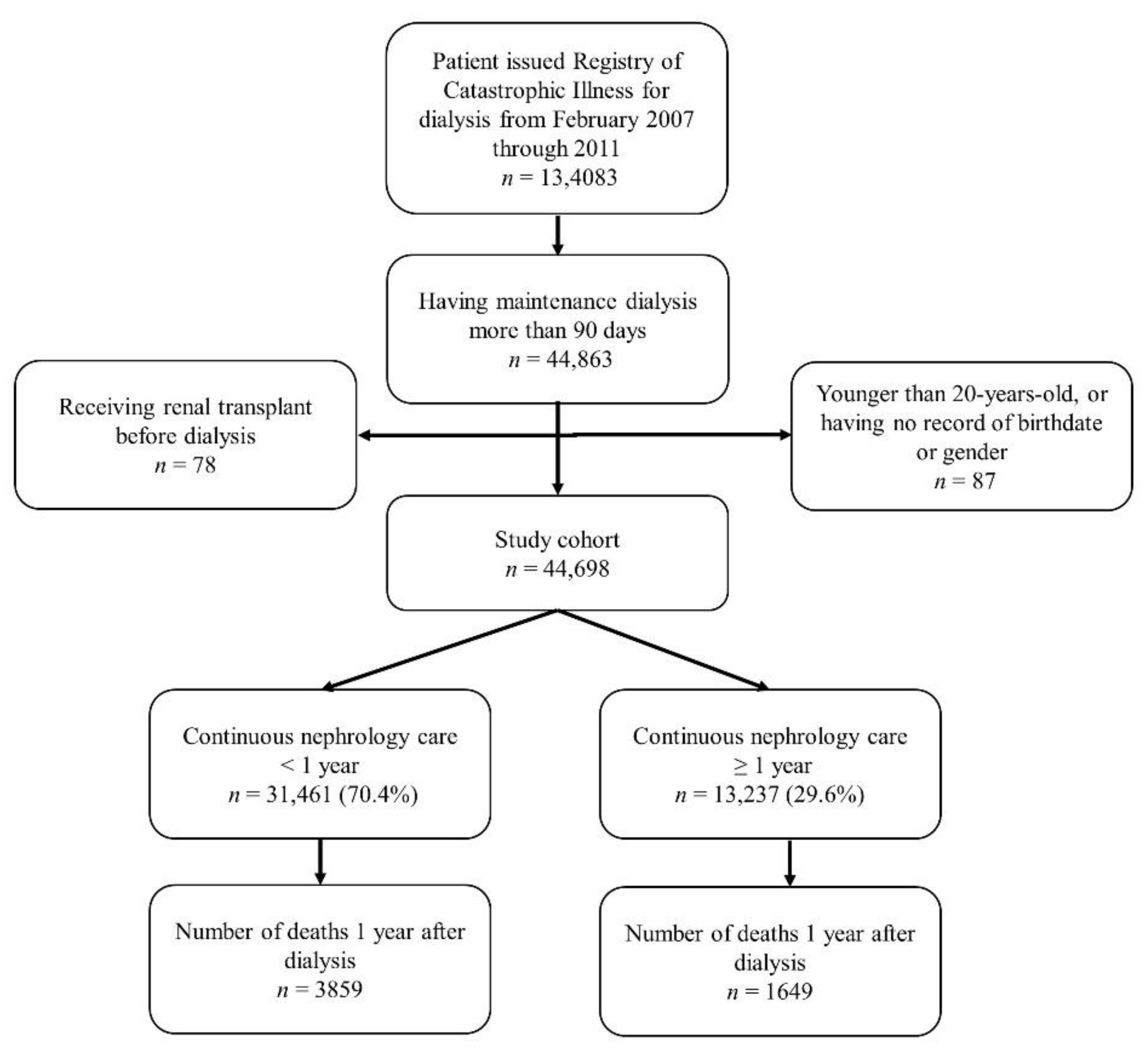
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Nephrology Care
2.3. Comorbidity Assessment
2.4. Death and Other Covariates
2.5. Statistical Analysis
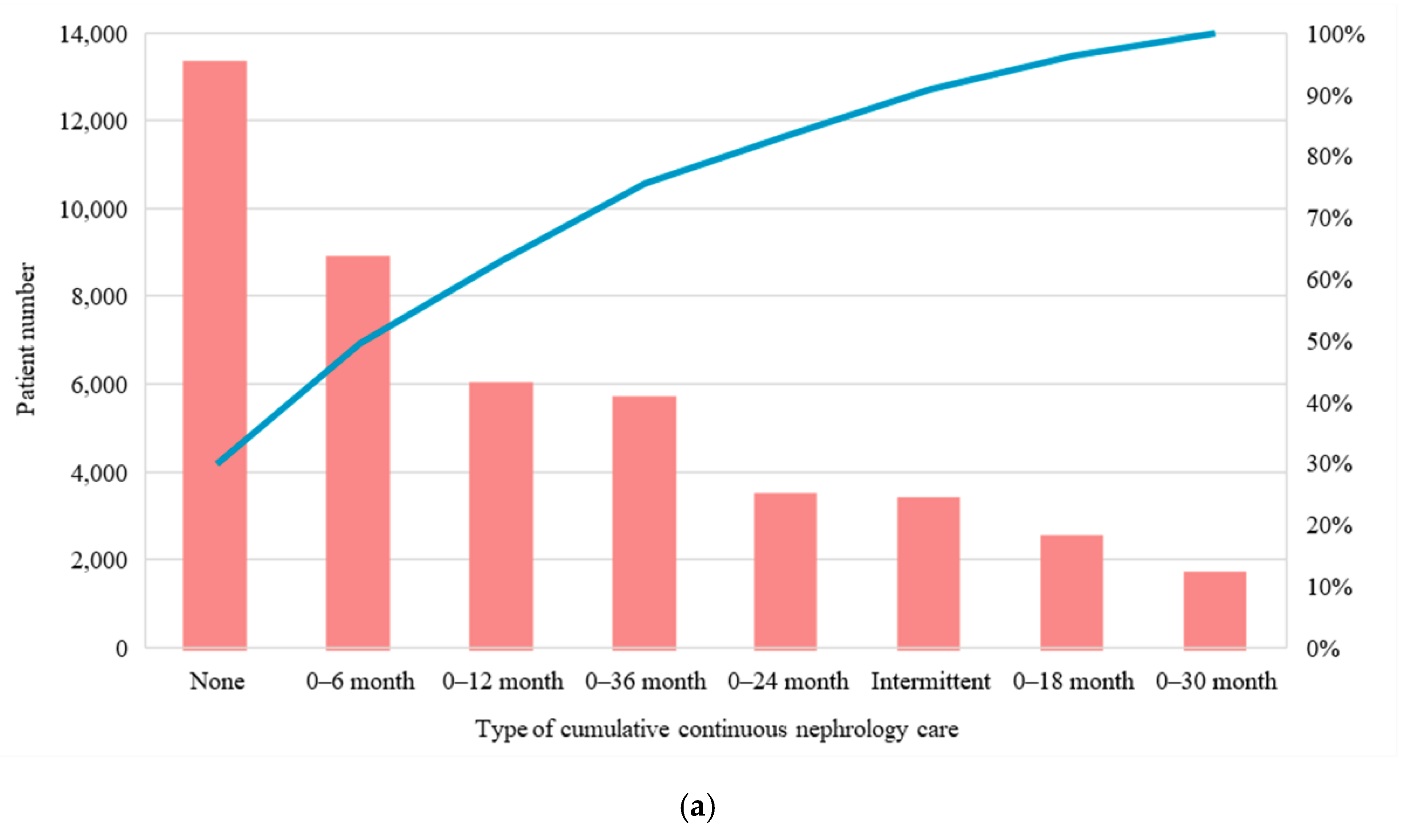
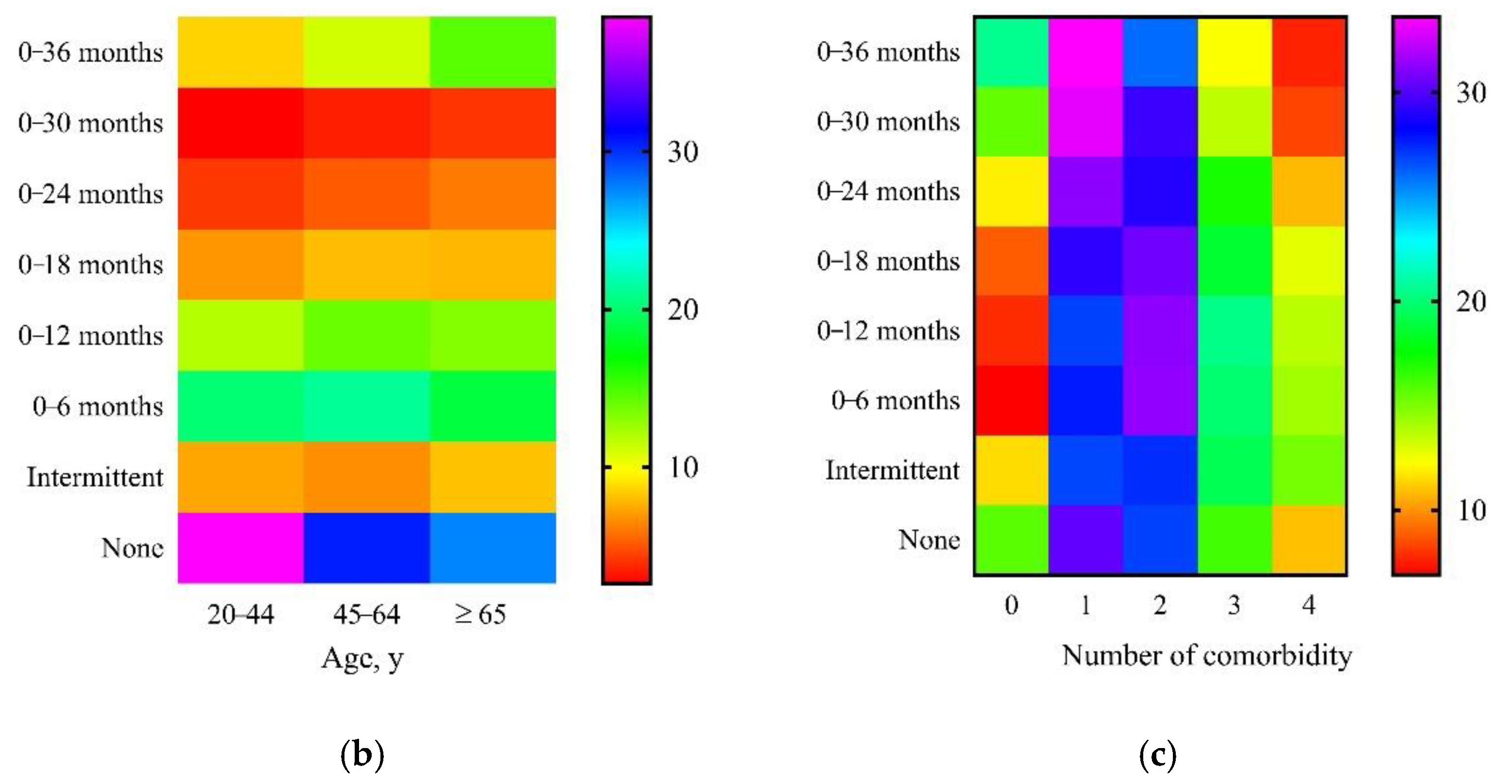
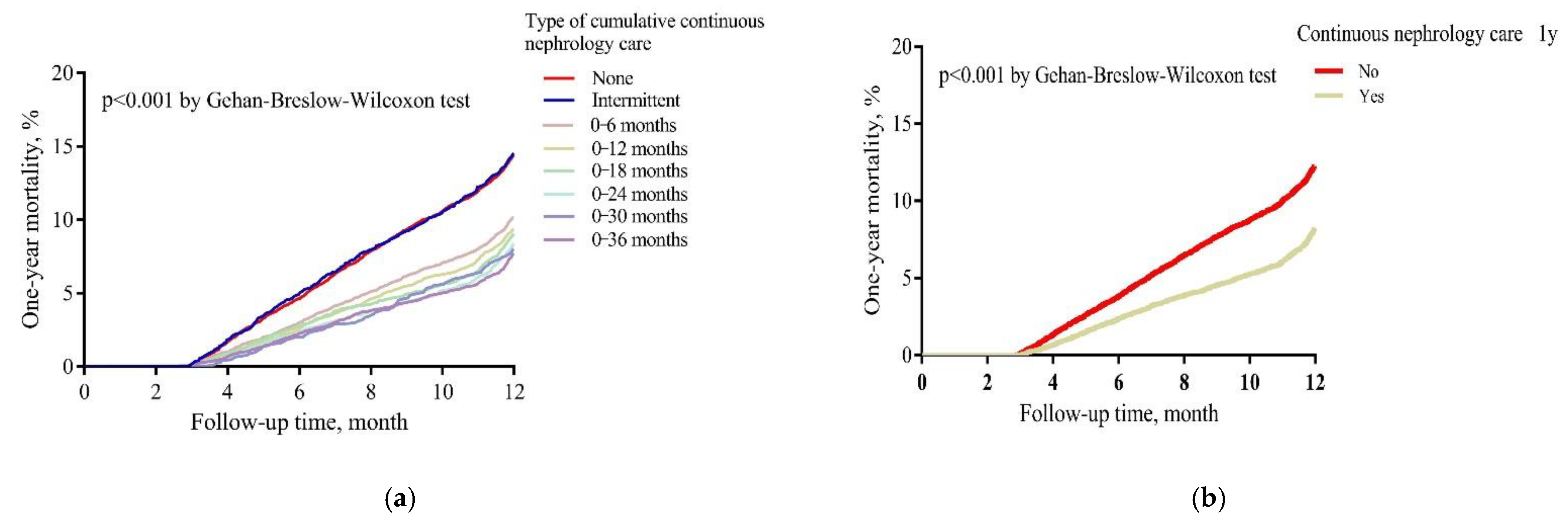
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Comorbidity and Nephrology Care
3.3. Distribution and Nephrology Care
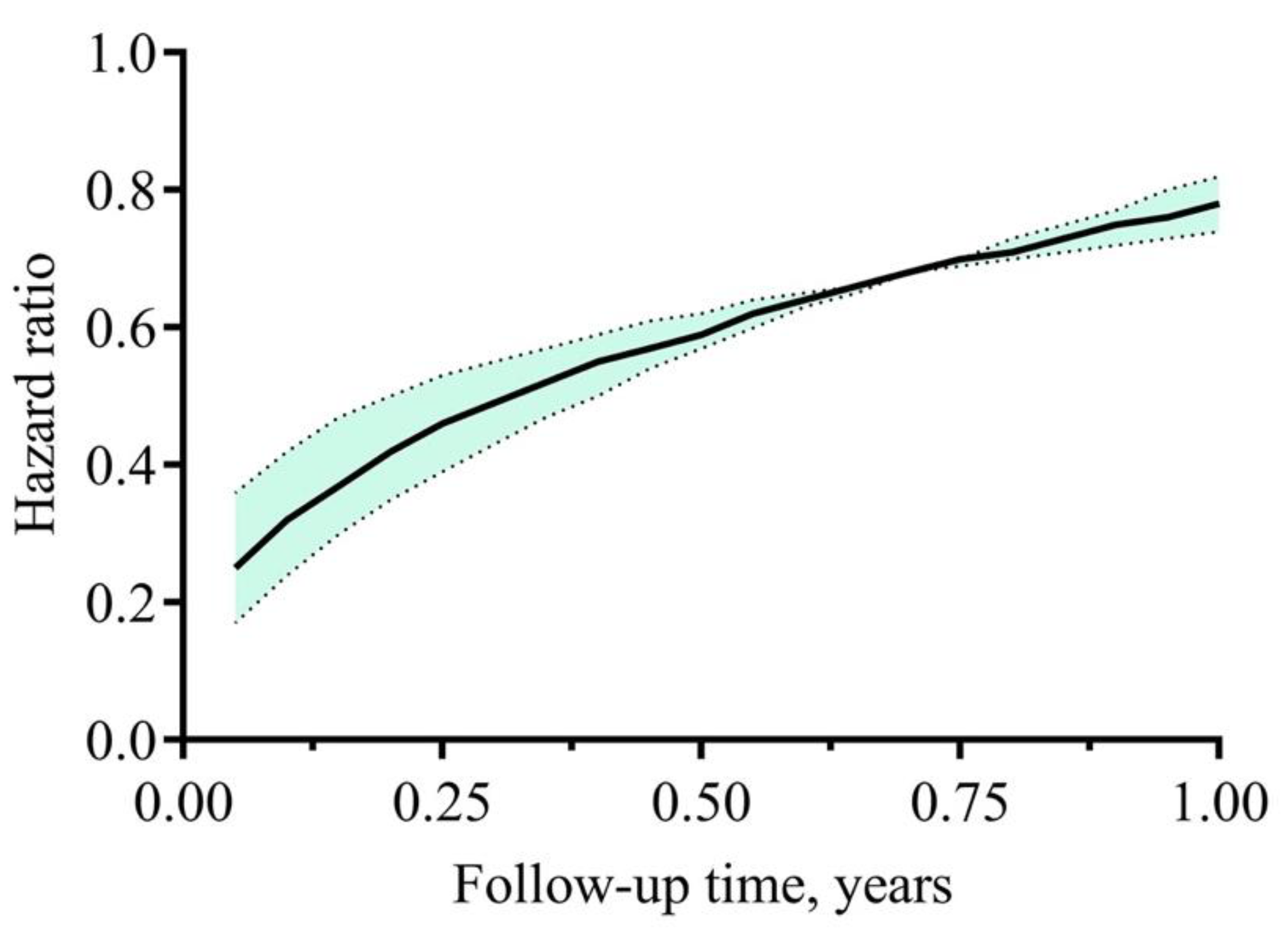
3.4. Nephrology Care and Mortality
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jager, K.J.; Kovesdy, C.; Langham, R.; Rosenberg, M.; Jha, V.; Zoccali, C. A single number for advocacy and communication-worldwide more than 850 million individuals have kidney diseases. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2019, 34, 1803–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ku, E.; Lee, B.J.; Wei, J.; Weir, M.R. Hypertension in CKD: Core Curriculum 2019. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2019, 74, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Boer, I.H.; Rue, T.C.; Hall, Y.N.; Heagerty, P.J.; Weiss, N.S.; Himmelfarb, J. Temporal trends in the prevalence of diabetic kidney disease in the United States. JAMA 2011, 305, 2532–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.-Y.; Lee, C.T.-C.; Kuo, M.-C.; Hwang, S.-J.; Chen, H.-C.; Chiu, Y.-W. Effects of physician's specialty on regular chronic kidney disease care in predialysis: A population-based cross-sectional study. Medicine 2018, 97, e11317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, A.C.; Nagler, E.V.; Morton, R.L.; Masson, P. Chronic kidney disease. Lancet 2017, 389, 1238–1252. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.-Y.; Huang, J.-W.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Pai, M.-F.; Tung, K.-T.; Peng, Y.-S.; Hung, K.-Y. Frequency of early predialysis nephrology care and postdialysis cardiovascular events. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2017, 70, 164–172. [Google Scholar]
