Prostate Artery Embolization for Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Men Unfit for Surgery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Population
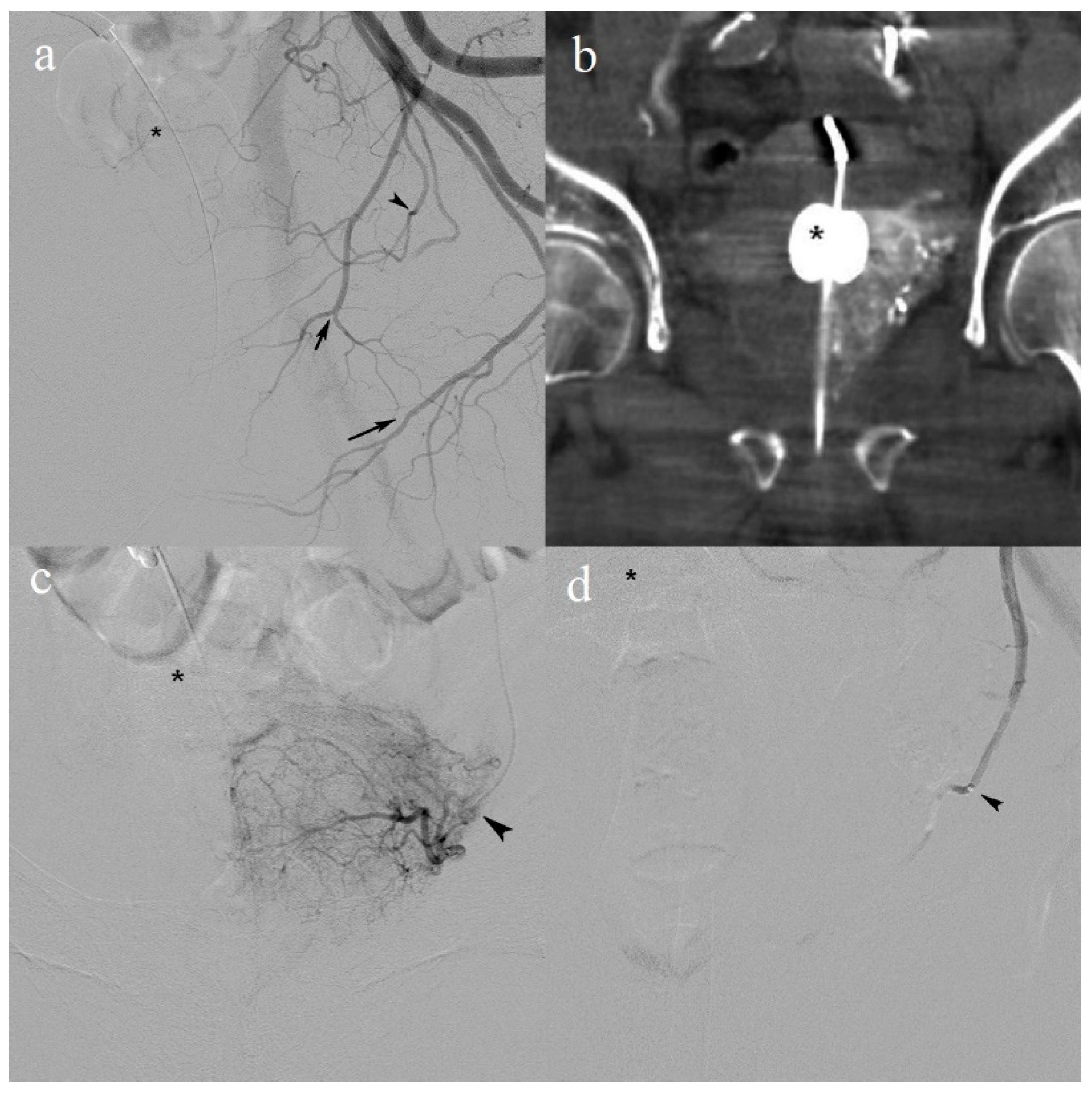
2.3. PAE Technique
2.4. Outcome Measures
2.5. Statistical Analysis
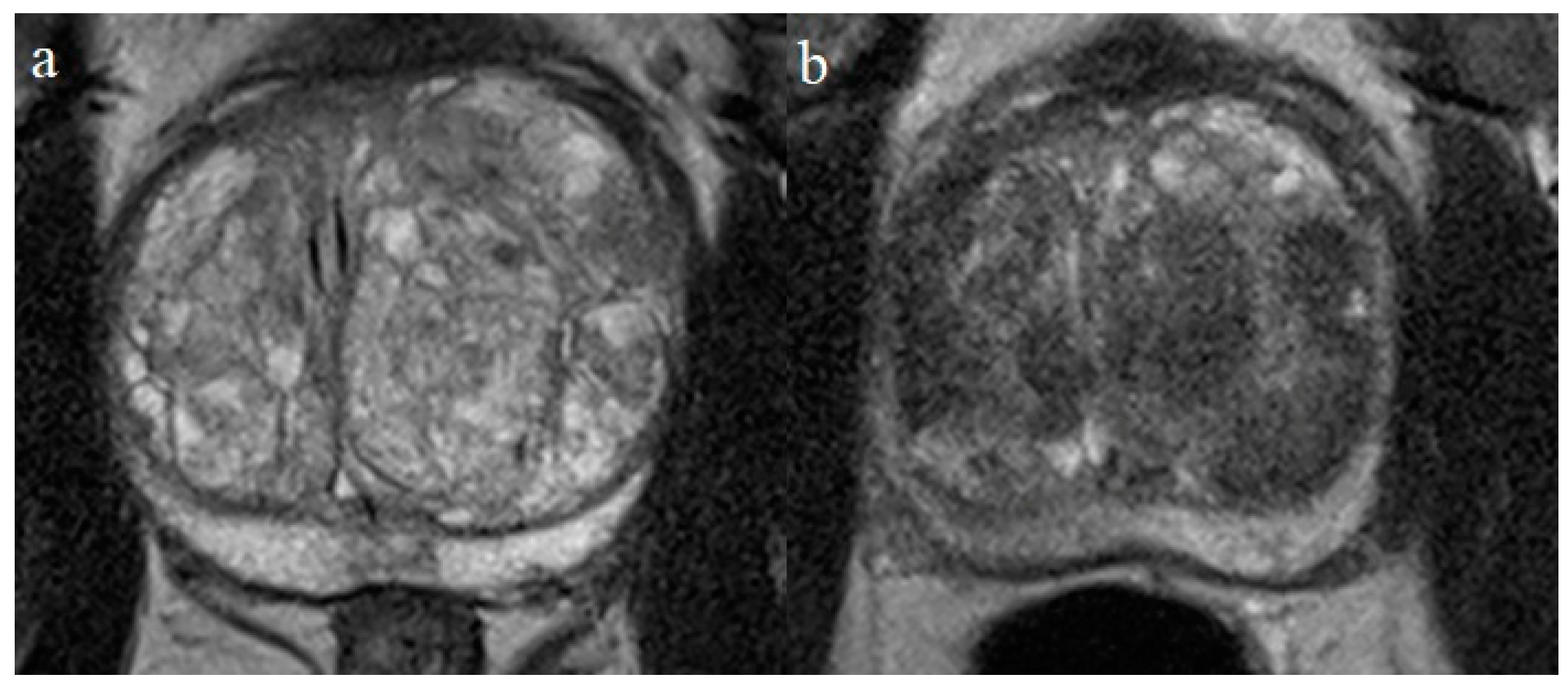
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roehrborn, C.G. Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: An Overview. Rev. Urol. 2005, 7, S3–S14. [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe, A.; Neal, D. Benign prostatic hyperplasia. Lancet 2003, 361, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girman, C.J.; Epstein, R.S.; Jacobsen, S.J.; Guess, H.A.; Panser, L.A.; Oesterling, J.E.; Lieber, M.M. Natural history of prostatism: Impact of urinary symptoms on quality of life in 2115 randomly selected community men. Urology 1994, 44, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girman, C.J.; Jacobsen, S.J.; Rhodes, T.; Guess, H.A.; Roberts, R.O.; Lieber, M.M. Association of health-related quality of life and benign prostatic enlargement. Eur. Urol. 1999, 35, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McConnell, J.D.; Roehrborn, C.G.; Bautista, O.M.; Andriole, G.L., Jr.; Dixon, C.M.; Kusek, J.W.; Lepor, H.; McVary, K.T.; Nyberg, L.M., Jr.; Clarke, H.S.; et al. The Long-Term Effect of Doxazosin, Finasteride, and Combination Therapy on the Clinical Progression of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. N. Eng. J. Med. 2003, 349, 2387–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, H.E.; Barry, M.J.; Dahm, P.; Gandhi, M.C.; Kaplan, S.A.; Kohler, T.S.; Lerner, L.B.; Lightner, D.J.; Parsons, J.K.; Roehrborn, C.G.; et al. Surgical Management of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Attributed to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: AUA Guideline. J. Urol. 2018, 200, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oelke, M.; Bachmann, A.; Descazeaud, A.; Emberton, M.; Gravas, S.; Michel, M.C.; N’dow, J.; Nordling, J.; de la Rosette, J.J. European Association of Urology EAU guidelines on the treatment and follow-up of non-neurogenic male lower urinary tract symptoms including benign prostatic obstruction. Eur. Urol. 2013, 64, 118–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahyai, S.A.; Gilling, P.; Kaplan, S.A.; Kuntz, R.M.; Madersbacher, S.; Montorsi, F.; Speakman, M.J.; Stief, C.G. Meta-analysis of functional outcomes and complications following transurethral procedures for lower urinary tract symptoms resulting from benign prostatic enlargement. Eur. Urol. 2010, 58, 384–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornu, J.-N.; Ahyai, S.; Bachmann, A.; de la Rosette, J.; Gilling, P.; Gratzke, C.; McVary, K.; Novara, G.; Woo, H.; Madersbacher, S. A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Functional Outcomes and Complications Following Transurethral Procedures for Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Resulting from Benign Prostatic Obstruction: An Update. Eur. Urol. 2015, 67, 1066–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Yu, W.