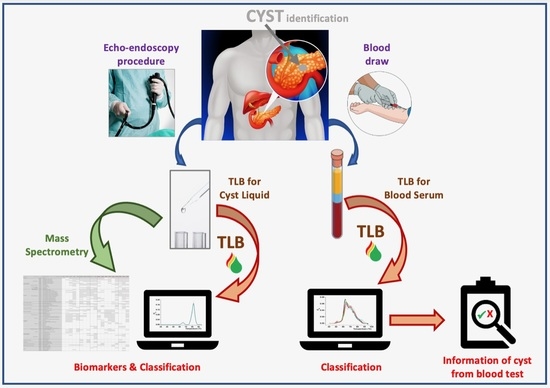
Thermal Liquid Biopsy (TLB) Focused on Benign and Premalignant Pancreatic Cyst Diagnosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects and Samples
2.2. Thermal Liquid Biopsy (TLB) Profile Determination
2.3. Data Analysis
2.4. Protein Sample Preparation and Protein Identification and Quantification by Mass Spectrometry
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Sample Description
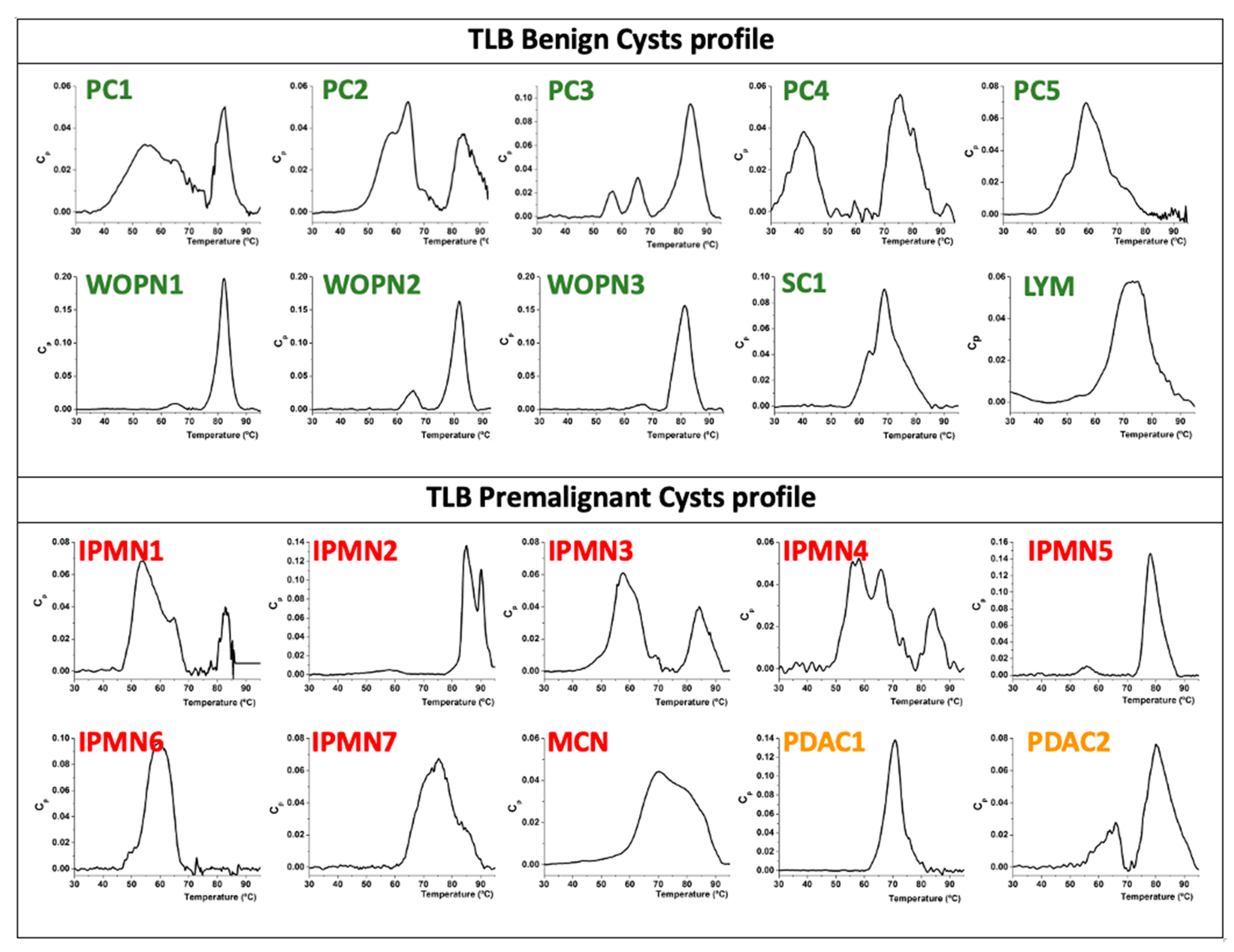
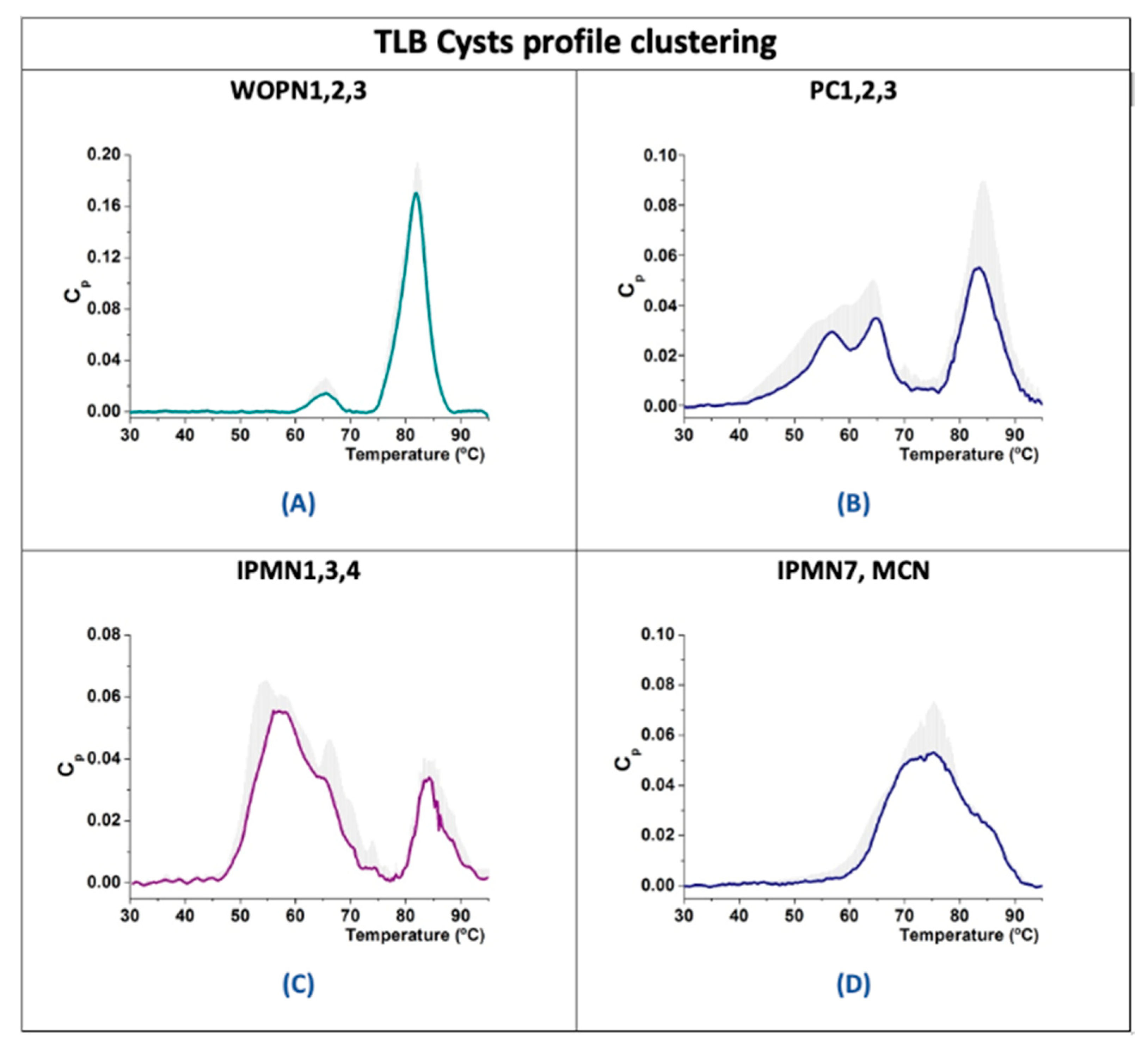
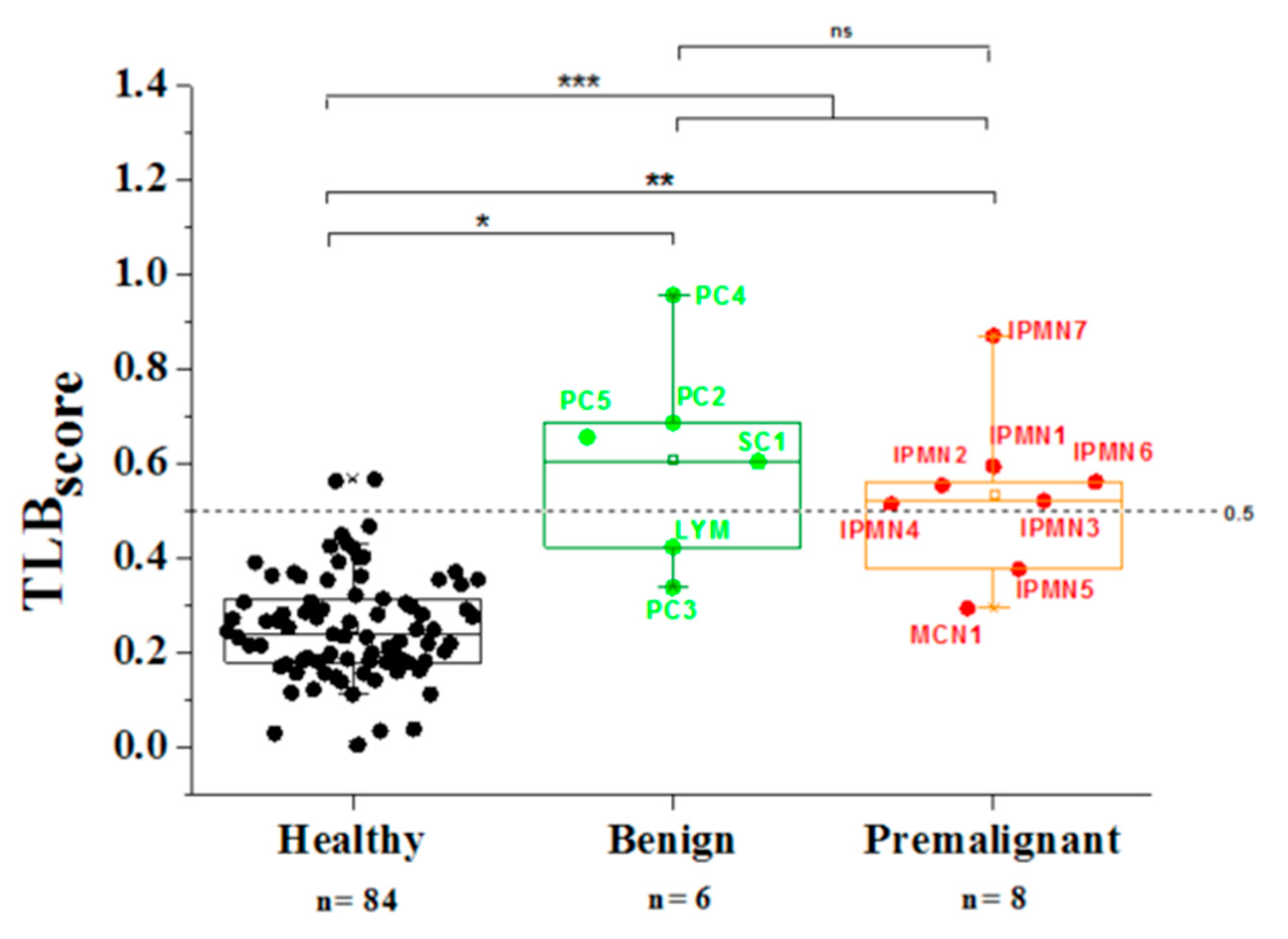
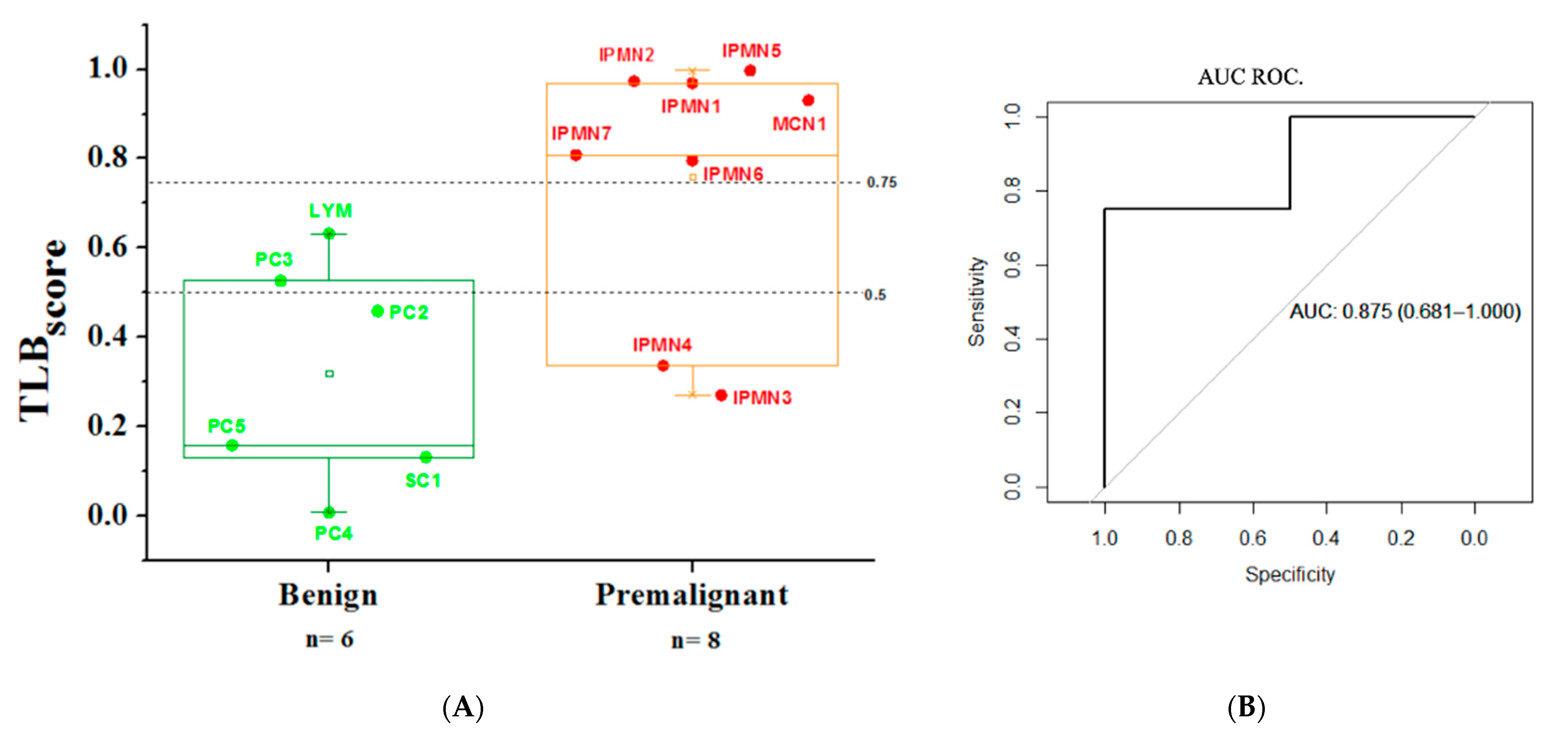
3.2. Analysis of TLB from Cystic Liquid Samples
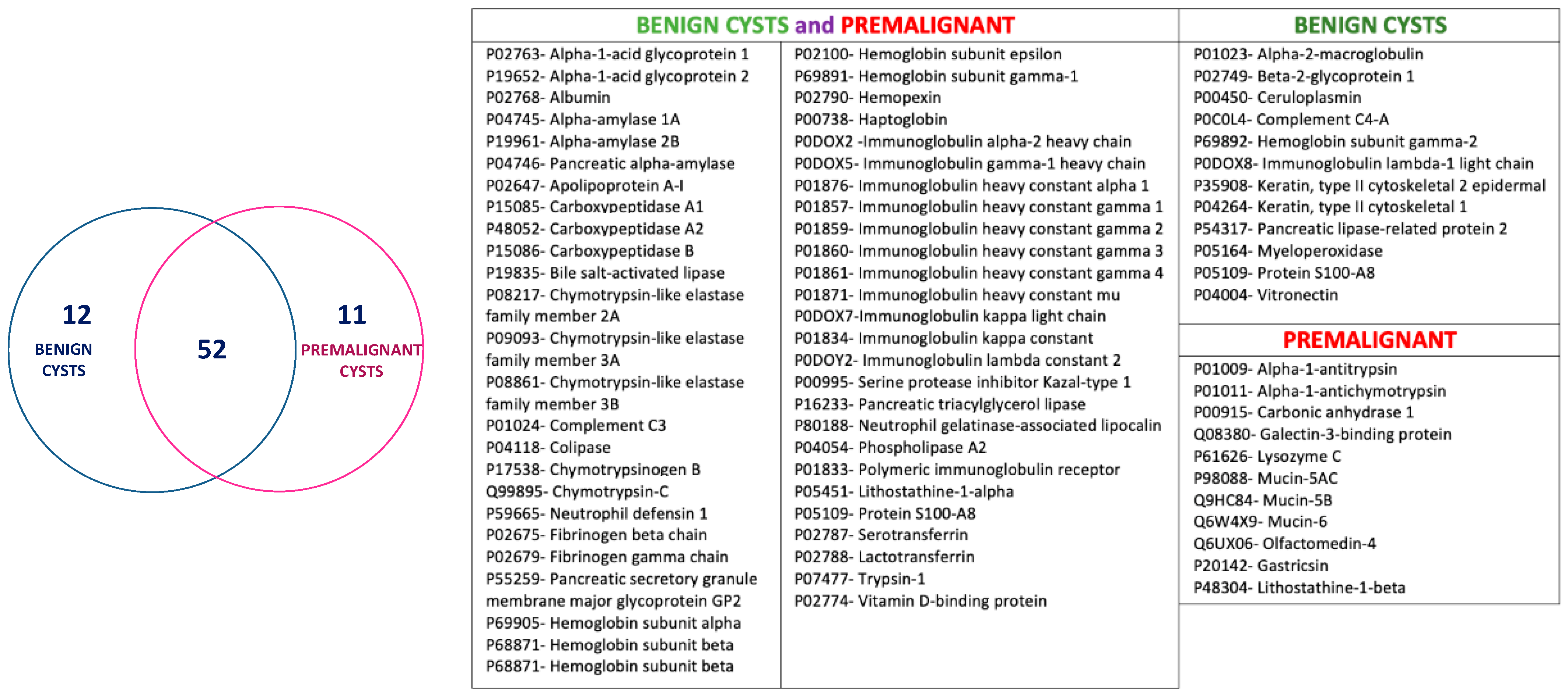
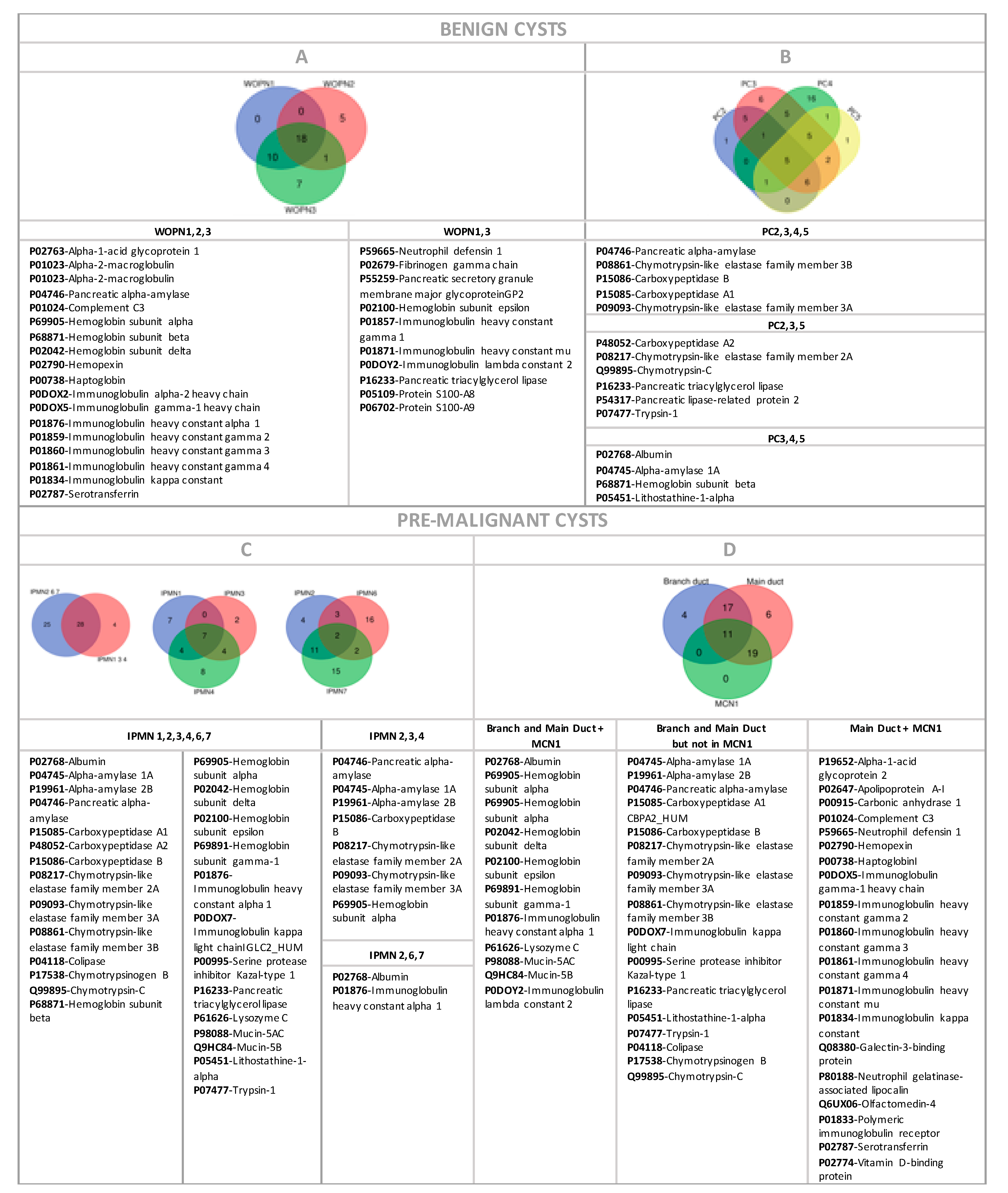
3.3. Analysis of Proteomic Signatures from Cystic Liquid Samples
3.3.1. Benign Cysts
3.3.2. Premalignant Cysts
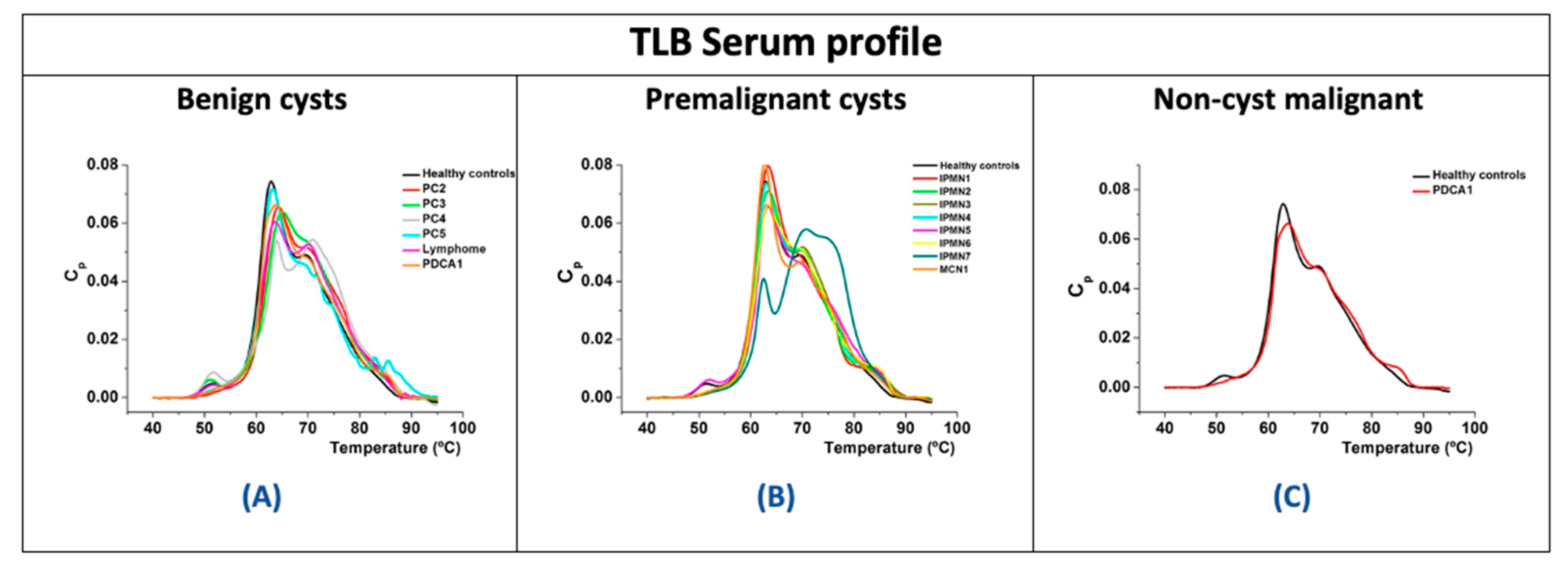
3.4. Analysis of TLB from Serum Samples
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Jong, K.; Nio, C.Y.; Hermans, J.J.; Dijkgraaf, M.G.; Gouma, D.J.; van Eijck, C.H.; van Heel, E.; Klass, G.; Fockens, P.; Bruno, M.J. High prevalence of pancreatic cysts detected by screening magnetic resonance imaging examinations. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 8, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Megibow, A.J.; Baker, M.E.; Gore, R.M.; Taylor, A. The incidental pancreatic cyst. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2011, 49, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klibansky, D.A.; Reid-Lombardo, K.M.; Gordon, S.R.; Gardner, T.B. The clinical relevance of the increasing incidence of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 555–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, B.C.; Baron, T.H.; Adler, D.G.; Davila, R.E.; Egan, J.; Hirota, W.K.; Leighton, J.A.; Qureshi, W.; Rajan, E.; Zuckerman, M.J.; et al. ASGE guideline: The role of endoscopy in the diagnosis and the management of cystic lesions and inflammatory fluid collections of the pancreas. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2005, 61, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Chari, S.; Adsay, V.; Fernandez-del Castillo, C.; Falconi, M.; Shimizu, M.; Yamaguchi, K.; Yamao, K.; Matsuno, S. International consensus guidelines for management of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms and mucinous cystic neoplasms of the pancreas. Pancreatology 2006, 6, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, A.; Brugge, W. ACG practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of neoplastic pancreatic cysts. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 102, 2339–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Fernandez-del Castillo, C.; Adsay, V.; Chari, S.; Falconi, M.; Jang, J.Y.; Kimura, W.; Levy, P.; Pitman, M.B.; Schmidt, C.M.; et al. International consensus guidelines 2012 for the management of IPMN and MCN of the pancreas. Pancreatology 2012, 12, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Fernández-Del Castillo, C.; Kamisawa, T.; Jang, J.Y.; Levy, P.; Ohtsuka, T.; Salvia, R.; Shimizu, Y.; Tada, M.; Wolfgang, C.L. Revisions of international consensus Fukuoka guidelines for the management of IPMN of the pancreas. In Pancreatology, © 2017 IAP and EPC; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 17, pp. 738–753. [Google Scholar]
- European evidence-based guidelines on pancreatic cystic neoplasms. Gut 2018, 67, 789–804. [CrossRef]
- Brugge, W.R.; Lauwers, G.Y.; Sahani, D.; Fernandez-del Castillo, C.; Warshaw, A.L. Cystic neoplasms of the pancreas. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1218–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthusamy, V.R.; Chandrasekhara, V.; Acosta, R.D.; Bruining, D.H.; Chathadi, K.V.; Eloubeidi, M.A.; Faulx, A.L.; Fonkalsrud, L.; Gurudu, S.R.; Khashab, M.A.; et al. The role of endoscopy in the diagnosis and treatment of cystic pancreatic neoplasms. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2016, 84, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Waaij, L.A.; van Dullemen, H.M.; Porte, R.J. Cyst fluid analysis in the differential diagnosis of pancreatic cystic lesions: A pooled analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2005, 62, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogart, J.N.; Loren, D.E.; Singu, B.S.; Kowalski, T.E. Cyst wall puncture and aspiration during EUS-guided fine needle aspiration may increase the diagnostic yield of mucinous cysts of the pancreas. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2011, 45, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.W.; Kim, M.H.; Jeong, S.U.; Kim, J.; Park, D.H.; Lee, S.S.; Seo, D.W.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, J.H. Clinical characteristics of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm manifesting as acute pancreatitis or acute recurrent pancreatitis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 28, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugge, W.R.; Lewandrowski, K.; Lee-Lewandrowski, E.; Centeno, B.A.; Szydlo, T.; Regan, S.; del Castillo, C.F.; Warshaw, A.L. Diagnosis of pancreatic cystic neoplasms: A report of the cooperative pancreatic cyst study. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 1330–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, H.; McGrath, K.; Singhi, A.D. Novel Biomarkers for Pancreatic Cysts. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017, 62, 1796–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, J.H.; Gonda, T.A. The Use of Biomarkers in the Risk Stratification of Cystic Neoplasms. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 28, 549–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moris, D.; Damaskos, C.; Spartalis, E.; Papalampros, A.; Vernadakis, S.; Dimitroulis, D.; Griniatsos, J.; Felekouras, E.; Nikiteas, N. Updates and Critical Evaluation on Novel Biomarkers for the Malignant Progression of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms of the Pancreas. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 2185–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyer, O.M.; Baran, B.; Ormeci, A.C.; Sahin, D.; Gokturk, S.; Evirgen, S.; Basar, R.; Firat, P.; Akyuz, F.; Demir, K.; et al. Role of biochemistry and cytological analysis of cyst fluid for the differential diagnosis of pancreatic cysts: A retrospective cohort study. Medicine 2017, 96, e5513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, A.; Popovici, T.; Bories, P.N. Tumor markers in pancreatic cystic fluids for diagnosis of malignant cysts. Int. J. Biol. Markers 2017, 32, e291–e296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngamruengphong, S.; Lennon, A.M. Analysis of Pancreatic Cyst Fluid. Surg. Pathol. Clin. 2016, 9, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Garbett, N.C.; Miller, J.J.; Jenson, A.B.; Chaires, J.B. Calorimetric analysis of the plasma proteome. Semin. Nephrol. 2007, 27, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garbett, N.C.; Miller, J.J.; Jenson, A.B.; Chaires, J.B. Calorimetry outside the box: A new window into the plasma proteome. Biophys. J. 2008, 94, 1377–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garbett, N.C.; Mekmaysy, C.S.; Helm, C.W.; Jenson, A.B.; Chaires, J.B. Differential scanning calorimetry of blood plasma for clinical diagnosis and monitoring. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2009, 86, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garbett, N.C.; Merchant, M.L.; Helm, C.W.; Jenson, A.B.; Klein, J.B.; Chaires, J.B. Detection of cervical cancer biomarker patterns in blood plasma and urine by differential scanning calorimetry and mass spectrometry. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e84710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbett, N.C.; Brock, G.N. Differential scanning calorimetry as a complementary diagnostic tool for the evaluation of biological samples. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1860, 981–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todinova, S.; Krumova, S.; Kurtev, P.; Dimitrov, V.; Djongov, L.; Dudunkov, Z.; Taneva, S.G. Calorimetry-based profiling of blood plasma from colorectal cancer patients. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1820, 1879–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todinova, S.; Krumova, S.; Radoeva, R.; Gartcheva, L.; Taneva, S.G. Calorimetric markers of Bence Jones and nonsecretory multiple myeloma serum proteome. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 12355–12361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todinova, S.; Krumova, S.; Danailova, A.; Petkova, V.; Guenova, M.; Mihaylov, G.; Gartcheva, L.; Taneva, S.G. Calorimetric markers for monitoring of multiple myeloma and Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia patients. Eur. Biophys. J. 2018, 47, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, S.; Garcia-Gonzalez, M.A.; Lanas, A.; Velazquez-Campoy, A.; Abian, O. Deconvolution analysis for classifying gastric adenocarcinoma patients based on differential scanning calorimetry serum thermograms. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagovetz, A.A.; Jensen, R.L.; Recht, L.; Glantz, M.; Chagovetz, A.M. Preliminary use of differential scanning calorimetry of cerebrospinal fluid for the diagnosis of glioblastoma multiforme. J. Neurooncol. 2011, 105, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagovetz, A.A.; Quinn, C.; Damarse, N.; Hansen, L.D.; Chagovetz, A.M.; Jensen, R.L. Differential scanning calorimetry of gliomas: A new tool in brain cancer diagnostics? Neurosurgery 2013, 73, 289–295, discussion 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigo, A.; Ojeda, J.L.; Vega, S.; Sanchez-Gracia, O.; Lanas, A.; Isla, D.; Velazquez-Campoy, A.; Abian, O. Thermal Liquid Biopsy (TLB): A Predictive Score Derived from Serum Thermograms as a Clinical Tool for Screening Lung Cancer Patients. Cancers 2019, 11, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velazquez-Campoy, A.; Vega, S.; Sanchez-Gracia, O.; Lanas, A.; Rodrigo, A.; Kaliappan, A.; Hall, M.B.; Nguyen, T.Q.; Brock, G.N.; Chesney, J.A.; et al. Thermal liquid biopsy for monitoring melanoma patients under surveillance during treatment: A pilot study. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2018, 1862, 1701–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigo, A.; Abian, O.; Velázquez-Campoy, A.; Callejo, A.; Vega-Sánchez, S.; Fernandez, A.; Sánchez-Gracia, O.; Iranzo, P.; Cruellas, M.; Quilez, E.; et al. Liquid thermal biopsy as a new non-invasive method of diagnosis for lung cancer patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, e21207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, P.A.; Bollen, T.L.; Dervenis, C.; Gooszen, H.G.; Johnson, C.D.; Sarr, M.G.; Tsiotos, G.G.; Vege, S.S.; Group, A.P.C.W. Classification of acute pancreatitis—2012: Revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut 2013, 62, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, S.T.; Day, A.S. S100 proteins in the pathogenesis and diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2006, 2, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedjadi, T.; Evans, A.; Sheikh, A.; Barerra, L.; Al-Ghamdi, S.; Oldfield, L.; Greenhalf, W.; Neoptolemos, J.P.; Costello, E. S100A8 and S100A9 proteins form part of a paracrine feedback loop between pancreatic cancer cells and monocytes. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, S.; Wang, Y.; Dal Molin, M.; Masica, D.L.; Jiao, Y.; Kinde, I.; Blackford, A.; Raman, S.P.; Wolfgang, C.L.; Tomita, T.; et al. A combination of molecular markers and clinical features improve the classification of pancreatic cysts. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 1501–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbett, N.C.; Miller, J.J.; Jenson, A.B.; Miller, D.M.; Chaires, J.B. Interrogation of the plasma proteome with differential scanning calorimetry. Clin. Chem. 2007, 53, 2012–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegand, N.; Bűcs, G.; Dandé, Á.; Lőrinczy, D. Investigation of protein content of synovial fluids with DSC in different arthritides. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandts, J.F.; Lin, L.N. Study of strong to ultratight protein interactions using differential scanning calorimetry. Biochemistry 1990, 29, 6927–6940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, M.; Han, D.; Wang, J.I.; Kim, H.; Kwon, W.; Han, Y.; Jang, J.Y.; Kim, Y. Quantitative proteomic analysis of pancreatic cyst fluid proteins associated with malignancy in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms. Clin. Proteom. 