- Singhal, R.; Hux, J.E.; Alibhai, S.M.; Oliver, M.J. Inadequate predialysis care and mortality after initiation of renal replacement therapy. Kidney Int. 2014, 86, 399–406. [Google Scholar]
- Roubicek, C.; Brunet, P.; Huiart, L.; Thirion, X.; Leonetti, F.; Dussol, B.; Jaber, K.; Andrieu, D.; Ramananarivo, P.; Berland, Y. Timing of nephrology referral: Influence on mortality and morbidity. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2000, 36, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rognant, N.; Laville, M. Early mortality in dialysis and adequacy of predialysis renal care: The picture is more complex than we thought. Kidney Int. 2014, 86, 238–240. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Levin, A.; Stevens, P.E. Summary of KDIGO 2012 CKD Guideline: Behind the scenes, need for guidance, and a framework for moving forward. Kidney Int. 2014, 85, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsieh, C.-Y.; Su, C.-C.; Shao, S.-C.; Sung, S.-F.; Lin, S.-J.; Yang, Y.-H.K.; Lai, E.C.-C. Taiwan’s National Health Insurance Research Database: Past and future. Clin. Epidemiol. 2019, 11, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, L.-Y.; Warren-Gash, C.; Smeeth, L.; Chen, P.-C. Data resource profile: The National Health Insurance Research Database (NHIRD). Epidemiol. Health 2018, 40, e2018062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonelli, M.; Wiebe, N.; Fortin, M.; Guthrie, B.; Hemmelgarn, B.R.; James, M.T.; Klarenbach, S.W.; Lewanczuk, R.; Manns, B.J.; Ronksley, P. Methods for identifying 30 chronic conditions: Application to administrative data. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2015, 15, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Piette, J.D.; Kerr, E.A. The impact of comorbid chronic conditions on diabetes care. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Redelmeier, D.A.; Tan, S.H.; Booth, G.L. The treatment of unrelated disorders in patients with chronic medical diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 338, 1516–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonelli, M.; Wiebe, N.; Guthrie, B.; James, M.T.; Quan, H.; Fortin, M.; Klarenbach, S.W.; Sargious, P.; Straus, S.; Lewanczuk, R. Comorbidity as a driver of adverse outcomes in people with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2015, 88, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deyo, R.A.; Cherkin, D.C.; Ciol, M.A. Adapting a clinical comorbidity index for use with ICD-9-CM administrative databases. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1992, 45, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridgeway, G.; McCaffrey, D.; Morral, A.; Burgette, L.; Griffin, B.A. Toolkit for Weighting and Analysis of Nonequivalent Groups: A Tutorial for the Twang Package; RAND Corporation: Santa Monica, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Quinn, R.R.; Karim, M.E.; Bello, A.; Tam-Tham, H.; Weaver, R.; Ronksley, P.E.; Quan, H.; Strippoli, G.F.; Manns, B. Nephrology consultation and mortality in people with stage 4 chronic kidney disease: A population-based study. CMAJ 2019, 191, E274–E282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, P.; Quinn, R.R.; Cortese, G.; Mahsin, M.; James, M.T.; Ronksley, P.E.; Quan, H.; Manns, B.; Hemmelgarn, B.R.; Tonelli, M. Nephrology consultation and kidney failure in people with stage 4 chronic kidney disease: A population-based cohort study. J. Nephrol. 2021, 34, 1225–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, P.C. An introduction to propensity score methods for reducing the effects of confounding in observational studies. Multivar. Behav. Res. 2011, 46, 399–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Levin, A.; Stevens, P.E.; Bilous, R.W.; Coresh, J.; De Francisco, A.L.M.; De Jong, P.E.; Griffith, K.E.; Hemmelgarn, B.R.; Iseki, K.; Lamb, E. J Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2013, 3, 1–150. [Google Scholar]