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, K.; Xu, B.; Xiao, Y.; Wu, S.; Pan, B. Correlation of ASA Grade and the Charlson Comorbidity Index With Complications in Patients After Transurethral Resection of Prostate. Urology 2016, 98, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, S.; Sankhwar, S.N.; Kathpalia, R.; Singh, M.K.; Kumar, M.; Goel, A.; Singh, V.; Sinha, R.J.; Singh, B.P.; Dalela, D. Grading complications after transurethral resection of prostate using modified Clavien classification system and predicting complications using the Charlson comorbidity index. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2013, 45, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayor, S. NICE recommends prostate artery embolisation as a treatment option for BPH symptoms. BMJ 2018, 361, k1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Hou, M.; Wang, Y. Benign prostatic hyperplasia: Prostatic arterial embolization versus transurethral resection of the prostate—A prospective, randomized, and controlled clinical trial. Radiology 2014, 270, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abt, D.; Hechelhammer, L.; Müllhaupt, G.; Markart, S.; Güsewell, S.; Kessler, T.M.; Schmid, H.-P.; Engeler, D.S.; Mordasini, L. Comparison of prostatic artery embolisation (PAE) versus transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) for benign prostatic hyperplasia: Randomised, open label, non-inferiority trial. BMJ 2018, 361, k2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnevale, F.C.; Iscaife, A.; Yoshinaga, E.M.; Moreira, A.M.; Antunes, A.A.; Srougi, M. Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) Versus Original and PErFecTED Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE) Due to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH): Preliminary Results of a Single Center, Prospective, Urodynamic-Controlled Analysis. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2016, 39, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, F.; Crisóstomo, V.; Báez-Díaz, C.; Sánchez, F.M. Prostatic Artery Embolization (PAE) for Symptomatic Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH): Part 2, Insights into the Technical Rationale. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2016, 39, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampoldi, A.; Barbosa, F.; Secco, S.; Migliorisi, C.; Galfano, A.; Prestini, G.; Harward, S.H.; di Trapani, D.; Brambillasca, P.M.; Ruggero, V.; et al. Prostatic Artery Embolization as an Alternative to Indwelling Bladder Catheterization to Manage Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia in Poor Surgical Candidates. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2017, 40, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.Q.; Wang, Y.; Yan, J.Y.; Yuan, K.; Zhang, G.D.; Duan, F.; Li, K. Prostatic artery embolization for the treatment of symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia in men ≥75 years: A prospective single-center study. World J. Urol. 2016, 34, 1275–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Assis, A.M.; Moreira, A.M.; de Paula Rodrigues, V.C.; Yoshinaga, E.M.; Antunes, A.A.; Harward, S.H.; Srougi, M.; Carnevale, F.C. Prostatic artery embolization for treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia in patients with prostates > 90 g: A prospective single-center study. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2015, 26, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, P.A.; Taylor, R.; Thielke, R.; Payne, J.; Gonzalez, N.; Conde, J.G. Research electronic data capture (REDCap)—A metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J. Biomed. Inform. 2009, 42, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnevale, F.C.; Moreira, A.M.; Antunes, A.A. The “PErFecTED Technique”: Proximal Embolization First, Then Embolize Distal for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2014, 37, 1602–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilhim, T.; Pisco, J.; Tinto, H.R.; Fernandes, L.; Pinheiro, L.C.; Duarte, M.; Pereira, J.A.; Oliveira, A.G.; O’Neill, J. Unilateral Versus Bilateral Prostatic Arterial Embolization for Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Patients with Prostate Enlargement. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2013, 36, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratzke, C.; Bachmann, A.; Descazeaud, A.; Drake, M.J.; Madersbacher, S.; Mamoulakis, C.; Oelke, M.; Tikkinen, K.A.O.; Gravas, S. EAU Guidelines on the Assessment of Non-neurogenic Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms including Benign Prostatic Obstruction. Eur. Urol. 2015, 67, 1099–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosset, A.; Spadola, L.; Ratib, O. OsiriX: An Open-Source Software for Navigating in Multidimensional DICOM Images. J. Digit. Imaging 2004, 17, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angle, J.F.; Siddiqi, N.H.; Wallace, M.J.; Kundu, S.; Stokes, L.; Wojak, J.C.; Cardella, J.F. Society of Interventional Radiology Standards of Practice Committee Quality improvement guidelines for percutaneous transcatheter embolization: Society of Interventional Radiology Standards of Practice Committee. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 21, 1479–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, A.M.; de Assis, A.M.; Carnevale, F.C.; Antunes, A.A.; Srougi, M.; Cerri, G.G. A Review of Adverse Events Related to Prostatic Artery Embolization for Treatment of Bladder Outlet Obstruction Due to BPH. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2017, 40, 1490–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2008; ISBN 3-900051-07-0. Available online: http://www.R-project.org (accessed on 20 March 2019).
- Malling, B.; Røder, M.A.; Brasso, K.; Forman, J.; Taudorf, M.; Lönn, L. Prostate artery embolisation for benign prostatic hyperplasia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roehrborn, C.G. The Epidemiology of Acute Urinary Retention in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Rev. Urol. 2001, 3, 187–192. [Google Scholar]