2018, 15, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, H.; Evstatiev, R.; Kornek, G.; Aapro, M.; Bauernhofer, T.; Buxhofer-Ausch, V.; Fridrik, M.; Geissler, D.; Geissler, K.; Gisslinger, H.; et al. Iron metabolism and iron supplementation in cancer patients. Wien. Klin Wochenschr. 2015, 127, 907–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forciniti, S.; Greco, L.; Grizzi, F.; Malesci, A.; Laghi, L. Iron Metabolism in Cancer Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Type of Cyst | Non-Cyst Malignant Lesions | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benign | Pre-Malignant | |||||||
| PC (n = 5) | WOPN (n = 3) | SC (n = 1) | LYM (n = 1) | IPMN (n = 7) | MCN (n = 1) | PDAC (n = 2) | Total (n = 20) | |
| Age (years) * | 63 ± 10 | 62 ± 10 | 72 ± 0 | 52 ± 0 | 72 ± 13 | 42 ± 0 | 40 ± 2 | 62 ± 13 |
| Male/female % | 80/20 | 67/33 | 100/0 | 0/100 | 71/29 | 0/100 | 0/100 | 60/40 |
| Group | Name | Localization in the Pancreas | Cyst Size (cm) | Amylase (U/L) | CEA (ng/mL) | Final Clinical Diagnosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benign Cysts | PC1 | Body | 5.5 | >11,000.0 | 9.23 | Pseudocyst (In Acute Pancreatitis Context) |
| PC2 | Head | 4.1 | >11,000.0 | 64.2 | Pseudocyst | |
| PC3 | Head | 3.5 | 5635.0 | 68.4 | Pseudocyst | |
| PC4 | Body | 15.0 | nd | nd | Pseudocyst (In Acute Pancreatitis Context) | |
| PC5 | Head | 3.0 | >11,000.0 | 28.8 | Pseudocyst (In Chronic Pancreatitis Context) | |
| WOPN1 | Tail | 6.4 | >11,000.0 | 2.4 | Walled-off pancreatic necrosis | |
| WOPN2 | Head | 10.0 | >11,000.0 | 2.0 | Walled-off pancreatic necrosis | |
| WOPN3 | Body | 4.0 | >11,000.0 | 50.0 | Walled-off pancreatic necrosis | |
| SC1 | Body | 5.0 | 41.0 | 0.7 | Serous Cyst | |
| LYM | Head | 4.9 | 24.0 | 0.8 | Lymphocele | |
| Pre-Malignant Cysts | IPMN1 | Body | 2.6 | >11,000.0 | 489.2 | Branch duct IPMN |
| IPMN2 | Head, Body, Tail | 2.0 | 162.0 | 1488.0 | Main duct IPMN | |
| IPMN3 | Head | 2.3 | >11,000.0 | 156.0 | Branch duct IPMN | |