- Iwata, Y.; Okushima, H.; Takatsuka, T.; Yoshimura, D.; Kawamura, T.; Iio, R.; Ueda, Y.; Shoji, T.; Hayashi, T.; Isaka, Y. Duration of predialysis nephrological care and mortality after dialysis initiation. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2020, 24, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Salman, B.; Tahir, M.; Qureshi, R.; Dhrolia, M.F.; Ahmad, A.; Imtiaz, S. Factor causing late referral of CKD patients to nephrology care. Arch. Ren. Dis. Manag. 2017, 3, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Before PS Matched | p-Value | After PS Matched | Standardized Difference | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | Continuous Nephrology Care ≥ 1 Year | Continuous Nephrology Care ≥ 1 Year | |||||
| No | Yes | No | Yes | ||||
| N | 44,698 | 31,461 (70.4) | 13,237 (29.6) | 13,193 | 13,193 | ||
| Age, year | 63.3 ± 14.2 | 62.7 ± 14.5 | 64.8 ± 13.3 | <0.001 | 65.0 ± 14.2 | 64.9 ± 13.4 | −0.01 |
| Female sex | 21,509 (48.1) | 14,467 (46.0) | 7042 (53.2) | <0.001 | 7017 (53.2) | 7017 (53.2) | 0.0 |
| Geographical region | <0.001 | - | |||||
| North | 19,464 (43.6) | 13,586 (43.2) | 5878 (44.4) | 5927 (44.9) | 5860 (44.4) | ||
| Central | 9850 (22.0) | 6978 (22.2) | 2872 (21.7) | 2905 (22.0) | 2862 (21.7) | ||
| South | 13,943 (31.2) | 9818 (31.2) | 4125 (31.2) | 4003 (30.3) | 4109 (30.2) | ||
| East | 1441 (3.2) | 1079 (3.4) | 362 (2.7) | 358 (2.7) | 362 (2.7) | ||
| Urbanization level | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||
| Rural | 12,642 (28.3) | 9214 (29.3) | 3428 (25.9) | 3394 (25.7) | 3423 (26.0) | ||
| Urban | 32,056 (71.7) | 22,247 (70.7) | 9809 (74.1) | 9799 (74.3) | 9770 (74.1) | ||
| Premium income, NTD | <0.001 | - | |||||
| Dependent | 15,820 (35.4) | 10,956 (34.8) | 4864 (36.7) | 4832 (36.6) | 4849 (36.8) | ||