- Barry, M.J.; Williford, W.O.; Chang, Y.; Machi, M.; Jones, K.M.; Walker-Corkery, E.; Lepor, H. Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Specific Health Status Measures in Clinical Research: How Much Change in the American Urological Association Symptom Index and the Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Impact Index is Perceptible to Patients? J. Urol. 1995, 154, 1770–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.B.; Kwon, K.S.; Kim, S.D.; Kim, H.J. Effect of discontinuation of 5alpha-reductase inhibitors on prostate volume and symptoms in men with BPH: A prospective study. Urology 2009, 73, 802–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardarelli-Leite, L.; de Assis, A.M.; Moreira, A.M.; Antunes, A.A.; Cerri, G.G.; Srougi, M.; Carnevale, F.C. Impact of 5-Alpha-Reductase Inhibitors Use at the Time of Prostatic Artery Embolization for Treatment of Benign Prostatic Obstruction. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 30, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, A.A.; Carnevale, F.C.; da Motta Leal Filho, J.M.; Yoshinaga, E.M.; Cerri, L.M.O.; Baroni, R.H.; Marcelino, A.S.Z.; Cerri, G.G.; Srougi, M. Clinical, Laboratorial, and Urodynamic Findings of Prostatic Artery Embolization for the Treatment of Urinary Retention Related to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. A Prospective Single-Center Pilot Study. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2013, 36, 978–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilhim, T.; Pisco, J.; Pereira, J.A.; Costa, N.V.; Fernandes, L.; Campos Pinheiro, L.; Duarte, M.; Oliveira, A.G. Predictors of Clinical Outcome after Prostate Artery Embolization with Spherical and Nonspherical Polyvinyl Alcohol Particles in Patients with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. Radiology 2016, 281, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Q.; Zhang, J.L.; Xin, H.N.; Yuan, K.; Yan, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.D.; Fu, J.X. Comparison of Clinical Outcomes of Prostatic Artery Embolization with 50-μm Plus 100-μm Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) Particles versus 100-μm PVA Particles Alone: A Prospective Randomized Trial. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2018, 29, 1694–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapping, C.R.; Little, M.W.; Boardman, P. Immediate Resolution of a Grade 3 Varicocele Post Prostatic Artery Embolisation (PAE). Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2017, 40, 1481–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastinehad, A.R.; Caplin, D.M.; Ost, M.C.; VanderBrink, B.A.; Lobko, I.; Badlani, G.H.; Weiss, G.H.; Kavoussi, L.R.; Siegel, D.N. Selective arterial prostatic embolization (SAPE) for refractory hematuria of prostatic origin. Urology 2008, 71, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roghmann, F.; Ghani, K.R.; Kowalczyk, K.J.; Bhojani, N.; Sammon, J.D.; Gandaglia, G.; Trudeau, V.; Becker, A.; Sukumar, S.; Menon, M.; et al. Incidence and Treatment Patterns in Males Presenting with Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms to the Emergency Department in the United States. J. Urol. 2013, 190, 1798–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrass, B.J.R.; Thurairaja, R.; McFarlane, J.; Persad, R.A. Haematuria in prostate cancer: New solutions for an old problem. BJU Int. 2006, 97, 900–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | n | Mean | SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 11 | 75.2 | 8.2 |
| BMI | 11 | 26.0 | 3.6 |
| IPSS | 6 | 18.7 | 11.2 |
| IPSS-QoL | 6 | 5.3 | 0.8 |
| IIEF-5 | 2 | 16.5 | 7.8 |
| PVR, mL | 4 | 60.5 | 71.7 |
| PSA, µg/L | 11 | 11.2 | 9.3 |
| PV, cm3 | 11 | 116.6 | 64.0 |
| Qmax, mL | 4 | 12.4 | 8.1 |
| Catheterization, months | 5 | 12.2 | 10.5 |
| Variable | n | Change | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IPSS | ||||
| 1 month | 6 | −10.2 | [−23.1; 2.8] | 0.10 |
| 6 months | 6 | −11.3 | [−24.1; 1.5] | 0.07 |
| IPSS-QoL | ||||
| 1 month | 6 | −3.5 | [−5.1; −1.9] | <0.01 |
| 6 months | 6 | −4.5 | [−5.6; −3.4] | <0.01 |
| IIEF-5 | ||||
| 1 month | 2 | 3.5 | [−91.8; 98.8] | 0.72 |
| 6 months | 2 | 5.5 | [−64.4; 75.4] | 0.50 |
| PVR, mL | ||||
| 1 month | 4 | 16.2 | [−84.6; 117.1] | 0.64 |
| 6 months | 2 | 7 | [−5.7; 19.7] | 0.09 |
| PSA, µg/L | ||||
| 24-h | 10 | 119.8 | [41.0; 198.7] | <0.01 |
| 1 month | 11 | −2.5 | [−7.6; 2.6] | 0.30 |
| 6 months | 11 | −4.6 | [−9.2; 0.0] | 0.051 |
| PV, cm3 | ||||
| 1 month | 10 | −17 | [−31.3; −2.7] | 0.03 |
| 6 months | 10 | −26.6 | [−50.9; −2.3] | 0.04 |
| Qmax, mL/s | ||||
| 1 month | 3 | 3.8 | [−5.7; 13.2] | 0.23 |
| 6 months | 2 | 0.4 | [−5.3;6.2] | 0.50 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malling, B.; Lönn, L.; Jensen, R.J.; Lindh, M.; Frevert, S.; Brasso, K.; Røder, M.A. Prostate Artery Embolization for Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Men Unfit for Surgery. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics9020046
Malling B, Lönn L, Jensen RJ, Lindh M, Frevert S, Brasso K, Røder MA. Prostate Artery Embolization for Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Men Unfit for Surgery. Diagnostics. 2019; 9(2):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics9020046
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalling, Brian, Lars Lönn, Ruben Juhl Jensen, Mats Lindh, Susanne Frevert, Klaus Brasso, and Martin Andreas Røder. 2019. "Prostate Artery Embolization for Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Men Unfit for Surgery" Diagnostics 9, no. 2: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics9020046
APA StyleMalling, B., Lönn, L., Jensen, R. J., Lindh, M., Frevert, S., Brasso, K., & Røder, M. A. (2019). Prostate Artery Embolization for Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Men Unfit for Surgery. Diagnostics, 9(2), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics9020046