| IPMN4 | Head | 2.5 | >11,000.0 | 556.0 | Branch duct IPMN | |
| IPMN5 | Isthmus | 3.5 | >11,000.0 | 225.0 | Mixed Branch and Main duct IPMN | |
| IPMN 6 | Head | 3.0 | 10.0 | 392.0 | Main Duct IPMN with pancreatic extension | |
| IPMN 7 | Head, Body, Tail | 3.5 | 4.0 | >50,000.0 | Main Duct IPMN with pancreatic extension | |
| MCN1 | Body | 3.3 | 3401.0 | 1617.0 | Mucinous Cystadenoma | |
| Non-Cyst Malignant Lesions | PDAC 1 | Body, Tail | 8.0 | nd | nd | Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma |
| PDAC 2 | Head | 0.5 | >11,000.0 | 1192.0 | Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hermoso-Durán, S.; García-Rayado, G.; Ceballos-Laita, L.; Sostres, C.; Vega, S.; Millastre, J.; Sánchez-Gracia, O.; Ojeda, J.L.; Lanas, Á.; Velázquez-Campoy, A.; et al. Thermal Liquid Biopsy (TLB) Focused on Benign and Premalignant Pancreatic Cyst Diagnosis. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11010025
Hermoso-Durán S, García-Rayado G, Ceballos-Laita L, Sostres C, Vega S, Millastre J, Sánchez-Gracia O, Ojeda JL, Lanas Á, Velázquez-Campoy A, et al. Thermal Liquid Biopsy (TLB) Focused on Benign and Premalignant Pancreatic Cyst Diagnosis. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2021; 11(1):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11010025
Chicago/Turabian StyleHermoso-Durán, Sonia, Guillermo García-Rayado, Laura Ceballos-Laita, Carlos Sostres, Sonia Vega, Judith Millastre, Oscar Sánchez-Gracia, Jorge L. Ojeda, Ángel Lanas, Adrián Velázquez-Campoy, and et al. 2021. "Thermal Liquid Biopsy (TLB) Focused on Benign and Premalignant Pancreatic Cyst Diagnosis" Journal of Personalized Medicine 11, no. 1: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11010025
APA StyleHermoso-Durán, S., García-Rayado, G., Ceballos-Laita, L., Sostres, C., Vega, S., Millastre, J., Sánchez-Gracia, O., Ojeda, J. L., Lanas, Á., Velázquez-Campoy, A., & Abian, O. (2021). Thermal Liquid Biopsy (TLB) Focused on Benign and Premalignant Pancreatic Cyst Diagnosis. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 11(1), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm11010025