Impact of Updating Pharmacogenetic Results: Lessons Learned from the PREDICT Program
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. Setting
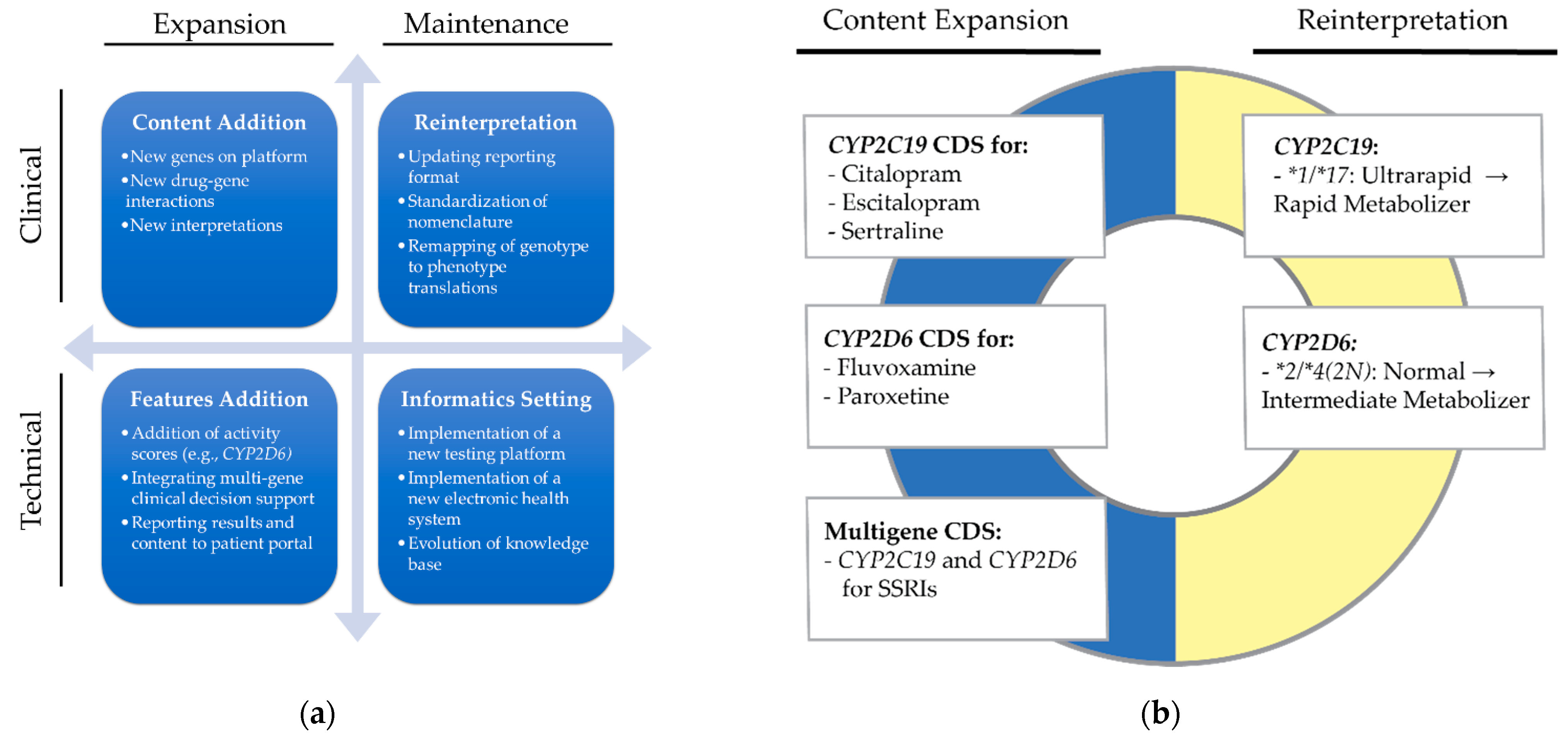
2.2. Definitions
2.3. Objective
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Environment
3.2. Initiation of Reprocessing
3.3. Automated Processes
3.4. Manual Processes
3.5. Organization Resources and Governance
3.6. Data Collection
4. Results
4.1. Reprocessing Timeline
4.2. Patient Cohort
4.3. Impact
4.3.1. Actionable PGx Interpretations
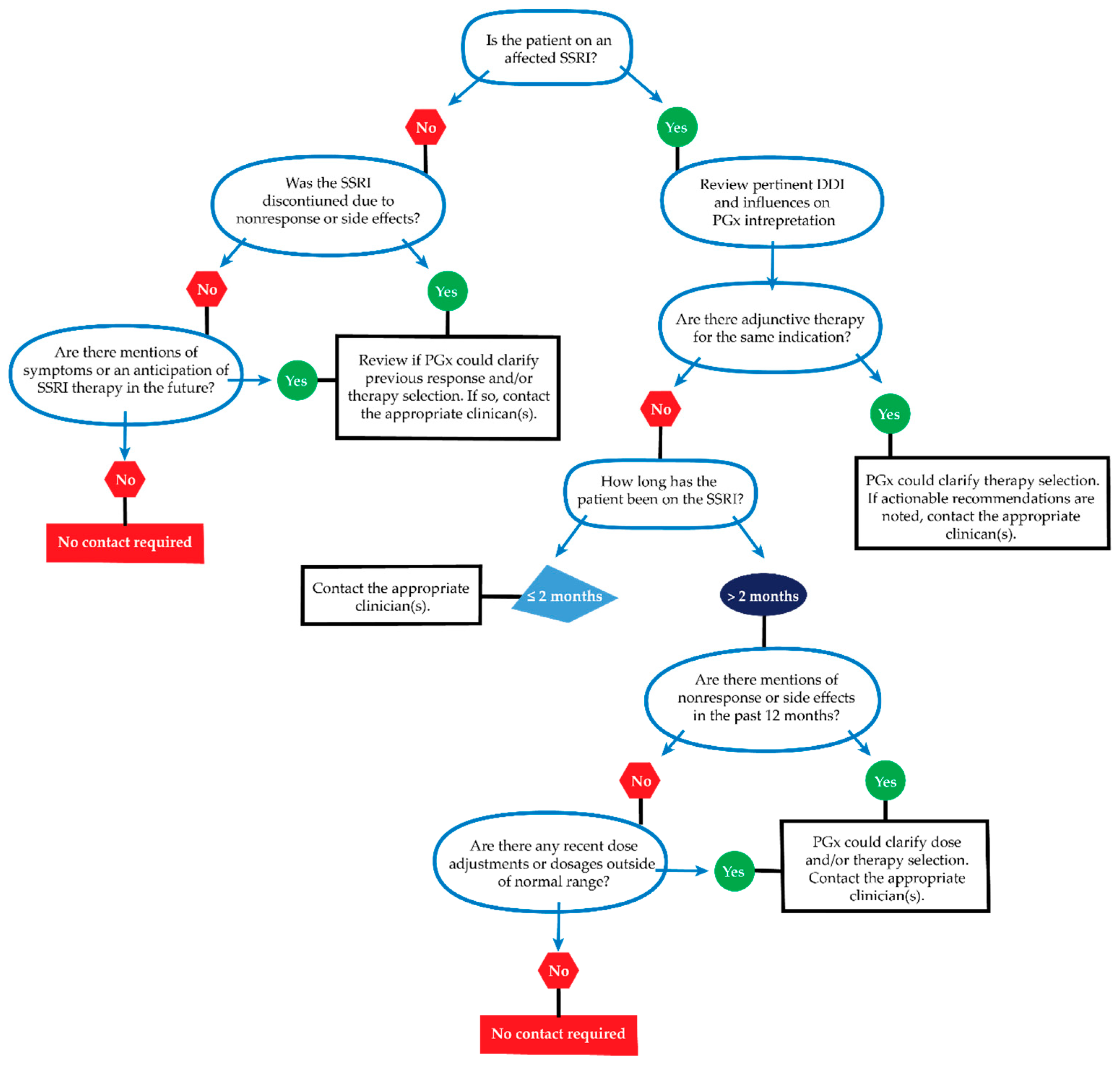
4.3.2. Clinician Contact for New Actionable Recommendations
4.3.3. Patient and Provider Notification
4.3.4. Clinical Decision Support
5. Discussion
5.1. Benefits of Reprocessing
5.2. Lessons Learned
5.3. Feasibility and Responsibility
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yoon, D.Y.; Lee, S.; Ban, M.S.; Jang, I.-J.; Lee, S. Pharmacogenomic information from CPIC and DPWG guidelines and its application on drug labels. Transl. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 28, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, B.Q.; Arwood, M.J.; Hicks, J.K.; Beitelshees, A.L.; Franchi, F.; Houder, J.T.; Limdi, N.A.; Cook, K.J.; Obeng, A.O.; Petry, N.; et al. Development of Customizable Implementation Guides to Support Clinical Adoption of Pharmacogenomics: Experiences of the Implementing GeNomics In pracTicE (IGNITE) Network. Pharm. Pers. Med. 2020, 13, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blagec, K.; Koopmann, R.; Crommentuijn-van Rhenen, M.; Holsappel, I.; van der Wouden, C.H.; Konta, L.; Xu, H.; Steinberger, D.; Just, E.; Swen, J.J.; et al. Implementing pharmacogenomics decision support across seven European countries: The Ubiquitous Pharmacogenomics (U-PGx) project. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2018, 25, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavallari, L.H.; Weitzel, K.W.; Elsey, A.R.; Liu, X.; Mosley, S.A.; Smith, D.M.; Staley, B.J.; Winterstein, A.G.; Mathews, C.A.; Franchi, F.; et al. Institutional profile: University of Florida Health Personalized Medicine Program. Pharmacogenomics 2017, 18, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, S.A.; Owusu Obeng, A.; Botton, M.R.; Yang, Y.; Scott, E.R.; Ellis, S.B.; Wallsten, R.; Kaszemacher, T.; Zhou, X.; Chen, R.; et al. Institutional profile: Translational pharmacogenomics at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. Pharmacogenomics 2017, 18, 1381–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, J.K.; Stowe, D.; Willner, M.A.; Wai, M.; Daly, T.; Gordon, S.M.; Lashner, B.A.; Parikh, S.; White, R.; Teng, K.; et al. Implementation of Clinical Pharmacogenomics within a Large Health System: From Electronic Health Record Decision Support to Consultation Services. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2016, 36, 940–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunnenberger, H.M.; Biszewski, M.; Bell, G.C.; Sereika, A.; May, H.; Johnson, S.G.; Hulick, P.J.; Khandekar, J. Implementation of a multidisciplinary pharmacogenomics clinic in a community health system. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2016, 73, 1956–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, G.; Weinshilboum, R.M. Challenges in implementing genomic medicine: The Mayo Clinic Center for Individualized Medicine. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 94, 204–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Petry, N.; Baye, J.; Aifaoui, A.; Wilke, R.A.; Lupu, R.A.; Savageau, J.; Gapp, B.; Massmann, A.; Hahn, D.; Hajek, C.; et al. Implementation of wide-scale pharmacogenetic testing in primary care. Pharmacogenomics 2019, 20, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krumm, N.; Shirts, B.H. Technical, Biological, and Systems Barriers for Molecular Clinical Decision Support. Clin. Lab. Med. 2019, 39, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, B.M.; Eilbeck, K.; Fiol, G.D.; Meyer, L.J.; Kawamoto, K. Technical desiderata for the integration of genomic data with clinical decision support. J. Biomed. Inform. 2014, 51, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pulley, J.M.; Denny, J.C.; Peterson, J.F.; Bernard, G.R.; Vnencak-Jones, C.L.; Ramirez, A.H.; Delaney, J.T.; Bowton, E.; Brothers, K.; Johnson, K.; et al. Operational implementation of prospective genotyping for personalized medicine: The design of the Vanderbilt PREDICT project. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 92, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Vnencak-Jones, C.L.; Roland, B.P.; Gatto, C.L.; Mathe, J.L.; Just, S.L.; Peterson, J.F.; Van Driest, S.L.; Weitkamp, A.O. A Tutorial for Pharmacogenomics Implementation Through End-to-End Clinical Decision Support Based on Ten Years of Experience from PREDICT. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 109, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caudle, K.E.; Klein, T.E.; Hoffman, J.M.; Muller, D.J.; Whirl-Carrillo, M.; Gong, L.; McDonagh, E.M.; Sangkuhl, K.; Thorn, C.F.; Schwab, M.; et al. Incorporation of pharmacogenomics into routine clinical practice: The Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) guideline development process. Curr. Drug Metab. 2014, 15, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scott, S.A.; Sangkuhl, K.; Shuldiner, A.R.; Hulot, J.S.; Thorn, C.F.; Altman, R.B.; Klein, T.E. PharmGKB summary: Very important pharmacogene information for cytochrome P450, family 2, subfamily C, polypeptide 19. Pharm. Genom. 