| <20,000 | 9837 (22.0) | 7338 (23.3) | 2499 (18.9) | 2434 (18.5) | 2497 (18.9) | ||
| 20,000–39,999 | 16,556 (37.0) | 11,607 (36.9) | 4949 (37.4) | 5049 (38.3) | 4,937 (37.4) | ||
| ≥40,000 | 2485 (5.6) | 1560 (5.0) | 925 (7.0) | 878 (6.7) | 910 (6.9) | ||
| Charlson index | <0.001 | - | |||||
| 0 | 3168 (7.1) | 2852 (9.1) | 316 (2.4) | 320 (2.4) | 316 (2.4) | ||
| 1–2 | 15,061 (33.7) | 9995 (31.8) | 5066 (38.3) | 5098 (38.6) | 5051 (38.3) | ||
| 3–4 | 16,149 (36.1) | 11,209 (35.6) | 4940 (37.3) | 4824 (36.6) | 4921 (37.3) | ||
| 5–6 | 8737 (19.6) | 6250 (19.9) | 2487 (18.8) | 2510 (19.0) | 2478 (18.8) | ||
| ≥7 | 1583 (3.5) | 1155 (3.7) | 428 (3.2) | 441 (3.3) | 427 (3.2) | ||
| Confounding drugs | |||||||
| Anticoagulation agents | 626 (1.4) | 450 (1.4) | 176 (1.3) | 0.41 | 165 (1.25) | 175 (1.33) | −0.01 |
| Antiplatelet agents | 3893 (8.7) | 2767 (8.8) | 1126 (8.5) | 0.32 | 1055 (8.0) | 1117 (8.5) | −0.02 |
| Antidiabetic agents | 16,770 (37.5) | 12,721 (40.4) | 4049 (30.6) | <0.001 | 4102 (31.1) | 4048 (30.7) | 0.01 |
| Insulin | 7028 (15.7) | 5015 (15.9) | 2013 (15.2) | 0.05 | 1985 (15.1) | 2010 (15.2) | −0.01 |
| Steroid | 2730 (6.1) | 1531 (4.9) | 1199 (9.1) | <0.001 | 995 (7.5) | 1161 (8.8) | −0.05 |
| NSAIDs | 3846 (8.6) | 2915 (9.3) | 931 (7.0) | <0.001 | 930 (7.1) | 931 (7.1) | <0.001 |
| Before PS Matched | After PS Matched | Standardized Difference | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | Continuous Nephrology Care ≥ 1 Year | p-Value | Continuous Nephrology Care ≥ 1 Year | ||||
| No | Yes | No | Yes | ||||
| N | 44,698 | 31,461 (70.4) | 13,237 (29.6) | 13,193 | 13,193 | ||
| Concordant comorbidities a | |||||||
| Atrial fibrillation | 238 (0.5) | 159 (0.5) | 79 (0.6) | 0.23 | 72 (0.5) | 79 (0.6) | −0.01 |
| Chronic heart failure | 6444 (14.4) | 5177 (16.5) | 1267 (9.6) | <0.001 | 1283 (9.7) | 1267 (9.6) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes | 21,668 (48.5) | 16,166 (51.4) | 5502 (41.6) | <0.001 | 5546 (42.0) | 5498 (41.7) | 0.01 |
