Changes in Muscle Stiffness in Infants with Congenital Muscular Torticollis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
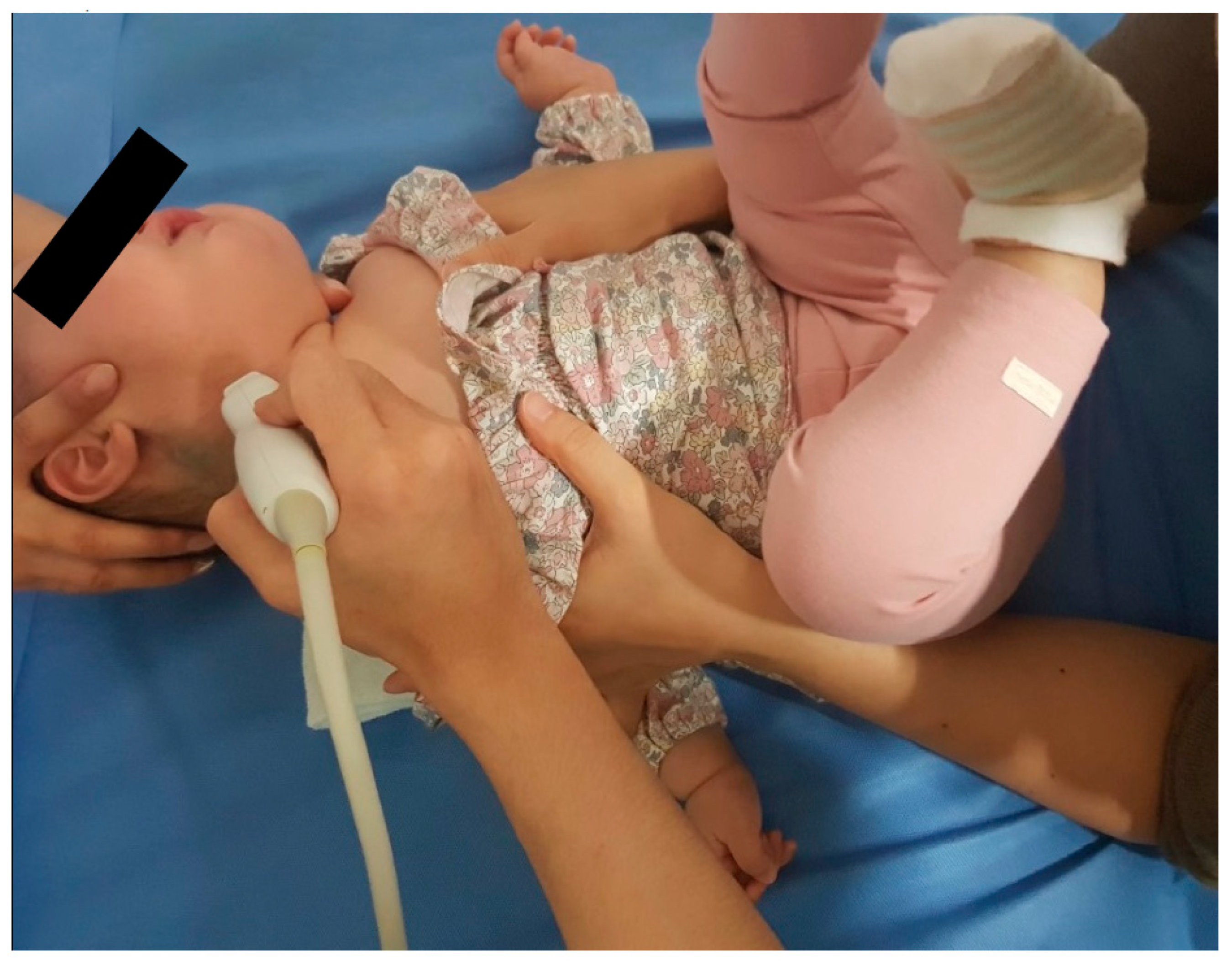
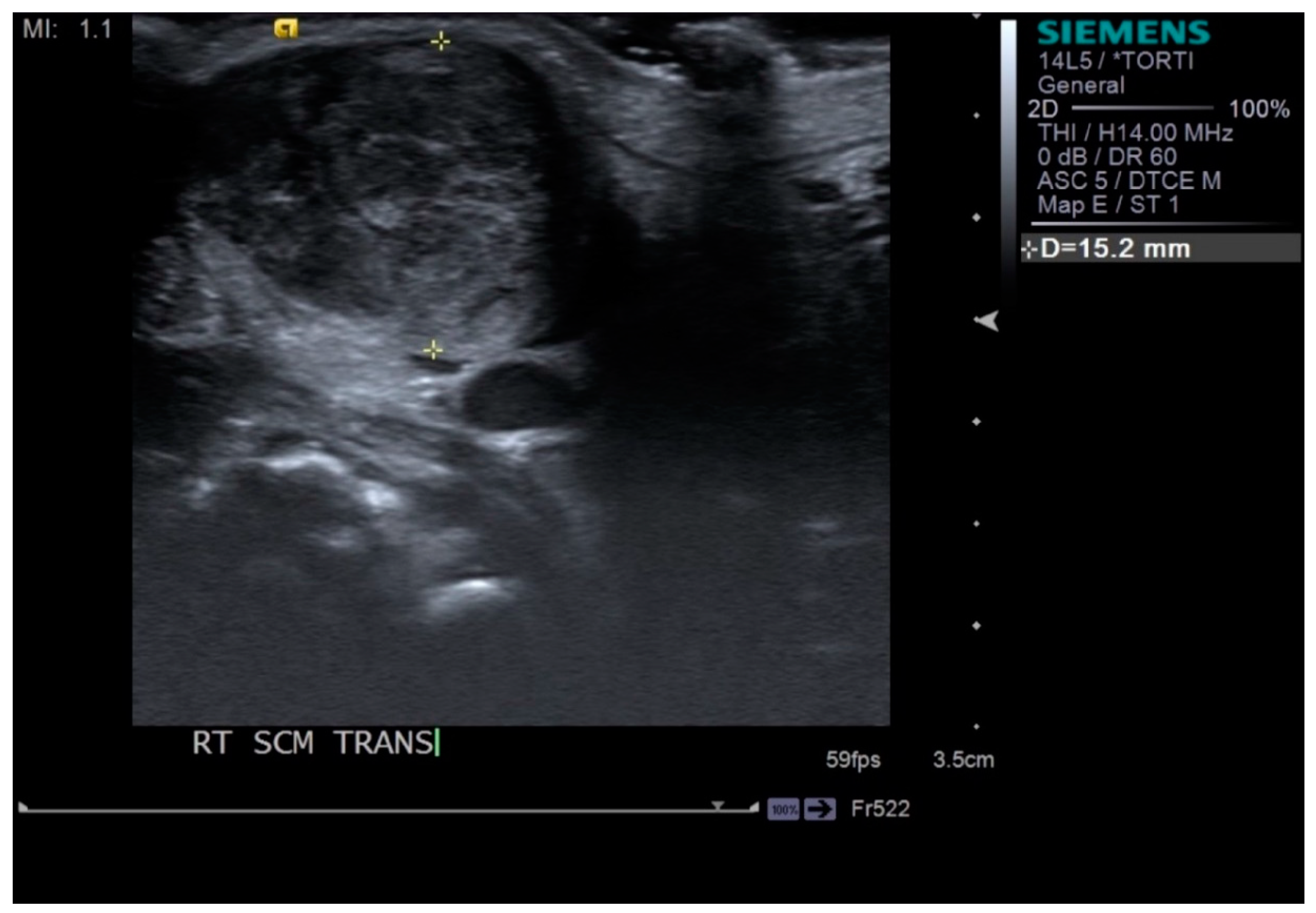
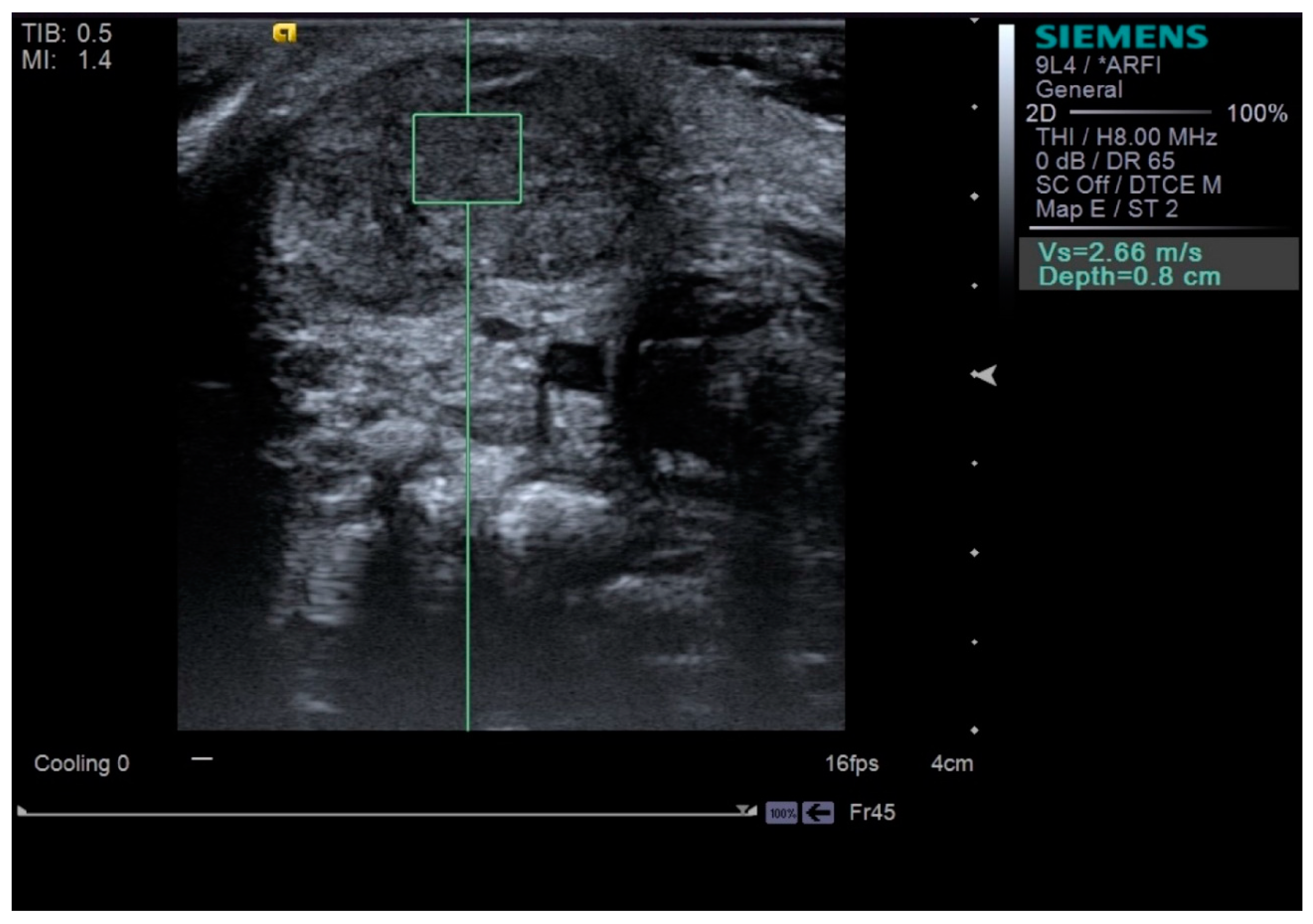
2.2. Outcome Measurement
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, Y.T.; Park, J.W.; Lim, M.; Yoon, K.J.; Kim, Y.B.; Chung, P.W.; Park, H.J.; Lee, S.Y. A clinical comparative study of ultrasound-normal versus ultrasound-abnormal congenital muscular torticollis. Pm. R. 2016, 8, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skelton, E.; Howlett, D. Fibromatosis colli: The sternocleidomastoid pseudotumour of infancy. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2014, 50, 833–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargent, B.; Kaplan, S.L.; Coulter, C.; Baker, C. Congenital muscular torticollis: Bridging the gap between research and clinical practice. Pediatrics 2019, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilesh, K.; Mukherji, S. Congenital muscular torticollis. Ann. Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 3, 198–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Han, J.D.; Lee, H.B.; Hwang, J.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, M.C.; Yim, S.Y. Comparison of clinical severity of congenital muscular torticollis based on the method of child birth. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2011, 35, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.-H.; Kang, J.Y.; Do, H.J.; Park, H.S.; Noh, H.J.; Cho, Y.-H.; Jang, D.-H. Comparison of clinical findings of congenital muscular torticollis between patients with and without sternocleidomastoid lesions as determined by ultrasonography. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2019, 39, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, D. Sternomastoid tumour and muscular torticollis. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 1969, 51, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, S.C.; Harnsberger, H.R.; Johnson, L.; Aoki, J.R.; Giley, J. Fibromatosis colli of infancy: CT and sonographic findings. Ajr. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1988, 151, 1183–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, K.C.; Estroff, J.A.; Rahbar, R. The presentation and management of fibromatosis colli. Ear Nose Throat J. 2010, 89, E4–E8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbilek, S.; Atayurt, H.F. Congenital muscular torticollis and sternomastoid tumor: Results of nonoperative treatment. J. Pediatr. Surg. 1999, 34, 549–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.V.; Wu, W.T.; Huang, K.C.; Jan, W.H.; Han, D.S. Limb muscle quality and quantity in elderly adults with dynapenia but not sarcopenia: An ultrasound imaging study. Exp. Gerontol. 2018, 108, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.V.; Wu, W.T.; Han, D.S.; Ozcakar, L. Static and Dynamic Shoulder Imaging to Predict Initial Effectiveness and Recurrence After Ultrasound-Guided Subacromial Corticosteroid Injections. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2017, 98, 1984–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyaci, A.; Tutoglu, A.; Boyaci, N.; Koca, I.; Calik, M.; Sakalar, A.; Kilicaslan, N. Changes in spastic muscle stiffness after botulinum toxin A injections as part of rehabilitation therapy in patients with spastic cerebral palsy. NeuroRehabilitation 2014, 35, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, M.; Youn, K.; Yang, S. Reliability and quantification of gastrocnemius elasticity at relaxing and at submaximal contracted condition. Med. Ultrason 2018, 20, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgici, M.C.; Bekci, T.; Ulus, Y.; Ozyurek, H.; Aydin, O.F.; Tomak, L.; Selcuk, M.B. Quantitative assessment of muscular stiffness in children with cerebral palsy using acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) ultrasound elastography. J. Med. Ultrason (2001) 2018, 45, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Wu, R.; Yao, M.; Xu, G.; Liu, H.; Pu, H.; Xiang, L.; Zhang, S. Acoustic radiation force impulse elastography in evaluation of triple-negative breast cancer: A preliminary experience. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2018, 70, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandenburg, J.E.; Eby, S.F.; Song, P.; Zhao, H.; Brault, J.S.; Chen, S.; An, K.N. Ultrasound elastography: The new frontier in direct measurement of muscle stiffness. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2014, 95, 2207–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgici, M.C.; Bekci, T.; Ulus, Y.; Bilgici, A.; Tomak, L.; Selcuk, M.B. Quantitative assessment of muscle stiffness with acoustic radiation force impulse elastography after botulinum toxin A injection in children with cerebral palsy. J. Med. Ultrason (2001) 2018, 45, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, D.R.; Park, G.Y. Diagnostic value of real-time sonoelastography in congenital muscular torticollis. J. Ultras Med. 2012, 31, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Park, H.J.; Choi, Y.J.; Choi, S.H.; Kook, S.H.; Rho, M.H.; Chung, E.C. Value of adding sonoelastography to conventional ultrasound in patients with congenital muscular torticollis. Pediatr. Radiol. 2013, 43, 1566–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.Y.; Kwon, D.R.; Kwon, D.G. Shear wave sonoelastography in infants with congenital muscular torticollis. Med. (Baltim.) 2018, 97, e9818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamoli, P.; Pavone, P.; Falsaperla, R.; Longo, R.; Vitaliti, G.; Andaloro, C.; Agostino, S.; Cocuzza, S. Rapid spontaneous resolution of fibromatosis colli in a 3-week-old girl. Case Rep. Otolaryngol. 2014, 2014, 264940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Yan, X.; Li, J.; Guan, B.; Ma, L.; Chen, Y.; Mai, J.; Xu, K. Comparison of 2 dosages of stretching treatment in infants with congenital muscular torticollis: A randomized trial. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2017, 96, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celayir, A.C. Congenital muscular torticollis: Early and intensive treatment is critical. A prospective study. Pediatr Int. 2000, 42, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petronic, I.; Brdar, R.; Cirovic, D.; Nikolic, D.; Lukac, M.; Janic, D.; Pavicevic, P.; Golubovic, Z.; Knezevic, T. Congenital muscular torticollis in children: Distribution, treatment duration and out come. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2010, 46, 153–157. [Google Scholar]
- Cortez, C.D.; Hermitte, L.; Ramain, A.; Mesmann, C.; Lefort, T.; Pialat, J.B. Ultrasound shear wave velocity in skeletal muscle: A reproducibility study. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2016, 97, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Infants with Congenital Muscular Torticollis (n = 22) | |
|---|---|
| Sex (male/female) | 14/8 |
| Postpartum age (days) | 34.68 ± 19.86 |
| IUP (days) | 273 ± 6 |
| Birth weight (g) | 3190 ± 262.8 |
| Delivery type (NSVD/C-sec) | 15/7 |
| Affected side (right/left) | 14/8 |
| Affected Side (n = 22) | Unaffected Side (n = 22) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCM thickness (mm) | Initial | 15.64 ± 5.24 | 5.76 ± 1.62 | <0.001 * |
| After 3 months | 11.36 ± 5.71 | 6.61 ± 1.06 | 0.001 * | |
| Cervical rotation ROM (°) | Initial | 64.77 ± 18.87 | 90 | <0.001 * |
| After 3 months | 87.27 ± 6.31 | 90 | 0.056 | |
| Cervical lateral flexion ROM (°) | Initial | 37.50 ± 11.31 | 57.27 ± 7.67 | <0.001 * |
| After 3 months | 53.64 ± 9.41 | 57.73 ± 7.52 | 0.119 | |
| SWV of SCM (m/s) | Initial | 2.33 ± 0.47 | 1.25 ± 0.27 | <0.001 * |
| After 3 months | 1.56 ± 0.63 | 1.22 ± 0.39 | 0.039 * |
| Initial SWV | Muscle Thickness | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCM muscle | Initial SWV | Correlation | - | - |
| p-value | ||||
| Muscle thickness | Correlation | 0.747 * | - | |
| p-value | <0.001 | |||
| Cervical ROM | Rotation | Correlation | −0.642 * | −0.752 * |
| p-value | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| Lateral flexion | Correlation | −0.643 * | −0.748 * | |