2012, 22, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hicks, J.K.; Bishop, J.R.; Sangkuhl, K.; Müller, D.J.; Ji, Y.; Leckband, S.G.; Leeder, J.S.; Graham, R.L.; Chiulli, D.L.; LLerena, A.; et al. Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 Genotypes and Dosing of Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 98, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caudle, K.E.; Sangkuhl, K.; Whirl-Carrillo, M.; Swen, J.J.; Haidar, C.E.; Klein, T.E.; Gammal, R.S.; Relling, M.V.; Scott, S.A.; Hertz, D.L.; et al. Standardizing CYP2D6 Genotype to Phenotype Translation: Consensus Recommendations from the Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium and Dutch Pharmacogenetics Working Group. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2020, 13, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caudle, K.E.; Dunnenberger, H.M.; Freimuth, R.R.; Peterson, J.F.; Burlison, J.D.; Whirl-Carrillo, M.; Scott, S.A.; Rehm, H.L.; Williams, M.S.; Klein, T.E.; et al. Standardizing terms for clinical pharmacogenetic test results: Consensus terms from the Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC). Genet. Med. 2017, 19, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, S.A.; Sangkuhl, K.; Gardner, E.E.; Stein, C.M.; Hulot, J.S.; Johnson, J.A.; Roden, D.M.; Klein, T.E.; Shuldiner, A.R. Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium guidelines for cytochrome P450-2C19 (CYP2C19) genotype and clopidogrel therapy. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 90, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, S.A.; Sangkuhl, K.; Stein, C.M.; Hulot, J.S.; Mega, J.L.; Roden, D.M.; Klein, T.E.; Sabatine, M.S.; Johnson, J.A.; Shuldiner, A.R. Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium guidelines for CYP2C19 genotype and clopidogrel therapy: 2013 update. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 94, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crews, K.R.; Gaedigk, A.; Dunnenberger, H.M.; Klein, T.E.; Shen, D.D.; Callaghan, J.T.; Kharasch, E.D.; Skaar, T.C. Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) guidelines for codeine therapy in the context of cytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6) genotype. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 91, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crews, K.R.; Gaedigk, A.; Dunnenberger, H.M.; Leeder, J.S.; Klein, T.E.; Caudle, K.E.; Haidar, C.E.; Shen, D.D.; Callaghan, J.T.; Sadhasivam, S.; et al. Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium guidelines for cytochrome P450 2D6 genotype and codeine therapy: 2014 update. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 95, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lima, J.J.; Thomas, C.D.; Barbarino, J.; Desta, Z.; Van Driest, S.L.; El Rouby, N.; Johnson, J.A.; Cavallari, L.H.; Shakhnovich, V.; Thacker, D.L.; et al. Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for CYP2C19 and Proton Pump Inhibitor Dosing. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 109, 1417–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriyama, B.; Obeng, A.O.; Barbarino, J.; Penzak, S.R.; Henning, S.A.; Scott, S.A.; Agúndez, J.A.; Wingard, J.R.; McLeod, H.L.; Klein, T.E.; et al. Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guidelines for CYP2C19 and Voriconazole Therapy. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 102, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown, J.T.; Bishop, J.R.; Sangkuhl, K.; Nurmi, E.L.; Mueller, D.J.; Dinh, J.C.; Gaedigk, A.; Klein, T.E.; Caudle, K.E.; McCracken, J.T.; et al. Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for CYP2D6 Genotype and Atomoxetine Therapy. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 106, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bell, G.C.; Caudle, K.E.; Whirl-Carrillo, M.; Gordon, R.J.; Hikino, K.; Prows, C.A.; Gaedigk, A.; Agundez, J.A.; Sadhasivam, S.; Klein, T.E.; et al. Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) guideline for CYP2D6 genotype and use of ondansetron and tropisetron. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 102, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, M.; Van Driest, S.L.; Vnencak-Jones, C.L.; Saucier, L.A.G.; Roland, B.P.; Gatto, C.L.; Just, S.L.; Weitkamp, A.O.; Peterson, J.F. Impact of Updating Pharmacogenetic Results: Lessons Learned from the PREDICT Program. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11111051
Liu M, Van Driest SL, Vnencak-Jones CL, Saucier LAG, Roland BP, Gatto CL, Just SL, Weitkamp AO, Peterson JF. Impact of Updating Pharmacogenetic Results: Lessons Learned from the PREDICT Program. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(11):1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11111051
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Michelle, Sara L. Van Driest, Cindy L. Vnencak-Jones, Leigh Ann G. Saucier, Bartholomew P. Roland, Cheryl L. Gatto, Shari L. Just, Asli O. Weitkamp, and Josh F. Peterson. 2021. "Impact of Updating Pharmacogenetic Results: Lessons Learned from the PREDICT Program" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 11: 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11111051
APA StyleLiu, M., Van Driest, S. L., Vnencak-Jones, C. L., Saucier, L. A. G., Roland, B. P., Gatto, C. L., Just, S. L., Weitkamp, A. O., & Peterson, J. F. (2021). Impact of Updating Pharmacogenetic Results: Lessons Learned from the PREDICT Program. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(11), 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11111051