| Hypertension | 23,643 (52.9) | 16,971 (53.9) | 6672 (50.4) | <0.001 | 6778 (51.4) | 6655 (50.4) | 0.02 |
| Peripheral vascular disease | 100 (0.2) | 75 (0.2) | 25 (0.2) | 0.31 | 24 (0.2) | 25 (0.2) | <0.001 |
| Stroke or TIA | 4857 (10.9) | 3780 (12.0) | 1,077 (8.1) | <0.001 | 1102 (8.4) | 1077 (8.2) | 0.01 |
| Discordant comorbidities a | |||||||
| Asthma | 779 (1.7) | 582 (1.9) | 197 (1.5) | 0.007 | 184 (1.4) | 197 (1.5) | −0.01 |
| Cancer, lymphoma | 97 (0.2) | 70 (0.2) | 27 (0.2) | 0.7 | 22 (0.2) | 27 (0.2) | −0.01 |
| Cancer, metastatic | 79 (0.2) | 57 (0.2) | 22 (0.2) | 0.73 | 19 (0.1) | 22 (0.2) | −0.01 |
| Cancer, non-metastatic | 1108 (2.5) | 713 (2.3) | 395 (3.0) | <0.001 | 376 (2.9) | 392 (3.0) | −0.01 |
| Chronic pulmonary disease | 2401 (5.4) | 1727 (5.5) | 674 (5.1) | 0.09 | 611 (4.6) | 670 (5.1) | −0.02 |
| Constipation, severe | 2062 (4.6) | 1441 (4.6) | 621 (4.7) | 0.6 | 604 (4.6) | 620 (4.7) | −0.01 |
| Dementia | 890 (2.0) | 624 (2.0) | 266 (2.0) | 0.86 | 267 (2.0) | 266 (2.0) | <0.001 |
| Inflammatory bowel disease | 245 (0.6) | 177 (0.6) | 68 (0.5) | 0.52 | 60 (0.5) | 68 (0.5) | −0.01 |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | 828 (1.9) | 582 (1.9) | 246 (1.9) | 0.95 | 233 (1.8) | 246 (1.9) | −0.01 |
| Mental disease and chronic pain a | |||||||
| Alcohol misuse | 169 (0.4) | 155 (0.5) | 14(0.1) | <0.001 | 14 (0.1) | 14 (0.1) | <0.001 |
| Chronic pain | 11,711 (26.2) | 8161 (25.9) | 3550 (26.8) | 0.05 | 3487 (26.4) | 3536 (26.8) | −0.01 |
| Depression | 923 (2.1) | 587 (1.9) | 336 (2.5) | <0.001 | 305 (2.3) | 329 (2.5) | −0.01 |
| Schizophrenia | 175 (0.4) | 137 (0.4) | 38 (0.3) | 0.02 | 32 (0.2) | 38 (0.3) | −0.01 |
| Other comorbidities a | |||||||
| Chronic hepatitis B | 513 (1.2) | 339 (1.1) | 174 (1.3) | 0.03 | 162(1.2) | 170 (1.3) | −0.01 |
| Cirrhosis | 924 (2.1) | 698 (2.2) | 226 (1.7) | <0.001 | 211 (1.6) | 225 (1.7) | −0.01 |