| p-value | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Initial Evaluation (n = 22) | After 3 Months (n = 22) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SCM thickness (mm) | 15.64 ± 5.24 | 11.36 ± 5.71 | <0.001 * |
| Cervical rotation ROM (°) | 64.77 ± 18.87 | 87.27 ± 6.31 | <0.001 * |
| Cervical lateral flexion ROM (°) | 37.50 ± 11.31 | 53.64 ± 9.41 | <0.001 * |
| SWV of SCM (m/s) | 2.33 ± 0.47 | 1.56 ± 0.63 | <0.001 * |
| Initial SWV | SWV Change | Thickness Change | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCM muscle | Initial SWV | Correlation | - | - | - |
| p-value | |||||
| SWV changes | Correlation | 0.518 * | - | - | |
| p-value | 0.014 | ||||
| Thickness changes | Correlation | 0.181 | 0.151 | - | |
| p-value | 0.420 | 0.502 | |||
| Cervical ROM | Rotation changes | Correlation | −0.253 | −0.073 | 0.141 |
| p-value | 0.255 | 0.746 | 0.531 | ||
| Lateral flexion changes | Correlation | −0.007 | −0.026 | 0.495 * | |
| p-value | 0.974 | 0.910 | 0.019 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hwang, D.; Shin, Y.J.; Choi, J.Y.; Jung, S.J.; Yang, S.-s. Changes in Muscle Stiffness in Infants with Congenital Muscular Torticollis. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics9040158
Hwang D, Shin YJ, Choi JY, Jung SJ, Yang S-s. Changes in Muscle Stiffness in Infants with Congenital Muscular Torticollis. Diagnostics. 2019; 9(4):158. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics9040158
Chicago/Turabian StyleHwang, Dongmin, Young Ju Shin, Ja Young Choi, Soo Jin Jung, and Shin-seung Yang. 2019. "Changes in Muscle Stiffness in Infants with Congenital Muscular Torticollis" Diagnostics 9, no. 4: 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics9040158
APA StyleHwang, D., Shin, Y. J., Choi, J. Y., Jung, S. J., & Yang, S.-s. (2019). Changes in Muscle Stiffness in Infants with Congenital Muscular Torticollis. Diagnostics, 9(4), 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics9040158