| Epilepsy | 187 (0.4) | 130 (0.4) | 57 (0.4) | 0.8 | 56 (0.4) | 57 (0.4) | <0.001 |
| Hypothyroidism | 210 (0.5) | 130 (0.4) | 80 (0.6) | 0.007 | 67 (0.5) | 78 (0.6) | −0.01 |
| Irritable bowel syndrome | 510 (1.1) | 332 (1.1) | 178 (1.3) | 0.009 | 173 (1.3) | 176 (1.3) | <0.001 |
| Multiple sclerosis | 62 (0.1) | 45 (0.1) | 17 (0.1) | 0.70 | 18 (0.1) | 17 (0.1) | <0.001 |
| Myocardial infarction | 1045 (2.3) | 861 (2.7) | 184 (1.4) | <0.001 | 186 (1.4) | 184 (1.4) | <0.001 |
| Parkinson’s disease | 531 (1.2) | 357 (1.13) | 174 (1.3) | 0.11 | 172 (1.3) | 174 (1.3) | <0.001 |
| Peptic ulcer disease | 3103 (6.9) | 2072 (6.6) | 1031 (7.8) | <0.001 | 967 (7.3) | 1023 (7.8) | −0.02 |
| Psoriasis | 258 (0.6) | 168 (0.5) | 90 (0.7) | 0.06 | 79 (0.6) | 87 (0.7) | −0.01 |
| Time Window before Dialysis, Month | Consistent Nephrology Care | Case, n | Number of Death, n | Follow-Up Time, Person-Years | Mortality Rate (95% CI), per 1000 Patient-Years | PS-Matching HR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–6 | No | 16,636 | 2401 | 15,765 | 152.3 (146.3–158.5) | 1.00 [reference] |
| Yes | 28,062 | 2546 | 27,228 | 93.5 (89.9–97.2) | 0.79 (0.75–0.83) | |
| 0–12 | No | 25,478 | 3298 | 24,303 | 135.7 (131.2–140.4) | 1.00 [reference] |
| Yes | 19,220 | 1649 | 18,691 | 88.2 (84.1–92.6) | 0.78 (0.74–0.82) | |
| 0–18 | No | 31,461 | 3859 | 30,102 | 128.2 (124.2–132.3) | 1.00 [reference] |
| Yes | 13,237 | 1088 | 12,892 | 84.4 (79.5–89.6) | 0.78 (0.74–0.82) | |
| 0–24 | No | 34,918 | 4172 | 33,458 | 124.7 (121.0–128.5) | 1.00 [reference] |
| Yes | 9780 | 775 | 9535 | 81.3 (75.8–87.2) | 0.78 (0.73–0.83) | |
| 0–30 | No | 37,390 | 4379 | 35,867 | 122.1 (118.5–125.8) | 1.00 [reference] |
| Yes | 7308 | 568 | 7126 | 79.7 (73.4–86.5) | 0.80 (0.74–0.86) | |
| 0–36 | No | 39,050 | 4512 | 37,485 | 120.4 (116.9–123.9) | 1.00 [reference] |
| Yes | 5648 | 435 | 5508 | 79.0 (71.9–86.8) | 0.77 (071–0.84) |
| Type of Continuous Nephrology Care | Case, n | Number of Deaths, n | Follow-Up Time, Person-Year | Mortality Rate (95% CI), per 1000 Patient-Years | Weighted HR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| None | 13,297 | 1916 | 12,595 | 152.1 (145.5–159.1) | 1.00 [reference] |
| Intermittent | 3339 | 485 | 3160 | 153.5 (140.4–167.8) | 0.88 (0.79–0.97) |
| 0–6 month | 8842 | 897 | 8531 | 105.1 (98.5–112.3) | 0.65 (0.60–0.71) |
| 0–12 month | 5983 | 561 | 5795 | 96.8 (89.1–105.2) | 0.60 (0.54–0.66) |
| 0–18 month | 3457 | 313 | 3354 | 93.3 (83.5–104.3) | 0.60 (0.52–0.69) |
| 0–24 month | 2472 | 207 | 2407 | 86.0 (75.1–98.6) | 0.48 (0.41–0.57) |
| 0–30 month | 1660 | 133 | 1617 | 82.3 (69.4–97.5) | 0.50 (0.41–0.60) |
| 0–36 month | 5648 | 435 | 5504 | 79.0 (71.9–86.8) | 0.52 (0.46–0.59) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chung, C.-Y.; Wu, P.-H.; Chiu, Y.-W.; Hwang, S.-J.; Lin, M.-Y. Effect of Nephrology Care on Mortality in Incident Dialysis Patients: A Population-Based Cohort Study. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11111071
Chung C-Y, Wu P-H, Chiu Y-W, Hwang S-J, Lin M-Y. Effect of Nephrology Care on Mortality in Incident Dialysis Patients: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(11):1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11111071
Chicago/Turabian StyleChung, Cheng-Yin, Ping-Hsun Wu, Yi-Wen Chiu, Shang-Jyh Hwang, and Ming-Yen Lin. 2021. "Effect of Nephrology Care on Mortality in Incident Dialysis Patients: A Population-Based Cohort Study" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 11: 1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11111071
APA StyleChung, C.-Y., Wu, P.-H., Chiu, Y.-W., Hwang, S.-J., & Lin, M.-Y. (2021). Effect of Nephrology Care on Mortality in Incident Dialysis Patients: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(11), 1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11111071








